Rack And Pinion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular
 Rack and pinion combinations are often used as part of a simple linear actuator, where the rotation of a shaft powered by hand or by a motor is converted to linear motion.
The rack carries the full load of the actuator directly and so the driving pinion is usually small, so that the gear ratio reduces the torque required. This force, thus torque, may still be substantial and so it is common for there to be a reduction gear immediately before this by either a gear or
Rack and pinion combinations are often used as part of a simple linear actuator, where the rotation of a shaft powered by hand or by a motor is converted to linear motion.
The rack carries the full load of the actuator directly and so the driving pinion is usually small, so that the gear ratio reduces the torque required. This force, thus torque, may still be substantial and so it is common for there to be a reduction gear immediately before this by either a gear or
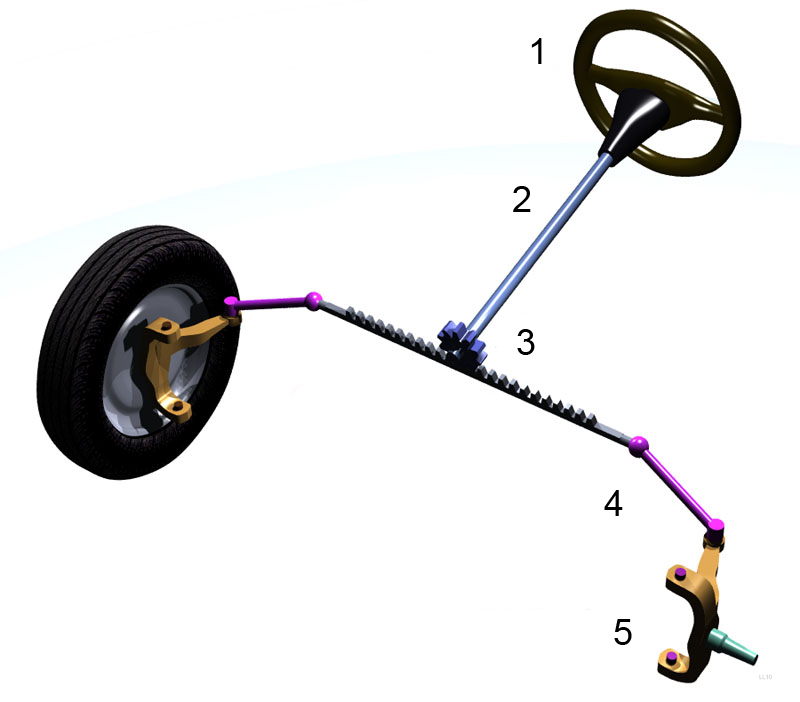 A rack and pinion is commonly found in the steering mechanism of cars or other wheeled, steered vehicles. Rack and pinion provides less mechanical advantage than other mechanisms such as
A rack and pinion is commonly found in the steering mechanism of cars or other wheeled, steered vehicles. Rack and pinion provides less mechanical advantage than other mechanisms such as

 A rack and pinion with two racks and one pinion is used in
A rack and pinion with two racks and one pinion is used in
gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic ...
(the '' pinion'') engaging a linear gear (the ''rack''). Together, they convert rotational motion into linear motion. Rotating the pinion causes the rack to be driven in a line. Conversely, moving the rack linearly will cause the pinion to rotate. A rack and pinion drive can use both straight and helical gears. Though some suggest helical gears are quieter in operation, no hard evidence supports this theory. Helical racks, while being more affordable, have proven to increase side torque on the datums, increasing operating temperature leading to premature wear. Straight racks require a lower driving force and offer increased torque and speed per percentage of gear ratio which allows lower operating temperature and lessens viscal friction and energy use. The maximum force that can be transmitted in a rack and pinion mechanism is determined by the tooth pitch and the size of the pinion as well as the gear ratio.
For example, in a rack railway
A rack railway (also rack-and-pinion railway, cog railway, or cogwheel railway) is a steep grade railway with a toothed rack rail, usually between the running rails. The trains are fitted with one or more cog wheels or pinions that mesh with t ...
, the rotation of a pinion mounted on a locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, motor coach, railcar or power car; the ...
or a railroad car engages a rack
Rack or racks may refer to:
Storage and installation
* Amp rack, short for amplifier rack, a piece of furniture in which amplifiers are mounted
* Bicycle rack, a frame for storing bicycles when not in use
* Bustle rack, a type of storage bin ...
placed between the rails and helps to move the train
In rail transport, a train (from Old French , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and transport people or freight. Trains are typically pulled or pushed by locomotives (often ...
up a steep gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p is the "direction and rate of fastest increase". If the gr ...
.
For every pair of conjugate involute profile, there is a basic rack. This basic rack is the profile of the conjugate gear of infinite pitch radius (i.e. a toothed straight edge).
A generating rack is a rack outline used to indicate tooth details and dimensions for the design of a generating tool, such as a hob or a gear shaper cutter.
Applications
 Rack and pinion combinations are often used as part of a simple linear actuator, where the rotation of a shaft powered by hand or by a motor is converted to linear motion.
The rack carries the full load of the actuator directly and so the driving pinion is usually small, so that the gear ratio reduces the torque required. This force, thus torque, may still be substantial and so it is common for there to be a reduction gear immediately before this by either a gear or
Rack and pinion combinations are often used as part of a simple linear actuator, where the rotation of a shaft powered by hand or by a motor is converted to linear motion.
The rack carries the full load of the actuator directly and so the driving pinion is usually small, so that the gear ratio reduces the torque required. This force, thus torque, may still be substantial and so it is common for there to be a reduction gear immediately before this by either a gear or worm gear
A worm drive is a gear arrangement in which a worm (which is a gear in the form of a screw) meshes with a worm wheel (which is similar in appearance to a spur gear). The two elements are also called the worm screw and worm gear. The terminol ...
reduction. Rack gears have a higher ratio, thus require a greater driving torque, than screw actuators.
Stairlifts
Moststairlift
A stair lift is a mechanical device for lifting people, typically those with disabilities, up and down stairs. For sufficiently wide stairs, a rail is mounted to the treads of the stairs. A chair or lifting platform is attached to the rail. A per ...
s today operate using the rack and pinion system.
Steering
 A rack and pinion is commonly found in the steering mechanism of cars or other wheeled, steered vehicles. Rack and pinion provides less mechanical advantage than other mechanisms such as
A rack and pinion is commonly found in the steering mechanism of cars or other wheeled, steered vehicles. Rack and pinion provides less mechanical advantage than other mechanisms such as recirculating ball
Recirculating ball, also known as recirculating ball and nut or worm and sector, is a steering mechanism commonly found in older automobiles, off-road vehicles, and some trucks. Most newer cars use the more economical rack and pinion steering ...
, but less backlash and greater feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled ...
, or steering "feel". The mechanism may be power-assisted, usually by hydraulic or electrical means.
The use of a variable rack (still using a normal pinion) was invented by Arthur Ernest Bishop
Arthur Ernest Bishop AM (19172006) was a noted Australian engineer and inventor.
Life
Bishop was born in Sydney, New South Wales in 1917. He demonstrated highly innovative capabilities during the Second World War relating to overcoming problem ...
in the 1970s, so as to improve vehicle response and steering "feel", especially at high speeds. He also created a low cost press forging process to manufacture the racks, eliminating the need to machine the gear teeth.
Rack railways

Rack railway
A rack railway (also rack-and-pinion railway, cog railway, or cogwheel railway) is a steep grade railway with a toothed rack rail, usually between the running rails. The trains are fitted with one or more cog wheels or pinions that mesh with t ...
s are mountain railway
A mountain railway is a railway that operates in a mountainous region. It may operate through the mountains by following mountain valleys and tunneling beneath mountain passes, or it may climb a mountain to provide transport to and from the ...
s that use a rack built into the center of the track and a pinion on their locomotives. This allows them to work on steep gradients, up to 45 degrees, as opposed to conventional railways which rely on friction alone for locomotion. Additionally, the rack and pinion addition provides these trains with controlled brakes, and reduces the effects of snow or ice on the rails.
Actuators
actuator
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover".
An actuator requires a control device (controlled by control signal) a ...
s. An example is pneumatic rack and pinion actuators that can be used to control valves in pipeline transport
Pipeline transport is the long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas through a system of Pipe (fluid conveyance), pipes—a pipeline—typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than ...
. The actuators in the picture on the right are used to control the valves of large water pipeline. In the top actuator, a gray control signal line can be seen connecting to a solenoid valve (the small black box attached to the back of the top actuator), which is used as the pilot for the actuator. The solenoid valve controls the air pressure coming from the input air line (the small green tube). The output air from the solenoid valve is fed to the chamber in the middle of the actuator, increasing the pressure. The pressure in the actuator's chamber pushes the pistons away. While the pistons are moving apart from each other, the attached racks are also moved along the pistons in the opposite directions of the two racks. The two racks are meshed to a pinion at the direct opposite teeth of the pinion. When the two racks move, the pinion is turned, causing the attached main valve of the water pipe to turn.
Arcuate rack
A rack gear that is curved is called an arcuate rack. The term appears in many patent applications.History
The rack and pinion mechanism was first developed in China by firearms designer Zhao Shizhen. In his book of 1598 AD, the Shen Qi Pu (神器譜), the Xuanyuan arquebus (軒轅銃) featured a firing mechanism using a rack and pinion system that was inspired by Turkish matchlock designs that featured a novel pivoting firing mechanism. The Xuanyuan arquebus was designed in response to contemporary firearm unreliability problems arising from rainy and windy conditions, and offered a trigger that simultaneously operated both the flash pan and serpentine. The '' Wu Pei Chih'' (1621) later described Ottoman Turkish muskets that used a rack-and-pinion mechanism.See also
* List of gear nomenclature * Machine element * Pitman arm *Rack phase difference
Rack Phase Difference (RPD) is a difference in the elevation between rack teeth of the chords of any single leg of a jackup rig with open truss-type legs. This type of jackup vessel operates with a rack and pinion drive system, as opposed to th ...
* Sprocket
A sprocket, sprocket-wheel or chainwheel is a profiled wheel with teeth that mesh with a chain, track or other perforated or indented material. The name 'sprocket' applies generally to any wheel upon which radial projections engage a chain pas ...
* Steep grade railway
A steep grade railway is a railway that ascends and descends a slope that has a steep grade. Such railways can use a number of different technologies to overcome the steepness of the grade.
Usage
Many steep grade railways are located in mountai ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rack and Pinion Automotive steering technologies Gears Actuators Turkish inventions