Rumelia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the
 ''
''
 Rumelia included the provinces of
Rumelia included the provinces of
 Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople.
The canonical hours ar ...
, was the name of a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, corresponding to the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and vassals in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
that would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans". During the period of its existence, it was more often known in English as Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
in Europe.
Etymology
 ''
''Rûm
Rūm ( ar, روم , collective; singulative: Rūmī ; plural: Arwām ; fa, روم Rum or Rumiyān, singular Rumi; tr, Rûm or , singular ), also romanized as ''Roum'', is a derivative of the Aramaic (''rhπmÈ'') and Parthian language, Par ...
'' in this context means "Greek", or a Christian Greek speaker and ''ėli'' means "land" and ''Rumelia'' ( ota, روم ايلى, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans, which formerly belonged to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
, known by its contemporaries as the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
. Although the term ''Byzantine Empire'' is used by modern historians, the empire's citizens and emperors called themselves Romans, meaning Christians, more specifically Greek Christians, and embraced a Christian identity. Various languages in the Balkans have long used the descriptor "Roman" to refer to the lands of the former Byzantine Empire. Indeed, today the term survives in the region as sq, Rumelia; bs, Rumelija; bg, Румелия, ''Rumeliya''; el, Ρωμυλία, ''Romylía'', or Ρούμελη, ''Roúmeli''; Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North M ...
; and sr, Румелија, ''Rumelija''. The old Latin documents in Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of t ...
use the term ''Romania'', the common name for the Byzantine Empire during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
.
Originally, the Seljuks used the name "Land of the Rûm
Rūm ( ar, روم , collective; singulative: Rūmī ; plural: Arwām ; fa, روم Rum or Rumiyān, singular Rumi; tr, Rûm or , singular ), also romanized as ''Roum'', is a derivative of the Aramaic (''rhπmÈ'') and Parthian language, Par ...
" (Romans) to define Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
, which the armies of the Seljuk Empire gradually conquered from the Byzantine Empire after the Battle of Manzikert in 1071. The Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate was called the Sultanate of Rum by its contemporaries, meaning the "Sultanate of the Roman Empire" or "Roman Sultanate", which mostly covered central Anatolia until the Battle of Köse Dağ in 1243. Anatolia was referred to as Land of the Christians, hence Rum. Afterwards, it was replaced by the Anatolian beyliks, among which the Ottoman Beylik rose to prominence in the 14th and 15th centuries and eventually became the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
.
However, following the expansion of the Ottoman Empire into Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
and the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
in the second half of the 14th century and after the conquest of Constantinople (now Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
) in 1453 by Mehmed II, the term ''Rumeli'' came to apply exclusively to the Balkan region of the Ottoman Empire. The region remained primarily populated by Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
; though gradually, the Albanians, Bosniaks and Pomaks, among others, converted to Islam.
Many grand viziers, viziers, pasha
Pasha, Pacha or Paşa ( ota, پاشا; tr, paşa; sq, Pashë; ar, باشا), in older works sometimes anglicized as bashaw, was a higher rank in the Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignita ...
s and beylerbeyis were originally from Rumelia.
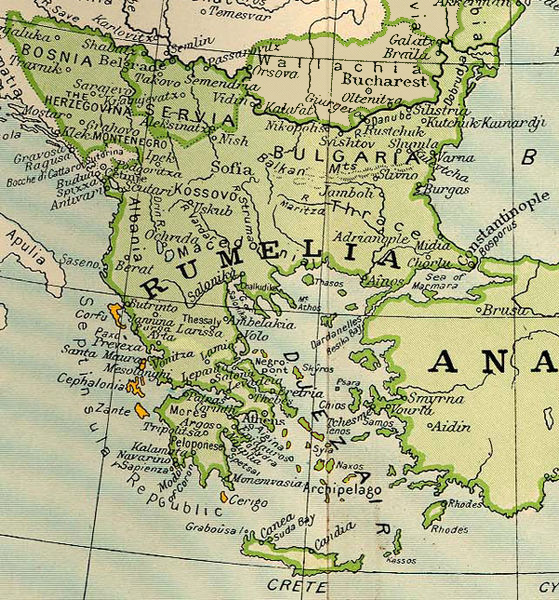
Geography
 Rumelia included the provinces of
Rumelia included the provinces of Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
, Macedonia
Macedonia most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a traditional geographic reg ...
and Moesia, which are now Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
and Turkish Thrace, bounded to the north by the rivers Sava and Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
, west by the Adriatic coast and south by the Morea
The Morea ( el, Μορέας or ) was the name of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The name was used for the Byzantine province known as the Despotate of the Morea, by the Ottom ...
. In the beginning the main town was the city of Plovdiv, then Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. ...
. The name "Rumelia" was ultimately applied to a province composed of central Albania and northwestern Macedonia, with Bitola
Bitola (; mk, Битола ) is a city in the southwestern part of North Macedonia. It is located in the southern part of the Pelagonia valley, surrounded by the Baba (North Macedonia), Baba, Nidže, and Kajmakčalan mountain ranges, north of th ...
being the main town.
Following the administrative reorganization made by the Ottoman government between 1870 and 1875, the name ''Rumelia'' ceased to correspond to any political division. Eastern Rumelia was constituted as an autonomous province of the Ottoman Empire by the Treaty of Berlin (1878), but on September 6, 1885, after a bloodless revolution, it was united with Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
. The Kosovo Vilayet was created in 1877.
In Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, the word ''Trakya'' (Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
) has now mostly replaced ''Rumeli'' (Rumelia) to refer to the part of Turkey that is in Europe (the provinces of Edirne, Kırklareli, Tekirdağ, the northern part of Çanakkale Province and the western part of Istanbul Province
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_ ...
). However, "Rumelia" remains in use in historical contexts and is still used in the context of the culture of the current Turkish populations of the Balkans and the descendants of Turkish immigrants from the Balkans. The region in Turkey is also referred to as Eastern Thrace
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
* China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
* Eastern Air ...
, or Turkish Thrace. In Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
, the term () has been used since Ottoman times to refer to Central Greece, especially when it is juxtaposed with the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge whi ...
or Morea. The word ''Rumeli'' is also used in some cases, mostly in Istanbul, to refer exclusively to the part of Istanbul Province that is west of the Bosphorus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
strait.
See also
* Turks in the Balkans * Sultanate of Rum * Millet (Ottoman Empire) * Rum Millet *Ottoman wars in Europe
A series of military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and various European states took place from the Late Middle Ages up through the early 20th century. The earliest conflicts began during the Byzantine–Ottoman wars, waged in Anatolia i ...
* Ada Kaleh
* Ottoman Greece
* Ottoman Bulgaria
* Ottoman Vardar Macedonia
Vardar Macedonia, the area that now makes up North Macedonia, was part of the Ottoman Empire for over five hundred years, from the mid-14th century to 1912. However, the Ottomans themselves did not keep any "Macedonia" as an administrative unit. ...
* Ottoman Serbia
* Ottoman Bosnia and Herzegovina
* Ottoman Albania
* Ottoman Kosovo
References
Sources
*External links
* {{Coord, 41.0000, N, 21.3333, E, source:wikidata, display=title 15th-century establishments in the Ottoman Empire Byzantine Empire Divided regions Historical regions History of the Balkans by region Ottoman Greece 01 Ottoman period in the history of Bulgaria Subdivisions of the Ottoman Empire Turkish toponyms