Rossby Number on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Rossby number (Ro), named for Carl-Gustav Arvid Rossby, is a
The Rossby number (Ro), named for Carl-Gustav Arvid Rossby, is a
 The Rossby number (Ro), named for Carl-Gustav Arvid Rossby, is a
The Rossby number (Ro), named for Carl-Gustav Arvid Rossby, is a dimensionless number
Dimensionless quantities, or quantities of dimension one, are quantities implicitly defined in a manner that prevents their aggregation into unit of measurement, units of measurement. ISBN 978-92-822-2272-0. Typically expressed as ratios that a ...
used in describing fluid flow. The Rossby number is the ratio of inertial force to Coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is a pseudo force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motio ...
, terms and in the Navier–Stokes equations
The Navier–Stokes equations ( ) are partial differential equations which describe the motion of viscous fluid substances. They were named after French engineer and physicist Claude-Louis Navier and the Irish physicist and mathematician Georg ...
respectively. It is commonly used in geophysical
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct investigations acros ...
phenomena in the oceans
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and ...
and atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, where it characterizes the importance of Coriolis accelerations arising from planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
ary rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
. It is also known as the Kibel number.
Definition and theory
The Rossby number (Ro, not Ro) is defined as : where ''U'' and ''L'' are respectively characteristic velocity and length scales of the phenomenon, and is the Coriolis frequency, with being theangular frequency
In physics, angular frequency (symbol ''ω''), also called angular speed and angular rate, is a scalar measure of the angle rate (the angle per unit time) or the temporal rate of change of the phase argument of a sinusoidal waveform or sine ...
of planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
ary rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
, and the latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
.
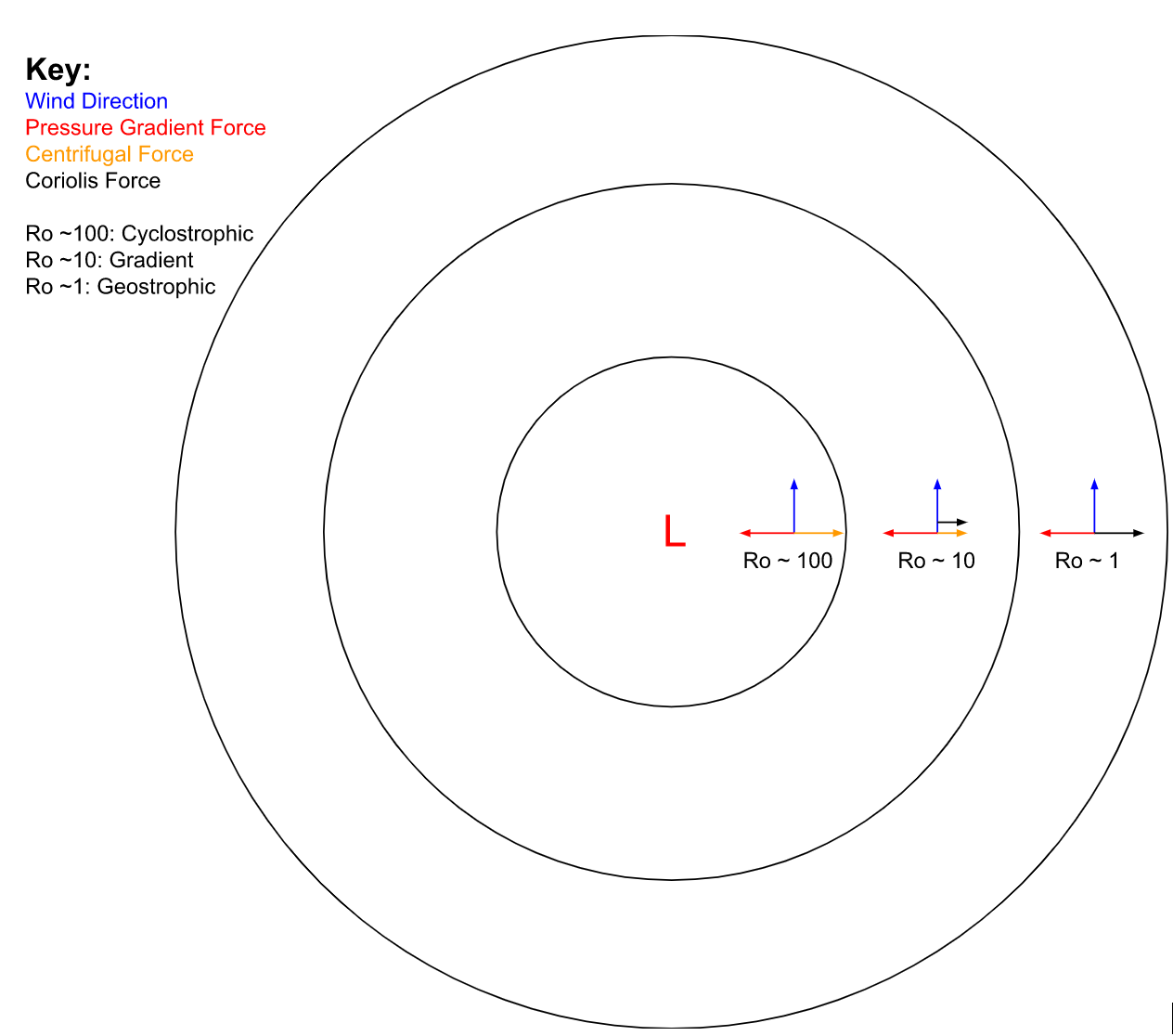
A small Rossby number signifies a system strongly affected by Coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is a pseudo force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motio ...
s, and a large Rossby number signifies a system in which inertial and centrifugal force
Centrifugal force is a fictitious force in Newtonian mechanics (also called an "inertial" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It appears to be directed radially away from the axi ...
s dominate. For example, in tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the ...
es, the Rossby number is large (≈ 103), in low-pressure systems it is low (≈ 0.1–1), and in oceanic systems it is of the order of unity, but depending on the phenomena can range over several orders of magnitude (≈ 10−2–102). As a result, in tornadoes the Coriolis force is negligible, and balance is between pressure and centrifugal forces (called ''cyclostrophic balance''). Cyclostrophic balance also commonly occurs in the inner core of a tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
. In low-pressure systems, centrifugal force is negligible, and balance is between Coriolis and pressure forces (called '' geostrophic balance''). In the oceans all three forces are comparable (called '' cyclogeostrophic balance''). For a figure showing spatial and temporal scales of motions in the atmosphere and oceans, see Kantha and Clayson.
When the Rossby number is large (either because ''f'' is small, such as in the tropics and at lower latitudes; or because ''L'' is small, that is, for small-scale motions such as flow in a bathtub; or for large speeds), the effects of planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
ary rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
are unimportant and can be neglected. When the Rossby number is small, then the effects of planetary rotation are large, and the net acceleration is comparably small, allowing the use of the geostrophic approximation.
See also
* *References and notes
Further reading
For more on numerical analysis and the role of the Rossby number, see: * * For an historical account of Rossby's reception in the United States, see * {{NonDimFluMech Atmospheric dynamics Dimensionless numbers of fluid mechanics