Ross 128 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ross 128 is a
 This low-mass star has a
This low-mass star has a 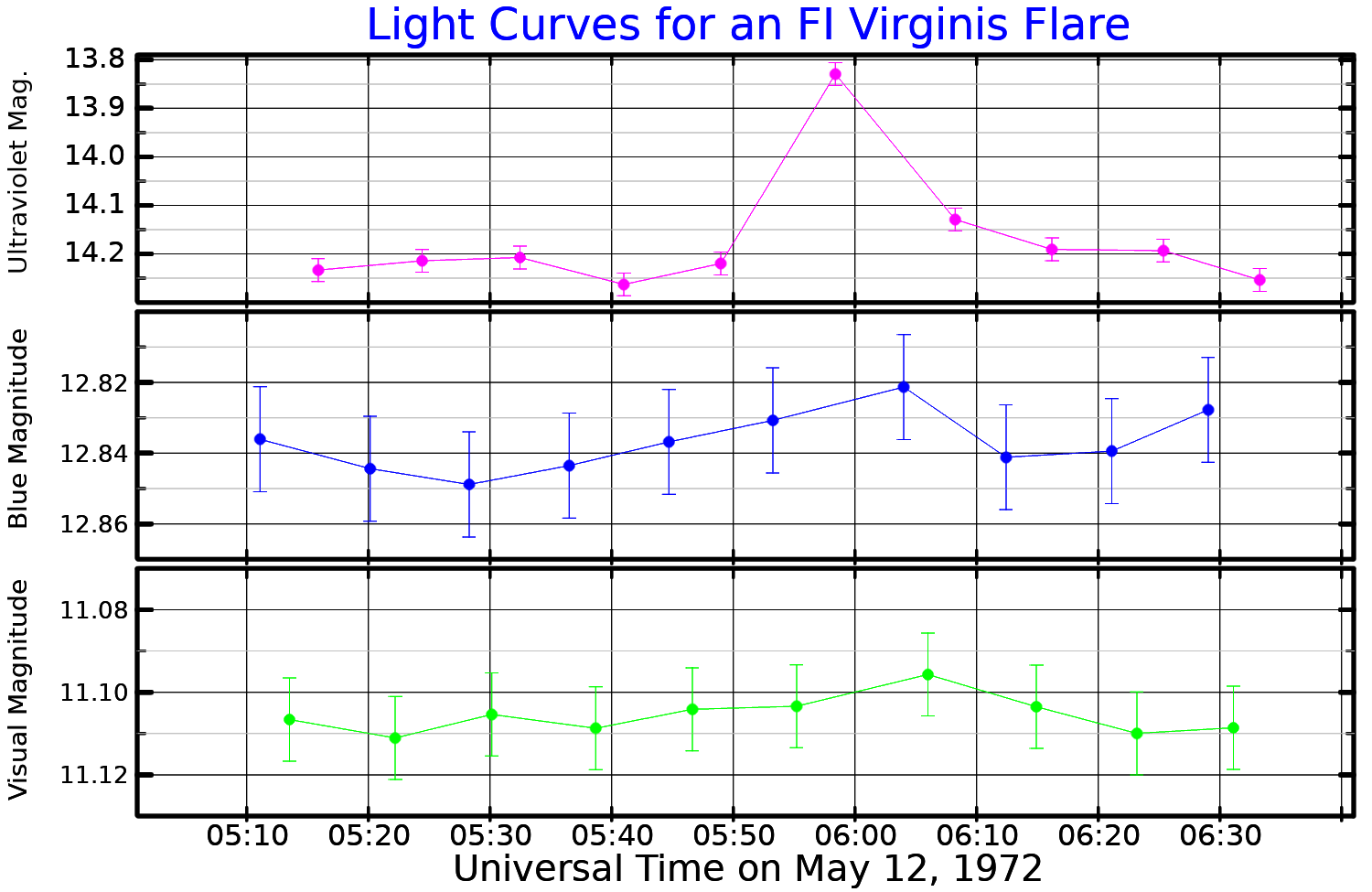 In 1972, a flare was detected from Ross 128. It was observed to increase in brightness by about half a magnitude in the
In 1972, a flare was detected from Ross 128. It was observed to increase in brightness by about half a magnitude in the
Ian O'Neill, ''How Stuff Works''. 15 November 2017. Quote: ''"Tidal lock ngis expected for Ross 128 b," says Nicola Astudillo-Defru, who works at the Geneva Observatory, University of Geneva in Switzerland, and is co-author of the study.'' Near-infrared high-resolution spectra from
SolStation.com: Ross 128
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ross 128 Local Bubble M-type main-sequence stars Virgo (constellation) Flare stars
red dwarf
A red dwarf is the smallest kind of star on the main sequence. Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of fusing star in the Milky Way, at least in the neighborhood of the Sun. However, due to their low luminosity, individual red dwarfs are ...
star in the equatorial zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
of Virgo
Virgo may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Virgo (film), a 1970 Egyptian film
* Virgo (character), several Marvel Comics characters
* Virgo Asmita, a character in the manga ''Saint Seiya: The Lost Canvas''
* ''Virgo'' (album), by Virgo Four, ...
, near β Virginis. The apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), ...
of Ross 128 is 11.13, which is too faint to be seen with the unaided eye. Based upon parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphica ...
measurements, the distance of this star from Earth is , making it the twelfth closest stellar system to the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
. It was first cataloged in 1926 by American astronomer Frank Elmore Ross
Frank Elmore Ross (April 2, 1874 – September 21, 1960) was an American astronomer and physicist. He was born in San Francisco, California and died in Altadena, California. In 1901 he received his doctorate from the University of California. ...
.
Properties
stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction gratin ...
of M4 V, which places it among the category of stars known as red dwarfs. It has about 18% of the mass of the Sun and 20% of the Sun's radius, but generates energy so slowly that it has only 0.033% of the Sun's visible luminosity; however, most of the energy being radiated by the star is in the infrared band, with the bolometric luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic energy per unit time, and is synonymous with the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per ...
being equal to 0.37% of solar. This energy is being radiated from the star's outer atmosphere at an effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
of 3,180 K. This gives it the cool orange-red glow of an M-type star
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the ...
.
Ross 128 is an old disk star, which means it has a low abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium, what astronomers term the star's metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the Abundance of the chemical elements, abundance of Chemical element, elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal currently detectable (i.e. non-Dark matter, dark) matt ...
, and it orbits near the plane of the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
galaxy. The star lacks a strong excess of infrared radiation. An infrared excess
An infrared excess is a measurement of an astronomical source, typically a star, that in their spectral energy distribution has a greater measured infrared flux than expected by assuming the star is a blackbody radiator. Infrared excesses are of ...
is usually an indicator of a dust ring in orbit around the star.
 In 1972, a flare was detected from Ross 128. It was observed to increase in brightness by about half a magnitude in the
In 1972, a flare was detected from Ross 128. It was observed to increase in brightness by about half a magnitude in the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
U band, returning to normal brightness in less than an hour. At optical wavelengths, the brightness changes were almost undetectable. It was classified as a flare star
A flare star is a variable star that can undergo unpredictable dramatic increases in brightness for a few minutes. It is believed that the flares on flare stars are analogous to solar flares in that they are due to magnetic reconnection, the magne ...
and given the variable star designation
In astronomy, a variable-star designation is a unique identifier given to variable stars. It extends the Bayer designation format, with an identifying label (as described below) preceding the Latin genitive of the name of the constellation in whic ...
FI Virginis. Because of the low rate of flare activity, it is thought to be a magnetically evolved star. That is, there is some evidence that the magnetic braking of the star's stellar wind has lowered the frequency of flares, but not the net yield.
Brightness variations thought to be due to rotation of the star and magnetic cycles similar to the sunspot cycle
The Solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surface. Ov ...
have also been detected. These cause changes of just a few thousandths of a magnitude. The rotation period is found to be 165.1 days, and the magnetic cycle length 4.1 years.
Ross 128 is orbiting through the galaxy with an eccentricity
Eccentricity or eccentric may refer to:
* Eccentricity (behavior), odd behavior on the part of a person, as opposed to being "normal"
Mathematics, science and technology Mathematics
* Off-Centre (geometry), center, in geometry
* Eccentricity (g ...
of 0.122, causing its distance from the Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a ...
to range between . This orbit will bring the star closer to the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
in the future. The nearest approach will occur in approximately 71,000 years, when it will come within .
Planetary system
Ross 128 b was discovered in July 2017 by theHARPS
The High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher (HARPS) is a high-precision Echelle grating, echelle planet-finding spectrograph installed in 2002 on the ESO 3.6 m Telescope, ESO's 3.6m telescope at La Silla Observatory in Chile. The First l ...
instrument at the La Silla Observatory
La Silla Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are also located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observato ...
in Chile, by measuring changes in radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity of a target with respect to an observer is the rate of change of the vector displacement between the two points. It is formulated as the vector projection of the target-observer relative velocity ...
of the host star. Its existence was confirmed on 15 November 2017. It is the second-closest known Earth-size exoplanet, after Proxima b
Proxima Centauri b is an exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of the red dwarf star Proxima Centauri in the constellation Centaurus. It can also be referred to as Proxima b, or Alpha Centauri Cb. The host star is the closest star to th ...
. Ross 128 b has a minimum mass
In astronomy, minimum mass is the lower-bound calculated mass of observed objects such as planets, stars, binary systems, nebulae, and black holes.
Minimum mass is a widely cited statistic for extrasolar planets detected by the radial velocit ...
1.4 times that of Earth; a 2019 study predicts a true mass about 1.8 times Earth and a radius about 1.6 times that of the Earth, with large margins of error. It orbits 20 times closer to its star than Earth orbits the Sun, intercepting only about 1.38 times more solar radiation than Earth, increasing the chance of retaining an atmosphere over a geological timescale. Ross 128 b is a closely orbiting planet, with a year (orbital period) lasting about 9.9 days. At that close distance from its host star, the planet is most likely tidally locked
Tidal locking between a pair of co-orbiting astronomical bodies occurs when one of the objects reaches a state where there is no longer any net change in its rotation rate over the course of a complete orbit. In the case where a tidally locked ...
, meaning that one side of the planet would have eternal daylight and the other would be in darkness.Nearby Earth-sized Alien World Orbits 'Quiet' Star, Boosting Habitable PotentialIan O'Neill, ''How Stuff Works''. 15 November 2017. Quote: ''"Tidal lock ngis expected for Ross 128 b," says Nicola Astudillo-Defru, who works at the Geneva Observatory, University of Geneva in Switzerland, and is co-author of the study.'' Near-infrared high-resolution spectra from
APOGEE
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values.
Apsides perta ...
have demonstrated that Ross 128 has near solar metallicity; Ross 128 b therefore most likely contains rock and iron. Furthermore, recent models generated with these data support the conclusion that Ross 128 b is a "temperate exoplanet in the inner edge of the habitable zone."
A 2024 study of the radial velocity data found an eccentricity of about 0.21 for Ross 128 b, higher than previous estimates and similar to that of Mercury. Given the planet's orbit near the inner edge of the habitable zone, such a high eccentricity would significantly decrease its potential for habitability. This study also searched for additional planets in the system, and did not find any.
Radio signals
In the spring of 2017, Arecibo astronomers detected strange radio signals thought to originate from Ross 128 that were unlike any they had seen before.SETI
Seti or SETI may refer to:
Astrobiology
* SETI, the search for extraterrestrial intelligence.
** SETI Institute, an astronomical research organization
*** SETIcon, a former convention organized by the SETI Institute
** Berkeley SETI Research Cent ...
's Allen Telescope Array was used for follow-up observations and was unable to detect the signal but did detect man made interference, making it seem clear that the Arecibo detections were due to transmissions from Earth satellites in geosynchronous orbit. Ross 128 has a declination (a coordinate which can be likened to latitude) of close to 0 degrees, which places it in the thick of a phalanx of these satellites. Therefore, it can be concluded that the signal was a result of man-made interference.
See also
*List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs
This list covers all known stars, white dwarfs, brown dwarfs, and sub-brown dwarfs within of the Sun. So far, 131 such objects have been found. Only List of nearest bright stars, 22 are bright enough to be visible without a telescope, for whi ...
* PSR B1919+21
PSR B1919+21 is a pulsar with a period of 1.3373 seconds and a pulse width of 0.04 seconds. Discovered by Jocelyn Bell Burnell on 28 November 1967, it is the first discovered radio pulsar. The power and regularity of the signals were ...
– pulsar mistaken for an alien radio signal (LGM-1)
References
External links
SolStation.com: Ross 128
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ross 128 Local Bubble M-type main-sequence stars Virgo (constellation) Flare stars
128 128 may refer to
*128 (number), a natural number
*AD 128, a year in the 2nd century AD
*128 BC, a year in the 2nd century BC
*128 (New Jersey bus)
*128 Nemesis, a main-belt asteroid
*Fiat 128, also known as the Zastava 128, a small family car
**SEAT ...
0447
057548
Virginis, FI
?
Emission-line stars
Orion–Cygnus Arm
Planetary systems with one confirmed planet
TIC objects