Rib (nautical) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

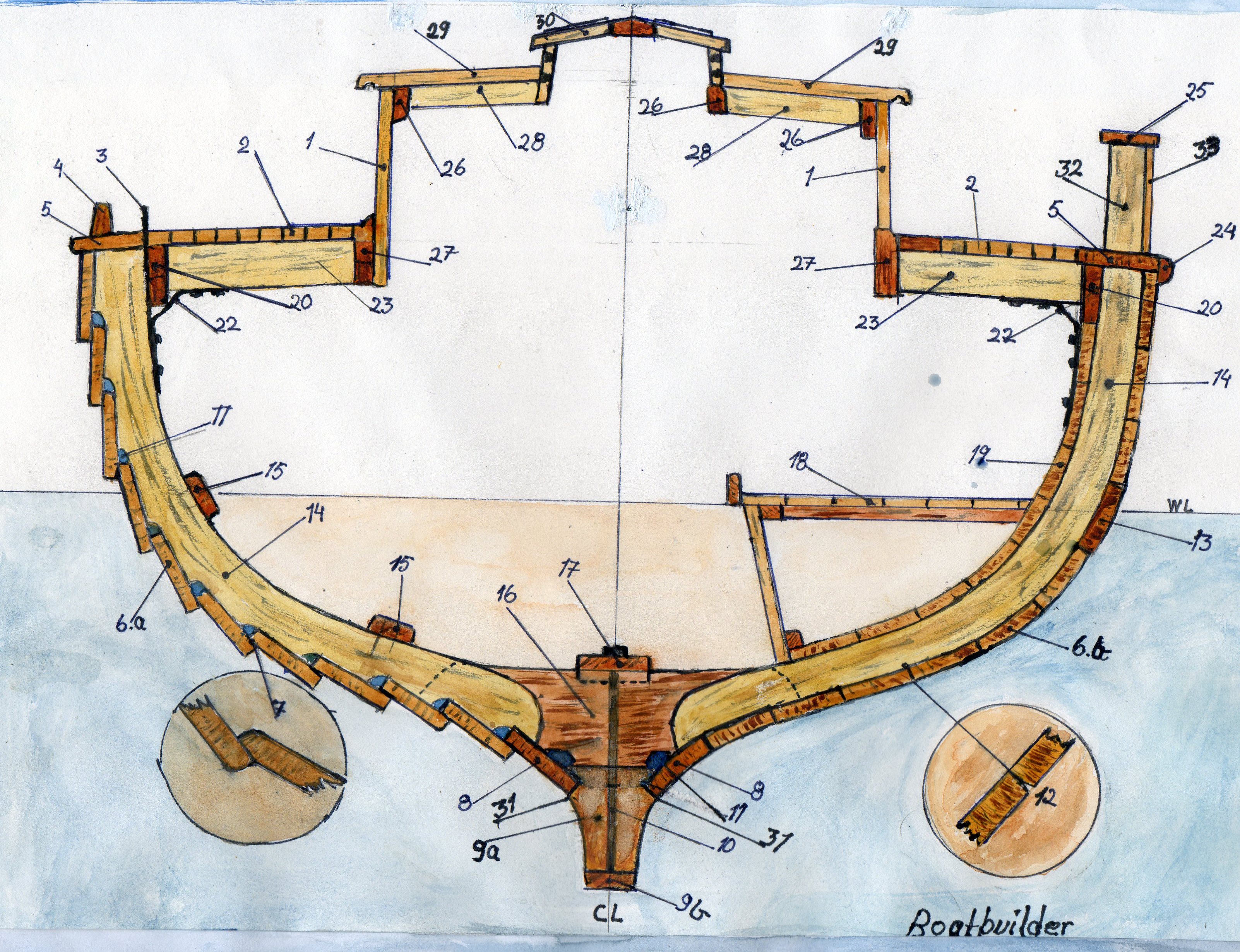 On a vessel's
On a vessel's

 On a vessel's
On a vessel's hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
, a rib is a lateral structural member which runs between gunwales and sprouts from the keel. They are called "ribs" because they resemble the human rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs ( la, costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ches ...
. The ship's outer planking and inner sheathing are attached to the ribs. For ships that are too large for a rib to be made out of a single piece of wood, the ribs are made of multiple sections called futtocks that are scarfed together. The ancient writers Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
and Plato held that, since the ribs of a ship were the most important part of the ship's framework, then if the ribs were new, then the ship as a whole was new. Iron was first used in shipbuilding to make the ribs and frames, with wood sheathing attached to them, but this proved inadequate compared to replacing the wood sheathing with iron plates.
See also
*Frame (nautical)
In ships, frames are ribs that are transverse bolted or welded to the keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the l ...
References
{{sailing ship elements Nautical terminology Shipbuilding