refracted on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
chromatic dispersion
in th
, accessed on 2014-09-08 and thus the angle of the refraction also varies correspondingly. This is called dispersion and causes prisms and
Dispersion
i
, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Georgia State University, accessed on 2014-09-08
 For light, refraction follows
For light, refraction follows 
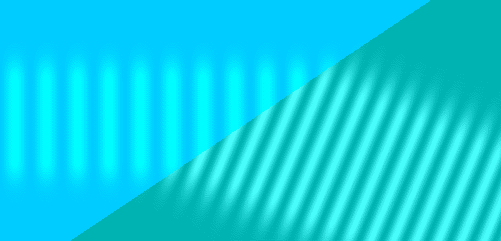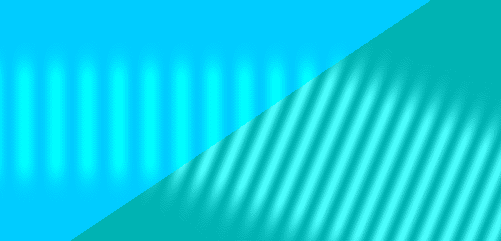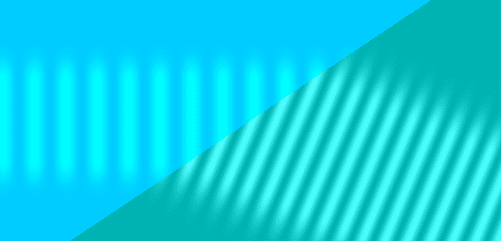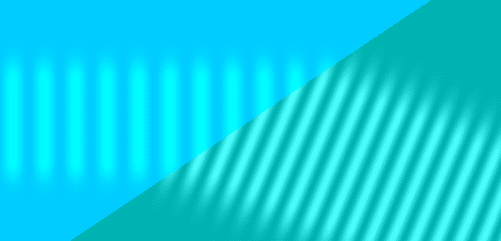 Refraction involves two related parts, both a result of the wave nature of light: a reduced speed in an optical medium and a change in angle when a wave front crosses between different media at an angle.
# Light slows as it travels through a medium other than vacuum (such as air, glass or water). This is not because of scattering or absorption. Rather it is because, as an electromagnetic oscillation, light itself causes other electrically charged particles such as
Refraction involves two related parts, both a result of the wave nature of light: a reduced speed in an optical medium and a change in angle when a wave front crosses between different media at an angle.
# Light slows as it travels through a medium other than vacuum (such as air, glass or water). This is not because of scattering or absorption. Rather it is because, as an electromagnetic oscillation, light itself causes other electrically charged particles such as
 Refraction occurs when light goes through a water surface since water has a refractive index of 1.33 and air has a refractive index of about 1. Looking at a straight object, such as a pencil in the figure here, which is placed at a slant, partially in the water, the object appears to bend at the water's surface. This is due to the bending of light rays as they move from the water to the air. Once the rays reach the eye, the eye traces them back as straight lines (lines of sight). The lines of sight (shown as dashed lines) intersect at a higher position than where the actual rays originated. This causes the pencil to appear higher and the water to appear shallower than it really is.
The depth that the water appears to be when viewed from above is known as the ''apparent depth''. This is an important consideration for spearfishing from the surface because it will make the target fish appear to be in a different place, and the fisher must aim lower to catch the fish. Conversely, an object above the water has a higher ''apparent height'' when viewed from below the water. The opposite correction must be made by an archer fish.
For small angles of incidence (measured from the normal, when is approximately the same as ), the ratio of apparent to real depth is the ratio of the refractive indexes of air to that of water. But, as the angle of incidence approaches 90°, the apparent depth approaches zero, albeit reflection increases, which limits observation at high angles of incidence. Conversely, the apparent height approaches infinity as the angle of incidence (from below) increases, but even earlier, as the angle of total internal reflection is approached, albeit the image also fades from view as this limit is approached.
Refraction occurs when light goes through a water surface since water has a refractive index of 1.33 and air has a refractive index of about 1. Looking at a straight object, such as a pencil in the figure here, which is placed at a slant, partially in the water, the object appears to bend at the water's surface. This is due to the bending of light rays as they move from the water to the air. Once the rays reach the eye, the eye traces them back as straight lines (lines of sight). The lines of sight (shown as dashed lines) intersect at a higher position than where the actual rays originated. This causes the pencil to appear higher and the water to appear shallower than it really is.
The depth that the water appears to be when viewed from above is known as the ''apparent depth''. This is an important consideration for spearfishing from the surface because it will make the target fish appear to be in a different place, and the fisher must aim lower to catch the fish. Conversely, an object above the water has a higher ''apparent height'' when viewed from below the water. The opposite correction must be made by an archer fish.
For small angles of incidence (measured from the normal, when is approximately the same as ), the ratio of apparent to real depth is the ratio of the refractive indexes of air to that of water. But, as the angle of incidence approaches 90°, the apparent depth approaches zero, albeit reflection increases, which limits observation at high angles of incidence. Conversely, the apparent height approaches infinity as the angle of incidence (from below) increases, but even earlier, as the angle of total internal reflection is approached, albeit the image also fades from view as this limit is approached.

 Air temperature variations close to the surface can give rise to other optical phenomena, such as mirages and Fata Morgana. Most commonly, air heated by a hot road on a sunny day deflects light approaching at a shallow angle towards a viewer. This makes the road appear reflecting, giving an illusion of water covering the road.
Air temperature variations close to the surface can give rise to other optical phenomena, such as mirages and Fata Morgana. Most commonly, air heated by a hot road on a sunny day deflects light approaching at a shallow angle towards a viewer. This makes the road appear reflecting, giving an illusion of water covering the road.
File:Fénytörés.jpg
File:Just a refraction.jpg
File:R-DSC00449-WMC.jpg
File:Light refraction.gif
File:Színszóródás prizmán2.jpg
File:Refraction.svg
File:Reading and drinking tea - sunlight.jpg
Reflections and Refractions in Ray Tracing
a simple but thorough discussion of the mathematics behind refraction and reflection.
Flash refraction simulation- includes source
Explains refraction and Snell's Law. {{Authority control Physical phenomena Geometrical optics Physical optics
 In
In physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, refraction is the redirection of a wave
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium ...
as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
is the most commonly observed phenomenon, but other waves such as sound wave
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ...
s and water waves also experience refraction. How much a wave is refracted is determined by the change in wave speed and the initial direction of wave propagation relative to the direction of change in speed.
Optical prisms and lenses use refraction to redirect light, as does the human eye
The human eye is a sensory organ in the visual system that reacts to light, visible light allowing eyesight. Other functions include maintaining the circadian rhythm, and Balance (ability), keeping balance.
The eye can be considered as a living ...
. The refractive index of materials varies with the wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of light,R. Paschotta, article ochromatic dispersion
in th
, accessed on 2014-09-08 and thus the angle of the refraction also varies correspondingly. This is called dispersion and causes prisms and
rainbow
A rainbow is an optical phenomenon caused by refraction, internal reflection and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a continuous spectrum of light appearing in the sky. The rainbow takes the form of a multicoloured circular ...
s to divide white light into its constituent spectral color
Color (or colour in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though co ...
s.Carl R. Nave, page oDispersion
i
, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Georgia State University, accessed on 2014-09-08
Law
Snell's law
Snell's law (also known as the Snell–Descartes law, the ibn-Sahl law, and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing th ...
, which states that, for a given pair of media, the ratio of the sines of the angle of incidence and angle of refraction
Snell's law (also known as the Snell–Descartes law, the ibn-Sahl law, and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing th ...
is equal to the ratio of phase velocities in the two media, or equivalently, to the refractive indices
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
of the two media:

General explanation
 Refraction involves two related parts, both a result of the wave nature of light: a reduced speed in an optical medium and a change in angle when a wave front crosses between different media at an angle.
# Light slows as it travels through a medium other than vacuum (such as air, glass or water). This is not because of scattering or absorption. Rather it is because, as an electromagnetic oscillation, light itself causes other electrically charged particles such as
Refraction involves two related parts, both a result of the wave nature of light: a reduced speed in an optical medium and a change in angle when a wave front crosses between different media at an angle.
# Light slows as it travels through a medium other than vacuum (such as air, glass or water). This is not because of scattering or absorption. Rather it is because, as an electromagnetic oscillation, light itself causes other electrically charged particles such as electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s, to oscillate. The oscillating electrons emit their own electromagnetic waves which interact with the original light. The resulting combined wave has a lower speed. When light returns to a vacuum and there are no electrons nearby, this slowing effect ends and its speed returns to .
# When light enters a slower medium at an angle, one side of the wavefront
In physics, the wavefront of a time-varying ''wave field (physics), field'' is the set (locus (mathematics), locus) of all point (geometry), points having the same ''phase (waves), phase''. The term is generally meaningful only for fields that, a ...
is slowed before the other. This asymmetrical slowing of the light causes it to change the angle of its travel. Once light is within the new medium with constant properties, it travels in a straight line again.
Slowing of light
As described above, thespeed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time i ...
is slower in a medium other than vacuum. This slowing applies to any medium such as air, water, or glass, and is responsible for phenomena such as refraction. On the other side of the medium its speed will again be the speed of light in vacuum, .
A correct explanation rests on light's nature as an electromagnetic wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength, ...
. Because light is an oscillating electrical/magnetic wave, light traveling in a medium causes the electrically charged electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s of the material to also oscillate. (The material's proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s also oscillate but as they are around 2000 times more massive, their movement and therefore their effect, is far smaller). A moving electrical charge
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
emits electromagnetic waves of its own. The electromagnetic waves emitted by the oscillating electrons interact with the electromagnetic waves that make up the original light, similar to water waves on a pond, a process known as constructive interference. When two waves interfere in this way, the resulting "combined" wave may have wave packets that pass an observer at a slower rate. The light has effectively been slowed. When the light leaves the material, this interaction with electrons no longer happens, and therefore the wave packet rate (and therefore its speed) return to normal.
Bending of light
Consider a wave going from one material to another where its speed is slower as in the figure. If it reaches the interface between the materials at an angle one side of the wave will reach the second material first, and therefore slow down earlier. With one side of the wave going slower the whole wave will pivot towards that side. This is why a wave will bend away from the surface or toward the normal when going into a slower material. In the opposite case of a wave reaching a material where the speed is higher, one side of the wave will speed up and the wave will pivot away from that side. Another way of understanding the same thing is to consider the change in wavelength at the interface. When the wave goes from one material to another where the wave has a different speed , thefrequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
of the wave will stay the same, but the distance between wavefront
In physics, the wavefront of a time-varying ''wave field (physics), field'' is the set (locus (mathematics), locus) of all point (geometry), points having the same ''phase (waves), phase''. The term is generally meaningful only for fields that, a ...
s or wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
will change. If the speed is decreased, such as in the figure to the right, the wavelength will also decrease. With an angle between the wave fronts and the interface and change in distance between the wave fronts the angle must change over the interface to keep the wave fronts intact. From these considerations the relationship between the angle of incidence , angle of transmission and the wave speeds and in the two materials can be derived. This is the law of refraction or Snell's law and can be written as
The phenomenon of refraction can in a more fundamental way be derived from the 2 or 3-dimensional wave equation. The boundary condition at the interface will then require the tangential component of the wave vector
In physics, a wave vector (or wavevector) is a vector used in describing a wave, with a typical unit being cycle per metre. It has a magnitude and direction. Its magnitude is the wavenumber of the wave (inversely proportional to the wavelength) ...
to be identical on the two sides of the interface. Since the magnitude of the wave vector depend on the wave speed this requires a change in direction of the wave vector.
The relevant wave speed in the discussion above is the phase velocity
The phase velocity of a wave is the rate at which the wave propagates in any medium. This is the velocity at which the phase of any one frequency component of the wave travels. For such a component, any given phase of the wave (for example, t ...
of the wave. This is typically close to the group velocity
The group velocity of a wave is the velocity with which the overall envelope shape of the wave's amplitudes—known as the ''modulation'' or ''envelope (waves), envelope'' of the wave—propagates through space.
For example, if a stone is thro ...
which can be seen as the truer speed of a wave, but when they differ it is important to use the phase velocity in all calculations relating to refraction.
A wave traveling perpendicular to a boundary, i.e. having its wavefronts parallel to the boundary, will not change direction even if the speed of the wave changes.
Dispersion of light
Refraction is also responsible forrainbow
A rainbow is an optical phenomenon caused by refraction, internal reflection and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a continuous spectrum of light appearing in the sky. The rainbow takes the form of a multicoloured circular ...
s and for the splitting of white light into a rainbow-spectrum as it passes through a glass prism. Glass and water have higher refractive indexes than air. When a beam of white light passes from air into a material having an index of refraction that varies with frequency (and wavelength), a phenomenon known as dispersion occurs, in which different coloured components of the white light are refracted at different angles, i.e., they bend by different amounts at the interface, so that they become separated. The different colors correspond to different frequencies and different wavelengths.
On water

Atmospheric
The refractive index of air depends on the airdensity
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
and thus vary with air temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
and pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
. Since the pressure is lower at higher altitudes, the refractive index is also lower, causing light rays to refract towards the earth surface when traveling long distances through the atmosphere. This shifts the apparent positions of stars slightly when they are close to the horizon and makes the sun visible before it geometrically rises above the horizon during a sunrise.
Temperature variations in the air can also cause refraction of light. This can be seen as a heat haze when hot and cold air is mixed e.g. over a fire, in engine exhaust, or when opening a window on a cold day. This makes objects viewed through the mixed air appear to shimmer or move around randomly as the hot and cold air moves. This effect is also visible from normal variations in air temperature during a sunny day when using high magnification telephoto lenses and is often limiting the image quality in these cases.
In a similar way, atmospheric turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers with no disruption between ...
gives rapidly varying distortions in the images of astronomical telescopes
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
limiting the resolution of terrestrial telescopes not using adaptive optics
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technique of precisely deforming a mirror in order to compensate for light distortion. It is used in Astronomy, astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of Astronomical seeing, atmo ...
or other techniques for overcoming these atmospheric distortions.
 Air temperature variations close to the surface can give rise to other optical phenomena, such as mirages and Fata Morgana. Most commonly, air heated by a hot road on a sunny day deflects light approaching at a shallow angle towards a viewer. This makes the road appear reflecting, giving an illusion of water covering the road.
Air temperature variations close to the surface can give rise to other optical phenomena, such as mirages and Fata Morgana. Most commonly, air heated by a hot road on a sunny day deflects light approaching at a shallow angle towards a viewer. This makes the road appear reflecting, giving an illusion of water covering the road.
In eye care
Inmedicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
, particularly optometry
Optometry is the healthcare practice concerned with examining the eyes for visual defects, prescribing corrective lenses, and detecting eye abnormalities.
In the United States and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a post-baccalaureate f ...
, ophthalmology
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a ...
and orthoptics
Orthoptics is a profession allied to the eye care profession. Orthoptists are the experts in diagnosing and treating defects in eye movements and problems with how the eyes work together, called binocular vision. These can be caused by issues with ...
, ''refraction'' (also known as ''refractometry'') is a clinical test in which a phoropter
A phoropter or refractor is an ophthalmic testing device. It is commonly used by eye care professionals during an eye examination, and contains different lenses used for refraction of the eye during sight testing, to measure an individual's ref ...
may be used by the appropriate eye care professional to determine the eye's refractive error
Refractive error is a problem with focus (optics), focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and/or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are myopia, near-sightedness, hyperopia, far-sightedness, astigmatis ...
and the best corrective lenses to be prescribed. A series of test lenses in graded optical power
In optics, optical power (also referred to as dioptric power, refractive power, focal power, focusing power, or convergence power) is the degree to which a lens, mirror, or other optical system converges or diverges light. It is equal to the ...
s or focal length
The focal length of an Optics, optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the Multiplicative inverse, inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system Converge ...
s are presented to determine which provides the sharpest, clearest vision.
Refractive surgery
Refractive surgery is an optional eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea ( keratomi ...
is a medical procedure to treat common vision disorders.
Mechanical waves
Water
Water waves travel slower in shallower water. This can be used to demonstrate refraction in ripple tanks and also explains why waves on a shoreline tend to strike the shore close to a perpendicular angle. As the waves travel from deep water into shallower water near the shore, they are refracted from their original direction of travel to an angle more normal to the shoreline.Sound
In underwater acoustics, refraction is the bending or curving of a sound ray that results when the ray passes through asound speed gradient
In acoustics, the sound speed gradient is the rate of change of the speed of sound with distance, for example with depth in the ocean,
or height in the Earth's atmosphere. A sound speed gradient leads to refraction of sound wavefronts in the dire ...
from a region of one sound speed to a region of a different speed. The amount of ray bending is dependent on the amount of difference between sound speeds, that is, the variation in temperature, salinity, and pressure of the water.
Similar acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician ...
effects are also found in the Earth's atmosphere. The phenomenon of refraction of sound in the atmosphere has been known for centuries. Beginning in the early 1970s, widespread analysis of this effect came into vogue through the designing of urban highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It includes not just major roads, but also other public roads and rights of way. In the United States, it is also used as an equivalent term to controlled-access highway, or ...
s and noise barrier
A noise barrier (also called a soundwall, noise wall, sound berm, sound barrier, or acoustical barrier) is an exterior structure designed to protect inhabitants of sensitive land use areas from noise pollution. Noise barriers are the most effecti ...
s to address the meteorological
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agriculture ...
effects of bending of sound rays in the lower atmosphere.
Gallery
See also
*Birefringence
Birefringence, also called double refraction, is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are described as birefrin ...
(double refraction)
* Geometrical optics
Geometrical optics, or ray optics, is a model of optics that describes light Wave propagation, propagation in terms of ''ray (optics), rays''. The ray in geometrical optics is an abstract object, abstraction useful for approximating the paths along ...
* Huygens–Fresnel principle
* List of indices of refraction
* Negative refraction
* Reflection
* Schlieren photography
Schlieren photography is a process for photographing fluid flow. Invented by the Germans, German physicist August Toepler in 1864 to study supersonic motion, it is widely used in aeronautical engineering to photograph the airflow, flow of air ar ...
* Seismic refraction
Seismic refraction is a geophysical principle governed by Snell's Law of refraction. The seismic refraction method utilizes the refraction of seismic waves by rock or soil layers to characterize the subsurface geologic conditions and Structural ge ...
* Super refraction
Anomalous propagation (sometimes shortened to anaprop or anoprop) Peter Meischner (ed.), ''Weather Radar: Principles and Advanced Applications'', Springer Science & Business Media, 2005, page 144 includes different forms of radio propagation due t ...
References
External links
Reflections and Refractions in Ray Tracing
a simple but thorough discussion of the mathematics behind refraction and reflection.
Flash refraction simulation- includes source
Explains refraction and Snell's Law. {{Authority control Physical phenomena Geometrical optics Physical optics