Rallet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Rallet, founded 1843 in Moscow by Alphonse Rallet (1819–1894), had become, by 1900, Russia's preeminent manufacturer of fine perfume, soap, and cosmetics and was an official supplier to the royal courts of Russia,
Rallet, founded 1843 in Moscow by Alphonse Rallet (1819–1894), had become, by 1900, Russia's preeminent manufacturer of fine perfume, soap, and cosmetics and was an official supplier to the royal courts of Russia,
 During the last 20 years of the 19th century, Rallet made huge profits from the sale of fashionable colognes. At some time during this period, Edward (Edwardovich) Beaux, a member of the board of directors, became Deputy Administrator of the company. Edward (Edwardovich) Beaux had previously served as a clerk for the trading company of Muir and Merrilees. In 1898 his younger brother,
During the last 20 years of the 19th century, Rallet made huge profits from the sale of fashionable colognes. At some time during this period, Edward (Edwardovich) Beaux, a member of the board of directors, became Deputy Administrator of the company. Edward (Edwardovich) Beaux had previously served as a clerk for the trading company of Muir and Merrilees. In 1898 his younger brother,
 In 1912, Rallet scored a major success with its ''Le Bouquet de Napoleon'', a fragrance launched with great fanfare to commemorate the centenary of the
In 1912, Rallet scored a major success with its ''Le Bouquet de Napoleon'', a fragrance launched with great fanfare to commemorate the centenary of the
 After nationalization, Rallet's French staff regrouped at the main Chiris plant in La Bocca, France, where the company struggled to reestablish itself. They were joined by Ernest Beaux in 1919. By 1926, Ernest Beaux had left Rallet to become technical director for Chanel and Bourjois and Rallet was sold to Coty. A June 1, 1926 stock certificate shows the company's name as ''Société Française des Parfums Rallet''.
The Rallet Corporation of America was chartered in Delaware in 1947 and Rallet fine fragrances were offered at least as late as 1948 but the company never regained its former prominence.
After nationalization, Rallet's French staff regrouped at the main Chiris plant in La Bocca, France, where the company struggled to reestablish itself. They were joined by Ernest Beaux in 1919. By 1926, Ernest Beaux had left Rallet to become technical director for Chanel and Bourjois and Rallet was sold to Coty. A June 1, 1926 stock certificate shows the company's name as ''Société Française des Parfums Rallet''.
The Rallet Corporation of America was chartered in Delaware in 1947 and Rallet fine fragrances were offered at least as late as 1948 but the company never regained its former prominence.
 Rallet, founded 1843 in Moscow by Alphonse Rallet (1819–1894), had become, by 1900, Russia's preeminent manufacturer of fine perfume, soap, and cosmetics and was an official supplier to the royal courts of Russia,
Rallet, founded 1843 in Moscow by Alphonse Rallet (1819–1894), had become, by 1900, Russia's preeminent manufacturer of fine perfume, soap, and cosmetics and was an official supplier to the royal courts of Russia, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, and Montenegro
, image_flag = Flag of Montenegro.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Montenegro.svg
, coa_size = 80
, national_motto =
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map = Europe-Mont ...
. In 1896, Rallet was purchased by Chiris of Grasse, France. When Rallet's Russian assets were nationalized in 1917, the company was reestablished in France. In 1920, Rallet's technical director, Ernest Beaux
Ernest Beaux (; – 9 June 1961) was a Russian-French perfumer who is best known for creating Chanel No. 5, which is perhaps the world's most famous perfume.
Family background
Born in Moscow, Ernest Beaux was the son of Edouard Hyppolite Beau ...
, created a series of perfumes for Gabrielle Chanel
Chanel ( , ) is a French luxury fashion house founded in 1910 by Coco Chanel in Paris. It is privately owned by French brothers, Alain and Gérard Wertheimer, through the holding company Chanel Limited, established in 2018 and headquarte ...
, one of which was ''No.5''. In 1926, Rallet was sold to François Coty
François Coty (; born Joseph Marie François Spoturno ; 3 May 1874 – 25 July 1934) was a French perfumer, businessman, newspaper publisher, politician and patron of the arts. He was the founder of the Coty, Coty perfume company, today a multin ...
.Nigel Groom: ''The New Perfume Handbook'', Chapman and Hall, London, 1997, p.281-282Philip Kraft, Christine Ledard, Philip Goutell: ''From Rallet No1 to Chanel No5 versus Mademoiselle Chanel No1,'' Perfumer & Flavorist, 2007, Vol. 32 (Oct), p. 36-48.
Alphonse Rallet
Born in Castle-Thierry, Alphonse Rallet (1819–1894), was the youngest of seven children born to Antoine (1771–1857) and Marie-Louise (Marry) Rallet. In 1842, Rallet traveled to Moscow and in the spring of 1843 established a soap and perfume works at 47 Vyatskaya Street, initially employing about 40 workers. Rallet was joined in Moscow by his older brother, Eugene (1814–1865), a professor of French literature who initially sought to pursue a teaching career but ultimately joined his younger brother in the soap and perfume enterprise. In Moscow, the brothers meet Emile Baudrand, a trader, also from France. Baudrand was married to a woman from the Dauphine region of France near Grenoble and through Baudrand Alphonse Rallet made the acquaintance of Mathilde Farconet, daughter of Frederic (1807–1863) and Mathilde Farconet, whom he married in 1854. Farconet, a republican lawyer, had become provisional mayor of Grenoble in 1848 and served for several years before political changes caused him to retire from office. In 1855, Rallet's only child, Olga, was born in Moscow. In 1856, having secured his fortune in Russia but suffering from lung problems, Rallet returned to France with his wife and daughter and began work on the restoration of the Château Servien at Biviers which he had purchased at the time of his marriage. From 1865 to 1888, Rallet served as mayor of Biviers. Eugene Rallet later married Lėonie Farconet, sister of Mathilde. In time, Olga Rallet, married Augustin Blanchet of the family of bank paper makers. She died in 1888 giving birth to her eighth child. In 1857, Alphonse Rallet, Emile Baudrand, and Napoleon Nayral join Joseph Vicat (1821–1902) to capitalize cements Vicat, Rallet supplying 25 percent of the capital. Blind for the last ten years of his life, Alphonse Rallet died in 1894 and is buried in Biviers.Perfume for Imperial Russia
In the early summer of 1843, Alphonse Rallet established a business at 47 Vyatskaya Street in Moscow to manufacturestearin
Stearin , or tristearin, or glyceryl tristearate is an odourless, white powder. It is a triglyceride derived from three units of stearic acid. Most triglycerides are derived from at least two and more commonly three different fatty acids. Like ...
candles. The factory was equipped with a single steam engine and employed 40 workers. He was joined by his older brother, Eugene. In 1818 stearin, often produced from palm oil, had been discovered to be a particularly suitable wax for candles as it produced minimal soot and retained its shape at higher temperatures. In Moscow the brothers met Emile Baudrand, a trader, also from France, who would become a Rallet business associate.
By 1855, manufacturing was being carried out in 22 wooden buildings on "warm lane" (Теплом переулке) in the Zamoskvoretsky district. Perfumers had been hired from France and raw materials were being sourced from France and Italy. In addition to candles, Rallet was now producing perfumes, colognes, soaps, powders, and lipsticks.
In 1855, Rallet achieved the prestigious title of Supplier of the Imperial Russian Household. In this same year The Trading House of Rallet also became owner of the Crystal Factory of Frederick Dyutfua, giving Rallet, for the first time, the capability of manufacturing their own original bottles decanters. Dyutfua, in turn, became a joint owner and Rallet shareholder.
In 1856, having lung problems, Alphonse Rallet sold the business and returned to France with his wife and infant daughter. The buyers were a group of investors that included Bodranu Byuzhonu and the purchase was made with the condition that the company would continue to bear the Rallet name. The company was now reorganized as "A. Rallet & Co.," the name which would appear on all Rallet bottles and advertising.
In 1898, the company was acquired by Chiris, the large ''Grassois'' fragrance house founded by Antoine Chiris in 1768.
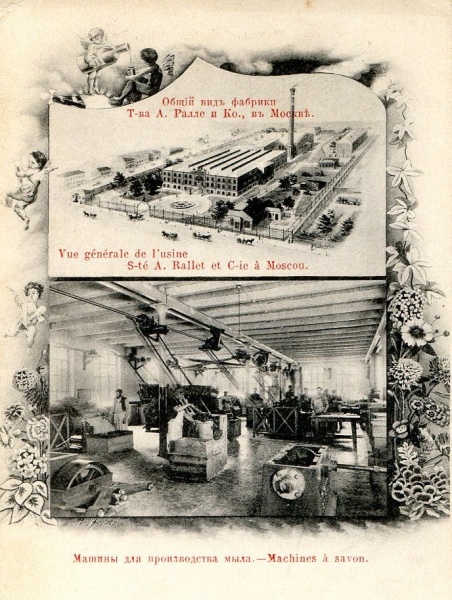
During the last half of the 19th century, Rallet continued to expand. Dependence on foreign suppliers was reduced through the acquisition of plantations in southern Russia for the cultivation of aromatic crops. A new factory was planned at Butyrskaya under the direction of the celebrated architect Oscar-Jean (Franzevich) DiDio. Completed in 1899, this factory featured the latest technology including steam engines, electricity, an elevator, and telephone service.
 During the last 20 years of the 19th century, Rallet made huge profits from the sale of fashionable colognes. At some time during this period, Edward (Edwardovich) Beaux, a member of the board of directors, became Deputy Administrator of the company. Edward (Edwardovich) Beaux had previously served as a clerk for the trading company of Muir and Merrilees. In 1898 his younger brother,
During the last 20 years of the 19th century, Rallet made huge profits from the sale of fashionable colognes. At some time during this period, Edward (Edwardovich) Beaux, a member of the board of directors, became Deputy Administrator of the company. Edward (Edwardovich) Beaux had previously served as a clerk for the trading company of Muir and Merrilees. In 1898 his younger brother, Ernest
Ernest is a given name derived from the Germanic languages, Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious", often shortened to Ernie.
Notable people and fictional characters with the name include:
People
*Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), ...
, joined the company as a lab assistant. In the late 19th century, A. Lemercier, a very original perfumer with an interest in all things modern including the new products of aroma chemistry, became Rallet's technical director. Yet, of perfumery technology in 1898, Ernest Beaux would later say, "perfumery consisted above all of preparing and mixing a small number of materials."
In December 1896, the company was reorganized with a basic capital of 1 million rubles. By 1903, capital had risen to 1.5 million rubles with net profit of around 75,000 rubles. By 1913, capital had reached 2,000,250 rubles and revenue estimated at 180,022 rubles.
By the early 20th century, Rallet was offering around 1,500 products and had three retail shops in Moscow and a wholesale business in St. Petersburgh. Shipments were made regularly by rail throughout Russia and also to China, Persia, and the Balkans.
Prizes and awards
Starting around 1855, when Rallet became an official supplier to the Imperial Court of Russia, the company achieved a number of distinctions for its products. Rallet later became official supplier to the courts of Persia and Montenegro. The company was awarded the state emblem of the Russian Empire four times, a very unusual distinction. In 1878, at the Paris World's Fair, Rallet received high awards. In 1900, at the Paris Exhibition, Rallet was awarded the ''Grand Prix''.''Bouquet de Catherine''
 In 1912, Rallet scored a major success with its ''Le Bouquet de Napoleon'', a fragrance launched with great fanfare to commemorate the centenary of the
In 1912, Rallet scored a major success with its ''Le Bouquet de Napoleon'', a fragrance launched with great fanfare to commemorate the centenary of the Battle of Borodino
The Battle of Borodino ( ) or Battle of Moscow (), in popular literature also known as the Battle of the Generals, took place on the outskirts of Moscow near the village of Borodino on 7 September 1812 during Napoleon's invasion of Russia. ...
, Napoleon's last victory in his failed Russian campaign. The fragrance was the creation of Rallet's technical director, perfumer Ernest Beaux
Ernest Beaux (; – 9 June 1961) was a Russian-French perfumer who is best known for creating Chanel No. 5, which is perhaps the world's most famous perfume.
Family background
Born in Moscow, Ernest Beaux was the son of Edouard Hyppolite Beau ...
.
In the same year, Houbigant introduced ''Quelques Fleurs'', created by perfumer Robert Bienaimė. ''Quelques Fleurs'' was novel in its use of aldehyde C-12 MNA (2-methyl undecanal) which had been synthesized by Georges Darzens in 1903. The inclusion of aldehyde C-12 MNA gave ''Quelques Fleurs'' a "modern" feeling which fascinated a number of Bienaime's young contemporaries including Chiris perfumers Vincent Roubert, Henri Alméras
Henri Alméras (1892 – 1965) was a French perfumer, author, and painter.
Early life and career
Alméras was born in a garrison in Brittany, the son of an officer. In school, he excelled in chemistry. He performed his military service in 1913 a ...
, and Henri Roubert, and Rallet's somewhat older Ernest Beaux
Ernest Beaux (; – 9 June 1961) was a Russian-French perfumer who is best known for creating Chanel No. 5, which is perhaps the world's most famous perfume.
Family background
Born in Moscow, Ernest Beaux was the son of Edouard Hyppolite Beau ...
.
The following year Rallet introduced the ''Bouquet de Catherine'' honoring Catherine the Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter I ...
and the tercentenary of the Romanov
The House of Romanov (also transliterated as Romanoff; , ) was the reigning dynasty, imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after Anastasia Romanovna married Ivan the Terrible, the first crowned tsar of all Russi ...
dynasty. Again the perfumer was Ernest Beaux
Ernest Beaux (; – 9 June 1961) was a Russian-French perfumer who is best known for creating Chanel No. 5, which is perhaps the world's most famous perfume.
Family background
Born in Moscow, Ernest Beaux was the son of Edouard Hyppolite Beau ...
.
Prewar examples of this fragrance no longer exist but it is believed that ''Bouquet de Catherine'' is close to or identical with to Rallet's post-war perfume, ''Le No.1''. When an early sample of ''Le No.1'' was subjected to GC-chromatography and GC-olfactometry analysis in 2007, ''Le No.1'' was found to make use of an aldehyde "cocktail" similar to that found in Chanel's ''No.5'', also an Ernest Beaux
Ernest Beaux (; – 9 June 1961) was a Russian-French perfumer who is best known for creating Chanel No. 5, which is perhaps the world's most famous perfume.
Family background
Born in Moscow, Ernest Beaux was the son of Edouard Hyppolite Beau ...
creation. The claim has been made by Marcel Carles, former director of the Roure perfumery school at Grasse, that Chanel's ''No.5'' was developed from ''Bouquet de Catherine''.
Nationalization & Soviet era
In 1917, A. Rallet & Co. was nationalized by the new Soviet government and renamed "Soap and Perfume Works No.7." r ''No.4'' - accounts vary.Operations were merged with its former chief competitor, Brocard, the former Rallet factories were directed to produce only soap. Brocard, the soap and perfume works established by Frenchman Henri Brocard in Moscow in 1861, had been renamed upon nationalization, "Soap and Perfume Works No. 5." Dissatisfied with "number" names, the new managers petitioned the Council of People's Commissioners and in 1922, the former Rallet enterprise became "Svoboda
Svoboda () means "freedom" in various Slavic languages. It may refer to:
People
* Svoboda (surname)
Organizations Media
* Radio Svoboda, operated by Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty
* ''Svoboda'' (newspaper), a daily Ukrainian language newspa ...
" ("Freedom") and the former Brocard enterprise, "Nova Zayra" ("New Dawn").
The factories fell under the supervision of Polina Zhemchuzhina
Polina Semyonovna Zhemchuzhina. (born Perl Solomonovna Karpovskaya; 27 February 1897 – 1 April 1970) was a Soviet politician and the wife of the Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov. Zhemchuzhina was the director of the Soviet national ...
, wife of Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov (; – 8 November 1986) was a Soviet politician, diplomat, and revolutionary who was a leading figure in the government of the Soviet Union from the 1920s to the 1950s, as one of Joseph Stalin's closest allies. ...
, who become head of the Soviet Union's cosmetics trust in the 1920s, a position she would hold until 1932 when she incurred Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
's displeasure at the time of his wife's suicide. In 1948, fluent in Yiddish
Yiddish, historically Judeo-German, is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated in 9th-century Central Europe, and provided the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with ...
, she acted as translator for a diplomatic meeting between her husband, Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov (; – 8 November 1986) was a Soviet politician, diplomat, and revolutionary who was a leading figure in the government of the Soviet Union from the 1920s to the 1950s, as one of Joseph Stalin's closest allies. ...
, the Soviet Union's foreign minister, and Golda Meir
Golda Meir (; 3 May 1898 – 8 December 1978) was the prime minister of Israel, serving from 1969 to 1974. She was Israel's first and only female head of government.
Born into a Jewish family in Kyiv, Kiev, Russian Empire (present-day Ukraine) ...
, foreign minister of the new state of Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
. Shortly afterward, she was exiled until after Stalin's death.
Nova Zayra continues to be a major cosmetics enterprise in post-Soviet Russia.
Post-Soviet era
Svoboda, employing about 1,500 workers, is specialized in skin care products and soap. It is among the top ten cosmetics companies in Russia together withProcter & Gamble
The Procter & Gamble Company (P&G) is an American multinational consumer goods corporation headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio. It was founded in 1837 by William Procter and James Gamble. It specializes in a wide range of personal health/con ...
, L'Oreal, Gilette
Gilette (; ; ) is a commune in the Alpes-Maritimes department in southeastern France.
Population
The inhabitants are called ''Gilettois'' in French.
See also
*Communes of the Alpes-Maritimes department
The following is a list of the ...
, Kalina, Schwarzkopf & Henkel, Unilever
Unilever PLC () is a British multinational consumer packaged goods company headquartered in London, England. It was founded on 2 September 1929 following the merger of Dutch margarine producer Margarine Unie with British soap maker Lever B ...
, Nevskaya Kosmetika, Colgate, and Beiersdorf
Beiersdorf AG is a German multinational company that manufactures personal-care products and pressure-sensitive adhesives headquartered in Hamburg, Germany. Its brands include Elastoplast, Eucerin (makers of Aquaphor), Labello, La Prairi ...
. Like the majority of Russian cosmetics companies, Svoboda continues to be located in Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
.
Rallet in France
 After nationalization, Rallet's French staff regrouped at the main Chiris plant in La Bocca, France, where the company struggled to reestablish itself. They were joined by Ernest Beaux in 1919. By 1926, Ernest Beaux had left Rallet to become technical director for Chanel and Bourjois and Rallet was sold to Coty. A June 1, 1926 stock certificate shows the company's name as ''Société Française des Parfums Rallet''.
The Rallet Corporation of America was chartered in Delaware in 1947 and Rallet fine fragrances were offered at least as late as 1948 but the company never regained its former prominence.
After nationalization, Rallet's French staff regrouped at the main Chiris plant in La Bocca, France, where the company struggled to reestablish itself. They were joined by Ernest Beaux in 1919. By 1926, Ernest Beaux had left Rallet to become technical director for Chanel and Bourjois and Rallet was sold to Coty. A June 1, 1926 stock certificate shows the company's name as ''Société Française des Parfums Rallet''.
The Rallet Corporation of America was chartered in Delaware in 1947 and Rallet fine fragrances were offered at least as late as 1948 but the company never regained its former prominence.
Perfumes by Rallet
Perfumes from Imperial Russia
[With the exception of several of the better known Rallet Imperial Era fragrances, information on the many fragrances Rallet produced between 1843 and 1914 is very sketchy. Fragrances were named in both Russian and in French. Advertising posters would confirm the existence of some Rallet fragrances but Rallet advertising posters are rare. The information below was compiled from the Perfume Intelligence website and from Michael Edwards "Perfume Legends" as cited below.] * ''Milskaya Liliya'' ("Spider Lily") (1880) * ''Bouquet nezabuduk and Rose''s (1887) *'' Le Lys de Nil'' (1889) * ''Fleur de Neige'' (1890) * ''Primavera'' (1890) * ''Mignonette-Reseda'' (1890) * ''Breath of Spring'' (1890) * ''Rose in Russia'' (1890) * ''Heliotrope'' (1890) * ''Rezeda'' (1890) * ''Royal Court'' (1893) * ''Perce-Neige'' ("Snow-Drops") (1895) * ''Vesovoi No.3'' (1895) * ''Double Flowering Lilac'' (1895) (Makhrovaya Siren) * ''Alienor'' (1900) * ''Sada Yakko'' (1900) he name was used again in France in 1925 for an altogether fragrance.* ''Orchidea'' (1910) * ''Bouquet de Napoleon'' (1912) * ''Bouquet de Catherine'' (1913) eleased post-war as ''Rallet Le No.1''Perfumes in post-war France
* ''Le No.1'' (post-1914/1923) * ''Sada Yakko'' (1925) * ''Gardénia'' (c.1926-1929) * ''Le No.3'' (c.1925-1929) * ''Le No.33'' (c.1925-1929) * ''Floric'' (1927) * ''Xyris'' (1928) * ''Maidou'' (1930) * ''La Giroflée'' (1932) * ''Confession'' (1934) * ''Last Paradise'' (1935) * ''Le Success'' (1935)References
External links
* Information garnered from Cleopatra's Boudoir. {{Authority control Cosmetics companies of Russia Companies established in 1843 Companies nationalised by the Soviet Union 1843 establishments in the Russian Empire Russian brands Cosmetics companies of France