Raft Paddle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a
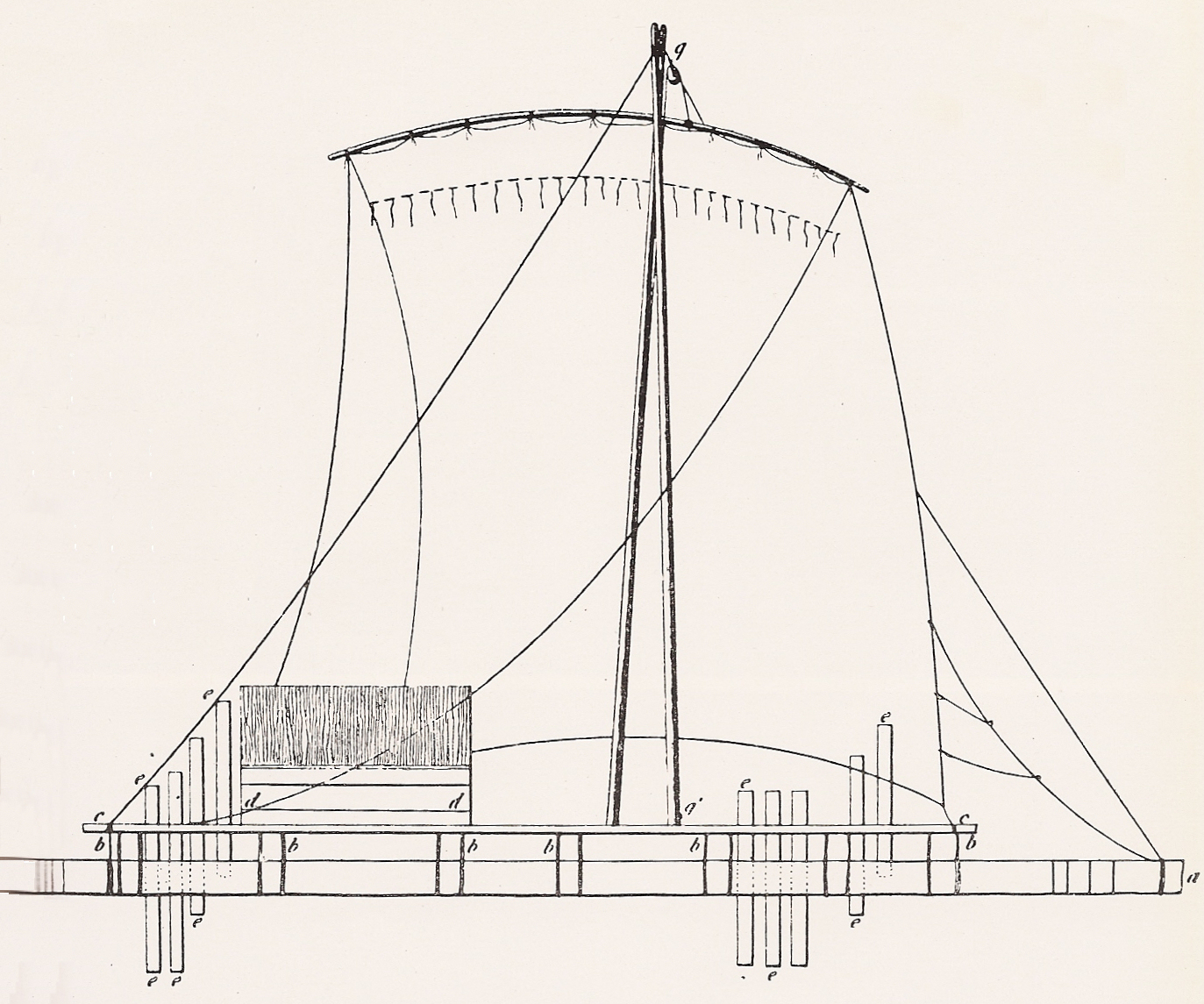 Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood, bamboo or reeds; early buoyed or float rafts use inflated animal skins or sealed clay pots which are lashed together. Modern float rafts may also use pontoons,
Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood, bamboo or reeds; early buoyed or float rafts use inflated animal skins or sealed clay pots which are lashed together. Modern float rafts may also use pontoons,
Rafting on the Drina River (1951) - BH Film - Official chanalWorld of Boats (EISCA) Collection ~ Australian Reed RaftWorld of Boats (EISCA) Collection ~ Brazilian JangadaHomemade Raft Plans and Photos of RaftsNeutrino Raft – vessels made from scrapTypes of Whitewater Rafts
{{Authority control !
hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* The hull of an armored fighting vehicle, housing the chassis
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a sea-going craft
* Submarine hull
Ma ...
. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
, sealed barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden stave (wood), staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers ...
s, or inflated air chambers (such as pontoons), and are typically not propelled by an engine. Rafts are an ancient mode of transport; naturally-occurring rafts such as entwined vegetation and pieces of wood have been used to traverse water since the dawn of humanity.
Human-made rafts
 Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood, bamboo or reeds; early buoyed or float rafts use inflated animal skins or sealed clay pots which are lashed together. Modern float rafts may also use pontoons,
Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood, bamboo or reeds; early buoyed or float rafts use inflated animal skins or sealed clay pots which are lashed together. Modern float rafts may also use pontoons, drums
The drum is a member of the percussion instrument, percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel–Sachs classification system, it is a membranophones, membranophone. Drums consist of at least one Acoustic membrane, membrane, c ...
, or extruded polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
blocks. Depending on its use and size, it may have a superstructure
A superstructure is an upward extension of an existing structure above a baseline. This term is applied to various kinds of physical structures such as buildings, bridges, or ships.
Aboard ships and large boats
On water craft, the superstruct ...
, masts, or rudders.
Timber rafting
Timber rafting is a method of transporting felled tree trunks by tying them together to make rafts, which are then drifted or pulled downriver, or across a lake or other body of water. It is arguably, after log driving, the second cheapest mea ...
is used by the logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidder, skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or trunk (botany), logs onto logging truck, trucksbalsa
''Ochroma pyramidale'', commonly known as balsa, is a large, fast-growing tree native to the Americas. It is the sole member of the genus ''Ochroma'', and is classified in the subfamily Bombacoideae of the mallow family Malvaceae. The tree is fa ...
logs and using sails for navigation were important in maritime trade on the Pacific Ocean coast of South America from pre-Columbian times until the 19th century. Voyages were made to locations as far away as Mexico, and many trans-Pacific voyages using replicas of ancient rafts have been undertaken to demonstrate possible contacts between South America and Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
.
Rafts used for recreational rafting
Rafting and whitewater rafting are recreational outdoor activities which use an inflatable raft to navigate a river or other body of water. This is often done on whitewater or different degrees of rough water. Dealing with risk is often a ...
are almost exclusively inflatable rafts, manufactured of flexible materials such as PVC, hypalon, polyurethane, and nylon. These materials are resistant to the collisions and heavy wear the boats experience when traveling through whitewater
Whitewater forms in the context of rapids, in particular, when a river's Stream gradient, gradient changes enough to generate so much turbulence that air is trapped within the water. This forms an unstable current that foam, froths, making t ...
. Whitewater rafts are also designed with high rocker, a raised bow and stern which allows them to pass over waves and obstacles more easily. Most have drain holes in the floor to prevent the boat from becoming swamped with water.
Natural rafts
Inbiology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
, particularly in island biogeography
Insular biogeography or island biogeography is a field within biogeography that examines the factors that affect the species richness and diversification of isolated natural communities. The theory was originally developed to explain the pattern ...
, non-manmade rafts are an important concept. Such rafts consist of matted clumps of vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plants and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular Taxon, taxa, life forms, structure, Spatial ecology, spatial extent, or any other specific Botany, botanic ...
that has been swept off the dry land by a storm
A storm is any disturbed state of the natural environment or the atmosphere of an astronomical body. It may be marked by significant disruptions to normal conditions such as strong wind, tornadoes, hail, thunder and lightning (a thunderstor ...
, tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
, tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
, earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
or similar event; in modern times they sometimes also incorporate other kind of flotsam and jetsam
In maritime law, flotsam'','' jetsam'','' lagan'','' and derelict are terms for various types of property lost or abandoned at sea. The words have specific nautical meanings, with legal consequences in the law of admiralty and marine salvage. A ...
, e.g. plastic containers. They stay afloat by its natural buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of t ...
and can travel for hundreds, even thousands of miles and are ultimately destroyed by wave
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium ...
action and decomposition
Decomposition is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is ess ...
, or make landfall.
Rafting events are important means of oceanic dispersal
Oceanic dispersal is a type of biological dispersal that occurs when Terrestrial animal, terrestrial organisms transfer from one land mass to another by way of a sea crossing. Island hopping is the crossing of an ocean by a series of shorter jour ...
for non-flying animals. For amphibia
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniotic, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all tetrapods, but excluding the amniotes (tetrapods with an amniotic ...
ns, reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s, and small mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, in particular, but for many invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s as well, such rafts of vegetation were often the only means by which they could reach and – if they were lucky – colonize ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
ic island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been ...
s before human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
-built vehicles provided another mode of transport
A mode of transport is a method or way of travelling, or of transporting people or cargo. The different modes of transport include air, water, and land transport, which includes rails or railways, road and off-road transport. Other modes of t ...
.
Image gallery
See also
*Floating island
A floating island is a mass of floating aquatic plants, mud, and peat ranging in thickness from several centimeters to a few meters. Sometimes referred to as ''tussocks'', ''floatons'', or ''suds'', floating islands are found in many parts of t ...
* Great Raft
* Kon-Tiki
The ''Kon-Tiki'' expedition was a 1947 journey by raft across the Pacific Ocean from South America to the Polynesian islands, led by Norwegian explorer and writer Thor Heyerdahl. The raft was named ''Kon-Tiki'' after the Inca god Viracocha, f ...
* L’Égaré II
* La Balsa and Las Balsas
Between 1966 and 1973, Spanish explorer Vital Alsar led three expeditions to cross the Pacific Ocean by raft – La Pacífica in 1966, La Balsa in 1970 and Las Balsas in 1973. Travelling from Ecuador, South America, to Australia, the first expedi ...
* Lifeboat
* Pre-Columbian rafts
Pre-Columbian rafts plied the Pacific Coast of South America for trade from about 100 BCE, and possibly much earlier. The 16th-century descriptions by the Spanish of the rafts used by Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans along th ...
* Pumice raft
A pumice raft is a floating raft of pumice created by some eruptions of submarine volcanoes or coastal subaerial volcanoes.
Pumice rafts have unique characteristics, such as the highest surface-area-to-volume ratio known for any rock type, long ...
* ''The Raft of the Medusa
''The Raft of the Medusa'' ( ) – originally titled ''Scène de Naufrage'' (''Shipwreck Scene'') – is an oil painting of 1818–1819 by the French Romantic painter and lithographer Théodore Géricault (1791–1824). Completed when the ar ...
''
* Thor Heyerdahl
Thor Heyerdahl KStJ (; 6 October 1914 – 18 April 2002) was a Norwegian adventurer and Ethnography, ethnographer with a background in biology with specialization in zoology, botany and geography.
Heyerdahl is notable for his Kon-Tiki expediti ...
* Poon Lim
Poon Lim BEM (; 8 March 1918 – 4 January 1991) was a Chinese seafarer. He was born on the island of Hainan, China. In 1942–43, he survived a record 133 days alone on a life raft in the South Atlantic.
Lim was Second Mess Steward on ...
References
External links
Rafting on the Drina River (1951) - BH Film - Official chanal
{{Authority control !