Radial piston pump on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A radial piston pump is a form of
 The stroke of each piston is caused by an eccentric drive shaft or an external eccentric tappet (e.g., stroke ring).
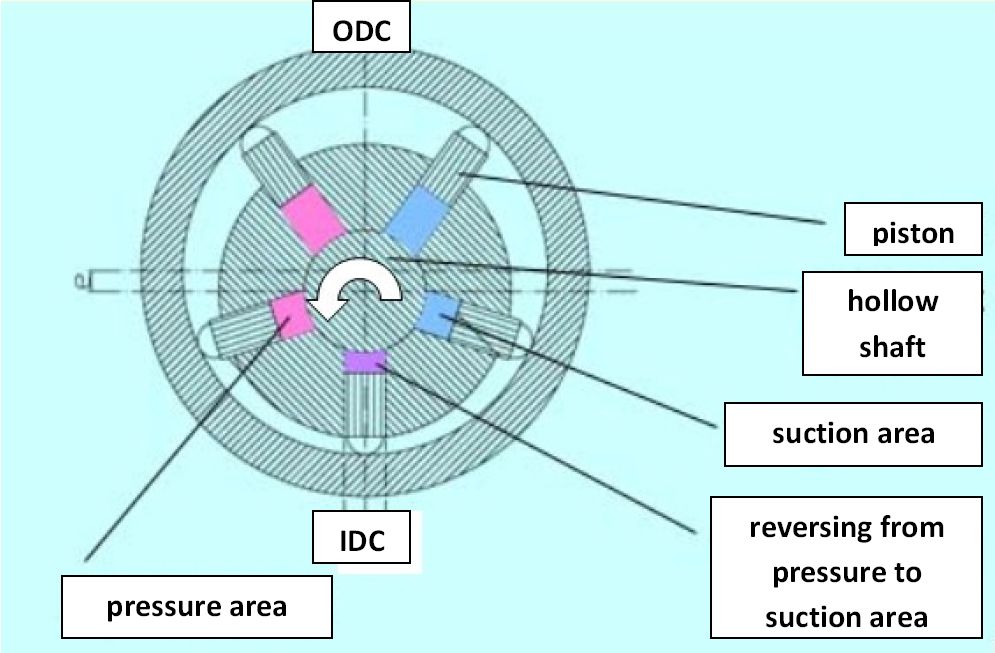
When filling the workspace of the pumping pistons from "inside" (e.g., over a hollow shaft) it is called an ''inside impinged'' (but outside braced) radial piston pump ''(picture 1)''. If the workspace is filled from "outside" it's called an ''outside impinged'' radial piston pump (but inside braced) ''(picture 2)''.
The stroke of each piston is caused by an eccentric drive shaft or an external eccentric tappet (e.g., stroke ring).
When filling the workspace of the pumping pistons from "inside" (e.g., over a hollow shaft) it is called an ''inside impinged'' (but outside braced) radial piston pump ''(picture 1)''. If the workspace is filled from "outside" it's called an ''outside impinged'' radial piston pump (but inside braced) ''(picture 2)''.
The outer ring for bracing of the pumping pistons is in eccentric position to the hollow shaft in the center. This eccentricity determines the stroke of the pumping piston. The piston starts in the inner dead center (IDC) with suction process. After a rotation angle of 180° it is finished and the workspace of the piston is filled with the moved medium. The piston is now in the outer dead center (ODC). From this point on the piston displaces the previously sucked medium in the pressure channel of the pump.
hydraulic pump
A hydraulic pump is a mechanical source of power that converts mechanical power into hydraulic energy ( hydrostatic energy i.e. flow, pressure). Hydraulic pumps are used in hydraulic drive systems and can be hydrostatic or hydrodynamic. They gen ...
. The working pistons extend in a radial direction symmetrically around the drive shaft, in contrast to the axial piston pump
An axial piston pump is a positive displacement pump that has a number of pistons in a circular array within a ''cylinder block''.
It can be used as a stand-alone pump, a hydraulic motor or an automotive air conditioning compressor.
Description
...
.
Construction

 The stroke of each piston is caused by an eccentric drive shaft or an external eccentric tappet (e.g., stroke ring).
When filling the workspace of the pumping pistons from "inside" (e.g., over a hollow shaft) it is called an ''inside impinged'' (but outside braced) radial piston pump ''(picture 1)''. If the workspace is filled from "outside" it's called an ''outside impinged'' radial piston pump (but inside braced) ''(picture 2)''.
The stroke of each piston is caused by an eccentric drive shaft or an external eccentric tappet (e.g., stroke ring).
When filling the workspace of the pumping pistons from "inside" (e.g., over a hollow shaft) it is called an ''inside impinged'' (but outside braced) radial piston pump ''(picture 1)''. If the workspace is filled from "outside" it's called an ''outside impinged'' radial piston pump (but inside braced) ''(picture 2)''.
Function
The general mode of operation will be explained at the movement of one pumping piston by means of picture 1:The outer ring for bracing of the pumping pistons is in eccentric position to the hollow shaft in the center. This eccentricity determines the stroke of the pumping piston. The piston starts in the inner dead center (IDC) with suction process. After a rotation angle of 180° it is finished and the workspace of the piston is filled with the moved medium. The piston is now in the outer dead center (ODC). From this point on the piston displaces the previously sucked medium in the pressure channel of the pump.
Attributes
These kinds of piston pumps are characterized by the following advantages: * high efficiency * high pressure (up to 1,000 bar or 14000psi) * low flow and pressure ripple (due to the small dead volume in the workspace of the pumping piston) * low noise level * very high load at lowest speed due to the hydrostatically balanced parts possible * no axial internal forces at the drive shaft bearing * high reliability A disadvantage is the bigger radial dimensions in comparison to theaxial piston pump
An axial piston pump is a positive displacement pump that has a number of pistons in a circular array within a ''cylinder block''.
It can be used as a stand-alone pump, a hydraulic motor or an automotive air conditioning compressor.
Description
...
, but it could be compensated with the shorter construction in axial direction.
Applications
Due to the hydrostatically balanced parts it is possible to use the pump with varioushydraulic fluid
A hydraulic fluid or hydraulic liquid is the medium by which power is transferred in hydraulic machinery. Common hydraulic fluids are based on mineral oil or water. Examples of equipment that might use hydraulic fluids are excavators and backho ...
s like mineral oil, biodegradable oil, HFA (oil in water), HFC (water-glycol), HFD (synthetic ester) or cutting emulsion. That implies the following main applications for a radial piston pump:
* machine tools (e.g., displace of cutting emulsion, supply for hydraulic equipment like cylinders)
* high pressure units (HPU) (e.g., for overload protection of presses)
* test rigs
* automotive sector (e.g., automatic transmission, hydraulic suspension control in upper-class cars)
* plastic- and powder injection molding
* wind energy
See also
*Axial piston pump
An axial piston pump is a positive displacement pump that has a number of pistons in a circular array within a ''cylinder block''.
It can be used as a stand-alone pump, a hydraulic motor or an automotive air conditioning compressor.
Description
...
*Hydraulics
Hydraulics () is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concer ...
*Pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes Slurry, slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of application ...
References
{{Reflist Pumps