quellung reaction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The quellung reaction, also called the Neufeld reaction, is a biochemical 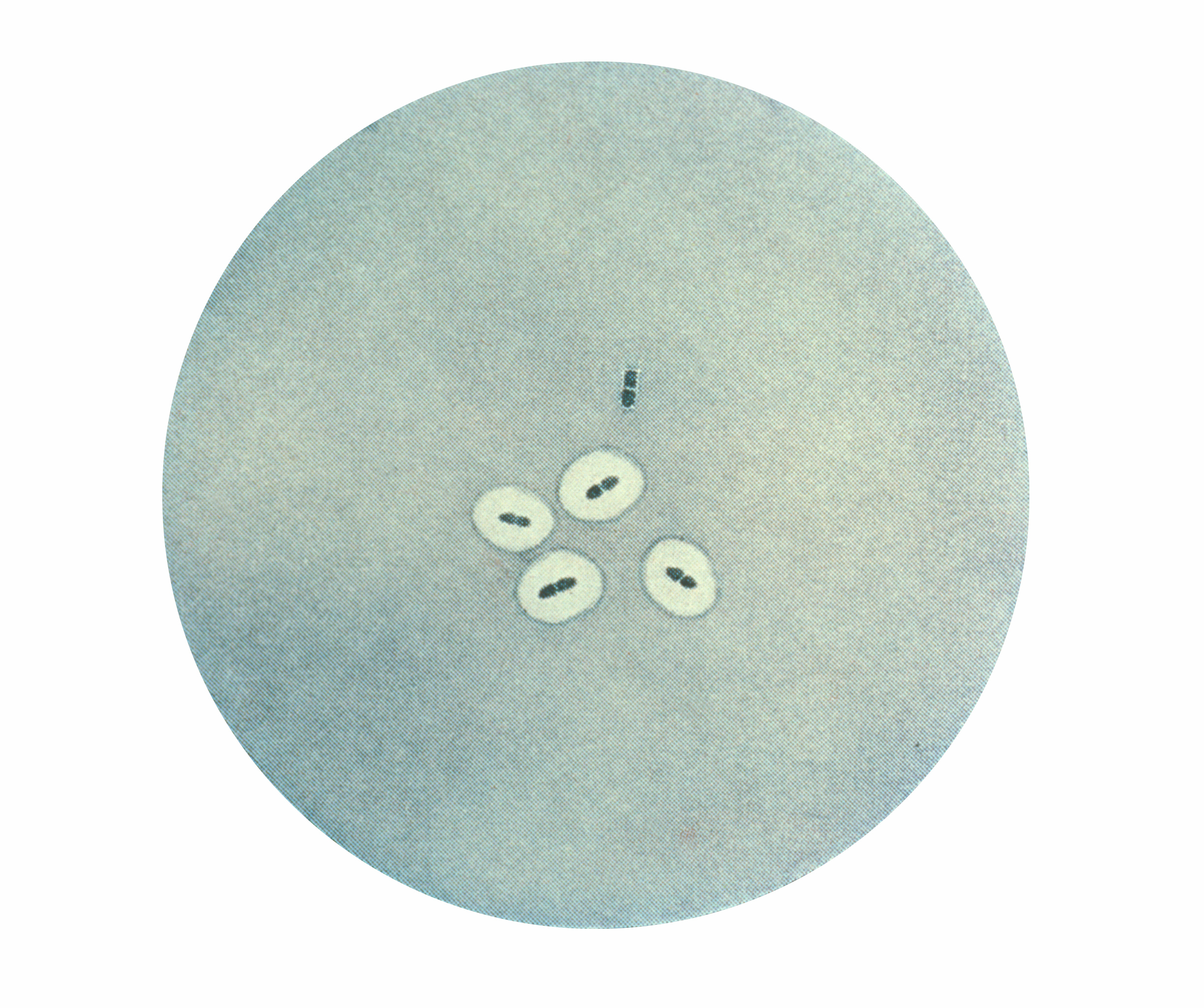 Quellung is the German word for "swelling" and describes the microscopic appearance of
Quellung is the German word for "swelling" and describes the microscopic appearance of
reaction
Reaction may refer to a process or to a response to an action, event, or exposure:
Physics and chemistry
*Chemical reaction
*Nuclear reaction
* Reaction (physics), as defined by Newton's third law
*Chain reaction (disambiguation).
Biology and m ...
in which antibodies bind to the bacterial capsule
The bacteria capsule is a large structure common to many bacteria. It is a polysaccharide layer that lies outside the cell envelope, and is thus deemed part of the outer envelope of a bacterial cell. It is a well-organized layer, not easily was ...
of ''Streptococcus pneumoniae
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic (under aerobic conditions) or beta-hemolytic (under anaerobic conditions), aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. They ar ...
'', ''Klebsiella pneumoniae
''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose- fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It appears as a mucoid lactose fermenter on MacConkey agar.
Although found in the normal flora of the mo ...
'', ''Neisseria meningitidis
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to as a ...
'', '' Bacillus anthracis'', ''Haemophilus influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacter ...
'', ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'', and '' Salmonella''. The antibody reaction allows these species to be visualized under a microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
. If the reaction is positive, the capsule becomes opaque and appears to enlarge.
 Quellung is the German word for "swelling" and describes the microscopic appearance of
Quellung is the German word for "swelling" and describes the microscopic appearance of pneumococcal
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic (under aerobic conditions) or beta-hemolytic (under anaerobic conditions), aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. They are ...
or other bacterial capsules after their polysaccharide antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respons ...
has combined with a specific antibody. The antibody usually comes from a bit of serum taken from an immunized laboratory animal. As a result of this combination, and precipitation of the large, complex molecule formed, the capsule appears to swell, because of increased surface tension, and its outlines become clearly demarcated.
The pneumococcal quellung reaction was first described in 1902 by the scientist Fred Neufeld, and applied only to ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', both as microscopic capsular swelling and macroscopic agglutination (clumping visible with the naked eye). It was initially an intellectual curiosity more than anything else, and could distinguish only the three pneumococcal serotypes known at that time. However, it acquired an important practical use with the advent of serum therapy to treat certain types of pneumococcal pneumonia in the 1920s because selection of the proper antiserum to treat an individual patient required correct identification of the infecting pneumococcal serotype, and the quellung reaction was the only method available to do this. Dr. Albert Sabin
Albert Bruce Sabin ( ; August 26, 1906 – March 3, 1993) was a Polish-American medical researcher, best known for developing the oral polio vaccine, which has played a key role in nearly eradicating the disease. In 1969–72, he served as th ...
made modifications to Neufeld's technique so that it could be done more rapidly, and other scientists expanded the technique to identify 29 additional serotypes.
Application of Neufeld’s discoveries to other important areas of research came when Fred Griffith showed that pneumococci could transfer information to transform one serotype into another. Oswald Avery
Oswald Theodore Avery Jr. (October 21, 1877 – February 20, 1955) was a Canadian-American physician and medical researcher. The major part of his career was spent at the Rockefeller Hospital in New York City. Avery was one of the first molecula ...
, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty later showed that the transforming factor was deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA.
Serum therapy for infectious diseases was displaced by antibiotics in the 1940s, but identification of specific serotypes remained important as the understanding of the epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evide ...
of pneumococcal infections still required their identification to determine where different serotypes spread, as well as the variable invasiveness of different serotypes. Understanding the prevalence of various serotypes was also critical to the development of pneumococcal vaccines to prevent invasive infections.
The quellung reaction has been used to identify the 93 known capsular serotypes of ''Streptococcus pneumoniae
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic (under aerobic conditions) or beta-hemolytic (under anaerobic conditions), aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. They ar ...
'' in diagnostic settings, but in recent years it has been challenged by the latex agglutination method, and further by molecular typing techniques such as the polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
, which detect DNA and therefore target genetic differences between serotypes. Currently, there are 100 known capsular serotypes.
References
Further reading
* Park, I. H., Pritchard, D., Cartee, R., Brandao, A., Brandileone, M. and Nahm, M. Discovery of a new capsular serotype (6C) within serogroup 6 of Streptococcus pneumoniae. ''Journal of Clinical Microbiology.'' 2007;45:1225–1233. * * {{cite journal , last1 = Austrian , first1 = R , year = 1976 , title = The Quellung Reaction, a Neglected Microbiologic Technique , journal = Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine , volume = 43 , issue = 6, pages = 699–709 , pmid = 13297 Biochemistry methods Staining 1902 introductions 1902 in biology