Pulp (paper) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
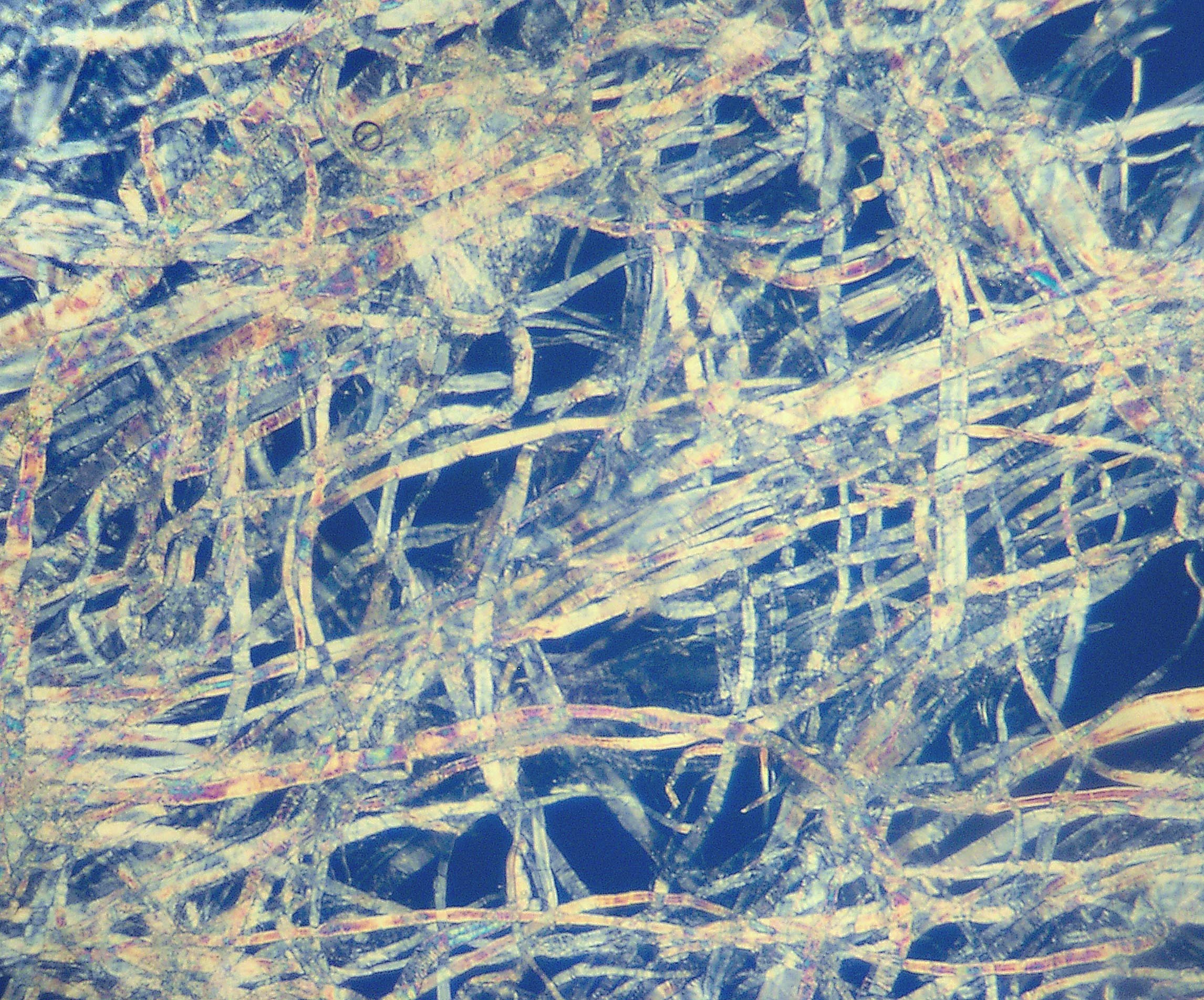
 Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from
'Charles Fenerty and his Paper Invention''. Toronto: Peter Burger, 2007. pp.25–30 Chemical processes quickly followed, first with
 The timber resources used to make wood pulp are referred to as pulpwood. While in theory any tree can be used for pulp-making, coniferous trees are preferred because the cellulose fibers in the pulp of these species are longer, and therefore make stronger paper.
Some of the most commonly used softwood trees for paper making include spruce,
The timber resources used to make wood pulp are referred to as pulpwood. While in theory any tree can be used for pulp-making, coniferous trees are preferred because the cellulose fibers in the pulp of these species are longer, and therefore make stronger paper.
Some of the most commonly used softwood trees for paper making include spruce,
 Thermomechanical pulp is pulp produced by processing wood chips using heat (thus " thermo-") and a mechanical refining movement (thus "-mechanical"). It is a two-stage process where the logs are first stripped of their
Thermomechanical pulp is pulp produced by processing wood chips using heat (thus " thermo-") and a mechanical refining movement (thus "-mechanical"). It is a two-stage process where the logs are first stripped of their
 Chemical pulp is produced by combining wood chips and chemicals in large vessels called digesters. There, heat and chemicals break down lignin, which binds
Chemical pulp is produced by combining wood chips and chemicals in large vessels called digesters. There, heat and chemicals break down lignin, which binds
Versuche und Muster ohne alle Lumpen oder doch mit enem geringen Zusatze derselben Papier zu machen
' by Jacob Christian Schäffer on Google Books * Johan Richter, developer of the process for continuous cooking of pulp *

 Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
, fiber crop
Fiber crops are field crops grown for their fibers, which are traditionally used to make paper, cloth, or rope.
Fiber crops are characterized by having a large concentration of cellulose, which is what gives them their strength. The fibers may b ...
s, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products.
History
Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around 105 AD, paper-like writing materials such aspapyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to ...
and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark
Bark may refer to:
* Bark (botany), an outer layer of a woody plant such as a tree or stick
* Bark (sound), a vocalization of some animals (which is commonly the dog)
Places
* Bark, Germany
* Bark, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland
Arts, e ...
or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers from the paper mulberry (kozo) plant along with hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a botanical class of '' Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial or medicinal use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants ...
rag and net scraps. By the 6th century, the mulberry tree was domesticated by farmers in China specifically for the purpose of producing pulp to be used in the papermaking process. In addition to mulberry, pulp was also made from bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, ...
, hibiscus bark, blue sandalwood, straw
Straw is an agricultural byproduct consisting of the dry stalks of cereal plants after the grain and chaff have been removed. It makes up about half of the yield of cereal crops such as barley, oats, rice, rye and wheat. It has a number ...
, and cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
. Papermaking using pulp made from hemp and linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
fibers from tattered clothing, fishing nets and fabric bags spread to Europe in the 13th century, with an ever-increasing use of rags being central to the manufacture and affordability of rag paper, a factor in the development of printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ...
. By the 1800s, production demands on the newly industrialized papermaking and printing industries led to a shift in raw materials, most notably the use of pulpwood and other tree products which today make up more than 95% of global pulp production.
The use of wood pulp and the invention of automatic paper machines in the late 18th- and early 19th-century contributed to paper's status as an inexpensive commodity in modern times. While some of the earliest examples of paper made from wood pulp include works published by Jacob Christian Schäffer in 1765 and Matthias Koops in 1800, large-scale wood paper production began in the 1840s with unique, simultaneous developments in mechanical pulping made by Friedrich Gottlob Keller in Germany and by Charles Fenerty in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
.Burger, Peter'Charles Fenerty and his Paper Invention''. Toronto: Peter Burger, 2007. pp.25–30 Chemical processes quickly followed, first with
J. Roth
''J. The Jewish News of Northern California'', formerly known as ''Jweekly'', is a weekly print newspaper in Northern California, with its online edition updated daily. It is owned and operated by San Francisco Jewish Community Publications In ...
's use of sulfurous acid
Sulfurous acid (also sulfuric(IV) acid, sulphurous acid (UK), sulphuric(IV) acid (UK)) is the chemical compound with the formula . There is no evidence that sulfurous acid exists in solution, but the molecule has been detected in the gas phase ...
to treat wood, then by Benjamin Tilghman
Benjamin Chew Tilghman (18211901) was an American soldier and inventor. He is best known as the inventor of the process of sandblasting.
Early life
He was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on October 26, 1821, the third child of Benjamin and An ...
's U.S. patent
Under United States law, a patent is a right granted to the inventor of a (1) process, machine, article of manufacture, or composition of matter, (2) that is new, useful, and non-obvious. A patent is the right to exclude others, for a limited ...
on the use of calcium bisulfite, Ca(HSO3)2, to pulp wood in 1867. Almost a decade later, the first commercial sulfite pulp mill was built, in Sweden. It used magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
as the counter ion and was based on work by Carl Daniel Ekman
Carl Daniel Ekman (March 17, 1845 – November 3, 1904) was a Swedish chemical engineer who invented the form of the sulfite process of wood pulp manufacturing which was first established on a firm commercial basis, helping to replace rags as the ...
. By 1900, sulfite pulping had become the dominant means of producing wood pulp, surpassing mechanical pulping methods. The competing chemical pulping process, the sulfate, or kraft, process, was developed by Carl F. Dahl Carl may refer to:
* Carl, Georgia, city in USA
* Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
*Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name
* Carl², a TV series
* "Carl", an episode of ...
in 1879; the first kraft mill started, in Sweden, in 1890. The invention of the recovery boiler, by G.H. Tomlinson
GH, Gh, gh, or .gh may refer to:
* gh (digraph), a digraph found in many languages
* Gästrike-Hälsinge nation, a student association at Uppsala University, Sweden
* ''General Hospital'', an American daytime medical drama
* Ghana (ISO 3166-1 alp ...
in the early 1930s, allowed kraft mills to recycle almost all of their pulping chemicals. This, along with the ability of the kraft process to accept a wider variety of types of wood and to produce stronger fibres, made the kraft process the dominant pulping process, starting in the 1940s.
Global production of wood pulp in 2006 was 175 million tons (160 million tonnes). In the previous year, 63 million tons (57 million tonnes) of market pulp (not made into paper in the same facility) was sold, with Canada being the largest source at 21 percent of the total, followed by the United States at 16 percent. The wood fiber sources required for pulping are "45% sawmill residue, 21% logs and chips, and 34% recycled paper" (Canada, 2014). Chemical pulp made up 93% of market pulp.
Wood pulp
 The timber resources used to make wood pulp are referred to as pulpwood. While in theory any tree can be used for pulp-making, coniferous trees are preferred because the cellulose fibers in the pulp of these species are longer, and therefore make stronger paper.
Some of the most commonly used softwood trees for paper making include spruce,
The timber resources used to make wood pulp are referred to as pulpwood. While in theory any tree can be used for pulp-making, coniferous trees are preferred because the cellulose fibers in the pulp of these species are longer, and therefore make stronger paper.
Some of the most commonly used softwood trees for paper making include spruce, pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic ...
, fir, larch and hemlock, and hardwood
Hardwood is wood from dicot trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen. Hardwood (which comes from ...
s such as eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as ...
, aspen
Aspen is a common name for certain tree species; some, but not all, are classified by botanists in the section ''Populus'', of the '' Populus'' genus.
Species
These species are called aspens:
*'' Populus adenopoda'' – Chinese aspen (C ...
and birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' cont ...
. There is also increasing interest in genetically modified tree species (such as GM eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as ...
and GM poplar) because of several major benefits these can provide, such as increased ease of breaking down lignin and increased growth rate.
A pulp mill is a manufacturing facility that converts wood chips or other plant fibre source into a thick fiberboard which can be shipped to a paper mill for further processing. Pulp can be manufactured using mechanical, semi-chemical or fully chemical methods (kraft and sulfite processes). The finished product may be either bleached or non-bleached, depending on the customer requirements.
Wood and other plant materials used to make pulp contain three main components (apart from water): cellulose fibers (desired for papermaking), lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity a ...
(a three-dimensional polymer that binds the cellulose fibres together) and hemicelluloses (shorter branched carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may o ...
polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
s). The aim of pulping is to break down the bulk structure of the fibre source, be it chips, stems or other plant parts, into the constituent fibres.
Chemical pulping achieves this by degrading the lignin and hemicellulose into small, water-soluble molecules which can be washed away from the cellulose fibres without depolymerizing the cellulose fibres (chemically depolymerizing the cellulose weakens the fibres). The various mechanical pulping methods, such as groundwood (GW) and refiner mechanical pulping (RMP), physically tear the cellulose fibres one from another. Much of the lignin remains adhering to the fibres. Strength is impaired because the fibres may be cut. There are a number of related hybrid pulping methods that use a combination of chemical and thermal treatment to begin an abbreviated chemical pulping process, followed immediately by a mechanical treatment to separate the fibres. These hybrid methods include thermomechanical pulping, also known as TMP, and chemithermomechanical pulping, also known as CTMP. The chemical and thermal treatments reduce the amount of energy subsequently required by the mechanical treatment, and also reduce the amount of strength loss suffered by the fibres.
Harvesting trees
Most pulp mills use good forest management practices in harvesting trees to ensure that they have a sustainable source of raw materials. One of the major complaints about harvesting wood for pulp mills is that it reduces thebiodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity'') ...
of the harvested forest. Pulp tree plantations
A tree plantation, forest plantation, plantation forest, timber plantation or tree farm is a forest planted for high volume production of wood, usually by planting one type of tree as a monoculture forest. The term ''tree farm'' also is used to ...
account for 16 percent of world pulp production, old-growth forests 9 percent, and second- and third- and more generation forests account for the rest. Reforestation
Reforestation (occasionally, reafforestation) is the natural or intentional restocking of existing forests and woodlands ( forestation) that have been depleted, usually through deforestation, but also after clearcutting.
Management
A de ...
is practiced in most areas, so trees are a renewable resource
A renewable resource, also known as a flow resource, is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of ti ...
. The FSC (Forest Stewardship Council
The Forest Stewardship Council A. C. (FSC) is an international non-profit, multistakeholder organization established in 1993 that promotes responsible management of the world's forests via timber certification. It is an example of a market ...
), SFI ( Sustainable Forestry Initiative), PEFC ( Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification), and other bodies certify paper made from trees harvested according to guidelines meant to ensure good forestry practices.
The number of trees consumed depends on whether mechanical processes or chemical processes are used. It has been estimated that based on a mixture of softwoods and hardwood
Hardwood is wood from dicot trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen. Hardwood (which comes from ...
s 12 metres (40 ft) tall and 15–20 centimetres (6–8 in) in diameter, it would take an average of 24 trees to produce 0.9 tonne (1 ton) of printing and writing paper, using the kraft process (chemical pulping). Mechanical pulping is about twice as efficient in using trees, since almost all of the wood is used to make fibre, therefore it takes about 12 trees to make 0.9 tonne (1 ton) of mechanical pulp or newsprint
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper consisting mainly of wood pulp and most commonly used to print newspapers and other publications and advertising material. Invented in 1844 by Charles Fenerty of Nova Scotia, Canada, it usually has a ...
.
There are roughly two short tons in a cord of wood.
Preparation for pulping
Wood chipping is the act and industry of chipping wood for pulp, but also for other processed wood products and mulch. Only the heartwood and sapwood are useful for making pulp.Bark
Bark may refer to:
* Bark (botany), an outer layer of a woody plant such as a tree or stick
* Bark (sound), a vocalization of some animals (which is commonly the dog)
Places
* Bark, Germany
* Bark, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland
Arts, e ...
contains relatively few useful fibers and is removed and used as fuel to provide steam for use in the pulp mill. Most pulping processes require that the wood be chipped and screened to provide uniform sized chips.
Pulping
There are a number of different processes which can be used to separate the wood fiber:Mechanical pulp
Manufactured grindstones with embedded silicon carbide or aluminum oxide can be used to grind small wood logs called "bolts" to make stone pulp (SGW). If the wood is steamed prior to grinding it is known as pressure ground wood pulp (PGW). Most modern mills use chips rather than logs and ridged metal discs called refiner plates instead of grindstones. If the chips are just ground up with the plates, the pulp is called refiner mechanical pulp (RMP) and if the chips are steamed while being refined the pulp is called thermomechanical pulp (TMP). Steam treatment significantly reduces the total energy needed to make the pulp and decreases the damage (cutting) to fibres. Mechanical pulps are used for products that require less strength, such asnewsprint
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper consisting mainly of wood pulp and most commonly used to print newspapers and other publications and advertising material. Invented in 1844 by Charles Fenerty of Nova Scotia, Canada, it usually has a ...
and paperboard
Paperboard is a thick paper-based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker (usually over 0.30 mm, 0.012 in, or 12 points) than paper and has certain superior attributes ...
s.
Thermomechanical pulp
 Thermomechanical pulp is pulp produced by processing wood chips using heat (thus " thermo-") and a mechanical refining movement (thus "-mechanical"). It is a two-stage process where the logs are first stripped of their
Thermomechanical pulp is pulp produced by processing wood chips using heat (thus " thermo-") and a mechanical refining movement (thus "-mechanical"). It is a two-stage process where the logs are first stripped of their bark
Bark may refer to:
* Bark (botany), an outer layer of a woody plant such as a tree or stick
* Bark (sound), a vocalization of some animals (which is commonly the dog)
Places
* Bark, Germany
* Bark, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland
Arts, e ...
and converted into small chips. These chips have a moisture content of around 25–30 percent. A mechanical force is applied to the wood chips in a crushing or grinding action which generates heat and water vapour and softens the lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity a ...
thus separating the individual fibres. The pulp is then screened and cleaned, any clumps of fibre are reprocessed. This process gives a high yield of fibre from the timber (around 95 percent) and as the lignin has not been removed, the fibres are hard and rigid.
Chemi-thermomechanical pulp
Wood chips can be pre-treated with sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide,sodium sulfate
Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 mil ...
and other chemicals prior to refining with equipment similar to a mechanical mill. The conditions of the chemical treatment are much less vigorous (lower temperature, shorter time, less extreme pH) than in a chemical pulping process since the goal is to make the fibers easier to refine, not to remove lignin as in a fully chemical process. Pulps made using these hybrid processes are known as chemi-thermomechanical pulps (CTMP).
Chemical pulp
 Chemical pulp is produced by combining wood chips and chemicals in large vessels called digesters. There, heat and chemicals break down lignin, which binds
Chemical pulp is produced by combining wood chips and chemicals in large vessels called digesters. There, heat and chemicals break down lignin, which binds cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wa ...
fibres together, without seriously degrading the cellulose fibres. Chemical pulp is used for materials that need to be stronger or combined with mechanical pulps to give a product different characteristics. The kraft process is the dominant chemical pulping method, with the sulfite process second. Historically soda pulping was the first successful chemical pulping method.
Recycled pulp
Recycled pulp is also called deinked pulp (DIP). DIP is recycled paper which has been processed by chemicals, thus removing printing inks and other unwanted elements and freed the paper fibres. The process is called deinking. DIP is used as raw material in papermaking. Manynewsprint
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper consisting mainly of wood pulp and most commonly used to print newspapers and other publications and advertising material. Invented in 1844 by Charles Fenerty of Nova Scotia, Canada, it usually has a ...
, toilet paper
Toilet paper (sometimes called toilet tissue or bathroom tissue) is a tissue paper product primarily used to clean the anus and surrounding anal region of feces after defecation, and to clean the perineal area and external genitalia of ur ...
and facial tissue grades commonly contain 100 percent deinked pulp and in many other grades, such as lightweight coated for offset and printing and writing papers for office and home use, DIP makes up a substantial proportion of the furnish.
Organosolv pulping
Organosolv pulping uses organic solvents at temperatures above 140 °C to break down lignin and hemicellulose into soluble fragments. The pulping liquor is easily recovered by distillation. The reason for using a solvent is to make thelignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity a ...
more soluble in the cooking liquor. Most common used solvents are methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is ...
, ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
, formic acid and acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main componen ...
often in combination with water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
.
Alternative pulping methods
Research is under way to develop biopulping (biological pulping), similar to chemical pulping but using certain species offungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
that are able to break down the unwanted lignin, but not the cellulose fibres. In the biopulping process, the fungal enzyme lignin peroxidase selectively digests lignin to leave remaining cellulose fibres. This could have major environmental benefits in reducing the pollution associated with chemical pulping. The pulp is bleached using chlorine dioxide stage followed by neutralization and calcium hypochlorite
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with formula Ca(OCl)2. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, chlorine powder, or chlorinated lime, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent. This ...
. The oxidizing agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxi ...
in either case oxidizes and destroys the dyes formed from the tannins of the wood and accentuated (reinforced) by sulfide
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds la ...
s present in it.
Steam exploded fibre is a pulping and extraction technique that has been applied to wood and other fibrous organic material.
Bleaching
The pulp produced up to this point in the process can be bleached to produce awhite paper
A white paper is a report or guide that informs readers concisely about a complex issue and presents the issuing body's philosophy on the matter. It is meant to help readers understand an issue, solve a problem, or make a decision. A white paper ...
product. The chemicals used to bleach pulp have been a source of environmental concern, and recently the pulp industry has been using alternatives to chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
, such as chlorine dioxide, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
, ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the l ...
and hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3 ...
.
Alternatives to wood pulp
Pulp made from non-wood plant sources or recycled textiles is manufactured today largely as a speciality product for fine-printing and art purposes. Modern machine- and hand-made art papers made with cotton, linen, hemp, abaca, kozo, and other fibers are often valued for their longer, stronger fibers and their lowerlignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity a ...
content. Lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity a ...
, present in virtually all plant materials, contributes to the acidification and eventual breakdown of paper products, often characterized by the browning and embrittling of paper with a high lignin content such as newsprint
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper consisting mainly of wood pulp and most commonly used to print newspapers and other publications and advertising material. Invented in 1844 by Charles Fenerty of Nova Scotia, Canada, it usually has a ...
. 100% cotton or a combination of cotton and linen pulp is widely used to produce documents intended for long-term use, such as certificates, currency, and passports.
Today, some groups advocate using field crop fibre or agricultural residues instead of wood fibre as a more sustainable means of production.
There is enough straw
Straw is an agricultural byproduct consisting of the dry stalks of cereal plants after the grain and chaff have been removed. It makes up about half of the yield of cereal crops such as barley, oats, rice, rye and wheat. It has a number ...
to meet much of North America's book, magazine, catalogue and copy paper needs. Agricultural-based paper does not come from tree farms. Some agricultural residue pulps take less time to cook than wood pulps. That means agricultural-based paper uses less energy, less water and fewer chemicals. Pulp made from wheat and flax straw has half the ecological footprint of pulp made from forests.
Hemp paper
Hemp paper is paper varieties consisting exclusively or to a large extent from pulp obtained from fibers of industrial hemp. The products are mainly specialty papers such as cigarette paper, banknotes and technical filter papers. Compared to wood p ...
is a possible replacement, but processing infrastructure, storage costs and the low usability percentage of the plant means it is not a ready substitute.
However, wood is also a renewable resource, with about 90 percent of pulp coming from plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
s or reforested areas. Non-wood fibre sources account for about 5–10 percent of global pulp production, for a variety of reasons, including seasonal availability, problems with chemical recovery, brightness of the pulp etc. In China, as of 2009, a higher proportion of non-wood pulp processing increased use of water and energy.
Nonwovens
Nonwoven fabric is a fabric-like material made from staple fibre (short) and long fibres (continuous long), bonded together by chemical, mechanical, heat or solvent treatment. The term is used in the textile manufacturing industry to denote fabri ...
are in some applications alternatives to paper made from wood pulp, like filter paper or tea bags.
Market pulp
Market pulp is any variety of pulp that is produced in one location, dried and shipped to another location for further processing. Important quality parameters for pulp not directly related to the fibres arebrightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target. The perception is not linear to luminance, ...
, dirt levels, viscosity and ash content. In 2004 it accounted for about 55 million metric tons
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
of market pulp.
Air dry pulp is the most common form to sell pulp. This is pulp dried to about 10 percent moisture content. It is normally delivered as sheeted bales of 250 kg. The reason to leave 10 percent moisture in the pulp is that this minimizes the fibre to fibre bonding and makes it easier to disperse the pulp in water for further processing to paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distribu ...
.
Roll pulp or ''reel pulp'' is the most common delivery form of pulp to non traditional pulp markets. Fluff pulp Fluff pulp (also called comminution pulp or fluffy pulp) is a type of chemical pulp made from long fibre softwoods. Important parameters for fluff pulp are bulk and water absorbency.
History
Fluff pulp was first developed for use in disposable sani ...
is normally shipped on rolls (reels). This pulp is dried to 5–6 percent moisture content. At the customer this is going to a comminution process to prepare for further processing.
Some pulps are flash dried. This is done by pressing the pulp to about 50 percent moisture content and then let it fall through silos that are 15–17 m high. Gas fired hot air is the normal heat source. The temperature is well above the char point of cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wa ...
, but large amount of moisture in the fibre wall and lumen prevents the fibres from being incinerated. It is often not dried down to 10 percent moisture (air dry). The bales are not as densely packed as air dry pulp.
Environmental concerns
The major environmental impacts of producing wood pulp come from its impact on forest sources and from its waste products.Forest resources
The impact of logging to provide the raw material for wood pulp is an area of intense debate. Modernlogging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars.
Logging is the beginning of a supply cha ...
practices, using forest management seek to provide a reliable, renewable source of raw materials for pulp mills. The practice of clear cutting is a particularly sensitive issue since it is a very visible effect of logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars.
Logging is the beginning of a supply cha ...
. Reforestation
Reforestation (occasionally, reafforestation) is the natural or intentional restocking of existing forests and woodlands ( forestation) that have been depleted, usually through deforestation, but also after clearcutting.
Management
A de ...
, the planting of tree seedlings on logged areas, has also been criticized for decreasing biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity'') ...
because reforested areas are monocultures.
Logging of old growth forests accounts for less than 10 percent of wood pulp, but is one of the most controversial issues.
Effluents from pulp mills
The process effluents are treated in a biological effluent treatment plant, which guarantees that the effluents are not toxic in the recipient. Mechanical pulp is not a major cause for environmental concern since most of the organic material is retained in the pulp, and the chemicals used (hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3 ...
and sodium dithionite) produce benign byproducts (water and sodium sulfate
Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 mil ...
(finally), respectively).
Chemical pulp mills, especially kraft mills, are energy self-sufficient and very nearly closed cycle with respect to inorganic chemicals.
Bleaching
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color (whitening) from a fabric or fiber or to clean or to remove stains in a process called bleaching. It often refers specifically, to ...
with chlorine produces large amounts of organochlorine compounds, including polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs). Many mills have adopted alternatives to chlorinated bleaching agents thereby reducing emissions of organochlorine pollution.
Odor problems
The kraft pulping reaction in particular releases foul-smelling compounds. The hydrogen sulfide reagent that degrades lignin structure also causes some demethylation to produce methanethiol,dimethyl sulfide
Dimethyl sulfide (DMS) or methylthiomethane is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2S. Dimethyl sulfide is a flammable liquid that boils at and has a characteristic disagreeable odor. It is a component of the smell produced from co ...
and dimethyl disulfide. These same compounds are released during many forms of microbial decay, including the internal microbial action in Camembert cheese
Camembert (, also , ) is a moist, soft, creamy, surface-ripened cow's milk cheese. It was first made in the late 18th century in Camembert, Normandy, in northwest France. It is sometimes compared in look and taste to brie cheese, albeit wi ...
, although the kraft process is a chemical one and does not involve any microbial degradation. These compounds have extremely low odor thresholds and disagreeable smells.
Applications
The main applications for pulp arepaper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distribu ...
and board
Board or Boards may refer to:
Flat surface
* Lumber, or other rigid material, milled or sawn flat
** Plank (wood)
** Cutting board
** Sounding board, of a musical instrument
* Cardboard (paper product)
* Paperboard
* Fiberboard
** Hardboard, a ty ...
production. The furnish of pulps used depends on the quality on the finished paper. Important quality parameters are wood furnish, brightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target. The perception is not linear to luminance, ...
, viscosity, extractives, dirt count and strength.
Chemical pulps are used for making nanocellulose
Nanocellulose is a term referring to nano-structured cellulose. This may be either cellulose nanocrystal (CNC or NCC), cellulose nanofibers (CNF) also called nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC), or bacterial nanocellulose, which refers to nano-struc ...
.
Speciality pulp grades have many other applications. Dissolving pulp Dissolving pulp, also called dissolving cellulose, is bleached wood pulp or cotton linters that has a high cellulose content (> 90%). It has special properties including a high level of brightness and uniform molecular-weight distribution. This pul ...
is used in making regenerated cellulose that is used textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, different #Fabric, fabric types, etc. At f ...
and cellophane production. It is also used to make cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wa ...
derivatives. Fluff pulp Fluff pulp (also called comminution pulp or fluffy pulp) is a type of chemical pulp made from long fibre softwoods. Important parameters for fluff pulp are bulk and water absorbency.
History
Fluff pulp was first developed for use in disposable sani ...
is used in diapers, feminine hygiene products and nonwovens
Nonwoven fabric is a fabric-like material made from staple fibre (short) and long fibres (continuous long), bonded together by chemical, mechanical, heat or solvent treatment. The term is used in the textile manufacturing industry to denote fabri ...
.
Paper production
The Fourdrinier Machine is the basis for most modern papermaking, and it has been used in some variation since its conception. It accomplishes all the steps needed to transform pulp into a finalpaper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distribu ...
product.
Economics
In 2009, NBSK pulp sold for $650/ton in the United States. The price had dropped due to falling demand when newspapers reduced their size, in part, as a result of the recession.See also
*Nanocellulose
Nanocellulose is a term referring to nano-structured cellulose. This may be either cellulose nanocrystal (CNC or NCC), cellulose nanofibers (CNF) also called nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC), or bacterial nanocellulose, which refers to nano-struc ...
* Paper chemicals
* Pulp mill
* Pulpwood
*Versuche und Muster ohne alle Lumpen oder doch mit enem geringen Zusatze derselben Papier zu machen
' by Jacob Christian Schäffer on Google Books * Johan Richter, developer of the process for continuous cooking of pulp *
World Forestry Congress
The World Forestry Congress (WFC) is the largest and most significant gathering of the world's forestry sector and it has been held every six years since 1926 under the auspices of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations ...
References
Bibliography
* . {{DEFAULTSORT:Pulp (Paper) Wood products Papermaking Cellulose