Pseudoautosomal region on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The pseudoautosomal regions or PARs are homologous sequences of
 The locations of the PARs within GRCh38 are:
The locations of the PARs within GRCh37 are:
The locations of the PARs within GRCh38 are:
The locations of the PARs within GRCh37 are:
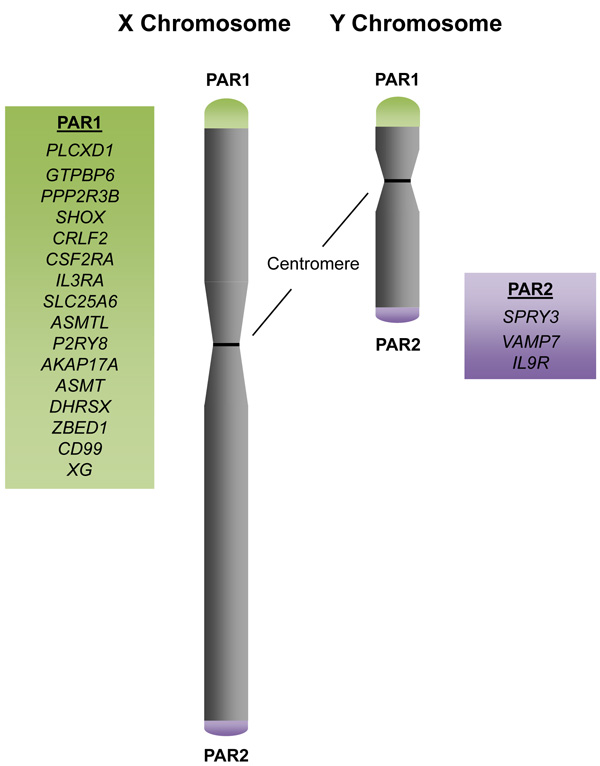 Pseudoautosomal genes are found in two different locations: PAR1 and PAR2. These are believed to have evolved independently.
Pseudoautosomal genes are found in two different locations: PAR1 and PAR2. These are believed to have evolved independently.
nucleotides
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
found within the sex chromosomes of species with an XY or ZW mechanism of sex determination.
The pseudoautosomal regions get their name because any genes within them (so far at least 29 have been found for humans) are inherited just like any autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosome ...
genes. In humans, these regions are referred to as PAR1 and PAR2. PAR1 comprises 2.6 Mbp of the short-arm tips of both X and Y chromosomes in humans and great apes (X and Y are 154 Mbp and 62 Mbp in total). PAR2 is at the tips of the long arms, spanning 320 kbp. The monotremes, including the platypus
The platypus (''Ornithorhynchus anatinus''), sometimes referred to as the duck-billed platypus, is a semiaquatic, egg-laying mammal endemic to eastern Australia, including Tasmania. The platypus is the sole living representative or monotypi ...
and echidna, have a multiple sex chromosome system, and consequently have 8 pseudoautosomal regions.
Location
 The locations of the PARs within GRCh38 are:
The locations of the PARs within GRCh37 are:
The locations of the PARs within GRCh38 are:
The locations of the PARs within GRCh37 are:
Inheritance and function
Normal male therian mammals have two copies of these genes: one in the pseudoautosomal region of their Y chromosome, the other in the corresponding portion of their X chromosome. Normal females also possess two copies of pseudoautosomal genes, as each of their two X chromosomes contains a pseudoautosomal region. Crossing over between the X and Y chromosomes is normally restricted to the pseudoautosomal regions; thus, pseudoautosomal genes exhibit an autosomal, rather than sex-linked, pattern of inheritance. So, females can inherit an allele originally present on the Y chromosome of their father. The function of these pseudoautosomal regions is that they allow the X and Ychromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s to pair and properly segregate during meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
in males.
Genes
 Pseudoautosomal genes are found in two different locations: PAR1 and PAR2. These are believed to have evolved independently.
Pseudoautosomal genes are found in two different locations: PAR1 and PAR2. These are believed to have evolved independently.
PAR1
* pseudoautosomal PAR1 ** AKAP17A **ASMT
N-Acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase, also known as ASMT, is an enzyme which catalyzes the final reaction in melatonin biosynthesis: converting Normelatonin to melatonin. This reaction is embedded in the more general tryptophan metabolism pathw ...
** ASMTL
** CD99
** CRLF2
Cytokine receptor-like factor 2 (also known as TSLP receptor, TSLP-R) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CRLF2'' gene. It forms a ternary signaling complex with TSLP and interleukin-7 receptor-α, capable of stimulating cell prolifer ...
** CSF2RA
** DHRSX
** GTPBP6
** IL3RA
** P2RY8
** PLCXD1
** PPP2R3B
** SHOX
** SLC25A6
** XG, which straddles the PAR1 region boundary
** ZBED1
in mice
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
, some PAR1 genes have transferred to autosome
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ...
s.
PAR2
* pseudoautosomal PAR2 ** IL9R ** SPRY3 ** VAMP7, also known as SYBL1 ** CXYorf1, also known as FAM39A and now mapped to thepseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Pseudogenes can be formed from both protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. In the case of protein-coding genes, most pseudogenes arise as superfluous copies of fun ...
WASH6P, but of interest due to its proximity to the telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see #Sequences, Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In ...
.
Pathology
Pairing (synapsis
Synapsis or Syzygy is the pairing of two chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. Synapsis takes place during prophase I of me ...
) of the X and Y chromosomes and crossing over ( recombination) between their pseudoautosomal regions appear to be necessary for the normal progression of male meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
. Thus, those cells in which X-Y recombination does not occur will fail to complete meiosis. Structural and/or genetic dissimilarity (due to hybridization or mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
) between the pseudoautosomal regions of the X and Y chromosomes can disrupt pairing and recombination, and consequently cause male infertility.
The SHOX gene in the PAR1 region is the gene most commonly associated with and well understood with regards to disorders in humans, but all pseudoautosomal genes escape X-inactivation and are therefore candidates for having gene dosage effects in sex chromosome aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, for example a human somatic (biology), somatic cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more plo ...
conditions (45,X
Turner syndrome (TS), commonly known as 45,X, or 45,X0,Also written as 45,XO. is a chromosomal disorder in which cells of females have only one X chromosome instead of two, or are partially missing an X chromosome (sex chromosome monosomy) lead ...
, 47,XXX, 47,XXY, 47,XYY, etc.).
Deletions have also been associated with Léri-Weill dyschondrosteosis and Madelung's deformity.
See also
* Interleukin-3 receptor * Interleukin-9 receptorReferences
External links
* * {{Chromosomes Molecular genetics Cytogenetics