Proline on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The "side chain" from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it as a

Proline MS Spectrum
Proline biosynthesis
{{Authority control AMPA receptor agonists Kainate receptor agonists NMDA receptor agonists Proteinogenic amino acids Glucogenic amino acids Glycine receptor agonists Cyclic amino acids Pyrrolidines Secondary amino acids Excitatory amino acids
aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane ...
amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L- glutamate. It is encoded by all the codon
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links ...
s starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG).
Proline is the only proteinogenic secondary amino acid which is a secondary amine, as the nitrogen atom is attached both to the α-carbon and to a chain of three carbons that together form a five-membered ring.
History and etymology
Proline was first isolated in 1900 by Richard Willstätter who obtained the amino acid while studying ''N''-methylproline, and synthesized proline by the reaction of sodium salt of diethyl malonate with 1,3-dibromopropane. The next year, Emil Fischer isolated proline fromcasein
Casein ( , from Latin ''caseus'' "cheese") is a family of related phosphoproteins ( αS1, aS2, β, κ) that are commonly found in mammalian milk, comprising about 80% of the proteins in cow's milk and between 20% and 60% of the proteins in hum ...
and the decomposition products of γ-phthalimido-propylmalonic ester, and published the synthesis of proline from phthalimide propylmalonic ester.
The name proline comes from pyrrolidine, one of its constituents.
Biosynthesis
Proline is biosynthetically derived from the amino acid L- glutamate. Glutamate-5-semialdehyde is first formed by glutamate 5-kinase (ATP-dependent) and glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (which requires NADH or NADPH). This can then either spontaneously cyclize to form1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid
1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid (systematic name 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid) is a cyclic imino acid. Its conjugate base and anion is 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C). In solution, P5C is in spontaneous equilibrium with glutamate-5-se ...
, which is reduced to proline by pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase (using NADH or NADPH), or turned into ornithine by ornithine aminotransferase, followed by cyclisation by ornithine cyclodeaminase to form proline.

Biological activity
L-Proline has been found to act as a weakagonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ag ...
of the glycine receptor
The glycine receptor (abbreviated as GlyR or GLR) is the receptor of the amino acid neurotransmitter glycine. GlyR is an ionotropic receptor that produces its effects through chloride current. It is one of the most widely distributed inhibitor ...
and of both NMDA and non-NMDA ( AMPA/ kainate) ionotropic glutamate receptors. It has been proposed to be a potential endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell.
In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism.
For example, ...
excitotoxin. In plants, proline accumulation is a common physiological response to various stresses but is also part of the developmental program in generative tissues (e.g. pollen).
A diet rich in proline was linked to an increased risk of depression in humans in a study from 2022 that was tested on a limited pre-clinical trial on humans and primarily in other organisms. Results were significant in the other organisms.
Properties in protein structure
The distinctive cyclic structure of proline's side chain gives proline an exceptional conformational rigidity compared to other amino acids. It also affects the rate of peptide bond formation between proline and other amino acids. When proline is bound as an amide in a peptide bond, its nitrogen is not bound to any hydrogen, meaning it cannot act as a hydrogen bond donor, but can be a hydrogen bond acceptor. Peptide bond formation with incoming Pro-tRNAPro is considerably slower than with any other tRNAs, which is a general feature of ''N''-alkylamino acids. Peptide bond formation is also slow between an incoming tRNA and a chain ending in proline; with the creation of proline-proline bonds slowest of all. The exceptional conformational rigidity of proline affects thesecondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary struct ...
of proteins near a proline residue and may account for proline's higher prevalence in the proteins of thermophilic organisms. Protein secondary structure can be described in terms of the dihedral angles φ, ψ and ω of the protein backbone. The cyclic structure of proline's side chain locks the angle φ at approximately −65°.
Proline acts as a structural disruptor in the middle of regular secondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary struct ...
elements such as alpha helices and beta sheets; however, proline is commonly found as the first residue of an alpha helix
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand- helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues ...
and also in the edge strands of beta sheets. Proline is also commonly found in turns (another kind of secondary structure), and aids in the formation of beta turns. This may account for the curious fact that proline is usually solvent-exposed, despite having a completely aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane ...
side chain.
Multiple prolines and/or hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelatin ...
s in a row can create a polyproline helix, the predominant secondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary struct ...
in collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whol ...
. The hydroxylation
In chemistry, hydroxylation can refer to:
*(i) most commonly, hydroxylation describes a chemical process that introduces a hydroxyl group () into an organic compound.
*(ii) the ''degree of hydroxylation'' refers to the number of OH groups in a ...
of proline by prolyl hydroxylase (or other additions of electron-withdrawing substituents such as fluorine) increases the conformational stability of collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whol ...
significantly. Hence, the hydroxylation of proline is a critical biochemical process for maintaining the connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
of higher organisms. Severe diseases such as scurvy
Scurvy is a deficiency disease, disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, anemia, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, ch ...
can result from defects in this hydroxylation, e.g., mutations in the enzyme prolyl hydroxylase or lack of the necessary ascorbate (vitamin C) cofactor.
''Cis''–''trans'' isomerization
Peptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
s to proline, and to other ''N''-substituted amino acids (such as sarcosine), are able to populate both the '' cis'' and '' trans'' isomers. Most peptide bonds overwhelmingly adopt the ''trans'' isomer (typically 99.9% under unstrained conditions), chiefly because the amide hydrogen (''trans'' isomer) offers less steric repulsion to the preceding Cα atom than does the following Cα atom (''cis'' isomer). By contrast, the ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers of the X-Pro peptide bond (where X represents any amino acid) both experience steric clashes with the neighboring substitution and have a much lower energy difference. Hence, the fraction of X-Pro peptide bonds in the ''cis'' isomer under unstrained conditions is significantly elevated, with ''cis'' fractions typically in the range of 3-10%. However, these values depend on the preceding amino acid, with Gly and aromatic residues yielding increased fractions of the ''cis'' isomer. ''Cis'' fractions up to 40% have been identified for aromatic–proline peptide bonds.
From a kinetic standpoint, ''cis''–''trans'' proline isomerization is a very slow process that can impede the progress of protein folding
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein chain is translated to its native three-dimensional structure, typically a "folded" conformation by which the protein becomes biologically functional. Via an expeditious and reproduc ...
by trapping one or more proline residues crucial for folding in the non-native isomer, especially when the native protein requires the ''cis'' isomer. This is because proline residues are exclusively synthesized in the ribosome as the ''trans'' isomer form. All organisms possess prolyl isomerase enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s to catalyze this isomerization, and some bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
have specialized prolyl isomerases associated with the ribosome. However, not all prolines are essential for folding, and protein folding may proceed at a normal rate despite having non-native conformers of many X–Pro peptide bonds.
Uses
Proline and its derivatives are often used as asymmetric catalysts inproline organocatalysis Proline organocatalysis is the use of proline as an organocatalyst in organic chemistry. This theme is often considered the starting point for the area of organocatalysis, even though early discoveries went unappreciated. Modifications, such as ...
reactions. The CBS reduction
CBS Broadcasting Inc., commonly shortened to CBS, the abbreviation of its former legal name Columbia Broadcasting System, is an American commercial broadcast television and radio network serving as the flagship property of the CBS Entertainme ...
and proline catalysed aldol condensation are prominent examples.
In brewing, proteins rich in proline combine with polyphenols to produce haze (turbidity).
L-Proline is an osmoprotectant and therefore is used in many pharmaceutical and biotechnological applications.
The growth medium used in plant tissue culture
Plant tissue culture is a collection of techniques used to maintain or grow plant cells, tissues or organs under sterile conditions on a nutrient culture medium of known composition. It is widely used to produce clones of a plant in a method known ...
may be supplemented with proline. This can increase growth, perhaps because it helps the plant tolerate the stresses of tissue culture. For proline's role in the stress response of plants, see .
Specialties
Proline is one of the two amino acids that do not follow along with the typical Ramachandran plot, along with glycine. Due to the ring formation connected to the beta carbon, the ''ψ'' and ''φ'' angles about the peptide bond have fewer allowable degrees of rotation. As a result, it is often found in "turns" of proteins as its free entropy (Δ''S'') is not as comparatively large to other amino acids and thus in a folded form vs. unfolded form, the change in entropy is smaller. Furthermore, proline is rarely found in α and β structures as it would reduce the stability of such structures, because its side chain α-nitrogen can only form one nitrogen bond. Additionally, proline is the only amino acid that does not form a red-purple colour when developed by spraying with ninhydrin for uses in chromatography. Proline, instead, produces an orange-yellow colour.Synthesis
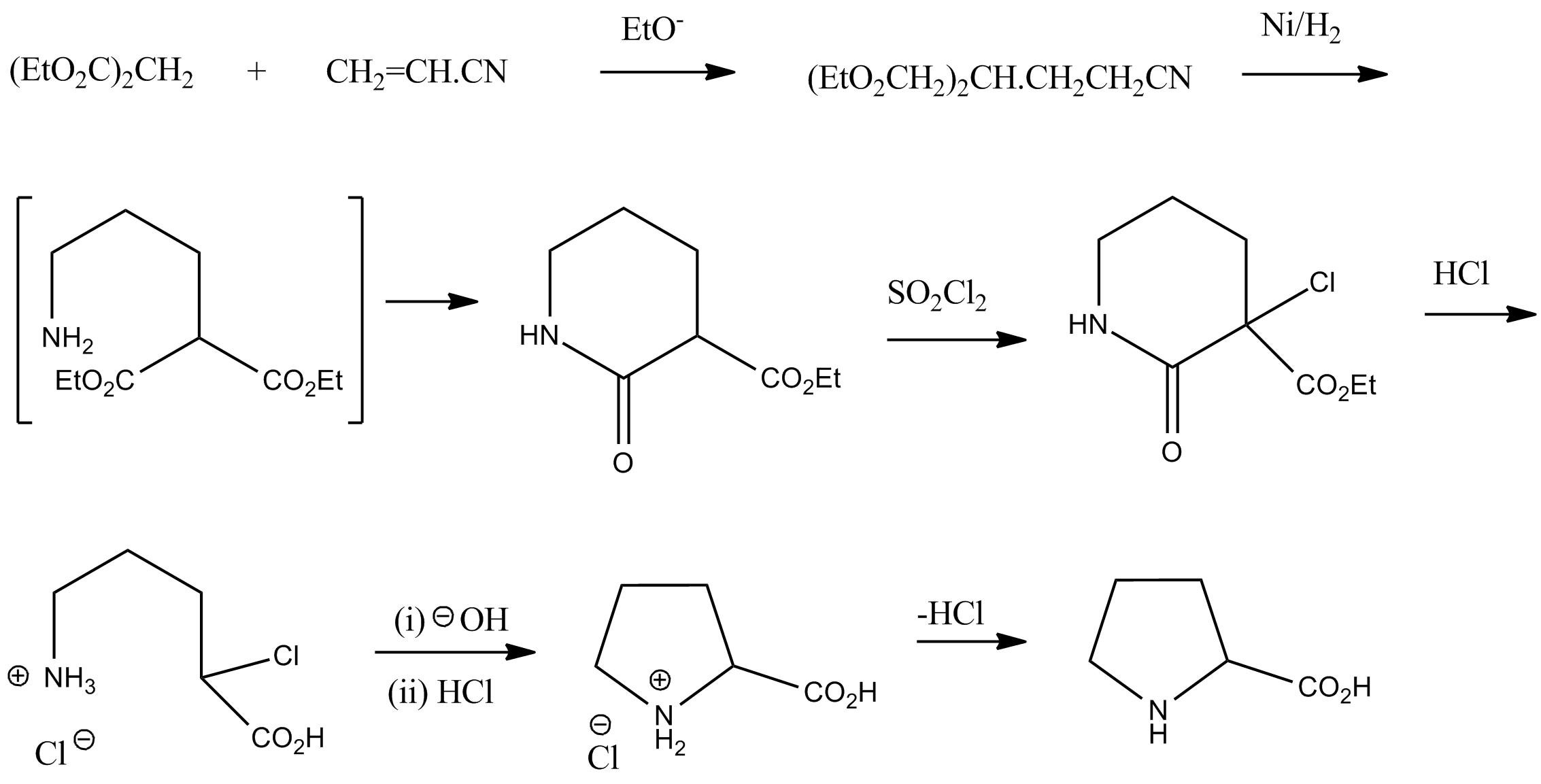
Racemic proline can be synthesized from diethyl malonate andacrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile is an organic compound with the formula and the structure . It is a colorless, volatile liquid although commercial samples can be yellow due to impurities. It has a pungent odor of garlic or onions. In terms of its molecula ...
:Vogel, ''Practical Organic Chemistry'' 5th edition
:
See also
*Hyperprolinemia
Hyperprolinemia is a condition which occurs when the amino acid proline is not broken down properly by the enzymes proline oxidase or pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase, causing a buildup of proline in the body.
Genetics
Mutations in the ...
* Inborn error of metabolism
Inborn errors of metabolism form a large class of genetic diseases involving congenital disorders of enzyme activities. The majority are due to defects of single genes that code for enzymes that facilitate conversion of various substances ( subst ...
* Prolidase deficiency
* Prolinol
References
Further reading
* .External links
Proline MS Spectrum
Proline biosynthesis
{{Authority control AMPA receptor agonists Kainate receptor agonists NMDA receptor agonists Proteinogenic amino acids Glucogenic amino acids Glycine receptor agonists Cyclic amino acids Pyrrolidines Secondary amino acids Excitatory amino acids