Principality of Wales on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Principality of Wales () was originally the territory of the native Welsh princes of the
 By 1200 Llywelyn Fawr (the Great) ap Iorwerth ruled over all of Gwynedd, with England endorsing all of Llywelyn's holdings that year. England's endorsement was part of a larger strategy of reducing the influence of Powys Wenwynwyn, as King John had given William de Breos licence in 1200 to "seize as much as he could" from the native Welsh. However, de Breos was in disgrace by 1208, and Llywelyn seized both Powys Wenwynwyn and northern Ceredigion.
In his expansion, the Prince was careful not to antagonise King John, his father-in-law. Llywelyn had married Joan, King John's illegitimate daughter, in 1204. In 1209 Prince Llywelyn joined King John on his campaign in Scotland. However, by 1211 King John recognised the growing influence of Prince Llywelyn as a threat to English authority in Wales. King John invaded Gwynedd and reached the banks of the Menai, and Llywelyn was forced to cede the Perfeddwlad, and recognize John as his heir presumptive if Llywelyn's marriage to Joan did not produce any legitimate successors. Succession was a complicated matter given that Welsh law recognized children born out of wedlock as equal to those in born in wedlock and sometimes accepted claims through the female line. By then, Llywelyn had several illegitimate children. Many of Llywelyn's Welsh allies had abandoned him during England's invasion of Gwynedd, preferring an overlord far away rather than one nearby. Welsh lords expected an unobtrusive English crown, but King John had a castle built at
By 1200 Llywelyn Fawr (the Great) ap Iorwerth ruled over all of Gwynedd, with England endorsing all of Llywelyn's holdings that year. England's endorsement was part of a larger strategy of reducing the influence of Powys Wenwynwyn, as King John had given William de Breos licence in 1200 to "seize as much as he could" from the native Welsh. However, de Breos was in disgrace by 1208, and Llywelyn seized both Powys Wenwynwyn and northern Ceredigion.
In his expansion, the Prince was careful not to antagonise King John, his father-in-law. Llywelyn had married Joan, King John's illegitimate daughter, in 1204. In 1209 Prince Llywelyn joined King John on his campaign in Scotland. However, by 1211 King John recognised the growing influence of Prince Llywelyn as a threat to English authority in Wales. King John invaded Gwynedd and reached the banks of the Menai, and Llywelyn was forced to cede the Perfeddwlad, and recognize John as his heir presumptive if Llywelyn's marriage to Joan did not produce any legitimate successors. Succession was a complicated matter given that Welsh law recognized children born out of wedlock as equal to those in born in wedlock and sometimes accepted claims through the female line. By then, Llywelyn had several illegitimate children. Many of Llywelyn's Welsh allies had abandoned him during England's invasion of Gwynedd, preferring an overlord far away rather than one nearby. Welsh lords expected an unobtrusive English crown, but King John had a castle built at 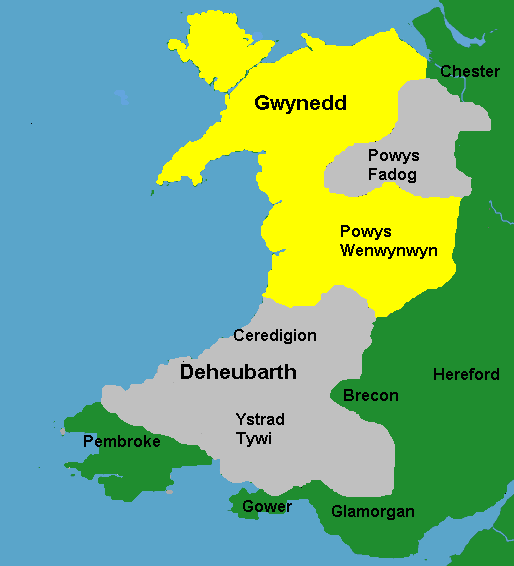 Early in 1212 Llywelyn had regained the Perfeddwlad and burned the castle at Aberystwyth. Llywelyn's revolt caused John to postpone his invasion of France, and
Early in 1212 Llywelyn had regained the Perfeddwlad and burned the castle at Aberystwyth. Llywelyn's revolt caused John to postpone his invasion of France, and

House of Aberffraw
The House of Aberffraw was a medieval royal court based in the village it was named after, Aberffraw, Anglesey (Wales, UK) within the borders of the then Kingdom of Gwynedd. The dynasty was founded in the 9th century by a King in Wales whose de ...
from 1216 to 1283, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales during its height of 1267–1277. Following the conquest of Wales by Edward I of England of 1277 to 1283, those parts of Wales retained under the direct control of the English crown, principally in the north and west of the country, were re-constituted as a new Principality of Wales and ruled either by the monarch or the monarch's heir though not formally incorporated into the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from the late 9th century, when it was unified from various Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to f ...
. This was ultimately accomplished with the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542 when the Principality ceased to exist as a separate entity.
The Principality was formally founded in 1216 by native Welshman and King of Gwynedd, Llywelyn the Great
Llywelyn ab Iorwerth (, – 11 April 1240), also known as Llywelyn the Great (, ; ), was a medieval Welsh ruler. He succeeded his uncle, Dafydd ab Owain Gwynedd, as King of Gwynedd in 1195. By a combination of war and diplomacy, he dominate ...
who gathered other leaders of ''pura Wallia'' at the Council of Aberdyfi. The agreement was later recognised by the 1218 Treaty of Worcester between Llywelyn the Great of Wales and Henry III of England
Henry III (1 October 1207 – 16 November 1272), also known as Henry of Winchester, was King of England, Lord of Ireland, and Duke of Aquitaine from 1216 until his death in 1272. The son of John, King of England, King John and Isabella of Ang ...
. The treaty gave substance to the political reality of 13th-century Wales and England, and the relationship of the former with the Angevin Empire
The Angevin Empire (; ) was the collection of territories held by the House of Plantagenet during the 12th and 13th centuries, when they ruled over an area covering roughly all of present-day England, half of France, and parts of Ireland and Wal ...
. The principality retained a great degree of autonomy, characterized by a separate legal jurisprudence
Jurisprudence, also known as theory of law or philosophy of law, is the examination in a general perspective of what law is and what it ought to be. It investigates issues such as the definition of law; legal validity; legal norms and values ...
based on the well-established laws of ''Cyfraith Hywel
''Cyfraith Hywel'' (; ''Laws of Hywel''), also known as ''Welsh law'' (), was the system of law practised in medieval Wales before its final conquest by England. Subsequently, the Welsh law's criminal codes were superseded by the Statute o ...
'', and by the increasingly sophisticated court
A court is an institution, often a government entity, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between Party (law), parties and Administration of justice, administer justice in Civil law (common law), civil, Criminal law, criminal, an ...
of the House of Aberffraw
The House of Aberffraw was a medieval royal court based in the village it was named after, Aberffraw, Anglesey (Wales, UK) within the borders of the then Kingdom of Gwynedd. The dynasty was founded in the 9th century by a King in Wales whose de ...
. Although it owed fealty
An oath of fealty, from the Latin (faithfulness), is a pledge of allegiance of one person to another.
Definition
In medieval Europe, the swearing of fealty took the form of an oath made by a vassal, or subordinate, to his lord. "Fealty" also r ...
to the Angevin king of England, the principality was ''de facto'' independent, with a similar status in the empire to the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe, traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a Anglo-Sc ...
. Its existence has been seen as proof that all the elements necessary for the growth of Welsh statehood were in place.
The period of ''de facto'' independence ended with Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
's conquest of the principality between 1277 and 1283. Under the Statute of Rhuddlan
The Statute of Rhuddlan (), also known as the Statutes of Wales ( or ''Valliae'') or as the Statute of Wales ( or ''Valliae''), was a royal ordinance by Edward I of England, which gave the constitutional basis for the government of the Principal ...
, the principality lost its independence and became effectively an annexed territory of the English crown. From 1301, the crown's lands in north and west Wales formed part of the appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a monarch, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture (where only the eldest inherits). It was ...
of England's heir apparent, with the title "Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales (, ; ) is a title traditionally given to the male heir apparent to the History of the English monarchy, English, and later, the British throne. The title originated with the Welsh rulers of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd who, from ...
". On accession of the prince to the English throne, the lands and title became merged with the Crown again. On two occasions Welsh claimants to the title rose up in rebellion during this period, although neither ultimately succeeded.
Since the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542, which formally incorporated all of Wales within the Kingdom of England, there has been no geographical or constitutional basis for describing any of the territory of Wales as a principality, although the term has occasionally been used in an informal sense to describe the country, and in relation to the honorary title of Prince of Wales.
Pre-conquest principality
The Principality of Wales was created in 1216 at the Council of Aberdyfi when it was agreed betweenLlywelyn the Great
Llywelyn ab Iorwerth (, – 11 April 1240), also known as Llywelyn the Great (, ; ), was a medieval Welsh ruler. He succeeded his uncle, Dafydd ab Owain Gwynedd, as King of Gwynedd in 1195. By a combination of war and diplomacy, he dominate ...
and the other sovereign princes among the Welsh that he was the paramount ruler amongst them, and they would pay homage to him. Later he obtained recognition, at least in part, of this agreement from the King of England, who agreed that Llywelyn's heirs and successors would enjoy the title "Prince of Wales" but with certain limitations to his realm and other conditions, including homage to the King of England as vassal, and adherence to rules regarding a legitimate succession. Llywelyn had been at pains to ensure that his heirs and successors would follow the "approved" (by the Pope at least) system of inheritance which excluded illegitimate sons. In so doing he excluded his elder bastard son Gruffydd ap Llywelyn from the inheritance, a decision which would have later ramifications. In 1240 Llywelyn died and Henry III of England
Henry III (1 October 1207 – 16 November 1272), also known as Henry of Winchester, was King of England, Lord of Ireland, and Duke of Aquitaine from 1216 until his death in 1272. The son of John, King of England, King John and Isabella of Ang ...
(who succeeded John) promptly invaded large areas of his former realm, usurping them from him. However, the two sides came to peace and Henry honoured at least part of the agreement and bestowed upon Dafydd ap Llywelyn
Dafydd ap Llywelyn (c. March 1212 – 25 February 1246) was List of rulers of Gwynedd, King of Gwynedd from 1240 to 1246.
Birth and descent
Though birth years of 1208, 1206, and 1215 have been put forward for Dafydd, it has recently been p ...
the title 'Prince of Wales'. This title would be granted to his successor Llywelyn in 1267 (after a campaign by him to achieve it) and was later claimed by his brother Dafydd and other members of the princely House of Aberffraw
The House of Aberffraw was a medieval royal court based in the village it was named after, Aberffraw, Anglesey (Wales, UK) within the borders of the then Kingdom of Gwynedd. The dynasty was founded in the 9th century by a King in Wales whose de ...
.
Aberffraw princes
Llywelyn ap Iorwerth 1195–1240
 By 1200 Llywelyn Fawr (the Great) ap Iorwerth ruled over all of Gwynedd, with England endorsing all of Llywelyn's holdings that year. England's endorsement was part of a larger strategy of reducing the influence of Powys Wenwynwyn, as King John had given William de Breos licence in 1200 to "seize as much as he could" from the native Welsh. However, de Breos was in disgrace by 1208, and Llywelyn seized both Powys Wenwynwyn and northern Ceredigion.
In his expansion, the Prince was careful not to antagonise King John, his father-in-law. Llywelyn had married Joan, King John's illegitimate daughter, in 1204. In 1209 Prince Llywelyn joined King John on his campaign in Scotland. However, by 1211 King John recognised the growing influence of Prince Llywelyn as a threat to English authority in Wales. King John invaded Gwynedd and reached the banks of the Menai, and Llywelyn was forced to cede the Perfeddwlad, and recognize John as his heir presumptive if Llywelyn's marriage to Joan did not produce any legitimate successors. Succession was a complicated matter given that Welsh law recognized children born out of wedlock as equal to those in born in wedlock and sometimes accepted claims through the female line. By then, Llywelyn had several illegitimate children. Many of Llywelyn's Welsh allies had abandoned him during England's invasion of Gwynedd, preferring an overlord far away rather than one nearby. Welsh lords expected an unobtrusive English crown, but King John had a castle built at
By 1200 Llywelyn Fawr (the Great) ap Iorwerth ruled over all of Gwynedd, with England endorsing all of Llywelyn's holdings that year. England's endorsement was part of a larger strategy of reducing the influence of Powys Wenwynwyn, as King John had given William de Breos licence in 1200 to "seize as much as he could" from the native Welsh. However, de Breos was in disgrace by 1208, and Llywelyn seized both Powys Wenwynwyn and northern Ceredigion.
In his expansion, the Prince was careful not to antagonise King John, his father-in-law. Llywelyn had married Joan, King John's illegitimate daughter, in 1204. In 1209 Prince Llywelyn joined King John on his campaign in Scotland. However, by 1211 King John recognised the growing influence of Prince Llywelyn as a threat to English authority in Wales. King John invaded Gwynedd and reached the banks of the Menai, and Llywelyn was forced to cede the Perfeddwlad, and recognize John as his heir presumptive if Llywelyn's marriage to Joan did not produce any legitimate successors. Succession was a complicated matter given that Welsh law recognized children born out of wedlock as equal to those in born in wedlock and sometimes accepted claims through the female line. By then, Llywelyn had several illegitimate children. Many of Llywelyn's Welsh allies had abandoned him during England's invasion of Gwynedd, preferring an overlord far away rather than one nearby. Welsh lords expected an unobtrusive English crown, but King John had a castle built at Aberystwyth
Aberystwyth (; ) is a University town, university and seaside town and a community (Wales), community in Ceredigion, Wales. It is the largest town in Ceredigion and from Aberaeron, the county's other administrative centre. In 2021, the popula ...
, and his direct interference in Powys and the Perfeddwlad caused many of these Welsh lords to rethink their position. Llywelyn capitalised on Welsh resentment against King John, and led a church-sanctioned revolt against him. As King John was an enemy of the church, Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III (; born Lotario dei Conti di Segni; 22 February 1161 – 16 July 1216) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 until his death on 16 July 1216.
Pope Innocent was one of the most power ...
gave his blessing to Llywelyn's revolt.
Philip Augustus
Philip II (21 August 1165 – 14 July 1223), also known as Philip Augustus (), was King of France from 1180 to 1223. His predecessors had been known as kings of the Franks (Latin: ''rex Francorum''), but from 1190 onward, Philip became the firs ...
, the King of France
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I, king of the Fra ...
, was so moved as to contact Llywelyn and propose that they ally against the English king, King John ordered the execution by hanging of his Welsh hostages, the sons of many of Llywelyn's supporters, Llywelyn I was the first prince to receive the fealty of other Welsh lords at the 1216 Council of Aberdyfi, thus becoming the ''de facto'' Prince of Wales and giving substance to the Aberffraw claims.
Dafydd ap Llywelyn 1240–46
On succeeding his father, Dafydd immediately had to contend with the claims of his half-brother, Gruffudd, to the throne. Having imprisoned Gruffudd, his ambitions were curbed by an invasion of Wales led by Henry III in league with a number of the captive Gruffudd's supporters. In August 1241, Dafydd capitulated and signed the Treaty of Gwerneigron, further restricting his powers. By 1244, however, Gruffudd was dead, and Dafydd seems to have benefited from the backing of many of his brother's erstwhile supporters. He was acknowledged by the Pope asPrince of Wales
Prince of Wales (, ; ) is a title traditionally given to the male heir apparent to the History of the English monarchy, English, and later, the British throne. The title originated with the Welsh rulers of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd who, from ...
for a time and defeated Henry III in battle in 1245 during the English king's second invasion of Wales. A truce was agreed in the autumn, and Henry withdrew, but Dafydd died unexpectedly in 1246 without issue. His wife, Isabella de Braose, returned to England; she was dead by 1248.
Dafydd married Isabella de Braose in 1231. Their marriage produced no children, and there is no contemporary evidence that Dafydd sired any heirs. According to late genealogical sources collected by Bartrum (1973), Dafydd had two children by an unknown woman (or women), a daughter, Annes, and a son, Llywelyn ap Dafydd, who apparently later became Constable of Rhuddlan and was succeeded in that post by his son Cynwrig ap Llywelyn.
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd 1246–82
After achieving victory over his brothers, Llywelyn went on to reconquer the areas of Gwynedd occupied by England (the Perfeddwlad and others). His alliance withSimon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, 1st Earl of Chester ( – 4 August 1265), also known as Simon V de Montfort, was an English nobleman of French origin and a member of the Peerage of England, English peerage, who led the baronial opposi ...
, in 1265 against King Henry III of England
Henry III (1 October 1207 – 16 November 1272), also known as Henry of Winchester, was King of England, Lord of Ireland, and Duke of Aquitaine from 1216 until his death in 1272. The son of John, King of England, King John and Isabella of Ang ...
allowed him to reconquer large areas of mid-Wales from the English Marcher Lord
A marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in Fra ...
s. At the Treaty of Montgomery
The Treaty of Montgomery was an Anglo- Welsh treaty signed on 29 September 1267 in Montgomeryshire by which Llywelyn ap Gruffudd was acknowledged as Prince of Wales by King Henry III of England (r. 1216–1272). It was the only time an English ...
between England and Wales in 1267 Llywelyn was granted the title "Prince of Wales" for his heirs and successors and allowed to keep the lands he had conquered as well as the homage of lesser Welsh princes in return for his own homage to the King of England and payment of a substantial fee. Disputes between him, his brother Dafydd, and English lords bordering his own led to renewed conflict with England (now ruled by Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
) in 1277. Following the Treaty of Aberconwy
The Treaty of Aberconwy was signed on the 10th of November 1277, and was made between King Edward I of England and Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, Prince of Wales. It followed Edward's invasion of Llywelyn's territories earlier that year. The treaty re-e ...
Llywelyn was confined to Gwynedd-uwch-Conwy. He joined a revolt instigated by his brother Dafydd in 1282 in which he died in battle.
Dafydd ap Gruffudd 1282–83
Dafydd assumed his elder brother's title in 1282 and led a brief period of continued resistance against England. He was captured and executed in 1283.Government, administration and law
The political maturation of the principality's government fostered a more defined relationship between the prince and the people. Emphasis was placed on the territorial integrity of the principality, with the prince as lord of all the land, and other Welsh lords swearing fealty to the prince directly, a distinction with which the Prince of Wales paid yearly tribute to the King of England. By treaty, the principality was obliged to pay the kingdom large annual sums. Between 1267 and 1272 Wales made a total payment of £11,500, "proof of a growing money economy... and testimony of the effectiveness of the principality's financial administration," wrote historian Dr. John Davies. Additionally, modifications and amendments to the Law Codes of Hywel Dda encouraged the decline of the galanas (blood-fine) and the use of the jury system. The Aberffraw dynasty maintained vigorous diplomatic and domestic policies; and patronized the Church in Wales, particularly that of theCistercian Order
The Cistercians (), officially the Order of Cistercians (, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contri ...
.
The princely court
At the end of the twelfth century, and beginning of the thirteenth century,Llywelyn ab Iorwerth
Llywelyn ab Iorwerth (, – 11 April 1240), also known as Llywelyn the Great (, ; ), was a medieval Welsh ruler. He succeeded his uncle, Dafydd ab Owain Gwynedd, as King of Gwynedd in 1195. By a combination of war and diplomacy, he dominate ...
(Llywelyn Fawr or Llywelyn the Great), built a royal home at Abergwyngregyn (known as ''Tŷ Hir'', the Long House, in later documents) on the site of the subsequent manor house of Pen y Bryn
Pen y Bryn is a two-storey manor house, in Abergwyngregyn, Gwynedd, in north-west Wales, adjacent to the A55, five miles east of Bangor and eight miles west of Conwy. It is constructed mainly of broken stone, with roughly dressed quoins an ...
. To the east was the newly endowed Cistercian Monastery of Aberconwy; to the west the cathedral city of Bangor. In 1211, King John of England
John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216) was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216. He lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin Empi ...
brought an army across the river Conwy, and occupied the royal home for a brief period; his troops went on to burn Bangor. Llywelyn's wife, John's daughter Joan, also known as Joanna, negotiated between the two men, and John withdrew. Joan died at Abergwyngregyn in 1237; Dafydd ap Llywelyn died there in 1246; Eleanor de Montfort, Lady of Wales, wife of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd ( – 11 December 1282), also known as Llywelyn II and Llywelyn the Last (), was List of rulers of Gwynedd, Prince of Gwynedd, and later was recognised as the Prince of Wales (; ) from 1258 until his death at Cilmeri in 128 ...
, died there on 19 June 1282, giving birth to a baby, Gwenllian of Wales
Gwenllian ferch Llywelyn (June 1282 – 7 June 1337), commonly known as Gwenllian of Wales, was the daughter of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, the last native Prince of Wales (). Gwenllian is sometimes confused with Gwenllian ferch Gruffudd, who lived ...
.
Population, culture and society
The 13th-century Principality of Wales encompassed three-quarters of the surface area of modern Wales; "fromAnglesey
Anglesey ( ; ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms the bulk of the Principal areas of Wales, county known as the Isle of Anglesey, which also includes Holy Island, Anglesey, Holy Island () and some islets and Skerry, sker ...
to Machen
Machen (from Welsh ' "place (of)" + ', a personal name) is a large village three miles east of Caerphilly, south Wales. It is situated in the Caerphilly borough within the historic boundaries of Monmouthshire. It neighbours Bedwas and Treth ...
, from the outskirts of Chester
Chester is a cathedral city in Cheshire, England, on the River Dee, Wales, River Dee, close to the England–Wales border. With a built-up area population of 92,760 in 2021, it is the most populous settlement in the borough of Cheshire West an ...
to the outskirts of Cydweli," wrote Davies. By 1271, Prince Llywelyn II could claim a growing population of about 200,000 people or a little less than three-quarters of the total Welsh population. The population increase was common throughout Europe in the 13th century, but in Wales it was more pronounced. By Llywelyn II's reign, as much as 10 percent of the population were town-dwellers. Additionally, "unfree slaves... had long disappeared" from within the territory of the principality, wrote Davies. The increase in men allowed the prince to call on and field a far more substantial army.
A more stable social and political environment provided by the Aberffraw administration allowed for the natural development of Welsh culture, particularly in literature, law, and religion. Tradition originating from ''The History of Gruffydd ap Cynan'' attributes Gruffydd I as reforming the orders of bard
In Celtic cultures, a bard is an oral repository and professional story teller, verse-maker, music composer, oral historian and genealogist, employed by a patron (such as a monarch or chieftain) to commemorate one or more of the patron's a ...
s and musician
A musician is someone who Composer, composes, Conducting, conducts, or Performing arts#Performers, performs music. According to the United States Employment Service, "musician" is a general Terminology, term used to designate a person who fol ...
s; Welsh literature
Welsh literature is any literature originating from Wales or by Welsh writers:
*Welsh-language literature
Welsh-language literature () has been produced continuously since the emergence of Welsh from Brythonic as a distinct language in a ...
demonstrated "vigor and a sense of commitment" as new ideas reached Wales, even in "the wake of the invaders", according to historian John Davies. Contacts with continental Europe "sharpened Welsh pride", wrote Davies in his ''History of Wales''.
Economy and trade
The increase in the Welsh population, especially in the lands of the principality, allowed for a greater diversification of the economy. The Meirionnydd tax rolls give evidence to the thirty-seven various professions present in Meirionnydd directly before the conquest. Of these professions, there were eightgoldsmith
A goldsmith is a Metalworking, metalworker who specializes in working with gold and other precious metals. Modern goldsmiths mainly specialize in jewelry-making but historically, they have also made cutlery, silverware, platter (dishware), plat ...
s, four bards (poets) by trade, 26 shoemaker
Shoemaking is the process of making footwear.
Originally, shoes were made one at a time by hand, often by groups of shoemakers, or '' cordwainers'' (sometimes misidentified as cobblers, who repair shoes rather than make them). In the 18th cen ...
s, a doctor in Cynwyd, and a hotel
A hotel is an establishment that provides paid lodging on a short-term basis. Facilities provided inside a hotel room may range from a modest-quality mattress in a small room to large suites with bigger, higher-quality beds, a dresser, a re ...
keeper in Maentwrog, and 28 priests; two of whom were university graduates. Also present were a significant number of fishermen
A fisherman or fisher is someone who captures fish and other animals from a body of water, or gathers shellfish.
Worldwide, there are about 38 million commercial and subsistence fishers and fish farmers. Fishermen may be professional or recr ...
, administrators, professional men and craftsmen.
With the average temperature of Wales a degree or two higher than it is today, more Welsh lands were arable for agriculture, "a crucial bonus for a country like Wales," wrote the historian John Davies. Of significant importance for the principality included more developed trade routes, which allowed for the introduction of new energy sources such as the windmill
A windmill is a machine operated by the force of wind acting on vanes or sails to mill grain (gristmills), pump water, generate electricity, or drive other machinery.
Windmills were used throughout the high medieval and early modern period ...
, the fulling mill and the horse collar
A horse collar is a part of a horse harness that is used to distribute the load around a horse's neck and shoulders when pulling a wagon or plough. The collar often supports and pads a pair of curved metal or wooden pieces, called hames, to wh ...
(which doubled the efficiency of horse-power).
The principality traded cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
, skins, cheese
Cheese is a type of dairy product produced in a range of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk (usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats or sheep). During prod ...
, timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into uniform and useful sizes (dimensional lumber), including beams and planks or boards. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). ...
, horses, wax, dogs, hawks, and fleeces, but also flannel
Flannel is a soft woven fabric, of varying fineness. Flannel was originally made from carded wool or worsted yarn, but is now often made from either wool, cotton, or synthetic fiber. Flannel is commonly used to make tartan clothing, blankets, ...
(with the growth of fulling mills). Flannel was second only to cattle among the principality's exports. In exchange, the principality imported salt, wine, wheat, and other luxuries from London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
and Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
. But most importantly for the defence of the principality, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
and specialised weapon
A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime (e.g., murder), law ...
ry were also imported. Welsh dependence on foreign imports was a tool that England used to wear down the principality during times of conflict between the two countries.
1284 to 1543: Annexation by the English crown
Establishment and governance
Between 1277 and 1283,Edward I of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 1254 ...
conquered the territories of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd ( – 11 December 1282), also known as Llywelyn II and Llywelyn the Last (), was List of rulers of Gwynedd, Prince of Gwynedd, and later was recognised as the Prince of Wales (; ) from 1258 until his death at Cilmeri in 128 ...
and the other last remaining native Welsh princes. The governance and constitutional position of the principality after its conquest was set out in the Statute of Rhuddlan
The Statute of Rhuddlan (), also known as the Statutes of Wales ( or ''Valliae'') or as the Statute of Wales ( or ''Valliae''), was a royal ordinance by Edward I of England, which gave the constitutional basis for the government of the Principal ...
of 1284. In the words of the statute, the principality was "annexed and united" to the English crown.
The principality's administration was overseen by the Prince of Wales's council comprising between 8 and 15 councillors sitting in London or, later, Ludlow
Ludlow ( ) is a market town and civil parish in Shropshire (district), Shropshire, England. It is located south of Shrewsbury and north of Hereford, on the A49 road (Great Britain), A49 road which bypasses the town. The town is near the conf ...
in Shropshire
Shropshire (; abbreviated SalopAlso used officially as the name of the county from 1974–1980. The demonym for inhabitants of the county "Salopian" derives from this name.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the West M ...
. The council acted as the principality's final court of appeal. By 1476, the council, which became known as the Council of Wales and the Marches, began taking responsibility not only for the principality itself but its authority was extended over the whole of Wales.
The territory of the principality fell into two distinct areas: the lands under direct royal control and lands that Edward I had distributed by feudal grants.
For lands under royal control, the administration, under the Statute of Rhuddlan, was divided into two territories: North Wales based at Caernarfon and West Wales based at Carmarthen. The Statute organized the Principality into shire counties. Carmarthenshire
Carmarthenshire (; or informally ') is a Principal areas of Wales, county in the South West Wales, south-west of Wales. The three largest towns are Llanelli, Carmarthen and Ammanford. Carmarthen is the county town and administrative centre. ...
and Cardiganshire
Ceredigion (), historically Cardiganshire (, ), is a county in the west of Wales. It borders Gwynedd across the Dyfi estuary to the north, Powys to the east, Carmarthenshire and Pembrokeshire to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. Ab ...
were administered by the Justiciar of South Wales The Justiciar of South Wales, sometimes referred to as the Justiciar of West Wales was a royal official of the Principality of Wales during the medieval period. He controlled the southern half of the principality.
Background
Justiciar was a title ...
(or "of West Wales") at Carmarthen. In the North, the counties of Anglesey
Anglesey ( ; ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms the bulk of the Principal areas of Wales, county known as the Isle of Anglesey, which also includes Holy Island, Anglesey, Holy Island () and some islets and Skerry, sker ...
, Merionethshire
Merionethshire, or Merioneth ( or '), was Historic counties of Wales, one of the thirteen counties of Wales that existed from 1536 until their abolishment in 1974. It was located in the North West Wales, north-west of Wales.
Name
'Merioneth' is a ...
, and Caernarfonshire were created under the control of Justiciar of North Wales
The Justiciar of North Wales was a legal office concerned with the government of the three counties in north-west Wales during the medieval period. Justiciar was a title which had been given to one of the monarch's chief ministers in both England a ...
and a provincial exchequer at Caernarfon, run by the Chamberlain of North Wales, who accounted for the revenues he collected to the Exchequer
In the Civil Service (United Kingdom), civil service of the United Kingdom, His Majesty's Exchequer, or just the Exchequer, is the accounting process of central government and the government's ''Transaction account, current account'' (i.e., mon ...
at Westminster
Westminster is the main settlement of the City of Westminster in Central London, Central London, England. It extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street and has many famous landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buckingham Palace, ...
. Under them were royal officials such as sheriff
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland, the , which is common ...
s, coroner
A coroner is a government or judicial official who is empowered to conduct or order an inquest into the manner or cause of death. The official may also investigate or confirm the identity of an unknown person who has been found dead within th ...
s, and bailiff
A bailiff is a manager, overseer or custodian – a legal officer to whom some degree of authority or jurisdiction is given. There are different kinds, and their offices and scope of duties vary.
Another official sometimes referred to as a '' ...
s to collect taxes and administer justice. Another county, Flintshire
Flintshire () is a county in the north-east of Wales. It borders the Irish Sea to the north, the Dee Estuary to the north-east, the English county of Cheshire to the east, Wrexham County Borough to the south, and Denbighshire to the west. ...
, was created out of the lordships of Tegeingl, Hopedale and Maelor Saesneg, and was administered with the Palatinate of Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Merseyside to the north-west, Greater Manchester to the north-east, Derbyshire to the east, Staffordshire to the south-east, and Shrop ...
by the Justiciar of Chester.
The remainder of the principality comprised lands that Edward I had granted to supporters shortly after the completion of the conquest in 1284, and which, in practice, became Marcher lordships: for example, the Lordship of Denbigh granted to the Earl of Lincoln
Earl of Lincoln is a title that has been created eight times in the peerage of England, most recently in 1572. The Hereditary peerage, earldom was held as a subsidiary title by the Duke of Newcastle, Dukes of Newcastle-under-Lyne, from 1768 to 1 ...
and the Lordship of Powys granted to Owain ap Gruffydd ap Gwenwynwyn, who became Owen de la Pole
Owen de la Pole (c. 1257 – c. 1293), also known as Owain ap Gruffydd ap Gwenwynwyn, was the heir presumptive to the Welsh principality of Powys Wenwynwyn until 1283 when it was abolished by the Parliament of Shrewsbury. He became the 1st Lo ...
. These lands after 1301 were held as tenants-in-chief
In medieval and early modern Europe, a tenant-in-chief (or vassal-in-chief) was a person who held his lands under various forms of feudal land tenure directly from the king or territorial prince to whom he did homage, as opposed to holding them ...
of the Principality of Wales, rather than from the Crown directly, but were, for all practical purposes, not part of the principality.
Law
The Statute of Rhuddlan also introducedEnglish common law
English law is the common law legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly criminal law and civil law, each branch having its own courts and procedures. The judiciary is independent, and legal principles like fairness, equality bef ...
to the principality, albeit with some local variation. Criminal law became entirely based on common law: the statute stated that "in thefts, larcenies, burnings, murders, manslaughters and manifest and notorious robberies – we will that they shall use the laws of England". However, Welsh law continued to be used in civil cases such as land inheritance, contracts, sureties, and similar matters, though with changes, for example, illegitimate sons could no longer claim part of the inheritance, which Welsh law had allowed them to do. In 1301, this modified principality was bestowed on the English monarch's heir apparent and thereafter became the territorial endowment of the heir to the throne.
There were few attempts by the English parliament to legislate in Wales and the lands of the principality remained subject to laws enacted by the king and his council. However, the king was prepared to allow Parliament to legislate in emergencies such as treason or rebellion. An example was the Penal Laws against Wales 1402 enacted to contain the Glyndŵr Rising Glyndŵr, also spelled Glyndwr, may refer to:
* Owain Glyndŵr – Medieval Welsh prince and leader
** Glyndŵr rebellion – 15th century Welsh uprising
* Glyndŵr (district) – District of Wales (1974–1996)
** Montgomeryshire and Glyndŵr ( ...
and which, ''inter alia'', prohibited the Welsh from intermarrying with the English or owning land in England or the Welsh boroughs. Some Welshman who were loyal to the Principality successfully petitioned for exemption from the penal laws. An example was Rhys ap Thomas ap Dafydd of Carmarthenshire who was a royal official in the southern part of the principality.
Castles, towns and colonisation
Edward's main concern following the conquest was to ensure the military security of his new territories and the stone castle was to be the primary means for achieving this. Under the supervision of James of Saint George, Edward's master-builder, a series of imposing castles was built, using a distinctive design and the most advanced defensive features of the day, to form a "ring of stone" around the northern part of the principality. Among the major buildings were the castles ofBeaumaris
Beaumaris (; ) is a town and community (Wales), community on the Anglesey, Isle of Anglesey in Wales, of which it is the former county town. It is located at the eastern entrance to the Menai Strait, the tidal waterway separating Anglesey fro ...
, Caernarfon
Caernarfon (; ) is a List of place names with royal patronage in the United Kingdom, royal town, Community (Wales), community and port in Gwynedd, Wales. It has a population of 9,852 (with Caeathro). It lies along the A487 road, on the easter ...
, Conwy
Conwy (, ), previously known in English as Conway, is a walled market town, community and the administrative centre of Conwy County Borough in North Wales. The walled town and castle stand on the west bank of the River Conwy, facing Deganwy ...
and Harlech
Harlech () is a seaside resort and community (Wales), community in Gwynedd, North Wales, and formerly in the Historic counties of Wales, historic county of Merionethshire. It lies on Tremadog Bay in the Snowdonia National Park. Before 1966, it ...
. Aside from their practical military role, the castles made a clear symbolic statement to the Welsh that the principality was subject to English rule on a permanent basis.
Outside of urban areas, the principality retained its Welsh character. Unlike in some of the newly created Marcher lordships, such as Denbigh, there was little evidence of the successful colonisation of rural areas by English settlers. For the royal shires, Edward established a series of new towns, usually attached to one of his stone castles, which would be the focus of English settlement. These "plantation boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English language, English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
...
", often with the castle constable as town mayor, were populated by English burgesses and acted as a support for the royal military establishment as well as being an anglicizing influence. Examples include Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
, Aberystwyth
Aberystwyth (; ) is a University town, university and seaside town and a community (Wales), community in Ceredigion, Wales. It is the largest town in Ceredigion and from Aberaeron, the county's other administrative centre. In 2021, the popula ...
, Beaumaris
Beaumaris (; ) is a town and community (Wales), community on the Anglesey, Isle of Anglesey in Wales, of which it is the former county town. It is located at the eastern entrance to the Menai Strait, the tidal waterway separating Anglesey fro ...
, Conwy
Conwy (, ), previously known in English as Conway, is a walled market town, community and the administrative centre of Conwy County Borough in North Wales. The walled town and castle stand on the west bank of the River Conwy, facing Deganwy ...
and Caernarfon
Caernarfon (; ) is a List of place names with royal patronage in the United Kingdom, royal town, Community (Wales), community and port in Gwynedd, Wales. It has a population of 9,852 (with Caeathro). It lies along the A487 road, on the easter ...
.
The boroughs were given economic rights over the surrounding Welsh rural areas and prospered as a result. For example, the burgesses of Caernarfon had a monopoly over trade within eight miles of the town. The burgesses of Carmarthen
Carmarthen (, ; , 'Merlin's fort' or possibly 'Sea-town fort') is the county town of Carmarthenshire and a community (Wales), community in Wales, lying on the River Towy north of its estuary in Carmarthen Bay. At the 2021 United Kingdom cen ...
were given the right to raise taxes from the surrounding population to maintain their town walls. Royal ordinances initially prohibited the Welsh from becoming burgesses, owning land, or even residing in the "English" towns. The enforcement of these laws weakened over time and, although they were temporarily reinforced in 1402 by Henry IV's penal laws following the Welsh Revolt
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, of or about Wales
* Welsh language, spoken in Wales
* Welsh people, an ethnic group native to Wales
Places
* Welsh, Arkansas, U.S.
* Welsh, Louisiana, U.S.
* Welsh, Ohio, U.S.
* Welsh Basin, during t ...
led by Owain Glyndŵr
Owain ap Gruffydd (28 May 135420 September 1415), commonly known as Owain Glyndŵr (Glyn Dŵr, , anglicised as Owen Glendower) was a Welsh people, Welsh leader, soldier and military commander in the Wales in the late Middle Ages, late Middle ...
, they had largely been abandoned by the Tudor period. Even so, in the 14th century in particular, the privileged "English" boroughs were a focus of intense Welsh resentment and the English burgesses continued to hold the Welsh in disdain and sought to maintain their own distinctiveness and settlers' rights.
Nevertheless, there is ample evidence of the gradual assimilation of the two groups, not least through intermarriage. A town such as Aberystwyth had become entirely Welsh in character by the end of the medieval period. At the time of the union with England in the 16th century, English migrant ethnic origin ceased to have the same significance, although upward mobility was linked to anglicisation and use of the English language. Nevertheless, as late as 1532, a group of burgesses from Caernarfon bitterly complained that some of their number had let properties in the town to "foreigners", all of whom had Welsh names.
Plantagenet and Tudor princes
From 1301, thePlantagenet
The House of Plantagenet ( /plænˈtædʒənət/ ''plan-TAJ-ə-nət'') was a royal house which originated from the French county of Anjou. The name Plantagenet is used by modern historians to identify four distinct royal houses: the Angev ...
(and later, Tudor) English kings gave their heir apparent, if he was the king's son or grandson, the lands and title of "Prince of Wales". The one exception was Edward II's son, Edward of Windsor
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after t ...
, who later became Edward III. Upon the heir's accession to the throne, the lands and title merged in the Crown.
The first "English" Prince of Wales was Edward I's son, Edward of Caernarfon. A late 16th-century story claimed that Edward I gave him the title following his declaration to the Welsh that there would be a Prince of Wales "that was borne in Wales and could speake never a word of English": Edward was born at Caernarfon Castle
Caernarfon Castle (; ) is a medieval fortress in Gwynedd, north-west Wales. The first fortification on the site was a motte-and-bailey castle built in the late 11th century, which King Edward I of England began to replace with the current st ...
and, in common with the rest of the English ruling elite, spoke French. However, there seems to be no basis for the story. On 7 February 1301, the king granted to Edward all the lands under royal control in Wales, mainly the territory of the former Principality. Although the documents granting the land made no reference to the title "Prince of Wales", it seems likely that Edward was invested with it at the same time, since, within a month of the grant, he was referred to as the "Prince of Wales" in official documents.
The following received the title while the Principality was in existence:
* Edward of Caernarfon, later Edward II (Prince from 1301 until he became King in 1307)
* Edward of Woodstock, the Black Prince (Prince from 1343 to his death in 1376)
* Richard of Bordeaux, later Richard II (Prince from 1376 until he became King in 1377)
* Henry of Monmouth, later Henry V (Prince from 1399 until he became King in 1413)
*Edward of Westminster
Edward of Westminster (13 October 1453 – 4 May 1471), also known as Edward of Lancaster, was the only child of Henry VI of England and Margaret of Anjou. He was killed aged seventeen at the Battle of Tewkesbury.
Early life
Edward was born at ...
(Prince from 1454 until his death in 1471)
* Edward of the Sanctuary, later Edward V (Prince from 1471 until he became King in 1483)
*Edward of Middleham
Edward of Middleham, Prince of Wales ( or 1476 9 April 1484), was the son and heir apparent of King Richard III of England by his wife Anne Neville. He was Richard's only legitimate child and died aged seven or ten.
Birth and titles
Edward was ...
(Prince from 1483 to his death in 1484)
*Arthur Tudor
Arthur, Prince of Wales (19/20 September 1486 – 2 April 1502), was the eldest son of King Henry VII of England and Elizabeth of York, and an older brother to the future King Henry VIII. He was Duke of Cornwall from birth, and he was crea ...
(Prince from 1489 to his death in 1502)
* Henry Tudor, later Henry VIII (Prince from 1504 until he became King in 1509)
* Edward Tudor, later Edward VI (Prince from 1537 until he became King in 1547, the last Prince of Wales created prior to 1542)
Welsh revolts
Madog ap Llywelyn led a Welsh revolt in 1294–95 against English rule in Wales, and was proclaimed "Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales (, ; ) is a title traditionally given to the male heir apparent to the History of the English monarchy, English, and later, the British throne. The title originated with the Welsh rulers of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd who, from ...
".
Owain Lawgoch
Owain ap Thomas ap Rhodri (, July 1378), commonly known as Owain Lawgoch (, ), was a Welsh soldier who served in Lombardy, France, Alsace, and Switzerland. He led a Free Company fighting for the French against the English in the Hundred Year ...
, a great-nephew of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd and Dafydd ap Gruffudd, claimed the title in exile in France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and supporters revolted in his name across Wales between 1372 and 1378. He was assassinated before being able to return to Wales to lead them.
Owain Glyndŵr
Owain ap Gruffydd (28 May 135420 September 1415), commonly known as Owain Glyndŵr (Glyn Dŵr, , anglicised as Owen Glendower) was a Welsh people, Welsh leader, soldier and military commander in the Wales in the late Middle Ages, late Middle ...
was crowned at Machynlleth
Machynlleth () is a market town, community and electoral ward in Powys, Wales and within the historic boundaries of Montgomeryshire. It is in the Dyfi Valley at the intersection of the A487 and the A489 roads. At the 2001 Census it had a po ...
in 1404 during a revolt
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
against Henry IV of England
Henry IV ( – 20 March 1413), also known as Henry Bolingbroke, was King of England from 1399 to 1413. Henry was the son of John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster (a son of King Edward III), and Blanche of Lancaster.
Henry was involved in the 1388 ...
. He claimed descent from Rhodri Mawr
Rhodri ap Merfyn, commonly known as , was a Welsh king whose legacy has impacted the history of Wales. Rhodri rose to power during a tumultuous era, where the fate of Welsh kingdoms was often determined by the power of their leaders.
Early life ...
through the House of Powys Fadog. He went on to establish diplomatic relations with foreign powers and liberated Wales from English rule. He was ultimately unsuccessful and was driven to the mountains where he led a guerrilla war
Guerrilla warfare is a form of unconventional warfare in which small groups of irregular military, such as rebels, partisans, paramilitary personnel or armed civilians, which may include recruited children, use ambushes, sabotage, terrorism ...
. When and where he died is not known, but it is believed he died disguised as a friar
A friar is a member of one of the mendicant orders in the Catholic Church. There are also friars outside of the Catholic Church, such as within the Anglican Communion. The term, first used in the 12th or 13th century, distinguishes the mendi ...
in the company of his daughter, Alys, at Monnington Straddle in Herefordshire
Herefordshire ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England, bordered by Shropshire to the north, Worcestershire to the east, Gloucestershire to the south-east, and the Welsh ...
.
Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542
The Principality ceased to exist as a legal entity with the passing byEnglish parliament
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the great council of bishops and peers that advised th ...
of the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542, without any representation from Wales. The act stated that Wales was already 'incorporated, annexed, united, and subjecte to and under the imperialle Crown of this Realme as a very member…of the same’. The law of England was applied as the only law in Wales, Justice of the peace administered the newly created counties and the act also made English the only language of the courts in Wales, and Wales gained a representation in English parliament. However, those using the Welsh language would not be able to take up office in the territories of the king of England. There were four Court of Great Sessions in Wales based on the three of the counties, e.g. north, east, south, west. The implementation of the act was delayed until a more detailed act was used in 1543.
After 1543: union with England
Later administration
The Encyclopaedia of Wales notes that the Council of Wales and the Marches was created byEdward IV
Edward IV (28 April 1442 – 9 April 1483) was King of England from 4 March 1461 to 3 October 1470, then again from 11 April 1471 until his death in 1483. He was a central figure in the Wars of the Roses, a series of civil wars in England ...
in 1471 as a household institution to manage the Prince of Wales's lands and finances. In 1473 it was enlarged and given the additional duty of maintaining law and order in the Principality and the Marches of Wales. Its meetings appear to have been intermittent, but it was revived by Henry VII for his heir, Prince Arthur. The Council was placed on a statutory basis in 1543 and played a central role in co-ordinating law and administration. The council at Ludlow was to have full administrative and legal powers until it declined in the early 17th century and was abolished by Parliament in 1641. It was revived at the Restoration before being finally abolished in 1689.
From 1689 to 1948 there was no differentiation between England's government and Wales's government. All laws relating to England included Wales and Wales was considered by the British Government as an indivisible part of England within the United Kingdom. The first piece of legislation to relate specifically to Wales was the Sunday Closing (Wales) Act 1881. A further exception was the Welsh Church Act 1914
The Welsh Church Act 1914 (4 & 5 Geo. 5. c. 91) is an act of Parliament (UK), act of Parliament under which the Church of England was separated and disestablishment, disestablished in Wales and Monmouthshire (historic), Monmouthshire, leading to ...
, which disestablished the Church in Wales
The Church in Wales () is an Anglican church in Wales, composed of six dioceses.
The Archbishop of Wales does not have a fixed archiepiscopal see, but serves concurrently as one of the six diocesan bishops. The position is currently held b ...
(which had formerly been part of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
) in 1920.
In 1948 the practice was established that all laws passed in the Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace ...
were designated as applicable to either "England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the Law of the United Kingdom#Legal jurisdictions, three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. Th ...
", "Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
" or "Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
", thus returning a legal identity to Wales which had not existed for hundreds of years following the Act of Union with Scotland in 1707. Also in 1948 a new Council for Wales was established as a parliamentary committee. In 1964 the Welsh Office
The Welsh Office () was a department in the Government of the United Kingdom with responsibilities for Wales. It was established in April 1965 to execute government policy in Wales, and was headed by the Secretary of State for Wales, a post wh ...
was established, based in London, to oversee and recommend improvements to the application of laws in Wales. This situation would continue until the devolution of government in Wales and the establishment of the autonomous National Assembly for Wales
The Senedd ( ; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, Its role is to scrutinise the Welsh Government and legislate on devolve ...
in 1998.
Other uses of the term
Although no principality has ever been created that covers Wales as a whole, the term "Principality" has been occasionally used since the sixteenth century as a synonym for Wales. For instance, the firstatlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
of Wales, by Thomas Taylor in 1718, was titled ''The Principality of Wales exactly described ...'', and the term is still used by such publications as ''Burke's Landed Gentry
''Burke's Landed Gentry'' (originally titled ''Burke's Commoners'') is a reference work listing families in Great Britain and Ireland who have owned rural estates of some size. The work has been in existence from the first half of the 19th cen ...
''. Publications such as Lewis's ''A Topographical Dictionary of Wales'', and Welsh newspapers in the 19th century commonly used the term.
In modern times, however, ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardi ...
'' style guide advises writers to "avoid the word 'principality in relation to Wales. The International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
M ...
(ISO) has defined Wales as a "country" rather than a "principality" since 2011, following a recommendation by the British Standards Institute
The British Standards Institution (BSI) is the Standards organization, national standards body of the United Kingdom. BSI produces technical standards on a wide range of products and services and also supplies standards certification services ...
and the Welsh Government
The Welsh Government ( ) is the Executive (government), executive arm of the Welsh devolution, devolved government of Wales. The government consists of Cabinet secretary, cabinet secretaries and Minister of State, ministers. It is led by the F ...
.
The use of the term to refer to the territory of Wales should be distinguished from its use to refer to the title of Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales (, ; ) is a title traditionally given to the male heir apparent to the History of the English monarchy, English, and later, the British throne. The title originated with the Welsh rulers of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd who, from ...
, which has been traditionally granted (together with the title Duke of Cornwall
Duke of Cornwall () is a title in the Peerage of England, traditionally held by the eldest son of the reigning Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarch, previously the English monarch. The Duchy of Cornwall was the first duchy created i ...
and various Scottish titles) to the heir apparent
An heir apparent is a person who is first in the order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person. A person who is first in the current order of succession but could be displaced by the birth of a more e ...
of the reigning British monarch. It confers no responsibility for government in Wales, and has no constitutional meaning. Plaid Cymru
Plaid Cymru ( ; , ; officially Plaid Cymru – the Party of Wales, and often referred to simply as Plaid) is a centre-left, Welsh nationalist list of political parties in Wales, political party in Wales, committed to Welsh independence from th ...
are in favour of scrapping the title altogether. The Honours of the Principality of Wales are the Crown Jewels
Crown jewels are the objects of metalwork and jewellery in the regalia of a current or former monarchy. They are often used for the coronation of a monarch and a few other ceremonial occasions. A monarch may often be shown wearing them in portra ...
used at the investiture of Princes of Wales.
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Principality of Wales 1282 disestablishments in EuropeWales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
Medieval history of Wales
12th century in Wales
13th century in Wales
14th century in Wales
15th century in Wales
16th century in Wales
States and territories established in 1216
States and territories disestablished in 1542