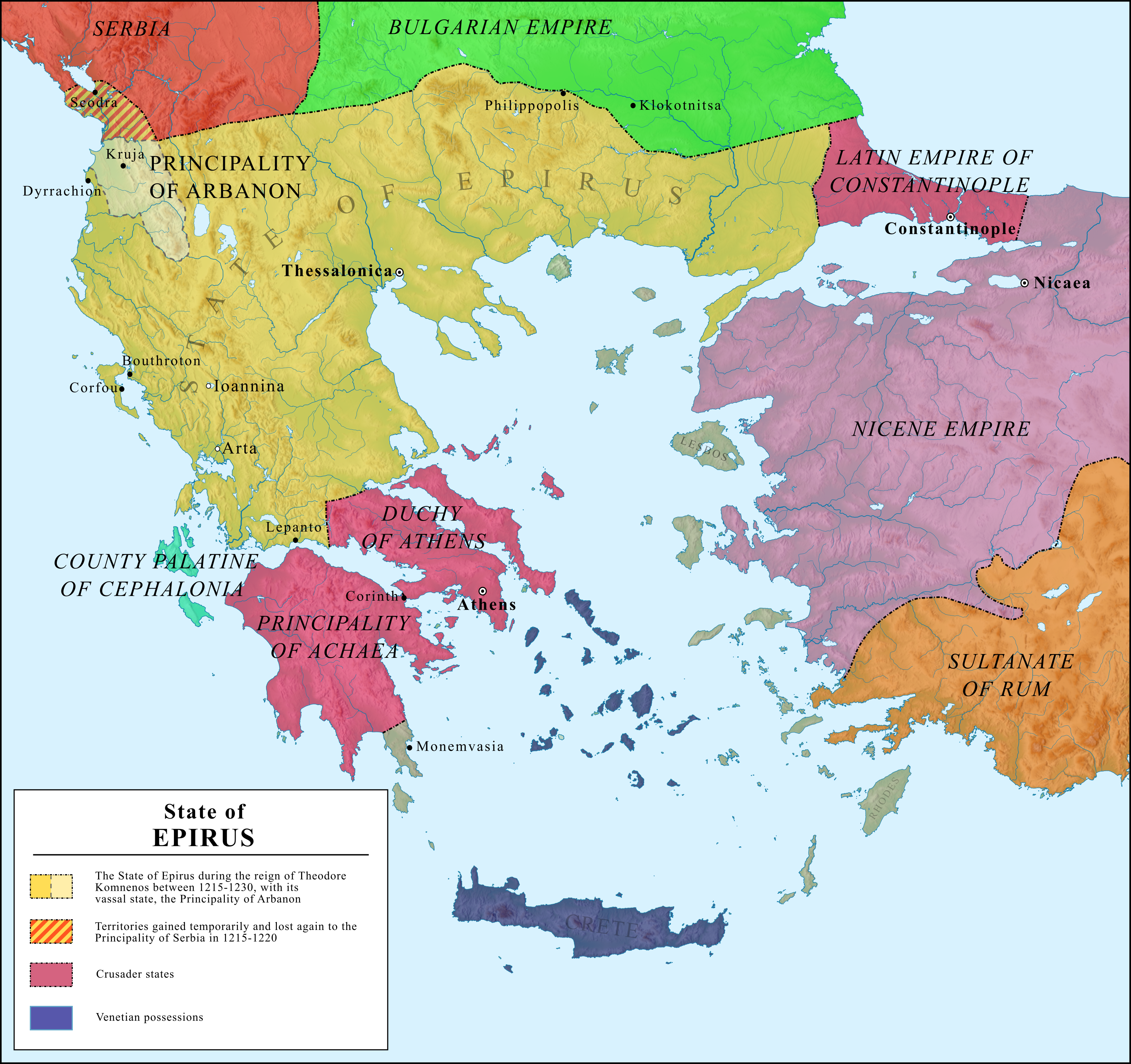
Principality Of Arbanon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arbanon ( sq, Arbër or , el, Ἄρβανον, ''Árvanon''; la, Arbanum) was a principality ruled by the native
 Nemanjić had previously promised military support to Venice if Progoni attacked Venetian territory, in a treaty signed on 3 July 1208. In 1208, he also had secured a marriage with Komnena Nemanjić, who was both the daughter of Stefan Nemanjić, rival of Đorđe Nemanjić and grand-daughter of the last Byzantine Emperor
Nemanjić had previously promised military support to Venice if Progoni attacked Venetian territory, in a treaty signed on 3 July 1208. In 1208, he also had secured a marriage with Komnena Nemanjić, who was both the daughter of Stefan Nemanjić, rival of Đorđe Nemanjić and grand-daughter of the last Byzantine Emperor
page 73: "'' Goulamos defected to the Emperor''" However, the initial Nicaean conquest where the Emperor Theodore II Laskaris appointed Constantine Chabaron as the ruler of the Principality, proved short-lived, for the events prompted the Rebellion of Arbanon in 1257. Golem is last mentioned in the historical records among other 'notables' of Arbanon, in a meeting with
Progoni
The Progoni were an Albanian noble family which established the first Albanian state to be recorded in history, the Principality of Arbanon.: "By 1190, Byzantium's power had so receded that the archon Progon succeeded in establishing the first ...
family, and the first Albanian state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
to emerge in recorded history. The principality was established in 1190 by the native ''archon
''Archon'' ( gr, ἄρχων, árchōn, plural: ἄρχοντες, ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem αρχ-, mean ...
'' Progon in the region surrounding Kruja, to the east and northeast of Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
territories. Progon was succeeded by his sons Gjin Gjin is an Albanian male given name, clan, surname and onomastic element. As a name, it is usually held by Albanian Christians, as it is derived from the name of a saint, although the identity of this saint is unclear, as both theologists and lingu ...
and then Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumi ...
(Dhimitër), who managed to retain a considerable degree of autonomy from the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. In 1204, Arbanon attained full, though temporary, political independence, taking advantage of the weakening of Constantinople following its pillage
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. ...
during the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
. However, Arbanon lost its large autonomy ca. 1216, when the ruler of Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinri ...
, Michael I Komnenos Doukas
Michael I Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Comnenus Ducas ( el, Μιχαήλ Κομνηνός Δούκας, Mikhaēl Komnēnos Doukas), and in modern sources often recorded as Michael I Angelos, a name he never used, was the founder and first rule ...
, started an invasion northward into Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
and Macedonia, taking Kruja and ending the independence of the principality. From this year, after the death of Demetrius, the last ruler of the Progon family, Arbanon was successively controlled by the Despotate of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It clai ...
, then by the Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, Българско царство, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the ...
and, from 1235, by the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhous ...
.
During this period, the area was ruled by the Greco-Albanian lord Gregorios Kamonas
Gregorios Kamonas ( 1215) was a Greek-Albanian Lord or Prince of Krujë ( Arbanon) in ca. 1215. Demetrios Chomatenos (1216–1236) mentioned him as having the title of ''sebastos'', given to him by the emperor Alexios III Angelos after 1205, dur ...
, the new spouse of Demetrius' former Serbian wife Komnena Nemanjić, and by Golem
A golem ( ; he, , gōlem) is an animated, anthropomorphic being in Jewish folklore, which is entirely created from inanimate matter (usually clay or mud). The most famous golem narrative involves Judah Loew ben Bezalel, the late 16th-century ...
(Gulam), a local magnate
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders, or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
who had married Kamonas' and Komnena's daughter. Arbanon was eventually annexed in the winter of 1256–57 by the Byzantine statesman George Akropolites George Akropolites ( Latinized as Acropolites or Acropolita; el, , ''Georgios Akropolites''; 1217 or 1220 – 1282) was a Byzantine Greek historian and statesman born at Constantinople.
Life
In his sixteenth year he was sent by his father, th ...
. Golem subsequently disappeared from historical records. The main primary source for late Arbanon and its history is the work of 13th century Byzantine historian George Akropolites George Akropolites ( Latinized as Acropolites or Acropolita; el, , ''Georgios Akropolites''; 1217 or 1220 – 1282) was a Byzantine Greek historian and statesman born at Constantinople.
Life
In his sixteenth year he was sent by his father, th ...
.
Etymology
The principality was known as ''Árvanon'' (Ἄρβανον) inGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, as ''Arbanum'' in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, and as ''Raban'' in the early 13th-century Serbian document '' Life of Stefan Nemanja''.
The term represents the name of a south Illyrian tribe attested in Ancient Greek Ἀλβανοί, later on denoting a proper name for an ethnic Albanian until it was replaced with ''Shqiptar'' in the 18th century. It is attributed directly to a Latin rendering of the tribal name Albanoi
The Albanoi ( grc, Ἀλβανοί, ''Albanoi''; la, Albani) were an Illyrian tribe. They were possibly first mentioned by Hecataeus of Miletus (550-476 BCE) under the name ''Abroi''. Ptolemy (200-118 BCE) is the first authors who mentions them u ...
by Orel.
Versions of "Arbën" have been observed since the 2nd century BC, the History of the World written by Polybius, mentions a location named Arbona (ancient greek Ἄρβωνα, latin Arbo) in which some Illyrian troops, under Queen Teuta, scattered and fled to in order to escape the Romans. Arbona was perhaps an island in Liburnia or another location within Illyria.
In the 6th century AD, Stephanus of Byzantium, in his important geographical dictionary entitled Ethnica (Ἐθνικά),Stephanus of Byzantium (1849). "Ἀρβών". Ethnika kat' epitomen (in Greek). Berolini : G. Reimeri. πόλις Ἰλλυρίας. Πολύβιος δευτέρᾳ. τὸ ἐθνικὸν Ἀρβώνιος καὶ Ἀρβωνίτης, ὡς Ἀντρώνιος καὶ Ἀσκαλωνίτης. mentions a city in Illyria called Arbon (Ἀρβών), and gives an ethnic name for its inhabitants, in two singular number forms, i.e. Arbonios (Ἀρβώνιος) and Arbonites (Ἀρβωνίτης) pl. Ἀρβωνῖται.. He cites Polybius (as he does many other times Polybius' own attitude to Rome has been variously interpreted, pro-Roman, … frequently cited in reference works such as Stephanus' Ethnica and the Suda. in Ethnica).
Status
Many scholars note that the Principality of Arbanon was the first Albanian state to emerge during theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
.Pickard-Çeliku 2008, p. 16 Arbanon is generally considered to have retained large autonomy until Demetrius death in 1216, when the principality fell under the vassalage of Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinri ...
or the Laskarids of Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
.
Between 1190 and 1204, Arbanon was a principality of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
and possessed a considerable degree of autonomy, although the titles 'archon
''Archon'' ( gr, ἄρχων, árchōn, plural: ἄρχοντες, ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem αρχ-, mean ...
' (held by Progon) and ' panhypersebastos' (held by Dhimitër) are evident signs of Byzantine dependence. In the context of a weakening of Byzantine power in the region following the sack of Constantinople
The sack of Constantinople occurred in April 1204 and marked the culmination of the Fourth Crusade. Crusader armies captured, looted, and destroyed parts of Constantinople, then the capital of the Byzantine Empire. After the capture of the ...
in 1204, Arbanon attained full autonomy for 12 years until the death of Demetrios in 1215 or 1216.
The Gëziq inscription mentions the Progon family as ''judices'', and notes their dependence on Vladin and Đorđe Nemanjić
Đorđe Nemanjić or George of Zeta ( sr-cyr, Ђорђе Немањић; fl. 1208–1243) was the Grand Prince of Zeta, from at least 1208 until at least 1243. For some time, he also was a self-styled King of Duklja. He was the son of rival Serbia ...
(r. 1208–1216), the princes of Zeta
Zeta (, ; uppercase Ζ, lowercase ζ; grc, ζῆτα, el, ζήτα, label= Demotic Greek, classical or ''zē̂ta''; ''zíta'') is the sixth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 7. It was derived f ...
. In its last phase, Arbanon was mainly connected to the Despotate of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It clai ...
and also maintained allied relation with the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Prin ...
. In 1252, Golem submitted to the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhous ...
.
Geography
In the 11th century AD, the name '' Arbanon'' (also ''Albanon'') was applied to a region in the mountainous area to the west ofOhrid Lake
Lake Ohrid ( mk, Охридско Езеро , al, Liqeni i Ohrit , also referred as ''Liqeni i Pogradecit'';) is a lake which straddles the mountainous border between the southwestern part of North Macedonia and eastern Albania. It is one of E ...
and the upper valley of the river Shkumbin. In 1198, a part of the area north of the Drin was briefly controlled by Stefan Nemanjić who recounts that in that year he captured Pult
Pult or Pulat ( sq-definite, Pulti or Pulati), is a region in northern Albania. It is bordered by the Malësia Region to its north and by the Dukagjin Highlands to its east and its south. The region has traditionally been inhabited by the Plani ...
from Arbanon (''ot Rabna''). In 1208, in the correspondence with Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 ...
, the territory that Demetrius Progoni claimed as ''princeps Arbanorum'' was the area between Shkodra, Prizren
)
, settlement_type = Municipality and city
, image_skyline = Prizren Collage.jpg
, imagesize = 290px
, image_caption = View of Prizren
, image_alt = View of Prizren
, image_flag ...
, Ohrid
Ohrid ( mk, Охрид ) is a city in North Macedonia and is the seat of the Ohrid Municipality. It is the largest city on Lake Ohrid and the List of cities in North Macedonia, eighth-largest city in the country, with the municipality recording ...
and Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of ...
(''regionis montosae inter Scodram, Dyrrachium, Achridam et Prizrenam sitae''). In general, Progoni brought the principality to its climax. The area the principality controlled at this time, ranged from the Shkumbin river valley to the Drin river valley in the north and from the Adriatic sea to the Black Drin
The Black Drin, or Black Drim ( sq, Drini i Zi, mk, , translit=Crn Drim) is a river in North Macedonia and Albania. It flows out of Lake Ohrid in Struga, North Macedonia. It is long and its drainage basin is . Its average discharge is . After abo ...
in the east. George Akropolites George Akropolites ( Latinized as Acropolites or Acropolita; el, , ''Georgios Akropolites''; 1217 or 1220 – 1282) was a Byzantine Greek historian and statesman born at Constantinople.
Life
In his sixteenth year he was sent by his father, th ...
, who wrote in detail about the area in the its last phase positioned its then territory between Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of ...
and Lake Ohrid in a west to east axis and between the Shkumbin
The Shkumbin (; ; la, Genusus, also la, Genessus, label=none or la, Scampis, label=none), also commonly Shkembi, is a river in Southern Europe. It is long and its drainage basin is . Its average discharge is .
Etymology
It derives from La ...
river valley and Mat river valley in a south to north axis. The fortress of Krujë
Krujë ( sq-definite, Kruja; see also the etymology section) is a town and a municipality in north central Albania. Located between Mount Krujë and the Ishëm River, the city is only 20 km north from the capital of Albania, Tirana.
Kru ...
was the military and administrative center of the region throughout its existence.
History
Early development
There are scarce sources about Arbanon, with the exception of the chronicles of Byzantine historianGeorge Akropolites George Akropolites ( Latinized as Acropolites or Acropolita; el, , ''Georgios Akropolites''; 1217 or 1220 – 1282) was a Byzantine Greek historian and statesman born at Constantinople.
Life
In his sixteenth year he was sent by his father, th ...
, whose work is the most detailed primary source for Arbanon and this period of Albanian history in general. In 1166, we know that ''prior Arbanensis'' Andrea and ''episcopis Arbanensis'' Lazarus participated in a ceremony held in Kotor
Kotor ( Montenegrin Cyrillic: Котор, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian: ), is a coastal town in Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has a population of 13,510 and is the administrative ...
,Thalóczy-Jireček-Sufflay 1913, p. 31 then under the Serbian Grand Principality
Grand Principality of Serbia ( sr, Великожупанска Србија, Velikožupanska Srbija), or Rascia ( sr, Рашка, Raška), was a medieval Serbian state that existed from the second half of the 11th century up until 1217, when it ...
. A year later in 1167, Pope Alexander III
Pope Alexander III (c. 1100/1105 – 30 August 1181), born Roland ( it, Rolando), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 September 1159 until his death in 1181.
A native of Siena, Alexander became pope after a con ...
, in a letter directed to Lazarus, congratulates him for returning his bishopric to Catholic faith and invites him to acknowledge the archbishop of Ragusa as his superior. After some resistance from local officials, the bishopric of Arbanon was put under the direct dependence of the Pope, as documented in a Papal letter dated in 1188.
Little is known about ''archon'' Progon who was, between 1190 and 1198, the first ruler of Kruja and its surroundings. The Kruja fortress stayed in the possession of the Progon family, and Progon was succeeded by his sons Gjin Gjin is an Albanian male given name, clan, surname and onomastic element. As a name, it is usually held by Albanian Christians, as it is derived from the name of a saint, although the identity of this saint is unclear, as both theologists and lingu ...
and later Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumi ...
(Dhimitër).
Reign of Demetrius Progoni
Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumi ...
was the third and last lord of the Progon family, ruling between 1208 (or 1207) and 1216 (or 1215). He succeeded his brother Gjin Gjin is an Albanian male given name, clan, surname and onomastic element. As a name, it is usually held by Albanian Christians, as it is derived from the name of a saint, although the identity of this saint is unclear, as both theologists and lingu ...
and brought the principality to its climax. Since the beginning of his rule, Dhimitër Progoni sought out to create friendly networks in foreign policy in order to preserve the sovereignty of Arbanon against external threats, the most important of whom were for much of his reign the Republic of Venice and later the Despotate of Epiros. In 1208-09, he considered conversion to Catholicism from Eastern Orthodoxy for the first time in order to obtain support against his Venetian rivals. As Venice had been given the nominal rights to control Albania, conversion to Catholicism would nullify Venetian claims over territory controlled by another Catholic state, the Principality of Arbanon. It would also protect him from expansion by post-Byzantine successor states like the Despotate of Epiros. In his preserved correspondence with Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 ...
, Progoni as leader of the ''iudices'' of Arbanon, who signed as his followers, asked the Pope to send missionaries to spread Catholicism in his land. The Pope responded that Nicolaus, the Catholic archdeacon of Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of ...
had been instructed to make preparations for the mission. Shortly after, however, Demetrio stopped the process because he didn't consider it important any longer. He had defeated Đorđe Nemanjić, a Venetian vassal whom he bordered to the north and thus felt less threatened by Venice.
 Nemanjić had previously promised military support to Venice if Progoni attacked Venetian territory, in a treaty signed on 3 July 1208. In 1208, he also had secured a marriage with Komnena Nemanjić, who was both the daughter of Stefan Nemanjić, rival of Đorđe Nemanjić and grand-daughter of the last Byzantine Emperor
Nemanjić had previously promised military support to Venice if Progoni attacked Venetian territory, in a treaty signed on 3 July 1208. In 1208, he also had secured a marriage with Komnena Nemanjić, who was both the daughter of Stefan Nemanjić, rival of Đorđe Nemanjić and grand-daughter of the last Byzantine Emperor Alexios III Angelos
Alexios III Angelos ( gkm, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνός Ἄγγελος, Alexios Komnēnos Angelos; 1211), Latinized as Alexius III Angelus, was Byzantine Emperor from March 1195 to 17/18 July 1203. He reigned under the name Alexios Komnen ...
. In this context, because of the relation of his consort to the Byzantine imperial family, Demetrius was recognized by the title of ''panhypersebastos''. After the death of the Catholic archbishop of Durrës, the Venetians and Progoni - each in their respective territories - seized church property. For his actions against church property, he was excommunicated. He used the title ''princeps Arbanorum'' ("prince of the Albanians") to refer to himself and was recognized as such by foreign dignitaries. In the correspondence with Innocent III, the territory he claimed as ''princeps Arbanorum'' was the area between Shkodra, Prizren
)
, settlement_type = Municipality and city
, image_skyline = Prizren Collage.jpg
, imagesize = 290px
, image_caption = View of Prizren
, image_alt = View of Prizren
, image_flag ...
, Ohrid
Ohrid ( mk, Охрид ) is a city in North Macedonia and is the seat of the Ohrid Municipality. It is the largest city on Lake Ohrid and the List of cities in North Macedonia, eighth-largest city in the country, with the municipality recording ...
and Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of ...
(''regionis montosae inter Scodram, Dyrrachium, Achridam et Prizrenam sitae''). In general, Progoni brought the principality to its climax. The area the principality controlled, ranged from the Shkumbin river valley to the Drin river valley in the north and from the Adriatic sea to the Black Drin
The Black Drin, or Black Drim ( sq, Drini i Zi, mk, , translit=Crn Drim) is a river in North Macedonia and Albania. It flows out of Lake Ohrid in Struga, North Macedonia. It is long and its drainage basin is . Its average discharge is . After abo ...
in the east. In Latin documents, Demetrius was is also referred to as ''iudex''. In Byzantine records, he is titled as ''megas archon
Magnús Þór Jónsson (born 7 April 1945), better known by the stage name Megas, is a vocalist, songwriter, and writer who is well known in his native Iceland.
Interest in music
Being an admirer of Elvis Presley, Megas welcomed the arrival of r ...
'' and after the consolidation of his rule as ''panhypersebastos''.
In 1209, in search for allies, he also signed a treaty with the Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; vec, Repùblega de Raguxa) was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' ...
which allowed for free passage of Ragusan merchants in Albanian territory. The following year, an agreement was concluded between the Republic of Venice and Michael I Komnenos Doukas
Michael I Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Comnenus Ducas ( el, Μιχαήλ Κομνηνός Δούκας, Mikhaēl Komnēnos Doukas), and in modern sources often recorded as Michael I Angelos, a name he never used, was the founder and first rule ...
of the Despotate of Epiros
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claime ...
under which Doukas would become a vassal of Venice, if the republic recognized his claims up to the Shkumbin
The Shkumbin (; ; la, Genusus, also la, Genessus, label=none or la, Scampis, label=none), also commonly Shkembi, is a river in Southern Europe. It is long and its drainage basin is . Its average discharge is .
Etymology
It derives from La ...
river valley, a core area of Arbanon. In 1212, Venice also allowed for the possession of the coastal duchy of Durrës to pass to Michael and abandoned its direct control of central Albania. The agreement had dire consequences for the principality, which surrounded by hostile forces, seems to have been reduced by the end of the life of Dhimitër Progoni to the area north of Shkumbin and south of Drin. Evidence for this period has been provided by the foundational inscription of the Catholic church of Gëziq in the Ndërfandë near modern Rreshen in Mirdita. The inscription is written in Latin and has been produced after Progoni's death. The inscription shows that Progoni, who had been reaccepted in the Catholic Church, had provided funds for the building of the church, which he might have planned to become the seat of the Diocese of Arbanum or a new diocese in the centre of his remaining domain. This is indicated by the fact that the new church was built on the site of an older church dedicated to St. Mary (Shën Mëri) but Progoni dedicated the new church to Shën Premte, the patron saint of Arbanum. He had maintained the semi-independence of this area under an agreement in which he accepted the high suzerainty of Zeta and the rulers of Zeta didn't get involved in internal affairs of the region in return. In the inscription which also serves as the last will of Progoni, the church is dedicated to his people (''nationi obtulit'') and his successor is designated, ''Progon'' - son of Gjin Progoni
Gjin Progoni ( la, Ginius) was an ''archon'' (or lord) of Kruja, located in present-day Albania, from c. 1198 until his death in 1208.: "Even if it is hard to identify the outlook of Prince Gjin, the son of Progon, who died in 1208, it is clear t ...
- as protosebastos The title of ''protosebastos'' ( el, πρωτοσέβαστος, ''prōtosébastos'', "first ''sebastos''") was a high Byzantine court title created by Emperor Alexios I Komnenos.
History
Although the title first appears in a document of 1049, whe ...
.
Reign of Gregory Kamonas and Gulem
After the death of Demetrius in 1215 or 1216, the power was left to his wife Komnena. She was soon married off to Gregory Kamonas, who himself had earlier been married to Gjin’s daughter and needed the wedding to happen to legitimize the succession of power. After he took control of Kruja, he strengthened relations with theGrand Principality of Serbia
Grand Principality of Serbia ( sr, Великожупанска Србија, Velikožupanska Srbija), or Rascia ( sr, Рашка, Raška), was a medieval Serbian state that existed from the second half of the 11th century up until 1217, when it ...
, which had weakened after a Slavic assault on Scutari.
Demetrius had no son to succeed him. Komnena had a daughter with Kamonas, who married a local magnate
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders, or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
named Golem
A golem ( ; he, , gōlem) is an animated, anthropomorphic being in Jewish folklore, which is entirely created from inanimate matter (usually clay or mud). The most famous golem narrative involves Judah Loew ben Bezalel, the late 16th-century ...
(Gulam). The latter continued to rule as a semi-independent ruler in Arbanon under Theodore Komnenos Doukas
Theodore Komnenos Doukas ( el, Θεόδωρος Κομνηνὸς Δούκας, ''Theodōros Komnēnos Doukas'', Latinized as Theodore Comnenus Ducas, died 1253) was ruler of Epirus and Thessaly from 1215 to 1230 and of Thessalonica and most ...
of the Despotate of Epiros
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claime ...
(until 1230) and then Ivan Asen II of Bulgaria
Ivan Asen II, also known as John Asen II ( bg, Иван Асен II, ; 1190s – May/June 1241), was Emperor (Tsar) of Bulgaria from 1218 to 1241. He was still a child when his father Ivan Asen I one of the founders of the Second Bulgarian Empi ...
until his death in 1241. He then oscillated between Doukas and the Nicaeans until he was finally annexed by the Nicaeans in the phase of reconstitution of the Byzantine Empire in 1252–1256. During the conflicts between Michael II Komnenos Doukas
Michael II Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Comnenus Ducas ( el, Μιχαήλ Β΄ Κομνηνός Δούκας, ''Mikhaēl II Komnēnos Doukas''), often called Michael Angelos in narrative sources, was from 1230 until his death in 1266/68 the rule ...
of Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinri ...
and the Emperor of Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
John III Doukas Vatatzes
John III Doukas Vatatzes, Latinized as Ducas Vatatzes ( el, Ιωάννης Δούκας Βατάτζης, ''Iōannēs Doukas Vatatzēs'', c. 1192 – 3 November 1254), was Emperor of Nicaea from 1221 to 1254. He was succeeded by his son, known ...
, Golem and Theodore Petraliphas
Theodore may refer to:
Places
* Theodore, Alabama, United States
* Theodore, Australian Capital Territory
* Theodore, Queensland, a town in the Shire of Banana, Australia
* Theodore, Saskatchewan, Canada
* Theodore Reservoir, a lake in Saskatche ...
, who were initially Michael's allies, eventually defected to John III in 1252.George Akropolites: the historypage 73: "'' Goulamos defected to the Emperor''" However, the initial Nicaean conquest where the Emperor Theodore II Laskaris appointed Constantine Chabaron as the ruler of the Principality, proved short-lived, for the events prompted the Rebellion of Arbanon in 1257. Golem is last mentioned in the historical records among other 'notables' of Arbanon, in a meeting with
George Akropolites George Akropolites ( Latinized as Acropolites or Acropolita; el, , ''Georgios Akropolites''; 1217 or 1220 – 1282) was a Byzantine Greek historian and statesman born at Constantinople.
Life
In his sixteenth year he was sent by his father, th ...
in Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of ...
that occurred in the winter of 1256–1257. Akropolites subsequently annexed the statelet and installed a Byzantine civil, military and fiscal administration.
Possessions
Arbanon extended over the modern districts of central Albania, with the capital at Kruja. It was a small territory in the 11th and 12th centuries, stretching from rivers Devoll toShkumbin
The Shkumbin (; ; la, Genusus, also la, Genessus, label=none or la, Scampis, label=none), also commonly Shkembi, is a river in Southern Europe. It is long and its drainage basin is . Its average discharge is .
Etymology
It derives from La ...
. Arbanon did not have direct access to the sea. Robert Elsie
Robert Elsie (June 29, 1950 – October 2, 2017) was a Canadian-born German scholar who specialized in Albanian literature and folklore.
Elsie was a writer, translator, interpreter, and specialist in Albanian studies, being the author of numerou ...
notes that the coastal cities of modern Albania did not have noticeable Albanian communities throughout the Middle Ages, whereas the coasts of Epiros further south, despite their control by Serbs and Greeks, were primarily inhabited by Albanians according to Alain Ducellier
Alain Ducellier (5 May 1934 – 29 September 2018) was a French historian and professor emeritus at Université de Toulouse-Le Mirail who specialized in Byzantine studies and Christianity in the middle east. He was the author or editor of more tha ...
.
The fortresses of Kruja was the seat of the state. Progon gained possession of the surroundings of the fortress which became hereditary.
Economy
Arbanon was a beneficiary of theVia Egnatia
The Via Egnatia was a road constructed by the Romans in the 2nd century BC. It crossed Illyricum, Macedonia, and Thracia, running through territory that is now part of modern Albania, North Macedonia, Greece, and European Turkey as a con ...
trade road, which brought wealth and benefits from the more economically developed Byzantine civilization.
Rulers
* Progon (between 1190–1198) *Gjin Progoni
Gjin Progoni ( la, Ginius) was an ''archon'' (or lord) of Kruja, located in present-day Albania, from c. 1198 until his death in 1208.: "Even if it is hard to identify the outlook of Prince Gjin, the son of Progon, who died in 1208, it is clear t ...
(1198–1208)
* Demetrio Progoni (ca. 1208 – ca. 1216)
* Gregory Kamonas (ca. 1216 – ?)
*Golem
A golem ( ; he, , gōlem) is an animated, anthropomorphic being in Jewish folklore, which is entirely created from inanimate matter (usually clay or mud). The most famous golem narrative involves Judah Loew ben Bezalel, the late 16th-century ...
(ca. 1252 – ca. 1256)
* Constantine Chabaron (ca. 1256 – ca. 1257)
See also
* Rebellion of Arbanon * Albanian principalities *History of Albania
The history of Albania forms a part of the history of Europe. During classical antiquity, Albania was home to several Illyrian tribes such as the Ardiaei, Albanoi, Amantini, Enchele, Taulantii and many others, but also Thracian and Gree ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Arbanon Albanian principalities States and territories established in 1190 Provinces of the Byzantine Empire Despotate of Epirus 1190 establishments in Europe Former countries in the Balkans Former monarchies