Prince of Orange on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Prince of Orange (or Princess of Orange if the holder is female) is a
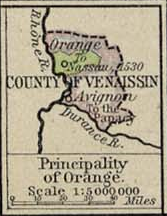 Those now distant cousins were the descendants of Alix de Chalon. Marie des Baux-Orange had stipulated in her will that if her son
Those now distant cousins were the descendants of Alix de Chalon. Marie des Baux-Orange had stipulated in her will that if her son
 An agnatic relative of William III, John William Friso of Nassau, who was also cognatically descended from
An agnatic relative of William III, John William Friso of Nassau, who was also cognatically descended from
The house of Baux succeeded to the principality of Orange when Bertrand of Baux married the heiress of the last native count of Orange, Tiburge, daughter of William of Orange, Omelaz, and Montpellier. Their son was William I of Baux-Orange. Bertrand was the son of Raymond of Baux and Stephanie of Gevaudan. Stephanie was the younger daughter of Gerberga, the heiress of the counts of Provence. For a genealogical table, see the reference cited:
Bertrand I used as Prince of Orange the coat of arms of the House of Baux: a 16-pointed white star placed on a field of gules. Later on, the Princes of Orange quartered the legendary bugle-horn as a heraldic figure into their coat of arms.
File:Arms of René de Chalon.svg, Coat of arms of René of Chalon as Prince of Orange.
File:Blason Nassau-Orange.svg, Coat of arms of
When William VI of Orange returned to the Netherlands in 1813 and was proclaimed Sovereign Prince of the Netherlands, he quartered the former Arms of the Dutch Republic (1st and 4th quarter) with the "Chalon-Orange" arms (2nd and 3rd quarter), which had come to symbolize Orange. As an in escutcheon he placed his ancestral arms of Nassau. When he became King in 1815, he combined the Dutch Republic Lion with the billets of the Nassau arms and added a royal crown to form the
File:Arms of Sovereign Prince William I of Orange.svg, Arms of William VI as sovereign prince of the Netherlands.
File:Arms of the Prince of Orange (1815-1884).svg, Arms of the Dutch Crown prince, the prince of Orange in the 19th Century.
File:Arms of the eldest son of the Prince of Orange (1815-1884).svg, Arms of the son of the Dutch Crown Prince in the 19th Century, who also held the title of Hereditary Prince of Orange.
File:Arms of Juliana of the Netherlands.svg, Juliana of the Netherlands & Oranje-Nassau Personal Arms
File:Arms of Beatrix of the Netherlands.svg, Beatrix of the Netherlands & Oranje-Nassau Personal Arms
File:Arms of the children of Beatrix of the Netherlands.svg, William Alexander of the Netherlands and Oranje-Nassau Personal Arms
File:Arms of the children of Margriet of the Netherlands.svg, Sons of Princess Margriet of the Netherlands, Pieter van Vollenhoven
As a former territory of the Holy Roman Empire, the princes of Orange used an independent prince's crown. Sometimes, only the coronet part was used ( see, here and here). After the establishment of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, they used the Dutch Royal Crowns:
File:Princely Hat.svg, Princely Hat
File:Princely crown.svg, Princely Crown
File:Royal Crown of the Netherlands (Heraldic).svg, Crown for a Prince or Princess of the Netherlands
File:Coronet of a Grandchild of the Dutch Monarch (Heraldic).svg, Crown of a Prince or Princess of Orange-Nassau (Heraldic)
Treaty ceding the Principality to Louis XIV
{{DEFAULTSORT:Prince Of Orange 1160s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire Noble titles created in 1163 Heirs to the throne * * * Orange Orange Frederick Barbarossa
title
A title is one or more words used before or after a person's name, in certain contexts. It may signify their generation, official position, military rank, professional or academic qualification, or nobility. In some languages, titles may be ins ...
associated with the sovereign Principality of Orange, in what is now southern France
Southern France, also known as the south of France or colloquially in French as , is a geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi atlantique'', Atlas e ...
and subsequently held by the stadtholders
In the Low Countries, a stadtholder ( ) was a Steward (office), steward, first appointed as a medieval official and ultimately functioning as a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during th ...
of, and then the heirs apparent of, the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
.
The title "Prince of Orange" was created in 1163 by Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (; ), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death in 1190. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aachen on 9 March 115 ...
, by elevating the county
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
of Orange to a principality
A principality (or sometimes princedom) is a type of monarchy, monarchical state or feudalism, feudal territory ruled by a prince or princess. It can be either a sovereign state or a constituent part of a larger political entity. The term "prin ...
, in order to bolster his support in that area in his conflict with the Papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
. The title and land passed to the French noble houses of Baux, in 1173, and of Chalons, in 1393, before arriving with René of Nassau in 1530. The principality then passed to René's cousin, the German-born nobleman from then Spanish Netherlands
The Spanish Netherlands (; ; ; ) (historically in Spanish: , the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of t ...
, William
William is a masculine given name of Germanic languages, Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman Conquest, Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle ...
(known as "the Silent"), in 1544. Subsequently, William led a successful Dutch revolt against Spain, however with independence the new country became a decentralized republic rather than a unitary monarchy.
In 1702, after William the Silent's great-grandson William III of England
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 1650 – 8 March 1702), also known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, Zeeland, Lordship of Utrecht, Utrec ...
died without children, a dispute arose between his cousins, Johan Willem Friso and Frederick I of Prussia
Frederick I (; 11 July 1657 – 25 February 1713), of the Hohenzollern dynasty, was (as Frederick III) List of margraves and electors of Brandenburg, Elector of Brandenburg (1688–1713) and Duke of Prussia in personal union (Brandenburg–Pr ...
. In 1713, under the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
Frederick William I of Prussia
Frederick William I (; 14 August 1688 – 31 May 1740), known as the Soldier King (), was King in Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg from 1713 until his death in 1740, as well as Prince of Neuchâtel.
Born in Berlin, he was raised by the Hugu ...
ceded the Principality of Orange to King Louis XIV of France
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
(while retaining the title as part of his dynastic titulature). In 1732, under the Treaty of Partition, Friso's son, William IV agreed to share use of the title "Prince of Orange" (which had accumulated prestige in the Netherlands and throughout the Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
world) with Frederick William.
With the 19th century emergence of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
The Kingdom of the Netherlands (, ;, , ), commonly known simply as the Netherlands, is a sovereign state consisting of a collection of constituent territories united under the monarch of the Netherlands, who functions as head of state. The re ...
, the title has been traditionally borne by the heir apparent
An heir apparent is a person who is first in the order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person. A person who is first in the current order of succession but could be displaced by the birth of a more e ...
of the Dutch monarch. Although originally only borne by men, since 1983 the title descends via absolute primogeniture, which means that the holder can be either Prince or Princess of Orange.
The current Dutch royal dynasty, the House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of Or ...
, is not the only family to claim the dynastical title. Rival claims to the title have been made by German emperors and kings of the House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, Prince-elector, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern Castle, Hohenzollern, Margraviate of Bran ...
and by the head of the French noble family of Mailly. The current users of the title are Princess Catharina-Amalia of the Netherlands (Orange-Nassau), Georg Friedrich (of Hohenzollern), and Guy (of Mailly-Nesle).
History
County of Orange
The title referred to Orange in theVaucluse
Vaucluse (; or ) is a department in the southeastern French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur. It had a population of 561,469 as of 2019.
department in the Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; Occitan language, Occitan: ''Ròse''; Franco-Provençal, Arpitan: ''Rôno'') is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and Southeastern France before dischargi ...
valley of southern France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, which was a property of the House of Orange, then of the House of Baux and the House of Chalon-Arlay before passing in 1544 to the Dillenburg branch of the House of Nassau, which since then is known as the House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of Or ...
.
The Principality originated as the ''County of Orange'', a fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, in the Empire's constituent Kingdom of Burgundy
Kingdom of Burgundy was a name given to various successive Monarchy, kingdoms centered in the historical region of Burgundy during the Middle Ages. The heartland of historical Burgundy correlates with the border area between France and Switze ...
. It was awarded to William of Gellone
William of Gellone ( 755 – 28 May 812 or 814), the medieval William of Orange, was the second Duke of Toulouse from 790 until 811. In 804, he founded the abbey of Gellone. He was canonized a saint in 1066 by Pope Alexander II.
(born 755), a grandson of Charles Martel
Charles Martel (; – 22 October 741), ''Martel'' being a sobriquet in Old French for "The Hammer", was a Franks, Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of ...
and therefore a cousin of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
, around the year 800 for his services in the wars against the Moors and in the reconquest of southern France and the Spanish March. His Occitan name is ''Guilhem''; however, as a Frankish lord, he probably knew himself by the old Germanic version of ''Wilhelm''. William also ruled as count of Toulouse
The count of Toulouse (, ) was the ruler of Toulouse during the 8th to 13th centuries. Originating as vassals of the Frankish kings,
the hereditary counts ruled the city of Toulouse and its surrounding county from the late 9th century until 12 ...
, duke of Aquitaine, and marquis of Septimania
Septimania is a historical region in modern-day southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of '' Gallia Narbonensis'' that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theod ...
.
The horn that came to symbolize Orange when heraldry came in vogue much later in the 12th century represented a pun on William of Gellone
William of Gellone ( 755 – 28 May 812 or 814), the medieval William of Orange, was the second Duke of Toulouse from 790 until 811. In 804, he founded the abbey of Gellone. He was canonized a saint in 1066 by Pope Alexander II.
's name in French, from the character his deeds inspired in the ''chanson de geste
The , from 'deeds, actions accomplished') is a medieval narrative, a type of epic poetry, epic poem that appears at the dawn of French literature. The earliest known poems of this genre date from the late 11th and early 12th centuries, shortly ...
'', the ''Chanson de Guillaume
The ''Chanson de Guillaume'', also called ''Chançun de Willame'' ( English: "Song of William"), is a ''chanson de geste
The , from 'deeds, actions accomplished') is a medieval narrative, a type of epic poetry, epic poem that appears at the ...
'': "Guillaume au Court-nez" (William the Short-Nosed) or its homophone "Guillaume au Cornet" (William the Horn).
The ''chanson'' appears to incorporate material relating to William of Gellone's battle at the Orbieu
The Orbieu (; ) is an long river in the Aude '' département'', in south central France. Its source is at Fourtou, in the Corbières Massif. It flows generally northeast. It is a right tributary of the Aude into which it flows between Raissac-d' ...
or Orbiel river near Carcassonne
Carcassonne is a French defensive wall, fortified city in the Departments of France, department of Aude, Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania. It is the prefectures in France, prefecture of the department.
...
in 793 as well as to his seizure of the town of Orange.
Principality of Orange
As the kingdom of Burgundy fragmented in the early Middle Ages, the Holy Roman EmperorFrederick I Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (; ), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death in 1190. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt am Main, Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aa ...
elevated the lordship of Orange to a principality in 1163 to shore up his supporters in Burgundy against the Pope and the King of France. As the Empire's boundaries retreated from those of the principality, the prince acceded to the sovereign rights that the Emperor formerly exercised. As William the Silent
William the Silent or William the Taciturn (; 24 April 153310 July 1584), more commonly known in the Netherlands as William of Orange (), was the leader of the Dutch revolt against the Spanish Habsburg Netherlands, Habsburgs that set off the ...
wrote in his marriage proposal to the uncle of his second wife, the Elector August of Saxony, he held Orange as "my own free property", not as a fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
of any suzerain; neither the Pope, nor the Kings of Spain or France. That historical position of honor and reputation would later drive William the Silent forward, as much as it also fueled the opposition of his great grandson William III to Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
, when that king invaded and occupied Orange.
The last direct descendant of the original princes, René of Chalon, exercised his sovereign right and left the principality to his cousin William the Silent
William the Silent or William the Taciturn (; 24 April 153310 July 1584), more commonly known in the Netherlands as William of Orange (), was the leader of the Dutch revolt against the Spanish Habsburg Netherlands, Habsburgs that set off the ...
, who was not a descendant of the original Orange family but the heir to the principality of Orange by testament. This was, however, against the inheritance pattern enacted by the last will of Mary of Baux-Orange, the Princess of Orange from the House of Baux who brought the principality into the Chalons family and through to whom Prince René derived his own inheritance right (see Genealogy of the House of Orange-Chalon). In this way, Rene transmitted his property to his nearest relative, rather than go back several generations to transmit it to now distant cousins.
 Those now distant cousins were the descendants of Alix de Chalon. Marie des Baux-Orange had stipulated in her will that if her son
Those now distant cousins were the descendants of Alix de Chalon. Marie des Baux-Orange had stipulated in her will that if her son Louis
Louis may refer to:
People
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
Other uses
* Louis (coin), a French coin
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
...
did not inherit Orange, her daughter Alix and her descendants should. Guillaume de Vienne, seigneur de Saint-Georges, was the husband of Alix. They had a daughter Marguerite, who married in 1449 Rudolf of Baden-Hochberg, lord of Neuchâtel and Rothelin (1427–87). Their son was Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male name derived from the Macedonian Old Koine language, Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominen ...
(d. 1503). His only child who reached maturity was Johanna
Johanna is a feminine name, a variant form of Joanna that originated in Latin in the Middle Ages, including an -h- by analogy with the Latin masculine name Johannes. The original Greek form ''Iōanna'' lacks a medial /h/ because in Greek Spiritus ...
(d. 1543). She married in 1504 Louis I of Orléans, duc de Longueville (1450–1516). Through this marriage, the Orléans-Longueville, an illegitimate branch of the house of Valois, were the claimants of Orange until their extinction in male line in 1694(see Famille d'Orléans-Longueville). When William the Silent of Nassau succeeded as prince of Orange, the Orléans-Longueville protested and obtained court decisions in their favor in France. However, as Orange was a sovereign state and not part of France, the courts' decisions were not enforceable and left the principality in the hands of the Nassau-Orange family.
In 1673, Louis XIV of France
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
annexed all territory of the principality to France and to the royal domain, as part of the war actions against the stadtholder
In the Low Countries, a stadtholder ( ) was a steward, first appointed as a medieval official and ultimately functioning as a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and ...
William III of Orange — who later became King William III of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
. Orange ceased to exist as a sovereign realm, de facto. Louis then bestowed the titular princedom on Louis Charles de Mailly, marquis de Nesle, whose wife was a direct descendant, and heiress-general by primogeniture, of the original princes of Orange,
After the marquise (who died in 1713), the next holder was , marquis de Nesle (1689–1764). Although no longer descended from Louis-Charles, a branch of the Mailly family still claim the title today.
In 1714 Louis XIV bestowed the usufruct of the principality on his kinsman, Louis Armand of Bourbon, Prince de Conti, who had a claim on the principality through the claims of the Orléans-Longueville via Alix of Chalon (see above). After his death in 1727 the principality was deemed merged in the Crown by 1731.
After the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
in 1713 ceded Orange to France, the following claimants came forward in official protests against the terms of the treaty:
* the house of Luynes/ Maison d'Albert de Luynes (protest, 14 Apr 1713)
* the house of Matignon (protest, 15 Apr and 2 Jun 1713)
* Paule-Françoise-Marguerite de Gondi de Retz, duchesse douairière de Lesdiguières, and the house of Villeroy/ Maison de Neufville de Villeroy (16 Apr 1713; also claimants to Neufchatel and Valengin)
* the house of Allegre (protest, 15 Apr 1713)
* the house of Duprat (protest, 15 Apr 1713)
However, as the treaty considered Orange to now be conquered by and annexed to France, their protests were ignored.
Abolition of the principality, continuation of the title
Because William III died without legitimate children, the principality was regarded as having been inherited by his closest cognate relative on the basis of the testament of Frederic-Henry,Frederick I of Prussia
Frederick I (; 11 July 1657 – 25 February 1713), of the Hohenzollern dynasty, was (as Frederick III) List of margraves and electors of Brandenburg, Elector of Brandenburg (1688–1713) and Duke of Prussia in personal union (Brandenburg–Pr ...
, who ceded the principality — at least the lands, but not the formal title — to France in 1713.
France supported his claim. In this way, the territory of the principality lost its feudal and secular privileges and became a part of France. The Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
allowed the King of Prussia to erect part of the duchy of Gelderland (the cities of Geldern, Straelen, and Wachtendonk with their bailiwicks, Krickenbeck, Viersen, the land of Kessel, and the lordships of Afferden, Arcen-Velden-Lomm, Walbeck-Twisteden, Raay and Klein-Kevelaer, Well, Bergen, and Middelaar) into a new ''Principality of Orange''.
The kings of Prussia and the German emperors styled themselves Princes of Orange till 1918.
 An agnatic relative of William III, John William Friso of Nassau, who was also cognatically descended from
An agnatic relative of William III, John William Friso of Nassau, who was also cognatically descended from William the Silent
William the Silent or William the Taciturn (; 24 April 153310 July 1584), more commonly known in the Netherlands as William of Orange (), was the leader of the Dutch revolt against the Spanish Habsburg Netherlands, Habsburgs that set off the ...
, was designated the heir to the Princes of Orange in the Netherlands by the last will of William III. Several of his descendants became stadtholders. They claim the principality of Orange on the basis of agnatic inheritance, similar to that of William the Silent, who had inherited Orange from his cousin René of Chalon. They did however have a claim, albeit distant, to the principality itself due to John William Friso's descent from Louise de Coligny, who was a descendant of the original Princes of Orange. (Louise's great grandmother, Anne Pot, Countess of Saint-Pol, was a descendant of Tiburge d'Orange, who married into the des Baux family)
They could also claim descent from the del Balzo, an Italian branch of the des Baux family, via the marriage of Princess Anne
Anne, Princess Royal (Anne Elizabeth Alice Louise; born 15 August 1950) is a member of the British royal family. She is the second child and only daughter of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, and the only sister of King ...
to William IV, Prince of Orange
William IV (Willem Karel Hendrik Friso; 1 September 1711 – 22 October 1751) was Prince of Orange from birth and the first hereditary stadtholder of all the United Provinces of the Netherlands from 1747 until his death in 1751. During his who ...
. Anne was the eldest daughter of George II of Great Britain
George II (George Augustus; ; 30 October / 9 November 1683 – 25 October 1760) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (Electorate of Hanover, Hanover) and a prince-elector of the Holy Roman Em ...
, who was a descendant of Elizabeth Woodville, wife of Edward IV of England
Edward IV (28 April 1442 – 9 April 1483) was King of England from 4 March 1461 to 3 October 1470, then again from 11 April 1471 until his death in 1483. He was a central figure in the Wars of the Roses, a series of civil wars in England ...
. Elizabeth Woodville's grandmother was Margherita del Balzo, another descendant of Tiburge d'Orange.
They also claimed on the basis of the testaments of Philip William, Maurice, and William III. Finally, they claimed on the basis that Orange was an independent state whose sovereign had the right to assign his succession according to his will. France never recognized any of this, nor allowed the Orange-Nassaus or the Hohenzollerns to obtain anything of the principality itself. The Oranje-Nassaus nevertheless assumed the title and also erected several of their lordships into a new principality of Orange.
From that derivation of the title comes the tradition of the House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of Or ...
(originally Nassau-Dietz), the later stadtholders of the Netherlands, and the present-day royal family of the Netherlands, of holding this title. They maintain the tradition of William the Silent and the House of Orange-Nassau.
There are two other
claimants to this title:
* The House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, Prince-elector, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern Castle, Hohenzollern, Margraviate of Bran ...
, who reigned in Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
until 1918
* The House of Mailly-Nesles
Bearers of the title
As Counts of Orange
As sovereign prince of Orange
Until 1340, it was customary for all sons of the prince of Orange to inherit the title. Only the direct line of descent to Raimond V is shown here.House of Chalon-Orange (also House of Ivrea of Anscarid dynasty)
The lords of Chalons and Arlay were a cadet branch of the ruling house of the county of Burgundy, the Anscarids or House of Ivrea. They married the heiress of Baux-Orange.House of Chalon-Orange
Rene inherited the principality of Orange from his uncle Philbert on the condition that he bear the name and arms of the house of Chalon-Orange. Therefore, he is usually counted as one of the Chalon-Orange and history knows him as Rene of Chalon, rather than "of Nassau".
House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of Or ...
(first incarnation)
William of Nassau inherited the principality of Orange from his cousin René. Although William descended from no previous Prince of Orange, as René had no children or siblings, he exercised his right as sovereign prince to will Orange to his first cousin on his father's side, who actually had no Orange blood. This began the Dutch Royal House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of Or ...
.
Title without territory
House of Orange-Nassau (second incarnation)
The 2nd house of Orange-Nassau (see House of Orange-Nassau family tree) were cousins on their father and mother's side of the 1st house.=Head of house
==Netherlands heir apparent
=House of Hohenzollern
*Frederick I of Prussia
Frederick I (; 11 July 1657 – 25 February 1713), of the Hohenzollern dynasty, was (as Frederick III) List of margraves and electors of Brandenburg, Elector of Brandenburg (1688–1713) and Duke of Prussia in personal union (Brandenburg–Pr ...
(1702–1713), a senior descendant in female line from William the Silent, who ceded his claims to the lands of Orange to France in 1713, and his descendants, but kept his right to use the title.
House of Mailly
* Louis de Mailly, Marquis de Nesle et de Mailly, appointed by the French king, and his descendants, descended through another line of the house of Chalons-Arlay, currently Guy, Marquis de Nesle et de Mailly, Prince d'Orange.House of Bourbon
* Louis Armand II, Prince of Conti, appointed by the French king, and his descendants, the Princes of Conti becoming extinct in 1815.Princes of Orange of the House of Orange-Nassau
Historical background
William the Silent
William the Silent or William the Taciturn (; 24 April 153310 July 1584), more commonly known in the Netherlands as William of Orange (), was the leader of the Dutch revolt against the Spanish Habsburg Netherlands, Habsburgs that set off the ...
(Willem I) was the first stadtholder
In the Low Countries, a stadtholder ( ) was a steward, first appointed as a medieval official and ultimately functioning as a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and ...
of the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
and the most significant representative of the House of Orange in the Netherlands. He was count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
of a portion of the German territory of Nassau and heir to some of his father's fiefs in Holland. William obtained more extensive lands in the Netherlands (the lordship of Breda and several other dependencies) as an inheritance from his cousin René of Chalon, Prince of Orange, when William was only 11 years old. After William's assassination
Assassination is the willful killing, by a sudden, secret, or planned attack, of a personespecially if prominent or important. It may be prompted by political, ideological, religious, financial, or military motives.
Assassinations are orde ...
in 1584, the title passed to his son Philip William (who had been held hostage in Spain until 1596), and after his death in 1618, to his second son Maurice, and finally to his youngest son, Frederick Henry.
The title of Prince of Orange became associated with the stadtholder of the Netherlands.
William III (Willem III) was also King of England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
and Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
, and his legacy is commemorated annually by the Protestant Orange Order
The Loyal Orange Institution, commonly known as the Orange Order, is an international Protestant fraternal order based in Northern Ireland and primarily associated with Ulster Protestants. It also has lodges in England, Grand Orange Lodge of ...
. William's mother, Mary, was the daughter of King Charles I of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland from 27 March 1625 until Execution of Charles I, his execution in 1649.
Charles was born ...
and therefore a princess of England as well as Princess of Orange by marriage.
William III and Mary II
Mary II (30 April 1662 – 28 December 1694) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England, List of Scottish monarchs, Scotland, and Monarchy of Ireland, Ireland with her husband, King William III and II, from 1689 until her death in 1694. Sh ...
had no legitimate children. After William's death in 1702, his heir in the Netherlands was John William Friso of Nassau-Diez, who assumed the title, King William having bequeathed it to him by testament. The other contender was the King in Prussia
King ''in'' Prussia (German language, German: ''König in Preußen'') was a title used by the Prussian kings (also in personal union Elector of Brandenburg, Electors of Brandenburg) from 1701 to 1772. Subsequently, they used the title King ''of' ...
, who based his claim to the title on the will of Frederick Henry, William III's grandfather. Eventually, a compromise was reached by which both families were entitled to bear the title of Prince of Orange. By then, it was no more than a title because the principality had been annexed by Louis XIV of France
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
.
Friso's line held it as their principal title during the 18th century. The French army expelled them from the Netherlands in 1795, but on their return, the Prince of Orange became the first sovereign of the Netherlands in 1813.
After the establishment of the current Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1815, the title was partly reconstitutionalized by legislation and granted to the eldest son of King William I of the Netherlands, Prince William, who later became William II of the Netherlands. Since 1983, the heir to the Dutch throne, whether male or female, bears the title Prince or Princess of Orange. The first-born child of the heir to the Dutch throne bears the title Hereditary Prince(ss) of Orange. When her father Willem-Alexander became King of the Netherlands following the abdication of Queen Beatrix, Princess Catharina-Amalia became the Princess of Orange.
Style
The Prince(ss) of Orange is styled ''His/Her Royal Highness the Prince(ss) of Orange'' (Dutch: ''Zijne/Hare Koninklijke Hoogheid de Prins(es) van Oranje''). During the 15th, 16th and 17th Centuries, the Prince(ss) of Orange was styled ''His/Her Highness the Prince(ss) of Orange'' (Dutch: ''Zijne/Hare Hoogheid de Prins(es) van Oranje''), except for William III, who rated the "Royal/Koninklijke".Arms
The princes of Orange in the 16th and 17th century used the following sets of arms. On becoming Prince of Orange, William placed the Chalon-Arlay arms in the center ("as an inescutcheon") of his father's arms. He used these arms until 1582 when he purchased the marquisate of Veere and Vlissingen. He then used the arms attributed to Frederick Henry, etc. with the arms of the marquisate in the top center, and the arms of the county of Buren in the bottom center. Their growing complexity shows how arms are used to reflect the growing political position and royal aspirations of thehouse of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of Or ...
.
William the Silent
William the Silent or William the Taciturn (; 24 April 153310 July 1584), more commonly known in the Netherlands as William of Orange (), was the leader of the Dutch revolt against the Spanish Habsburg Netherlands, Habsburgs that set off the ...
as Prince of Orange until 1582 and his eldest son Philip William
File:Maurits Nassau wapen klein.svg, The coat of arms used by Maurice showing the county of Moers (top left center and bottom right center) and his mother's arms of Saxony (center)
File:Blason Nassau-Orange (Cadets).svg, The coat of arms used by William the Silent
William the Silent or William the Taciturn (; 24 April 153310 July 1584), more commonly known in the Netherlands as William of Orange (), was the leader of the Dutch revolt against the Spanish Habsburg Netherlands, Habsburgs that set off the ...
after 1582, Frederick Henry, William II, and William III as Prince of Orange
File:Blason Nassau-Orange (Cadets) Alternate.PNG, An alternate coat of arms sometimes used by Frederick Henry, William II, and William III as Prince of Orange showing the county of Moers in the top center rather than Veere.
Coat of arms of the Netherlands
The coat of arms of the Kingdom of the Netherlands was originally adopted in 1815 and later modified in 1907. The arms are a composite of the arms of the former Dutch Republic and the arms of the House of Nassau, it features a checkered shield wit ...
. In the 19th century, the Dutch Crown prince, who holds the title "Prince of Orange" ("Prins van Oranje"), and his son, who holds the title "Hereditary Prince of Orange" ("Erfprins van Oranje") had their own pre-defined arms. The House of Orange, now the Royal House of the Netherlands, and their descendants the House of Orange-Nassau, kept this title for their family. Wilhelmina further decreed that in perpetuity her descendants should be styled "princes and princesses of Orange-Nassau" and that the name of the house would be "Orange-Nassau" (in Dutch "Oranje-Nassau"). Since then, individual members of the House of Orange-Nassau are also given their own arms by the reigning monarch, similar to the United Kingdom. This is usually the royal arms, quartered with the arms of the principality of Orange, and an in escutcheon of their paternal arms.
See also
*List of heirs to the Dutch throne
This page is a list of heirs to the Dutch throne. The list includes all individuals who were considered to Inheritance, inherit the Monarchy of the Netherlands, throne of the Netherlands, either as heir apparent or as heir presumptive, since the c ...
References
Literature
* Herbert H. Rowen, ''The princes of Orange: the stadholders in the Dutch Republic''. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press, 1988. * John Lothrop Motley, "History of the United Netherlands from the Death of William the Silent to the Synod of Dort". London: John Murray, 1860. * John Lothrop Motley, "The Life and Death of John of Barenvelt". New York & London: Harper and Brothers Publishing, 1900. * Petrus Johannes Blok, "History of the people of the Netherlands". New York: G. P. Putnam's sons, 1898. * Reina van Ditzhuyzen, ''Het Huis van Oranje: prinsen, stadhouders, koningen en koninginnen''. Haarlem : De Haan, 979External links
Treaty ceding the Principality to Louis XIV
{{DEFAULTSORT:Prince Of Orange 1160s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire Noble titles created in 1163 Heirs to the throne * * * Orange Orange Frederick Barbarossa