Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th
president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the
Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
* Botswana Democratic Party
* Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*De ...
, Obama was the first African-American president of the United States.
He previously served as a
U.S. senator
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and power ...
from
Illinois from 2005 to 2008 and as an
Illinois state senator from 1997 to 2004, and previously worked as a civil rights lawyer before entering politics.
Obama was born in
Honolulu, Hawaii. After graduating from
Columbia University in 1983, he worked as a
community organizer
Community organizing is a process where people who live in proximity to each other or share some common problem come together into an organization that acts in their shared self-interest.
Unlike those who promote more-consensual community bui ...
in Chicago. In 1988, he enrolled in
Harvard Law School
Harvard Law School (Harvard Law or HLS) is the law school of Harvard University, a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1817, it is the oldest continuously operating law school in the United States.
Each class i ...
, where he was the first black president of the ''
Harvard Law Review''. After graduating, he became a civil rights attorney and an academic, teaching constitutional law at the
University of Chicago Law School from 1992 to 2004. Turning to elective politics, he
represented the 13th district in the
Illinois Senate from 1997 until 2004, when he
ran for the U.S. Senate. Obama received national attention in 2004 with his March Senate primary win, his well-received July
Democratic National Convention keynote address
A keynote in public speaking is a talk that establishes a main underlying theme. In corporate or commercial settings, greater importance is attached to the delivery of a keynote speech or keynote address. The keynote establishes the framework f ...
, and his landslide November election to the Senate. In 2008, after
a close primary campaign against
Hillary Clinton, he was nominated by the Democratic Party for president and chose
Joe Biden as his running mate. Obama was elected over
Republican nominee
John McCain in the
presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The p ...
and was
inaugurated
In government and politics, inauguration is the process of swearing a person into office and thus making that person the incumbent. Such an inauguration commonly occurs through a formal ceremony or special event, which may also include an inaugur ...
on January 20, 2009. Nine months later, he was named the
2009 Nobel Peace Prize laureate, a decision that drew a mixture of praise and criticism.
Obama's first-term actions addressed the
global financial crisis and included a
major stimulus package, a partial extension of
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
's
tax cuts, legislation to
reform health care, a major
financial regulation reform bill, and the end of a major US
military presence in
Iraq. Obama also appointed
Supreme Court Justices
Sonia Sotomayor
Sonia Maria Sotomayor (, ; born June 25, 1954) is an American lawyer and jurist who serves as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. She was nominated by President Barack Obama on May 26, 2009, and has served since ...
and
Elena Kagan, the former being the first
Hispanic American on the Supreme Court. He ordered
the counterterrorism raid which killed
Osama bin Laden and downplayed Bush's counterinsurgency model, expanding air strikes and making extensive use of special forces while encouraging greater reliance on host-government militaries.
After winning
re-election
The incumbent is the current holder of an office or position, usually in relation to an election. In an election for president, the incumbent is the person holding or acting in the office of president before the election, whether seeking re-ele ...
by defeating Republican opponent
Mitt Romney, Obama was
sworn in for a second term on January 20, 2013. In his second term, Obama took steps to
combat climate change, signing a major
international climate agreement and an
executive order to limit
carbon emission
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and larg ...
s. Obama also presided over the implementation of the
Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and colloquially known as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by Presid ...
and other legislation passed in his first term, and he negotiated a
nuclear agreement with Iran and
normalized relations with Cuba. The number of
American soldiers in
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
fell dramatically during Obama's second term, though U.S. soldiers remained in Afghanistan throughout
Obama's presidency
Barack Obama's tenure as the 44th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 2009, and ended on January 20, 2017. A Democrat from Illinois, Obama took office following a decisive victory over Republic ...
. Obama left office on January 20, 2017, and continues to reside in
Washington, D.C. His
presidential library
A presidential library, presidential center, or presidential museum is a facility either created in honor of a former president and containing their papers, or affiliated with a country's presidency.
In the United States
* The presidential libr ...
in Chicago began construction in 2021.
During Obama's terms as president, the United States'
reputation abroad and the American
economy improved significantly, although the country experienced high levels of partisan divide. As the first person of color elected president, Obama faced
racist sentiments and was the target of
numerous conspiracy theories. Since leaving office, Obama has remained active in Democratic politics, including campaigning for candidates in various American elections. Outside of politics, Obama has published three
bestselling books
This page provides lists of best-selling individual books and book series to date and in any language. ''"Best-selling"'' refers to the estimated number of copies sold of each book, rather than the number of books printed or currently owned. Com ...
: ''
Dreams from My Father'' (1995)'',
The Audacity of Hope
''The Audacity of Hope: Thoughts on Reclaiming the American Dream'' is the second book written by Barack Obama. It became number one on both the ''New York Times'' and Amazon.com bestsellers lists in the fall of 2006, after Obama had been endor ...
'' (2006) and ''
A Promised Land
''A Promised Land'' is a memoir by Barack Obama, the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. Published on November 17, 2020, it is the first of a planned two-volume series. Remaining focused on his political career, the preside ...
'' (2020).
Rankings by scholars and historians, in which he has been featured since 2010, view his presidency favorably and place him among the upper tier of American presidents.
Early life and career
Obama was born on August 4, 1961,
at
Kapiolani Medical Center for Women and Children
Kapiolani Medical Center for Women and Children is part of Hawaii Pacific Health's network of hospitals. It is located in Honolulu, Hawaii, within the residential inner-city district of Makiki. Kapiolani Medical Center is Hawaii's only children ...
in
Honolulu,
Hawaii.
He is the only president born outside the
contiguous 48 states
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
.
He was born to an American mother and a Kenyan father. His mother,
Ann Dunham (1942–1995), was born in
Wichita, Kansas and was mostly of English descent, though in 2007 it was discovered her great-great-grandfather Falmouth Kearney emigrated from the village of
Moneygall, Ireland to the US in 1850. In July 2012,
Ancestry.com found a strong likelihood that Dunham was descended from
John Punch, an enslaved African man who lived in the
Colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (histor ...
during the seventeenth century.
["Ancestry.com Discovers Ph Suggests"](_blank)
, '' The New York Times''. July 30, 2012. Obama's father,
Barack Obama Sr.
Barack Hussein Obama Sr. (; 18 June 1934 – 24 November 1982) was a Kenyan senior governmental economist and the father of Barack Obama, the 44th president of the United States. He is a central figure of his son's memoir, '' Dreams from My Fa ...
(1934–1982), was a married
from
Nyang'oma Kogelo
Nyang'oma Kogelo, also known as Kogelo, is a village in Siaya County, Kenya. It is located near the equator, 60 kilometres (37 mi) west-northwest of Kisumu, the former Nyanza provincial capital. The population of Nyangoma-Kogelo is 3,648 ...
.
Obama's parents met in 1960 in a
Russian language class at the
University of Hawaii at Manoa, where his father was a foreign student on a scholarship.
[Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 9–10.
* Scott (2011), pp. 80–86.
* Jacobs (2011), pp. 115–118.
* Maraniss (2012), pp. 154–160.] The couple married in
Wailuku, Hawaii, on February 2, 1961, six months before Obama was born.
In late August 1961, a few weeks after he was born, Barack and his mother moved to the
University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington.
Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seattle ...
in
Seattle, where they lived for a year. During that time, Barack's father completed his undergraduate degree in
economics in Hawaii, graduating in June 1962. He left to attend graduate school on a scholarship at
Harvard University, where he earned an
M.A.
A Master of Arts ( la, Magister Artium or ''Artium Magister''; abbreviated MA, M.A., AM, or A.M.) is the holder of a master's degree awarded by universities in many countries. The degree is usually contrasted with that of Master of Science. ...
in economics. Obama's parents divorced in March 1964. Obama Sr. returned to Kenya in 1964, where he married for a third time and worked for the Kenyan government as the Senior Economic Analyst in the Ministry of Finance. He visited his son in Hawaii only once, at Christmas 1971, before he was killed in an automobile accident in 1982, when Obama was 21 years old. Recalling his early childhood, Obama said: "That my father looked nothing like the people around me—that he was black as pitch, my mother white as milk—barely registered in my mind."
He described his struggles as a young adult to reconcile social perceptions of his multiracial heritage.
In 1963, Dunham met
Lolo Soetoro
Lolo Soetoro ( EYD: Lolo Sutoro; ; 2 January 1935 Google Translate'sEnglish translationLolo studied geography at Gadjah Mada University and got a scholarship from the Indonesian Army Topographic Service. After working for the Indonesian Army Topo ...
at the
University of Hawaii; he was an
Indonesian
Indonesian is anything of, from, or related to Indonesia, an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It may refer to:
* Indonesians, citizens of Indonesia
** Native Indonesians, diverse groups of local inhabitants of the archipelago
** Indonesian ...
East–West Center
The East–West Center (EWC), or the Center for Cultural and Technical Interchange Between East and West, is an education and research organization established by the U.S. Congress in 1960 to strengthen relations and understanding among the peop ...
graduate student in
geography. The couple married on
Molokai on March 15, 1965. After two one-year extensions of his
J-1 visa
A J-1 visa is a non-immigrant visa issued by the United States to research scholars, professors and exchange visitors participating in programs that promote cultural exchange, especially to obtain medical or business training within the U.S. All ...
, Lolo returned to
Indonesia in 1966. His wife and stepson followed sixteen months later in 1967. The family initially lived in the Menteng Dalam neighborhood in the
Tebet district of
South Jakarta
South Jakarta ( id, Jakarta Selatan; bew, Jakarte Beludik ), colloquially known as ''Jaksel'', is one of the five administrative cities which form the Special Capital Region of Jakarta, Indonesia. South Jakarta is not self-governed and does not ...
. From 1970, they lived in a wealthier neighborhood in the
Menteng district of
Central Jakarta
Central Jakarta ( id, Jakarta Pusat) is one of the five administrative cities () which form the Special Capital Region of Jakarta. It had 902,973 inhabitants according to the 2010 censusBiro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. and 1,056,896 at the 2 ...
.
Education
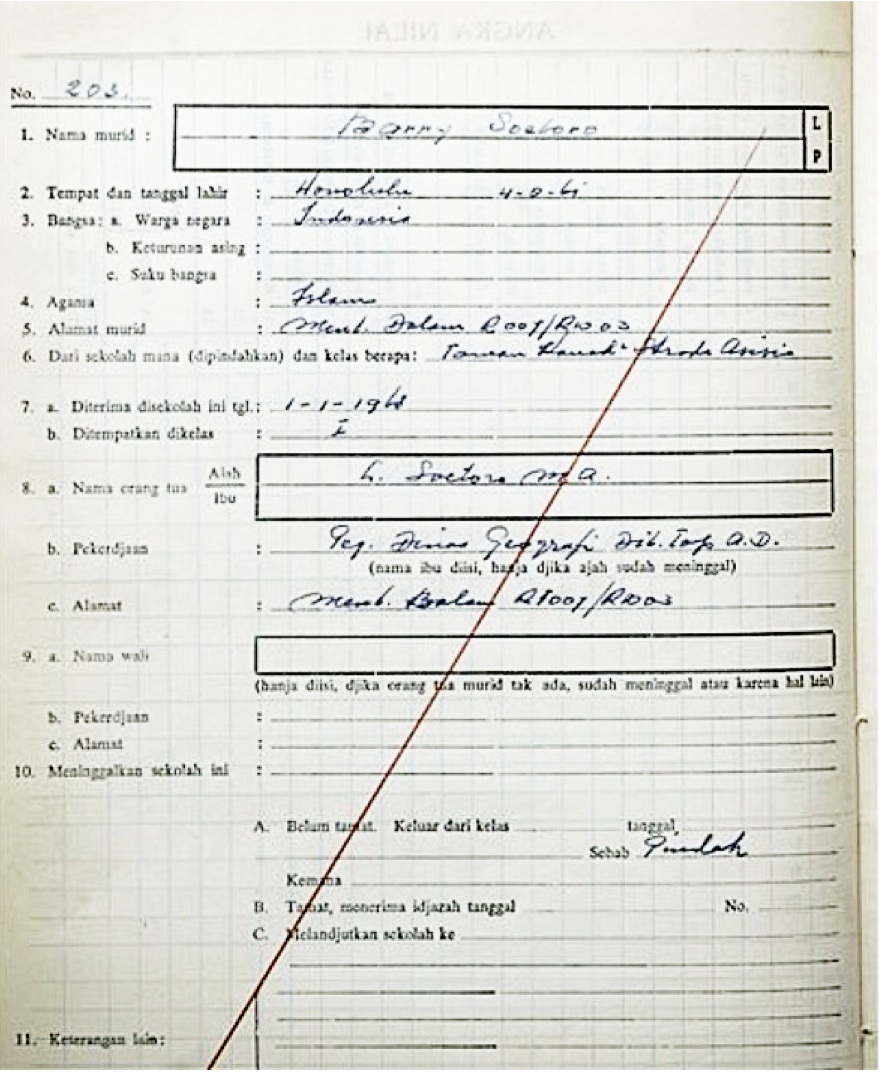
At the age of six, Obama and his mother had moved to Indonesia to join his stepfather. From age six to ten, he attended local
Indonesian-language schools: ''Sekolah Dasar Katolik Santo Fransiskus Asisi'' (St. Francis of Assisi Catholic Elementary School) for two years and
''Sekolah Dasar Negeri Menteng 01'' (State Elementary School Menteng 01) for one and a half years, supplemented by English-language
Calvert School
Calvert School, founded in 1897, is an independent, non-sectarian, co-educational lower and middle school located in Baltimore, Maryland.
Calvert School is a member of the National Association of Independent Schools (NAIS) as well as the As ...
homeschooling by his mother. As a result of his four years in
Jakarta, he was able to speak
Indonesian
Indonesian is anything of, from, or related to Indonesia, an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It may refer to:
* Indonesians, citizens of Indonesia
** Native Indonesians, diverse groups of local inhabitants of the archipelago
** Indonesian ...
fluently as a child.
During his time in Indonesia, Obama's stepfather taught him to be resilient and gave him "a pretty hardheaded assessment of how the world works."
In 1971, Obama returned to
Honolulu to live with his maternal grandparents,
Madelyn
Madelyn or Madalyn is a feminine first name. Notable people with these names include:
Madelyn
* Madelyn Clare (1894–1975), American actress
* Madelyn Cline (born 1997), American actress
* Madelyn Dunham (1922–2008), maternal grandmother of ...
and
Stanley Dunham. He attended
Punahou School
Punahou School (known as Oahu College until 1934) is a private, co-educational, college preparatory school in Honolulu, Hawaii. More than 3,700 students attend the school from kindergarten through twelfth grade, 12th grade. Protestant missionar ...
—a private
college preparatory school
A college-preparatory school (usually shortened to preparatory school or prep school) is a type of secondary school. The term refers to public, private independent or parochial schools primarily designed to prepare students for higher educat ...
—with the aid of a scholarship from fifth grade until he graduated from high school in 1979. In his youth, Obama went by the nickname "Barry." Obama lived with his mother and half-sister,
Maya Soetoro, in Hawaii for three years from 1972 to 1975 while his mother was a graduate student in
anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of behavi ...
at the
University of Hawaii. Obama chose to stay in Hawaii when his mother and half-sister returned to Indonesia in 1975, so his mother could begin anthropology field work. His mother spent most of the next two decades in Indonesia, divorcing Lolo in 1980 and earning a
PhD degree in 1992, before dying in 1995 in Hawaii following unsuccessful treatment for
ovarian
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
and
uterine cancer.
Of his years in Honolulu, Obama wrote: "The opportunity that Hawaii offered — to experience a variety of cultures in a climate of mutual respect — became an integral part of my world view, and a basis for the values that I hold most dear." Obama has also written and talked about using
alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
,
marijuana, and
cocaine during his teenage years to "push questions of who I was out of my mind." Obama was also a member of the "choom gang", a self-named group of friends who spent time together and occasionally smoked marijuana.
College and research jobs
After graduating from high school in 1979, Obama moved to
Los Angeles to attend
Occidental College on a full scholarship. In February 1981, Obama made his first public speech, calling for Occidental to participate in the
disinvestment from South Africa in response to that nation's policy of
apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid wa ...
.
In mid-1981, Obama traveled to Indonesia to visit his mother and half-sister Maya, and visited the families of college friends in
Pakistan for three weeks.
Later in 1981, he
transferred to
Columbia University in
New York City as a
junior, where he majored in
political science with a specialty in
international relations and in
English literature and lived off-campus on West 109th Street. He graduated with a
Bachelor of Arts degree in 1983 and a 3.7
GPA
Grading in education is the process of applying standardized measurements for varying levels of achievements in a course. Grades can be assigned as letters (usually A through F), as a range (for example, 1 to 6), as a percentage, or as a numbe ...
. After graduating, Obama worked for about a year at the
Business International Corporation
Business International Corporation (BI) was a publishing and advisory firm dedicated to assisting American companies in operating abroad. It was founded in 1953. It organized conferences, and worked with major corporations. Former president Barack ...
, where he was a financial researcher and writer, then as a project coordinator for the
New York Public Interest Research Group
The New York Public Interest Research Group (NYPIRG) is a New York statewide student-directed, non-partisan, not for profit political organization. It has existed since 1973. Its current executive director is Blair Horner and its founding directo ...
on the
City College of New York
The City College of the City University of New York (also known as the City College of New York, or simply City College or CCNY) is a public university within the City University of New York (CUNY) system in New York City. Founded in 1847, Cit ...
campus for three months in 1985.
Community organizer and Harvard Law School
Two years after graduating from Columbia, Obama moved from New York to Chicago when he was hired as director of the
Developing Communities Project
The Developing Communities Project (DCP) is a faith-based organization in Chicago, Illinois. DCP was organized in 1984 as a branch of the Calumet Community Religious Conference (CCRC) in response to lay-offs and plant closings in Southeast Chica ...
, a church-based community organization originally comprising eight Catholic parishes in
Roseland,
West Pullman
West Pullman is a neighborhood located on the far south side of the city of Chicago, Illinois. It is one of the 77 official community areas of Chicago. The Neighborhood of West Pullman was largely inhabited by workers of the Pullman Train Comp ...
, and
Riverdale on Chicago's
South Side. He worked there as a community organizer from June 1985 to May 1988.
He helped set up a job training program, a college preparatory tutoring program, and a tenants' rights organization in
Altgeld Gardens
Riverdale is one of the 77 official community areas of Chicago, Illinois and is located
on the city's far south side.
As originally designated by the Social Science Research Committee at the University of Chicago and officially adopted by the ...
.
[
* ] Obama also worked as a consultant and instructor for the
Gamaliel Foundation
Gamaliel Foundation provides training and consultation and develops national strategy for its affiliated congregation-based community organizations. As of 2013, Gamaliel has 45 affiliates in 17 U.S. states, the United Kingdom, and South Africa, ...
, a community organizing institute. In mid-1988, he traveled for the first time in Europe for three weeks and then for five weeks in Kenya, where he met many of his
paternal relatives for the first time.
Despite being offered a full scholarship to
Northwestern University School of Law
Northwestern University Pritzker School of Law is the law school of Northwestern University, a Private university, private research university. It is located on the university's Chicago campus. Northwestern Law has been ranked among the top 14, ...
, Obama enrolled at
Harvard Law School
Harvard Law School (Harvard Law or HLS) is the law school of Harvard University, a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1817, it is the oldest continuously operating law school in the United States.
Each class i ...
in the fall of 1988, living in nearby
Somerville, Massachusetts. He was selected as an editor of the ''
Harvard Law Review'' at the end of his first year,
[
*
*
* Mendell (2007), pp. 80–92.] president of the journal in his second year,
[
*
*
*
* ] and research assistant to the constitutional scholar
Laurence Tribe
Laurence Henry Tribe (born October 10, 1941) is an American legal scholar who is a University Professor Emeritus at Harvard University. He previously served as the Carl M. Loeb University Professor at Harvard Law School.
A constitutional law sc ...
while at Harvard. During his summers, he returned to Chicago, where he worked as a
summer associate at the law firms of
Sidley Austin in 1989 and
Hopkins & Sutter in 1990. Obama's election as the
first black president of the ''Harvard Law Review'' gained national media attention
and led to a publishing contract and advance for a book about race relations,
[
* Obama (1995, 2004), pp. xiii–xvii.] which evolved into a personal memoir. The manuscript was published in mid-1995 as ''
Dreams from My Father''.
Obama graduated from Harvard Law in 1991 with a
Juris Doctor ''
magna cum laude
Latin honors are a system of Latin phrases used in some colleges and universities to indicate the level of distinction with which an academic degree has been earned. The system is primarily used in the United States. It is also used in some Sou ...
''.
University of Chicago Law School
In 1991, Obama accepted a two-year position as Visiting Law and Government Fellow at the
University of Chicago Law School to work on his first book.
He then taught
constitutional law
Constitutional law is a body of law which defines the role, powers, and structure of different entities within a state, namely, the executive, the parliament or legislature, and the judiciary; as well as the basic rights of citizens and, in feder ...
at the University of Chicago Law School for twelve years, first as a
lecturer from 1992 to 1996, and then as a senior lecturer from 1996 to 2004.
From April to October 1992, Obama directed Illinois's
Project Vote
Project Vote (and Voting for America, Inc.) was a national nonpartisan, nonprofit 501(c)(3) organization that worked to mobilize marginalized and under-represented voters until it ceased operations on May 31, 2017. Project Vote's efforts to engage ...
, a
voter registration campaign with ten staffers and seven hundred volunteer registrars; it achieved its goal of registering 150,000 of 400,000 unregistered African Americans in the state, leading ''
Crain's Chicago Business
''Crain's Chicago Business'' is a weekly business newspaper in Chicago, Illinois, IL. It is owned by Detroit-based Crain Communications Inc., Crain Communications, a privately held publishing company with more than 30 magazines, including ''Adve ...
'' to name Obama to its 1993 list of "40 under Forty" powers to be.
Family and personal life
In a 2006 interview, Obama highlighted the diversity of
his extended family: "It's like a little mini-United Nations," he said. "I've got relatives who look like
Bernie Mac
Bernard Jeffrey McCullough (October 5, 1957 – August 9, 2008), better known by his stage name Bernie Mac, was an American comedian and actor. Born and raised on Chicago's South Side, Mac gained popularity as a stand-up comedian. He joined fell ...
, and I've got relatives who look like
Margaret Thatcher." Obama has a half-sister with whom he was raised (
Maya Soetoro-Ng
Maya Kasandra Soetoro-Ng (; ; born August 15, 1970) is an Indonesian-American academic, who is a faculty specialist at the Spark M. Matsunaga Institute for Peace and Conflict Resolution, based in the College of Social Sciences at the University ...
) and seven other half-siblings from his Kenyan father's family—six of them living. Obama's mother was survived by her Kansas-born mother,
Madelyn Dunham
Madelyn Lee Payne Dunham ( ; October 26, 1922 – November 2, 2008) was the American maternal grandmother of Barack Obama, the 44th president of the United States. She and her husband Stanley Armour Dunham raised Obama from age ten in their ...
, until her death on November 2, 2008, two days before his election to the presidency. Obama also has roots in Ireland; he met with his Irish cousins in
Moneygall
Moneygall () is a small village on the border of counties Offaly and Tipperary, in Ireland. It is situated on the R445 road between Dublin and Limerick. There were 313 people living in the village as of the 2016 census. Moneygall has a Catholic ...
in May 2011. In ''Dreams from My Father'', Obama ties his mother's family history to possible Native American ancestors and distant relatives of
Jefferson Davis,
President of the Confederate States of America during the
American Civil War. He also shares distant ancestors in common with
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
and
Dick Cheney
Richard Bruce Cheney ( ; born January 30, 1941) is an American politician and businessman who served as the 46th vice president of the United States from 2001 to 2009 under President George W. Bush. He is currently the oldest living former ...
, among others.
Obama lived with anthropologist
Sheila Miyoshi Jager
Sheila Miyoshi Jager (born 1963) is an American historian. She is a Professor of East Asian Studies at Oberlin College, author of two books on Korea, co-editor of a third book on Asian nations in the post-Cold War era, and a forthcoming book on gr ...
while he was a community organizer in Chicago in the 1980s.
He proposed to her twice, but both Jager and her parents turned him down.
The relationship was not made public until May 2017, several months after his presidency had ended.

In June 1989, Obama met
Michelle Robinson when he was employed as a summer associate at the Chicago law firm of
Sidley Austin. Robinson was assigned for three months as Obama's adviser at the firm, and she joined him at several group social functions but declined his initial requests to date. They began dating later that summer, became engaged in 1991, and were married on October 3, 1992. After suffering a miscarriage, Michelle underwent
in vitro fertilization to conceive their children. The couple's first daughter, Malia Ann, was born in 1998, followed by a second daughter, Natasha ("Sasha"), in 2001. The Obama daughters attended the
University of Chicago Laboratory Schools
The University of Chicago Laboratory Schools (also known as Lab or Lab Schools and abbreviated as UCLS though the high school is nicknamed U-High) is a private, co-educational day Pre-K and K-12 school in Chicago, Illinois. It is affiliated w ...
. When they moved to Washington, D.C., in January 2009, the girls started at the
Sidwell Friends School. The Obamas had two
Portuguese Water Dog
The Portuguese Water Dog originated from the Algarve region of Portugal. From there the breed expanded to all around Portugal's coast, where they were taught to herd fish into fishermen's nets, retrieve lost tackle or broken nets, and act as ...
s; the first, a male named
Bo, was a gift from Senator
Ted Kennedy
Edward Moore Kennedy (February 22, 1932 – August 25, 2009) was an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States senator from Massachusetts for almost 47 years, from 1962 until his death in 2009. A member of the Democratic ...
. In 2013, Bo was joined by
Sunny, a female.
Bo died of cancer on May 8, 2021.

Obama is a supporter of the
Chicago White Sox
The Chicago White Sox are an American professional baseball team based in Chicago. The White Sox compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Central division. The team is owned by Jerry Reinsdorf, and ...
, and he threw out the first pitch at the
2005 ALCS when he was still a senator. In 2009, he threw out the ceremonial first pitch at the
All-Star Game
An all-star game is an exhibition game that purports to showcase the best players (the "stars") of a sports league. The exhibition is between two teams organized solely for the event, usually representing the league's teams based on region or div ...
while wearing a White Sox jacket. He is also primarily a
Chicago Bears
The Chicago Bears are a professional American football team based in Chicago. The Bears compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's National Football Conference (NFC) North division. The Bears have won nine NF ...
football fan in the
NFL, but in his childhood and adolescence was a
fan of the Pittsburgh Steelers, and rooted for them ahead of their victory in
Super Bowl XLIII 12 days after he took office as president.
In 2011, Obama invited the
1985 Chicago Bears
The year 1985 was designated as the International Youth Year by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
** The Internet's Domain Name System is created.
** Greenland withdraws from the European Economic Community as a result of a ...
to the White House; the team had not visited the White House after their
Super Bowl win in 1986 due to the
Space Shuttle Challenger disaster
On January 28, 1986, the broke apart 73 seconds into its flight, killing all seven crew members aboard. The spacecraft disintegrated above the Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of Cape Canaveral, Florida, at 11:39a.m. EST (16:39 UTC). It was ...
. He plays basketball, a sport he participated in as a member of his high school's varsity team, and he is left-handed.
In 2005, the Obama family applied the proceeds of a book deal and moved from a
Hyde Park, Chicago condominium to a $1.6million house (equivalent to $million in ) in neighboring
Kenwood, Chicago
Kenwood, one of Chicago's 77 community areas, is on the shore of Lake Michigan on the South Side of the city. Its boundaries are 43rd Street, 51st Street, Cottage Grove Avenue, and the lake. Kenwood was originally part of Hyde Park Township, ...
. The purchase of an adjacent lot—and sale of part of it to Obama by the wife of developer, campaign donor and friend
Tony Rezko
Antoin Rezko (born 1955) is an American businessman and convict. He was a fundraiser for Illinois Democratic and Republican politicians. After becoming a major contributor to Rod Blagojevich's successful election for governor, Rezko assisted Bla ...
—attracted media attention because of Rezko's subsequent indictment and conviction on political corruption charges that were unrelated to Obama.
In December 2007, ''
Money Magazine
''Money'' is an American personal finance brand and website owned by Ad Practitioners LLC and formerly also a monthly magazine, first published by Time Inc. (1972–2018) and later by Meredith Corporation (2018–2019). Its articles cover the g ...
'' estimated Obama's net worth at $1.3million (equivalent to $million in ). Their 2009 tax return showed a household income of $5.5million—up from about $4.2million in 2007 and $1.6million in 2005—mostly from sales of his books. On his 2010 income of $1.7million, he gave 14 percent to non-profit organizations, including $131,000 to
Fisher House Foundation
Fisher House Foundation is a charity and foundation that builds comfort homes where military & veterans families can stay free of charge, while a loved one is in the hospital. Fisher Houses are located at major military and VA medical centers n ...
, a charity assisting wounded veterans' families, allowing them to reside near where the veteran is receiving medical treatments. Per his 2012 financial disclosure, Obama may be worth as much as $10million.
Last name
Obama's last name originates from
Luo people
The Luo of Kenya and Tanzania are a Nilotic ethnic group native to western Kenya and the Mara Region of northern Tanzania in East Africa. The Luo are the fourth-largest ethnic group (10.65%) in Kenya, after the Kikuyu (17.13%), the Luhya ...
. In Luo language, it means "bent over" or "limping".
Religious views
Obama is a
Protestant Christian whose religious views developed in his adult life.
He wrote in ''
The Audacity of Hope
''The Audacity of Hope: Thoughts on Reclaiming the American Dream'' is the second book written by Barack Obama. It became number one on both the ''New York Times'' and Amazon.com bestsellers lists in the fall of 2006, after Obama had been endor ...
'' that he "was not raised in a religious household." He described his mother, raised by non-religious parents, as being detached from religion, yet "in many ways the most spiritually awakened person... I have ever known", and "a lonely witness for
secular humanism." He described his father as a "confirmed
atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
" by the time his parents met, and his stepfather as "a man who saw religion as not particularly useful." Obama explained how, through working with
black church
The black church (sometimes termed Black Christianity or African American Christianity) is the faith and body of Christian congregations and denominations in the United States that minister predominantly to African Americans, as well as thei ...
es as a
community organizer
Community organizing is a process where people who live in proximity to each other or share some common problem come together into an organization that acts in their shared self-interest.
Unlike those who promote more-consensual community bui ...
while in his twenties, he came to understand "the power of the African-American religious tradition to spur social change."

In January 2008, Obama told ''
Christianity Today
''Christianity Today'' is an evangelical Christian media magazine founded in 1956 by Billy Graham. It is published by Christianity Today International based in Carol Stream, Illinois. ''The Washington Post'' calls ''Christianity Today'' "evange ...
'': "I am a Christian, and I am a devout Christian. I believe in the
redemptive death and
resurrection of Jesus Christ
The resurrection of Jesus ( grc-x-biblical, ἀνάστασις τοῦ Ἰησοῦ) is the Christian belief that God raised Jesus on the third day after his crucifixion, starting – or restoring – his exalted life as Christ and Lord ...
. I believe that faith gives me a path to be cleansed of sin and have eternal life." On September 27, 2010, Obama released a statement commenting on his religious views, saying:
Obama met
Trinity United Church of Christ
Trinity United Church of Christ is a predominantly African-American church with more than 8,500 members. It is located in the Washington Heights community on the South Side of Chicago. It is the largest church affiliated with the United Chur ...
pastor
Jeremiah Wright
Jeremiah Alvesta Wright Jr. (born September 22, 1941) is a pastor emeritus of Trinity United Church of Christ in Chicago, a congregation he led for 36 years, during which its membership grew to over 8,000 parishioners. Following retirement, his ...
in October 1987 and became a member of Trinity in 1992.
During Obama's first presidential campaign in May 2008, he resigned from Trinity after
some of Wright's statements were criticized. Since moving to Washington, D.C., in 2009, the Obama family has attended several Protestant churches, including
Shiloh Baptist Church and
St. John's Episcopal Church, as well as Evergreen Chapel at
Camp David
Camp David is the country retreat for the president of the United States of America. It is located in the wooded hills of Catoctin Mountain Park, in Frederick County, Maryland, near the towns of Thurmont and Emmitsburg, about north-northwes ...
, but the members of the family do not attend church on a regular basis.
In 2016, he said that he gets inspiration from a few items that remind him "of all the different people I've met along the way", adding: "I carry these around all the time. I'm not that superstitious, so it's not like I think I necessarily have to have them on me at all times." The items, "a whole bowl full", include rosary beads given to him by
Pope Francis, a figurine of the Hindu deity
Hanuman, a
Coptic cross
The Coptic cross refers to a number of Christian cross variants associated in some way with Coptic Christians.
Typical form
The typical form of the "Coptic cross" used in the Coptic Church is made up of two bold lines of equal length that inte ...
from Ethiopia, a small
Buddha statue
Much Buddhist art uses depictions of the historical Buddha, Gautama Buddha, which are known as Buddharūpa (literally, "Form of the Awakened One") in Sanskrit and Pali. These may be statues or other images such as paintings. The main figure in ...
given by a monk, and a metal poker chip that used to be the lucky charm of a motorcyclist in Iowa.
Legal career
Civil Rights attorney
He joined Davis, Miner, Barnhill & Galland, a 13-attorney law firm specializing in civil rights litigation and neighborhood economic development, where he was an
associate for three years from 1993 to 1996, then
of counsel from 1996 to 2004. In 1994, he was listed as one of the lawyers in ''Buycks-Roberson v. Citibank Fed. Sav. Bank'', 94 C 4094 (N.D. Ill.). This
class action lawsuit
A class action, also known as a class-action lawsuit, class suit, or representative action, is a type of lawsuit where one of the parties is a group of people who are represented collectively by a member or members of that group. The class actio ...
was filed in 1994 with Selma Buycks-Roberson as lead plaintiff and alleged that Citibank Federal Savings Bank had engaged in practices forbidden under the
Equal Credit Opportunity Act
The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA) is a United States law (codified at et seq.), enacted 28 October 1974, that makes it unlawful for any creditor to discriminate against any applicant, with respect to any aspect of a credit transaction, on ...
and the
Fair Housing Act
The Civil Rights Act of 1968 () is a landmark law in the United States signed into law by United States President Lyndon B. Johnson during the King assassination riots.
Titles II through VII comprise the Indian Civil Rights Act, which appli ...
. The case was settled out of court. Final judgment was issued on May 13, 1998, with Citibank Federal Savings Bank agreeing to pay attorney fees.
From 1994 to 2002, Obama served on the boards of directors of the
Woods Fund of Chicago—which in 1985 had been the first foundation to fund the Developing Communities Project—and of the
Joyce Foundation
The Joyce Foundation is a non-operating private foundation based in Chicago, Illinois. As of 2021, it had assets of approximately $1.1 billion and distributes $50 million in grants per year and primarily funds organizations in the Great Lakes re ...
.
He served on the board of directors of the
Chicago Annenberg Challenge
The Chicago Annenberg Challenge (CAC) was a Chicago public school reform project from 1995 to 2001 that worked with half of Chicago's public schools and was funded by a $49.2 million, 2-to-1 matching challenge grant over five years from the Annenbe ...
from 1995 to 2002, as founding president and chairman of the board of directors from 1995 to 1999.
Obama's law license became inactive in 2007.
Legislative career
Illinois Senate (1997–2004)

Obama was elected to the
Illinois Senate in 1996, succeeding Democratic State Senator
Alice Palmer from Illinois's 13th District, which, at that time, spanned Chicago South Side neighborhoods from
Hyde Park–
Kenwood south to
South Shore and west to
Chicago Lawn
Chicago Lawn is one of the 77 community areas of Chicago, Illinois. It is located on the southwest side of the city. Its community neighbors include Gage Park, West Englewood, Ashburn, and West Lawn. It is bounded by Bell Avenue on the east, ...
. Once elected, Obama gained bipartisan support for legislation that reformed ethics and health care laws. He sponsored a law that increased
tax credits for low-income workers, negotiated
welfare reform, and promoted increased subsidies for childcare.
In 2001, as co-chairman of the bipartisan Joint Committee on Administrative Rules, Obama supported Republican Governor Ryan's
payday loan regulations and
predatory mortgage lending Predatory lending refers to unethical practices conducted by lending organizations during a loan origination process that are unfair, deceptive, or fraudulent. While there are no internationally agreed legal definitions for predatory lending, a 2006 ...
regulations aimed at averting home
foreclosures.
He was reelected to the Illinois Senate in 1998, defeating Republican Yesse Yehudah in the general election, and was re-elected again in 2002. In 2000, he lost a
Democratic primary race for
Illinois's 1st congressional district
Illinois's first congressional district is a congressional district in the U.S. state of Illinois. Based in Cook County, the district includes much of the South Side of Chicago, and continues southwest to Joliet.
From 2003 to early 2013 it ext ...
in the
United States House of Representatives to four-term incumbent
Bobby Rush
Bobby Lee Rush (born November 23, 1946) is an American politician, activist and pastor who served as the U.S. representative for for three decades. A civil rights activist during the 1960s, Rush co-founded the Illinois chapter of the Black Pant ...
by a margin of two to one.
In January 2003, Obama became chairman of the Illinois Senate's Health and Human Services Committee when Democrats, after a decade in the minority, regained a majority. He sponsored and led unanimous, bipartisan passage of legislation to monitor
racial profiling
Racial profiling or ethnic profiling is the act of suspecting, targeting or discriminating against a person on the basis of their ethnicity, religion or nationality, rather than on individual suspicion or available evidence. Racial profiling involv ...
by requiring police to record the race of drivers they detained, and legislation making Illinois the first state to mandate videotaping of homicide interrogations.
During his 2004 general election campaign for the U.S. Senate, police representatives credited Obama for his active engagement with police organizations in enacting
death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that ...
reforms. Obama resigned from the Illinois Senate in November 2004 following his election to the U.S. Senate.
2004 U.S. Senate campaign

In May 2002, Obama commissioned a poll to assess his prospects in a 2004 U.S. Senate race. He created a campaign committee, began raising funds, and lined up political media consultant
David Axelrod by August 2002. Obama formally announced his candidacy in January 2003.
Obama was an early opponent of the
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
administration's
2003 invasion of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq was a United States-led invasion of the Ba'athist Iraq, Republic of Iraq and the first stage of the Iraq War. The invasion phase began on 19 March 2003 (air) and 20 March 2003 (ground) and lasted just over one mont ...
. On October 2, 2002, the day President Bush and Congress agreed on the
joint resolution
In the United States Congress, a joint resolution is a legislative measure that requires passage by the Senate and the House of Representatives and is presented to the President for their approval or disapproval. Generally, there is no legal differ ...
authorizing the
Iraq War,
Obama addressed the first high-profile Chicago
anti-Iraq War rally,
and spoke out against the war.
He addressed another anti-war rally in March 2003 and told the crowd "it's not too late" to stop the war.
Decisions by Republican incumbent
Peter Fitzgerald and his Democratic predecessor
Carol Moseley Braun
Carol Elizabeth Moseley Braun, also sometimes Moseley-Braun (born August 16, 1947), is a former U.S. Senator, an American diplomat, politician, and lawyer who represented Illinois in the United States Senate from 1993 to 1999. Prior to her Senate ...
to not participate in the election resulted in wide-open Democratic and Republican primary contests involving 15 candidates. In the March 2004 primary election, Obama won in an unexpected landslide—which overnight made him a rising star within the
national Democratic Party, started speculation about a presidential future, and led to the reissue of his memoir, ''Dreams from My Father''.
In July 2004, Obama delivered the keynote address at the
2004 Democratic National Convention
The 2004 Democratic National Convention convened from July 26 to 29, 2004 at the FleetCenter (now the TD Garden) in Boston, Massachusetts, and nominated Senator John Kerry from Massachusetts for president and Senator John Edwards from North ...
, seen by nine million viewers. His speech was well received and elevated his status within the Democratic Party.
Obama's expected opponent in the general election, Republican primary winner
Jack Ryan, withdrew from the race in June 2004. Six weeks later,
Alan Keyes
Alan Lee Keyes (born August 7, 1950) is an American politician, political activist, author, and perennial candidate who served as the Assistant Secretary of State for International Organization Affairs from 1985 to 1987. A member of the Repub ...
accepted the Republican nomination to replace Ryan. In the
November 2004 general election, Obama won with 70 percent of the vote, the largest margin of victory for a Senate candidate in Illinois history.
He took 92 of the state's 102 counties, including several where Democrats traditionally do not do well.
U.S. Senate (2005–2008)

Obama was sworn in as a senator on January 3, 2005, becoming the only Senate member of the
Congressional Black Caucus
The Congressional Black Caucus (CBC) is a caucus made up of most African-American members of the United States Congress. Representative Karen Bass from California chaired the caucus from 2019 to 2021; she was succeeded by Representative Joyce B ...
. He introduced two initiatives that bore his name: Lugar–Obama, which expanded the
Nunn–Lugar Cooperative Threat Reduction
As the collapse of the Soviet Union appeared imminent, the United States and their NATO allies grew concerned of the risk of nuclear weapons held in the Soviet republics falling into enemy hands. The Cooperative Threat Reduction (CTR) program was ...
concept to conventional weapons; and the
Federal Funding Accountability and Transparency Act of 2006
The Federal Funding Accountability and Transparency Act of 2006 (S. 2590) is an Act of Congress that requires the full disclosure to the public of all entities or organizations receiving federal funds beginning in fiscal year (FY) 2007. The websit ...
, which authorized the establishment of USAspending.gov, a web search engine on federal spending. On June 3, 2008, Senator Obama—along with Senators
Tom Carper,
Tom Coburn, and
John McCain—introduced follow-up legislation: Strengthening Transparency and Accountability in Federal Spending Act of 2008. He also
cosponsored the
Secure America and Orderly Immigration Act
Secure America and Orderly Immigration Act ("McCain-Kennedy Bill," ) was an immigration reform bill introduced in the United States Senate on May 12, 2005 by Senators John McCain and Ted Kennedy. It was the first of its kind since the early 2000s ...
.
In December 2006, President Bush signed into law the
Democratic Republic of the Congo Relief, Security, and Democracy Promotion Act, marking the first federal legislation to be enacted with Obama as its primary sponsor. In January 2007, Obama and Senator Feingold introduced a corporate jet provision to the
Honest Leadership and Open Government Act, which was signed into law in September 2007.

Later in 2007, Obama sponsored an amendment to the Defense Authorization Act to add safeguards for personality-disorder military discharges. This amendment passed the full Senate in the spring of 2008. He sponsored the
Iran Sanctions Enabling Act supporting divestment of state pension funds from Iran's oil and gas industry, which was never enacted but later incorporated in the
Comprehensive Iran Sanctions, Accountability, and Divestment Act of 2010; and co-sponsored legislation to reduce risks of nuclear terrorism.
Obama also sponsored a Senate amendment to the
State Children's Health Insurance Program
The Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) – formerly known as the State Children's Health Insurance Program (SCHIP) – is a program administered by the United States Department of Health and Human Services that provides matching funds to ...
, providing one year of job protection for family members caring for soldiers with combat-related injuries.
Obama held assignments on the Senate Committees for
Foreign Relations,
Environment and Public Works and
Veterans' Affairs
Veterans' affairs is an area of public policy concerned with relations between a government and its communities of military veterans. Some jurisdictions have a designated government agency or department, a Department of Veterans' Affairs, Minist ...
through December 2006. In January 2007, he left the Environment and Public Works committee and took additional assignments with
Health, Education, Labor and Pensions and
Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs. He also became Chairman of the Senate's subcommittee on
European Affairs
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. As a member of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, Obama made official trips to Eastern Europe, the Middle East, Central Asia and Africa. He met with
Mahmoud Abbas before Abbas became
President of the Palestinian National Authority
The president of the Palestinian National Authority ( ar, رئيس السلطة الوطنية الفلسطينية) is the highest-ranking political position (equivalent to head of state) in the Palestinian National Authority (PNA). The presiden ...
, and gave a speech at the
University of Nairobi in which he condemned corruption within the Kenyan government.
Obama
resigned his Senate seat on November 16, 2008, to focus on his transition period for the presidency.
Presidential campaigns
2008

On February 10, 2007, Obama announced his candidacy for President of the
United States in front of the
Old State Capitol building in
Springfield, Illinois
Springfield is the capital of the U.S. state of Illinois and the county seat and largest city of Sangamon County. The city's population was 114,394 at the 2020 census, which makes it the state's seventh most-populous city, the second largest o ...
.
The choice of the announcement site was viewed as symbolic, as it was also where
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
delivered his
"House Divided" speech in 1858.
Obama emphasized issues of rapidly ending the
Iraq War, increasing
energy independence, and
reforming the health care system.
Numerous candidates entered the
Democratic Party presidential primaries. The field narrowed to Obama and Senator
Hillary Clinton after early contests, with the race remaining close throughout the primary process, but with Obama gaining a steady lead in pledged
delegates due to better long-range planning, superior fundraising, dominant organizing in
caucus
A caucus is a meeting of supporters or members of a specific political party or movement. The exact definition varies between different countries and political cultures.
The term originated in the United States, where it can refer to a meeting ...
states, and better exploitation of delegate allocation rules.
On June 2, 2008, Obama had received enough votes to clinch his election. After an initial hesitation to concede, on June 7, Clinton ended her campaign and endorsed Obama.
On August 23, 2008, Obama announced his
selection of
Delaware Senator
Joe Biden as his vice presidential running mate.
Obama selected Biden from a field speculated to include former Indiana Governor and Senator
Evan Bayh and Virginia Governor
Tim Kaine
Timothy Michael Kaine (; born February 26, 1958) is an American lawyer and politician serving as the junior United States senator from Virginia since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as the 38th lieutenant governor of Virgi ...
.
At the
Democratic National Convention in
Denver, Colorado, Hillary Clinton called for her supporters to endorse Obama, and she and
Bill Clinton gave convention speeches in his support. Obama delivered his acceptance speech at
Invesco Field at Mile High
Empower Field at Mile High (previously known as Broncos Stadium at Mile High, Invesco Field at Mile High and Sports Authority Field at Mile High, and commonly known as Mile High, New Mile High or Mile High Stadium) is an American football stadium ...
stadium to a crowd of about eighty-four thousand; the speech was viewed by over three million people worldwide.
During both the primary process and the general election, Obama's campaign set numerous fundraising records, particularly in the quantity of small donations.
On June 19, 2008, Obama became the first major-party presidential candidate to turn down
public financing
Public finance is the study of the role of the government in the economy. It is the branch of economics that assesses the government revenue and government expenditure of the public authorities and the adjustment of one or the other to achie ...
in the general election since the system was created in 1976.
was nominated as the Republican candidate, and he selected
Sarah Palin as his running mate. Obama and McCain engaged in three
presidential debates in September and October 2008.
On November 4, Obama won the presidency with 365
electoral votes to 173 received by McCain.
Obama won 52.9 percent of the
popular vote
Popularity or social status is the quality of being well liked, admired or well known to a particular group.
Popular may also refer to:
In sociology
* Popular culture
* Popular fiction
* Popular music
* Popular science
* Populace, the total ...
to McCain's 45.7 percent. He became the first African-American to be elected president.
[
*
* ] Obama delivered
his victory speech before hundreds of thousands of supporters in Chicago's
Grant Park.
He is one of the three United States senators moved directly from the U.S. Senate to the White House, the others are
Warren G. Harding and
John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination i ...
.
2012

On April 4, 2011, Obama filed election papers with the
Federal Election Commission
The Federal Election Commission (FEC) is an independent regulatory agency of the United States whose purpose is to enforce campaign finance law in United States federal elections. Created in 1974 through amendments to the Federal Election Camp ...
and then announced his reelection campaign for 2012 in a video titled "It Begins with Us" that he posted on his website. As the incumbent president, he ran virtually unopposed in the
Democratic Party presidential primaries,
and on April 3, 2012, Obama secured the 2778
convention delegates needed to win the Democratic nomination.
At the
Democratic National Convention in
Charlotte, North Carolina
Charlotte ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of North Carolina. Located in the Piedmont region, it is the county seat of Mecklenburg County. The population was 874,579 at the 2020 census, making Charlotte the 16th-most populo ...
, Obama and
Joe Biden were formally nominated by former President
Bill Clinton as the Democratic Party candidates for president and vice president in the general election. Their main opponents were Republicans
Mitt Romney, the former governor of Massachusetts, and Representative
Paul Ryan of Wisconsin.
On November 6, 2012, Obama won 332
electoral votes, exceeding the 270 required for him to be reelected as president. With 51.1 percent of the popular vote,
Obama became the first Democratic president since
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As th ...
to win the
majority of the popular vote twice. Obama addressed supporters and volunteers at Chicago's
McCormick Place
McCormick Place is the largest convention center in North America. It consists of four interconnected buildings and one indoor arena sited on and near the shore of Lake Michigan, about south of downtown Chicago, Illinois, United States. McCorm ...
after his reelection and said: "Tonight you voted for action, not politics as usual. You elected us to focus on your jobs, not ours. And in the coming weeks and months, I am looking forward to reaching out and working with leaders of both parties."
Presidency (2009–2017)

First 100 days

The
inauguration of Barack Obama as the 44th president took place on January 20, 2009. In his first few days in office, Obama issued
executive orders and
presidential memoranda
A presidential memorandum is a type of directive issued by the president of the United States to manage and govern the actions, practices, and policies of the various departments and agencies found under the executive branch of the United States ...
directing the U.S. military to develop plans to withdraw troops from Iraq. He ordered the closing of the
Guantanamo Bay detention camp, but Congress prevented the closure by refusing to appropriate the required funds and preventing moving any Guantanamo detainee. Obama reduced the secrecy given to presidential records. He also revoked President
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
's restoration of President
Ronald Reagan's
Mexico City policy which prohibited federal aid to international
family planning organizations that perform or provide counseling about
abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregnan ...
.
Domestic policy
The first bill signed into law by Obama was the
Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act of 2009
The Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act of 2009 (, ) is a landmark federal statute in the United States that was the first bill signed into law by U.S. President Barack Obama on January 29, 2009. The act amends Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 an ...
, relaxing the
statute of limitations for equal-pay lawsuits. Five days later, he signed the reauthorization of the
State Children's Health Insurance Program
The Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) – formerly known as the State Children's Health Insurance Program (SCHIP) – is a program administered by the United States Department of Health and Human Services that provides matching funds to ...
to cover an additional four million uninsured children. In March 2009, Obama reversed a Bush-era policy that had limited funding of
embryonic stem cell research and pledged to develop "strict guidelines" on the research.

Obama appointed two women to serve on the Supreme Court in the first two years of his presidency. He nominated
Sonia Sotomayor
Sonia Maria Sotomayor (, ; born June 25, 1954) is an American lawyer and jurist who serves as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. She was nominated by President Barack Obama on May 26, 2009, and has served since ...
on May 26, 2009, to replace retiring
Associate Justice
Associate justice or associate judge (or simply associate) is a judicial panel member who is not the chief justice in some jurisdictions. The title "Associate Justice" is used for members of the Supreme Court of the United States and some state ...
David Souter; she was confirmed on August 6, 2009, becoming the first Supreme Court Justice of
Hispanic descent. Obama nominated
Elena Kagan on May 10, 2010, to replace retiring Associate Justice
John Paul Stevens. She was confirmed on August 5, 2010, bringing the number of women sitting simultaneously on the Court to three for the first time in American history.
On March 11, 2009, Obama created the
White House Council on Women and Girls, which formed part of the
Office of Intergovernmental Affairs
The White House Office of Intergovernmental Affairs is a unit of the White House Office, within the Executive Office of the President. It serves as the primary liaison between the White House and state, county (or county-equivalent), local, and ...
, having been established by with a broad mandate to advise him on issues relating to the welfare of American women and girls. The council was chaired by
Senior Advisor to the President
Senior Advisor to the President is a title used by high-ranking political advisors to the president of the United States. White House senior advisors are senior members of the White House Office. The title has been formally used since 1993.
Res ...
Valerie Jarrett
Valerie June Jarrett ( Bowman; born November 14, 1956) is an American businesswoman and former government official. She currently serves as the Chief Executive Officer of the Obama Foundation. She previously served as the senior advisor to U.S. Pr ...
. Obama also established the
White House Task Force to Protect Students from Sexual Assault through a government memorandum on January 22, 2014, with a broad mandate to advise him on issues relating to sexual assault on college and university campuses throughout the United States. The co-chairs of the Task Force were Vice President Joe Biden and Jarrett. The Task Force was a development out of the White House Council on Women and Girls and
Office of the Vice President of the United States
The Office of the Vice President includes personnel who directly support or advise the vice president of the United States. The office is headed by the chief of staff to the vice president of the United States, currently Lorraine Voles. The off ...
, and prior to that the 1994
Violence Against Women Act first drafted by Biden.
In a
major space policy speech in April 2010, Obama announced a planned change in direction at
NASA, the U.S. space agency. He ended plans for a return of
human spaceflight
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be ...
to the moon and development of the
Ares I
Ares I was the crew launch vehicle that was being developed by NASA as part of the Constellation program. The name "Ares" refers to the Greek deity Ares, who is identified with the Roman god Mars. Ares I was originally known as the "Crew Launch ...
rocket,
Ares V
The Ares V (formerly known as the Cargo Launch Vehicle or CaLV) was the planned cargo launch component of the cancelled NASA Constellation program, which was to have replaced the Space Shuttle after its retirement in 2011. Ares V was also pla ...
rocket and
Constellation program
The Constellation program (abbreviated CxP) was a crewed spaceflight program developed by NASA, the space agency of the United States, from 2005 to 2009. The major goals of the program were "completion of the International Space Station" and a ...
, in favor of funding
Earth science projects, a new rocket type, research and development for an eventual crewed mission to Mars, and ongoing missions to the
International Space Station.

On January 16, 2013, one month after the
Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting
The Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting occurred on December 14, 2012, in Newtown, Connecticut, United States, when 20-year-old Adam Lanza shot and killed 26 people. Twenty of the victims were children between six and seven years old, and th ...
, Obama signed 23 executive orders and outlined a series of sweeping proposals regarding
gun control. He urged Congress to reintroduce an
expired ban on military-style
assault weapons
In the United States, ''assault weapon'' is a controversial term used to define firearms with specified characteristics. The definition varies among regulating jurisdictions, but usually includes semi-automatic firearms with a detachable magaz ...
, such as those used in several recent mass shootings, impose limits on ammunition magazines to 10 rounds, introduce background checks on all gun sales, pass a ban on possession and sale of armor-piercing bullets, introduce harsher penalties for gun-traffickers, especially unlicensed dealers who buy arms for criminals and approving the appointment of the head of the federal
Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives
The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (BATFE), commonly referred to as the ATF, is a domestic law enforcement agency within the United States Department of Justice. Its responsibilities include the investigation and prevent ...
for the first time since 2006. On January 5, 2016, Obama announced new executive actions extending background check requirements to more gun sellers.
In a 2016 editorial in ''The New York Times'', Obama compared the struggle for what he termed "common-sense gun reform" to
women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the right of women to vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to grant women the right to vot ...
and other
civil rights movements in American history. On January 5, 2016, Obama announced new executive actions extending background check requirements to more gun sellers.
In 2011, Obama signed a four-year renewal of the Patriot Act. Following the
2013 global surveillance disclosures
Thirteen or 13 may refer to:
* 13 (number), the natural number following 12 and preceding 14
* One of the years 13 BC, AD 13, 1913, 2013
Music
* 13AD (band), an Indian classic and hard rock band
Albums
* ''13'' (Black Sabbath album), 2013
* ...
by
whistleblower Edward Snowden, Obama condemned the leak as unpatriotic,
but called for increased restrictions on the
National Security Agency (NSA) to address violations of privacy. Obama continued and expanded surveillance programs set up by George W. Bush, while implementing some reforms.
He supported legislation that would have limited the NSA's ability to collect phone records in bulk under a single program and supported bringing more transparency to the
Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court
The United States Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court (FISC), also called the FISA Court, is a U.S. federal court established under the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act of 1978 (FISA) to oversee requests for surveillance warrants aga ...
(FISC).
Racial issues
In his speeches as president, Obama did not make more overt references to race relations than his predecessors, but according to one study, he implemented stronger policy action on behalf of African-Americans than any president since the Nixon era.
Following Obama's election, many pondered the existence of a "
postracial America."
However, lingering racial tensions quickly became apparent,
and many African-Americans expressed outrage over what they saw as an intense racial animosity directed at Obama.
The
acquittal
In common law jurisdictions, an acquittal certifies that the accused is free from the charge of an offense, as far as criminal law is concerned. The finality of an acquittal is dependent on the jurisdiction. In some countries, such as th ...
of
George Zimmerman following the
killing of Trayvon Martin
On the night of February 26, 2012, in Sanford, Florida, United States, George Zimmerman fatally shot Trayvon Martin, a 17-year-old African-American boy. Zimmerman, a 28-year-old man of mixed race, was the neighborhood watch coordinator for ...
sparked national outrage, leading to Obama giving a speech in which he noted that "Trayvon Martin could have been me 35 years ago."
The shooting of
Michael Brown in
Ferguson, Missouri sparked a wave of protests.
These and other events led to the birth of the
Black Lives Matter
Black Lives Matter (abbreviated BLM) is a decentralized political and social movement that seeks to highlight racism, discrimination, and racial inequality experienced by black people. Its primary concerns are incidents of police brutali ...
movement, which campaigns against violence and
systemic racism
Institutional racism, also known as systemic racism, is a form of racism that is embedded in the laws and regulations of a society or an organization. It manifests as discrimination in areas such as criminal justice, employment, housing, healt ...
toward
black people
Black is a racialized classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin; in certain countries, often in ...
.
Though Obama entered office reluctant to talk about race, by 2014 he began openly discussing the disadvantages faced by many members of minority groups.
Several incidents during Obama's presidency generated disapproval from the
African-American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ensla ...
community and/or with law enforcement, and Obama sought to build trust between law enforcement officials and civil rights activists, with mixed results. Some in law enforcement criticized Obama's condemnation of racial bias after incidents in which police action led to the death of African-American men, while some racial justice activists criticized Obama's expressions of empathy for the police.
In a March 2016 Gallup poll, nearly one third of Americans said they worried "a great deal" about race relations, a higher figure than in any previous Gallup poll since 2001.
LGBT rights and same-sex marriage
On October 8, 2009, Obama signed the
Matthew Shepard and James Byrd Jr. Hate Crimes Prevention Act
The Matthew Shepard and James Byrd Jr. Hate Crimes Prevention Act is a landmark United States federal law, passed on October 22, 2009, and signed into law by President Barack Obama on October 28, 2009, as a rider to the National Defense Aut ...
, a measure that expanded the
1969 United States federal hate-crime law to include crimes motivated by a victim's actual or perceived gender, sexual orientation, gender identity, or disability. On October 30, 2009, Obama lifted the ban on travel to the United States by those infected with
HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
. The lifting of the ban was celebrated by
Immigration Equality
Immigration Equality is a United States nonprofit organization founded in 1994. Based in New York, it both advocates for and directly represents LGBTQ and HIV-positive people, HIV-positive people in the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services ...
. On December 22, 2010, Obama signed the
Don't Ask, Don't Tell Repeal Act of 2010
The Don't Ask, Don't Tell Repeal Act of 2010 (, ) is a landmark United States federal statute enacted in December 2010 that established a process for ending the "don't ask, don't tell" (DADT) policy (), thus allowing gay, lesbian, and bisex ...
, which fulfilled a promise made in the 2008 presidential campaign to end the
don't ask, don't tell
"Don't ask, don't tell" (DADT) was the official United States policy on military service of non-heterosexual people, instituted during the Clinton administration. The policy was issued under Department of Defense Directive 1304.26 on Decembe ...
policy of 1993 that had prevented gay and lesbian people from serving openly in the
United States Armed Forces. In 2016, the Pentagon ended the policy that barred
transgender people from serving openly in the military.

As a candidate for the Illinois state senate in 1996, Obama stated he favored legalizing
same-sex marriage.
During his Senate run in 2004, he said he supported civil unions and domestic partnerships for same-sex partners but opposed same-sex marriages.
In 2008, he reaffirmed this position by stating "I believe marriage is between a man and a woman. I am not in favor of gay marriage." On May 9, 2012, shortly after the official launch of his campaign for re-election as president, Obama said his views had evolved, and he publicly affirmed his personal support for the legalization of same-sex marriage, becoming the first sitting U.S. president to do so.
During his second
inaugural address on January 21, 2013,
Obama became the first U.S. president in office to call for full equality for gay Americans, and the first to mention
gay rights
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.
Notably, , ...
or the word "gay" in an inaugural address. In 2013, the Obama administration filed briefs that urged the
Supreme Court to rule in favor of same-sex couples in the cases of ''
Hollingsworth v. Perry
''Hollingsworth v. Perry'' was a series of United States federal court cases that re-legalized same-sex marriage in the state of California. The case began in 2009 in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California, which found th ...
'' (regarding
same-sex marriage)
and ''
United States v. Windsor
''United States v. Windsor'', 570 U.S. 744 (2013), is a landmark United States Supreme Court civil rights case concerning same-sex marriage. The Court held that Section 3 of the Defense of Marriage Act (DOMA), which denied federal recognition ...
'' (regarding the
Defense of Marriage Act).
Economic policy
On February 17, 2009, Obama signed the
American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA) (), nicknamed the Recovery Act, was a stimulus package enacted by the 111th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama in February 2009. Developed in response to the Gr ...
, a $787billion (equivalent to $ billion in )
economic stimulus package aimed at helping the economy recover from the
deepening worldwide recession. The act includes increased federal spending for health care, infrastructure, education, various tax breaks and
incentives
In general, incentives are anything that persuade a person to alter their behaviour. It is emphasised that incentives matter by the basic law of economists and the laws of behaviour, which state that higher incentives amount to greater levels of ...
, and direct assistance to individuals.
In March 2009, Obama's
Treasury Secretary,
Timothy Geithner
Timothy Franz Geithner (; born August 18, 1961) is a former American central banker who served as the 75th United States Secretary of the Treasury under President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013. He was the President of the Federal Reserve Bank ...
, took further steps to manage the
financial crisis
A financial crisis is any of a broad variety of situations in which some financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with banking panics, and man ...
, including introducing the
Public–Private Investment Program for Legacy Assets, which contains provisions for buying up to $2trillion in depreciated real estate assets.

Obama intervened in the
troubled automotive industry in March 2009, renewing loans for
General Motors (GM) and
Chrysler
Stellantis North America (officially FCA US and formerly Chrysler ()) is one of the " Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. It is the American subsidiary of the multinational automotiv ...
to continue operations while reorganizing. Over the following months the White House set terms for both firms' bankruptcies, including the
sale of Chrysler to Italian automaker
Fiat and a
reorganization of GM giving the U.S. government a temporary 60 percent equity stake in the company. In June 2009, dissatisfied with the pace of economic stimulus, Obama called on his cabinet to accelerate the investment.
He signed into law the
Car Allowance Rebate System
The Car Allowance Rebate System (CARS), colloquially known as "cash for clunkers", was a $3 billion U.S. federal scrappage program intended to provide economic incentives to U.S. residents to purchase a new, more fuel-efficient vehicle whe ...
, known colloquially as "Cash for Clunkers", which temporarily boosted the economy.
The Bush and Obama administrations authorized spending and loan guarantees from the
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after ...
and the
Department of the Treasury. These guarantees totaled about $11.5trillion, but only $3trillion had been spent by the end of November 2009. On August 2, 2011, after a lengthy congressional debate over whether to raise the nation's debt limit, Obama signed the bipartisan
Budget Control Act of 2011
The Budget Control Act of 2011 () is a federal statute enacted by the 112th United States Congress and signed into law by US President Barack Obama on August 2, 2011. The Act brought conclusion to the 2011 US debt-ceiling crisis.
The law in ...
. The legislation enforced limits on discretionary spending until 2021, established a procedure to increase the debt limit, created a Congressional Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction to propose further deficit reduction with a stated goal of achieving at least $1.5trillion in budgetary savings over 10 years, and established automatic procedures for reducing spending by as much as $1.2trillion if legislation originating with the new joint select committee did not achieve such savings. By passing the legislation, Congress was able to prevent a
U.S. government default
Default may refer to:
Law
* Default (law), the failure to do something required by law
** Default (finance), failure to satisfy the terms of a loan obligation or failure to pay back a loan
** Default judgment, a binding judgment in favor of ei ...
on its obligations.
The unemployment rate rose in 2009, reaching a peak in October at 10.0 percent and averaging 10.0 percent in the fourth quarter. Following a decrease to 9.7 percent in the first quarter of 2010, the unemployment rate fell to 9.6 percent in the second quarter, where it remained for the rest of the year.
Between February and December 2010, employment rose by 0.8 percent, which was less than the average of 1.9 percent experienced during comparable periods in the past four employment recoveries.
By November 2012, the unemployment rate fell to 7.7 percent, decreasing to 6.7 percent in the last month of 2013. During 2014, the unemployment rate continued to decline, falling to 6.3 percent in the first quarter. GDP growth returned in the third quarter of 2009, expanding at a rate of 1.6 percent, followed by a 5.0 percent increase in the fourth quarter.
Growth continued in 2010, posting an increase of 3.7 percent in the first quarter, with lesser gains throughout the rest of the year.
In July 2010, the
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after ...
noted that economic activity continued to increase, but its pace had slowed, and chairman
Ben Bernanke
Ben Shalom Bernanke ( ; born December 13, 1953) is an American economist who served as the 14th chairman of the Federal Reserve from 2006 to 2014. After leaving the Fed, he was appointed a distinguished fellow at the Brookings Institution. Duri ...
said the economic outlook was "unusually uncertain." Overall, the economy expanded at a rate of 2.9 percent in 2010.

The
Congressional Budget Office
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) is a federal agency within the legislative branch of the United States government that provides budget and economic information to Congress.
Inspired by California's Legislative Analyst's Office that manages ...
(CBO) and a broad range of economists credit Obama's stimulus plan for economic growth.
The CBO released a report stating that the stimulus bill increased employment by 1–2.1million,
while conceding that "it is impossible to determine how many of the reported jobs would have existed in the absence of the stimulus package."
Although an April 2010, survey of members of the
National Association for Business Economics showed an increase in job creation (over a similar January survey) for the first time in two years, 73 percent of 68 respondents believed the stimulus bill has had no impact on employment. The economy of the United States has grown faster than the other original
NATO members by a wider margin under President Obama than it has anytime since the end of
World War II. The
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
credits the much faster growth in the United States to the stimulus plan of the U.S. and the austerity measures in the European Union.
Within a month of the
2010 midterm elections
The 2010 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010, in the middle of Democratic President Barack Obama's first term. Republicans ended unified Democratic control of Congress and the presidency by winning a majority in the H ...
, Obama announced a compromise deal with the Congressional Republican leadership that included a temporary, two-year extension of the
2001 and 2003 income tax rates, a one-year
payroll tax
Payroll taxes are taxes imposed on employers or employees, and are usually calculated as a percentage of the salaries that employers pay their employees. By law, some payroll taxes are the responsibility of the employee and others fall on the em ...
reduction, continuation of unemployment benefits, and a new rate and exemption amount for
estate taxes
An inheritance tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property of a person who has died, whereas an estate tax is a levy on the estate (money and property) of a person who has died.
International tax law distinguishes between an es ...
. The compromise overcame opposition from some in both parties, and the resulting $858billion (equivalent to $ trillion in )
Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization, and Job Creation Act of 2010 passed with bipartisan majorities in both houses of Congress before Obama signed it on December 17, 2010.
In December 2013, Obama declared that growing
income inequality is a "defining challenge of our time" and called on Congress to bolster the safety net and raise wages. This came on the heels of the
nationwide strikes of fast-food workers and
Pope Francis' criticism of inequality and
trickle-down economics
Trickle-down economics is a term used in critical references to economic policies that favor the upper income brackets, corporations, and individuals with substantial wealth or capital. In recent history, the term has been used by critics of ...
. Obama urged Congress to ratify a 12-nation free trade pact called the
Trans-Pacific Partnership
The Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), or Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement, was a highly contested proposed trade agreement between 12 Pacific Rim economies, Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Pe ...
.
Environmental policy

On April 20, 2010, an explosion destroyed an offshore
drilling rig at the
Macondo Prospect
The Macondo Prospect (Mississippi Canyon Block 252, abbreviated MC252) is an oil and gas prospect in the United States Exclusive Economic Zone of the Gulf of Mexico, off the coast of Louisiana. The prospect was the site of the ''Deepwater Horiz ...
in the
Gulf of Mexico, causing a
major sustained oil leak. Obama visited the Gulf, announced a federal investigation, and formed a bipartisan commission to recommend new safety standards, after a review by
Secretary of the Interior Secretary of the Interior may refer to:
* Secretary of the Interior (Mexico)
* Interior Secretary of Pakistan
* Secretary of the Interior and Local Government (Philippines)
* United States Secretary of the Interior
See also
*Interior ministry
An ...
Ken Salazar and concurrent Congressional hearings. He then announced a six-month moratorium on new
deepwater drilling
Deepwater drilling, or deep well drilling, is the process of creating holes in the Earth's crust using a drilling rig for oil extraction under the deep sea. There are approximately 3400 deepwater wells in the Gulf of Mexico with depths greater t ...
permits and leases, pending regulatory review. As multiple efforts by BP failed, some in the media and public expressed confusion and criticism over various aspects of the incident, and stated a desire for more involvement by Obama and the federal government. Prior to the oil spill, on March 31, 2010, Obama ended a ban on oil and gas drilling along the majority of the
East Coast of the United States and along the coast of
northern Alaska
Arctic Alaska or Far North Alaska is a region of the U.S. state of Alaska generally referring to the northern areas on or close to the Arctic Ocean.
It commonly includes North Slope Borough, Northwest Arctic Borough, Nome Census Area, and is ...
in an effort to win support for an energy and climate bill and to reduce foreign imports of oil and gas.
In July 2013, Obama expressed reservations and said he "would reject the
Keystone XL pipeline if it increased carbon pollution
rgreenhouse emissions." On February 24, 2015, Obama vetoed a bill that would have authorized the pipeline. It was the third veto of Obama's presidency and his first major veto.
In December 2016, Obama permanently banned new offshore oil and gas drilling in most United States-owned waters in the
Atlantic and
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
s using the 1953 Outer Continental Shelf Act.
Obama emphasized the
conservation of
federal lands
Federal lands are lands in the United States owned by the federal government. Pursuant to the Property Clause of the United States Constitution ( Article 4, section 3, clause 2), Congress has the power to retain, buy, sell, and regulate federal ...
during his term in office. He used his power under the
Antiquities Act to create 25 new
national monuments during his presidency and expand four others, protecting a total of of federal lands and waters, more than any other U.S. president.
Health care reform
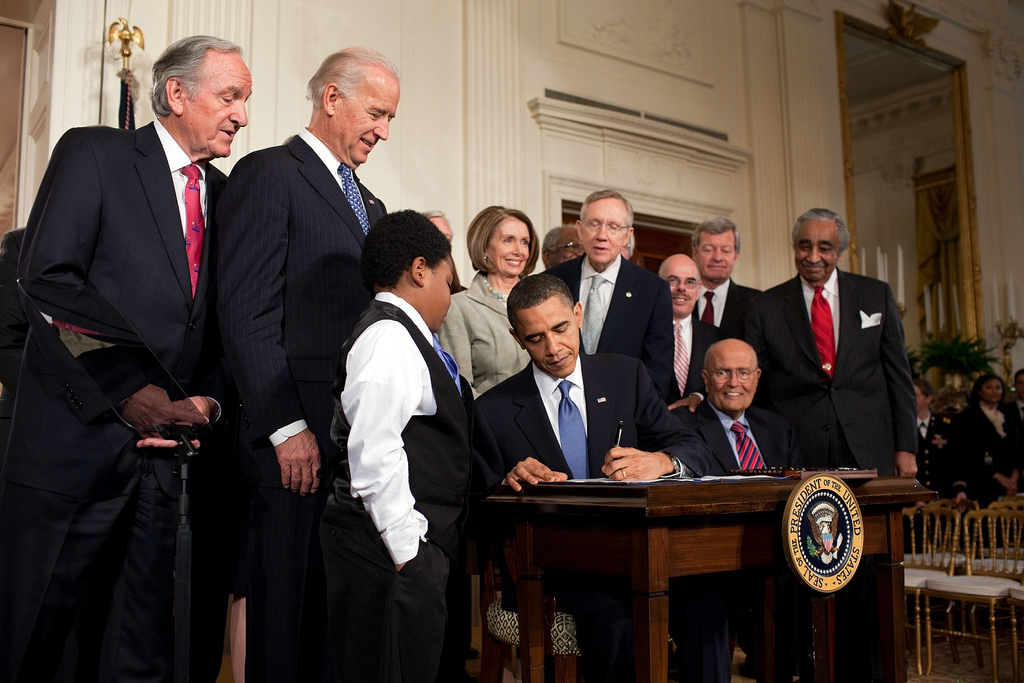

Obama called for
Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
to pass legislation reforming
health care in the United States
The United States far outspends any other nation on health care, measured both in ''per capita'' spending and as a percentage of GDP. Despite this, the country has significantly worse healthcare outcomes when compared to peer nations. The Un ...
, a key campaign promise and a top legislative goal.
He proposed an expansion of health insurance coverage to cover the uninsured, cap premium increases, and allow people to retain their coverage when they leave or change jobs. His proposal was to spend $900billion over ten years and include a government insurance plan, also known as the
public option
The public health insurance option, also known as the public insurance option or the public option, is a proposal to create a government-run health insurance agency that would compete with other private health insurance companies within the United ...
, to compete with the corporate insurance sector as a main component to lowering costs and improving quality of health care. It would also make it illegal for insurers to drop sick people or deny them coverage for
pre-existing conditions, and require every American to carry health coverage. The plan also includes medical spending cuts and taxes on insurance companies that offer expensive plans.
On July 14, 2009, House Democratic leaders introduced a 1,017-page plan for overhauling the U.S. health care system, which Obama wanted Congress to approve by the end of 2009.
After public debate during the Congressional summer recess of 2009, Obama delivered
a speech to a joint session of Congress on September 9 where he addressed concerns over the proposals. In March 2009, Obama lifted a ban on using federal funds for stem cell research.
On November 7, 2009, a health care bill featuring the public option was passed in the House.
On December 24, 2009, the Senate passed its own bill—without a public option—on a party-line vote of 60–39. On March 21, 2010, the
Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) passed by the Senate in December was passed in the House by a vote of 219 to 212. Obama signed the bill into law on March 23, 2010.
The ACA includes
health-related provisions, most of which took effect in 2014, including expanding
Medicaid eligibility for people making up to 133 percentof the
federal poverty level
In the United States, poverty has both social and political implications. In 2020, there were 37.2 million people in poverty. Some of the many causes include income inequality, inflation, unemployment, debt traps and poor education.Western, ...
(FPL) starting in 2014,
subsidizing insurance premiums for people making up to 400 percentof the FPL ($88,000 for family of four in 2010) so their maximum "out-of-pocket" payment for annual premiums will be from 2 percent to 9.5 percent of income, providing incentives for businesses to provide health care benefits, prohibiting denial of coverage and denial of claims based on pre-existing conditions, establishing
health insurance exchanges, prohibiting annual coverage caps, and support for medical research. According to White House and CBO figures, the maximum share of income that enrollees would have to pay would vary depending on their income relative to the federal poverty level.

The costs of these provisions are offset by taxes, fees, and cost-saving measures, such as new Medicare taxes for those in high-income
brackets, taxes on
indoor tanning
Indoor tanning involves using a device that emits ultraviolet radiation to produce a cosmetic tan. Typically found in tanning salons, gyms, spas, hotels, and sporting facilities, and less often in private residences, the most common device is a h ...
, cuts to the
Medicare Advantage
Medicare Advantage (Medicare Part C, MA) is a capitated program for providing Medicare benefits in the United States. Under Part C, Medicare pays a private-sector health insurer a fixed payment. The insurer then pays for the health care expense ...
program in favor of traditional Medicare, and fees on medical devices and pharmaceutical companies; there is also a tax penalty for those who do not obtain health insurance, unless they are exempt due to low income or other reasons. In March 2010, the CBO estimated that the net effect of both laws will be a reduction in the federal deficit by $143billion over the first decade.
The law faced several legal challenges, primarily based on the argument that an individual mandate requiring Americans to buy health insurance was unconstitutional. On June 28, 2012, the Supreme Court ruled by a 5–4 vote in ''
National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius
''National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius'', 567 U.S. 519 (2012), was a landmark United States Supreme Court decision in which the Court upheld Congress's power to enact most provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Car ...
'' that the mandate was constitutional under the U.S. Congress's taxing authority.
In ''
Burwell v. Hobby Lobby
''Burwell v. Hobby Lobby Stores, Inc.'', 573 U.S. 682 (2014), is a landmark decision in United States corporate law by the United States Supreme Court allowing privately held for-profit corporations to be exempt from a regulation its owners relig ...
'' the Court ruled that "closely-held" for-profit corporations could be exempt on religious grounds under the
Religious Freedom Restoration Act
The Religious Freedom Restoration Act of 1993, Pub. L. No. 103-141, 107 Stat. 1488 (November 16, 1993), codified at through (also known as RFRA, pronounced "rifra"), is a 1993 United States federal law that "ensures that interests in religiou ...
from regulations adopted under the ACA that would have required them to pay for insurance that covered certain contraceptives. In June 2015, the Court ruled 6–3 in ''
King v. Burwell
''King v. Burwell'', 576 U.S. 473 (2015), was a 6–3 decision by the Supreme Court of the United States interpreting provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA). The Court's decision upheld, as consistent with the statute, ...
'' that subsidies to help individuals and families purchase health insurance were authorized for those doing so on both the federal exchange and state exchanges, not only those purchasing plans "established by the State", as the statute reads.
Foreign policy

In February and March 2009, Vice President Joe Biden and
Secretary of State Hillary Clinton made separate overseas trips to announce a "new era" in U.S. foreign relations with Russia and Europe, using the terms "break" and "
reset" to signal major changes from the policies of the preceding administration.
Obama attempted to reach out to Arab leaders by granting his first interview to an Arab satellite TV network,
Al Arabiya
Arabiya ( ar, العربية, transliterated: '; meaning "The Arabic One" or "The Arab One") is an international Arabic news television channel, currently based in Dubai, that is operated by the media conglomerate MBC.
The channel is a fla ...
. On March 19, Obama continued his outreach to the Muslim world, releasing a New Year's video message to the people and government of Iran. On June 4, 2009, Obama delivered a speech at
Cairo University
Cairo University ( ar, جامعة القاهرة, Jāmi‘a al-Qāhira), also known as the Egyptian University from 1908 to 1940, and King Fuad I University and Fu'ād al-Awwal University from 1940 to 1952, is Egypt's premier public university ...
in Egypt calling for "
A New Beginning" in relations between the Islamic world and the United States and promoting Middle East peace.
On June 26, 2009, Obama condemned the Iranian government's actions towards protesters following
Iran's 2009 presidential election.
In 2011, Obama ordered a drone strike in Yemen which targeted and killed
Anwar al-Awlaki
Anwar Nasser al-Awlaki (also spelled al-Aulaqi, al-Awlaqi; ar, أنور العولقي, Anwar al-‘Awlaqī; April 21 or 22, 1971 – September 30, 2011) was an American imam who was killed in 2011 in Yemen by a U.S. government drone stri ...
, an American imam suspected of being a leading
Al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
organizer. al-Awlaki became the first
U.S. citizen
Citizenship of the United States is a legal status that entails Americans with specific rights, duties, protections, and benefits in the United States. It serves as a foundation of fundamental rights derived from and protected by the Constitu ...
to be targeted and killed by a
U.S. drone strike. The Department of Justice released a memo justifying al-Awlaki's death as a lawful act of war, while civil liberties advocates described it as a violation of al-Awlaki's constitutional right to
due process. The killing led to significant controversy. His
teenage son and
young daughter, also Americans, were later killed in separate
US military actions, although they were not targeted specifically.

In March 2015, Obama declared that he had authorized U.S. forces to provide logistical and intelligence support to the Saudis in their
military intervention in Yemen
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
, establishing a "Joint Planning Cell" with Saudi Arabia. In 2016, the Obama administration proposed a series of
arms deals with Saudi Arabia worth $115billion. Obama halted the sale of guided munition technology to
Saudi Arabia after Saudi warplanes
targeted a funeral in Yemen's capital Sanaa, killing more than 140 people.
War in Iraq
On February 27, 2009, Obama announced that combat operations in Iraq would end within 18 months. The Obama administration scheduled the withdrawal of combat troops to be completed by August 2010, decreasing troop's levels from 142,000 while leaving a transitional force of about 50,000 in Iraq until the end of 2011. On August 19, 2010, the last U.S. combat brigade exited Iraq. Remaining troops transitioned from combat operations to
counter-terrorism
Counterterrorism (also spelled counter-terrorism), also known as anti-terrorism, incorporates the practices, military tactics, techniques, and strategies that governments, law enforcement, business, and intelligence agencies use to combat or ...
and the training, equipping, and advising of Iraqi security forces. On August 31, 2010, Obama announced that the United States combat mission in Iraq was over. On October 21, 2011, President Obama announced that all U.S. troops would leave Iraq in time to be "home for the holidays."

In June 2014, following the
capture of Mosul by
ISIL, Obama sent 275 troops to provide support and security for U.S. personnel and the U.S. Embassy in Baghdad. ISIS continued to gain ground and to commit
widespread massacres and ethnic cleansing. In August 2014, during the
Sinjar massacre
The Sinjar massacre () marked the beginning of the genocide of Yazidis by ISIL, the killing and abduction of thousands of Yazidi men, women and children. It took place in August 2014 in Sinjar city and Sinjar District in Iraq's Nineveh Governor ...
, Obama ordered a
campaign of U.S. airstrikes against ISIL.
By the end of 2014, 3,100 American ground troops were committed to the conflict and 16,000 sorties were flown over the battlefield, primarily by U.S. Air Force and Navy pilots. In early 2015, with the addition of the "Panther Brigade" of the
82nd Airborne Division
The 82nd Airborne Division is an airborne infantry division of the United States Army specializing in parachute assault operations into denied areasSof, Eric"82nd Airborne Division" ''Spec Ops Magazine'', 25 November 2012. Archived from thori ...
the number of U.S. ground troops in Iraq increased to 4,400, and by July American-led coalition air forces counted 44,000 sorties over the battlefield.
Afghanistan and Pakistan

In his election campaign, Obama called the war in Iraq a "dangerous distraction" and that emphasis should instead be put on the war in Afghanistan, the region he cites as being most likely where an attack against the United States could be launched again. Early in his presidency, Obama moved to bolster U.S. troop strength in Afghanistan. He announced an increase in U.S. troop levels to 17,000 military personnel in February 2009 to "stabilize a deteriorating situation in Afghanistan", an area he said had not received the "strategic attention, direction and resources it urgently requires." He replaced the military commander in Afghanistan, General
David D. McKiernan
David D. McKiernan (born December 11, 1950) is a retired United States Army four-star general who served in Afghanistan as Commander, International Security Assistance Force (ISAF). He served concurrently as Commander, United States Forces – Af ...
, with former
Special Forces commander Lt. Gen.
Stanley A. McChrystal
Stanley Allen McChrystal (born August 14, 1954) is a retired United States Army general best known for his command of Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC) from 2003 to 2008 where his organization was credited with the death of Abu Musab al-Zarq ...
in May 2009, indicating that McChrystal's Special Forces experience would facilitate the use of counterinsurgency tactics in the war.
On December 1, 2009, Obama announced the deployment of an additional 30,000 military personnel to Afghanistan and proposed to begin troop withdrawals 18 months from that date; this took place in July 2011.
David Petraeus replaced McChrystal in June 2010, after McChrystal's staff criticized White House personnel in a magazine article. In February 2013, Obama said the U.S. military would reduce the troop level in Afghanistan from 68,000 to 34,000 U.S. troops by February 2014. In October 2015, the White House announced a plan to keep U.S. Forces in Afghanistan indefinitely in light of the deteriorating security situation.
Regarding neighboring
Pakistan, Obama called its tribal border region the "greatest threat" to the security of Afghanistan and Americans, saying that he "cannot tolerate a terrorist sanctuary." In the same speech, Obama claimed that the U.S. "cannot succeed in Afghanistan or secure our homeland unless we change our Pakistan policy."
=Death of Osama bin Laden
=
Starting with information received from Central Intelligence Agency operatives in July 2010, the CIA developed intelligence over the next several months that determined what they believed to be the hideout of
Osama bin Laden. He was living in seclusion in
a large compound in
Abbottabad
Abbottabad (; Urdu, Punjabi language(HINDKO dialect) آباد, translit=aibṭabād, ) is the capital city of Abbottabad District in the Hazara region of eastern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is the 40th largest city in Pakistan and four ...
, Pakistan, a suburban area from
Islamabad.
CIA head
Leon Panetta reported this intelligence to President Obama in March 2011.
Meeting with his national security advisers over the course of the next six weeks, Obama rejected a plan to bomb the compound, and authorized a "surgical raid" to be conducted by
United States Navy SEALs.
The operation took place on May 1, 2011, and resulted in the shooting death of bin Laden and the seizure of papers, computer drives and disks from the compound.
DNA testing was one of five methods used to positively identify bin Laden's corpse,
which was buried at sea several hours later.
Within minutes of the President's announcement from Washington, DC, late in the evening on May 1, there were spontaneous celebrations around the country as crowds gathered outside the White House, and at New York City's
Ground Zero
In relation to nuclear explosions and other large bombs, ground zero (also called surface zero) is the point on the Earth's surface closest to a detonation. In the case of an explosion above the ground, ''ground zero'' is the point on the ground ...
and
Times Square.
was positive across party lines, including from former presidents Bill Clinton and George W. Bush.
Relations with Cuba
Since the spring of 2013, secret meetings were conducted between the United States and Cuba in the neutral locations of Canada and
Vatican City. The Vatican first became involved in 2013 when
Pope Francis advised the U.S. and Cuba to
exchange prisoners as a gesture of goodwill. On December 10, 2013, Cuban President
Raúl Castro, in a significant public moment, greeted and shook hands with Obama at the
Nelson Mandela memorial service in
Johannesburg.
In December 2014, after the secret meetings, it was announced that Obama, with
Pope Francis as an intermediary, had negotiated a restoration of relations with Cuba, after nearly sixty years of détente. Popularly dubbed the
Cuban Thaw, ''
The New Republic'' deemed the Cuban Thaw to be "Obama's finest foreign policy achievement." On July 1, 2015, President Obama announced that formal diplomatic relations between Cuba and the United States would resume, and embassies would be opened in Washington and
Havana. The countries' respective "interests sections" in one another's capitals were upgraded to embassies on July 20 and August 13, 2015, respectively. Obama visited Havana, Cuba for two days in March 2016, becoming the first sitting U.S. president to arrive since
Calvin Coolidge in 1928.
Israel

During the initial years of the Obama administration, the U.S. increased military cooperation with Israel, including increased military aid, re-establishment of the
U.S.-Israeli Joint Political Military Group and the Defense Policy Advisory Group, and an increase in visits among high-level military officials of both countries. The Obama administration asked Congress to allocate money toward funding the
Iron Dome
Iron Dome ( he, כִּפַּת בַּרְזֶל, Kippat Barzel) is a mobile all-weather air defense system developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems and Israel Aerospace Industries. The system is designed to intercept and destroy short-r ...
program in response to the waves of
Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel. In March 2010, Obama took a public stance against plans by the government of Israeli Prime Minister
Benjamin Netanyahu to continue building Jewish housing projects in predominantly Arab neighborhoods of
East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the sector of Jerusalem that was held by Jordan during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to the western sector of the city, West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel.
Jerusalem was envisaged as a separat ...
. In 2011, the United States vetoed a Security Council resolution condemning
Israeli settlement
Israeli settlements, or Israeli colonies, are civilian communities inhabited by Israeli citizens, overwhelmingly of Jewish ethnicity, built on lands occupied by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. The international community considers Israeli se ...
s, with the United States being the only nation to do so. Obama supports the
two-state solution
The two-state solution to the Israeli–Palestinian conflict envisions an independent State of Palestine alongside the State of Israel, west of the Jordan River. The boundary between the two states is still subject to dispute and negotiation ...
to the
Arab–Israeli conflict
The Arab–Israeli conflict is an ongoing intercommunal phenomenon involving political tension, military conflicts, and other disputes between Arab countries and Israel, which escalated during the 20th century, but had mostly faded out by th ...
based on the 1967 borders with land swaps.
In 2013,
Jeffrey Goldberg
Jeffrey Mark Goldberg (born September 22, 1965) is an American journalist and editor-in-chief of ''The Atlantic'' magazine. During his nine years at ''The Atlantic'' prior to becoming editor, Goldberg became known for his coverage of foreign affa ...
reported that, in Obama's view, "with each new settlement announcement, Netanyahu is moving his country down a path toward near-total isolation."
In 2014, Obama likened the
Zionist movement to the
civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional racial segregation, discrimination, and disenfranchisement throughout the United ...
in the United States. He said both movements seek to bring justice and equal rights to historically persecuted peoples, explaining: "To me, being pro-Israel and pro-Jewish is part and parcel with the values that I've been fighting for since I was politically conscious and started getting involved in politics." Obama expressed support for Israel's right to defend itself during the
2014 Israel–Gaza conflict
The 2014 Gaza War, also known as Operation Protective Edge ( he, מִבְצָע צוּק אֵיתָן, translit=Miv'tza Tzuk Eitan, ),
was a military operation launched by Israel on 8 July 2014 in the Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory that ha ...
. In 2015, Obama was harshly criticized by Israel for advocating and signing the
Iran Nuclear Deal; Israeli Prime Minister
Benjamin Netanyahu, who had advocated the U.S. congress to oppose it, said the deal was "dangerous" and "bad."
On December 23, 2016, under the Obama Administration, the United States abstained from
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2334
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2334 was adopted on 23 December 2016. It concerns the Israeli settlements in " Palestinian territories occupied since 1967, including East Jerusalem". The resolution passed in a 14–0 vote by member ...
, which condemned
Israeli settlement
Israeli settlements, or Israeli colonies, are civilian communities inhabited by Israeli citizens, overwhelmingly of Jewish ethnicity, built on lands occupied by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. The international community considers Israeli se ...
building in the occupied
Palestinian territories
The Palestinian territories are the two regions of the former British Mandate for Palestine that have been militarily occupied by Israel since the Six-Day War of 1967, namely: the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip. The ...
as a violation of international law, effectively allowing it to pass. Netanyahu strongly criticized the Obama administration's actions, and the Israeli government withdrew its annual dues from the organization, which totaled $6million, on January 6, 2017. On January 5, 2017, the
United States House of Representatives voted 342–80 to condemn the UN Resolution.
Libya

In February 2011, protests in Libya began against long-time dictator
Muammar Gaddafi as part of the
Arab Spring
The Arab Spring ( ar, الربيع العربي) was a series of anti-government protests, uprisings and armed rebellions that spread across much of the Arab world in the early 2010s. It began in Tunisia in response to corruption and econom ...
. They soon turned violent. In March, as forces loyal to Gaddafi advanced on rebels across Libya, calls for a no-fly zone came from around the world, including Europe, the
Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, E ...
, and a resolution passed unanimously by the U.S. Senate. In response to the unanimous passage of
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973 on March 17, Gaddafi—who had previously vowed to "show no mercy" to the rebels of Benghazi—announced an immediate cessation of military activities.
The next day, on Obama's orders, the U.S. military took part in air strikes to destroy the Libyan government's air defense capabilities to protect civilians and enforce a no-fly-zone, including the use of
Tomahawk missiles
The Tomahawk () Land Attack Missile (TLAM) is a long-range, all-weather, jet-powered, subsonic cruise missile that is primarily used by the United States Navy and Royal Navy in ship and submarine-based land-attack operations.
Under contract f ...
,
B-2 Spirits, and fighter jets. Six days later, on March 25, by unanimous vote of all its 28 members,
NATO took over leadership of the effort, dubbed
Operation Unified Protector
Operation Unified Protector was a NATO operation in 2011 enforcing United Nations Security Council resolutions 1970 and 1973 concerning the Libyan Civil War and adopted on 26 February and 17 March 2011, respectively. These resolutions imposed s ...
.
Some Representatives
questioned whether Obama had the constitutional authority to order military action in addition to questioning its cost, structure and aftermath. Obama later expressed regret for playing a leading role in the destabilization of Libya, calling the certain situation there "a mess." He has stated that the lack of preparation surrounding the days following the government's overthrow was the "worst mistake" of his presidency.
Syrian civil war
On August 18, 2011, several months after the start of the
Syrian civil war, Obama issued a written statement that said: "The time has come for
President Assad to step aside."
This stance was reaffirmed in November 2015. In 2012, Obama authorized multiple
programs run by the CIA and the Pentagon to train anti-Assad rebels. The Pentagon-run program was later found to have failed and was formally abandoned in October 2015.
In the wake of a
chemical weapons attack in Syria,
formally blamed by the Obama administration on the Assad government, Obama chose not to enforce the "red line" he had pledged
and, rather than authorize the promised military action against Assad, went along with the Russia-brokered deal that led to Assad
giving up chemical weapons; however attacks with
chlorine gas
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is ...
continued. In 2014, Obama authorized an
air campaign aimed primarily at ISIL.
Iran nuclear talks

On October 1, 2009, the Obama administration went ahead with a Bush administration program, increasing nuclear weapons production. The "Complex Modernization" initiative expanded two existing nuclear sites to produce new bomb parts. The administration built new plutonium pits at the Los Alamos lab in New Mexico and expanded enriched uranium processing at the Y-12 facility in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. In November 2013, the Obama administration opened
negotiations with Iran to prevent it from acquiring
nuclear weapons, which included an
interim agreement
The Oslo I Accord or Oslo I, officially called the Declaration of Principles on Interim Self-Government Arrangements or short Declaration of Principles (DOP), was an attempt in 1993 to set up a framework that would lead to the resolution of th ...
. Negotiations took two years with numerous delays, with a deal being announced on July 14, 2015. The deal titled the "Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action" saw sanctions removed in exchange for measures that would prevent Iran from producing nuclear weapons. While Obama hailed the agreement as being a step towards a more hopeful world, the deal drew strong criticism from Republican and conservative quarters, and from Israeli Prime Minister
Benjamin Netanyahu. In addition, the transfer of $1.7billion in cash to Iran shortly after the deal was announced was criticized by the Republican party. The Obama administration said that the payment in cash was because of the "effectiveness of U.S. and international sanctions." In order to advance the deal, the Obama administration shielded
Hezbollah from the
Drug Enforcement Administration's
Project Cassandra investigation regarding drug smuggling and from the
Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.
On a side note, the very same year, in December 2015, Obama started a $348billion worth program to back the biggest U.S. buildup of nuclear arms since Ronald Reagan left the White House.
Russia

In March 2010, an agreement was reached with the administration of Russian President
Dmitry Medvedev
Dmitry Anatolyevich Medvedev ( rus, links=no, Дмитрий Анатольевич Медведев, p=ˈdmʲitrʲɪj ɐnɐˈtolʲjɪvʲɪtɕ mʲɪdˈvʲedʲɪf; born 14 September 1965) is a Russian politician who has been serving as the dep ...
to replace the
1991 Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty with a new pact reducing the number of long-range nuclear weapons in the arsenals of both countries by about a third. Obama and Medvedev signed the
New START treaty in April 2010, and the
U.S. Senate ratified it in December 2010. In December 2011, Obama instructed agencies to consider
LGBT rights when issuing financial aid to foreign countries. In August 2013, he criticized Russia's law that discriminates against gays,
but he stopped short of advocating a boycott of the upcoming
2014 Winter Olympics
, ''Zharkie. Zimnie. Tvoi'')
, nations = 88
, events = 98 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, athletes = 2,873
, opening = 7 February 2014
, closing = 23 February 2014
, opened_by = President Vladimir Putin
, cauldron =
, stadium = Fisht Olympi ...
in
Sochi
Sochi ( rus, Со́чи, p=ˈsotɕɪ, a=Ru-Сочи.ogg) is the largest resort city in Russia. The city is situated on the Sochi River, along the Black Sea in Southern Russia, with a population of 466,078 residents, up to 600,000 residents in ...
, Russia.
After
Russia's invasion of Crimea in 2014,
military intervention in Syria in 2015, and the
interference in the
2016 U.S. presidential election
The 2016 United States presidential election was the 58th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket of businessman Donald Trump and Indiana governor Mike Pence defeated the Democratic ticket ...
,
, a former UK defense secretary and NATO secretary-general, said Obama had "allowed Putin to jump back on the world stage and test the resolve of the West", adding that the legacy of this disaster would last.
Cultural and political image
Obama's family history, upbringing, and
Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight schools ...
education differ markedly from those of African-American politicians who launched their careers in the 1960s through participation in the
civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional racial segregation, discrimination, and disenfranchisement throughout the United ...
. Expressing puzzlement over questions about whether he is "black enough", Obama told an August 2007 meeting of the
National Association of Black Journalists
The National Association of Black Journalists (NABJ) is an organization of African-American journalists, students, and media professionals. Founded in 1975 in Washington, D.C., by 44 journalists, the NABJ's stated purpose is to provide quality p ...
that "we're still locked in this notion that if you appeal to white folks then there must be something wrong." Obama acknowledged his youthful image in an October 2007 campaign speech, saying: "I wouldn't be here if, time and again, the torch had not been passed to a new generation." Additionally, Obama has frequently been referred to as an exceptional orator.
During his pre-inauguration transition period and continuing into his presidency, Obama delivered a series of weekly Internet video addresses.

According to the
Gallup Organization, Obama began his presidency with a 68 percent approval rating before gradually declining for the rest of the year, and eventually bottoming out at 41 percent in August 2010, a trend similar to
Ronald Reagan's and
Bill Clinton's first years in office. He experienced a small poll bounce shortly after the
death of Osama bin Laden on May 2, 2011. This bounce lasted until around June 2011, when his approval numbers dropped back to where they were previously. His approval ratings rebounded around the same time as his reelection in 2012, with polls showing an average job approval of 52 percent shortly after his second inauguration. Despite approval ratings dropping to 39 percent in late-2013 due to the ACA roll-out, they climbed to 50 percent in January 2015 according to Gallup.

Polls showed strong support for Obama in other countries both before and during his presidency. In a February 2009 poll conducted in Western Europe and the U.S. by
Harris Interactive for
France 24 and the ''
International Herald Tribune
The ''International Herald Tribune'' (''IHT'') was a daily English-language newspaper published in Paris, France for international English-speaking readers. It had the aim of becoming "the world's first global newspaper" and could fairly be sai ...
'', Obama was rated as the most respected world leader, as well as the most powerful. In a similar poll conducted by Harris in May 2009, Obama was rated as the most popular world leader, as well as the one figure most people would pin their hopes on for pulling the world out of the economic downturn.
On October 9, 2009, the
Norwegian Nobel Committee announced that Obama had won the
2009 Nobel Peace Prize "for his extraordinary efforts to strengthen international diplomacy and cooperation between peoples,"
which drew a mixture of praise and criticism from world leaders and media figures. He became the fourth U.S. president to be awarded the Nobel Peace Prize, and the third to become a Nobel laureate while in office.
Racism towards Obama
Obama's election was also met with hostile reactions connected to his race, birthplace, and religion, and as president, he faced numerous taunts, racist remarks and generally racialized criticisms by some conservative pundits.
Some also falsely
claimed that Obama practiced
Islam – at a time when
anti-Muslim sentiments were
prevalent
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
in the United States – with a 2015 CNN poll finding that 29% of Americans believed Obama to be a Muslim.
Starting in 2011,
Donald Trump – who would later directly succeed Obama as president – would regularly promote conspiracy theories that Obama had
been born in
Kenya, and therefore, was not an American citizen. Trump winning the presidency right after Obama was described by some commentators as the culmination of decades of
white backlash against Black Americans achieving social mobility in the face of racist policies against them. Carol Anderson, author of the book ''White Rage'' and a professor of Black studies, African-American studies, said that Obama was caught off guard by the backlash, and "was surprised by how racist this country is."
In September 2009, former President Jimmy Carter stated that “I think an overwhelming portion of the intensely demonstrated animosity toward President Barack Obama is based on the fact that he is a black man.” Though Obama publicly disagreed with Carter's assessment at the time, in a 2015 interview with ''NPR'', he also said, when asked about critics who believed he was making their country worse:
In the same interview, however, he also stated that, despite the existence of racially motivated criticism against him, others who criticize his policies may still have "perfectly good reasons" for doing so.
Post-presidency (2017–present)

Obama's presidency ended on January 20, 2017, upon the Inauguration of Donald Trump, inauguration of his successor,
Donald Trump. The family moved to a house they rented in Kalorama, Washington, D.C. On March 2, 2017, the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum awarded the Profile in Courage Award to Obama "for his enduring commitment to democratic ideals and elevating the standard of political courage." His first public appearance since leaving the office was a seminar at the University of Chicago on April 24, where he appealed for a new generation to participate in politics.

On September 7, 2017, Obama partnered with former presidents Jimmy Carter, George H. W. Bush, Bill Clinton, and George W. Bush to work with One America Appeal to help the victims of Hurricane Harvey and Hurricane Irma in the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast and Texas communities.
Obama hosted the inaugural summit of the Obama Foundation in Chicago from October 31 to November 1, 2017. He intends for the foundation to be the central focus of his post-presidency and part of his ambitions for his subsequent activities following his presidency to be more consequential than his time in office.
Barack and Michelle Obama signed a deal on May 22, 2018, to produce docu-series, documentaries and features for Netflix under the Obamas' newly formed production company, Higher Ground Productions. Higher Ground's first film, ''American Factory,'' won the Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature in 2020.

He received a 63% approval rating in Gallup's 2018 job approval poll for the past 10 U.S. presidents.
A pipe bomb addressed to Obama was intercepted by the Secret Service on October 24, 2018. It was one of several pipe-bombs that had been October 2018 United States mail bombing attempts, mailed out to Democratic lawmakers and officials.
In 2019, Barack and Michelle Obama bought a home on Martha's Vineyard from Wyc Grousbeck. On October 29, 2019, Obama criticized "wokeness" and Cancel culture, call-out culture at the Obama Foundation's annual summit.
Obama was reluctant to make an endorsement in the 2020 Democratic presidential primaries because he wanted to position himself to unify the party, no matter who the nominee was. On April 14, 2020, Obama endorsed his former vice president
Joe Biden, the presumptive Democratic nominee, for president in the 2020 United States presidential election, 2020 election, stating that he has "all the qualities we need in a president right now." In May 2020, Obama criticized President Trump for Trump administration communication during the COVID-19 pandemic, his handling of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, COVID-19 pandemic, calling his response to the crisis "an absolute chaotic disaster", and stating that the consequences of Presidency of Donald Trump, the Trump presidency have been "our worst impulses unleashed, our proud reputation around the world badly diminished, and our democratic institutions threatened like never before." Trump retaliated by accusing Obama of having committed "the biggest political crime in American history", although he refused to say what he was talking about, telling reporters: "You know what the crime is, the crime is very obvious to everybody."
Obama wrote a presidential memoir, in a $65million deal with Penguin Random House.
The book, ''
A Promised Land
''A Promised Land'' is a memoir by Barack Obama, the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. Published on November 17, 2020, it is the first of a planned two-volume series. Remaining focused on his political career, the preside ...
'', was released on November 17, 2020.
In February 2021, Obama and musician Bruce Springsteen started a podcast called ''Renegades: Born in the USA'' where the two talk about "their backgrounds, music and their 'enduring love of America. In late 2021, Regina Hicks had signed a deal with Netflix, in a venture with his and Michelle Obama, Michelle's Higher Ground Productions, Higher Ground to develop comedy projects. On March 4, 2022, Obama won an Audio Publishers Association (APA) Award in the best narration by the author category for the narration of his memoir ''A Promised Land''.

On April 5, 2022, Obama visited the White House for the first time since leaving office, in an event celebrating the 12th annual anniversary of the signing of the Affordable Care Act.
In 2022, he narrated the Netflix documentary series ''Our Great National Parks'', which later won him a Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Narrator.
In June 2022, it was announced that the Obamas and their podcast production company, Higher Ground Productions, Higher Ground, signed a multi-year deal with Audible (service), Audible.
In September 2022, Obama visited the White House to unveil his and Michelle's official White House portraits.
Legacy

Historian Julian E. Zelizer, Julian Zelizer credits Obama with "a keen sense of how the institutions of government work and the ways that his team could design policy proposals." Zelizer notes Obama's policy successes included the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, economic stimulus package which ended the Great Recession in the United States, Great Recession and the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, Dodd-Frank financial and consumer protection reforms, as well as the
Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and colloquially known as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by Presid ...
. Zelizer also notes the Democratic Party lost power and numbers of elected officials during Obama's term, saying that the consensus among historians is that Obama "turned out to be a very effective policymaker but not a tremendously successful party builder." Zelizer calls this the "defining paradox of Obama’s presidency".
The Brookings Institution noted that Obama passed "only one major legislative achievement (Obamacare)—and a fragile one at that—the legacy of Obama’s presidency mainly rests on its tremendous symbolic importance and the fate of a patchwork of executive actions." David W. Wise noted that Obama fell short "in areas many Progressives hold dear", including the continuation of drone strikes, not going after big banks during the Great Recession, and failing to strengthen his coalition before pushing for Obamacare. Wise called Obama's legacy that of "a disappointingly conventional president".
Obama's most significant accomplishment is generally considered to be the
Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and colloquially known as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by Presid ...
(ACA), provisions of which went into effect from 2010 to 2020. Many attempts by Senate Republicans to repeal the ACA, including a "skinny repeal", have thus far failed.
However, in 2017, the penalty for violating the individual mandate was repealed effective 2019.
Together with the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act amendment, it represents the Health care in the United States, U.S. healthcare system's most significant regulatory overhaul and expansion of coverage since the passage of Medicare (United States), Medicare and
Medicaid in 1965.
Many commentators credit Obama with averting a threatened Depression (economics), depression and pulling the economy back from the Great Recession.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the Obama administration created 11.3 million jobs from the month after first inauguration of Barack Obama, his first inauguration to the end of his term. In 2010, Obama signed into effect the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. Passed as a response to the financial crisis of 2007–08, it brought the most significant changes to financial regulation in the United States since the regulatory reform that followed the Great Depression under Democratic President
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As th ...
.
In 2009, Obama signed into law the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2010, which contained in it the
Matthew Shepard and James Byrd Jr. Hate Crimes Prevention Act
The Matthew Shepard and James Byrd Jr. Hate Crimes Prevention Act is a landmark United States federal law, passed on October 22, 2009, and signed into law by President Barack Obama on October 28, 2009, as a rider to the National Defense Aut ...
, the first addition to existing federal hate crime law in the United States since Democratic President
Bill Clinton signed into law the Church Arson Prevention Act of 1996. The act expanded Hate crime laws in the United States, existing federal hate crime laws in the United States, and made it a federal crime to assault people based on sexual orientation, gender identity, or disability.
As president, Obama advanced LGBT rights. In 2010, he signed the Don't Ask, Don't Tell Repeal Act of 2010, Don't Ask, Don't Tell Repeal Act, which brought an end to "
don't ask, don't tell
"Don't ask, don't tell" (DADT) was the official United States policy on military service of non-heterosexual people, instituted during the Clinton administration. The policy was issued under Department of Defense Directive 1304.26 on Decembe ...
" policy in the U.S. armed forces that banned open service from Lesbian, gay and bisexual, LGB people; the law went into effect the following year. In 2016, his administration brought an end to the ban on transgender people serving openly in the U.S. armed forces.
A Gallup poll, taken in the final days of Obama's term, showed that 68 percent of Americans believed the U.S. had made progress on LGBT rights during Obama's eight years in office.
Obama substantially escalated the use of drone strikes against suspected militants and terrorists associated with al-Qaeda and the Taliban. In 2016, the last year of his presidency, the U.S. dropped 26,171 bombs on seven different countries. Obama left about 8,400 U.S. troops in
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, 5,262 in Iraq, 503 in Syria, 133 in Pakistan, 106 in Somalia, seven in Yemen, and two in Libya at the end of his presidency.
According to Pew Research Center and United States Bureau of Justice Statistics, from December 31, 2009, to December 31, 2015, inmates sentenced in U.S. federal custody declined by five percent. This is the largest decline in sentenced inmates in U.S. federal custody since Democratic President Jimmy Carter. By contrast, the federal prison population increased significantly under presidents
Ronald Reagan, George H. W. Bush,
Bill Clinton, and
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
.
Human Rights Watch (HRW) called Obama's human rights record "mixed", adding that "he has often treated human rights as a secondary interest — nice to support when the cost was not too high, but nothing like a top priority he championed."
Obama left office in January 2017 with a 60 percent approval rating. Obama gained 10 spots from the same survey in 2015 from the Brookings Institution that ranked him the 18th-greatest American president.
Presidential library
The Barack Obama Presidential Center is Obama's planned Presidential library system, presidential library. It will be hosted by the University of Chicago and located in Jackson Park (Chicago), Jackson Park on the South Side, Chicago, South Side of Chicago.
Bibliography
Books
*
*
*
*
Audiobooks
* 2006: ''The Audacity of Hope: Thoughts on Reclaiming the American Dream'' (read by the author), Random House Audio,
* 2020: ''A Promised Land'' (read by the author)
Articles
*
* Uncredited case comment.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
See also
Politics
* DREAM Act
* Fraud Enforcement and Recovery Act of 2009
* Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986
* IRS targeting controversy
* Middle Class Tax Relief and Job Creation Act of 2012
* National Broadband Plan (United States)
* Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy
* Social policy of the Barack Obama administration
* SPEECH Act
* Stay with It
* White House Office of Energy and Climate Change Policy
Other
* Roberts Court
* Speeches of Barack Obama
Lists
* Assassination threats against Barack Obama
* List of African-American United States senators
* List of Barack Obama 2008 presidential campaign endorsements
* List of Barack Obama 2012 presidential campaign endorsements
* Political scandals during the Obama administration, List of federal political scandals, 2009–17
* List of people granted executive clemency by Barack Obama
* List of things named after Barack Obama
References
[
*
*
*
*
*
* ]
[
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 92–112.
* Mendell (2007), pp. 55–62.]
[ ]
[
*
*
*
*
* ]
[
*
*
* ]
[
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Obama (1995, 2004), pp. 438–439.
* Mendell (2007), pp. 104–106.]
[
*
*
*
*
*
* ]
[
* ]
[
*
*
*
* Mendell (2007), pp. 172–177.]
[
*
* ]
[
* ]
[
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Mendell (2007), pp. 235–259.]
[
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Mendell (2007), pp. 272–285.]
[
*
*
* ]
*
*
[
*
*
*
* ]
[
* ]
[
* ]
[
*
* ]
[
* ]
[
* ]
[
* ]
[
* ]
[
* ]
[
*
*
* ]
[
* ]
[
* ]
[Obama (2006), pp. 202–208. Portions excerpted in:
* ]
[
*
*
*
* Maraniss (2012), p. 557]
/span>: It would take time for Obama to join and become fully engaged in Wright's church, a place where he would be baptized and married; that would not happen until later, during his second time around in Chicago, but the process started then, in October 1987... Jerry Kellman: "He wasn't a member of the church during those first three years, but he was drawn to Jeremiah."
*
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Parmar, Inderjeet, and Mark Ledwidge. "...'a foundation-hatched black': Obama, the US establishment, and foreign policy." ''International Politics'' 54.3 (2017): 373–38
online
External links
Official
* of The Obama Foundation
* of the Barack Obama Presidential Library
* of Organizing for Action
White House biography
Other
Column archiveat ''HuffPost, The Huffington Post''
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Barack Obamaat Politifact
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Obama, Barack
Barack Obama,
1961 births
20th-century American male writers
20th-century American non-fiction writers
20th-century Protestants
20th-century African-American academics
20th-century American academics
21st-century American male writers
21st-century American non-fiction writers
21st-century American politicians
21st-century presidents of the United States
21st-century Protestants
21st-century scholars
Activists from Hawaii
Activists from Illinois
African-American Christians
African-American educators
African-American feminists
African-American lawyers
African-American non-fiction writers
African-American politicians
African-American state legislators in Illinois
African-American candidates for President of the United States
African-American United States senators
American civil rights lawyers
American community activists
American feminist writers
American gun control activists
American legal scholars
American male non-fiction writers
American memoirists
American Nobel laureates
American people of English descent
American people of French descent
American people of German descent
American people of Irish descent
American people of Kenyan descent
American people of Luo descent
American people of Scottish descent
American people of Swiss descent
American people of Welsh descent
American political writers
American Protestants
Articles containing video clips
Candidates in the 2008 United States presidential election
Candidates in the 2012 United States presidential election
Columbia College (New York) alumni
Democratic Party presidents of the United States
Democratic Party (United States) presidential nominees
Democratic Party United States senators from Illinois
Grammy Award winners
Harvard Law School alumni
Illinois lawyers
Democratic Party Illinois state senators
LGBT rights activists from the United States
Living people
Male feminists
Members of the American Philosophical Society
Netflix people
Nobel Peace Prize laureates
Obama family
Outstanding Narrator Primetime Emmy Award winners
Politicians from Chicago
Politicians from Honolulu
Presidents of the United States
Proponents of Christian feminism
Punahou School alumni
Scholars of constitutional law
Time Person of the Year
University of Chicago Law School faculty
Writers from Chicago
Writers from Honolulu
 At the age of six, Obama and his mother had moved to Indonesia to join his stepfather. From age six to ten, he attended local Indonesian-language schools: ''Sekolah Dasar Katolik Santo Fransiskus Asisi'' (St. Francis of Assisi Catholic Elementary School) for two years and ''Sekolah Dasar Negeri Menteng 01'' (State Elementary School Menteng 01) for one and a half years, supplemented by English-language
At the age of six, Obama and his mother had moved to Indonesia to join his stepfather. From age six to ten, he attended local Indonesian-language schools: ''Sekolah Dasar Katolik Santo Fransiskus Asisi'' (St. Francis of Assisi Catholic Elementary School) for two years and ''Sekolah Dasar Negeri Menteng 01'' (State Elementary School Menteng 01) for one and a half years, supplemented by English-language  In June 1989, Obama met Michelle Robinson when he was employed as a summer associate at the Chicago law firm of Sidley Austin. Robinson was assigned for three months as Obama's adviser at the firm, and she joined him at several group social functions but declined his initial requests to date. They began dating later that summer, became engaged in 1991, and were married on October 3, 1992. After suffering a miscarriage, Michelle underwent in vitro fertilization to conceive their children. The couple's first daughter, Malia Ann, was born in 1998, followed by a second daughter, Natasha ("Sasha"), in 2001. The Obama daughters attended the
In June 1989, Obama met Michelle Robinson when he was employed as a summer associate at the Chicago law firm of Sidley Austin. Robinson was assigned for three months as Obama's adviser at the firm, and she joined him at several group social functions but declined his initial requests to date. They began dating later that summer, became engaged in 1991, and were married on October 3, 1992. After suffering a miscarriage, Michelle underwent in vitro fertilization to conceive their children. The couple's first daughter, Malia Ann, was born in 1998, followed by a second daughter, Natasha ("Sasha"), in 2001. The Obama daughters attended the  Obama is a supporter of the
Obama is a supporter of the  In January 2008, Obama told ''
In January 2008, Obama told '' Obama was elected to the Illinois Senate in 1996, succeeding Democratic State Senator Alice Palmer from Illinois's 13th District, which, at that time, spanned Chicago South Side neighborhoods from Hyde Park– Kenwood south to South Shore and west to
Obama was elected to the Illinois Senate in 1996, succeeding Democratic State Senator Alice Palmer from Illinois's 13th District, which, at that time, spanned Chicago South Side neighborhoods from Hyde Park– Kenwood south to South Shore and west to  Obama was sworn in as a senator on January 3, 2005, becoming the only Senate member of the
Obama was sworn in as a senator on January 3, 2005, becoming the only Senate member of the  Later in 2007, Obama sponsored an amendment to the Defense Authorization Act to add safeguards for personality-disorder military discharges. This amendment passed the full Senate in the spring of 2008. He sponsored the Iran Sanctions Enabling Act supporting divestment of state pension funds from Iran's oil and gas industry, which was never enacted but later incorporated in the Comprehensive Iran Sanctions, Accountability, and Divestment Act of 2010; and co-sponsored legislation to reduce risks of nuclear terrorism. Obama also sponsored a Senate amendment to the
Later in 2007, Obama sponsored an amendment to the Defense Authorization Act to add safeguards for personality-disorder military discharges. This amendment passed the full Senate in the spring of 2008. He sponsored the Iran Sanctions Enabling Act supporting divestment of state pension funds from Iran's oil and gas industry, which was never enacted but later incorporated in the Comprehensive Iran Sanctions, Accountability, and Divestment Act of 2010; and co-sponsored legislation to reduce risks of nuclear terrorism. Obama also sponsored a Senate amendment to the  On February 10, 2007, Obama announced his candidacy for President of the United States in front of the Old State Capitol building in
On February 10, 2007, Obama announced his candidacy for President of the United States in front of the Old State Capitol building in 
 The inauguration of Barack Obama as the 44th president took place on January 20, 2009. In his first few days in office, Obama issued executive orders and
The inauguration of Barack Obama as the 44th president took place on January 20, 2009. In his first few days in office, Obama issued executive orders and  Obama appointed two women to serve on the Supreme Court in the first two years of his presidency. He nominated
Obama appointed two women to serve on the Supreme Court in the first two years of his presidency. He nominated  On January 16, 2013, one month after the
On January 16, 2013, one month after the  As a candidate for the Illinois state senate in 1996, Obama stated he favored legalizing same-sex marriage. During his Senate run in 2004, he said he supported civil unions and domestic partnerships for same-sex partners but opposed same-sex marriages. In 2008, he reaffirmed this position by stating "I believe marriage is between a man and a woman. I am not in favor of gay marriage." On May 9, 2012, shortly after the official launch of his campaign for re-election as president, Obama said his views had evolved, and he publicly affirmed his personal support for the legalization of same-sex marriage, becoming the first sitting U.S. president to do so. During his second inaugural address on January 21, 2013, Obama became the first U.S. president in office to call for full equality for gay Americans, and the first to mention
As a candidate for the Illinois state senate in 1996, Obama stated he favored legalizing same-sex marriage. During his Senate run in 2004, he said he supported civil unions and domestic partnerships for same-sex partners but opposed same-sex marriages. In 2008, he reaffirmed this position by stating "I believe marriage is between a man and a woman. I am not in favor of gay marriage." On May 9, 2012, shortly after the official launch of his campaign for re-election as president, Obama said his views had evolved, and he publicly affirmed his personal support for the legalization of same-sex marriage, becoming the first sitting U.S. president to do so. During his second inaugural address on January 21, 2013, Obama became the first U.S. president in office to call for full equality for gay Americans, and the first to mention  Obama intervened in the troubled automotive industry in March 2009, renewing loans for General Motors (GM) and
Obama intervened in the troubled automotive industry in March 2009, renewing loans for General Motors (GM) and  On April 20, 2010, an explosion destroyed an offshore drilling rig at the
On April 20, 2010, an explosion destroyed an offshore drilling rig at the  Obama called for
Obama called for  On July 14, 2009, House Democratic leaders introduced a 1,017-page plan for overhauling the U.S. health care system, which Obama wanted Congress to approve by the end of 2009. After public debate during the Congressional summer recess of 2009, Obama delivered a speech to a joint session of Congress on September 9 where he addressed concerns over the proposals. In March 2009, Obama lifted a ban on using federal funds for stem cell research.
On November 7, 2009, a health care bill featuring the public option was passed in the House. On December 24, 2009, the Senate passed its own bill—without a public option—on a party-line vote of 60–39. On March 21, 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) passed by the Senate in December was passed in the House by a vote of 219 to 212. Obama signed the bill into law on March 23, 2010.
The ACA includes health-related provisions, most of which took effect in 2014, including expanding Medicaid eligibility for people making up to 133 percentof the
On July 14, 2009, House Democratic leaders introduced a 1,017-page plan for overhauling the U.S. health care system, which Obama wanted Congress to approve by the end of 2009. After public debate during the Congressional summer recess of 2009, Obama delivered a speech to a joint session of Congress on September 9 where he addressed concerns over the proposals. In March 2009, Obama lifted a ban on using federal funds for stem cell research.
On November 7, 2009, a health care bill featuring the public option was passed in the House. On December 24, 2009, the Senate passed its own bill—without a public option—on a party-line vote of 60–39. On March 21, 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) passed by the Senate in December was passed in the House by a vote of 219 to 212. Obama signed the bill into law on March 23, 2010.
The ACA includes health-related provisions, most of which took effect in 2014, including expanding Medicaid eligibility for people making up to 133 percentof the  The costs of these provisions are offset by taxes, fees, and cost-saving measures, such as new Medicare taxes for those in high-income brackets, taxes on
The costs of these provisions are offset by taxes, fees, and cost-saving measures, such as new Medicare taxes for those in high-income brackets, taxes on  In February and March 2009, Vice President Joe Biden and Secretary of State Hillary Clinton made separate overseas trips to announce a "new era" in U.S. foreign relations with Russia and Europe, using the terms "break" and " reset" to signal major changes from the policies of the preceding administration. Obama attempted to reach out to Arab leaders by granting his first interview to an Arab satellite TV network,
In February and March 2009, Vice President Joe Biden and Secretary of State Hillary Clinton made separate overseas trips to announce a "new era" in U.S. foreign relations with Russia and Europe, using the terms "break" and " reset" to signal major changes from the policies of the preceding administration. Obama attempted to reach out to Arab leaders by granting his first interview to an Arab satellite TV network,  In March 2015, Obama declared that he had authorized U.S. forces to provide logistical and intelligence support to the Saudis in their
In March 2015, Obama declared that he had authorized U.S. forces to provide logistical and intelligence support to the Saudis in their  In June 2014, following the capture of Mosul by ISIL, Obama sent 275 troops to provide support and security for U.S. personnel and the U.S. Embassy in Baghdad. ISIS continued to gain ground and to commit widespread massacres and ethnic cleansing. In August 2014, during the
In June 2014, following the capture of Mosul by ISIL, Obama sent 275 troops to provide support and security for U.S. personnel and the U.S. Embassy in Baghdad. ISIS continued to gain ground and to commit widespread massacres and ethnic cleansing. In August 2014, during the  In his election campaign, Obama called the war in Iraq a "dangerous distraction" and that emphasis should instead be put on the war in Afghanistan, the region he cites as being most likely where an attack against the United States could be launched again. Early in his presidency, Obama moved to bolster U.S. troop strength in Afghanistan. He announced an increase in U.S. troop levels to 17,000 military personnel in February 2009 to "stabilize a deteriorating situation in Afghanistan", an area he said had not received the "strategic attention, direction and resources it urgently requires." He replaced the military commander in Afghanistan, General
In his election campaign, Obama called the war in Iraq a "dangerous distraction" and that emphasis should instead be put on the war in Afghanistan, the region he cites as being most likely where an attack against the United States could be launched again. Early in his presidency, Obama moved to bolster U.S. troop strength in Afghanistan. He announced an increase in U.S. troop levels to 17,000 military personnel in February 2009 to "stabilize a deteriorating situation in Afghanistan", an area he said had not received the "strategic attention, direction and resources it urgently requires." He replaced the military commander in Afghanistan, General  During the initial years of the Obama administration, the U.S. increased military cooperation with Israel, including increased military aid, re-establishment of the U.S.-Israeli Joint Political Military Group and the Defense Policy Advisory Group, and an increase in visits among high-level military officials of both countries. The Obama administration asked Congress to allocate money toward funding the
During the initial years of the Obama administration, the U.S. increased military cooperation with Israel, including increased military aid, re-establishment of the U.S.-Israeli Joint Political Military Group and the Defense Policy Advisory Group, and an increase in visits among high-level military officials of both countries. The Obama administration asked Congress to allocate money toward funding the  In February 2011, protests in Libya began against long-time dictator Muammar Gaddafi as part of the
In February 2011, protests in Libya began against long-time dictator Muammar Gaddafi as part of the  On October 1, 2009, the Obama administration went ahead with a Bush administration program, increasing nuclear weapons production. The "Complex Modernization" initiative expanded two existing nuclear sites to produce new bomb parts. The administration built new plutonium pits at the Los Alamos lab in New Mexico and expanded enriched uranium processing at the Y-12 facility in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. In November 2013, the Obama administration opened negotiations with Iran to prevent it from acquiring nuclear weapons, which included an
On October 1, 2009, the Obama administration went ahead with a Bush administration program, increasing nuclear weapons production. The "Complex Modernization" initiative expanded two existing nuclear sites to produce new bomb parts. The administration built new plutonium pits at the Los Alamos lab in New Mexico and expanded enriched uranium processing at the Y-12 facility in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. In November 2013, the Obama administration opened negotiations with Iran to prevent it from acquiring nuclear weapons, which included an  In March 2010, an agreement was reached with the administration of Russian President
In March 2010, an agreement was reached with the administration of Russian President  Polls showed strong support for Obama in other countries both before and during his presidency. In a February 2009 poll conducted in Western Europe and the U.S. by Harris Interactive for France 24 and the ''
Polls showed strong support for Obama in other countries both before and during his presidency. In a February 2009 poll conducted in Western Europe and the U.S. by Harris Interactive for France 24 and the '' Obama's presidency ended on January 20, 2017, upon the Inauguration of Donald Trump, inauguration of his successor, Donald Trump. The family moved to a house they rented in Kalorama, Washington, D.C. On March 2, 2017, the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum awarded the Profile in Courage Award to Obama "for his enduring commitment to democratic ideals and elevating the standard of political courage." His first public appearance since leaving the office was a seminar at the University of Chicago on April 24, where he appealed for a new generation to participate in politics.
Obama's presidency ended on January 20, 2017, upon the Inauguration of Donald Trump, inauguration of his successor, Donald Trump. The family moved to a house they rented in Kalorama, Washington, D.C. On March 2, 2017, the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum awarded the Profile in Courage Award to Obama "for his enduring commitment to democratic ideals and elevating the standard of political courage." His first public appearance since leaving the office was a seminar at the University of Chicago on April 24, where he appealed for a new generation to participate in politics.
 On September 7, 2017, Obama partnered with former presidents Jimmy Carter, George H. W. Bush, Bill Clinton, and George W. Bush to work with One America Appeal to help the victims of Hurricane Harvey and Hurricane Irma in the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast and Texas communities.
Obama hosted the inaugural summit of the Obama Foundation in Chicago from October 31 to November 1, 2017. He intends for the foundation to be the central focus of his post-presidency and part of his ambitions for his subsequent activities following his presidency to be more consequential than his time in office.
Barack and Michelle Obama signed a deal on May 22, 2018, to produce docu-series, documentaries and features for Netflix under the Obamas' newly formed production company, Higher Ground Productions. Higher Ground's first film, ''American Factory,'' won the Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature in 2020.
On September 7, 2017, Obama partnered with former presidents Jimmy Carter, George H. W. Bush, Bill Clinton, and George W. Bush to work with One America Appeal to help the victims of Hurricane Harvey and Hurricane Irma in the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast and Texas communities.
Obama hosted the inaugural summit of the Obama Foundation in Chicago from October 31 to November 1, 2017. He intends for the foundation to be the central focus of his post-presidency and part of his ambitions for his subsequent activities following his presidency to be more consequential than his time in office.
Barack and Michelle Obama signed a deal on May 22, 2018, to produce docu-series, documentaries and features for Netflix under the Obamas' newly formed production company, Higher Ground Productions. Higher Ground's first film, ''American Factory,'' won the Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature in 2020.
 He received a 63% approval rating in Gallup's 2018 job approval poll for the past 10 U.S. presidents.
A pipe bomb addressed to Obama was intercepted by the Secret Service on October 24, 2018. It was one of several pipe-bombs that had been October 2018 United States mail bombing attempts, mailed out to Democratic lawmakers and officials.
In 2019, Barack and Michelle Obama bought a home on Martha's Vineyard from Wyc Grousbeck. On October 29, 2019, Obama criticized "wokeness" and Cancel culture, call-out culture at the Obama Foundation's annual summit.
Obama was reluctant to make an endorsement in the 2020 Democratic presidential primaries because he wanted to position himself to unify the party, no matter who the nominee was. On April 14, 2020, Obama endorsed his former vice president Joe Biden, the presumptive Democratic nominee, for president in the 2020 United States presidential election, 2020 election, stating that he has "all the qualities we need in a president right now." In May 2020, Obama criticized President Trump for Trump administration communication during the COVID-19 pandemic, his handling of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, COVID-19 pandemic, calling his response to the crisis "an absolute chaotic disaster", and stating that the consequences of Presidency of Donald Trump, the Trump presidency have been "our worst impulses unleashed, our proud reputation around the world badly diminished, and our democratic institutions threatened like never before." Trump retaliated by accusing Obama of having committed "the biggest political crime in American history", although he refused to say what he was talking about, telling reporters: "You know what the crime is, the crime is very obvious to everybody."
Obama wrote a presidential memoir, in a $65million deal with Penguin Random House. The book, ''
He received a 63% approval rating in Gallup's 2018 job approval poll for the past 10 U.S. presidents.
A pipe bomb addressed to Obama was intercepted by the Secret Service on October 24, 2018. It was one of several pipe-bombs that had been October 2018 United States mail bombing attempts, mailed out to Democratic lawmakers and officials.
In 2019, Barack and Michelle Obama bought a home on Martha's Vineyard from Wyc Grousbeck. On October 29, 2019, Obama criticized "wokeness" and Cancel culture, call-out culture at the Obama Foundation's annual summit.
Obama was reluctant to make an endorsement in the 2020 Democratic presidential primaries because he wanted to position himself to unify the party, no matter who the nominee was. On April 14, 2020, Obama endorsed his former vice president Joe Biden, the presumptive Democratic nominee, for president in the 2020 United States presidential election, 2020 election, stating that he has "all the qualities we need in a president right now." In May 2020, Obama criticized President Trump for Trump administration communication during the COVID-19 pandemic, his handling of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, COVID-19 pandemic, calling his response to the crisis "an absolute chaotic disaster", and stating that the consequences of Presidency of Donald Trump, the Trump presidency have been "our worst impulses unleashed, our proud reputation around the world badly diminished, and our democratic institutions threatened like never before." Trump retaliated by accusing Obama of having committed "the biggest political crime in American history", although he refused to say what he was talking about, telling reporters: "You know what the crime is, the crime is very obvious to everybody."
Obama wrote a presidential memoir, in a $65million deal with Penguin Random House. The book, '' On April 5, 2022, Obama visited the White House for the first time since leaving office, in an event celebrating the 12th annual anniversary of the signing of the Affordable Care Act.
In 2022, he narrated the Netflix documentary series ''Our Great National Parks'', which later won him a Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Narrator.
In June 2022, it was announced that the Obamas and their podcast production company, Higher Ground Productions, Higher Ground, signed a multi-year deal with Audible (service), Audible.
In September 2022, Obama visited the White House to unveil his and Michelle's official White House portraits.
On April 5, 2022, Obama visited the White House for the first time since leaving office, in an event celebrating the 12th annual anniversary of the signing of the Affordable Care Act.
In 2022, he narrated the Netflix documentary series ''Our Great National Parks'', which later won him a Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Narrator.
In June 2022, it was announced that the Obamas and their podcast production company, Higher Ground Productions, Higher Ground, signed a multi-year deal with Audible (service), Audible.
In September 2022, Obama visited the White House to unveil his and Michelle's official White House portraits.
 Historian Julian E. Zelizer, Julian Zelizer credits Obama with "a keen sense of how the institutions of government work and the ways that his team could design policy proposals." Zelizer notes Obama's policy successes included the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, economic stimulus package which ended the Great Recession in the United States, Great Recession and the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, Dodd-Frank financial and consumer protection reforms, as well as the
Historian Julian E. Zelizer, Julian Zelizer credits Obama with "a keen sense of how the institutions of government work and the ways that his team could design policy proposals." Zelizer notes Obama's policy successes included the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, economic stimulus package which ended the Great Recession in the United States, Great Recession and the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, Dodd-Frank financial and consumer protection reforms, as well as the