Prehistory of Central Asia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of Central Asia concerns the history of the various peoples that have inhabited Central Asia. The lifestyle of such people has been determined primarily by the area's climate and
The history of Central Asia concerns the history of the various peoples that have inhabited Central Asia. The lifestyle of such people has been determined primarily by the area's climate and
 Anatomically modern humans (''
Anatomically modern humans (''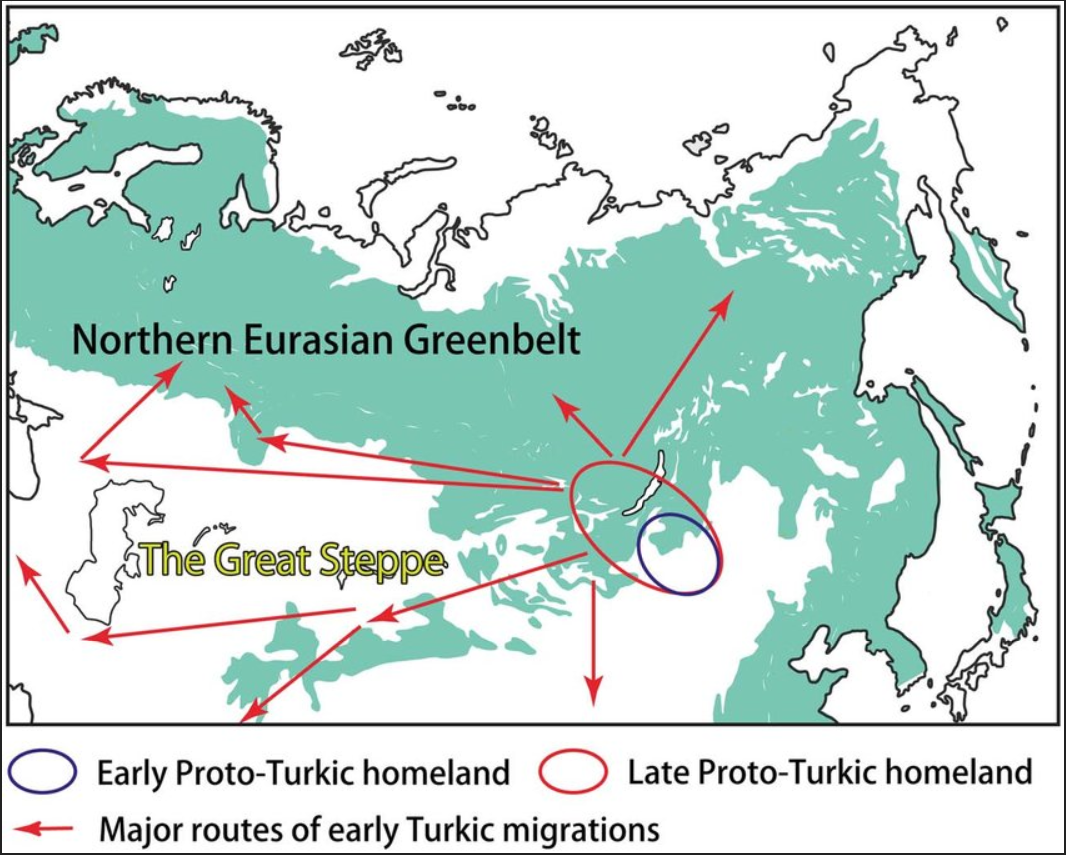 Paleolithic Central Asia was characterized by an distinctive but deeply European-related population (
Paleolithic Central Asia was characterized by an distinctive but deeply European-related population (
 The history of Central Asia concerns the history of the various peoples that have inhabited Central Asia. The lifestyle of such people has been determined primarily by the area's climate and
The history of Central Asia concerns the history of the various peoples that have inhabited Central Asia. The lifestyle of such people has been determined primarily by the area's climate and geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ...
. The arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most a ...
ity of the region makes agriculture difficult and distance from the sea cut it off from much trade. Thus, few major cities developed in the region. Nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the pop ...
ic horse peoples of the steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands ...
dominated the area for millennia.
Relations between the steppe nomads and the settled people in and around Central Asia were marked by conflict. The nomadic lifestyle was well suited to warfare, and the steppe horse riders became some of the most militarily potent people in the world, due to the devastating techniques and ability of their horse archers. Periodically, tribal leaders or changing conditions would cause several tribes to organize themselves into a single military force, which would then often launch campaigns of conquest, especially into more 'civilized' areas. A few of these types of tribal coalitions included the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
' invasion of Europe, various Turkic migrations into Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
, the Wu Hu attacks on China and most notably the Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
conquest of much of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
.
The dominance of the nomads ended in the 16th century as firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes c ...
s allowed settled people to gain control of the region. The Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The ...
, the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
of China, and other powers expanded into the area and seized the bulk of Central Asia by the end of the 19th century. After the Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
, the Soviet Union incorporated most of Central Asia; only Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; literal translation, lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia Mongolia–Russia border, to the north and China China–Mongolia border, to the s ...
and Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
remained nominally independent, although Mongolia existed as a Soviet satellite state
A satellite state or dependent state is a country that is formally independent in the world, but under heavy political, economic, and military influence or control from another country. The term was coined by analogy to planetary objects orbiting ...
and Soviet troops invaded Afghanistan in the late 20th century. The Soviet areas of Central Asia saw much industrialization
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econom ...
and construction of infrastructure, but also the suppression of local cultures and a lasting legacy of ethnic tensions and environmental problems.
With the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, five Central Asian countries gained independence — Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbekis ...
, Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
, Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east ...
, and Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
. In all of the new states, former Communist Party
A communist party is a political party that seeks to realize the socio-economic goals of communism. The term ''communist party'' was popularized by the title of '' The Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (1848) by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. ...
officials retained power as local strongmen, with the partial exception of Kyrgyzstan which, despite ousting three post-Soviet presidents in popular uprisings, has as yet been unable to consolidate a stable democracy.
Prehistory
 Anatomically modern humans (''
Anatomically modern humans (''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, a ...
'') reached Central Asia by 50,000 to 40,000 years ago. The Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Ti ...
is thought to have been reached by 38,000 years ago. The currently oldest modern human sample found in northern Central Asia, is a 45,000-year-old remain, which was genetically closest to ancient and modern East Asians
East Asian people (East Asians) are the people from East Asia, which consists of China, Taiwan, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, and South Korea. The total population of all countries within this region is estimated to be 1.677 billion and 21% of th ...
, but his lineage died out quite early.
 Paleolithic Central Asia was characterized by an distinctive but deeply European-related population (
Paleolithic Central Asia was characterized by an distinctive but deeply European-related population (Ancient North Eurasian
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient North Eurasian (generally abbreviated as ANE) is the name given to an ancestral component that represents a lineage ancestral to the people of the Mal'ta–Buret' culture and populations closely related to the ...
), with subsequent geneflow from Paleo-Siberians, contributing East Asian-related ancestry towards Paleolithic Central Asians. During the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
, ancient Central Asia received various migration events from Europe and the Middle East, associated with Indo-Europeans. Bronze Age Central Asia consisted largely of Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separat ...
, with some groups being of Paleo-Siberian and Samoyedic (Uralic) origin. Since the early Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ap ...
, Central Asia received noteworthy amounts of migration from East Asian-related populations, and became increasingly diverse. The Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
slowly replaced and assimilated the previous Iranian-speaking locals, turning the population of Central Asia from largely Iranian, into primarily of East Asian descent. Modern Central Asians are characterized by both West-Eurasian and East-Eurasian ancestry, with the majority being of primarily East Asian ancestry, and can be linked to expanding Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
outgoing from Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; literal translation, lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia Mongolia–Russia border, to the north and China China–Mongolia border, to the s ...
and Northeast Asia
Northeast Asia or Northeastern Asia is a geographical subregion of Asia; its northeastern landmass and islands are bounded by the Pacific Ocean.
The term Northeast Asia was popularized during the 1930s by American historian and political scienti ...
.
The term Ceramic Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymousl ...
is used of late Mesolithic cultures of Central Asia, during the 6th to 5th millennia BC
(in Russian archaeology
Russian archaeology begins in the Russian Empire in the 1850s and becomes Soviet archaeology in the early 20th century.
The journal '' Sovetskaya arkheologiya'' is published from 1957.
Archaeologists
Sites
major archaeological cultures and ...
, these cultures are described as Neolithic even though farming is absent). It is characterized by its distinctive type of pottery, with point or knob base and flared rims, manufactured by methods not used by the Neolithic farmers. The earliest manifestation of this type of pottery may be in the region around Lake Baikal in Siberia. It appears in the Elshan or Yelshanka or Samara culture
The Samara culture was an Eneolithic (Copper Age) culture that flourished around the turn of the 5th millennium BCE, at the Samara Bend of the Volga River (modern Russia). The Samara culture is regarded as related to contemporaneous or subseque ...
on the Volga in Russia by about 7000 BC. and from there spread via the Dnieper-Donets culture to the Narva culture
Narva culture or eastern Baltic was a European Neolithic archaeological culture found in present-day Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Kaliningrad Oblast (former East Prussia), and adjacent portions of Poland, Belarus and Russia. A successor of the M ...
of the Eastern Baltic.
The Botai culture
The Botai culture is an archaeological culture (c. 3700–3100 BC) of prehistoric northern Central Asia. It was named after the settlement of Botai in today's northern Kazakhstan. The Botai culture has two other large sites: Krasnyi ...
(c. 3700–3100 BC) is suggested to be the earliest culture to have domesticated the horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a Domestication, domesticated, odd-toed ungulate, one-toed, ungulate, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two Extant taxon, extant subspecies of wild horse, ''Equus fer ...
. The four analyzed Botai samples had about 2/3 European-related and 1/3 East Asian-related ancestry. The Botai samples also showed high affinity towards the Mal'ta boy sample in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
.
In the Pontic–Caspian steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, formed by the Caspian steppe and the Pontic steppe, is the steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the Pontus Euxinus of antiquity) to the northern area around the Caspian Sea. It extend ...
, Chalcolithic cultures develop in the second half of the 5th millennium BC, small communities in permanent settlements which began to engage in agricultural practices as well as herding. Around this time, some of these communities began the domestication of the horse
A number of hypotheses exist on many of the key issues regarding the domestication of the horse. Although horses appeared in Paleolithic cave art as early as 30,000 BCE, these were wild horses and were probably hunted for meat.
How and when hor ...
. According to the Kurgan hypothesis
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory, Kurgan model, or steppe theory) is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and par ...
, the north-west of the region is also considered to be the source of the root of the Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
.
The horse-drawn chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&nb ...
appears in the 3rd millennium BC, by 2000 BC, in the form of war chariots with spoked wheel
A spoke is one of some number of rods radiating from the center of a wheel (the hub where the axle connects), connecting the hub with the round traction surface.
The term originally referred to portions of a log that had been riven (split l ...
s, thus being made more maneuverable, and dominated the battlefields. The growing use of the horse, combined with the failure, roughly around 2000 BC, of the always precarious irrigation systems that had allowed for extensive agriculture in the region, gave rise and dominance of pastoral nomadism
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
by 1000 BC, a way of life that would dominate the region for the next several millennia, giving rise to the Scythia
Scythia (Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
H ...
n expansion of the Iron Age.
Scattered nomadic groups maintained herds of sheep, goats, horses, and camels, and conducted annual migrations to find new pastures (a practice known as transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower vall ...
). The people lived in yurt
A yurt (from the Turkic languages) or ger ( Mongolian) is a portable, round tent covered and insulated with skins or felt and traditionally used as a dwelling by several distinct nomadic groups in the steppes and mountains of Central Asia. ...
s (or gers) – tents made of hides and wood that could be disassembled and transported. Each group had several yurts, each accommodating about five people.
While the semi-arid plains were dominated by the nomads, small city-states and sedentary agrarian societies arose in the more humid areas of Central Asia. The Bactria-Margiana Archaeological Complex of the early 2nd millennium BC was the first sedentary civilization of the region, practicing irrigation farming of wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeological ...
and barley and possibly a form of writing. Bactria-Margiana probably interacted with the contemporary Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
nomads of the Andronovo culture
The Andronovo culture (russian: Андроновская культура, translit=Andronovskaya kul'tura) is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1450 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo ...
, the originators of the spoke-wheeled chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&nb ...
, who lived to their north in western Siberia, Russia, and parts of Kazakhstan, and survived as a culture until the 1st millennium BC. These cultures, particularly Bactria-Margiana, have been posited as possible representatives of the hypothetical Aryan
Aryan or Arya (, Indo-Iranian *''arya'') is a term originally used as an ethnocultural self-designation by Indo-Iranians in ancient times, in contrast to the nearby outsiders known as 'non-Aryan' (*''an-arya''). In Ancient India, the term ' ...
culture ancestral to the speakers of the Indo-Iranian languages
The Indo-Iranian languages (also Indo-Iranic languages or Aryan languages) constitute the largest and southeasternmost extant branch of the Indo-European language family (with over 400 languages), predominantly spoken in the geographical subre ...
(see Indo-Iranians
Indo-Iranian peoples, also known as Indo-Iranic peoples by scholars, and sometimes as Arya or Aryans from their self-designation, were a group of Indo-European peoples who brought the Indo-Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European ...
).
Later the strongest of Sogdian city-states of the Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley (; ; ) in Central Asia lies mainly in eastern Uzbekistan, but also extends into southern Kyrgyzstan and northern Tajikistan.
Divided into three republics of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse and in the ...
rose to prominence. After the 1st century BC, these cities became home to the traders of the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
and grew wealthy from this trade. The steppe nomads were dependent on these settled people for a wide array of goods that were impossible for transient populations to produce. The nomads traded for these when they could, but because they generally did not produce goods of interest to sedentary people, the popular alternative was to carry out raids.
A wide variety of people came to populate the steppes. Nomadic groups in Central Asia included the Huns and other Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic o ...
, as well as Indo-Europeans such as the Tocharians
The Tocharians, or Tokharians ( US: or ; UK: ), were speakers of Tocharian languages, Indo-European languages known from around 7600 documents from around 400 to 1200 AD, found on the northern edge of the Tarim Basin (modern Xinjiang, China) ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, Scythia
Scythia (Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
H ...
ns, Saka
The Saka (Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who hist ...
, Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat at ...
, Wusun
The Wusun (; Eastern Han Chinese *''ʔɑ-suən'' < (140 BCE < 436 BCE): *''Ɂâ-sûn'') were an ancient semi-, and others, and a number of
 In the 2nd and 1st millennia BC, a series of large and powerful states developed on the southern periphery of Central Asia (the
In the 2nd and 1st millennia BC, a series of large and powerful states developed on the southern periphery of Central Asia (the
83–144
/ref> The vast fortified settlement of Kamenka on the
 It was during the Sui and Tang dynasties that China expanded into eastern Central Asia. Chinese foreign policy to the north and west now had to deal with Turkic nomads, who were becoming the most dominant ethnic group in Central Asia. To handle and avoid any threats posed by the Turks, the Sui government repaired fortifications and received their trade and tribute missions. They sent royal princesses off to marry Turkic clan leaders, a total of four of them in 597, 599, 614, and 617. The Sui army intervened in Turks’ civil war and stirred conflict amongst ethnic groups against the Turks.
As early as the Sui dynasty, the Turks had become a major militarised force employed by the Chinese. When the
It was during the Sui and Tang dynasties that China expanded into eastern Central Asia. Chinese foreign policy to the north and west now had to deal with Turkic nomads, who were becoming the most dominant ethnic group in Central Asia. To handle and avoid any threats posed by the Turks, the Sui government repaired fortifications and received their trade and tribute missions. They sent royal princesses off to marry Turkic clan leaders, a total of four of them in 597, 599, 614, and 617. The Sui army intervened in Turks’ civil war and stirred conflict amongst ethnic groups against the Turks.
As early as the Sui dynasty, the Turks had become a major militarised force employed by the Chinese. When the 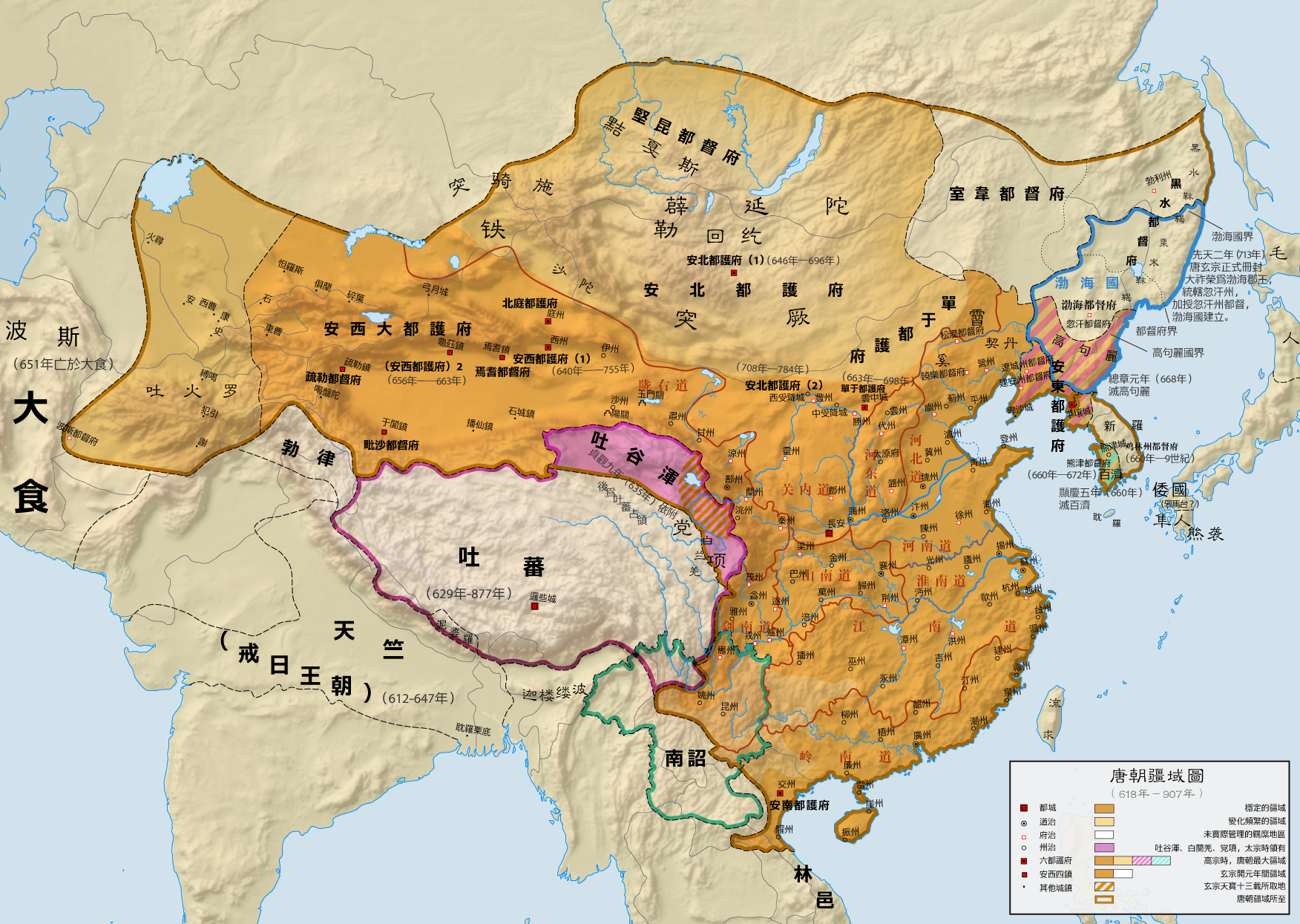 The expansion into Central Asia continued under Taizong's successor, Emperor Gaozong, who invaded the Western Turks ruled by the qaghan
The expansion into Central Asia continued under Taizong's successor, Emperor Gaozong, who invaded the Western Turks ruled by the qaghan
 The Tang Empire competed with the
The Tang Empire competed with the

 Over time, as new technologies were introduced, the nomadic horsemen grew in power. The
Over time, as new technologies were introduced, the nomadic horsemen grew in power. The  Once the foreign powers were expelled, several indigenous empires formed in Central Asia. The
Once the foreign powers were expelled, several indigenous empires formed in Central Asia. The
 An even more important development was the introduction of
An even more important development was the introduction of
 The Russians also expanded south, first with the transformation of the
The Russians also expanded south, first with the transformation of the
 The forces of the
The forces of the
China’s Belt and Road Initiative through the Lens of Central Asia
��, in Fanny M. Cheung and Ying-yi Hong (eds) ''Regional Connection under the Belt and Road Initiative. The Prospects for Economic and Financial Cooperation''. London: Routledge, p. 116.
UNESCO History of Civilizations of Central Asia
' (Paris:
Rediscovering Central Asia
'
Encyclopædia Iranica: Central Asia in pre-Islamic Times (R. Fryer)
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20090224083111/http://www.iranica.com/newsite/search/searchpdf.isc?ReqStrPDFPath=%2Fhome%2Firanica%2Fpublic_html%2Fnewsite%2Fpdfarticles%2Fv5_articles%2Fcentral_asia%2Fmongol_and_timurid_periods&OptStrLogFile=%2Fhome%2Firanica%2Fpublic_html%2Fnewsite%2Flogs%2Fpdfdownload.html Encyclopædia Iranica: Central Asia in the Mongol and Timurid Periods (B. Spuler)]
Encyclopædia Iranica: Central Asia from the 16th to the 18th centuries (R.D. McChesney)
( Yuri Bregel)
Center for the Study of Eurasian Nomads
perseus project
* * * * * * * * * * * * *
New Directions Post-Independence
from th
Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
{{Authority control Archaeology of Central Asia Prehistoric Asia Geography of Central Asia
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
groups. Despite these ethnic and linguistic differences, the steppe lifestyle led to the adoption of very similar culture across the region.
Ancient era
 In the 2nd and 1st millennia BC, a series of large and powerful states developed on the southern periphery of Central Asia (the
In the 2nd and 1st millennia BC, a series of large and powerful states developed on the southern periphery of Central Asia (the Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran (Elam, ...
). These empires launched several attempts to conquer the steppe people but met with only mixed success. The Median Empire
The Medes (Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, t ...
and Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
both ruled parts of Central Asia. The Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209& ...
Empire (209 BC-93 (156) AD) may be seen as the first central Asian empire which set an example for later Göktürk and Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
empires.Christoph Baumer "The History of Central Asia – The Age of the Silk Roads (Volume 2); PART I: EARLY EMPIRES AND KINGDOMS IN EAST CENTRAL ASIA 1. The Xiongnu, the First Steppe Nomad Empire" Xiongnu's ancestor Xianyu tribe founded Zhongshan state (c. 6th century BC – c. 296 BC) in Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
province, China. The title chanyu
Chanyu () or Shanyu (), short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu (), was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "''Khagan''" in 402 CE. The title was most famously used by the ruling ...
was used by the Xiongnu rulers before Modun Chanyu
Modu, Maodun, Modun (, from Old Chinese (220 B.C.E.): *''mouᴴ-tuən'' or *''mək-tuən'', c. 234 – c. 174 BCE) was the son of Touman and the founder of the empire of the Xiongnu. He came to power by ordering his men to kill his father in 209 ...
so it is possible that statehood
A state is a centralized political organization that imposes and enforces rules over a population within a territory. There is no undisputed definition of a state. One widely used definition comes from the German sociologist Max Weber: a "sta ...
history of the Xiongnu began long before Modun's rule.
Following the success of the Han–Xiongnu War
The Han–Xiongnu War,. also known as the Sino–Xiongnu War, was a series of military battles fought between the Han Empire and the nomadic Xiongnu confederation from 133 BC to 89 AD.
Starting from Emperor Wu's reign (r. 141–87 BC), the Han ...
, Chinese states would also regularly strive to extend their power westwards. Despite their military might, these states found it difficult to conquer the whole region.
When faced by a stronger force, the nomads could simply retreat deep into the steppe and wait for the invaders to leave. With no cities and little wealth other than the herds they took with them, the nomads had nothing they could be forced to defend. An example of this is given by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for ha ...
's detailed account of the futile Persian campaigns against the Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
. The Scythians, like most nomad empires, had permanent settlements of various sizes, representing various degrees of civilisation.Herodotus, IV83–144
/ref> The vast fortified settlement of Kamenka on the
Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and ...
River, settled since the end of the 5th century BC, became the centre of the Scythian kingdom ruled by Ateas
Ateas (ca. 429 BC – 339 BC) was described in Greek and Roman sources as the most powerful king of Scythia, who lost his life and empire in the conflict with Philip II of Macedon in 339 BC. His name also occurs as ''Atheas'', ''Ateia'', ' ...
, who lost his life in a battle against Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king (''basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the a ...
in 339 BC.
Some empires, such as the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
and Macedonian empires, did make deep inroads into Central Asia by founding cities and gaining control of the trading centres. Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
's conquests spread Hellenistic civilisation all the way to Alexandria Eschate
Alexandria Eschate ( grc-x-attic, Ἀλεξάνδρεια Ἐσχάτη, grc-x-doric, Αλεχάνδρεια Ἐσχάτα, Alexandria Eschata, "Furthest Alexandria") was a city founded by Alexander the Great, at the south-western end of the Fe ...
(Lit. “Alexandria the Furthest”), established in 329 BC in modern Tajikistan. After Alexander's death in 323 BC, his Central Asian territory fell to the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
during the Wars of the Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi ( grc, Πόλεμοι τῶν Διαδόχων, '), or Wars of Alexander's Successors, were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule h ...
.
In 250 BC, the Central Asian portion of the empire (Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
) seceded as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the Indi ...
, which had extensive contacts with India and China until its end in 125 BC. The Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent ( ...
, mostly based in the Punjab region
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprisin ...
but controlling a fair part of Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, pioneered the development of Greco-Buddhism
Greco-Buddhism, or Graeco-Buddhism, is the cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism, which developed between the fourth century BC and the fifth century AD in Gandhara, in present-day north-western Pakistan and parts of nort ...
. The Kushan Kingdom thrived across a wide swath of the region from the 2nd century BC to the 4th century AD, and continued Hellenistic and Buddhist traditions. These states prospered from their position on the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
linking China and Europe.
Likewise, in eastern Central Asia, the Chinese Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a war ...
expanded into the region at the height of its imperial power. From roughly 115 to 60 BC, Han forces fought the Xiongnu over control of the oasis city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
s in the Tarim Basin. The Han was eventually victorious and established the Protectorate of the Western Regions
The Protectorate of the Western Regions () was an imperial administration (a protectorate) of Han China in the Western Regions.
The "Western Regions" referred to areas west of Yumen Pass, especially the Tarim Basin. These areas would later be ...
in 60 BC, which dealt with the region's defence and foreign affairs. Chinese rule in Tarim Basin was replaced successively with Kushans
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
and Hephthalites
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
.
Later, external powers such as the Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
would come to dominate this trade. One of those powers, the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conque ...
, was of Central Asian origin, but adopted Persian-Greek cultural traditions. This is an early example of a recurring theme of Central Asian history: occasionally nomads of Central Asian origin would conquer the kingdoms and empires surrounding the region, but quickly merge into the culture of the conquered peoples.
At this time Central Asia was a heterogeneous region with a mixture of cultures and religions. Buddhism remained the largest religion, but was concentrated in the east. Around Persia, Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ont ...
became important. Nestorian Christianity entered the area, but was never more than a minority faith. More successful was Manichaeism
Manichaeism (;
in New Persian ; ) is a former major religionR. van den Broek, Wouter J. Hanegraaff ''Gnosis and Hermeticism from Antiquity to Modern Times''SUNY Press, 1998 p. 37 founded in the 3rd century AD by the Parthian prophet Mani (A ...
, which became the third largest faith.
Turkic expansion
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
began in the 6th century; the Turkic speaking Uyghurs were one of many distinct cultural groups brought together by the trade of the Silk Route at Turfan
Turpan (also known as Turfan or Tulufan, , ug, تۇرپان) is a prefecture-level city located in the east of the autonomous region of Xinjiang, China. It has an area of and a population of 632,000 (2015).
Geonyms
The original name of the ci ...
, which was then ruled by China's Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
. The Uyghurs, primarily pastoral nomads, observed a number of religions including Manichaeism, Buddhism, and Nestorian Christianity. Many of the artefacts from this period were found in the 19th century in this remote desert region.
Medieval
Sui and early Tang dynasty
 It was during the Sui and Tang dynasties that China expanded into eastern Central Asia. Chinese foreign policy to the north and west now had to deal with Turkic nomads, who were becoming the most dominant ethnic group in Central Asia. To handle and avoid any threats posed by the Turks, the Sui government repaired fortifications and received their trade and tribute missions. They sent royal princesses off to marry Turkic clan leaders, a total of four of them in 597, 599, 614, and 617. The Sui army intervened in Turks’ civil war and stirred conflict amongst ethnic groups against the Turks.
As early as the Sui dynasty, the Turks had become a major militarised force employed by the Chinese. When the
It was during the Sui and Tang dynasties that China expanded into eastern Central Asia. Chinese foreign policy to the north and west now had to deal with Turkic nomads, who were becoming the most dominant ethnic group in Central Asia. To handle and avoid any threats posed by the Turks, the Sui government repaired fortifications and received their trade and tribute missions. They sent royal princesses off to marry Turkic clan leaders, a total of four of them in 597, 599, 614, and 617. The Sui army intervened in Turks’ civil war and stirred conflict amongst ethnic groups against the Turks.
As early as the Sui dynasty, the Turks had become a major militarised force employed by the Chinese. When the Khitans
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East.
As a people desce ...
began raiding north-east China in 605, a Chinese general led 20,000 Turks against them, distributing Khitan livestock and women to the Turks as a reward. On two occasions between 635 and 636, Tang royal princesses were married to Turk mercenaries or generals in Chinese service.
Throughout the Tang dynasty until the end of 755, there were approximately ten Turkic generals serving under the Tang. While most of the Tang army was made of '' fubing(府兵)'' Chinese conscripts, the majority of the troops led by Turkic generals were of non-Chinese origin, campaigning largely in the western frontier where the presence of '' fubing(府兵)'' troops was low. Some "Turkic" troops were nomadisized Han Chinese, a desinicized people.
Civil war in China was almost totally diminished by 626, along with the defeat in 628 of the Ordos Chinese warlord Liang Shidu
Liang Shidu (梁師都) (died June 3, 628) was an agrarian leader who rebelled against the rule of the Chinese dynasty Sui Dynasty near the end of the reign of Emperor Yang of Sui. He, claiming the title of Emperor of Liang with the aid from East ...
; after these internal conflicts, the Tang began an offensive against the Turks. In the year 630, Tang armies captured areas of the Ordos Desert, modern-day Inner Mongolia province, and southern Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; literal translation, lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia Mongolia–Russia border, to the north and China China–Mongolia border, to the s ...
from the Turks.
After this military victory, Emperor Taizong won the title of Great Khan amongst the various Turks in the region who pledged their allegiance to him and the Chinese empire (with several thousand Turks traveling into China to live at Chang'an). On June 11, 631, Emperor Taizong also sent envoys to the Eastern Turkic tribes bearing gold and silk in order to persuade the release of enslaved Chinese prisoners who were captured during the transition from Sui to Tang
The transition from Sui to Tang (613–628) was the period of Chinese history between the end of the Sui dynasty and the start of the Tang dynasty. The Sui dynasty's territories were carved into a handful of short-lived states by its officials, ...
from the northern frontier; this embassy succeeded in freeing 80,000 Chinese men and women who were then returned to China.
While the Turks were settled in the Ordos region (former territory of the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209& ...
), the Tang government took on the military policy of dominating the central steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands ...
. Like the earlier Han dynasty, the Tang dynasty, along with Turkic allies like the Uyghurs, conquered and subdued Central Asia during the 640s and 650s. During Emperor Taizong's reign alone, large campaigns were launched against not only the Göktürks, but also separate campaigns against the Tuyuhun
Tuyuhun (; LHC: *''tʰɑʔ-jok-guənʔ''; Wade-Giles: ''T'u-yühun''), also known as Henan () and Azha (; ), was a dynastic kingdom established by the nomadic peoples related to the Xianbei in the Qilian Mountains and upper Yellow River valley, ...
, and the Xueyantuo
The Xueyantuo were an ancient Tiele tribe and khaganate in Northeast Asia who were at one point vassals of the Göktürks, later aligning with the Tang dynasty against the Eastern Göktürks.
Names Xue
''Xue'' 薛 appeared earlier as ''Xin ...
. Taizong also launched campaigns against the oasis states of the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
, beginning with the annexation of Gaochang in 640. The nearby kingdom of Karasahr
Karasahr or Karashar ( ug, قاراشەھەر, Qarasheher, 6=Қарашәһәр), which was originally known, in the Tocharian languages as ''Ārśi'' (or Arshi) and Agni or the Chinese derivative Yanqi ( zh, s=焉耆, p=Yānqí, w=Yen-ch'i), is an ...
was captured by the Tang in 644 and the kingdom of Kucha
Kucha, or Kuche (also: ''Kuçar'', ''Kuchar''; ug, كۇچار, Кучар; zh, t= 龜茲, p=Qiūcí, zh, t=庫車, p=Kùchē; sa, कूचीन, translit=Kūcīna), was an ancient Buddhist kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road t ...
was conquered in 649.
 The expansion into Central Asia continued under Taizong's successor, Emperor Gaozong, who invaded the Western Turks ruled by the qaghan
The expansion into Central Asia continued under Taizong's successor, Emperor Gaozong, who invaded the Western Turks ruled by the qaghan Ashina Helu
Ishbara Khagan (Old Turkic: 𐰃𐱁𐰉𐰺𐰀𐰴𐰍𐰣, Ïšbara qaγan, , personal name Ashina Helu - ) (ruled 651–658) was the last khagan of the Western Turkic Khaganate.
Name
The khagan's underlying Turkic name, transcribed with Ch ...
in 657 with an army led by Su Dingfang
Su Dingfang () (591–667), formal name Su Lie () but went by the courtesy name of Dingfang, formally Duke Zhuang of Xing (), was a Chinese military general of the Tang Dynasty who succeeded in destroying the Western Turkic Khaganate in 657. He wa ...
. Ashina was defeated and the khaganate was absorbed into the Tang empire. The territory was administered through the Anxi Protectorate
The Protectorate General to Pacify the West (Anxi Grand Protectorate), initially the Protectorate to Pacify the West (Anxi Protectorate), was a protectorate (640 – ) established by the Chinese Tang dynasty in 640 to control the Tarim Basin. T ...
and the Four Garrisons of Anxi
The Four Garrisons of Anxi were Chinese military garrisons installed by the Tang dynasty between 648 and 658. They were stationed at the Indo-European city-states of Qiuci (Kucha), Yutian (Hotan), Shule (Kashgar) and Yanqi ( Karashahr). The ...
. Tang hegemony beyond the Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia and Pakistan. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world' ...
in Afghanistan ended with revolts by the Turks in 665, but the Tang retained a military presence in Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan. These holdings were later invaded by the Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (, ; ) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of imperial expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. The empire further expanded under the 3 ...
to the south in 670.
Tang rivalry with the Tibetan Empire
 The Tang Empire competed with the
The Tang Empire competed with the Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (, ; ) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of imperial expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. The empire further expanded under the 3 ...
for control of areas in Inner and Central Asia, which was at times settled with marriage alliances such as the marrying of Princess Wencheng
Princess Wencheng (; ) was a member of a minor branch of the royal clan of the Tang Dynasty who married King Songtsen Gampo of the Tibetan Empire in 641. She is also known by the name Gyasa or "Chinese wife" in Tibet. Some Tibetan historians cons ...
(d. 680) to Songtsän Gampo
Songtsen Gampo (; 569–649? 650), also Songzan Ganbu (), was the 33rd Tibetan king and founder of the Tibetan Empire, and is traditionally credited with the introduction of Buddhism to Tibet, influenced by his Nepali consort Bhrikuti, of Nepal ...
(d. 649). A Tibetan tradition mentions that after Songtsän Gampo's death in 649 AD, Chinese troops captured Lhasa. The Tibetan scholar Tsepon W. D. Shakabpa believes that the tradition is in error and that "those histories reporting the arrival of Chinese troops are not correct" and claims that the event is mentioned neither in the Chinese annals nor in the manuscripts of Dunhuang.
There was a long string of conflicts with Tibet over territories in the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
between 670–692 and in 763 the Tibetans even captured the capital of China, Chang'an, for fifteen days during the An Shi Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general offic ...
. In fact, it was during this rebellion that the Tang withdrew its western garrisons stationed in what is now Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
and Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest ...
, which the Tibetans then occupied along with the territory of Central Asia. Hostilities between the Tang and Tibet continued until they signed a formal peace treaty in 821. The terms of this treaty, including the fixed borders between the two countries, are recorded in a bilingual inscription on a stone pillar outside the Jokhang
The Jokhang (, ), also known as the Qoikang Monastery, Jokang, Jokhang Temple, Jokhang Monastery and Zuglagkang ( or Tsuklakang), is a Buddhist temple in Barkhor Square in Lhasa, the capital city of Tibet Autonomous Region of China. Tibetans, ...
temple in Lhasa.
Arrival of Islam
In the 8th century, Islam began to penetrate the region, the desert nomads ofArabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
could militarily match the nomads of the steppe, and the early Arab Empire
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
gained control over parts of Central Asia. The early conquests under Qutayba ibn Muslim
Abū Ḥafṣ Qutayba ibn Abī Ṣāliḥ Muslim ibn ʿAmr al-Bāhilī ( ar, أبو حفص قتيبة بن أبي صالح مسلم بن عمرو الباهلي; 669–715/6) was an Arab commander of the Umayyad Caliphate who became governor of ...
(705–715) were soon reversed by a combination of native uprisings and invasion by the Turgesh, but the collapse of the Turgesh khaganate after 738 opened the way for the re-imposition of Muslim authority under Nasr ibn Sayyar
Naṣr ibn Sayyār al-Lāythi al-Kināni ( ar, نصر بن سيار الليثي الكناني; 663 – 9 December 748) was an Arab general and the last Umayyad governor of Khurasan in 738–748. Nasr played a distinguished role in the wars agai ...
.
The Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, No ...
invasion also saw Chinese influence expelled from western Central Asia. At the Battle of Talas
The Battle of Talas or Battle of Artlakh (; ar, معركة نهر طلاس, translit=Maʿrakat nahr Ṭalās, Persian: Nabard-i Tarāz) was a military encounter and engagement between the Abbasid Caliphate along with its ally, the Tibetan Empir ...
in 751 an Arab army decisively defeated a Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
force, and for the next several centuries Middle Eastern influences would dominate the region. Large-scale Islamization however did not begin until the 9th century, running parallel with the fragmentation of Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
political authority and the emergence of local Iranian and Turkic dynasties like the Samanids People
Samanid
Samanid
Samanid
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan origin ...
.
Steppe empires

Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
developed the saddle
The saddle is a supportive structure for a rider of an animal, fastened to an animal's back by a girth. The most common type is equestrian. However, specialized saddles have been created for oxen, camels and other animals. It is not kn ...
, and by the time of the Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Al ...
the use of the stirrup
A stirrup is a light frame or ring that holds the foot of a rider, attached to the saddle by a strap, often called a ''stirrup leather''. Stirrups are usually paired and are used to aid in mounting and as a support while using a riding animal (u ...
had begun. Horses continued to grow larger and sturdier so that chariots were no longer needed as the horses could carry men with ease. This greatly increased the mobility of the nomads; it also freed their hands, allowing them to use the bow from horseback.
Using small but powerful composite bow
A composite bow is a traditional bow made from horn, wood, and sinew laminated together, a form of laminated bow. The horn is on the belly, facing the archer, and sinew on the outer side of a wooden core. When the bow is drawn, the sinew (stre ...
s, the steppe people gradually became the most powerful military force in the world. From a young age, almost the entire male population was trained in riding and archery, both of which were necessary skills for survival on the steppe. By adulthood, these activities were second nature. These mounted archers were more mobile than any other force at the time, being able to travel forty miles per day with ease.
The steppe peoples quickly came to dominate Central Asia, forcing the scattered city states and kingdoms to pay them tribute or face annihilation. The martial ability of the steppe peoples was limited, however, by the lack of political structure within the tribes. Confederations of various groups would sometimes form under a ruler known as a khan. When large numbers of nomads acted in unison they could be devastating, as when the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
arrived in Western Europe. However, tradition dictated that any dominion conquered in such wars should be divided among all of the khan's sons, so these empires often declined as quickly as they formed.
 Once the foreign powers were expelled, several indigenous empires formed in Central Asia. The
Once the foreign powers were expelled, several indigenous empires formed in Central Asia. The Hephthalites
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
were the most powerful of these nomad groups in the 6th and 7th century and controlled much of the region. In the 10th and 11th centuries the region was divided between several powerful states including the Samanid
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan origin. The empire was centred in Kh ...
dynasty, that of the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
, and the Khwarezmid Empire
The Khwarazmian or Khwarezmian Empire) or the Khwarazmshahs ( fa, خوارزمشاهیان, Khwārazmshāhiyān) () was a Turko-Persian Sunni Muslim empire that ruled large parts of present-day Central Asia, Afghanistan, and Iran in the appr ...
.
The most spectacular power to rise out of Central Asia developed when Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
united the tribes of Mongolia. Using superior military techniques, the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
spread to comprise all of Central Asia and China as well as large parts of Russia, and the Middle East. After Genghis Khan died in 1227, most of Central Asia continued to be dominated by the Mongol successor Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, or Chagatai Ulus ( xng, , translit=Čaɣatay-yin Ulus; mn, Цагаадайн улс, translit=Tsagaadain Uls; chg, , translit=Čağatāy Ulusi; fa, , translit=Xânât-e Joghatây) was a Mongol and later Turkicized kh ...
. This state proved to be short lived, as in 1369 Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kür ...
, a Turco-Mongol ruler, conquered most of the region.
Even harder than keeping a steppe empire together was governing conquered lands outside the region. While the steppe peoples of Central Asia found conquest of these areas easy, they found governing almost impossible. The diffuse political structure of the steppe confederacies was maladapted to the complex states of the settled peoples. Moreover, the armies of the nomads were based upon large numbers of horses, generally three or four for each warrior. Maintaining these forces required large stretches of grazing land, not present outside the steppe. Any extended time away from the homeland would thus cause the steppe armies to gradually disintegrate. To govern settled peoples the steppe peoples were forced to rely on the local bureaucracy, a factor that would lead to the rapid assimilation of the nomads into the culture of those they had conquered. Another important limit was that the armies, for the most part, were unable to penetrate the forested regions to the north; thus, such states as Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ol ...
and Muscovy began to grow in power.
In the 14th century much of Central Asia, and many areas beyond it, were conquered by Timur (1336–1405) who is known in the west as Tamerlane. It was during Timur's reign that the nomadic steppe culture of Central Asia fused with the settled culture of Iran. One of its consequences was an entirely new visual language that glorified Timur and subsequent Timurid rulers. This visual language was also used to articulate their commitment to Islam. Timur's large empire collapsed soon after his death, however. The region then became divided among a series of smaller Khanates, including the Khanate of Khiva
The Khanate of Khiva ( chg, ''Khivâ Khânligi'', fa, ''Khânât-e Khiveh'', uz, Xiva xonligi, tk, Hywa hanlygy) was a Central Asian polity that existed in the historical region of Khwarezm in Central Asia from 1511 to 1920, except fo ...
, the Khanate of Bukhara
The Khanate of Bukhara (or Khanate of Bukhoro) ( fa, , Khānāt-e Bokhārā; ) was an Uzbek state in Central Asia from 1500 to 1785, founded by the Abu'l-Khayrid dynasty, a branch of the Shaybanids. From 1533 to 1540, Bukhara briefly became it ...
, the Khanate of Kokand
The Khanate of Kokand ( fa, ; ''Khānneshin-e Khoqand'', chg, ''Khoqand Khānligi'') was a Central Asian polity in the Fergana Valley centred on the city of Kokand between 1709 and 1876. Its territory is today divided between Uzbekistan, Kyr ...
, and the Khanate of Kashgar.
Early modern period (16th to 19th centuries)
The lifestyle that had existed largely unchanged since 500 BCE began to disappear after 1500. Important changes to the world economy in the 14th and 15th century reflected the impact of the development of nautical technology. Ocean trade routes were pioneered by the Europeans, who had been cut off from theSilk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
by the Muslim states that controlled its western termini. The long-distance trade linking East Asia and India to Western Europe increasingly began to move over the seas and not through Central Asia. However, the emergence of Russia as a world power enabled Central Asia to continue its role as a conduit for overland trade of other sorts, now linking India with Russia on a north–south axis.
 An even more important development was the introduction of
An even more important development was the introduction of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
-based weapons. The gunpowder revolution allowed settled peoples to defeat the steppe horsemen in open battle for the first time. Construction of these weapons required the infrastructure and economies of large societies and were thus impractical for nomadic peoples to produce. The domain of the nomads began to shrink as, beginning in the 15th century, the settled powers gradually began to conquer Central Asia.
The last steppe empire to emerge was that of the Dzungars
The Dzungar people (also written as Zunghar; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') were the many Mongol Oirat tribes who formed and maintained the Dzungar Khanate in the 17th and 18th centuries. Historically they were one of major tr ...
who conquered much of East Turkestan
East Turkestan ( ug, شەرقىي تۈركىستان, Sherqiy Türkistan, bold=no; zh, s=东突厥斯坦; also spelled East Turkistan), is a loosely-defined geographical and historical region in the western provinces of the People's Republic of ...
and Mongolia. However, in a sign of the changed times they proved unable to match the Chinese and were decisively defeated by the forces of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
. In the 18th century the Qing emperors, themselves originally from the far eastern edge of the steppe, campaigned in the west and in Mongolia, with the Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, born Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1735 t ...
taking control of Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
in 1758. The Mongol threat was overcome and much of Inner Mongolia was annexed to China.
One Turko-Mongolic dynasty that remained prominent during this period was the Mughal Empire, whose founder Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his ...
traced descent to Timur. While the Mughals were never able to conquer Babur's original domains in Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley (; ; ) in Central Asia lies mainly in eastern Uzbekistan, but also extends into southern Kyrgyzstan and northern Tajikistan.
Divided into three republics of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse and in the ...
, which fell to the Shaybanids
The Shibanids or Shaybanids ( fa, سلسله شیبانیان) or more accurately the Abu'l-Khayrid-Shibanids were a Persianized''Introduction: The Turko-Persian tradition'', Robert L. Canfield, Turko-Persia in Historical Perspective, ed. Robert L. ...
, they maintained influence in the Afghanistan region until the late 17th century even as they dominated India. After the Mughal Empire's decline in the 18th century, the Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire ( ps, د درانيانو ټولواکمني; fa, امپراتوری درانیان) or the Afghan Empire ( ps, د افغانان ټولواکمني, label=none; fa, امپراتوری افغان, label=none), also know ...
from Afghanistan would briefly overrun the North Western region of India, by the 19th century, the rise of the British Empire would limit the impact of Afghan conquerors.
The Chinese dominions stretched into the heart of Central Asia and included the Khanate of Kokand
The Khanate of Kokand ( fa, ; ''Khānneshin-e Khoqand'', chg, ''Khoqand Khānligi'') was a Central Asian polity in the Fergana Valley centred on the city of Kokand between 1709 and 1876. Its territory is today divided between Uzbekistan, Kyr ...
, which paid tribute to Beijing. Outer Mongolia and Xinjiang did not become provinces of the Chinese empire, but rather were directly administered by the Qing dynasty. The fact that there was no provincial governor meant that the local rulers retained most of their powers and this special status also prevented emigration from the rest of China into the region. Persia also began to expand north, especially under the rule of Nadir Shah
Nader Shah Afshar ( fa, نادر شاه افشار; also known as ''Nader Qoli Beyg'' or ''Tahmāsp Qoli Khan'' ) (August 1688 – 19 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian ...
, who extended Persian dominion well past the Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
. After his death, however, the Persian empire rapidly crumbled.
Russian expansion into Central Asia (19th century)
 The Russians also expanded south, first with the transformation of the
The Russians also expanded south, first with the transformation of the Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
steppe into an agricultural heartland, and subsequently onto the fringe of the Kazakh steppes, beginning with the foundation of the fortress of Orenburg
Orenburg (russian: Оренбу́рг, ), formerly known as Chkalov (1938–1957), is the administrative center of Orenburg Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Ural River, southeast of Moscow. Orenburg is also very close to the border with Kazakhst ...
. The slow Russian conquest of the heart of Central Asia began in the early 19th century, although Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
had sent a failed expedition under Prince Bekovitch-Cherkassky against Khiva
Khiva ( uz, Xiva/, خىۋا; fa, خیوه, ; alternative or historical names include ''Kheeva'', ''Khorasam'', ''Khoresm'', ''Khwarezm'', ''Khwarizm'', ''Khwarazm'', ''Chorezm'', ar, خوارزم and fa, خوارزم) is a district-level city ...
as early as the 1720s.
By the 1800s, the locals could do little to resist the Russian advance, although the Kazakhs of the Great Horde under Kenesary Kasimov rose in rebellion from 1837 to 1846. Until the 1870s, for the most part, Russian interference was minimal, leaving native ways of life intact and local government structures in place. With the conquest of Turkestan
Turkestan, also spelled Turkistan ( fa, ترکستان, Torkestân, lit=Land of the Turks), is a historical region in Central Asia corresponding to the regions of Transoxiana and Xinjiang.
Overview
Known as Turan to the Persians, western Turk ...
after 1865 and the consequent securing of the frontier, the Russians gradually expropriated large parts of the steppe and gave these lands to Russian farmers, who began to arrive in large numbers. This process was initially limited to the northern fringes of the steppe and it was only in the 1890s that significant numbers of Russians began to settle farther south, especially in Zhetysu
Zhetysu, or Jeti-Suu ( kk, , Жетісу, pronounced ; ky, ''Jeti-Suu'', (), meaning "seven rivers"; also transcribed ''Zhetisu'', ''Jetisuw'', ''Jetysu'', ''Jeti-su'', ''Jity-su'', ''Жетысу'',, United States National Geospatial-I ...
(Semirechye).
The Great Game
Russian campaigns
 The forces of the
The forces of the khanates
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire.
Mongo ...
were poorly equipped and could do little to resist Russia's advances, although the Kokandian commander Alimqul `Alimqul (also spelt Alymkul, Alim quli, Alim kuli) (ca. 1833 – 1865) was a warlord in the Kokand Khanate, and its ''de facto'' ruler from 1863 to 1865.
Alimqul was born in Budjun Batken, 1833, into a family of a Kyrgyz- Kipchak '' beys''. ...
led a quixotic campaign before being killed outside Chimkent. The main opposition to Russian expansion into Turkestan came from the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, who felt that Russia was growing too powerful and threatening the northwest frontiers of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
. This rivalry came to be known as The Great Game
The Great Game is the name for a set of political, diplomatic and military confrontations that occurred through most of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century – involving the rivalry of the British Empire and the Russian Empi ...
, where both powers competed to advance their own interests in the region. It did little to slow the pace of conquest north of the Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
, but did ensure that Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
remained independent as a buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between ...
between the two Empires.
After the fall of Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of ...
to General Cherniaev in 1865, Khodjend, Djizak, and Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
fell to the Russians in quick succession over the next three years as the Khanate of Kokand
The Khanate of Kokand ( fa, ; ''Khānneshin-e Khoqand'', chg, ''Khoqand Khānligi'') was a Central Asian polity in the Fergana Valley centred on the city of Kokand between 1709 and 1876. Its territory is today divided between Uzbekistan, Kyr ...
and the Emirate of Bukhara
The Emirate of Bukhara ( fa, , Amārat-e Bokhārā, chg, , Bukhārā Amirligi) was a Muslim polity in Central Asia that existed from 1785 to 1920 in what is modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan. It occupied the land ...
were repeatedly defeated. In 1867 the Governor-General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
ship of Russian Turkestan
Russian Turkestan (russian: Русский Туркестан, Russkiy Turkestan) was the western part of Turkestan within the Russian Empire’s Central Asian territories, and was administered as a Krai or Governor-Generalship. It comprised the ...
was established under General Konstantin Petrovich Von Kaufman
Konstantin Petrovich von Kaufmann (russian: Константи́н Петро́вич Ка́уфман; 2 March 1818 – 16 May 1882), was the first Governor-General of Russian Turkestan.
Early life
His family was German in origin (from Holst ...
, with its headquarters at Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of ...
. In 1881–85 the Transcaspia
The Transcaspian Oblast (russian: Закаспійская область), or just simply Transcaspia (russian: Закаспія), was the section of Russian Empire and early Soviet Russia to the east of the Caspian Sea during the second half of ...
n region was annexed in the course of a campaign led by Generals Mikhail Annenkov
General Mikhail Nikolayevich Annenkov (russian: Михаил Николаевич Анненков; formerly also transcribed Michael Nicolaivitch Annenkoff) (1835 in St. Petersburg, Russia – January 21, 1899 (New Style) in St. Petersburg, Ru ...
and Mikhail Skobelev
Mikhail Dmitriyevich Skobelev (russian: Михаил Дмитриевич Скобелев; 29 September 1843 – 7 July 1882), a Russian general, became famous for his conquest of Central Asia and for his heroism during the Russo-Turkish War ...
, and Ashkhabad
Ashgabat or Asgabat ( tk, Aşgabat, ; fa, عشقآباد, translit='Ešqābād, formerly named Poltoratsk ( rus, Полтора́цк, p=pəltɐˈratsk) between 1919 and 1927), is the capital and the largest city of Turkmenistan. It lies ...
(from Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
), Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
and Pendjeh (from Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
) all came under Russian control.
Russian expansion was halted in 1887 when Russia and Great Britain delineated the northern border of Afghanistan. Bukhara and the Khanate of Khiva
The Khanate of Khiva ( chg, ''Khivâ Khânligi'', fa, ''Khânât-e Khiveh'', uz, Xiva xonligi, tk, Hywa hanlygy) was a Central Asian polity that existed in the historical region of Khwarezm in Central Asia from 1511 to 1920, except fo ...
remained quasi-independent, but were essentially protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its inter ...
s along the lines of the Princely States
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a ...
of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
. Although the conquest was prompted by almost purely military concerns, in the 1870s and 1880s Turkestan came to play a reasonably important economic role within the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The ...
.
Because of the American Civil War, cotton shot up in price in the 1860s, becoming an increasingly important commodity in the region, although its cultivation was on a much lesser scale than during the Soviet period. The cotton trade led to improvements: the Transcaspian Railway
The Trans-Caspian Railway (also called the Central Asian Railway, russian: Среднеазиатская железная дорога) is a railway that follows the path of the Silk Road through much of western Central Asia. It was built by ...
from Krasnovodsk to Samarkand and Tashkent, and the Trans-Aral Railway
The broad gauge Trans-Aral Railway (also known as the Tashkent Railway) was built in 1906 connecting Kinel and Tashkent, then both in the Russian Empire. For the first part of the 20th century it was the only railway connection between European R ...
from Orenburg
Orenburg (russian: Оренбу́рг, ), formerly known as Chkalov (1938–1957), is the administrative center of Orenburg Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Ural River, southeast of Moscow. Orenburg is also very close to the border with Kazakhst ...
to Tashkent were constructed. In the long term the development of a cotton monoculture would render Turkestan dependent on food imports from Western Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
, and the Turkestan-Siberia Railway was already planned when the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighti ...
broke out.
Russian rule still remained distant from the local populace, mostly concerning itself with the small minority of Russian inhabitants of the region. The local Muslims were not considered full Russian citizens. They did not have the full privileges of Russians, but nor did they have the same obligations, such as military service. The Tsarist regime left substantial elements of the previous regimes (such as Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
religious courts) intact, and local self-government at the village level was quite extensive.
Qing dynasty
During the 17th and 18th centuries theQing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
made several campaigns to conquer the Dzungar Mongols. In the meantime, they incorporated parts of Central Asia into the Chinese Empire
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the ''Book of Documents'' (early chapter ...
.
Internal turmoil largely halted Chinese expansion in the 19th century. In 1867 Yakub Beg
Muhammad Yaqub Bek (محمد یعقوب بیگ; uz, Яъқуб-бек, ''Ya’qub-bek''; ; 182030 May 1877) was a Khoqandi ruler of Yettishar (Kashgaria) during his invasion of Xinjiang from 1865 to 1877. He held the title of Atalik Ghazi ("C ...
led a rebellion that saw Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan. ...
declaring its independence as the Taiping and Nian Rebellion
The Nian Rebellion () was an armed uprising that took place in northern China from 1851 to 1868, contemporaneously with Taiping Rebellion (1851–1864) in South China. The rebellion failed to topple the Qing dynasty, but caused immense economic ...
s in the heartland of the empire prevented the Chinese from reasserting their control.
Instead, the Russians expanded, annexing the Chu and Ili Valleys and the city of Kuldja from the Chinese Empire. After Yakub Beg's death at Korla
Korla,The official spelling according to also known as Kurla, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency or from Mandarin Chinese as Ku'erle or Kuerle, is the second largest city in Xinjiang. It is a county-level city and the seat of ...
in 1877 his state collapsed as the area was reconquered by China. After lengthy negotiations Kuldja was returned to Beijing by Russia in 1884.
Revolution and revolt
During theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighti ...
the Muslim exemption from conscription was removed by the Russians, sparking the Central Asian Revolt of 1916. When the Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
occurred, a provisional Government of Jadid
The Jadids were Muslim modernist reformers within the Russian Empire in the late 19th and early 20th century. They normally referred to themselves by the Turkic terms ''Taraqqiparvarlar'' ('progressives'), ''Ziyalilar'' ('intellectuals') or simpl ...
Reformers, also known as the Turkestan Muslim Council met in Kokand
Kokand ( uz, Qo‘qon/Қўқон/قوقان, ; russian: Кока́нд; fa, خوقند, Xuqand; Chagatai: خوقند, ''Xuqand''; ky, Кокон, Kokon; tg, Хӯқанд, Xöqand) is a city in Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan, at the sou ...
and declared Turkestan's autonomy. This new government was quickly crushed by the forces of the Tashkent Soviet, and the semi-autonomous states of Bukhara and Khiva were also invaded. The main independence forces were rapidly crushed, but guerrillas known as basmachi continued to fight the Communists until 1924. Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; literal translation, lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia Mongolia–Russia border, to the north and China China–Mongolia border, to the s ...
was also swept up by the Russian Revolution and, though it never became a Soviet republic, it became a communist People's Republic
People's republic is an official title, usually used by some currently or formerly communist or left-wing states. It is mainly associated with soviet republics, socialist states following people's democracy, sovereign states with a democratic- ...
in 1924.
The creation of the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeas ...
in 1911 and the general turmoil in China affected the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
's holdings in Central Asia. Republic of China's control of the region was relegated to southern Xinjiang and there was a dual threat from Islamic separatists and communists. Eventually the region became largely independent under the control of the provincial governor. Rather than invade, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
established a network of consulates in the region and sent aid and technical advisors.
By the 1930s, the governor of Xinjiang's relationship with Moscow was far more important than that with Nanking
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. T ...
. The Chinese Civil War further destabilised the region and saw Turkic nationalists make attempts at independence. In 1933, the First East Turkestan Republic
The Turkic Islamic Republic of East Turkestan (TIRET; ug, شەرقىي تۈركىستان تۈرك ئىسلام جۇمھۇرىيىتى, , Шәрқий Түркистан Түрк-Ислам Җумхурийити; ) was a short-lived breakaway ...
was declared, but it was destroyed soon after with the aid of the Soviet troops.
After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, Governor Sheng Shicai
Sheng Shicai (; 3 December 189513 July 1970) was a Chinese warlord who ruled Xinjiang from 1933 to 1944. Sheng's rise to power started with a coup d'état in 1933 when he was appointed the ''duban'' or Military Governor of Xinjiang. His rule o ...
of Xinjiang gambled and broke his links to Moscow, moving to ally himself with the Kuomintang. This led to a civil war within the region. Sheng was eventually forced to flee and the Soviet-backed Second East Turkestan Republic
The East Turkestan Republic (ETR) was a short-lived satellite state of the Soviet Union in northwest Xinjiang (East Turkestan), between November 12, 1944, and December 22, 1949. To differentiate it from the First East Turkestan Republic (1933� ...
was formed in northern Dzungaria, while the Republic of China retained control of southern Xinjiang. Both states were annexed by the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
in 1949.
Soviet era (1918–1991)
After being conquered byBolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
forces, Soviet Central Asia
Soviet Central Asia (russian: link=no, Советская Средняя Азия, Sovetskaya Srednyaya Aziya) was the part of Central Asia administered by the Soviet Union between 1918 and 1991, when the Central Asian republics declared in ...
experienced a flurry of administrative reorganisation. In 1918 the Bolsheviks set up the Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (initially, the Turkestan Socialist Federative Republic; 30 April 191827 October 1924) was an autonomous republic of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic located in Soviet Central As ...
, and Bukhara and Khiva also became SSRs. In 1919 the Conciliatory Commission for Turkestan Affairs was established, to try to improve relations between the locals and the Communists. New policies were introduced, respecting local customs and religion. In 1920, the Kirghiz Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, covering modern Kazakhstan, was set up. It was renamed the Kazakh Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Kazakh Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic (russian: Казахская Автономная Социалистическая Советская Республика; kk, Qazaq Aptonom Sotsijalistik Sovettik Respublikasь), abbreviated as K ...
in 1925. In 1924, the Soviets created the Uzbek SSR
Uzbekistan (, ) is the common English name for the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (Uzbek SSR; uz, Ўзбекистон Совет Социалистик Республикаси, Oʻzbekiston Sovet Sotsialistik Respublikasi, in Russian: Уз� ...
and the Turkmen SSR
Turkmen, Türkmen, Turkoman, or Turkman may refer to:
Peoples Historical ethnonym
* Turkoman (ethnonym), ethnonym used for the Oghuz Turks during the Middle Ages
Ethnic groups
* Turkmen in Anatolia and the Levant (Seljuk and Ottoman-Turkish desc ...
. In 1929 the Tajik SSR
The Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic,, ''Çumhuriji Şūraviji Sotsialistiji Toçikiston''; russian: Таджикская Советская Социалистическая Республика, ''Tadzhikskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Resp ...
was split from the Uzbek SSR. The Kyrgyz Autonomous Oblast became an SSR in 1936.
These borders had little to do with ethnic make-up, but the Soviets felt it important to divide the region. They saw both Pan-Turkism
Pan-Turkism is a political movement that emerged during the 1880s among Turkic intellectuals who lived in the Russian region of Kazan (Tatarstan), Caucasus (modern-day Azerbaijan) and the Ottoman Empire (modern-day Turkey), with its aim be ...
and Pan-Islamism
Pan-Islamism ( ar, الوحدة الإسلامية) is a political movement advocating the unity of Muslims under one Islamic country or state – often a caliphate – or an international organization with Islamic principles. Pan-Islamism was ...
as threats, which dividing Turkestan would limit. Under the Soviets, the local languages and cultures were systematised and codified, and their differences clearly demarcated and encouraged. New Cyrillic
, bg, кирилица , mk, кирилица , russian: кириллица , sr, ћирилица, uk, кирилиця
, fam1 = Egyptian hieroglyphs
, fam2 = Proto-Sinaitic
, fam3 = Phoenician
, fam4 = Gr ...
writing systems were introduced, to break links with Turkey and Iran. Under the Soviets the southern border was almost completely closed and all travel and trade was directed north through Russia.
During the period of forced collectivisation under Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet Union, Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as Ge ...
at least a million persons died, mostly in the Kazakh SSR. Islam, as well as other religions, were also attacked. In the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
several million refugees and hundreds of factories were moved to the relative security of Central Asia; and the region permanently became an important part of the Soviet industrial complex. Several important military facilities were also located in the region, including nuclear testing facilities and the Baikonur Cosmodrome
''Baiqoñyr ğaryş ailağy'' rus, Космодром Байконур''Kosmodrom Baykonur''
, image = Baikonur Cosmodrome Soyuz launch pad.jpg
, caption = The Baikonur Cosmodrome's " Gagarin's Start" Soyu ...
. The Virgin Lands Campaign, starting in 1954, was a massive Soviet agricultural resettlement program that brought more than 300,000 individuals, mostly from the Ukraine, to the northern Kazakh SSR and the Altai region of the Russian SFSR. This was a major change in the ethnicity of the region.
Similar processes occurred in Xinjiang and the rest of Western China where the PRC quickly established control from the Second East Turkestan Republic
The East Turkestan Republic (ETR) was a short-lived satellite state of the Soviet Union in northwest Xinjiang (East Turkestan), between November 12, 1944, and December 22, 1949. To differentiate it from the First East Turkestan Republic (1933� ...
that controlled northern Xinjiang and the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeas ...
forces that controlled southern Xinjiang after the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
. The area was subject to a number of development schemes and, like Soviet Central Asia, one focus was on the growing of the cotton cash crop. These efforts were overseen by the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps
The Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps (), also known as XPCC or Bingtuan ("The Corps"), is a state-owned economic and paramilitary organization in China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (XUAR).
In its history, the XPCC has built ...
. The XPCC also encouraged Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive var ...
to return to Xinjiang after many had migrated out during the Muslim revolts against the Qing dynasty.
Political turmoil has led to major demographic shifts in the region: During the Qing dynasty there were 60% Turkic and 30% Han Chinese in the region, after the Muslim revolts the percentage of Han Chinese dropped to as low as 7%, and by the year 2000 some 40% of the population of Xinjiang were Han. As with the Soviet Union local languages and cultures were mostly encouraged and Xinjiang was granted autonomous status. However, Islam was much persecuted, especially during the Cultural Revolution. Many people from other parts of China fled to Xinjiang due to the failed agricultural policies of the Great Leap Forward
The Great Leap Forward (Second Five Year Plan) of the People's Republic of China (PRC) was an economic and social campaign led by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 1958 to 1962. CCP Chairman Mao Zedong launched the campaign to reconstruc ...
in other provinces. However, the Great Leap Forward did not affect much of Xinjiang due to its geographical isolation from other parts of China.
Soviet evacuation and WWII population deportations
The Second World War sparked the widespread migration of Soviet citizens to the rear of the USSR. Much of this movement was directed to Soviet Central Asia. These migrations included official, state-organised evacuations and deportations as well as the non-sanctioned, panicked flight from the front by both general citizenry and important officials. The evacuation of Soviet citizens and industry during World War II was an essential element of their overall success in the war, and Central Asia served as a main destination for evacuees. TheGerman invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
began on June 22, 1941. A decree from the Presidium of the executive committee on the same day forbade the entry or exit from the USSR's border regions, which were under a state of martial law. Such mandates demonstrated the Soviets' fear of spreading panic and their commitment to asserting direct state control over wartime relocations to maintain order. Soviet wartime population policy consisted of two distinct operations: deportation and evacuation. Deportation aimed to clear regions near the front of potentially insidious anti-Soviet elements that could hamper the war effort, while evacuation policy aimed to move Soviet industry and intelligentsia to the rear, where they would be safe.
Deportations along ethnic lines
Soviet officials organised their wartime deportation policy largely along ethnic lines. As a response to the German invasion, Soviet citizens ofGerman descent
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
in border regions were targeted for deportation to the rear where Soviet authorities had no need to worry of their conspiring with the enemy. Such dubious ethnically derived logic was not reserved for Germans. Many Finns were also forcibly relocated in the first year of the war simply for their heritage, though they were mainly sent to remote areas in the northern rear, such as Siberia, rather than Central Asia. A large portion of the German deportees, however, were sent to Kazakhstan. The remobilisation of relocated human resources into the labour force was pivotal to Soviet wartime production policy, and to that end many able-bodied deportees were conscripted into a “labour army” with military style discipline.
By early 1942 as many as 20,800 ethnic Germans had been organised into battalions in this labour army, though this number would grow to as much as 222,000 by early 1944 as conscription criteria were broadened. The NKVD employed about 101,000 members of the labour army at construction sites to develop infrastructure for the war effort. Those who were not assigned to the labour army were used for timber harvesting, the construction of railways and other infrastructure, or sent to collective farms.
As the tide turned in the war, and the Soviets began to reclaim the territories they lost to the initial German advance, they began a new wave of deportations of unfavoured ethnic groups. Karachais, Kalmyks, Chechens, Ingushetians, Kabardians, and Crimean Tatars were all deported to Central Asia for their supposed fraternisation with occupying German forces. These groups were sent mostly to Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan for their infidelity. These punitive deportations were also conducted to keep “anti-Soviet elements” far from the border – where the Soviet offensive against Germany was progressing – for fear of spying or sabotage.
Evacuation of Soviet citizens to Central Asia
Many Soviet citizens ended up in Central Asia during World War II, not as a result of deportation, but evacuation. The evacuation focused on the movement of critical wartime industry and the factory workers responsible for overseeing such production. Whole factories and their employees were moved together via railway eastward to cities like Tashkent, which received a lion's share of the evacuees. The initial attempts at evacuation while the war was still in its early stages through early 1942 were a far cry from the organised affair that the Soviet central bureaucracy envisaged. Throughout the summer and fall of 1941, numerous Soviet frontier cities evacuated in a haphazard and panicked fashion before the German onslaught. A number of factors led to this lack of organisation. For one, the Soviet evacuation plans were thrown together fairly hurriedly, and a lot of the logistical planning was done on the fly as the German advance was already sweeping through the Soviet border zone. The German invasion also hampered the effectiveness of the Soviet response by shattering their communications in the war's early stages; many Soviet leaders were unable to gather reliable information about the positions of German forces until it was too late to effect an orderly evacuation. There was also a desire on the part of Soviet officials to forestall any evacuations until it was absolutely necessary, the marching orders were often to continue factory production until the eve of occupation before hurriedly dismantling and transporting factory equipment, and destroying what couldn't be moved in time. As a result of the delay in evacuations, they were often carried out under German aerial bombardment, which led to additional confusion among the frightened citizenry. Historian Rebecca Manley describes these early evacuations as being charactered by “three phenomena: the 'flight' of officials, the flight of the population, and 'panic'”. The early flight of Soviet officials who were supposed to manage the evacuation was roundly condemned by Soviet leaders, but often their retreat resulted from a realisation that evacuation procedures had started too late, and that there was no way to effectively execute it. Additionally, Soviet officials who remained in a city captured by German forces feared execution by Nazis on the hunt for communists. Avoiding that, the officials knew that they would be subject to intense interrogation as to what happened by suspicious Soviets upon returning to the fold. Despite these setbacks in the implementation of evacuation policy early in the war, around 12 million Soviet citizens successfully evacuated in 1941, even if a number of these were the result of disorganised, “spontaneous self-evacuation,” and another 4.5 million evacuated the following year. In addition, the factories that were successfully evacuated to the Central Asian rear would help provide the productive capacity the Soviets needed to eventually win the war, as well as preventing the Germans from acquiring additional industrial resources. By providing a safe haven from the German advance for Soviet citizens, Central Asia played a critical role in securing Allied victory. The evacuation itself was only part of the difficulty, however, as evacuees arriving in Central Asia faced many trials and tribulations. Due to the haphazard nature of evacuation, many labourers did not arrive with their factory, and had to find labour on their own, though jobs were hard to come by. Additionally, cities like Tashkent became overwhelmed at the sheer volume of people arriving at its gates and had great difficulty supplying the food and shelter necessary for evacuees. Upon arrival, many evacuees died of illness or starvation in extreme poverty in Central Asia. Uzbek officials set up aid stations at Tashkent, which were mirrored at other railway stations to help combat the poverty, but they could only do so much as little could be spared economically for the war effort. Despite these troubles, the ability of Central Asia to absorb Soviet industry and population to the extent that it did and in the harried manner that it did was impressive. The Germans certainly didn't foresee the preparedness of Soviet Central Asia, and in the end they paid dearly for it.Since 1991
From 1988 to 1992, a free press and multi-party system developed in the Central Asian republics asperestroika
''Perestroika'' (; russian: links=no, перестройка, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg) was a political movement for reform within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s widely associated wit ...
pressured the local Communist parties to open up. What Svat Soucek calls the "Central Asian Spring" was very short-lived, as soon after independence former Communist Party officials recast themselves as local strongmen. Political stability in the region has mostly been maintained, with the major exception of the Tajik Civil War
The Tajikistani Civil War ( tg, Ҷанги шаҳрвандии Тоҷикистон, translit=Jangi shahrvandiyi Tojikiston / Çangi shahrvandiji Toçikiston; russian: Гражданская война в Таджикистане), also known ...
that lasted from 1992 to 1997. 2005 also saw the largely peaceful ousting of Kyrgyz president Askar Akayev
Askar Akayevich Akayev ( ky, Аскар Акаевич (Акай уулу) Акаев, translit=Askar Akayevich (Akay Uulu) Akayev ; ; born 10 November 1944) is a Kyrgyz politician who served as President of Kyrgyzstan from 1990 until being ov ...
in the Tulip Revolution
The Tulip Revolution or First Kyrgyz Revolution (russian: Тюльпановая революция; ky, Жоогазын революциясы) led to President of Kyrgyzstan Askar Akayev's fall from power. The revolution began after parliame ...
and an outbreak of violence in Andijan, Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
.
Much of the population of Soviet Central Asia was indifferent to the collapse of the Soviet Union, even the large Russian populations in Kazakhstan (roughly 40% of the total) and Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of ...
, Uzbekistan. Aid from the Kremlin had also been central to the economies of Central Asia, each of the republics receiving massive transfers of funds from Moscow.
Independence largely resulted from the efforts of the small groups of nationalistic, mostly local intellectuals, and from little interest in Moscow for retaining the expensive region. While never a part of the Soviet Union, Mongolia followed a somewhat similar path. Often acting as the unofficial sixteenth Soviet republic, it shed the communist system only in 1996, but quickly ran into economic problems. See: History of independent Mongolia.
The economic performance of the region since independence has been mixed. It contains some of the largest reserves of natural resources in the world, but there are important difficulties in transporting them. Since it lies farther from the ocean than anywhere else in the world, and its southern borders lay closed for decades, the main trade routes and pipelines run through Russia. As a result, Russia still exerts more influence over the region than in any other former Soviet republics. Nevertheless, the rising energy importance of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asi ...
entails a great involvement in the region by the US. The former Soviet republics of the Caucasus now have their own US Special Envoy
Diplomatic rank is a system of professional and social rank used in the world of diplomacy and international relations. A diplomat's rank determines many ceremonial details, such as the order of precedence at official processions, table seatings ...
and inter-agency working groups. Former US Secretary of Energy Bill Richardson
William Blaine Richardson III (born November 15, 1947) is an American politician, author, and diplomat who served as the 30th governor of New Mexico from 2003 to 2011. He was also the U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations and Energy Secretar ...
had claimed that "the Caspian region will hopefully save us he USfrom total dependence on Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europea ...
oil".
Some analysts, such as Myers Jaffe and Robert A. Manning, estimate however that US' entry into the region (with initiatives such as the US-favored Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipeline) as a major actor may complicate Moscow's chances of making a decisive break with its past economic mistakes and geopolitical excesses in Central Asia. They also regard as a myth the assertion that Caspian oil and gas will be a cheaper and more secure alternative to supplies from the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The body ...
.
Despite these reservations and fears, since the late 1980s, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
, Kazakhstan, and Turkmenistan have gradually moved to centre stage in the global energy markets and are now regarded as key factors of the international energy security
Energy security is the association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to (relatively) cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven ...
. Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan in particular have succeeded in attracting massive foreign investment to their oil and gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
sectors. According to Gawdat Bahgat, the investment flow suggests that the geological potential of the Caspian region as a major source of oil and gas is not in doubt.
Russia and Kazakhstan started a closer energy co-operation in 1998, which was further consolidated in May 2002, when Presidents Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime min ...
and Nursultan Nazarbayev
Nursultan Abishuly Nazarbayev ( kk, Нұрсұлтан Әбішұлы Назарбаев, Nūrsūltan Äbişūlı Nazarbaev, ; born 6 July 1940) is a Kazakh politician and military officer who served as the first President of Kazakhstan, in off ...
signed a protocol dividing three gas fields – Kurmangazy, Tsentralnoye, and Khvalynskoye – on an equal basis. Following the ratification of bilateral treaties, Russia, Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan declared that the northern Caspian was open for business and investment as they had reached a consensus on the legal status of the basin. Iran and Turkmenistan refused however to recognise the validity of these bilateral agreements; Iran is rejecting any bilateral agreement to divide the Caspian. On the other hand, US' choices in the region (within the framework of the so-called "pipeline diplomacy"), such as the strong support of the Baku pipeline (the project was eventually approved and was completed in 2005), reflect a political desire to avoid both Russia and Iran.
Increasingly, other powers have begun to involve themselves in Central Asia. Soon after the Central Asian states won their independence, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
began to look east, and a number of organizations are attempting to build links between the western and eastern Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic o ...
. Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...
, which for millennia had close links with the region, has also been working to build ties and the Central Asian states now have good relations with the Islamic Republic. One important player in the new Central Asia has been Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia ...
, which has been funding the Islamic revival in the region. Olcott notes that soon after independence Saudi money paid for massive shipments of Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing. ...
s to the region and for the construction and repair of a large number of mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers (sujud) are performed, in ...
s. In Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
alone an estimated 500 mosques per year have been erected with Saudi money.
The formerly atheistic Communist Party leaders have mostly converted to Islam. Small Islamist groups have formed in several of the countries, but radical Islam has little history in the region; the Central Asian societies have remained largely secular and all five states enjoy good relations with Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. Central Asia is still home to a large Jewish population
As of 2020, the world's "core" Jewish population (those identifying as Jews above all else) was estimated at 15 million, 0.2% of the 8 billion worldwide population. This number rises to 18 million with the addition of the "connected" Jewish pop ...
, the largest group being the Bukharan Jews
Bukharan Jews ( Bukharian: יהודיאני בוכארא/яҳудиёни Бухоро, ''Yahudiyoni Bukhoro''; he, יהודי בוכרה, ''Yehudey Bukhara''), in modern times also called Bukharian Jews ( Bukharian: יהודיאני בוכאר ...
, and important trade and business links have developed between those that left for Israel after independence and those remaining.
The People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
sees the region as an essential future source of raw materials; most Central Asian countries are members of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
russian: Шанхайская Организация Сотрудничества
, image =
, caption =
, logo = SCO logo.svg
, logo_size = 160px
, map = Shanghai Cooperati ...
. This has affected Xinjiang and other parts of western China that have seen infrastructure programs building new links and also new military facilities. Chinese Central Asia has been far from the centre of that country's economic boom and the area has remained considerably poorer than the coast. China also sees a threat in the potential of the new states to support separatist movements among its own Turkic minorities.
One important Soviet legacy that has only gradually been appreciated is the vast ecological destruction. Most notable is the gradual drying of the Aral Sea. During the Soviet era, it was decided that the traditional crops of melons and vegetables would be replaced by water-intensive growing of cotton for Soviet textile mills. Massive irrigation efforts were launched that diverted a considerable percentage of the annual inflow to the sea, causing it to shrink steadily. Furthermore, vast tracts of Kazakhstan were used for nuclear testing
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by ...
, and there exists a plethora of decrepit factories and mines.
In the first part of 2008 Central Asia experienced a severe energy crisis, a shortage of both electricity and fuel, aggravated by abnormally cold temperatures, failing infrastructure, and a shortage of food in which aid from the west began to assist the region.
As of 2019, despite its common cultural and historical past Central Asia has been "one of the least integrated regions in the world".Vakulchuk, Roman and Indra Overland (2019) �China’s Belt and Road Initiative through the Lens of Central Asia
��, in Fanny M. Cheung and Ying-yi Hong (eds) ''Regional Connection under the Belt and Road Initiative. The Prospects for Economic and Financial Cooperation''. London: Routledge, p. 116.
See also
*Eurasian nomads
The Eurasian nomads were a large group of nomadic peoples from the Eurasian Steppe, who often appear in history as invaders of Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, Eastern Asia, and South Asia.
A nomad is a member of people having no permanent ...
* Eurasian Steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova and Transnistri ...
* History of Afghanistan
The history of Afghanistan as a state began in 1823 as the Emirate of Afghanistan after the exile of the Sadozai monarchy to Herat. The Sadozai monarchy ruled the Afghan Durrani Empire, considered the founding state of modern Afghanistan. The w ...
* History of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, the largest country fully within the Eurasian Steppe, has been a historical crossroads and home to numerous different peoples, states and empires throughout history. Throughout history, peoples on the territory of modern Kazakhstan ...
* History of Kyrgyzstan
The history of the Kyrgyz people and the land now called Kyrgyzstan goes back more than 3,000 years. Although geographically isolated by its mountainous location, it had an important role as part of the historical Silk Road trade route. Turkic ...
* History of Mongolia
Various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu (3rd century BC–1st century AD), the Xianbei state ( AD 93–234), the Rouran Khaganate (330–555), the First (552–603) and Second Turkic Khaganates (682–744) and others, ruled the area of ...
* History of Tajikistan
Tajikistan harkens to the Samanid Empire (819–999). The Tajik people came under Russian rule in the 1860s. The Basmachi revolt broke out in the wake of the Russian Revolution of 1917 and was quelled in the early 1920s during the Russian Civ ...
* History of the central steppe
This is a short History of the central steppe, an area roughly equivalent to modern Kazakhstan. Because the history is complex it is mainly an outline and index to the more detailed articles given in the links. It is a companion to History of ...
* History of Turkmenistan
The history of Turkmenistan traditionally began with the arrival of Indo-European Iranian tribes around 2000 BC. Early tribes were nomadic or semi-nomadic due to the arid conditions of the region that prevented widespread adoption of agricultur ...
* History of Uzbekistan
* History of Xinjiang
Xinjiang historically consisted of two main geographically, historically, and ethnically distinct regions with different historical names: Dzungaria north of the Tianshan Mountains; and the Tarim Basin south of the Tianshan Mountains, currently ...
Further reading
* V.V. Barthold, ''Turkestan Down to the Mongol Invasion'' (London) 1968 (Third Edition) * Bacon, Elizabeth A. ''Central Asians under Russian Rule'' (Cornell UP, 1966) * Becker, Seymour, ''Russia’s Protectorates in Central Asia: Bukhara and Khiva, 1865 - 1924'' (1968) *Brower, Daniel ''Turkestan and the Fate of the Russian Empire'' (London) 2003. *Dani, A.H. and V.M. Masson eds.UNESCO History of Civilizations of Central Asia
' (Paris:
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
) 1992–
*Hildinger, Erik. ''Warriors of the Steppe: A Military History of Central Asia, 500 BC. to 1700 AD.'' (Cambridge: Da Capo) 2001.
* Maitdinova, Guzel. The Dialogue of Civilizations in the Central Asian area of the Great Silk Route: Historical experience of integration and reference points of XXI century. Dushanbe: 2015.
* Maitdinova, Guzel. The Kirpand State – an Empire in Middle Asia. Dushanbe: 2011.
*O'Brien, Patrick K. (General Editor). ''Oxford Atlas of World History.'' New York: Oxford University Press, 2005.
*Olcott, Martha Brill. ''Central Asia's New States: Independence, Foreign policy, and Regional security.'' (Washington, D.C.: United States Institute of Peace Press) 1996.
*Sinor, Denis ''The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia'' (Cambridge) 1990 (2nd Edition).
*S. Frederick Starr
Stephen Frederick Starr (born March 24, 1940) is an American expert on Russian and Eurasian affairs, a musician, and a former president of Oberlin College.
Founder and chairman of the Central Asia-Caucasus Institute, he is fluent in Russian a ...
, Rediscovering Central Asia
'
Other languages
* В.В. Бартольд ''История Культурной Жизни Туркестана'' ("''Istoriya Kul'turnoy zhizni Turkestana''") (Москва) 1927 *Н.А. Халфин; ''Россия и Ханства Средней Азии'' ("''Rossiya i Hanstva Sredney Azii''") (Москва) 1974Encyclopædia Iranica: Central Asia in pre-Islamic Times (R. Fryer)
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20090224083111/http://www.iranica.com/newsite/search/searchpdf.isc?ReqStrPDFPath=%2Fhome%2Firanica%2Fpublic_html%2Fnewsite%2Fpdfarticles%2Fv5_articles%2Fcentral_asia%2Fmongol_and_timurid_periods&OptStrLogFile=%2Fhome%2Firanica%2Fpublic_html%2Fnewsite%2Flogs%2Fpdfdownload.html Encyclopædia Iranica: Central Asia in the Mongol and Timurid Periods (B. Spuler)]
Encyclopædia Iranica: Central Asia from the 16th to the 18th centuries (R.D. McChesney)
( Yuri Bregel)
Center for the Study of Eurasian Nomads
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * *Herodotus, ''Histories'', IV. See original text iperseus project
* * * * * * * * * * * * *
External links
New Directions Post-Independence
from th
Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
{{Authority control Archaeology of Central Asia Prehistoric Asia Geography of Central Asia