Portuguese Communist Party on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Portuguese Communist Party ( pt, Partido Comunista Português, , PCP) is a
a
pcp.pt
https://web.archive.org/web/20201028205209/http://www.pcp.pt/partit-of-the-class-operate-of-all-workers--paper-of-the-pcp-no-reforco-organization-unity Filed] in Wayback Machine"Ficará para história a reposição de direitos que se julgavam perdidos"
in Notícias ao Minuto
Archived
in Wayback Machine Currently, the PCP is the fifth largest in the Portuguese Assembly of the Republic, where it holds 6 of the 230 assembly seats. The party publishes the weekly ''
Portuguese Communist Party, URL accessed 20 June 2006 In September 1919, the working-class movement founded the first Portuguese Labour Union Confederation, the General Confederation of Labour; however, the feeling of political powerlessness, due to the lack of a coherent political strategy among the Portuguese working class, plus the growing popularity of the
 After the 1933 rise of Salazar's dictatorial Estado Novo regime, suppression of the party grew. Many members were arrested, tortured, and executed. Many were sent to the
After the 1933 rise of Salazar's dictatorial Estado Novo regime, suppression of the party grew. Many members were arrested, tortured, and executed. Many were sent to the

 The following months were marked by radical changes in the country, always closely followed and supported by PCP. A stormy process to give independence to the colonies started with the full support of the party and, within a year,
The following months were marked by radical changes in the country, always closely followed and supported by PCP. A stormy process to give independence to the colonies started with the full support of the party and, within a year,
 In December 1996, the fifteenth congress was held, this time in
In December 1996, the fifteenth congress was held, this time in

Portuguese Electoral Commission
) Note: * ''In 2004, after the enlargement of the European Union, the number of MEPs elected by
Portuguese Electoral Commission
) Notes: * ''In 1980, Carlos Brito withdrew in favour of Ramalho Eanes, won.'' * ''In 1986, the Party's first candidate was

 The Portuguese Communist Party publishes the weekly ''
The Portuguese Communist Party publishes the weekly ''
Portuguese Communist party, URL accessed 2 July 2006 Many times, the newspaper distribution suffered breakdowns due to the suppression by the political police of party members who helped to distribute the newspaper, or due to the destruction of the clandestine printing offices. Successfully evading official censorship, ''Avante!'' was one of the very few Portuguese newspapers that freely reported on events like
Portuguese Communist Party, URL accessed 2 July 2006
 Every year, in the first weekend of September, the party holds a festival called the
Every year, in the first weekend of September, the party holds a festival called the
communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
, Marxist–Leninist political party
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular country's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific ideological or p ...
in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
based upon democratic centralism. The party also considers itself patriotic and internationalist,Portuguese Communist Party (2005). ''Program and Statutes of the Portuguese Communist Party''. Edições Avante!. and it is characterized as being between the left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in soci ...
and far-left on the political spectrum.
The party was founded in 1921, establishing contacts with the Comintern in 1922 and becoming is Portuguese section in 1923. The PCP was banned after the 1926 military coup and subsequently played a major role in the opposition against the dictatorial regime
In politics, a regime (also "régime") is the form of government or the set of rules, cultural or social norms, etc. that regulate the operation of a government or institution and its interactions with society. According to Yale professor Juan Jo ...
of António de Oliveira Salazar
António de Oliveira Salazar (, , ; 28 April 1889 – 27 July 1970) was a Portuguese dictator who served as President of the Council of Ministers from 1932 to 1968. Having come to power under the ("National Dictatorship"), he reframed the re ...
. During the nearly five-decade-long dictatorship, the PCP was constantly suppressed by the secret police
Secret police (or political police) are intelligence, security or police agencies that engage in covert operations against a government's political, religious, or social opponents and dissidents. Secret police organizations are characteristic ...
, which forced the party's members to live in clandestine status under the threat of arrest, torture, and murder. After the Carnation Revolution in 1974, which overthrew the regime, the 36 members of party's Central Committee had, in the aggregate, experienced more than 300 years in jail.Cunhal, Álvaro (1997). ''O caminho para o derrubamento do fascismo''. Edições Avante!.
After the end of the dictatorship, the party became a major political force in the new democratic government. One of its goals, according to the party is to maintain its "vanguard
The vanguard (also called the advance guard) is the leading part of an advancing military formation. It has a number of functions, including seeking out the enemy and securing ground in advance of the main force.
History
The vanguard derives f ...
role in the service of the class interests of the workers".Working-class party and all workers: the role of the PCP in strengthening the organization, unity and struggle of the workersa
pcp.pt
https://web.archive.org/web/20201028205209/http://www.pcp.pt/partit-of-the-class-operate-of-all-workers--paper-of-the-pcp-no-reforco-organization-unity Filed] in Wayback Machine"Ficará para história a reposição de direitos que se julgavam perdidos"
in Notícias ao Minuto
Archived
in Wayback Machine Currently, the PCP is the fifth largest in the Portuguese Assembly of the Republic, where it holds 6 of the 230 assembly seats. The party publishes the weekly ''
Avante!
''Avante!'' (''Onwards!'') is the official newspaper of the Portuguese Communist Party (PCP). Founded in 1931, it continues to be published to this day. The newspaper's motto is ''Workers of the World, Unite!'' and has been present in every e ...
'', founded in 1931. Its youth organization is the Portuguese Communist Youth, a member of the World Federation of Democratic Youth.
History
Origins
At the end ofWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, in 1918, Portugal fell into a serious economic crisis, in part due to the Portuguese military intervention in the war. The Portuguese working classes responded to the deterioration in their living standards with a wave of strikes. Supported by an emerging labour movement
The labour movement or labor movement consists of two main wings: the trade union movement (British English) or labor union movement (American English) on the one hand, and the political labour movement on the other.
* The trade union movement ...
, the workers achieved some of their objectives, such as an eight-hour working day
The eight-hour day movement (also known as the 40-hour week movement or the short-time movement) was a social movement to regulate the length of a working day, preventing excesses and abuses.
An eight-hour work day has its origins in the 16 ...
.''Como nasceu o Partido Comunista Português''Portuguese Communist Party, URL accessed 20 June 2006 In September 1919, the working-class movement founded the first Portuguese Labour Union Confederation, the General Confederation of Labour; however, the feeling of political powerlessness, due to the lack of a coherent political strategy among the Portuguese working class, plus the growing popularity of the
Bolshevik revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
in Russia in 1917, led to the foundation of the Portuguese Maximalist Federation
The Portuguese Maximalist Federation ( or ) was a revolutionary movement founded on April 27, 1919 in Lisbon. The organization was inspired by the most radical factions involved in the Russian revolution of 1917, and was mostly composed by anarc ...
(FMP) in 1919. The goal of FMP was to promote socialist and revolutionary ideas and to organize and develop the worker movement.
After some time, members of the FMP began to feel the need for a "revolutionary vanguard" among Portuguese workers. After several meetings at various trade union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ...
offices, and with the aid of the Comintern, this desire culminated in the foundation of the Portuguese Communist Party as the Portuguese Section of the Comintern on 6 March 1921.
Unlike virtually all other European communist parties, the PCP was not formed after a split of a social democratic or socialist party, but from the ranks of anarcho-syndicalist and revolutionary syndicalist groups, the most active factions in the Portuguese labor movement. The party opened its first headquarters in the Arco do Marquês do Alegrete Street in Lisbon. Seven months after its creation, the first issue of ''O Comunista'' (The Communist), the first newspaper of the party, was published.
The first congress of the party took place in Lisbon in November 1923, with Carlos Rates
Carlos may refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Carlos, Alberta, a locality
;United States
* Carlos, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Carlos, Maryland, a place in Allegany County
* Carlos, Minnesota, a small city
* Carlos, West Virginia
;Elsewhere ...
as the leader. The congress was attended by about a hundred members of the party and asserted its solidarity with socialism in the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
and the need for a strong struggle for similar policies in Portugal; it also stated that a fascist coup in Portugal was a serious threat to the party and to the country.Vasconcelos, José Carlos de (dir.). (1982) ''Revista História'' (History Magazine) - Number 47
Outlawed
After the military coup of 28 May 1926, the party was outlawed and had to operate in secrecy. By coincidence, the coup was carried out on the eve of the second congress, forcing the suspension of party business. In 1927, the party's main office was closed. The party was first re-organized in 1929 under Bento Gonçalves. Adapting its new illegal status, the party re-organized as a network of clandestine cells. Meanwhile, in 1938, the PCP had been expelled from the Comintern. The reason for the expulsion was a sense of distrust in the Comintern caused by a sudden breakdown in the party's activity after a period of strong communist tumult in the country, accusations of alleged embezzlement of money carried out by some important members of the party and, mainly, the weak internal structure of the party, dominated by internal wars. The action against the PCP, signed by Georgi Dimitrov, was in part taken due to some persecution against Comintern member parties or persons (like the Communist Party of Poland or Béla Kun) led byJoseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet Union, Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as Ge ...
. These series of events would, in part, lead to the end of the Comintern in 1943. The PCP would only re-establish its relations with the communist movement and the Soviet Union in 1947, after sporadic contacts made through the communist parties of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and later through Mikhail Suslov.Rosas, Fernando (dir.) (1997). ''Revista História'' (History Magazine) - Number 28 (New Series)
 After the 1933 rise of Salazar's dictatorial Estado Novo regime, suppression of the party grew. Many members were arrested, tortured, and executed. Many were sent to the
After the 1933 rise of Salazar's dictatorial Estado Novo regime, suppression of the party grew. Many members were arrested, tortured, and executed. Many were sent to the Tarrafal concentration camp
Tarrafal was a concentration camp located in the village of Chão Bom, in the Municipality of Tarrafal, on the island of Santiago in Cape Verde.
It was established in 1936, during a reorganization process of the Portuguese Estado Novo prison ...
in the Cape Verde Islands. This included Bento Gonçalves, who would die there. The vast wave of arrests led to a major re-organization in 1940 and 1941, named the "Reorganization of '40". The first congress held after these changes was held in 1943, and stated that the party should unite with all those who also wanted an end to the dictatorship. Another important conclusion was the need to increase the party's influence inside the Portuguese army. The party was able, for the first time, to assure a strong clandestine organization, with a network of clandestine cadres, which would significantly aid the resistance against Salazar's regime.
In 1945, with the defeat of the major fascist regimes in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Salazar was forced to fake some democratic changes to keep up a good image in the eyes of the West, so in October of that year, the democratic resistance was authorized to form a platform, which was named Movement of Democratic Unity (Portuguese: ''Movimento de Unidade Democrática'', or MUD). Initially, the MUD was controlled by the moderate opposition, but it soon became strongly influenced by the PCP, which controlled its youth wing. In the leadership of the youth wing were several communists, among them Octávio Pato
Octávio Floriano Rodrigues Pato (1 April 1925, Vila Franca de Xira – 19 February 1999) was a Portuguese communist leader.
Biography
Octávio started working at 14 in a shoe factory. At the same time he also played soccer on S.L. Benfica's you ...
, Salgado Zenha, Mário Soares, Júlio Pomar
Júlio Artur da Silva Pomar, GOL, GCM (10 January 1926 – 22 May 2018) was a Portuguese painter and visual artist. He was often considered the greatest Portuguese painter of his generation.
Early life and career (1940s and 1950s)
Pomar first ...
, and Mário Sacramento
Mário Emílio de Morais Sacramento (July 7, 1920 – March 27, 1969) was a Portuguese physician and essayist that became famous for his antifascist activities against the dictatorial regime led by Oliveira Salazar in Portugal.
Mário Sacram ...
. This influence led to the MUD being outlawed by the government in 1948, after several waves of suppression.
The fourth congress, held in July 1946, pointed to massive popular struggle as the only way to overthrow the regime, and stated the policies that would help the party leaders that same popular movement. This, along with the consolidation of the clandestine work, was the main conclusion of the congress. A brief report of the conclusions of this congress were published by the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. At this time, Álvaro Cunhal
Álvaro Barreirinhas Cunhal (; 10 November 1913 – 13 June 2005) was a Portuguese communist revolutionary and politician. He was one of the major opponents of the dictatorial regime of the '' Estado Novo''. He served as secretary-general of the ...
travelled to Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
with the aid of Bento de Jesus Caraça to improve relations with the Socialist Bloc. Later, in 1948, he travelled to the Soviet Union to speak with Mikhail Suslov, after which the bonds between the PCP and the International Communist Movement
The history of communism encompasses a wide variety of ideologies and political movements sharing the core theoretical values of common ownership of wealth, economic enterprise, and property. Most modern forms of communism are grounded at leas ...
were re-established. Soon after returning from the Soviet Union, Cunhal was arrested by the PIDE.
The fifth congress, held in September 1957, was the only congress to be held outside Portugal. In Kiev, the Party approved its first program and statutes. For the first time, the party took an official position on colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their reli ...
, stating that every people had the right of self-determination, and made clear its support of the liberation movements in the Portuguese colonies, such as MPLA in Angola
, national_anthem = "Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordinat ...
, FRELIMO
FRELIMO (; from the Portuguese , ) is a democratic socialist political party in Mozambique. It is the dominant party in Mozambique and has won a majority of the seats in the Assembly of the Republic in every election since the country's firs ...
in Mozambique, and PAIGC in Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ) ...
.
In January 1960, a group of ten PCP members managed to escape from the high-security prison in Peniche. The escape returned to freedom many of the leading figures of the Party, among them, Álvaro Cunhal, who would be elected in the following year the first secretary-general in nineteen years. Among the escapees was also Jaime Serra, who would help to organize a secret commando group, the Armed Revolutionary Action
The Armed Revolutionary Action (ARA) was the armed arm of the Portuguese Communist Party (PCP), as a semi-autonomous organization that was active from 1970 to 1973, under the ''Estado Novo'' dictatorship then led by Marcelo Caetano. The first m ...
(Portuguese: ''Acção Revolucionária Armada'' or ARA). The ARA was the armed branch of the PCP that would be responsible in the 1970s for some military action against the dictatorial regime.
In 1961, the Colonial War
Colonial war (in some contexts referred to as small war) is a blanket term relating to the various conflicts that arose as the result of overseas territories being settled by foreign powers creating a colony. The term especially refers to wars ...
in Africa began - first in Angola
, national_anthem = "Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordinat ...
, and in the next year in Mozambique and Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ) ...
. The war lasted thirteen years and devastated Portuguese society, forcing many thousands of Portuguese citizens to leave the country, both to seek a better future in countries like France, Germany, or Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
and to escape conscription. The PCP, which had been involved in the formation of the nationalist guerrilla movements, along with the Soviet Union, immediately stated its opposition to the war, and its support for the anti-colonial movements. The war prompted unrest in Portuguese society and helped lead to the decline of the Salazar regime.
In 1962, the Academic Crisis The Academic Crisis ( pt, Crise académica) is the name given to a Portuguese governmental policy instigated in 1962 by the '' Estado Novo'' entailing the boycott and closure of several student associations and organizations, including the National ...
occurred. The Salazar regime, fearing the growing popularity of democratic ideas among students, made several student associations and organizations illegal, including the National Secretariat of Portuguese Students. Most members of this organization were intellectual communist militants who were persecuted and forbidden to continue their university studies. With assistance from the PCP, the students responded with demonstrations that culminated on 24 March with a large student demonstration in Lisbon. The demonstration was brutally suppressed by the police, leading to hundreds of injuries among the protesters. Immediately thereafter, the students began a strike against the regime.
In the sixth congress, in 1965, Álvaro Cunhal, elected secretary-general in 1961, released the report, ''The Path to Victory—The Tasks of the Party in the National and Democratic Revolution'', written while he was in exile in Moscow in collaboration with Margarida Tengarrinha
Margarida Tengarrinha (7 May 1928 – 26 October 2023) was a Portuguese teacher, writer, artist and illustrator. As a member of the Portuguese Communist Party (PCP) she was active as an opponent of the authoritarian '' Estado Novo'' regime that g ...
, which became a document of major influence in the democratic movement. Widely distributed among the clandestine members, it contained eight political goals, such as "the end of the monopolies in the economy", "the need for agrarian reform and redistribution of the land", and "the democratization of access to culture and education" — policies that the Party considered essential to make Portugal a fully democratic country. Nine years later, on 25 April 1974, the Carnation Revolution occurred, putting an end to 48 years of resistance and marking the beginning of a new cycle in the party's life.
Carnation Revolution
Immediately after the revolution, basic democratic rights were re-established in Portugal. On 27 April, political prisoners were freed. On 30 April,Álvaro Cunhal
Álvaro Barreirinhas Cunhal (; 10 November 1913 – 13 June 2005) was a Portuguese communist revolutionary and politician. He was one of the major opponents of the dictatorial regime of the '' Estado Novo''. He served as secretary-general of the ...
returned to Lisbon, where he was received by thousands of people. May Day was commemorated for the first time in 48 years, and an estimated half million people gathered in the FNAT Stadium (now 1 May Stadium) in Lisbon to hear speeches by Cunhal and the socialist Mário Soares. On 17 May, the party's newspaper, ''Avante!
''Avante!'' (''Onwards!'') is the official newspaper of the Portuguese Communist Party (PCP). Founded in 1931, it continues to be published to this day. The newspaper's motto is ''Workers of the World, Unite!'' and has been present in every e ...
'', produced the first legal issue in its history.

Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ) ...
, Angola
, national_anthem = "Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordinat ...
, Mozambique, Cape Verde, and São Tomé and Príncipe became independent countries.
Six months after the Carnation Revolution, on 20 October 1974, the party's seventh congress took place. More than a thousand delegates and hundreds of Portuguese and foreign guests attended. The congress set forth important statements that discussed the ongoing revolution in the country. The 36 members of the elected central committee had in the aggregate experienced more than 300 years in jail. On 26 December 1974, the PCP became the first legally recognized party.
The revolutionary process continued. On 11 March 1975, the left-wing military forces defeated a coup attempt by rightists in the military. This resulted in a turn in the revolutionary process to the political left, with the main sectors of the economy, such as the banks, transportation, steel mills, mines, and communications companies, being nationalized. This was done under the lead of Vasco Gonçalves
General Vasco dos Santos Gonçalves OA (; Lisbon 3 May 1921 – 11 June 2005) was a Portuguese army officer in the Engineering Corps who took part in the Carnation Revolution and later served as the 104th Prime Minister from 18 July 1974 to ...
, a member of the military wing who supported the party and who had become prime minister after the first provisional government resigned. The party then asserted its complete support for these changes and for the Agrarian Reform process that implemented collectivization of the agricultural sector and the land in a region named the "Zone of Intervention of the Agrarian Reform" or "ZIRA", which included the land south of the Tagus River. The PCP took the lead of that process and drove it according to the party's program, organizing thousands of peasants into cooperatives. Combined with the party's strong clandestine organization and support of the peasants' movement during the preceding years in that region, these efforts made the south of Portugal the major stronghold of the PCP. The party gained more than half of the votes in Beja, Évora, and Setúbal
Setúbal (, , ; cel-x-proto, Caetobrix) is a city and a municipality in Portugal. The population in 2014 was 118,166, occupying an area of . The city itself had 89,303 inhabitants in 2001. It lies within the Lisbon metropolitan area.
In the t ...
in subsequent elections.
One year after the revolution, the first democratic elections took place to elect the parliament that would write a new constitution to replace the constitution of 1933. The party achieved 12.52% of the vote and elected 30 members of parliament. In the end, as the party wanted, the constitution included several references to "socialism" and a "classless society" and was approved with the opposition of only one party, the right-wing Democratic and Social Centre (Portuguese: ''Centro Democrático Social'' or CDS).
In 1976, after the approval of the constitution, the second democratic election was carried out and the PCP raised its share of the vote to 14.56% and 40 seats. In the same year, the first Avante! Festival
The ''Avante!'' Festival ( pt, Festa do Avante!) is an annual cultural festival held during the first weekend of September. It was started in 1976 by the Portuguese Communist Party and is named after the party's official newspaper, '' Avante!'' ...
took place, and the eighth congress was held in Lisbon from 11–14 November. The congress mainly stated the need to continue the quest for socialism in Portugal and the need to defend the achievements of the revolution against what the party considered to be a political step backward, led by a coalition of the Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. All of these parties claim to uphold some form of socialism, though they may have very different interpretations of what "socialism" means. Statistically, most of ...
and the right-wing Centro Democrático Social, who opposed the agrarian reform process.
In 1979, the party held its ninth congress, which analysed the state of post-revolutionary Portugal, right-wing politics, and the party's struggles to nationalize the economy. In December 1979, new elections took place. The party formed the United People Alliance
The United People Alliance (Portuguese: Aliança Povo Unido or APU) was an electoral and political coalition between the Portuguese Communist Party (PCP) and the Portuguese Democratic Movement (MDP-CDE). After 1983, the Ecologist Party "The Greens ...
(Portuguese: ''Aliança Povo Unido'' or APU) in coalition with the Portuguese Democratic Movement
The Portuguese Democratic Movement/Democratic Electoral Commissions (Portuguese: ''Movimento Democrático Português / Comissões Democráticas Eleitorais'', MDP/CDE or just MDP) was one of the most important organizations of the democratic oppo ...
(Portuguese: ''Movimento Democrático Português'' or MDP/CDE) and increased its vote to 18.96% and 47 seats. The election was won by a centrist/right-wing coalition led by Francisco Sá Carneiro, which immediately initiated policies that the party considered to be contrary to working-class interests. Despite a setback in a subsequent election in 1980, in which the PCP dropped to 41 seats, the party achieved several victories in local elections, winning the leadership of dozens of municipalities in the FEPU coalition. After the sudden death of Sá Carneiro in an air crash in 1980, the party achieved 44 seats and 18.20% of the vote as part of the APU in the 1983 elections. Also in 1983, the party held its tenth congress, which again criticized what it saw as the dangers of right-wing politics.
In 1986, the surprising rise of Mário Soares, who reached the second round in the presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The p ...
, defeating the party's candidate, Salgado Zenha, made the party call an extra congress. The eleventh congress was called with only two weeks' notice, in order to decide whether or not to support Soares against Freitas do Amaral. Soares was supported, and he won by a slight margin. Had he not been supported by the PCP, he would have probably lost. In 1987, after the resignation of the government, another election took place. The PCP, now in the Unitary Democratic Coalition (Portuguese: ''Coligação Democrática Unitária'' or CDU) with the Ecologist Party "The Greens" (Portuguese: ''Partido Ecologista "Os Verdes"'' or PEV) and the Democratic Intervention
The Democratic Intervention (Portuguese: ''Intervenção Democrática'' or ID) is a Portuguese left-wing political association founded in order to promote and defend socialist ideas in Portugal and other countries. Members of it take part as ...
(Portuguese: ''Intervenção Democrática'' or ID), saw an electoral decline to 12.18% and 31 seats.
Fall of the Socialist Bloc
In 1988, the PCP held another congress, the twelfth, in which more than 2000 delegates participated and which put forth a new program entitled ''Portugal, an Advanced Democracy for the 21st Century''. At the end of the 1980s, the Socialist Bloc of Eastern Europe started to disintegrate, and the party faced one of the biggest crises in its history. With many members leaving, the party called a thirteenth congress for May 1990, in which a huge ideological battle occurred. The majority of the more than 2000 delegates decided to continue the party's "revolutionary way to Socialism" — i. e., to retain its Leninist ideology. By so doing, it clashed with what many other communist parties around the world were doing. The congress asserted that socialism in the Soviet Union had failed, but a unique historical experience, several social changes, and several achievements by the labour movement had been influenced by the Socialist Bloc. Álvaro Cunhal was re-elected secretary-general, butCarlos Carvalhas
Carlos Alberto do Vale Gomes Carvalhas, GCC (born in São Pedro do Sul, 9 November 1941) is a Portuguese economist and politician and former Secretary-General of the Portuguese Communist Party (1993–2004), succeeding the historical leader ...
was elected assistant secretary-general.
In the legislative election of 1991, the party won 8.84% of the national vote and 17 seats, continuing its electoral decline.
The fourteenth congress took place in 1992, and Carlos Carvalhas
Carlos Alberto do Vale Gomes Carvalhas, GCC (born in São Pedro do Sul, 9 November 1941) is a Portuguese economist and politician and former Secretary-General of the Portuguese Communist Party (1993–2004), succeeding the historical leader ...
was elected the new secretary-general, replacing Álvaro Cunhal. The congress analysed the new international situation created by the disappearance of the Soviet Union and the defeat of socialism in Eastern Europe. The party also traced the guidelines intended to put Cavaco Silva and the right-wing government on its way out, a fact that would happen shortly after. In 1995, the right-wing Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
For ...
was replaced in the government by the Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. All of these parties claim to uphold some form of socialism, though they may have very different interpretations of what "socialism" means. Statistically, most of ...
after the October legislative election, in which the PCP received 8.61% of the votes.
Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropo ...
, with more than 1600 delegates participating. The congress criticized the right-wing policies of the socialist government of António Guterres, and debated the future of the PCP following the debacle of the Socialist Bloc. In the subsequent local elections, the party continued to decline, but in the legislative election of 1999, the party increased its voting percentage for the first time in many years. The sixteenth congress was held in December 2000, and Carlos Carvalhas was re-elected secretary-general. In the legislative election of 2002, the PCP achieved its lowest voting result ever, with only 7.0% of the vote.
In November 2004, the seventeenth party congress elected Jerónimo de Sousa
Jerónimo Carvalho de Sousa (; born 13 April 1947) is a Portuguese politician who served as General Secretary of the Portuguese Communist Party
The Portuguese Communist Party ( pt, Partido Comunista Português, , PCP) is a communist, Marxi ...
, a former metal worker, as the new secretary-general.
In the legislative election of February 2005, the Party increased its share of the vote, and won 12 of the 230 seats in parliament, receiving about 430,000 votes (7.60%).
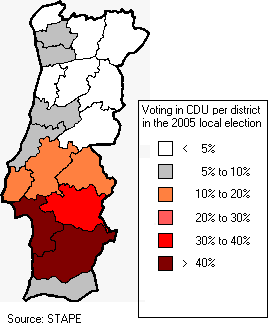
After the 2005 local election, in which the PCP regained the presidency of 7 municipalities, the party holds the leadership of 32 (of 308) municipalities, most of them in Alentejo and Setúbal
Setúbal (, , ; cel-x-proto, Caetobrix) is a city and a municipality in Portugal. The population in 2014 was 118,166, occupying an area of . The city itself had 89,303 inhabitants in 2001. It lies within the Lisbon metropolitan area.
In the t ...
, and holds the leadership of hundreds of civil parishes and local assemblies. The local administration by PCP is usually marked by concern about such issues as preventing privatization of the water supply, funding culture and education, providing access to sports, and promoting health, facilitating participatory democracy, and preventing corruption. The presence of the Greens in the coalition also keeps an eye on environmental issues such as recycling
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. The Energy recycling, recovery of energy from waste materials is often included in this concept. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability t ...
and water treatment.
The PCP's work now follows the program of an "Advanced Democracy for the 21st Century". Issues like the decriminalization of abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pre ...
, workers' rights
Labor rights or workers' rights are both legal rights and human rights relating to labor relations between workers and employers. These rights are codified in national and international labor and employment law. In general, these rights inf ...
, the increasing fees for the health service and education, the erosion of the social safety net, low salaries and pensions, imperialism and war, and solidarity with other countries such as Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, Palestine, Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribb ...
, and the Basque Country are constant concerns in the party's agenda.
The party has three members elected to the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
, after the European election of 2014. They sit in the European United Left–Nordic Green Left group.
Since the 2015 legislative election, the party supports the government headed by António Costa
António Luís Santos da Costa GCIH (; born 17 July 1961) is a Portuguese lawyer and politician serving as the 119th and current prime minister of Portugal since 26 November 2015, presiding over the XXI (2015–2019), XXII (2019–2022) and ...
, together with the Left Bloc and the Greens. However, the PCP has been historically critical of the Socialist Party.
In in 2017, the party, alongside the Portuguese Socialist Party
The Portuguese Socialist Party ( pt, Partido Socialista Português) was a political party in Portugal.
The party was founded in 1875. During its initial phase the party was heavily influenced by Proudhonism, and rejected revolutionary Marxism. T ...
, the social-democratic PSD, BE and the ecologist party PEV, voted in favour of abolishing party fundraising limits, thereby opening all portuguese parties to private political donorship, with no obligation to disclose the donations source. The new proposal was reluctantly approved by the Portuguese president Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa.
After the 2019 European Parliament election in Portugal the party lost one european deputy, it now has two members who sit in the European United Left-Nordic Green Left
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
group in the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
.
Reaction to the 2022 invasion of Ukraine
Since the beginning of the2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. A ...
, the PCP has come under the spotlight for being the sole political party represented in Parliament to have avoided a clear condemnation of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
from the start, choosing instead to repeatedly blame Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
and the West for the war.
On 24 February (the first day of the invasion), the party refused to condemn Russia, upon being explicitly invited to do so by Foreign Affairs Minister In many countries, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs is the government department responsible for the state's diplomacy, bilateral, and multilateral relations affairs as well as for providing support for a country's citizens who are abroad. The entit ...
Augusto Santos Silva (Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. All of these parties claim to uphold some form of socialism, though they may have very different interpretations of what "socialism" means. Statistically, most of ...
) in a parliamentary debate. The communists stated that the conflict was "more profound" than "a problem between Russians and Ukrainians", and instead blamed the United States, accusing them of being "the party that is truly interested in having a new war in Europe" and of "promoting" it in order to "turn attentions away from internal problems" and to "ensure a large-scale sale of weapons".
On 1 March, the two communist members of the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
voted against a resolution condemning the invasion. The party explained its decision by accusing the resolution of "fuelling the escalation", of "seeking to impose a unilateral view" and of "justifying the colossal process of increasing military expenditures, the strengthening and expansion of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
and the militarisation of the EU". The document was approved with more than 600 votes in favour, 13 against and 26 abstentions.
On 8 March, the PCP's leader Jerónimo de Sousa blamed all entities involved in the war (Russia included, although referring to its actions by the Kremlin's language of a "military operation"). He stated the party condemned "the whole process of meddling and of confrontation which took place n Ukraine
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''.
History
...
the US-promoted coup d'état in 2014, Russia's recent military intervention and the intensification of the bellicose escalation made by the US, NATO and the EU".
On 20 April, the PCP announced that it would not attend the Parliament's solemn session where President of Ukraine Volodymyr Zelensky
Volodymyr Oleksandrovych Zelenskyy, ; russian: Владимир Александрович Зеленский, Vladimir Aleksandrovich Zelenskyy, (born 25 January 1978; also transliterated as Zelensky or Zelenskiy) is a Ukrainian politicia ...
would speak, the following day. The party's parliamentary leader Paula Santos rejected condoning "the participation of someone who personifies a xenophobic and bellicose power", calling the session a "stage to contribute for the escalation of war".
On 23 April, questioned by a journalist as to whether he considered that there was an invasion going on, party leader Jerónimo de Sousa replied: "There was a military operation which we have condemned." Following the journalist's insistence on the question, he rejected using the word 'invasion' and instead hesitantly responded: "At least, from the images we have... from the images we have, there is a conflict, there is a war. That is unavoidable and must be recognised."
Electoral results


Since 1987
(sourcePortuguese Electoral Commission
) Note: * ''In 2004, after the enlargement of the European Union, the number of MEPs elected by
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
decreased from the original 25 to 24.''
*''The Local election results report the voting for the Municipal Chambers only and don't include occasional coalitions in some municipalities, e.g. in Lisbon, between 1989 and 2001. Voting for the Municipal Assemblies and Parish Assemblies
''Freguesia'' (), usually translated as "parish" or "civil parish", is the third-level administrative subdivision of Portugal, as defined by the 1976 Constitution. It is also the designation for local government jurisdictions in the former Por ...
is usually higher (11.7% and 12.0%, respectively, in 2005).''
*''The number of mandates denotes the number of councillors in Local elections, MPs in Parliamentary elections and MEPs in European Parliament elections.''
*''The CDU is composed of the PCP, the PEV and the ID ''
Presidential elections
(sourcePortuguese Electoral Commission
) Notes: * ''In 1980, Carlos Brito withdrew in favour of Ramalho Eanes, won.'' * ''In 1986, the Party's first candidate was
Ângelo Veloso
Ângelo Matos Mendes Veloso (1930-1990; ) was a Portuguese politician.
A member of the Portuguese Communist Party since the days of the ''Estado Novo'' (New State) dictatorial fascist regime of António de Oliveira Salazar, Veloso was imprisoned ...
, that later withdrew in favour of Salgado Zenha, lost.''
* ''In 1986, in the second round, the Party supported Mário Soares, won.''
* ''In 1996, Jerónimo de Sousa withdrew in favour of Jorge Sampaio, won.''
Organization

Principles
The PCP's statutes define the party as thevanguard
The vanguard (also called the advance guard) is the leading part of an advancing military formation. It has a number of functions, including seeking out the enemy and securing ground in advance of the main force.
History
The vanguard derives f ...
of the Portuguese proletariat. That vanguard role results from its class nature and its close liaison with the masses, mobilizing them and winning their support.
The PCP organizes in its ranks industrial and office workers, small and medium farmers, intellectuals and technical workers, small and medium shopkeepers, and industrialists, who fight for democracy and for socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes th ...
. The party considers itself the legitimate pursuer of the Portuguese people's best traditions of struggle and of their progressive and revolutionary achievements throughout their history.
The PCP upholds Marxism–Leninism
Marxism–Leninism is a communist ideology which was the main communist movement throughout the 20th century. Developed by the Bolsheviks, it was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, its satellite states in the Eastern Bloc, and vario ...
as its theoretical basis, which is a materialist and dialectical
Dialectic ( grc-gre, διαλεκτική, ''dialektikḗ''; related to dialogue; german: Dialektik), also known as the dialectical method, is a discourse between two or more people holding different points of view about a subject but wishing t ...
conception of the world and a scientific tool of social analysis. These principles guide the party's action and enable it to systematically answer new challenges and realities. The party also orients its members and its activity in the spirit of proletarian internationalism
Proletarian internationalism, sometimes referred to as international socialism, is the perception of all communist revolutions as being part of a single global class struggle rather than separate localized events. It is based on the theory that ...
, of cooperation between the communist parties and revolutionary and progressive forces, and of solidarity with the workers of other countries.
Aside from upholding Marxism–Leninism
Marxism–Leninism is a communist ideology which was the main communist movement throughout the 20th century. Developed by the Bolsheviks, it was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, its satellite states in the Eastern Bloc, and vario ...
and maintaining its "proletarian vanguard
The vanguard (also called the advance guard) is the leading part of an advancing military formation. It has a number of functions, including seeking out the enemy and securing ground in advance of the main force.
History
The vanguard derives f ...
role", its goals, according to the party are:
*to bring about the process of social transformation and the defeat of capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
through revolutionary means,
*to uphold dialectical and historical materialism as an "instrument of analysis and guide for action",
*the rupture with right-wing policies,
*the realization of a patriotic and left-wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in soci ...
alternative, and
*the realization of an "Advanced Democracy" with the values of the April revolution, for a future socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
and communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
Portugal.
Secretaries-General
* José Carlos Rates (1921–1929) * Bento António Gonçalves (1929–1942) * period with no secretary-general (1942–1961) *Álvaro Cunhal
Álvaro Barreirinhas Cunhal (; 10 November 1913 – 13 June 2005) was a Portuguese communist revolutionary and politician. He was one of the major opponents of the dictatorial regime of the '' Estado Novo''. He served as secretary-general of the ...
(1961–1992)
* Carlos Carvalhas
Carlos Alberto do Vale Gomes Carvalhas, GCC (born in São Pedro do Sul, 9 November 1941) is a Portuguese economist and politician and former Secretary-General of the Portuguese Communist Party (1993–2004), succeeding the historical leader ...
(1992–2004)
* Jerónimo de Sousa
Jerónimo Carvalho de Sousa (; born 13 April 1947) is a Portuguese politician who served as General Secretary of the Portuguese Communist Party
The Portuguese Communist Party ( pt, Partido Comunista Português, , PCP) is a communist, Marxi ...
(2004–2022)
* Paulo Raimundo (2022–present)
Internal organization
The main principle that guides the party's internal structure, being a Leninist party, is democratic centralism, which implies that: *all party organs, from top to bottom, are elected and may be dismissed by those who elected them, if needed; *the members who have tasks in any structure of the party are responsible to both lower and upper levels, being obliged to report the activities to both and to give consideration to their opinions and criticisms; *lower-level structures must respect the decisions of the upper structures; *every member is free to give his opinion during the discussion, and the structures must take in account the contribution of every member; *every member must obey the decisions achieved by consensus or by a majority; *every member must work along with his own structure; and *the party does not recognize the existence of organized factions inside it. The structure and internal organization of the PCP are defined by its statutes. The most recent statutes were approved in the seventeenth congress, held in 2004. The upper organs of the PCP at the national level are thecongress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
, the central committee, and the central commission of control.
The supreme organ of the party is its congress, which is summoned by the outgoing central committee and held every four years. The congress is composed of delegates elected by the respective lower organs proportional to each organ's membership size. The congress approves its theses
A thesis ( : theses), or dissertation (abbreviated diss.), is a document submitted in support of candidature for an academic degree or professional qualification presenting the author's research and findings.International Standard ISO 7144: ...
after a wide discussion period inside the organizations and may also change the party's program and statutes. All the decisions of the congress are made by the delegates voting. With the exception of the voting for the central committee, which a recent Portuguese law requires to be secret, all voting, including the approval of the theses, are conducted by a show of hands. The theses, after approval, guide all the party's political actions and stances until the next congress.
The main organ between the congresses is the central committee, which is elected in the congresses under a proposal of the retiring central committee. This proposal may only be made after a long period of hearing the lower structures in order to include in it the names they propose. The CC may not change the orientation present in the congress' theses. The main task of the central committee is to define the guidelines of the party's political work and decide the immediate tasks of the party, assuring that the lower structures comply with those decisions. The CC elects, from its members, its Political Bureau
A politburo () or political bureau is the executive committee for communist parties. It is present in most former and existing communist states.
Names
The term "politburo" in English comes from the Russian ''Politbyuro'' (), itself a contraction ...
, its Secretariat, and also the Central Commission of Control. This last must assure the compliance between the Party's activities and the statutes, and control the Party's finances. The CC may, or may not, elect the party's secretary-general from its members.
The intermediate organs of the Party are, by rule, the organs that coordinate an organization of district, municipality, and parish levels, but organizations at a neighbourhood or professional class level also exist. The main organ of an intermediate part of the party's structure is the Assembly. The Assembly works as a small Congress for the organization members. The Assembly elects the regional or municipal committees, which are responsible for applying the theses of the Assembly to the organization's work.
The base level organ of the Party is the cell. The cell is defined as being the link between the party and the working class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colou ...
and the masses. A cell is composed of a minimum of three Party members and exists at a work place or neighborhood level. The cell may elect its own secretariat, which has the responsibility of discussing and putting into practice the Party's guidelines. The cell must ensure the recruitment of new members, promote the reading of Avante!
''Avante!'' (''Onwards!'') is the official newspaper of the Portuguese Communist Party (PCP). Founded in 1931, it continues to be published to this day. The newspaper's motto is ''Workers of the World, Unite!'' and has been present in every e ...
and the other publications, ensure that the members pay their membership fees and keep the upper structures aware of the cell's political work.
Media
 The Portuguese Communist Party publishes the weekly ''
The Portuguese Communist Party publishes the weekly ''Avante!
''Avante!'' (''Onwards!'') is the official newspaper of the Portuguese Communist Party (PCP). Founded in 1931, it continues to be published to this day. The newspaper's motto is ''Workers of the World, Unite!'' and has been present in every e ...
'' (''Onward!''), widely distributed throughout the country, and also the magazine of theoretical discussion ''O Militante
''O Militante'' (''The Militant'') is a magazine of theoretical discussion, founded in 1932 and published by the Portuguese Communist Party. ''O Militante'' forms, along with the weekly '' Avante!'', the essential core of the Party's press, but, ...
'' (''The Militant''), published bi-monthly. The party's press also includes the bulletin ''Emigração'' (''Emigration''), targeted at the large Portuguese diaspora, and the magazine ''Portugal e a UE'' (''Portugal and the EU''), directed by the party's members elected in the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
, which presents information related to the European politics and to the European United Left–Nordic Green Left group. Both ''Avante!'' and ''O Militante'' are sold in the party's offices to the members. Buying ''Avante!'' is considered one of the members' duties. ''Avante!'' is also sold among other newspapers in many news stands around the country.
''Avante!'' was illegally printed and distributed from February 1931 until May 1974.''As décadas do Avante!''Portuguese Communist party, URL accessed 2 July 2006 Many times, the newspaper distribution suffered breakdowns due to the suppression by the political police of party members who helped to distribute the newspaper, or due to the destruction of the clandestine printing offices. Successfully evading official censorship, ''Avante!'' was one of the very few Portuguese newspapers that freely reported on events like
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the Colonial War
Colonial war (in some contexts referred to as small war) is a blanket term relating to the various conflicts that arose as the result of overseas territories being settled by foreign powers creating a colony. The term especially refers to wars ...
in Africa or massive workers' strikes and waves of student protest against the dictatorship. ''Avante!'' continues to be printed after more than three decades of democracy, and has now a full online edition. The Avante! Festival
The ''Avante!'' Festival ( pt, Festa do Avante!) is an annual cultural festival held during the first weekend of September. It was started in 1976 by the Portuguese Communist Party and is named after the party's official newspaper, '' Avante!'' ...
was named after the newspaper.
During the campaign for the Portuguese legislative election of 2005
The 2005 Portuguese legislative election took place on 20 February. The election renewed all 230 members of the Assembly of the Republic (Portugal), Assembly of the Republic.
These elections were called after the decision of President of Portugal, ...
, the party created a radio broadcast on its website and also a digital forum, being the first Portuguese party to use the internet actively in an electoral campaign. After the last Congress, the statutes were changed and the party now considers its website as another official media and it is regularly updated. The campaign radio broadcast evolved into an online radio station named ''Comunic''. It broadcasts thematic interviews with party's members, music and propaganda.
Usually, the party's largest political campaigns and struggles are supported by the distribution of a massive number of leaflets and advertising posters in hot spots like train stations, factories, universities, main streets, and avenues or markets. The free television spots that the Portuguese law grants to the parties, either in the campaign time or out of it, are used by PCP to promote initiatives and political campaigns.
The party also owns a publishing company, ''Edições Avante!'' (''Avante! Editions''), that publishes and sells several books related to the party's history or to Marxism. Classics of Marxism–Leninism, such as '' The Communist Manifesto'', ''Capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
'', '' On the Jewish Question'', or ''What is to be Done?
''What Is to Be Done? Burning Questions of Our Movement'' is a political pamphlet written by Russian revolutionary Vladimir Lenin (credited as N. Lenin) in 1901 and published in 1902. Lenin said that the article represented "a skeleton plan ...
'', several books of Portuguese authors on the history of the party and the resistance, official documents like the program or the statutes, books from foreign authors, like ''Ten Days that Shook the World
''Ten Days That Shook the World'' (1919) is a book by the American journalist and socialist John Reed. Here, Reed presented a firsthand account of the 1917 Russian October Revolution. Reed followed many of the most prominent Bolsheviks closely ...
'' and several other works are present in the Avante! Edition's catalog.''Edições Avante!''Portuguese Communist Party, URL accessed 2 July 2006
Youth organization
The youth organization of PCP is the Portuguese Communist Youth ( pt, Juventude Comunista Portuguesa), and was founded on 10 November 1979, after the unification of theCommunist Students League
The Communist Students League (Portuguese: ''União dos Estudantes Comunistas'' or UEC) was the student wing of the Portuguese Communist Party. UEC was founded in 1972.
On November 10, 1979 UEC merged with the Young Communist League
The Young C ...
and the Young Communist League. The Portuguese Communist Youth is a member of the World Federation of Democratic Youth, a youth non-governmental organization that congregates several left-wing youth organizations from all the continents. The WFDY holds an international event, named World Festival of Youth and Students
The World Festival of Youth and Students is an international event organized by the World Federation of Democratic Youth (WFDY) and the International Union of Students after 1947. History
The festival has been held regularly since 1947 as an ev ...
, in which the Portuguese Communist Youth uses to participate.
The youth wing follows a structure similar to the Party's, also based on the Leninist principle of democratic centralism, and both organizations maintain a cooperative relationship. JCP is, however, an independent organization.
Mainly composed by students and some working-class young people, the Portuguese Communist Youth has, as its main political concerns, such issues as the promotion of a free and public education for all ages, employment, peace, and housing. It also promotes international solidarity brigades for countries like Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribb ...
, Palestine, or Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, alone or with other European Communist youth organizations like KNE
The Communist Youth of Greece ( el, Κομμουνιστική Νεολαία Ελλάδας ''Kommounistiki Neolea Elladas'', KNE) is the youth wing of the Communist Party of Greece (KKE).
It publishes the monthly newspaper ''Odigitis'' (Greek: � ...
or SDAJ. It has its main organizational strength among high-school and university students, with a strong presence among the Students' unions.
Avante! Festival
 Every year, in the first weekend of September, the party holds a festival called the
Every year, in the first weekend of September, the party holds a festival called the Avante! Festival
The ''Avante!'' Festival ( pt, Festa do Avante!) is an annual cultural festival held during the first weekend of September. It was started in 1976 by the Portuguese Communist Party and is named after the party's official newspaper, '' Avante!'' ...
(Portuguese: ''Festa do Avante!''). After taking place in different locations around Lisbon, like the Lisbon International Fair
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits ...
, Ajuda
Ajuda () is a ''freguesia'' (civil parish) and district of Lisbon, the capital of Portugal. Ajuda is located in western Lisbon, northeast of Belém and west of Alcântara. The population in 2011 was 15,617.Loures, it is now held in Amora, a city near
Portuguese Communist Party official web sitePortuguese Communist Youth official web siteAvante Festival! official websiteAvante! newspaper online editionPCP's short biography by the Carnation Revolution archive centre
''In English'':
Portuguese Communist Party web sitePortuguese Communist Youth official web site
{{Authority control Political parties in Portugal Far-left political parties 1921 establishments in Portugal Comintern sections Communist parties in Portugal Eurosceptic parties in Portugal Formerly banned communist parties Organisations based in Lisbon Political history of Portugal Political parties established in 1921 Left-wing parties International Meeting of Communist and Workers Parties
Seixal
Seixal () is a Portuguese city and municipality, located in the district of Setúbal, in the metropolitan area of Lisbon. Its population includes 184,269 inhabitants (2011), in an area of that includes six parishes. It is situated across th ...
, on land bought by the Party after a massive fundraising campaign in the early 1990s. The Party considered this campaign to be the only way to avoid the boycott organized by the owners of the previous festival grounds, a boycott that ultimately resulted in the Festival not being held in 1987.
The festival attracts hundreds of thousands of visitors. The events themselves consist of a three-day festival of music, with hundreds of Portuguese and international bands and artists across five different stages, ethnography, gastronomy, debates, a books and music fair, theatre (Avanteatro), cinema (Cineavante) and sporting events. Several foreign communist parties also participate.
Famous artists, Communist and non-Communist, Portuguese and non-Portuguese, have performed at the Festival, including Chico Buarque, Baden Powell, Ivan Lins, Zeca Afonso, Buffy Sainte-Marie
Buffy Sainte-Marie, (born Beverly Sainte-Marie, February 20, 1941) is an Indigenous Canadian-American (Piapot Cree Nation) singer-songwriter, musician, composer, visual artist, educator, pacifist, and social activist. While working in these ar ...
, Holly Near, Johnny Clegg, Charlie Haden, Judy Collins, Richie Havens, Tom Paxton, Ska-P, The Soviet Circus Company, the Kuban Cossack Choir, Dexys Midnight Runners, The Band, Hevia
José Ángel Hevia Velasco, known professionally as Hevia (born October 11, 1967 in Villaviciosa, Asturias), is a Spanish bagpiper – specifically, an Asturian gaita player. He commonly performs with his sister, María José, on drums. I ...
, Brigada Victor Jara
''Brigada'' (russian: Бригада), also known as ''Law of the Lawless'', is a Russian 15-episode crime television miniseries that debuted in 2002. It became very popular in Russia and ex-Soviet countries as well as Eastern Europe, but recei ...
, Adriano Correia de Oliveira
Adriano Maria Correia Gomes de Oliveira, GCIH, ComL, or just Adriano (April 9, 1942 – October 16, 1982) was a Portuguese musician, born to a conservative Roman Catholic family in Porto. His family moved to Avintes after his birth. He went to ...
, Carlos Paredes, Jorge Palma
Jorge Manuel de Abreu Palma (born 4 June 1950) is a Portuguese singer and songwriter.
A well-known and acclaimed songwriter in Portugal, Palma has achieved success with songs such as "Deixa-me Rir", "Frágil" and "Encosta-te a Mim".
Early lif ...
, Manoel de Oliveira, Babylon Circus
Babylon Circus is a nine piece ska and reggae group founded in 1995 in Lyon, France. Since forming, they have released six full - length albums and one EP. They have played over 1500 shows throughout Europe, and have toured as far as Syria, Austr ...
, and many others.
The preparation of the party begins right after the end of the previous festival. Hundreds of the Party's members and friends, mostly young people, volunteer.
See also
* Politics of Portugal * List of political parties in Portugal * Carnation Revolution * Unitary Democratic Coalition *Avante!
''Avante!'' (''Onwards!'') is the official newspaper of the Portuguese Communist Party (PCP). Founded in 1931, it continues to be published to this day. The newspaper's motto is ''Workers of the World, Unite!'' and has been present in every e ...
*Armed Revolutionary Action
The Armed Revolutionary Action (ARA) was the armed arm of the Portuguese Communist Party (PCP), as a semi-autonomous organization that was active from 1970 to 1973, under the ''Estado Novo'' dictatorship then led by Marcelo Caetano. The first m ...
Footnotes
Bibliography
Academic sources
Further reading
* Carlos Cunha, "Nationalist or Internationalist? The Portuguese Communist Party's Autonomy and the Communist International", in Tim Rees and Andrew Thorpe (eds.), ''International Communism and the Communist International, 1919-1943.'' Manchester: Manchester University Press, 1998. * Carlos Cunha, ''The Portuguese Communist Party's Strategy for Power, 1921-1986.'' New York: Garland Publishing, 1992. * J.G.P. Quintela, ''Para a História do Movimento Comunista em Portugal: 1. A Construção do Partido (Primeiro Periodo 1919-1929).'' owards a History of the Communist Movement in Portugal: 1. Construction of the Party (First Period, 1919-1929).Oporto: Afrontamento, 1976.External links
''In Portuguese'':Portuguese Communist Party official web site
''In English'':
Portuguese Communist Party web site
{{Authority control Political parties in Portugal Far-left political parties 1921 establishments in Portugal Comintern sections Communist parties in Portugal Eurosceptic parties in Portugal Formerly banned communist parties Organisations based in Lisbon Political history of Portugal Political parties established in 1921 Left-wing parties International Meeting of Communist and Workers Parties