Pons Fabricius on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
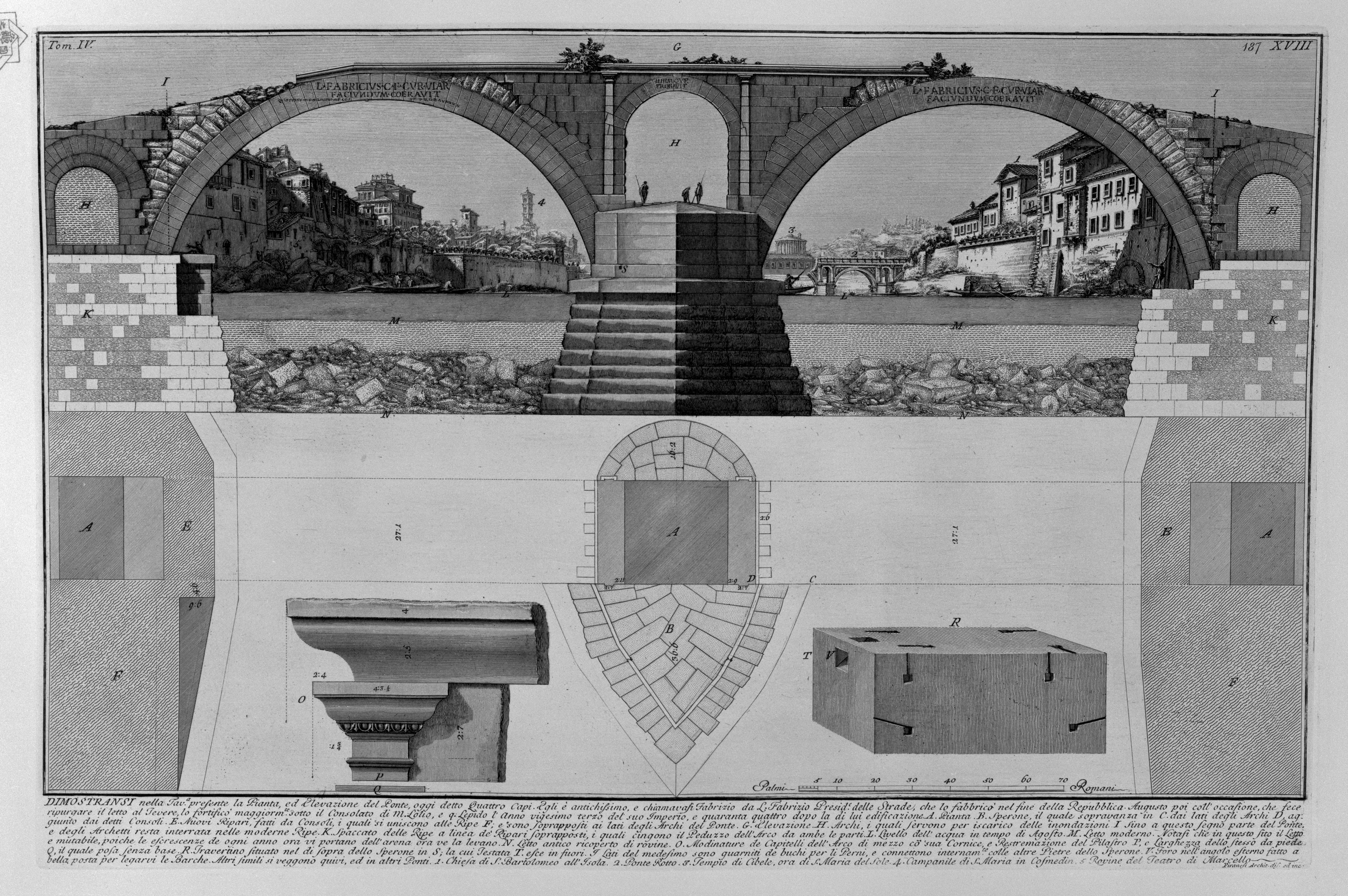
The Pons Fabricius ( it, Ponte Fabricio, "Fabrician Bridge") or Ponte dei Quattro Capi, is the oldest
Rome: An Oxford Archaeological Guide
'. Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press
 According to
According to
 An original inscription on the travertine commemorates its builder in Latin: L . FABRICIVS . C . F . CVR . VIAR , FACIVNDVM . COERAVIT , IDEMQVE , PROBAVIT ("Lucius Fabricius, son of Gaius, superintendent of the roads, took care and likewise approved that it be built"). It is repeated four times, once on each side of each arch.
A later inscription, in smaller lettering, records that the bridge was restored under
An original inscription on the travertine commemorates its builder in Latin: L . FABRICIVS . C . F . CVR . VIAR , FACIVNDVM . COERAVIT , IDEMQVE , PROBAVIT ("Lucius Fabricius, son of Gaius, superintendent of the roads, took care and likewise approved that it be built"). It is repeated four times, once on each side of each arch.
A later inscription, in smaller lettering, records that the bridge was restored under
LacusCurtius: Pons Fabricius
*
The Waters of Rome: Tiber River Bridges and the Development of the Ancient City of Rome
Tiber Island information
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Fabricius, Pons Bridges in Rome Roman bridges in Italy Deck arch bridges Stone bridges in Italy Bridges completed in the 1st century BC Rome R. XII Ripa
Roman bridge
The ancient Romans were the first civilization to build large, permanent bridges. Early Roman bridges used techniques introduced by Etruscan immigrants, but the Romans improved those skills, developing and enhancing methods such as arches and ...
in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, still existing in its original state. Built in 62 BC, it spans half of the Tiber
The Tiber ( ; it, Tevere ; la, Tiberis) is the third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by th ...
River, from the Campus Martius
The Campus Martius (Latin for the "Field of Mars", Italian ''Campo Marzio'') was a publicly owned area of ancient Rome about in extent. In the Middle Ages, it was the most populous area of Rome. The IV rione of Rome, Campo Marzio, which cove ...
on the east side to Tiber Island in the middle (the Pons Cestius is west of the island). ''Quattro Capi'' ("four heads") refers to the two marble pillars of the two-faced Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; la, Ianvs ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Jan ...
herms on the parapet, which were moved here from the nearby Church of St Gregory (Monte Savello) in the 14th century.Claridge, Amanda (1998). Rome: An Oxford Archaeological Guide
'. Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press
Bridge
 According to
According to Dio Cassius
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
, the bridge was built in 62 BC, the year after Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
was consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throu ...
, to replace an earlier wooden bridge destroyed by fire. It was commissioned by Lucius Fabricius, the curator of the roads and a member of the gens
In ancient Rome, a gens ( or , ; plural: ''gentes'' ) was a family consisting of individuals who shared the same nomen and who claimed descent from a common ancestor. A branch of a gens was called a ''stirps'' (plural: ''stirpes''). The ''gen ...
Fabricia of Rome. Completely intact from Roman antiquity, it has been in continuous use ever since.
The Pons Fabricius has a length of 62 m, and is 5.5 m wide. It is constructed from two wide arches spanning 80 feet, supported by a central pillar in the middle of the stream. The arches of this bridge are the first ones on any Roman bridge that were not semi-circular. This is possibly caused by the semi-circle being located below the water line. Its core is constructed of tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock ...
. Its outer facing today is made of bricks and travertine
Travertine ( ) is a form of terrestrial limestone deposited around mineral springs, especially hot springs. It often has a fibrous or concentric appearance and exists in white, tan, cream-colored, and even rusty varieties. It is formed by a p ...
. A relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
is located 20 feet above the pier. During times of flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
, this relief served as an additional waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary ...
.
Inscription
 An original inscription on the travertine commemorates its builder in Latin: L . FABRICIVS . C . F . CVR . VIAR , FACIVNDVM . COERAVIT , IDEMQVE , PROBAVIT ("Lucius Fabricius, son of Gaius, superintendent of the roads, took care and likewise approved that it be built"). It is repeated four times, once on each side of each arch.
A later inscription, in smaller lettering, records that the bridge was restored under
An original inscription on the travertine commemorates its builder in Latin: L . FABRICIVS . C . F . CVR . VIAR , FACIVNDVM . COERAVIT , IDEMQVE , PROBAVIT ("Lucius Fabricius, son of Gaius, superintendent of the roads, took care and likewise approved that it be built"). It is repeated four times, once on each side of each arch.
A later inscription, in smaller lettering, records that the bridge was restored under Pope Innocent XI
Pope Innocent XI ( la, Innocentius XI; it, Innocenzo XI; 16 May 1611 – 12 August 1689), born Benedetto Odescalchi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 21 September 1676 to his death on August 12, 1689.
Poli ...
, probably in 1679.
See also
* * List of Roman bridges *List of ancient monuments in Rome
This is a list of ancient monuments from Republican and Imperial periods in the city of Rome, Italy.
Amphitheaters
* Amphitheater of Caligula
* Amphitheatrum Castrense
* Amphitheater of Nero
* Amphitheater of Statilius Taurus
* Colosseum
Ba ...
* Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered on ...
* Roman engineering
The ancient Romans were famous for their advanced engineering accomplishments. Technology for bringing running water into cities was developed in the east, but transformed by the Romans into a technology inconceivable in Greece. The architecture ...
References
Sources
*External links
LacusCurtius: Pons Fabricius
*
The Waters of Rome: Tiber River Bridges and the Development of the Ancient City of Rome
Tiber Island information
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Fabricius, Pons Bridges in Rome Roman bridges in Italy Deck arch bridges Stone bridges in Italy Bridges completed in the 1st century BC Rome R. XII Ripa