Polyploid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Polyploidy is a condition in which the
Polyploidy is a condition in which the
 Polyploid types are labeled according to the number of chromosome sets in the nucleus. The letter ''x'' is used to represent the number of chromosomes in a single set:
*haploid (one set; 1x)
*diploid (two sets; 2x)
*triploid (three sets; 3''x''), for example sterile saffron crocus, or seedless watermelons, also common in the phylum
Polyploid types are labeled according to the number of chromosome sets in the nucleus. The letter ''x'' is used to represent the number of chromosomes in a single set:
*haploid (one set; 1x)
*diploid (two sets; 2x)
*triploid (three sets; 3''x''), for example sterile saffron crocus, or seedless watermelons, also common in the phylum
 Ancient genome duplications probably occurred in the evolutionary history of all life. Duplication events that occurred long ago in the history of various evolutionary lineages can be difficult to detect because of subsequent diploidization (such that a polyploid starts to behave cytogenetically as a diploid over time) as mutations and gene translations gradually make one copy of each chromosome unlike the other copy. Over time, it is also common for duplicated copies of genes to accumulate mutations and become inactive pseudogenes.
In many cases, these events can be inferred only through comparing sequenced genomes. Examples of unexpected but recently confirmed ancient genome duplications include
Ancient genome duplications probably occurred in the evolutionary history of all life. Duplication events that occurred long ago in the history of various evolutionary lineages can be difficult to detect because of subsequent diploidization (such that a polyploid starts to behave cytogenetically as a diploid over time) as mutations and gene translations gradually make one copy of each chromosome unlike the other copy. Over time, it is also common for duplicated copies of genes to accumulate mutations and become inactive pseudogenes.
In many cases, these events can be inferred only through comparing sequenced genomes. Examples of unexpected but recently confirmed ancient genome duplications include
 Polyploidy is frequent in plants, some estimates suggesting that 30–80% of living plant species are polyploid, and many lineages show evidence of ancient polyploidy ( paleopolyploidy) in their genomes. Huge explosions in
Polyploidy is frequent in plants, some estimates suggesting that 30–80% of living plant species are polyploid, and many lineages show evidence of ancient polyploidy ( paleopolyploidy) in their genomes. Huge explosions in
 As for plants and animals, fungal hybrids and polyploids display structural and functional modifications compared to their progenitors and diploid counterparts. In particular, the structural and functional outcomes of polyploid ''Saccharomyces'' genomes strikingly reflect the evolutionary fate of plant polyploid ones. Large chromosomal rearrangements leading to chimeric chromosomes have been described, as well as more punctual genetic modifications such as gene loss. The homoealleles of the allotetraploid yeast ''S. pastorianus'' show unequal contribution to the transcriptome. Phenotypic diversification is also observed following polyploidization and/or hybridization in fungi, producing the fuel for natural selection and subsequent
As for plants and animals, fungal hybrids and polyploids display structural and functional modifications compared to their progenitors and diploid counterparts. In particular, the structural and functional outcomes of polyploid ''Saccharomyces'' genomes strikingly reflect the evolutionary fate of plant polyploid ones. Large chromosomal rearrangements leading to chimeric chromosomes have been described, as well as more punctual genetic modifications such as gene loss. The homoealleles of the allotetraploid yeast ''S. pastorianus'' show unequal contribution to the transcriptome. Phenotypic diversification is also observed following polyploidization and/or hybridization in fungi, producing the fuel for natural selection and subsequent
Polyploidy on Kimball's Biology Pages
The polyploidy portal
a community-editable project with information, research, education, and a bibliography about polyploidy. {{Authority control Classical genetics Speciation he:פלואידיות#פוליפלואידיות fi:Ploidia#Polyploidia sv:Ploiditet#Polyploiditet
cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
s of an organism have more than one pair of ( homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei ( eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes, where each set contains one or more chromosomes and comes from each of two parents, resulting in pairs of homologous chromosomes between sets. However, some organisms are polyploid. Polyploidy is especially common in plants. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells
A somatic cell (from Ancient Greek σῶμα ''sôma'', meaning "body"), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Such cells comp ...
, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Males of bee
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyletic lineage within the superfami ...
s and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude ...
and multicellular algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from u ...
have life cycle
Life cycle, life-cycle, or lifecycle may refer to:
Science and academia
*Biological life cycle, the sequence of life stages that an organism undergoes from birth to reproduction ending with the production of the offspring
*Life-cycle hypothesis, ...
s with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte
A sporophyte () is the diploid multicellular stage in the life cycle of a plant or alga which produces asexual spores. This stage alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase.
Life cycle
The sporophyte develops from the zygote p ...
generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.
Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there a ...
, either during mitosis, or more commonly from the failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis or from the fertilization of an egg by more than one sperm. In addition, it can be induced in plants and cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This t ...
s by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin
Oryzalin is an herbicide of the dinitroaniline class. It acts through the disruption ( depolymerization) of microtubules, thus blocking anisotropic growth of plant cells. It can also be used to induce polyploidy in plants as an alternative to co ...
will also double the existing chromosome content.
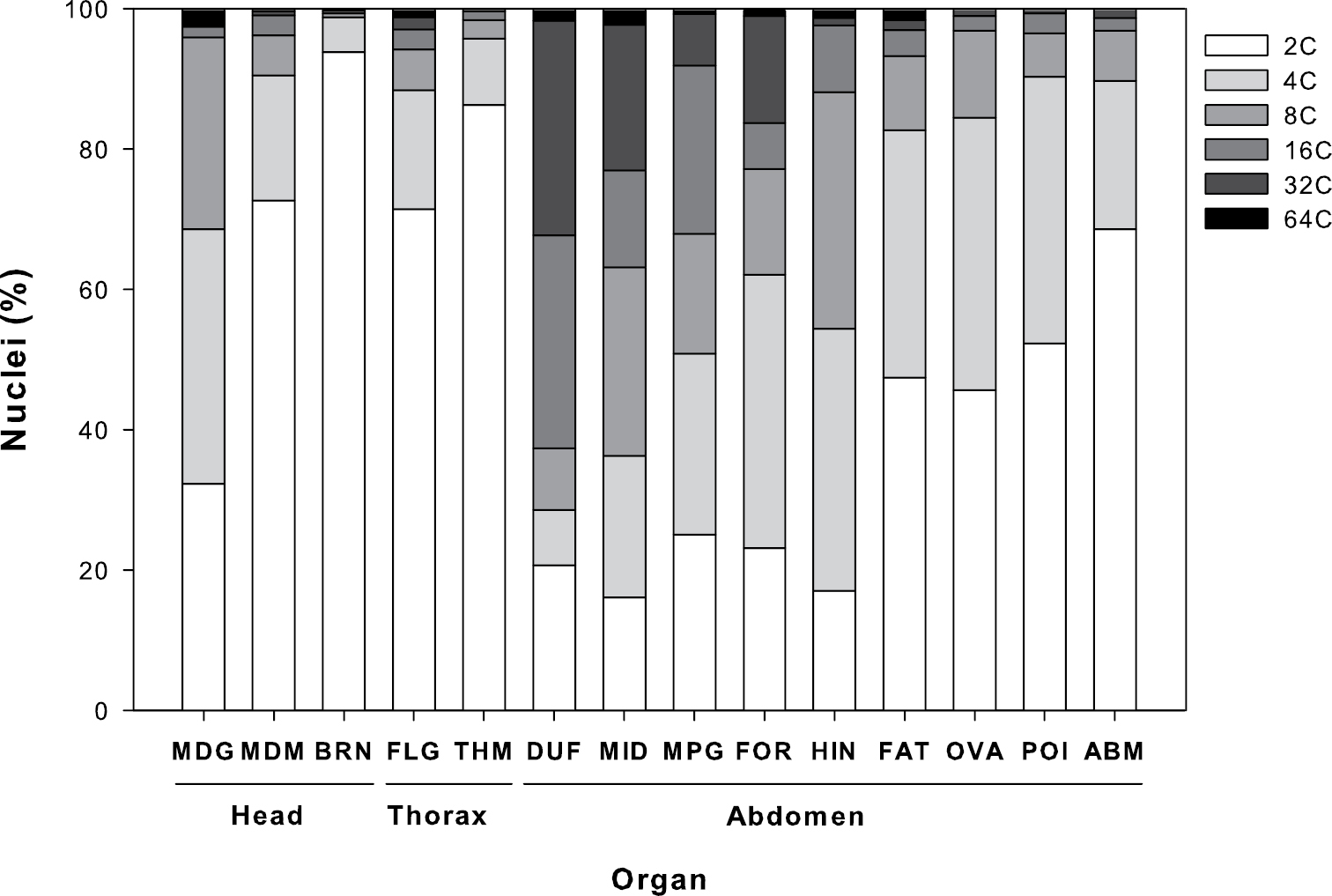
Polyploidy occurs in highly differentiated human tissues in the liver, heart muscle, bone marrow and the placenta.
It occurs in the somatic cells of some animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
s, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see '' Hibiscus rosa-sinensis''), including both wild and cultivated species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of ...
. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization
Hybridization (or hybridisation) may refer to:
*Hybridization (biology), the process of combining different varieties of organisms to create a hybrid
*Orbital hybridization, in chemistry, the mixing of atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals
*Nu ...
and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus ''Brassica
''Brassica'' () is a genus of plants in the cabbage and mustard family (Brassicaceae). The members of the genus are informally known as cruciferous vegetables, cabbages, or mustard plants. Crops from this genus are sometimes called ''cole cro ...
'' are also tetraploids. Sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalks ...
can have ploidy levels higher than octaploid.
Polyploidization can be a mechanism of sympatric speciation because polyploids are usually unable to interbreed with their diploid ancestors. An example is the plant ''Erythranthe peregrina
''Erythranthe peregrina'' is a species of monkeyflower. Its Latin name means "foreign", or more loosely "the foreigner". This species is a rare example of polyploidization and speciation where sterility did not occur. It was discovered in 2011, ...
''. Sequencing confirmed that this species originated from ''E. × robertsii'', a sterile triploid hybrid between ''E. guttata'' and ''E. lutea,'' both of which have been introduced and naturalised in the United Kingdom. New populations of ''E. peregrina'' arose on the Scottish mainland and the Orkney Islands
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
via genome duplication from local populations of ''E. × robertsii''. Because of a rare genetic mutation, ''E. peregrina'' is not sterile.
Terminology
Types
 Polyploid types are labeled according to the number of chromosome sets in the nucleus. The letter ''x'' is used to represent the number of chromosomes in a single set:
*haploid (one set; 1x)
*diploid (two sets; 2x)
*triploid (three sets; 3''x''), for example sterile saffron crocus, or seedless watermelons, also common in the phylum
Polyploid types are labeled according to the number of chromosome sets in the nucleus. The letter ''x'' is used to represent the number of chromosomes in a single set:
*haploid (one set; 1x)
*diploid (two sets; 2x)
*triploid (three sets; 3''x''), for example sterile saffron crocus, or seedless watermelons, also common in the phylum Tardigrada
Tardigrades (), known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them Kleiner Wasserbär ...
*tetraploid (four sets; 4''x''), for example, Plains viscacha rat
The plains viscacha rat, plains vizcacha rat, red viscacha rat, or red vizcacha rat (''Tympanoctomys barrerae'') is a species of rodent in the family Octodontidae native to Argentina. It is one of three species in the genus ''Tympanoctomys''.
Des ...
, Salmonidae
Salmonidae is a family of ray-finned fish that constitutes the only currently extant family in the order Salmoniformes . It includes salmon (both Atlantic and Pacific species), trout (both ocean-going and landlocked), chars, freshwater whitefis ...
fish, the cotton '' Gossypium hirsutum''
*pentaploid (five sets; 5''x''), for example Kenai Birch (''Betula kenaica
''Betula kenaica'', or Kenai birch, is a species of birch that can be found in Alaska and northwestern North America at above sea level.
Description
It grows up to tall, with reddish-brown bark that may become pink or grayish-white. The leaf b ...
'')
*hexaploid (six sets; 6''x''), for example some species of wheat, kiwifruit
Kiwifruit (often shortened to kiwi in North American, British and continental European English) or Chinese gooseberry is the edible berry of several species of woody vines in the genus ''Actinidia''. The most common cultivar group of kiwifru ...
*heptaploid or septaploid (seven sets; 7''x'')
*octaploid or octoploid, (eight sets; 8''x''), for example ''Acipenser
''Acipenser'' is a genus of sturgeons. With 17 living species (others are only known from fossil remains), it is the largest genus in the order Acipenseriformes. The genus is paraphyletic, containing all sturgeons that do not belong to ''Huso'', ...
'' (genus of sturgeon fish), dahlias
*decaploid (ten sets; 10''x''), for example certain strawberries
*dodecaploid or duodecaploid (twelve sets; 12''x''), for example the plants ''Celosia argentea
''Celosia argentea'', commonly known as the plumed cockscomb or silver cock's comb, is a herbaceous plant of tropical origin in the Amaranthaceae family from India and Nepal. The plant is known for its very bright colors. In India and China it is ...
'' and '' Spartina anglica'' or the amphibian '' Xenopus ruwenzoriensis''.
Classification
Autopolyploidy
Autopolyploids are polyploids with multiple chromosome sets derived from a single taxon. Two examples of natural autopolyploids are the piggyback plant, '' Tolmiea menzisii'' and the white sturgeon, '' Acipenser transmontanum''. Most instances of autopolyploidy result from the fusion of unreduced (2''n'') gametes, which results in either triploid (''n'' + 2''n'' = 3''n'') or tetraploid (2''n'' + 2''n'' = 4''n'') offspring. Triploid offspring are typically sterile (as in the phenomenon of triploid block), but in some cases they may produce high proportions of unreduced gametes and thus aid the formation of tetraploids. This pathway to tetraploidy is referred to as the ''triploid bridge''. Triploids may also persist throughasexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the f ...
. In fact, stable autotriploidy in plants is often associated with apomictic
In botany, apomixis is asexual reproduction without fertilization. Its etymology is Greek for "away from" + "mixing". This definition notably does not mention meiosis. Thus "normal asexual reproduction" of plants, such as propagation from cutt ...
mating systems. In agricultural systems, autotriploidy can result in seedlessness, as in watermelons and banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguis ...
s. Triploidy is also utilized in salmon and trout farming to induce sterility.
Rarely, autopolyploids arise from spontaneous, somatic genome doubling, which has been observed in apple (''Malus domesticus'') bud sports. This is also the most common pathway of artificially induced polyploidy, where methods such as protoplast fusion
Somatic fusion, also called protoplast fusion, is a type of genetic modification in plants by which two distinct species of plants are fused together to form a new hybrid plant with the characteristics of both, a somatic hybrid. Hybrids have be ...
or treatment with colchicine, oryzalin
Oryzalin is an herbicide of the dinitroaniline class. It acts through the disruption ( depolymerization) of microtubules, thus blocking anisotropic growth of plant cells. It can also be used to induce polyploidy in plants as an alternative to co ...
or mitotic inhibitor
A mitotic inhibitor is a drug that inhibits mitosis, or cell division. These drugs disrupt microtubules, which are structures that pull the chromosomes apart when a cell divides. Mitotic inhibitors are used in cancer treatment, because cancer cell ...
s are used to disrupt normal mitotic division, which results in the production of polyploid cells. This process can be useful in plant breeding, especially when attempting to introgress germplasm across ploidal levels.
Autopolyploids possess at least three homologous chromosome sets, which can lead to high rates of multivalent pairing during meiosis (particularly in recently formed autopolyploids, also known as neopolyploids) and an associated decrease in fertility due to the production of aneuploid
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any ...
gametes. Natural or artificial selection for fertility can quickly stabilize meiosis in autopolyploids by restoring bivalent pairing during meiosis, but the high degree of homology among duplicated chromosomes causes autopolyploids to display polysomic inheritance
Polysomy is a condition found in many species, including fungi, plants, insects, and mammals, in which an organism has at least one more chromosome than normal, i.e., there may be three or more copies of the chromosome rather than the expected t ...
. This trait is often used as a diagnostic criterion to distinguish autopolyploids from allopolyploids, which commonly display disomic inheritance after they progress past the neopolyploid stage. While most polyploid species are unambiguously characterized as either autopolyploid or allopolyploid, these categories represent the ends of a spectrum of divergence between parental subgenomes. Polyploids that fall between these two extremes, which are often referred to as segmental allopolyploids, may display intermediate levels of polysomic inheritance that vary by locus.
About half of all polyploids are thought to be the result of autopolyploidy, although many factors make this proportion hard to estimate.
Allopolyploidy
Allopolyploids or amphipolyploids or heteropolyploids are polyploids with chromosomes derived from two or more diverged taxa. As in autopolyploidy, this primarily occurs through the fusion of unreduced (2''n'') gametes, which can take place before or afterhybridization
Hybridization (or hybridisation) may refer to:
*Hybridization (biology), the process of combining different varieties of organisms to create a hybrid
*Orbital hybridization, in chemistry, the mixing of atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals
*Nu ...
. In the former case, unreduced gametes from each diploid taxon – or reduced gametes from two autotetraploid taxa – combine to form allopolyploid offspring. In the latter case, one or more diploid F1 hybrids produce unreduced gametes that fuse to form allopolyploid progeny. Hybridization followed by genome duplication may be a more common path to allopolyploidy because F1 hybrids between taxa often have relatively high rates of unreduced gamete formation – divergence between the genomes of the two taxa result in abnormal pairing between homoeologous chromosomes or nondisjunction during meiosis. In this case, allopolyploidy can actually restore normal, bivalent Bivalent may refer to:
* Bivalent (chemistry), a molecule formed from two or more atoms bound together
*Bivalent (engine), an engine that can operate on two different types of fuel
*Bivalent (genetics), a pair of homologous chromosomes
*Bivalent log ...
meiotic pairing by providing each homoeologous chromosome with its own homologue. If divergence between homoeologous chromosomes is even across the two subgenomes, this can theoretically result in rapid restoration of bivalent pairing and disomic inheritance following allopolyploidization. However multivalent pairing is common in many recently formed allopolyploids, so it is likely that the majority of meiotic stabilization occurs gradually through selection.
Because pairing between homoeologous chromosomes is rare in established allopolyploids, they may benefit from fixed heterozygosity of homoeologous alleles. In certain cases, such heterozygosity can have beneficial heterotic effects, either in terms of fitness in natural contexts or desirable traits in agricultural contexts. This could partially explain the prevalence of allopolyploidy among crop species. Both bread wheat and '' Triticale'' are examples of an allopolyploids with six chromosome sets. Cotton, peanut, or quinoa are allotetraploids with multiple origins. In Brassicaceous crops, the Triangle of U describes the relationships between the three common diploid Brassicas ('' B. oleracea, B. rapa,'' and '' B. nigra'') and three allotetraploids ('' B. napus, B. juncea,'' and '' B. carinata'') derived from hybridization among the diploid species. A similar relationship exists between three diploid species of ''Tragopogon
''Tragopogon'', also known as goatsbeard or salsify, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. It includes the vegetable known as salsify, as well as a number of common wild flowers.
Salsifies are forbs growing as biennial or per ...
'' ('' T. dubius, T. pratensis,'' and '' T. porrifolius'') and two allotetraploid species ('' T. mirus'' and '' T. miscellus''). Complex patterns of allopolyploid evolution have also been observed in animals, as in the frog genus ''Xenopus
''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos''=strange, πους, ''pous''=foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known ...
.''
Aneuploid
Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or over-represented are said to beaneuploid
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any ...
(from the Greek words meaning "not", "good", and "fold"). Aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.
Endopolyploidy
Polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, prokaryotes, may be polyploid, as seen in the largebacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
'' Epulopiscium fishelsoni''. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell.
Monoploid
A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. The more general term for such organisms is haploid.Temporal terms
Neopolyploidy
A polyploid that is newly formed.Mesopolyploidy
That has become polyploid in more recent history; it is not as new as a neopolyploid and not as old as a paleopolyploid. It is a middle aged polyploid. Often this refers to whole genome duplication followed by intermediate levels of diploidization.Paleopolyploidy
 Ancient genome duplications probably occurred in the evolutionary history of all life. Duplication events that occurred long ago in the history of various evolutionary lineages can be difficult to detect because of subsequent diploidization (such that a polyploid starts to behave cytogenetically as a diploid over time) as mutations and gene translations gradually make one copy of each chromosome unlike the other copy. Over time, it is also common for duplicated copies of genes to accumulate mutations and become inactive pseudogenes.
In many cases, these events can be inferred only through comparing sequenced genomes. Examples of unexpected but recently confirmed ancient genome duplications include
Ancient genome duplications probably occurred in the evolutionary history of all life. Duplication events that occurred long ago in the history of various evolutionary lineages can be difficult to detect because of subsequent diploidization (such that a polyploid starts to behave cytogenetically as a diploid over time) as mutations and gene translations gradually make one copy of each chromosome unlike the other copy. Over time, it is also common for duplicated copies of genes to accumulate mutations and become inactive pseudogenes.
In many cases, these events can be inferred only through comparing sequenced genomes. Examples of unexpected but recently confirmed ancient genome duplications include baker's yeast
Baker's yeast is the common name for the strains of yeast commonly used in baking bread and other bakery products, serving as a leavening agent which causes the bread to rise (expand and become lighter and softer) by converting the fermentable s ...
(''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been ...
''), mustard weed/thale cress (''Arabidopsis thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small flowering plant native to Eurasia and Africa. ''A. thaliana'' is considered a weed; it is found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land.
A winter a ...
''), rice (''Oryza sativa
''Oryza sativa'', commonly known as Asian rice or indica rice, is the plant species most commonly referred to in English as ''rice''. It is the type of farmed rice whose cultivars are most common globally, and was first domesticated in the Yan ...
''), and an early evolutionary ancestor
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or (recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from whom ...
of the vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
(which includes the human lineage) and another near the origin of the teleost fishes. Angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s ( flowering plants) have paleopolyploidy in their ancestry. All eukaryotes probably have experienced a polyploidy event at some point in their evolutionary history.
Other similar terms
Karyotype
A karyotype is the characteristic chromosome complement of a eukaryotespecies
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of ...
. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and ...
and, more specifically, cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis an ...
.
Although the replication and transcription of DNA is highly standardized in eukaryotes, the same cannot be said for their karyotypes, which are highly variable between species in chromosome number and in detailed organization despite being constructed out of the same macromolecules. In some cases, there is even significant variation within species. This variation provides the basis for a range of studies in what might be called evolutionary cytology.
Homoeologous chromosomes
Homoeologous chromosomes are those brought together following inter-species hybridization and allopolyploidization, and whose relationship was completely homologous in an ancestral species. For example, durum wheat is the result of the inter-species hybridization of two diploid grass species ''Triticum urartu'' and ''Aegilops speltoides''. Both diploid ancestors had two sets of 7 chromosomes, which were similar in terms of size and genes contained on them. Durum wheat contains a hybrid genome with two sets of chromosomes derived from ''Triticum urartu'' and two sets of chromosomes derived from ''Aegilops speltoides''. Each chromosome pair derived from the ''Triticum urartu'' parent is homoeologous to the opposite chromosome pair derived from the ''Aegilops speltoides'' parent, though each chromosome pair unto itself is homologous.Examples
Animals
Examples in animals are more common in non-vertebrates such asflatworm
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegment ...
s, leech
Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodie ...
es, and brine shrimp
''Artemia'' is a genus of aquatic crustaceans also known as brine shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Artemiidae. The first historical record of the existence of ''Artemia'' dates back to the first half of the 10th century AD from Urmia L ...
. Within vertebrates, examples of stable polyploidy include the salmonids
Salmonidae is a family of ray-finned fish that constitutes the only currently extant family in the order Salmoniformes . It includes salmon (both Atlantic and Pacific species), trout (both ocean-going and landlocked), chars, freshwater whitefi ...
and many cyprinids
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family. It includes the carps, the true minnows, and relatives like the barbs and barbels. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family and the largest vert ...
(i.e. carp). Some fish have as many as 400 chromosomes. Polyploidy also occurs commonly in amphibians; for example the biomedically important genus ''Xenopus
''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos''=strange, πους, ''pous''=foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known ...
'' contains many different species with as many as 12 sets of chromosomes (dodecaploid). Polyploid lizards are also quite common. Most are sterile and reproduce by parthenogenesis; others, like '' Liolaemus chiliensis'', maintain sexual reproduction. Polyploid mole salamanders
The mole salamanders (genus ''Ambystoma'') are a group of advanced salamanders endemic to North America. The group has become famous due to the presence of the axolotl (''A. mexicanum''), widely used in research due to its paedomorphosis, and t ...
(mostly triploids) are all female and reproduce by kleptogenesis, "stealing" spermatophores from diploid males of related species to trigger egg development but not incorporating the males' DNA into the offspring.
While mammalian liver cells are polyploid, rare instances of polyploid mammals are known, but most often result in prenatal death. An octodontid rodent of Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
's harsh desert regions, known as the plains viscacha rat
The plains viscacha rat, plains vizcacha rat, red viscacha rat, or red vizcacha rat (''Tympanoctomys barrerae'') is a species of rodent in the family Octodontidae native to Argentina. It is one of three species in the genus ''Tympanoctomys''.
Des ...
(''Tympanoctomys barrerae'') has been reported as an exception to this 'rule'. However, careful analysis using chromosome paints shows that there are only two copies of each chromosome in ''T. barrerae'', not the four expected if it were truly a tetraploid. This rodent is not a rat, but kin to guinea pigs and chinchilla
Chinchillas are either of two species (''Chinchilla chinchilla'' and ''Chinchilla lanigera'') of crepuscular rodents of the parvorder Caviomorpha. They are slightly larger and more robust than ground squirrels, and are native to the Andes mounta ...
s. Its "new" diploid (2''n'') number is 102 and so its cells are roughly twice normal size. Its closest living relation is '' Octomys mimax'', the Andean
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
Viscacha-Rat of the same family, whose 2''n'' = 56. It was therefore surmised that an ''Octomys''-like ancestor produced tetraploid (i.e., 2''n'' = 4''x'' = 112) offspring that were, by virtue of their doubled chromosomes, reproductively isolated from their parents.
Polyploidy was induced in fish by Har Swarup (1956) using a cold-shock treatment of the eggs close to the time of fertilization, which produced triploid embryos that successfully matured. Cold or heat shock has also been shown to result in unreduced amphibian gametes, though this occurs more commonly in eggs than in sperm. John Gurdon
Sir John Bertrand Gurdon (born 2 October 1933) is a British developmental biologist. He is best known for his pioneering research in nuclear transplantation and cloning. He was awarded the Lasker Award in 2009. In 2012, he and Shinya Yamanaka ...
(1958) transplanted intact nuclei from somatic cells to produce diploid eggs in the frog, ''Xenopus
''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos''=strange, πους, ''pous''=foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known ...
'' (an extension of the work of Briggs and King in 1952) that were able to develop to the tadpole stage. The British scientist J. B. S. Haldane hailed the work for its potential medical applications and, in describing the results, became one of the first to use the word " clone" in reference to animals. Later work by Shinya Yamanaka showed how mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent, extending the possibilities to non-stem cells. Gurdon and Yamanaka were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in 2012 for this work.
Humans
True polyploidy rarely occurs in humans, although polyploid cells occur in highly differentiated tissue, such as liverparenchyma
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. In zoology it is the name for the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms.
Etymology
The term ''parenchyma'' is New Latin from the word � ...
, heart muscle, placenta and in bone marrow. Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any ...
is more common.
Polyploidy occurs in humans in the form of triploidy, with 69 chromosomes (sometimes called 69, XXX), and tetraploidy with 92 chromosomes (sometimes called 92, XXXX). Triploidy, usually due to polyspermy, occurs in about 2–3% of all human pregnancies and ~15% of miscarriages. The vast majority of triploid conceptions end as a miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical lo ...
; those that do survive to term typically die shortly after birth. In some cases, survival past birth may be extended if there is mixoploidy with both a diploid and a triploid cell population present. There has been one report of a child surviving to the age of seven months with complete triploidy syndrome. He failed to exhibit normal mental or physical neonatal development, and died from a ''Pneumocystis carinii
''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' (previously ''P. carinii'') is a yeast-like fungus of the genus ''Pneumocystis''. The causative organism of ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia, it is an important human pathogen, particularly among immunocompromised hosts. Pr ...
'' infection, which indicates a weak immune system.
Triploidy may be the result of either digyny (the extra haploid set is from the mother) or diandry (the extra haploid set is from the father). Diandry is mostly caused by reduplication of the paternal haploid set from a single sperm, but may also be the consequence of dispermic (two sperm) fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Proce ...
of the egg. Digyny is most commonly caused by either failure of one meiotic division during oogenesis leading to a diploid oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female g ...
or failure to extrude one polar body
A polar body is a small haploid cell that is formed at the same time as an egg cell during oogenesis, but generally does not have the ability to be fertilized. It is named from its polar position in the egg.
When certain diploid cells in animals ...
from the oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female g ...
. Diandry appears to predominate among early miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical lo ...
s, while digyny predominates among triploid zygotes that survive into the fetal period. However, among early miscarriages, digyny is also more common in those cases less than weeks gestational age or those in which an embryo is present. There are also two distinct phenotypes in triploid placentas and fetuses that are dependent on the origin of the extra haploid set. In digyny, there is typically an asymmetric poorly grown fetus, with marked adrenal hypoplasia and a very small placenta. In diandry, a partial hydatidiform mole
A molar pregnancy also known as a hydatidiform mole, is an abnormal form of pregnancy in which a non-viable fertilized egg implants in the uterus. A molar pregnancy is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease that used to be known as a ''hyda ...
develops. These parent-of-origin effects reflect the effects of genomic imprinting.
Complete tetraploidy is more rarely diagnosed than triploidy, but is observed in 1–2% of early miscarriages. However, some tetraploid cells are commonly found in chromosome analysis at prenatal diagnosis and these are generally considered 'harmless'. It is not clear whether these tetraploid cells simply tend to arise during ''in vitro'' cell culture or whether they are also present in placental cells ''in vivo''. There are, at any rate, very few clinical reports of fetuses/infants diagnosed with tetraploidy mosaicism.
Mixoploidy is quite commonly observed in human preimplantation embryos and includes haploid/diploid as well as diploid/tetraploid mixed cell populations. It is unknown whether these embryos fail to implant and are therefore rarely detected in ongoing pregnancies or if there is simply a selective process favoring the diploid cells.
Fish
A polyploidy event occurred within the stem lineage of the teleost fish.Plants
angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
species diversity appear to have coincided with the timing of ancient genome duplications shared by many species. It has been established that 15% of angiosperm and 31% of fern speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species. The biologist Orator F. Cook coined the term in 1906 for cladogenesis, the splitting of lineages, as opposed to anagenesis, phyletic evolution within ...
events are accompanied by ploidy increase.
Polyploid plants can arise spontaneously in nature by several mechanisms, including meiotic or mitotic failures, and fusion of unreduced (2''n'') gametes. Both autopolyploids (e.g. potato) and allopolyploids (such as canola, wheat and cotton) can be found among both wild and domesticated plant species.
Most polyploids display novel variation or morphologies relative to their parental species, that may contribute to the processes of speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species. The biologist Orator F. Cook coined the term in 1906 for cladogenesis, the splitting of lineages, as opposed to anagenesis, phyletic evolution within ...
and eco-niche exploitation. The mechanisms leading to novel variation in newly formed allopolyploids may include gene dosage effects (resulting from more numerous copies of genome content), the reunion of divergent gene regulatory hierarchies, chromosomal rearrangements, and epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "o ...
remodeling, all of which affect gene content and/or expression levels. Many of these rapid changes may contribute to reproductive isolation and speciation. However seed generated from interploidy crosses, such as between polyploids and their parent species, usually have aberrant endosperm development which impairs their viability, thus contributing to polyploid speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species. The biologist Orator F. Cook coined the term in 1906 for cladogenesis, the splitting of lineages, as opposed to anagenesis, phyletic evolution within ...
.
Some plants are triploid. As meiosis is disturbed, these plants are sterile, with all plants having the same genetic constitution: Among them, the exclusively vegetatively propagated saffron crocus (''Crocus sativus''). Also, the extremely rare Tasmanian shrub '' Lomatia tasmanica'' is a triploid sterile species.
There are few naturally occurring polyploid conifers
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All exta ...
. One example is the Coast Redwood '' Sequoia sempervirens'', which is a hexaploid (6''x'') with 66 chromosomes (2''n'' = 6''x'' = 66), although the origin is unclear.
Aquatic plants, especially the Monocotyledon
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, ( Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of ...
s, include a large number of polyploids.
Crops
The induction of polyploidy is a common technique to overcome the sterility of a hybrid species during plant breeding. For example, triticale is the hybrid of wheat (''Triticum turgidum'') andrye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is a member of the wheat tribe (Triticeae) and is closely related to both wheat (''Triticum'') and barley (genus ''Hordeum''). Rye grain is u ...
(''Secale cereale''). It combines sought-after characteristics of the parents, but the initial hybrids are sterile. After polyploidization, the hybrid becomes fertile and can thus be further propagated to become triticale.
In some situations, polyploid crops are preferred because they are sterile. For example, many seedless fruit varieties are seedless as a result of polyploidy. Such crops are propagated using asexual techniques, such as grafting.
Polyploidy in crop plants is most commonly induced by treating seeds with the chemical colchicine.
= Examples
= * Triploid crops: some apple varieties (such asBelle de Boskoop
Belle de Boskoop (also called Goudrenet, Goudreinet or Goudreinnette) is an apple cultivar which originated in Boskoop, Netherlands, where it began as a chance seedling in 1856. Variants include Boskoop red, yellow and green. This rustic apple is ...
, Jonagold
Jonagold is a cultivar of apple which was developed in 1953 in New York State Agricultural Experiment Station of Cornell University's College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, a cross between the crisp Golden Delicious and the blush-crimson ...
, Mutsu, Ribston Pippin
'Ribston Pippin' is a triploid cultivar of apples, also known by other names including 'Essex Pippin', 'Beautiful Pippin', 'Formosa', 'Glory of York', 'Ribstone', 'Rockhill's Russet', 'Travers', and 'Travers's Reinette'.
Origin
This apple was gro ...
), banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguis ...
, citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is nativ ...
, ginger, watermelon, saffron crocus, white pulp of coconut
* Tetraploid crops: very few apple varieties, durum or macaroni
Macaroni (, Italian: maccheroni) is dry pasta shaped like narrow tubes.Oxford DictionaryMacaroni/ref> Made with durum wheat, macaroni is commonly cut in short lengths; curved macaroni may be referred to as elbow macaroni. Some home machine ...
wheat, cotton, potato, canola
Close-up of canola blooms
Canola flower
Rapeseed oil is one of the oldest known vegetable oils. There are both edible and industrial forms produced from rapeseed, the seed of several cultivars of the plant family Brassicaceae. Historicall ...
/rapeseed
Rapeseed (''Brassica napus ''subsp.'' napus''), also known as rape, or oilseed rape, is a bright-yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae (mustard or cabbage family), cultivated mainly for its oil-rich seed, which naturally contains ...
, leek
The leek is a vegetable, a cultivar of '' Allium ampeloprasum'', the broadleaf wild leek ( syn. ''Allium porrum''). The edible part of the plant is a bundle of leaf sheaths that is sometimes erroneously called a stem or stalk. The genus ''Alli ...
, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus ''Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the chie ...
, peanut, kinnow
The Kinnow is a high yield mandarin hybrid cultivated extensively in the wider Punjab region of India and Pakistan.
It is a hybrid of two citrus cultivars — 'King' ('' Citrus nobilis'') × 'Willow Leaf' ('' Citrus × deliciosa'') — first de ...
, Pelargonium
* Hexaploid crops: chrysanthemum
Chrysanthemums (), sometimes called mums or chrysanths, are flowering plants of the genus ''Chrysanthemum'' in the family Asteraceae. They are native to East Asia and northeastern Europe. Most species originate from East Asia and the center o ...
, bread wheat, triticale, oat
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural, unlike other cereals and pseudocereals). While oats are suitable for human con ...
, kiwifruit
Kiwifruit (often shortened to kiwi in North American, British and continental European English) or Chinese gooseberry is the edible berry of several species of woody vines in the genus ''Actinidia''. The most common cultivar group of kiwifru ...
* Octaploid crops: strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus ''Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely ap ...
, dahlia, pansies
The garden pansy (''Viola'' × ''wittrockiana'') is a type of large-flowered hybrid plant cultivated as a garden flower. It is derived by hybridization from several species in the section ''Melanium'' ("the pansies") of the genus ''Viola'', p ...
, sugar cane, oca ('' Oxalis tuberosa'')
* Dodecaploid crops: some sugar cane hybrids
Some crops are found in a variety of ploidies: tulips and lilies
''Lilium'' () is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants growing from bulbs, all with large prominent flowers. They are the true lilies. Lilies are a group of flowering plants which are important in culture and literature in much of the world. M ...
are commonly found as both diploid and triploid; daylilies
A daylily or day lily is a flowering plant in the genus ''Hemerocallis'' , a member of the family Asphodelaceae, subfamily Hemerocallidoideae. Despite the common name, it is not in fact a lily. Gardening enthusiasts and horticulturists have long ...
(''Hemerocallis'' cultivars) are available as either diploid or tetraploid; apples and kinnow mandarins can be diploid, triploid, or tetraploid.
Fungi
Besides plants and animals, the evolutionary history of various fungal species is dotted by past and recent whole-genome duplication events (see Albertin and Marullo 2012 for review). Several examples of polyploids are known: *autopolyploid: the aquatic fungi of genus ''Allomyces'', some ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been ...
'' strains used in baker
A baker is a tradesperson who bakes and sometimes sells breads and other products made of flour by using an oven or other concentrated heat source. The place where a baker works is called a bakery.
History
Ancient history
Since grains ha ...
y, etc.
*allopolyploid: the widespread '' Cyathus stercoreus'', the allotetraploid lager yeast '' Saccharomyces pastorianus'', the allotriploid wine spoilage yeast '' Dekkera bruxellensis'', etc.
*paleopolyploid: the human pathogen '' Rhizopus oryzae'', the genus '' Saccharomyces'', etc.
In addition, polyploidy is frequently associated with hybridization
Hybridization (or hybridisation) may refer to:
*Hybridization (biology), the process of combining different varieties of organisms to create a hybrid
*Orbital hybridization, in chemistry, the mixing of atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals
*Nu ...
and reticulate evolution that appear to be highly prevalent in several fungal taxa. Indeed, homoploid speciation (hybrid speciation without a change in chromosome number) has been evidenced for some fungal species (such as the basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basi ...
'' Microbotryum violaceum'').
 As for plants and animals, fungal hybrids and polyploids display structural and functional modifications compared to their progenitors and diploid counterparts. In particular, the structural and functional outcomes of polyploid ''Saccharomyces'' genomes strikingly reflect the evolutionary fate of plant polyploid ones. Large chromosomal rearrangements leading to chimeric chromosomes have been described, as well as more punctual genetic modifications such as gene loss. The homoealleles of the allotetraploid yeast ''S. pastorianus'' show unequal contribution to the transcriptome. Phenotypic diversification is also observed following polyploidization and/or hybridization in fungi, producing the fuel for natural selection and subsequent
As for plants and animals, fungal hybrids and polyploids display structural and functional modifications compared to their progenitors and diploid counterparts. In particular, the structural and functional outcomes of polyploid ''Saccharomyces'' genomes strikingly reflect the evolutionary fate of plant polyploid ones. Large chromosomal rearrangements leading to chimeric chromosomes have been described, as well as more punctual genetic modifications such as gene loss. The homoealleles of the allotetraploid yeast ''S. pastorianus'' show unequal contribution to the transcriptome. Phenotypic diversification is also observed following polyploidization and/or hybridization in fungi, producing the fuel for natural selection and subsequent adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the po ...
and speciation.
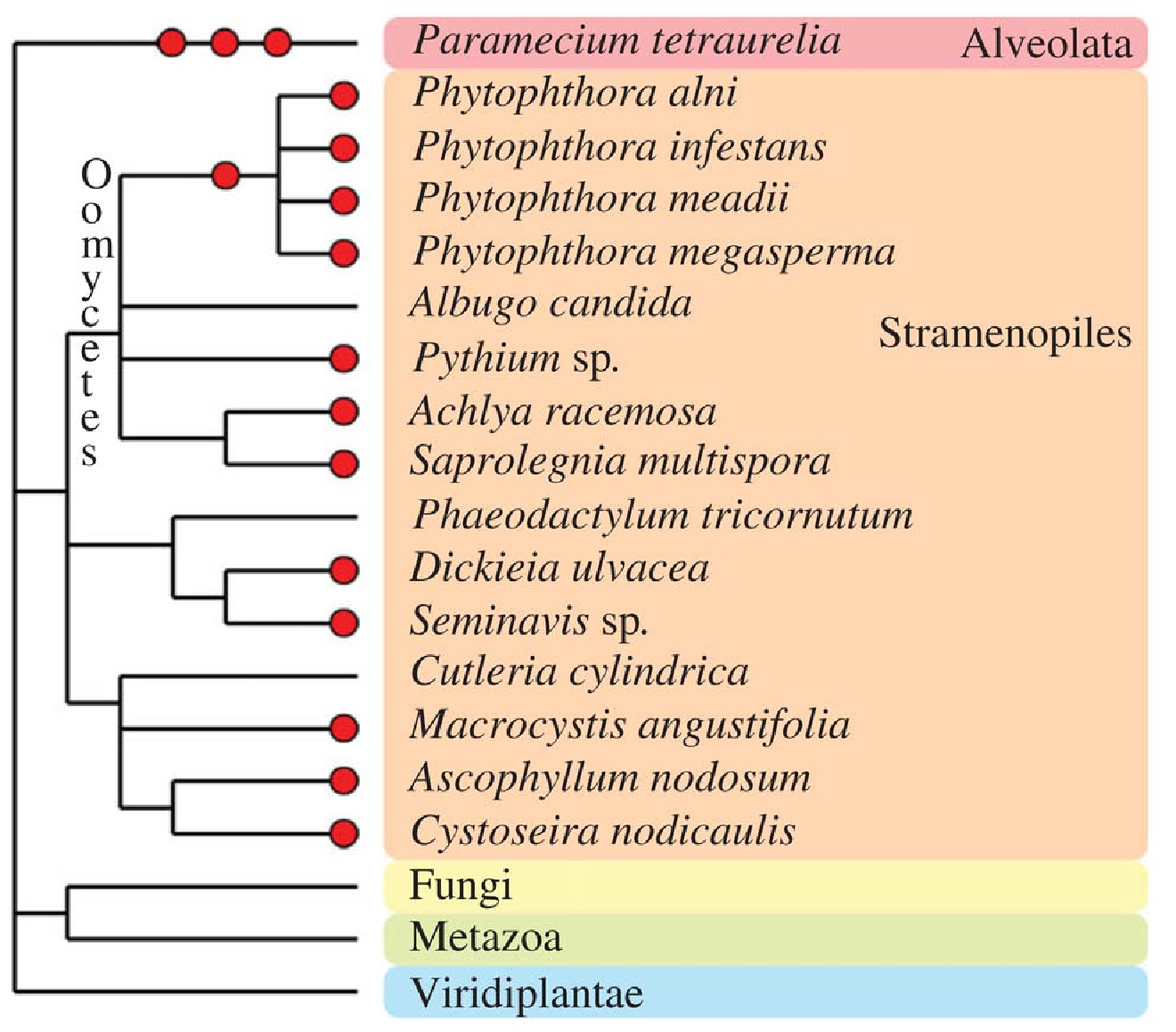
Chromalveolata
Other eukaryotictaxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
have experienced one or more polyploidization events during their evolutionary history (see Albertin and Marullo, 2012 for review). The oomycetes
Oomycota forms a distinct phylogenetic lineage of fungus-like eukaryotic microorganisms, called oomycetes (). They are filamentous and heterotrophic, and can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction of an oospore is the resul ...
, which are non-true fungi members, contain several examples of paleopolyploid and polyploid species, such as within the genus ''Phytophthora
''Phytophthora'' (from Greek (''phytón''), "plant" and (), "destruction"; "the plant-destroyer") is a genus of plant-damaging oomycetes (water molds), whose member species are capable of causing enormous economic losses on crops worldwide, a ...
''. Some species of brown algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from u ...
(Fucales
The Fucales (fucoids) are an order in the brown algae (class Phaeophyceae). The list of families in the Fucales, as well as additional taxonomic information on algae, is publicly accessible at Algaebaseref name="Guiry and Guiry">Guiry, M.D. and ...
, Laminariales and diatoms) contain apparent polyploid genomes. In the Alveolata group, the remarkable species '' Paramecium tetraurelia'' underwent three successive rounds of whole-genome duplication and established itself as a major model for paleopolyploid studies.
Bacteria
Each ''Deinococcus radiodurans
''Deinococcus radiodurans'' is an extremophilic bacterium and one of the most radiation-resistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and therefore is known as a polyextremophile. It has been listed as the world ...
'' bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
contains 4-8 copies of its chromosome. Exposure of ''D. radiodurans'' to X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 ...
irradiation or desiccation
Desiccation () is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container.
...
can shatter its genomes into hundred of short random fragments. Nevertheless, ''D. radiodurans'' is highly resistant to such exposures. The mechanism by which the genome is accurately restored involves RecA-mediated homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in cellular organisms but may be ...
and a process referred to as extended synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA).
'' Azotobacter vinelandii'' can contain up to 80 chromosome copies per cell. However this is only observed in fast growing cultures, whereas cultures grown in synthetic minimal media are not polyploid.
Archaea
Thearchaeon
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaeba ...
'' Halobacterium salinarium'' is polyploid and, like ''Deinococcus radiodurans
''Deinococcus radiodurans'' is an extremophilic bacterium and one of the most radiation-resistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and therefore is known as a polyextremophile. It has been listed as the world ...
'', is highly resistant to X-ray irradiation and desiccation, conditions that induce DNA double-strand breaks. Although chromosomes are shattered into many fragments, complete chromosomes can be regenerated by making use of overlapping fragments. The mechanism employs single-stranded DNA binding protein
DNA-binding proteins are proteins that have DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for single- or double-stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, beca ...
and is likely homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in cellular organisms but may be ...
al repair.
See also
* Diploidization *Eukaryote hybrid genome
Eukaryote hybrid genomes result from interspecific hybridization, where closely related species mate and produce offspring with admixed genomes. The advent of large-scale genomic sequencing has shown that hybridization is common, and that it ma ...
* Ploidy
* Polyploid complex
* Polysomy
* Reciprocal silencing
* Sympatry
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Polyploidy on Kimball's Biology Pages
The polyploidy portal
a community-editable project with information, research, education, and a bibliography about polyploidy. {{Authority control Classical genetics Speciation he:פלואידיות#פוליפלואידיות fi:Ploidia#Polyploidia sv:Ploiditet#Polyploiditet