Political terminology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with
 The history of politics spans
The history of politics spans
 The
The
 The study of politics is called political science, It comprises numerous subfields, namely three:
The study of politics is called political science, It comprises numerous subfields, namely three:

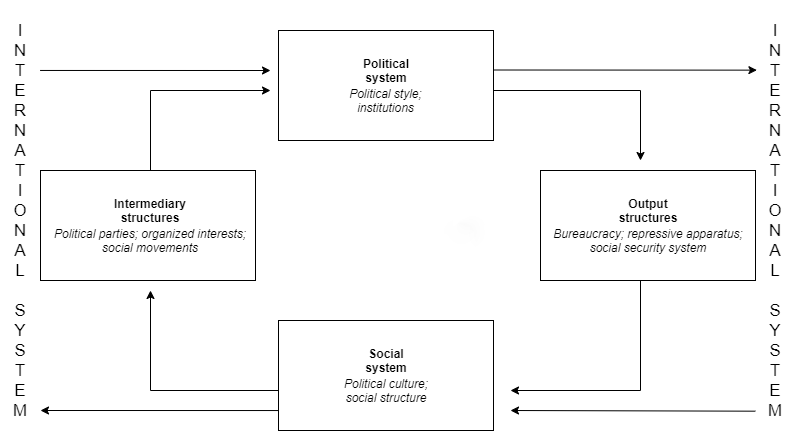 The political system defines the process for making official
The political system defines the process for making official
 Forms of government can be classified by several ways. In terms of the structure of power, there are
Forms of government can be classified by several ways. In terms of the structure of power, there are

 All the above forms of government are variations of the same basic
All the above forms of government are variations of the same basic
 Macropolitics can either describe political issues that affect an entire political system (e.g. the
Macropolitics can either describe political issues that affect an entire political system (e.g. the
 Mesopolitics describes the politics of intermediary structures within a political system, such as national political parties or
Mesopolitics describes the politics of intermediary structures within a political system, such as national political parties or
 Equality is a state of affairs in which all people within a specific
Equality is a state of affairs in which all people within a specific
What Is Libertarian?
" ''Institute for Humane Studies''.
making decisions
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either rati ...
in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of status
Status (Latin plural: ''statūs''), is a state, condition, or situation, and may refer to:
* Status (law)
** Legal status, in law
** Political status, in international law
** Small entity status, in patent law
** Status conference
** Status c ...
or resource
''Resource'' refers to all the materials available in our environment which are Technology, technologically accessible, Economics, economically feasible and Culture, culturally Sustainability, sustainable and help us to satisfy our needs and want ...
s.
The branch of social science
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the ...
that studies politics and government is referred to as political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and Power (social and political), power, and the analysis of political activities, political philosophy, political thought, polit ...
.
Politics may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and non-violent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but the word often also carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or in a limited way, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it.
A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation
Negotiation is a dialogue between two or more parties to resolve points of difference, gain an advantage for an individual or Collective bargaining, collective, or craft outcomes to satisfy various interests. The parties aspire to agree on m ...
with other political subjects, making law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the ar ...
s, and exercising internal and external force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitu ...
, including warfare
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
against adversaries..... Politics is exercised on a wide range of social levels, from clans
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, a clan may claim descent from a founding member or apical ancestor who serves as a symbol of the clan's unity. Many societie ...
and tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide use of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. The definition is contested, in part due to conflict ...
of traditional societies, through modern local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.
Local governments typically constitute a subdivision of a higher-level political or administrative unit, such a ...
s, companies
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of legal people, whether natural, juridical or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specifi ...
and institutions up to sovereign state
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the ter ...
s, to the international level.
In modern states
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
, people often form political parties
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular area's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific ideological or p ...
to represent their ideas. Members of a party often agree to take the same position on many issues and agree to support the same changes to law and the same leaders. An election
An election is a formal group decision-making process whereby a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold Public administration, public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative d ...
is usually a competition between different parties.
A political system
In political science, a political system means the form of Political organisation, political organization that can be observed, recognised or otherwise declared by a society or state (polity), state.
It defines the process for making official gov ...
is a framework which defines acceptable political methods within a society. The history of political thought
The history of political thought encompasses the chronology and the substantive and methodological changes of human political thought. The study of the history of political thought represents an intersection of various academic disciplines, su ...
can be traced back to early antiquity, with seminal works such as Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
's ''Republic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
'', Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
's ''Politics
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social sta ...
'', Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the phil ...
's political manuscripts and Chanakya
Chanakya (ISO 15919, ISO: ', चाणक्य, ), according to legendary narratives preserved in various traditions dating from the 4th to 11th century CE, was a Brahmin who assisted the first Mauryan emperor Chandragupta Maurya, Chandragup ...
's ''Arthashastra
''Kautilya's Arthashastra'' (, ; ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, politics, economic policy and military strategy. The text is likely the work of several authors over centuries, starting as a compilation of ''Arthashas ...
''.
Etymology
The English word ''politics'' has its roots in the name ofAristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
's classic work, '' Politiká'', which introduced the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
term ()''.'' In the mid-15th century, Aristotle's composition was rendered in Early Modern English
Early Modern English (sometimes abbreviated EModEFor example, or EMnE) or Early New English (ENE) is the stage of the English language from the beginning of the Tudor period to the English Interregnum and Restoration, or from the transit ...
as ,"The book of " (Bhuler 1961/1941:154). which became ''Politics'' in Modern English
Modern English, sometimes called New English (NE) or present-day English (PDE) as opposed to Middle and Old English, is the form of the English language that has been spoken since the Great Vowel Shift in England
England is a Count ...
.
The singular ''politic'' first attested in English in 1430, coming from Middle French
Middle French () is a historical division of the French language that covers the period from the mid-14th to the early 17th centuries. It is a period of transition during which:
* the French language became clearly distinguished from the other co ...
—itself taking from , a Latinization of the Greek () from () and ().
Definitions
*Harold Lasswell
Harold Dwight Lasswell (February 13, 1902 – December 18, 1978) was an American political scientist and communications theorist. He earned his bachelor's degree in philosophy and economics and his Ph.D. from the University of Chicago. He was a ...
: "who gets what, when, how"
* David Easton
David Easton (June 24, 1917 – July 19, 2014) was a Canadian-born American political scientist. From 1947 to 1997, he served as a professor of political science at the University of Chicago.
At the forefront of both the behavioralist and pos ...
: "the authoritative allocation of values for a society".
* Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
: "the most concentrated expression of economics"
* Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (; born ''Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck''; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898) was a German statesman and diplomat who oversaw the unification of Germany and served as ...
: "the capacity of always choosing at each instant, in constantly changing situations, the least harmful, the most useful"
* Bernard Crick
Sir Bernard Rowland Crick (16 December 1929 – 19 December 2008) was a British political theorist and democratic socialist whose views can be summarised as "politics is ethics done in public". He sought to arrive at a "politics of action", as ...
: "a distinctive form of rule whereby people act together through institutionalized procedures to resolve differences"
* Adrian Leftwich: "comprises all the activities of co-operation, negotiation and conflict within and between societies"
Approaches
There are several ways in which approaching politics has been conceptualized.Extensive and limited
Adrian Leftwich has differentiated views of politics based on how extensive or limited their perception of what accounts as 'political' is. The extensive view sees politics as present across the sphere of human social relations, while the limited view restricts it to certain contexts. For example, in a more restrictive way, politics may be viewed as primarily aboutgovernance
Governance is the overall complex system or framework of Process, processes, functions, structures, Social norm, rules, Law, laws and Norms (sociology), norms born out of the Interpersonal relationship, relationships, Social interaction, intera ...
, while a feminist perspective could argue that sites which have been viewed traditionally as non-political, should indeed be viewed as political as well. This latter position is encapsulated in the slogan "''the personal is political
''The personal is political'', also termed ''The private is political'', is a political argument used as a rallying slogan by student activist movements and second-wave feminism from the late 1960s. In the feminist movement of the 1960s and 1970 ...
''", which disputes the distinction between private and public issues. Politics may also be defined by the use of power, as has been argued by Robert A. Dahl
Robert Alan Dahl (; December 17, 1915 – February 5, 2014) was an American Political philosophy, political theorist and Sterling Professor, Sterling Professor of Political Science at Yale University.
He established the pluralism (political the ...
.
Moralism and realism
Some perspectives on politics view it empirically as an exercise of power, while others see it as a social function with anormative
Normativity is the phenomenon in human societies of designating some actions or outcomes as good, desirable, or permissible, and others as bad, undesirable, or impermissible. A Norm (philosophy), norm in this sense means a standard for evaluatin ...
basis. This distinction has been called the difference between political ''moralism'' and political ''realism''''.''. For moralists, politics is closely linked to ethics
Ethics is the philosophy, philosophical study of Morality, moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates Normativity, normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches inclu ...
, and is at its extreme in utopia
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imagined community or society that possesses highly desirable or near-perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia (book), Utopia'', which describes a fictiona ...
n thinking. For example, according to Hannah Arendt
Hannah Arendt (born Johanna Arendt; 14 October 1906 – 4 December 1975) was a German and American historian and philosopher. She was one of the most influential political theory, political theorists of the twentieth century.
Her work ...
, the view of Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
was that, "to be political…meant that everything was decided through words and persuasion and not through violence"; while according to Bernard Crick
Sir Bernard Rowland Crick (16 December 1929 – 19 December 2008) was a British political theorist and democratic socialist whose views can be summarised as "politics is ethics done in public". He sought to arrive at a "politics of action", as ...
, "politics is the way in which free societies are governed. Politics is politics, and other forms of rule are something else." In contrast, for realists, represented by those such as Niccolò Machiavelli
Niccolò di Bernardo dei Machiavelli (3 May 1469 – 21 June 1527) was a Florentine diplomat, author, philosopher, and historian who lived during the Italian Renaissance. He is best known for his political treatise '' The Prince'' (), writte ...
, Thomas Hobbes
Thomas Hobbes ( ; 5 April 1588 – 4 December 1679) was an English philosopher, best known for his 1651 book ''Leviathan (Hobbes book), Leviathan'', in which he expounds an influential formulation of social contract theory. He is considered t ...
, and Harold Lasswell
Harold Dwight Lasswell (February 13, 1902 – December 18, 1978) was an American political scientist and communications theorist. He earned his bachelor's degree in philosophy and economics and his Ph.D. from the University of Chicago. He was a ...
, politics is based on the use of power, irrespective of the ends being pursued.
Conflict and co-operation
Agonism
Agonism (from Greek 'struggle') is a political and social theory that emphasizes the potentially positive aspects of certain forms of conflict. It accepts a permanent place for such conflict in the political sphere, but seeks to show how indivi ...
argues that politics essentially comes down to conflict between conflicting interests. Political scientist Elmer Schattschneider argued that "at the root of all politics is the universal language of conflict", while for Carl Schmitt
Carl Schmitt (11 July 1888 – 7 April 1985) was a German jurist, author, and political theorist.
Schmitt wrote extensively about the effective wielding of political power. An authoritarian conservative theorist, he was noted as a critic of ...
the essence of politics is the distinction of 'friend' from 'foe'. This is in direct contrast to the more co-operative views of politics by Aristotle and Crick. However, a more mixed view between these extremes is provided by Irish political scientist Michael Laver, who noted that:Politics is about the characteristic blend of conflict and co-operation that can be found so often in human interactions. Pure conflict is war. Pure co-operation is true love. Politics is a mixture of both.
History
 The history of politics spans
The history of politics spans human history
Human history or world history is the record of humankind from prehistory to the present. Early modern human, Modern humans evolved in Africa around 300,000 years ago and initially lived as hunter-gatherers. They Early expansions of hominin ...
and is not limited to modern institutions of government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
.
Prehistoric
Frans de Waal
Franciscus Bernardus Maria de Waal (29 October 1948 – 14 March 2024) was a Dutch-American primatologist and ethologist. He was the Charles Howard Candler Professor of Primate Behavior in the Department of Psychology at Emory University in ...
argued that chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (; ''Pan troglodytes''), also simply known as the chimp, is a species of Hominidae, great ape native to the forests and savannahs of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed one. When its close rel ...
s engage in politics through "social manipulation to secure and maintain influential positions". Early human forms of social organization—bands and tribes—lacked centralized political structures. These are sometimes referred to as stateless societies
A stateless society is a society that is not governed by a state. In stateless societies, there is little concentration of authority. Most positions of authority that do exist are very limited in power, and they are generally not perman ...
.
Early states
In ancient history,civilizations
A civilization (also spelled civilisation in British English) is any complex society characterized by the development of the state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond signed or spoken languag ...
did not have definite boundaries as state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
s have today, and their borders could be more accurately described as frontier
A frontier is a political and geographical term referring to areas near or beyond a boundary.
Australia
The term "frontier" was frequently used in colonial Australia in the meaning of country that borders the unknown or uncivilised, th ...
s. Early dynastic Sumer, and early dynastic Egypt were the first civilization
A cradle of civilization is a location and a culture where civilization was developed independent of other civilizations in other locations. A civilization is any complex society characterized by the development of the state, social stratifi ...
s to define their border
Borders are generally defined as geography, geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by polity, political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other administrative divisio ...
s. Moreover, up to the 12th century, many people lived in non-state societies. These range from relatively egalitarian bands Bands may refer to:
* Bands (song), song by American rapper Comethazine
* Bands (neckwear), form of formal neckwear
* Bands (Italian Army irregulars)
Bands () was an Italian military term for Irregular military, irregular forces, composed of nati ...
and tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide use of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. The definition is contested, in part due to conflict ...
s to complex and highly stratified chiefdom
A chiefdom is a political organization of people representation (politics), represented or government, governed by a tribal chief, chief. Chiefdoms have been discussed, depending on their scope, as a stateless society, stateless, state (polity) ...
s.
State formation
There are a number of different theories and hypotheses regarding early state formation that seek generalizations to explain whythe state
A state is a political entity that regulates society and the population within a definite territory. Government is considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states.
A country often has a single state, with various administrat ...
developed in some places but not others. Other scholars believe that generalizations are unhelpful and that each case of early state formation should be treated on its own.
Voluntary theories contend that diverse groups of people came together to form states as a result of some shared rational interest.. The theories largely focus on the development of agriculture, and the population and organizational pressure that followed and resulted in state formation. One of the most prominent theories of early and primary state formation is the ''hydraulic hypothesis'', which contends that the state was a result of the need to build and maintain large-scale irrigation projects.
Conflict theories
Conflict theories are perspectives in political philosophy and sociology which argue that individuals and groups (social classes) within society interact on the basis of conflict rather than agreement, while also emphasizing social psychology ...
of state formation regard conflict and dominance of some population over another population as key to the formation of states. In contrast with voluntary theories, these arguments believe that people do not voluntarily agree to create a state to maximize benefits, but that states form due to some form of oppression by one group over others. Some theories in turn argue that warfare was critical for state formation.
Ancient history
The first states of sorts were those of early dynastic Sumer and early dynastic Egypt, which arose from theUruk period
The Uruk period (; also known as Protoliterate period) existed from the protohistory, protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the S ...
and Predynastic Egypt
Prehistoric Egypt and Predynastic Egypt was the period of time starting at the first human settlement and ending at the First Dynasty of Egypt around 3100 BC.
At the end of prehistory, "Predynastic Egypt" is traditionally defined as the period ...
respectively around approximately 3000 BC.. Early dynastic Egypt was based around the Nile River
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
in the north-east of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, the kingdom's boundaries being based around the Nile and stretching to areas where oases
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentSumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
was located in southern Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, with its borders extending from the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
to parts of the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
and Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabia ...
rivers.
Egyptians, Romans, and the Greeks were the first people known to have explicitly formulated a political philosophy of the state, and to have rationally analyzed political institutions. Prior to this, states were described and justified in terms of religious myths.
Several important political innovations of classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
came from the Greek city-states
Polis (: poleis) means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word ''polis'' had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, Modern Greek πόλη (polē) is located within a (''khôra''), "country", which is a πατ ...
(''polis
Polis (: poleis) means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word ''polis'' had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, Modern Greek πόλη (polē) is located within a (''khôra''), "country", which is a πατ ...
'') and the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
. The Greek city-states before the 4th century granted citizenship
Citizenship is a membership and allegiance to a sovereign state.
Though citizenship is often conflated with nationality in today's English-speaking world, international law does not usually use the term ''citizenship'' to refer to nationalit ...
rights to their free population; in Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
these rights were combined with a directly democratic form of government that was to have a long afterlife in political thought and history.
Modern states
 The
The Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
(1648) is considered by political scientists
The following is a list of notable political scientists. Political science is the scientific study of politics, a social science dealing with systems of governance and power.
A
* Robert Abelson – Yale University psychologist and political ...
to be the beginning of the modern international system,.. in which external powers should avoid interfering in another country's domestic affairs.. The principle of non-interference in other countries' domestic affairs was laid out in the mid-18th century by Swiss jurist Emer de Vattel
Emmerich de Vattel ( 25 April 171428 December 1767) was a philosopher, diplomat, and jurist.
Vattel's work profoundly influenced the development of international law. He is most famous for his 1758 work ''The Law of Nations''. This work was his ...
. States became the primary institutional agents in an interstate system of relations. The Peace of Westphalia is said to have ended attempts to impose supranational authority on European states. The "Westphalian" doctrine of states as independent agents was bolstered by the rise in 19th century thought of nationalism
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, I ...
, under which legitimate states
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
were assumed to correspond to ''nations
A nation is a type of social organization where a collective identity, a national identity, has emerged from a combination of shared features across a given population, such as language, history, ethnicity, culture, territory, or societ ...
''—groups of people united by language and culture.
In Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, during the 18th century, the classic non-national states were the multinational empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
s: the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
, Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
, Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
, the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, and the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
. Such empires also existed in Asia, Africa, and the Americas; in the Muslim world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
, immediately after the death of Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monotheistic teachings of Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, ...
in 632, Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
s were established, which developed into multi-ethnic transnational empires. The multinational empire was an absolute monarchy ruled by a king, emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
or sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
. The population belonged to many ethnic groups, and they spoke many languages. The empire was dominated by one ethnic group, and their language was usually the language of public administration. The ruling dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family, usually in the context of a monarchy, monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A dynasty may also be referred to as a "house", "family" or "clan", among others.
H ...
was usually, but not always, from that group. Some of the smaller European states were not so ethnically diverse, but were also dynastic states, ruled by a royal house
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family, usually in the context of a monarchy, monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A dynasty may also be referred to as a "house", "family" or "clan", among others.
H ...
. A few of the smaller states survived, such as the independent principalities of Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
, Andorra
Andorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, is a Sovereignty, sovereign landlocked country on the Iberian Peninsula, in the eastern Pyrenees in Southwestern Europe, Andorra–France border, bordered by France to the north and Spain to A ...
, Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, ...
, and the republic of San Marino
San Marino, officially the Republic of San Marino, is a landlocked country in Southern Europe, completely surrounded by Italy. Located on the northeastern slopes of the Apennine Mountains, it is the larger of two European microstates, microsta ...
.
Most theories see the nation state as a 19th-century European phenomenon, facilitated by developments such as state-mandated education, mass literacy
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was ...
, and mass media
Mass media include the diverse arrays of media that reach a large audience via mass communication.
Broadcast media transmit information electronically via media such as films, radio, recorded music, or television. Digital media comprises b ...
. However, historians also note the early emergence of a relatively unified state and identity in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
and the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
. Scholars such as Steven Weber
Steven Robert Weber (born March 4, 1961) is an American actor and comedian. He is best known for his role as Brian Hackett on the television series '' Wings'', and as Dr. Dean Archer on NBC’s Chicago Med. He also voiced Charlie B. Barkin in '' ...
, David Woodward, Michel Foucault
Paul-Michel Foucault ( , ; ; 15 October 192625 June 1984) was a French History of ideas, historian of ideas and Philosophy, philosopher who was also an author, Literary criticism, literary critic, Activism, political activist, and teacher. Fo ...
, and Jeremy Black have advanced the hypothesis that the nation state did not arise out of political ingenuity or an unknown undetermined source, nor was it an accident of history or political invention. Rather, the nation state is an inadvertent byproduct of 15th-century intellectual discoveries in political economy
Political or comparative economy is a branch of political science and economics studying economic systems (e.g. Marketplace, markets and national economies) and their governance by political systems (e.g. law, institutions, and government). Wi ...
, capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
, mercantilism
Mercantilism is a economic nationalism, nationalist economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports of an economy. It seeks to maximize the accumulation of resources within the country and use those resources ...
, political geography
Political geography is concerned with the study of both the spatially uneven outcomes of political processes and the ways in which political processes are themselves affected by spatial structures. Conventionally, for the purposes of analysis, ...
, and geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
combined with cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
and advances in map-making technologies.
Some nation states, such as Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, came into existence at least partly as a result of political campaigns by nationalists
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, Id ...
, during the 19th century. In both cases, the territory was previously divided among other states, some of them very small. Liberal ideas of free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold Economic liberalism, economically liberal positions, while economic nationalist politica ...
played a role in German unification, which was preceded by a customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set u ...
, the Zollverein
The (), or German Customs Union, was a coalition of States of the German Confederation, German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1 ...
. National self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
was a key aspect of United States President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
's Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms to the United States Congress ...
, leading to the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military and diplomatic alliance, it consist ...
and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
after the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, while the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
became the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
after the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
. Decolonization
Decolonization is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby Imperialism, imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholar ...
lead to the creation of new nation states in place of multinational empires in the Third World
The term Third World arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, the Southern Cone, NATO, Western European countries and oth ...
.
Globalization
Political globalization began in the 20th century throughintergovernmental organization
Globalization is social change associated with increased connectivity among societies and their elements and the explosive evolution of transportation and telecommunication technologies to facilitate international cultural and economic exchange. ...
s and supranational union
A supranational union is a type of international organization and political union that is empowered to directly exercise some of the powers and functions otherwise reserved to State (polity), states. A supranational organization involves a g ...
s. The League of Nations was founded after World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, and after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
it was replaced by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
. Various international treaties
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, conventi ...
have been signed through it. Regional integration
Regional Integration is a process in which neighboring countries enter into an agreement in order to upgrade cooperation through common institutions and rules. The objectives of the agreement could range from economic to political to envir ...
has been pursued by the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The b ...
, ASEAN
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations,
commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a regional grouping of 10 states in Southeast Asia "that aims to promote economic and security cooperation among its ten members." Together, its member states r ...
, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, and Mercosur
The Southern Common Market (commonly known by abbreviation ''Mercosur'' in Spanish and ''Mercosul'' in Portuguese) is a South American trade bloc established by the Treaty of Asunción in 1991 and Protocol of Ouro Preto in 1994. Its full me ...
. International political institutions on the international level include the International Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC) is an intergovernmental organization and International court, international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute ...
, the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
, and the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland that regulates and facilitates international trade. Governments use the organization to establish, revise, and enforce the rules that g ...
.
Political science
 The study of politics is called political science, It comprises numerous subfields, namely three:
The study of politics is called political science, It comprises numerous subfields, namely three: Comparative politics
Comparative politics is a field in political science characterized either by the use of the '' comparative method'' or other empirical methods to explore politics both within and between countries. Substantively, this can include questions relat ...
, international relations
International relations (IR, and also referred to as international studies, international politics, or international affairs) is an academic discipline. In a broader sense, the study of IR, in addition to multilateral relations, concerns al ...
and political philosophy
Political philosophy studies the theoretical and conceptual foundations of politics. It examines the nature, scope, and Political legitimacy, legitimacy of political institutions, such as State (polity), states. This field investigates different ...
. Political science is related to, and draws upon, the fields of economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
, law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the ar ...
, sociology
Sociology is the scientific study of human society that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of Interpersonal ties, social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. The term sociol ...
, history
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some t ...
, philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
, geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
, psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
, psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of deleterious mental disorder, mental conditions. These include matters related to cognition, perceptions, Mood (psychology), mood, emotion, and behavior.
...
, anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, society, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including archaic humans. Social anthropology studies patterns of behav ...
, and neurosciences
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, ...
.
Comparative politics
Comparative politics is a field in political science characterized either by the use of the '' comparative method'' or other empirical methods to explore politics both within and between countries. Substantively, this can include questions relat ...
is the science of comparison and teaching of different types of constitutions
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
, political actors, legislature and associated fields. International relations
International relations (IR, and also referred to as international studies, international politics, or international affairs) is an academic discipline. In a broader sense, the study of IR, in addition to multilateral relations, concerns al ...
deals with the interaction between nation-state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly or ideally) con ...
s as well as intergovernmental and transnational organizations. Political philosophy
Political philosophy studies the theoretical and conceptual foundations of politics. It examines the nature, scope, and Political legitimacy, legitimacy of political institutions, such as State (polity), states. This field investigates different ...
is more concerned with contributions of various classical and contemporary thinkers and philosophers.
Political science is methodologically diverse and appropriates many methods originating in psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
, social research
Social research is research conducted by social scientists following a systematic plan. Social research methodologies can be classified as quantitative and qualitative.
* Quantitative designs approach social phenomena through quantifiable ...
, and cognitive neuroscience
Cognitive neuroscience is the scientific field that is concerned with the study of the Biology, biological processes and aspects that underlie cognition, with a specific focus on the neural connections in the brain which are involved in mental ...
. Approaches include positivism
Positivism is a philosophical school that holds that all genuine knowledge is either true by definition or positivemeaning '' a posteriori'' facts derived by reason and logic from sensory experience.John J. Macionis, Linda M. Gerber, ''Soci ...
, interpretivism, rational choice theory
Rational choice modeling refers to the use of decision theory (the theory of rational choice) as a set of guidelines to help understand economic and social behavior. The theory tries to approximate, predict, or mathematically model human behav ...
, behavioralism
Behavioralism is an approach in the philosophy of science, describing the scope of the fields now collectively called the behavioral sciences; this approach dominated the field until the late 20th century. Behavioralism attempts to explain human b ...
, structuralism
Structuralism is an intellectual current and methodological approach, primarily in the social sciences, that interprets elements of human culture by way of their relationship to a broader system. It works to uncover the structural patterns t ...
, post-structuralism
Post-structuralism is a philosophical movement that questions the objectivity or stability of the various interpretive structures that are posited by structuralism and considers them to be constituted by broader systems of Power (social and poli ...
, realism, institutionalism Institutionalism may refer to:
* Institutional theory, an approach to the study of politics that focuses on formal institutions of government
* New institutionalism, a social theory that focuses on developing a sociological view of institutions, the ...
, and pluralism
Pluralism in general denotes a diversity of views or stands, rather than a single approach or method.
Pluralism or pluralist may refer more specifically to:
Politics and law
* Pluralism (political philosophy), the acknowledgement of a diversi ...
. Political science, as one of the social science
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the ...
s, uses methods and techniques that relate to the kinds of inquiries sought: primary sources such as historical documents and official records, secondary sources such as scholarly journal articles, survey research, statistical analysis
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying probability distribution.Upton, G., Cook, I. (2008) ''Oxford Dictionary of Statistics'', OUP. . Inferential statistical analysis infers properties of ...
, case studies
A case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular case (or cases) within a real-world context. For example, case studies in medicine may focus on an individual patient or ailment; case studies in business might cover a particular fi ...
, experimental research
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when ...
, and model building.
Political system
 The political system defines the process for making official
The political system defines the process for making official government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
decisions. It is usually compared to the legal system
A legal system is a set of legal norms and institutions and processes by which those norms are applied, often within a particular jurisdiction or community. It may also be referred to as a legal order. The comparative study of legal systems is th ...
, economic system
An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within an economy. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making proces ...
, cultural system
A cultural system is the interaction of different elements in culture. While a cultural system is very different from a social system, sometimes both systems together are referred to as the sociocultural system.
Social theory
A major concern ...
, and other social system
In sociology, a social system is the patterned network of relationships constituting a coherent whole that exist between individuals, groups, and institutions. It is the formal Social structure, structure of role and status that can form in a smal ...
s. According to David Easton
David Easton (June 24, 1917 – July 19, 2014) was a Canadian-born American political scientist. From 1947 to 1997, he served as a professor of political science at the University of Chicago.
At the forefront of both the behavioralist and pos ...
, "A political system can be designated as the interactions through which values are authoritatively allocated for a society." Each political system is embedded in a society with its own political culture, and they in turn shape their societies through public policy
Public policy is an institutionalized proposal or a Group decision-making, decided set of elements like laws, regulations, guidelines, and actions to Problem solving, solve or address relevant and problematic social issues, guided by a conceptio ...
. The interactions between different political systems are the basis for global politics
Global politics, also known as world politics, names both the discipline that studies the political and economic patterns of the world and the field that is being studied. At the centre of that field are the different processes of political global ...
.
Forms of government
 Forms of government can be classified by several ways. In terms of the structure of power, there are
Forms of government can be classified by several ways. In terms of the structure of power, there are monarchies
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for the rest of their life, or until abdication. The extent of the authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutio ...
(including constitutional monarchies
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
) and republic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
s (usually presidential, semi-presidential
A semi-presidential republic, or dual executive republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamen ...
, or parliamentary
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
).
The separation of powers
The separation of powers principle functionally differentiates several types of state (polity), state power (usually Legislature#Legislation, law-making, adjudication, and Executive (government)#Function, execution) and requires these operat ...
describes the degree of horizontal integration between the legislature
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial power ...
, the executive
Executive ( exe., exec., execu.) may refer to:
Role or title
* Executive, a senior management role in an organization
** Chief executive officer (CEO), one of the highest-ranking corporate officers (executives) or administrators
** Executive dir ...
, the judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
, and other independent institutions.
Source of power
The source of power determines the difference betweendemocracies
Democracy (from , ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which political power is vested in the people or the population of a state. Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitiv ...
, oligarchies
Oligarchy (; ) is a form of government in which power rests with a small number of people. Members of this group, called oligarchs, generally hold usually hard, but sometimes soft power through nobility, fame, wealth, or education; or thr ...
, and autocracies
Autocracy is a form of government in which absolute power is held by the head of state and government, known as an autocrat. It includes some forms of monarchy and all forms of dictatorship, while it is contrasted with democracy and feudalism. ...
.
In a democracy, political legitimacy is based on popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the leaders of a state and its government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associativ ...
. Forms of democracy include representative democracy
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy or electoral democracy, is a type of democracy where elected delegates represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies func ...
, direct democracy
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the Election#Electorate, electorate directly decides on policy initiatives, without legislator, elected representatives as proxies, as opposed to the representative democracy m ...
, and demarchy
In governance, sortition is the selection of public officer, officials or jurors at random, i.e. by Lottery (probability), lottery, in order to obtain a representative sample.
In ancient Athenian democracy, sortition was the traditional and pr ...
. These are separated by the way decisions are made, whether by elected representatives, referendum
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate (rather than their Representative democracy, representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either bin ...
s, or by citizen juries. Democracies can be either republics or constitutional monarchies.
Oligarchy is a power structure where a minority rules. These may be in the form of anocracy
Anocracy, or semi-democracy, is a form of government that is loosely defined as part democracy and part dictatorship, or as a "regime that mixes democratic with autocratic features". Another definition classifies anocracy as "a regime that permi ...
, aristocracy
Aristocracy (; ) is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats.
Across Europe, the aristocracy exercised immense Economy, economic, Politics, political, and soc ...
, ergatocracy
This article lists forms of government and political systems, which are not mutually exclusive, and often have much overlap. According to Yale professor Juan José Linz there are three main types of political systems today: democracies,
totalit ...
, geniocracy
Geniocracy is the framework for a system of government which was first proposed by Raël (leader of the International Raëlian Movement) in 1977 and which advocates a certain minimal criterion of intelligence for political candidates and also ...
, gerontocracy
A gerontocracy is a form of rule in which an entity is ruled by leaders who are substantially older than most of the adult population.
In many political structures, power within the ruling class accumulates with age, making the oldest individu ...
, kakistocracy
Kakistocracy ( ) is government by the worst, least qualified, or most unscrupulous people.
The word was coined as early as the 17th century and derives from two Greek words, (, ) and (, ), together
meaning .
History
The earliest use of the ...
, kleptocracy
Kleptocracy (from Greek , "thief", or , "I steal", and from , "power, rule"), also referred to as thievocracy, is a government whose corrupt leaders (kleptocrats) use political power to expropriate the wealth of the people and land the ...
, meritocracy
Meritocracy (''merit'', from Latin , and ''-cracy'', from Ancient Greek 'strength, power') is the notion of a political system in which economic goods or political power are vested in individual people based on ability and talent, rather than ...
, noocracy
Noocracy (, ''nous'' meaning 'mind" or 'intellect', and ''kratos'' meaning 'power' or 'authority') is a type of government where decisions are delegated to those deemed wisest. The idea is classically advanced, among others, by Plato, al-Farab ...
, particracy
Particracy, also known as partitocracy or partocracy, is a form of government in which the political parties are the primary basis of rule rather than citizens or individual politicians.
As argued by Italian political scientist Mauro Calise in 1 ...
, plutocracy
A plutocracy () or plutarchy is a society that is ruled or controlled by people of great wealth or income. The first known use of the term in English dates from 1631. Unlike most political systems, plutocracy is not rooted in any established ...
, stratocracy
A stratocracy is a list of forms of government, form of government headed by military chiefs. The Separation of powers, branches of government are administered by military forces, the government is legal under the laws of the jurisdiction at issu ...
, technocracy
Technocracy is a form of government in which decision-makers appoint knowledge experts in specific domains to provide them with advice and guidance in various areas of their policy-making responsibilities. Technocracy follows largely in the tra ...
, theocracy
Theocracy is a form of autocracy or oligarchy in which one or more deity, deities are recognized as supreme ruling authorities, giving divine guidance to human intermediaries, with executive and legislative power, who manage the government's ...
, or timocracy
A timocracy (from Greek τιμή ''timē'', "honor, worth" and -κρατία ''-kratia'', "rule") in Aristotle's ''Politics'' is a state where only property owners may participate in government. More advanced forms of timocracy, where power der ...
.
Autocracies are either dictatorship
A dictatorship is an autocratic form of government which is characterized by a leader, or a group of leaders, who hold governmental powers with few to no Limited government, limitations. Politics in a dictatorship are controlled by a dictator, ...
s (including military dictatorship
A military dictatorship, or a military regime, is a type of dictatorship in which Power (social and political), power is held by one or more military officers. Military dictatorships are led by either a single military dictator, known as a Polit ...
s) or absolute monarchies.
Vertical integration
In terms of level of vertical integration, political systems can be divided into (from least to most integrated)confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
s, federation
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
s, and unitary state
A unitary state is a (Sovereign state, sovereign) State (polity), state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create or abolish administrative divisions (sub-national or ...
s.
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity
A polity is a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of political institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources.
A polity can be any group of people organized for governance ...
characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
(federalism
Federalism is a mode of government that combines a general level of government (a central or federal government) with a regional level of sub-unit governments (e.g., provinces, State (sub-national), states, Canton (administrative division), ca ...
). In a federation, the self-governing status of the component states, as well as the division of power between them and the central government, is typically constitutionally entrenched and may not be altered by a unilateral decision of either party, the states or the federal political body. Federations were formed first in Switzerland, then in the United States in 1776, in Canada in 1867 and in Germany in 1871 and in 1901, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
. Compared to a federation
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
, a confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
has less centralized power.
State
polity
A polity is a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of political Institutionalisation, institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources.
A polity can be any group of people org ...
, the sovereign state
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the ter ...
. The state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
has been defined by Max Weber
Maximilian Carl Emil Weber (; ; 21 April 186414 June 1920) was a German Sociology, sociologist, historian, jurist, and political economy, political economist who was one of the central figures in the development of sociology and the social sc ...
as a political entity that has monopoly on violence
In political philosophy, a monopoly on violence or monopoly on the legal use of force is the property of a polity that is the only entity in its jurisdiction to legitimately use force, and thus the supreme authority of that area.
While the mon ...
within its territory, while the Montevideo Convention
The Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties of States is a treaty signed at Montevideo, Uruguay, on December 26, 1933, during the Seventh International Conference of American States. At the conference, United States President Franklin D. R ...
holds that states need to have a defined territory; a permanent population; a government; and a capacity to enter into international relations.
A stateless society is a society
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. ...
that is not governed by a state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
.. In stateless societies, there is little concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'', ...
of authority
Authority is commonly understood as the legitimate power of a person or group of other people.
In a civil state, ''authority'' may be practiced by legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government,''The New Fontana Dictionary of M ...
; most positions of authority that do exist are very limited in power
Power may refer to:
Common meanings
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power, a type of energy
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
Math ...
and are generally not permanently held positions; and social bodies that resolve disputes through predefined rules tend to be small. Stateless societies are highly variable in economic organization and cultural practices.
While stateless societies were the norm in human prehistory, few stateless societies exist today; almost the entire global population resides within the jurisdiction of a sovereign state
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the ter ...
. In some regions nominal state authorities may be very weak and wield little or no actual power. Over the course of history most stateless peoples have been integrated into the state-based societies around them.
Some political philosophies consider the state undesirable, and thus consider the formation of a stateless society a goal to be achieved. A central tenet of anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and Political movement, movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or Social hierarchy, hierarchy, primarily targeting the state (polity), state and capitalism. A ...
is the advocacy of society without states. The type of society sought for varies significantly between anarchist schools of thought
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or hierarchy, primarily targeting the state and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state ...
, ranging from extreme individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote realizing one's goals and desires, valuing independence and self-reliance, and a ...
to complete collectivism
In sociology, a social organization is a pattern of relationships between and among individuals and groups. Characteristics of social organization can include qualities such as sexual composition, spatiotemporal cohesion, leadership, struct ...
. In Marxism
Marxism is a political philosophy and method of socioeconomic analysis. It uses a dialectical and materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to analyse class relations, social conflict, ...
, Marx's theory of the state
Karl Marx's thought envisages dividing the history of the State into three phases: pre-capitalist states, states in the capitalist (i.e. present) era and the state (or absence of one) in post-capitalist society. Complicating this is the fact ...
considers that in a post-capitalist society the state, an undesirable institution, would be unnecessary and wither away. A related concept is that of stateless communism
Anarchist communism is a far-left political ideology and anarchist school of thought that advocates communism. It calls for the abolition of private real property but retention of personal property and collectively-owned items, goods, and se ...
, a phrase sometimes used to describe Marx's anticipated post-capitalist society.
Constitutions
Constitutions
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
are written documents that specify and limit the powers of the different branches of government. Although a constitution is a written document, there is also an unwritten constitution. The unwritten constitution is continually being written by the legislative and judiciary branch of government; this is just one of those cases in which the nature of the circumstances determines the form of government that is most appropriate. England did set the fashion of written constitutions during the Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
but after the Restoration abandoned them to be taken up later by the American Colonies after their emancipation
Emancipation generally means to free a person from a previous restraint or legal disability. More broadly, it is also used for efforts to procure Economic, social and cultural rights, economic and social rights, civil and political rights, po ...
and then France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
after the Revolution
In political science, a revolution (, 'a turn around') is a rapid, fundamental transformation of a society's class, state, ethnic or religious structures. According to sociologist Jack Goldstone, all revolutions contain "a common set of elements ...
and the rest of Europe including the European colonies.
Constitutions often set out separation of powers
The separation of powers principle functionally differentiates several types of state (polity), state power (usually Legislature#Legislation, law-making, adjudication, and Executive (government)#Function, execution) and requires these operat ...
, dividing the government into the executive
Executive ( exe., exec., execu.) may refer to:
Role or title
* Executive, a senior management role in an organization
** Chief executive officer (CEO), one of the highest-ranking corporate officers (executives) or administrators
** Executive dir ...
, the legislature
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial power ...
, and the judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
(together referred to as the trias politica), in order to achieve checks and balances within the state. Additional independent branches may also be created, including civil service commission
A civil service commission (also known as a Public Service Commission) is a government agency or public body that is established by the constitution, or by the legislature, to regulate the employment and working conditions of civil servants, overse ...
s, election commission
An election commission is a body charged with overseeing the implementation of electioneering process of any country. The formal names of election commissions vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, and may be styled an electoral commission, a c ...
s, and supreme audit institution
A supreme audit institution is an independent national-level institution which conducts audits of government activities. Most supreme audit institutions are established in their country's constitution, and their mandate is further refined in natio ...
s.
Political culture

Political culture
Political culture describes how culture impacts politics. Every political system is embedded in a particular political culture.
Political culture is what the people, the voters, the electorates believe and do based on their understanding of the ...
describes how culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
impacts politics. Every political system
In political science, a political system means the form of Political organisation, political organization that can be observed, recognised or otherwise declared by a society or state (polity), state.
It defines the process for making official gov ...
is embedded in a particular political culture. Lucian Pye
Lucian W. Pye (; October 21, 1921 – September 5, 2008) was an American political scientist, sinologist and comparative politics expert.
Pye focused on the characteristics of specific cultures in forming theories of political development of m ...
's definition is that, "Political culture is the set of attitudes, beliefs, and sentiments, which give order and meaning to a political process and which provide the underlying assumptions and rules that govern behavior in the political system."
Trust is a major factor in political culture, as its level determines the capacity of the state to function.. Postmaterialism
In sociology, postmaterialism is the transformation of individual values from materialist, physical, and economic to new individual values of autonomy and self-expression.
The term was popularized by the political scientist Ronald Inglehart in hi ...
is the degree to which a political culture is concerned with issues which are not of immediate physical or material concern, such as human rights
Human rights are universally recognized Morality, moral principles or Social norm, norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both Municipal law, national and international laws. These rights are considered ...
and environmentalism
Environmentalism is a broad philosophy, ideology, and social movement about supporting life, habitats, and surroundings. While environmentalism focuses more on the environmental and nature-related aspects of green ideology and politics, ecolog ...
. Religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or ...
has also an impact on political culture.
Political dysfunction
Political corruption
Political corruption is the use of powers for illegitimate private gain, conducted by government officials or their network contacts. Forms of political corruption includebribery
Bribery is the corrupt solicitation, payment, or Offer and acceptance, acceptance of a private favor (a bribe) in exchange for official action. The purpose of a bribe is to influence the actions of the recipient, a person in charge of an official ...
, cronyism
Cronyism is a specific form of in-group favoritism, the spoils system practice of partiality in awarding jobs and other advantages to friends or trusted colleagues, especially in politics and between politicians and supportive organizations. ...
, nepotism
Nepotism is the act of granting an In-group favoritism, advantage, privilege, or position to Kinship, relatives in an occupation or field. These fields can include business, politics, academia, entertainment, sports, religion or health care. In ...
, and political patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, art patronage refers to the support that princes, popes, and other wealthy and influential people ...
. Forms of political patronage, in turn, includes clientelism
Clientelism or client politics is the exchange of goods and services for political support, often involving an implicit or explicit ''quid-pro-quo''. It is closely related to patronage politics and vote buying.
Clientelism involves an asymmetri ...
, earmarking, pork barrel
''Pork barrel'', or simply ''pork'', is a metaphor for allocating government spending to localized projects in the representative's district or for securing direct expenditures primarily serving the sole interests of the representative. The u ...
ing, slush fund
A slush fund is a fund or account used for miscellaneous income and expenses, particularly when these are corrupt or illegal. Such funds may be kept hidden and maintained separately from money that is used for legitimate purposes. Slush funds m ...
s, and spoils system
In politics and government, a spoils system (also known as a patronage system) is a practice in which a political party, after winning an election, gives government jobs to its supporters, friends (cronyism), and relatives (nepotism) as a rewar ...
s; as well as political machine
In the politics of representative democracies, a political machine is a party organization that recruits its members by the use of tangible incentives (such as money or political jobs) and that is characterized by a high degree of leadership c ...
s, which is a political system that operates for corrupt ends.
When corruption is embedded in political culture, this may be referred to as patrimonialism
Patrimonialism is a form of governance in which the ruler governs on the basis of personal loyalties which are derived from patron-client relations, personal allegiances, kin ties and combinations thereof. Patrimonialism is closely related to corr ...
or neopatrimonialism
Neopatrimonialism is a system of social hierarchy where patrons use state resources to secure the loyalty of clients in the general population. It is an informal patron–client relationship that can reach from very high up in state structures do ...
. A form of government that is built on corruption is called a ''kleptocracy
Kleptocracy (from Greek , "thief", or , "I steal", and from , "power, rule"), also referred to as thievocracy, is a government whose corrupt leaders (kleptocrats) use political power to expropriate the wealth of the people and land the ...
'' ('rule of thieves').
Insincere politics
The words "politics" and "political" are sometimes used as pejoratives to mean political action that is deemed to be overzealous, performative, or insincere.Levels of politics
Macropolitics
 Macropolitics can either describe political issues that affect an entire political system (e.g. the
Macropolitics can either describe political issues that affect an entire political system (e.g. the nation state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the State (polity), state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly ...
), or refer to interactions between political systems (e.g. international relations
International relations (IR, and also referred to as international studies, international politics, or international affairs) is an academic discipline. In a broader sense, the study of IR, in addition to multilateral relations, concerns al ...
).
Global politics (or world politics) covers all aspects of politics that affect multiple political systems, in practice meaning any political phenomenon crossing national borders. This can include cities
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
, nation-states, multinational corporation
A multinational corporation (MNC; also called a multinational enterprise (MNE), transnational enterprise (TNE), transnational corporation (TNC), international corporation, or stateless corporation, is a corporate organization that owns and cont ...
s, non-governmental organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
s or international organization
An international organization, also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is an organization that is established by a treaty or other type of instrument governed by international law and possesses its own le ...
s. An important element is international relations: the relations between nation-states may be peaceful when they are conducted through diplomacy
Diplomacy is the communication by representatives of State (polity), state, International organization, intergovernmental, or Non-governmental organization, non-governmental institutions intended to influence events in the international syste ...
, or they may be violent, which is described as war
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
. States that are able to exert strong international influence are referred to as superpower
Superpower describes a sovereign state or supranational union that holds a dominant position characterized by the ability to Sphere of influence, exert influence and Power projection, project power on a global scale. This is done through the comb ...
s, whereas less-powerful ones may be called regional
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
or middle power
A middle power is a state that is not a superpower or a great power, but still exerts influence and plays a significant role in international relations. These countries often possess certain capabilities, such as strong economies, advanced tech ...
s. The international system of power
Power may refer to:
Common meanings
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power, a type of energy
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
Math ...
is called the ''world order'', which is affected by the balance of power that defines the degree of polarity in the system. Emerging power
''Emerging'' is the title of the only album by the Phil Keaggy, Phil Keaggy Band, released in 1977 on NewSong Records. The album's release was delayed due to a shift in record pressing plant priorities following the death of Elvis Presley. The ...
s are potentially destabilizing to it, especially if they display revanchism
Revanchism (, from ''revanche'', "revenge") is the political manifestation of the will to reverse the territorial losses which are incurred by a country, frequently after a war or after a social movement. As a term, ''revanchism'' originated i ...
or irredentism
Irredentism () is one State (polity), state's desire to Annexation, annex the territory of another state. This desire can be motivated by Ethnicity, ethnic reasons because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to or the same as the ...
.
Politics inside the limits of political systems, which in contemporary context correspond to national border
Borders are generally defined as geography, geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by polity, political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other administrative divisio ...
s, are referred to as domestic politics
Domestic policy, also known as internal policy, is a type of public policy overseeing administrative decisions that are directly related to all issues and activity within a state's borders. It differs from foreign policy, which refers to the ways ...
. This includes most forms of public policy
Public policy is an institutionalized proposal or a Group decision-making, decided set of elements like laws, regulations, guidelines, and actions to Problem solving, solve or address relevant and problematic social issues, guided by a conceptio ...
, such as social policy
Some professionals and universities consider social policy a subset of public policy, while other practitioners characterize social policy and public policy to be two separate, competing approaches for the same public interest (similar to MD a ...
, economic policy
''Economic Policy'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Oxford University Press, Oxford Academic on behalf of the Centre for Economic Policy Research, the Center for Economic Studies (University of Munich), and the Paris Scho ...
, or law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of the government or other social institutions who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by investigating, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms gove ...
, which are executed by the state bureaucracy
Bureaucracy ( ) is a system of organization where laws or regulatory authority are implemented by civil servants or non-elected officials (most of the time). Historically, a bureaucracy was a government administration managed by departments ...
.
Mesopolitics
 Mesopolitics describes the politics of intermediary structures within a political system, such as national political parties or
Mesopolitics describes the politics of intermediary structures within a political system, such as national political parties or movements
Movement may refer to:
Generic uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Movement (sign language), a hand movement when signing
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
* Movement (music), a division of a larger c ...
.
A political party is a political organization
A political organization is any organization that involves itself in the political process, including political parties, non-governmental organizations, and special interest advocacy groups. Political organizations are those engaged in polit ...
that typically seeks to attain and maintain political power within government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
, usually by participating in political campaign
A political campaign is an organized effort which seeks to influence the decision making progress within a specific group. In democracy, democracies, political campaigns often refer to election, electoral campaigns, by which representatives a ...
s, educational outreach, or protest action
A protest (also called a demonstration, remonstration, or remonstrance) is a public act of objection, disapproval or dissent against political advantage. Protests can be thought of as acts of cooperation in which numerous people cooperate ...
s. Parties often espouse an expressed ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or values attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely about belief in certain knowledge, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones". Form ...
or vision, bolstered by a written platform with specific goals, forming a coalition
A coalition is formed when two or more people or groups temporarily work together to achieve a common goal. The term is most frequently used to denote a formation of power in political, military, or economic spaces.
Formation
According to ''A G ...
among disparate interests.
Political parties within a particular political system together form the party system
A party system is a concept in comparative political science concerning the system of government by political parties in a democratic country. The idea is that political parties have basic similarities: they control the government, have a stable ...
, which can be either multiparty
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional r ...
, two-party, dominant-party, or one-party
A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system or single-party system is a governance structure in which only a single political party controls the ruling system. In a one-party state, all opposition parties are either outlawed or en ...
, depending on the level of pluralism
Pluralism in general denotes a diversity of views or stands, rather than a single approach or method.
Pluralism or pluralist may refer more specifically to:
Politics and law
* Pluralism (political philosophy), the acknowledgement of a diversi ...
. This is affected by characteristics of the political system, including its electoral system
An electoral or voting system is a set of rules used to determine the results of an election. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, nonprofit organizations and inf ...
. According to Duverger's law
In political science, Duverger's law ( ) holds that in political systems with single-member districts and the first-past-the-post voting system, as in, for example, the United States and Britain, only 2 powerful political parties tend to control ...
, first-past-the-post
First-past-the-post (FPTP)—also called choose-one, first-preference plurality (FPP), or simply plurality—is a single-winner voting rule. Voters mark one candidate as their favorite, or First-preference votes, first-preference, and the cand ...
systems are likely to lead to two-party systems, while proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to any electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions (Political party, political parties) amon ...
systems are more likely to create a multiparty system.
Micropolitics
Micropolitics describes the actions of individual actors within the political system. This is often described aspolitical participation
Citizen participation or public participation in social science refers to different mechanisms for the public to express opinions—and ideally exert influence—regarding political, economic, management or other social decisions. Participato ...
. Political participation may take many forms, including:
* Activism
Activism consists of efforts to promote, impede, direct or intervene in social, political, economic or environmental reform with the desire to make Social change, changes in society toward a perceived common good. Forms of activism range from ...
* Boycott
A boycott is an act of nonviolent resistance, nonviolent, voluntary abstention from a product, person, organisation, or country as an expression of protest. It is usually for Morality, moral, society, social, politics, political, or Environmenta ...
* Civil disobedience
Civil disobedience is the active and professed refusal of a citizenship, citizen to obey certain laws, demands, orders, or commands of a government (or any other authority). By some definitions, civil disobedience has to be nonviolent to be cal ...
* Demonstration
* Petition
A petition is a request to do something, most commonly addressed to a government official or public entity. Petitions to a deity are a form of prayer called supplication.
In the colloquial sense, a petition is a document addressed to an officia ...
* Picketing
Picketing is a form of protest in which people (called pickets or picketers) congregate outside a place of work or location where an event is taking place. Often, this is done in an attempt to dissuade others from going in (" crossing the pi ...
* Strike action
Strike action, also called labor strike, labour strike in British English, or simply strike, is a work stoppage caused by the mass refusal of employees to Working class, work. A strike usually takes place in response to employee grievances. Str ...
* Tax resistance
Tax resistance is the refusal to pay tax because of opposition to the government that is imposing the tax, or to government policy, or as opposition to taxation in itself. Tax resistance is a form of direct action and, if in violation of the ta ...
* Voting
Voting is the process of choosing officials or policies by casting a ballot, a document used by people to formally express their preferences. Republics and representative democracies are governments where the population chooses representative ...
(or its opposite, abstentionism
Abstentionism is the political practice of standing for election to a deliberative assembly while refusing to take up any seats won or otherwise participate in the assembly's business. Abstentionism differs from an election boycott in that abs ...
)
Political values
Democracy
Democracy is a system of processing conflicts in which outcomes depend on what participants do, but no single force controls what occurs and its outcomes. The uncertainty of outcomes is inherent in democracy. Democracy makes all forces struggle repeatedly to realize their interests and devolves power from groups of people to sets of rules. Among modern political theorists, there are three contending conceptions of democracy: ''aggregative'', ''deliberative
Deliberative may refer to:
*Deliberative agent
*Deliberative assembly
*Deliberative Council of Princes and Ministers
*Deliberative democracy
*Deliberative mood
*Deliberative opinion poll
*Deliberative planning
*Deliberative process privilege
*Deli ...
'', and ''radical
Radical (from Latin: ', root) may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
*Classical radicalism, the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and Latin America in the 19th century
*Radical politics ...
''.
Aggregation
The theory of ''aggregative democracy'' claims that the aim of the democratic processes is to solicit the preferences of citizens, and aggregate them together to determine what social policies the society should adopt. Therefore, proponents of this view hold that democratic participation should primarily focus onvoting
Voting is the process of choosing officials or policies by casting a ballot, a document used by people to formally express their preferences. Republics and representative democracies are governments where the population chooses representative ...
, where the policy with the most votes gets implemented.
Different variants of aggregative democracy exist. Under ''minimalism'', democracy is a system of government in which citizens have given teams of political leaders the right to rule in periodic elections. According to this minimalist conception, citizens cannot and should not "rule" because, for example, on most issues, most of the time, they have no clear views or their views are not well-founded. Joseph Schumpeter
Joseph Alois Schumpeter (; February 8, 1883 – January 8, 1950) was an Austrian political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at Harvard Unive ...
articulated this view most famously in his book '' Capitalism, Socialism, and Democracy''. Contemporary proponents of minimalism include William H. Riker
William Harrison Riker (September 22, 1920 – June 26, 1993) was an American political scientist known for applying game theory and mathematics to political science. He helped establish University of Rochester as a center of the behavioral revo ...
, Adam Przeworski
Adam Przeworski (; born May 5, 1940) is a Polish-American professor of political science specializing in comparative politics. He is Carroll and Milton Professor Emeritus in the Department of Politics of New York University. He is a scholar of dem ...
, and Richard Posner
Richard Allen Posner (; born January 11, 1939) is an American legal scholar and retired United States circuit judge who served on the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Seventh Circuit from 1981 to 2017. A senior lecturer at the University of Chicag ...
.
According to the theory of ''direct democracy
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the Election#Electorate, electorate directly decides on policy initiatives, without legislator, elected representatives as proxies, as opposed to the representative democracy m ...
'', on the other hand, citizens should vote directly, not through their representatives, on legislative proposals. Proponents of direct democracy offer varied reasons to support this view. Political activity can be valuable in itself, it socialises and educates citizens, and popular participation can check powerful elites. Most importantly, citizens do not rule themselves unless they directly decide laws and policies.
Governments will tend to produce laws and policies that are close to the views of the median voter—with half to their left and the other half to their right. This is not a desirable outcome as it represents the action of self-interested and somewhat unaccountable political elites competing for votes. Anthony Downs
James Anthony Downs (November 21, 1930October 2, 2021) was an American economist specializing in public policy and public administration. His research focuses included political choice theory, rent control, affordable housing, and transportatio ...
suggests that ideological political parties are necessary to act as a mediating broker between individual and governments. Downs laid out this view in his 1957 book ''An Economic Theory of Democracy
''An Economic Theory of Democracy'' is a treatise of economics written by Anthony Downs, published in 1957. The book set forth a model with precise conditions under which economic theory could be applied to non- market political decision-making. ...
''.
Polyarchy
Robert A. Dahl
Robert Alan Dahl (; December 17, 1915 – February 5, 2014) was an American Political philosophy, political theorist and Sterling Professor, Sterling Professor of Political Science at Yale University.
He established the pluralism (political the ...
argues that the fundamental democratic principle is that, when it comes to binding collective decisions, each person in a political community is entitled to have his/her interests be given equal consideration (not necessarily that all people are equally satisfied by the collective decision). He uses the term polyarchy
In political science, the term polyarchy ( "many", ''arkhe'' "rule") was used by Robert A. Dahl to describe a form of government in which power is invested in multiple people. It takes the form of neither a dictatorship nor a democracy.Robert D ...
to refer to societies in which there exists a certain set of institutions and procedures which are perceived as leading to such democracy. First and foremost among these institutions is the regular occurrence of free and open elections
An election is a formal group decision-making process whereby a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated ...
which are used to select representatives who then manage all or most of the public policy of the society. However, these polyarchic procedures may not create a full democracy if, for example, poverty prevents political participation. Similarly, Ronald Dworkin
Ronald Myles Dworkin (; December 11, 1931 – February 14, 2013) was an American legal philosopher, jurist, and scholar of United States constitutional law. At the time of his death, he was Frank Henry Sommer Professor of Law and Philosophy at ...
argues that "democracy is a substantive, not a merely procedural, ideal".
Deliberation
Deliberative democracy
Deliberative democracy or discursive democracy is a form of democracy in which deliberation is central to decision-making. Deliberative democracy seeks quality over quantity by limiting decision-makers to a smaller but more representative sample ...
is based on the notion that democracy is government by deliberation
Deliberation is a process of thoughtfully weighing options, for example prior to voting. Deliberation emphasizes the use of logic and reason as opposed to power-struggle, creativity, or dialogue. Group decision-making, Group decisions are general ...
. Unlike aggregative democracy, deliberative democracy holds that, for a democratic decision to be legitimate, it must be preceded by authentic deliberation, not merely the aggregation of preferences that occurs in voting. ''Authentic deliberation'' is deliberation among decision-makers that is free from distortions of unequal political power, such as power a decision-maker obtained through economic wealth or the support of interest groups. If the decision-makers cannot reach consensus after authentically deliberating on a proposal, then they vote on the proposal using a form of majority rule.
Equality
society
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. ...
or isolated group have the same social status
Social status is the relative level of social value a person is considered to possess. Such social value includes respect, honour, honor, assumed competence, and deference. On one hand, social scientists view status as a "reward" for group members ...
, especially socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is a measurement used by economics, economists and sociology, sociologsts. The measurement combines a person's work experience and their or their family's access to economic resources and social position in relation t ...
, including protection of human rights
Human rights are universally recognized Morality, moral principles or Social norm, norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both Municipal law, national and international laws. These rights are considered ...
and dignity
Dignity is a human's contentment attained by satisfying physiological needs and a need in development. The content of contemporary dignity is derived in the new natural law theory as a distinct human good.
As an extension of the Enlightenment- ...
, as well as access to certain social goods
In economics, a public good (also referred to as a social good or collective good)Oakland, W. H. (1987). Theory of public goods. In Handbook of public economics (Vol. 2, pp. 485–535). Elsevier. is a commodity, product or service that is bo ...
and social services
Social services are a range of public services intended to provide support and assistance towards particular groups, which commonly include the disadvantaged. Also available amachine-converted HTML They may be provided by individuals, private and i ...
. Furthermore, it may also include health equality
Health equity arises from access to the social determinants of health, specifically from wealth, power and prestige. Individuals who have consistently been deprived of these three determinants are significantly disadvantaged from health inequiti ...
, economic equality and other social securities. Social equality requires the absence of legally enforced social class
A social class or social stratum is a grouping of people into a set of Dominance hierarchy, hierarchical social categories, the most common being the working class and the Bourgeoisie, capitalist class. Membership of a social class can for exam ...
or caste
A caste is a Essentialism, fixed social group into which an individual is born within a particular system of social stratification: a caste system. Within such a system, individuals are expected to marry exclusively within the same caste (en ...
boundaries and the absence of discrimination
Discrimination is the process of making unfair or prejudicial distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong, such as race, gender, age, class, religion, or sex ...
based on by an inalienable aspect of a person's identity. To this end, there must be equal justice under law
Equal justice under law is a phrase engraved on the West Pediment, above the front entrance of the United States Supreme Court building in Washington D.C. It is also a societal ideal that has influenced the American legal system.
The phrase w ...
, and equal opportunity
Equal opportunity is a state of fairness in which individuals are treated similarly, unhampered by artificial barriers, prejudices, or preferences, except when particular distinctions can be explicitly justified. For example, the intent of equal ...
regardless of, sex, gender, ethnicity, age, sexual orientation, origin, caste
A caste is a Essentialism, fixed social group into which an individual is born within a particular system of social stratification: a caste system. Within such a system, individuals are expected to marry exclusively within the same caste (en ...
or class, income or property, language, religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or ...
, convictions, opinions, health or disability.
Left–right spectrum
A common way of understanding politics is through theleft–right political spectrum
The left–right political spectrum is a system of classifying political positions, ideologies and political parties, parties, with emphasis placed upon issues of social equality and social hierarchy. In addition to positions on the left and on ...
, which ranges from left-wing politics
Left-wing politics describes the range of Ideology#Political ideologies, political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy either as a whole or of certain social ...
via centrism
Centrism is the range of political ideologies that exist between left-wing politics and right-wing politics on the left–right political spectrum. It is associated with moderate politics, including people who strongly support moderate policie ...
to right-wing politics
Right-wing politics is the range of Ideology#Political ideologies, political ideologies that view certain social orders and Social stratification, hierarchies as inevitable, natural, normal, or desirable, typically supporting this position b ...
. This classification is comparatively recent and dates from the French Revolution, when those members of the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repr ...
who supported the republic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
, the common people and a secular society sat on the left and supporters of the monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for the rest of their life, or until abdication. The extent of the authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutio ...
, aristocratic
Aristocracy (; ) is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats.
Across Europe, the aristocracy exercised immense economic, political, and social influence. In Western Christian co ...
privilege and the Church sat on the right.
Today, the left is generally progressivist
Progressivism is a left-leaning political philosophy and reform movement that seeks to advance the human condition through social reform. Adherents hold that progressivism has universal application and endeavor to spread this idea to human so ...
, seeking social progress
Progress is movement towards a perceived refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. It is central to the philosophy of progressivism, which interprets progress as the set of advancements in technology, science, and social organization effic ...
in society
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. ...
. The more extreme elements of the left, named the far-left
Far-left politics, also known as extreme left politics or left-wing extremism, are politics further to the left on the left–right political spectrum than the standard political left. The term does not have a single, coherent definition; some ...
, tend to support revolution
In political science, a revolution (, 'a turn around') is a rapid, fundamental transformation of a society's class, state, ethnic or religious structures. According to sociologist Jack Goldstone, all revolutions contain "a common set of elements ...
ary means for achieving this. This includes ideologies such as Communism
Communism () is a political sociology, sociopolitical, political philosophy, philosophical, and economic ideology, economic ideology within the history of socialism, socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a ...
and Marxism
Marxism is a political philosophy and method of socioeconomic analysis. It uses a dialectical and materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to analyse class relations, social conflict, ...
. The center-left
Centre-left politics is the range of left-wing political ideologies that lean closer to the political centre. Ideologies commonly associated with it include social democracy, social liberalism, progressivism, and green politics. Ideas commonl ...
, on the other hand, advocates for more reformist
Reformism is a political tendency advocating the reform of an existing system or institution – often a political or religious establishment – as opposed to its abolition and replacement via revolution.
Within the socialist movement, ref ...
approaches, for example that of social democracy
Social democracy is a Social philosophy, social, Economic ideology, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achi ...
.
In contrast, the right is generally motivated by conservatism
Conservatism is a Philosophy of culture, cultural, Social philosophy, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, Convention (norm), customs, and Value (ethics and social science ...
, which seeks to conserve what it sees as the important elements of society such as law and order, limited government and preserving individual freedoms. The far-right
Far-right politics, often termed right-wing extremism, encompasses a range of ideologies that are marked by ultraconservatism, authoritarianism, ultranationalism, and nativism. This political spectrum situates itself on the far end of the ...
goes beyond this, and often represents a reactionary
In politics, a reactionary is a person who favors a return to a previous state of society which they believe possessed positive characteristics absent from contemporary.''The New Fontana Dictionary of Modern Thought'' Third Edition, (1999) p. 729. ...
turn against progress, seeking to undo it. Examples of such ideologies have included Fascism
Fascism ( ) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It is characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural social hie ...
and Nazism
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During Hitler's rise to power, it was fre ...
. The center-right
Centre-right politics is the set of right-wing politics, right-wing political ideologies that lean closer to the political centre. It is commonly associated with conservatism, Christian democracy, liberal conservatism, and conservative liberalis ...
may be less clear-cut and more mixed in this regard, with neoconservatives
Neoconservatism (colloquially neocon) is a political movement which began in the United States during the 1960s among liberal hawks who became disenchanted with the increasingly pacifist Democratic Party along with the growing New Left and ...
supporting the spread of free market
In economics, a free market is an economic market (economics), system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of ...
s and capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
, and one-nation conservatives more open to social welfare programs.
According to Norberto Bobbio
Norberto Bobbio (; 18 October 1909 – 9 January 2004) was an Italian philosopher of law and political sciences and a historian of political thought. He also wrote regularly for the Turin-based daily '' La Stampa''.
Bobbio was a social lib ...
, one of the major exponents of this distinction, the left believes in attempting to eradicate social inequality—believing it to be unethical or unnatural, while the right regards most social inequality as the result of ineradicable natural inequalities, and sees attempts to enforce social equality as utopian or authoritarian..
Some ideologies, notably Christian Democracy
Christian democracy is an ideology inspired by Christian social teaching to respond to the challenges of contemporary society and politics.
Christian democracy has drawn mainly from Catholic social teaching and neo-scholasticism, as well ...
, claim to combine left and right-wing politics; according to Geoffrey K. Roberts and Patricia Hogwood, "In terms of ideology, Christian Democracy has incorporated many of the views held by liberals, conservatives and socialists within a wider framework of moral and Christian principles." Movements which claim or formerly claimed to be above the left-right divide include Fascist Terza Posizione
Terza Posizione () was a short-lived neo-fascist political movement founded in Rome in 1978. The group published a journal, also called ''Terza Posizione'' which promoted Third Position politics. It was formed by teenagers and students from a pre ...
economic politics in Italy and Peronism
Peronism, also known as justicialism, is an Argentine ideology and movement based on the ideas, doctrine and legacy of Juan Perón (1895–1974). It has been an influential movement in 20th- and 21st-century Argentine politics. Since 1946, P ...
in Argentina.
Freedom
Political freedom (also known as political liberty or autonomy) is a centralconcept
A concept is an abstract idea that serves as a foundation for more concrete principles, thoughts, and beliefs.
Concepts play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied within such disciplines as linguistics, ...
in political thought and one of the most important features of democratic societies. Negative liberty
Negative liberty, or negative freedom, is freedom from interference by other people. Negative liberty is primarily concerned with freedom from external restraint and contrasts with positive liberty (the possession of the power and resources to ...
has been described as freedom from oppression or coercion and unreasonable external constraints on action, often enacted through civil and political rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' political freedom, freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and ...
, while positive liberty
Positive liberty, or positive freedom, is the possession of the power and resources to act in the context of the structural limitations of the broader society which impacts a person's ability to act, as opposed to negative liberty, which is freed ...
is the absence of disabling conditions for an individual and the fulfillment of enabling conditions, e.g. economic compulsion, in a society. This capability approach
The capability approach (also referred to as the capabilities approach) is a normative approach to human welfare spending, welfare that concentrates on the actual capability of persons to achieve lives they value rather than solely having a right ...
to freedom requires economic, social and cultural rights
Economic, social and cultural rights (ESCR) are Socioeconomics, socio-economic human rights, such as the right to education, right to housing, right to an adequate standard of living, right to health, victims' rights and the right to science and ...
in order to be realized.
Authoritarianism and libertarianism
Authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in democracy, separation of powers, civil liberties, and ...
and libertarianism
Libertarianism (from ; or from ) is a political philosophy that holds freedom, personal sovereignty, and liberty as primary values. Many libertarians believe that the concept of freedom is in accord with the Non-Aggression Principle, according t ...
disagree the amount of individual freedom
Freedom is the power or right to speak, act, and change as one wants without hindrance or restraint. Freedom is often associated with liberty and autonomy in the sense of "giving oneself one's own laws".
In one definition, something is "free" i ...
each person possesses in that society relative to the state. One author describes authoritarian political systems as those where "individual rights
Rights are law, legal, social, or ethics, ethical principles of freedom or Entitlement (fair division), entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal sy ...
and goals are subjugated to group goals, expectations and conformities", while libertarians generally oppose the state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
and hold the individual
An individual is one that exists as a distinct entity. Individuality (or self-hood) is the state or quality of living as an individual; particularly (in the case of humans) as a person unique from other people and possessing one's own needs or g ...
as sovereign. In their purest form, libertarians are anarchists
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or hierarchy, primarily targeting the state and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state w ...
, who argue for the total abolition of the state, of political parties
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular area's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific ideological or p ...
and of other political entities, while the purest authoritarians are, by definition, totalitarians who support state control over all aspects of society.
For instance, classical liberalism
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics and civil liberties under the rule of law, with special emphasis on individual autonomy, limited governmen ...
(also known as ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( , from , ) is a type of economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies or regulations). As a system of thought, ''laissez-faire'' ...
liberalism'')Adams, Ian. 2001. ''Political Ideology Today''. Manchester: Manchester University Press
Manchester University Press is the university press of the University of Manchester, England, and a publisher of academic books and journals. Manchester University Press has developed into an international publisher. It maintains its links with t ...
. p. 20. is a doctrine stressing individual freedom and limited government
In political philosophy, limited government is the concept of a government limited in power. It is a key concept in the history of liberalism.Amy Gutmann, "How Limited Is Liberal Government" in Liberalism Without Illusions: Essays on Liberal ...
. This includes the importance of human rationality, individual property rights
The right to property, or the right to own property (cf. ownership), is often classified as a human right for natural persons regarding their Possession (law), possessions. A general recognition of a right to private property is found more rarely ...
, free market
In economics, a free market is an economic market (economics), system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of ...
s, natural rights
Some philosophers distinguish two types of rights, natural rights and legal rights.
* Natural rights are those that are not dependent on the laws or customs of any particular culture or government, and so are ''universal'', ''fundamental rights ...
, the protection of civil liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties of ...
, constitutional limitation of government, and individual freedom from restraint as exemplified in the writings of John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) – 28 October 1704 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.)) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of the Enlightenment thi ...
, Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptised 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the field of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as the "father of economics"——— or ...
, David Hume
David Hume (; born David Home; – 25 August 1776) was a Scottish philosopher, historian, economist, and essayist who was best known for his highly influential system of empiricism, philosophical scepticism and metaphysical naturalism. Beg ...
, David Ricardo
David Ricardo (18 April 1772 – 11 September 1823) was a British political economist, politician, and member of Parliament. He is recognized as one of the most influential classical economists, alongside figures such as Thomas Malthus, Ada ...
, Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778), known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' Voltaire (, ; ), was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, philosopher (''philosophe''), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit ...
, Montesquieu
Charles Louis de Secondat, baron de La Brède et de Montesquieu (18 January 168910 February 1755), generally referred to as simply Montesquieu, was a French judge, man of letters, historian, and political philosopher.
He is the principal so ...
and others. According to the libertarian Institute for Humane Studies
The Institute for Humane Studies (IHS) is a non-profit organization that promotes the teaching and research of classical liberalism in higher education in the United States. IHS offers funding opportunities, programs, and events for faculty and g ...
, "the libertarian, or 'classical liberal', perspective is that individual well-being, prosperity, and social harmony are fostered by 'as much liberty as possible' and 'as little government as necessary'."IHS. 2019.What Is Libertarian?
" ''Institute for Humane Studies''.
George Mason University
George Mason University (GMU) is a Public university, public research university in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. Located in Northern Virginia near Washington, D.C., the university is named in honor of George Mason, a Founding Father ...
. For anarchist political philosopher L. Susan Brown (1993), "liberalism and anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and Political movement, movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or Social hierarchy, hierarchy, primarily targeting the state (polity), state and capitalism. A ...
are two political philosophies that are fundamentally concerned with individual freedom
Freedom is the power or right to speak, act, and change as one wants without hindrance or restraint. Freedom is often associated with liberty and autonomy in the sense of "giving oneself one's own laws".
In one definition, something is "free" i ...
yet differ from one another in very distinct ways. Anarchism shares with liberalism a radical commitment to individual freedom while rejecting liberalism's competitive property relations." Brown, L. Susan. 1993. '' The Politics of Individualism: Liberalism, Liberal Feminism, and Anarchism''. Black Rose Books
Dimitrios I. Roussopoulos (born 1936) is a Canadian political activist and publisher.
Early life
Roussopoulos studied philosophy, politics, and economics at several Montreal and London universities. He has remained institutionally independent ...
.
See also
*Historic recurrence
Historic recurrence is the repetition of similar events in history. The concept of historic recurrence has variously been applied to overall human history (''e.g.'', to the rises and falls of empires), to repetitive patterns in the history of ...
* Horseshoe theory
In popular discourse, the horseshoe theory asserts that advocates of the far-left and the far-right, rather than being at opposite and opposing ends of a linear continuum of the political spectrum, closely resemble each other, analogous to the ...
* Index of politics articles – alphabetical list of political subjects
* List of banned political parties
* List of politics awards
This list of politics awards is an index to articles that describe notable awards related to politics. It includes awards for political science, for governance and civic leadership, and for books on political subjects. The list gives the country of ...
* List of years in politics
This page indexes the individual year in politics pages.
20th century
*1900s in political history, 1900s
*1910s in political history, 1910s
*1920s in political history, 1920s
*1930s in politics, 1930s
*1940s in politics, 1940s
*1950s in politic ...
* Outline of political science
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to politics and political science:
Politics – the exercise of power; process by which groups of people make collective decisions. Politics is the art or science of run ...
– structured list of political topics, arranged by subject area
* Political lists – lists of political topics
* Political censorship
Political censorship exists when a government attempts to conceal, misinformation, fake, distort, or disinformation, falsify information that its citizens receive by suppressing or crowding out political news that the public might receive through ...
* Political corruption
Political corruption is the use of powers by government officials or their network contacts for illegitimate private gain. Forms of corruption vary but can include bribery, lobbying, extortion, cronyism, nepotism, parochialism, patronage, influen ...
* Political polarization
Political polarization (spelled ''polarisation'' in British English, Australian English, and New Zealand English) is the divergence of political attitudes away from the center, towards ideological extremes. Scholars distinguish between ideologi ...
* Political scandal
In politics, a political scandal is an action or event regarded as morally or legally wrong and causing general public outrage. Politicians, government officials, Political party, party officials and Lobbying, lobbyists can be accused of various ...
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * ** * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Adcock, Robert. 2014. ''Liberalism and the Emergence of American Political Science: A Transatlantic Tale''. New York: Oxford University Press. * Adcock, Robert, Mark Bevir, and Shannon Stimson (eds.). 2007. ''Modern Political Science: Anglo-American Exchanges Since 1870''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. * Almond, Gabriel A. 1996. "Political Science: The History of the Discipline", pp. 50–96, in Robert E. Goodin and Hans-Dieter Klingemann (eds.), ''The New Handbook of Political Science''. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. * * * Mount, Ferdinand, "Ruthless and Truthless" (review ofPeter Oborne
Peter Alan Oborne (; born 11 July 1957) is a British journalist and broadcaster. He is the former chief political commentator of ''The Daily Telegraph'', from which he resigned in early 2015. He is author of ''The Rise of Political Lying'' (2005 ...
, ''The Assault on Truth: Boris Johnson, Donald Trump and the Emergence of a New Moral Barbarism'', Simon and Schuster, 2021, , 192 pp.; and Colin Kidd and Jacqueline Rose
Jacqueline Rose (born 1949) is a British academic who is Professor of Humanities at the Birkbeck Institute for the Humanities. She is known for her work on the relationship between psychoanalysis, feminism and literature.
Life and work
Rose ...
, eds., ''Political Advice: Past, Present and Future'', I.B. Tauris, February 2021, , 240 pp.), ''London Review of Books
The ''London Review of Books'' (''LRB'') is a British literary magazine published bimonthly that features articles and essays on fiction and non-fiction subjects, which are usually structured as book reviews.
History
The ''London Review of Book ...
'', vol. 43, no. 9 (6 May 2021), pp. 3, 5–8.
* Munck, Gerardo L., and Richard Snyder (eds.). ''Passion, Craft, and Method in Comparative Politics.'' Johns Hopkins University Press, 2007.
* Ross, Dorothy. 1991. ''The Origins of American Social Science
''The Origins of American Social Science'' is a 1991 book by Dorothy Ross on the early history of social science in the United States.
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Externa ...
''. New York: Cambridge University Press.
*
{{Authority control
Main topic articles