Plate trick on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In mathematics and physics, the plate trick, also known as Dirac's string trick, the belt trick, or the Balinese cup trick, is any of several demonstrations of the idea that rotating an object with strings attached to it by 360 degrees does not return the system to its original state, while a second rotation of 360 degrees, a total rotation of 720 degrees, does. Mathematically, it is a demonstration of the theorem that SU(2) (which double-covers SO(3)) is simply connected. To say that SU(2) double-covers SO(3) essentially means that the unit quaternions represent the group of rotations twice over. A detailed, intuitive, yet semi-formal articulation can be found in the article on tangloids.

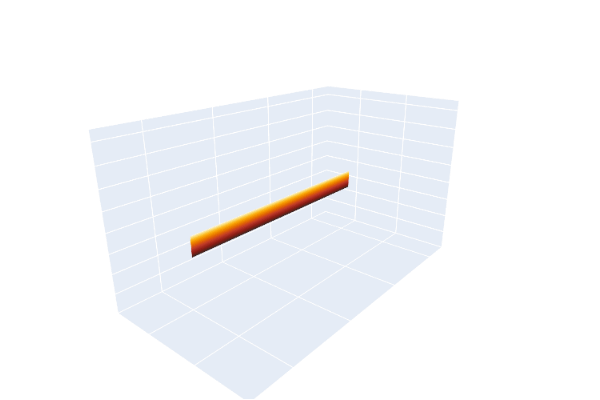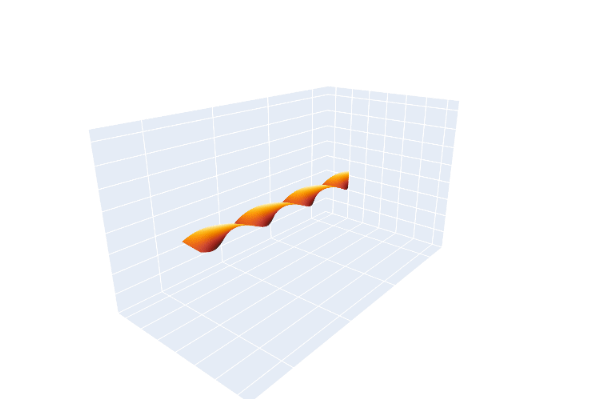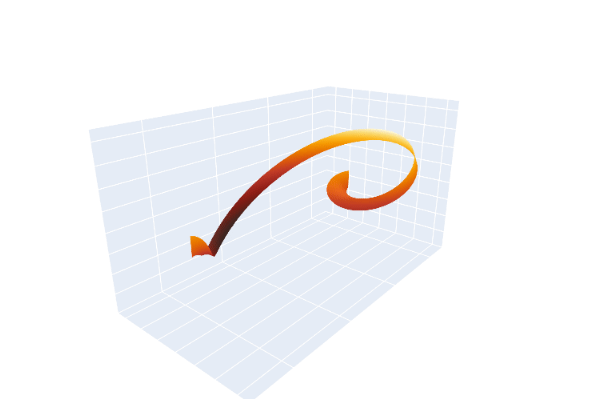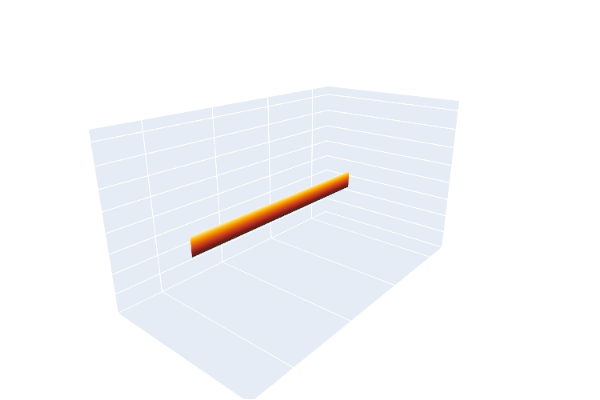 The same phenomenon can be demonstrated using a leather belt with an ordinary frame buckle, whose prong serves as a pointer. The end opposite the buckle is clamped so it cannot move. The belt is extended without a twist and the buckle is kept horizontal while being turned clockwise one complete turn (360°), as evidenced by watching the prong. The belt will then appear twisted, and no maneuvering of the buckle that keeps it horizontal and pointed in the same direction can undo the twist. Obviously a 360° turn counterclockwise would undo the twist. The surprise element of the trick is that a second 360° turn in the clockwise direction, while apparently making the belt even more twisted, does allow the belt to be returned to its untwisted state by maneuvering the buckle under the clamped end while always keeping the buckle horizontal and pointed in the same direction.
Mathematically, the belt serves as a record, as one moves along it, of how the buckle was transformed from its original position, with the belt untwisted, to its final rotated position. The clamped end always represents the null rotation. The trick demonstrates that a path in rotation space (SO(3)) that produces a 360 degree rotation is not homotopy equivalent to a null rotation, but a path that produces a double rotation (720°) is null equivalent.
Belt trick has been witnessed in 1-d Classical Heisenberg model as a breather solution.
The same phenomenon can be demonstrated using a leather belt with an ordinary frame buckle, whose prong serves as a pointer. The end opposite the buckle is clamped so it cannot move. The belt is extended without a twist and the buckle is kept horizontal while being turned clockwise one complete turn (360°), as evidenced by watching the prong. The belt will then appear twisted, and no maneuvering of the buckle that keeps it horizontal and pointed in the same direction can undo the twist. Obviously a 360° turn counterclockwise would undo the twist. The surprise element of the trick is that a second 360° turn in the clockwise direction, while apparently making the belt even more twisted, does allow the belt to be returned to its untwisted state by maneuvering the buckle under the clamped end while always keeping the buckle horizontal and pointed in the same direction.
Mathematically, the belt serves as a record, as one moves along it, of how the buckle was transformed from its original position, with the belt untwisted, to its final rotated position. The clamped end always represents the null rotation. The trick demonstrates that a path in rotation space (SO(3)) that produces a 360 degree rotation is not homotopy equivalent to a null rotation, but a path that produces a double rotation (720°) is null equivalent.
Belt trick has been witnessed in 1-d Classical Heisenberg model as a breather solution.
Animation of the Dirac belt trick, including the path through SU(2)Animation of the Dirac belt trick, with a double beltAnimation of the extended Dirac belt trick, showing that spin 1/2 particles are fermions: they can be untangled after switching particle positions twice, but not onceMechanical linkage implementing the belt trick
* ttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rzt_byhgujg Video of Balinese cup trickbr>
Rotation in three dimensions Spinors Topology of Lie groups Science demonstrations
Demonstrations
Resting a small plate flat on the palm, it is possible to perform two rotations of one's hand while keeping the plate upright. After the first rotation of the hand, the arm will be twisted, but after the second rotation it will end in the original position. To do this, the hand makes one rotation passing over the elbow, twisting the arm, and then another rotation passing under the elbow untwists it. In mathematical physics, the trick illustrates the quaternionic mathematics behind the spin of spinors. As with the plate trick, these particles' spins return to their original state only after two full rotations, not after one.The belt trick

 The same phenomenon can be demonstrated using a leather belt with an ordinary frame buckle, whose prong serves as a pointer. The end opposite the buckle is clamped so it cannot move. The belt is extended without a twist and the buckle is kept horizontal while being turned clockwise one complete turn (360°), as evidenced by watching the prong. The belt will then appear twisted, and no maneuvering of the buckle that keeps it horizontal and pointed in the same direction can undo the twist. Obviously a 360° turn counterclockwise would undo the twist. The surprise element of the trick is that a second 360° turn in the clockwise direction, while apparently making the belt even more twisted, does allow the belt to be returned to its untwisted state by maneuvering the buckle under the clamped end while always keeping the buckle horizontal and pointed in the same direction.
Mathematically, the belt serves as a record, as one moves along it, of how the buckle was transformed from its original position, with the belt untwisted, to its final rotated position. The clamped end always represents the null rotation. The trick demonstrates that a path in rotation space (SO(3)) that produces a 360 degree rotation is not homotopy equivalent to a null rotation, but a path that produces a double rotation (720°) is null equivalent.
Belt trick has been witnessed in 1-d Classical Heisenberg model as a breather solution.
The same phenomenon can be demonstrated using a leather belt with an ordinary frame buckle, whose prong serves as a pointer. The end opposite the buckle is clamped so it cannot move. The belt is extended without a twist and the buckle is kept horizontal while being turned clockwise one complete turn (360°), as evidenced by watching the prong. The belt will then appear twisted, and no maneuvering of the buckle that keeps it horizontal and pointed in the same direction can undo the twist. Obviously a 360° turn counterclockwise would undo the twist. The surprise element of the trick is that a second 360° turn in the clockwise direction, while apparently making the belt even more twisted, does allow the belt to be returned to its untwisted state by maneuvering the buckle under the clamped end while always keeping the buckle horizontal and pointed in the same direction.
Mathematically, the belt serves as a record, as one moves along it, of how the buckle was transformed from its original position, with the belt untwisted, to its final rotated position. The clamped end always represents the null rotation. The trick demonstrates that a path in rotation space (SO(3)) that produces a 360 degree rotation is not homotopy equivalent to a null rotation, but a path that produces a double rotation (720°) is null equivalent.
Belt trick has been witnessed in 1-d Classical Heisenberg model as a breather solution.
See also
* Anti-twister mechanism * Spin–statistics theorem * Orientation entanglement * TangloidsReferences
* * {{Cite journal, last1=Pengelley, first1=David, last2=Ramras, first2=Daniel, date=2017-02-21, title=How Efficiently Can One Untangle a Double-Twist? Waving is Believing!, journal=The Mathematical Intelligencer, volume=39, language=en, pages=27–40, doi=10.1007/s00283-016-9690-x, issn=0343-6993, arxiv=1610.04680, s2cid=119577398External links
Animation of the Dirac belt trick, including the path through SU(2)
* ttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rzt_byhgujg Video of Balinese cup trickbr>
Rotation in three dimensions Spinors Topology of Lie groups Science demonstrations