Philosophy of accounting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The philosophy of accounting is the conceptual framework for the professional preparation and auditing of
- appropriate, the special needs of small and medium-sized entities and emerging
- economies; and to bring about convergence of national accounting standards and IFRSs to high quality solutions.


financial statement
Financial statements (or financial reports) are formal records of the financial activities and position of a business, person, or other entity.
Relevant financial information is presented in a structured manner and in a form which is easy to un ...
s and accounts. The issues which arise include the difficulty of establishing a ''true and fair'' value of an enterprise
Enterprise (or the archaic spelling Enterprize) may refer to:
Business and economics
Brands and enterprises
* Enterprise GP Holdings, an energy holding company
* Enterprise plc, a UK civil engineering and maintenance company
* Enterpris ...
and its asset
In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned or controlled by a business or an economic entity. It is anything (tangible or intangible) that can be used to produce positive economic value. Assets represent value of ownership that can b ...
s; the moral
A moral (from Latin ''mor─ülis'') is a message that is conveyed or a lesson to be learned from a story or event. The moral may be left to the hearer, reader, or viewer to determine for themselves, or may be explicitly encapsulated in a maxim. ...
basis of disclosure and discretion; the standards and laws required to satisfy the political
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social sta ...
needs of investor
An investor is a person who allocates financial capital with the expectation of a future Return on capital, return (profit) or to gain an advantage (interest). Through this allocated capital the investor usually purchases some species of pr ...
s, employee
Employment is a relationship between two party (law), parties Regulation, regulating the provision of paid Labour (human activity), labour services. Usually based on a employment contract, contract, one party, the employer, which might be a cor ...
s and other stakeholders.
The discipline of accounting insists that transparency is achievable. Fairness has an important role in the practice of accounting. Accordingly, it seems appropriate that philosophy as a relevant way of understanding truth and fairness in accounting is well considered. Some authors have already underlined the key role played by philosophy in accounting with principles such as substance over form, ethics, and accountability, therefore more abstract concepts like fairness, justice, equity, and truth have a due place in accounting.
Introduction
Often, accountants are trusted to provide the information upon which financial/managerial decisions are based. According to the IASB project, conceptual framework, it states the role of financial report as'The primary users need information about the resources of the entity not only to assess an entity's prospects for future net cash inflows but also how effectively and efficiently management has discharged their responsibilities to use the entity's existing resources'Such great significance is put on the role of accounting in business industry yet the issue of trust has always been the fundamental problem. Mackenzie says 'Trust in numbers, however, works only if those who produce the numbers can be trusted.' Evaluating and understanding the fundamental ideas of accounting is extremely important as they establish the foundational structures of accounting in which most of the constructed knowledge is based on. It introduces the principles of accounting which provide the understanding of reasons behind all decisions.
Objectives of accountancy
Financial reporting aims to provide information about firms' financial performance of which the firm uses to record the past transactions and apply changes to the future financial plan.IASB (International Accounting Standard Board)
The ultimate aims of the IASB and other accounting standard-setters are: * to develop, in the public interest, a single set of high quality, understandable and enforceable global accounting standards that require high quality, transparent and comparable information in financial statements and other financial reporting to help participants in the worldŌĆÖs capital markets and other users make economic decisions; * to promote the use and rigorous application of those standards; * in fulfilling the objectives associated with (a) and (b), to take account of, as- appropriate, the special needs of small and medium-sized entities and emerging
- economies; and to bring about convergence of national accounting standards and IFRSs to high quality solutions.
IFRS
International Financial Reporting Standards, commonly called IFRS, are accounting standards issued by the IFRS Foundation and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). They constitute a standardised way of describing the company's fina ...
(International Financial Reporting Standard)
The mission of IFRS is to bring transparency, accountability and efficiency to financial markets around the world. It aims to build trust in the society and also to provide long-term financial stability.
* IFRS brings transparency by enhancing the international comparability and quality of financial information, enabling investors and other market participants to make informed economic decisions.
* IFRS strengthens accountability by reducing the information gap between the providers of capital and the people to whom they have entrusted their money. Our standards provide information that is needed to hold management to account. As a source of globally comparable information, IFRS is also of vital importance to regulators around the world.
* IFRS contributes to economic efficiency by helping investors to identify opportunities and risks across the world, thus improving capital allocation. For businesses, the use of a single, trusted accounting language lowers the cost of capital and reduces international reporting costs.
Foundational perspectives
Art versus science perspective
Art is defined as the expression or application of human creative skill and imagination, while thephilosophy of art
Aesthetics (also spelled esthetics) is the branch of philosophy concerned with the nature of beauty and taste, which in a broad sense incorporates the philosophy of art.Slater, B. H.Aesthetics ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy,'' , acces ...
also deals with the nature of human creativity.
Science is defined as the knowledge acquired through observation and experimentation which is critically tested, systematised and brought under general principles. The philosophy of science is the investigation of questions that arise from reflection upon the science and scientific practice.
Mattessich says making the accounting discipline more scientific would not be achievable. 'In its functional perspective, accounting can be defined as the generic term for the activities carried out by accountants but also as a broad term that covers the preparation, analysis and audit for all financial information thus as the art of accounting.'
True income versus decision usefulness
This perspective discusses whether the financial paper should provide the information that reflects the true income or that supports decision making which is not necessarily objective or factually true.True income thought
ŌĆśMeasurement of wealth and its effectiveness is judged based on how well it approximates the value of the wealth items.' Although one can argue that the meaning of 'true value' needs to be defined and it is true, but at least there exists a value and the accountants attempt to measure it.Decision usefulness thought
'This approach focuses on measuring and disclosing business in effectiveness is judged based on how well such disclosure and communication are concluded.' Although the businesses try to reduce uncertainty, the multidimensionality of any businesses makes the effective communication difficult to achieve.Approaches
In accounting, it is obligatory to follow the prescribed structure that the pre-factual controversies can be engaged in. In science, the knowledge can be principle negotiable and changeable but in accounting, standards are pre-established in the allowable form of knowledge which must be followed. This may seem insignificant as most other sciences operate in a given paradigm yet it provides different motivation: scientists can pursue to seek knowledge at a paradigmatic level yet accountants are restricted and only able to know about particularities in a way that is consistent with their existing knowledge.Technocratism
The word ''technical'' is in relation to accounting work as applying techniques of knowledge construction that are generally and mostly factual. It can be derived from various accepted readings of accounting standards, or from generally accepted accounting principles. Hence, technocratism refers to a belief that the best method of crystallising and resolving the controversies is a technical one.Economic rationalisation
Max Weber adopts the term ''rationalisation'' to illustrate the gradual increase in what he calls ''rationality'' in societies. Formal rationality is described as 'calculability of means and procedures'. Weber defines economic rationalisation as'The extent of quantitative calculation or accounting which is technically possible and which is actually applied.'Nowadays, there are many evidence of economic rationalisation in the society. Accounting practice is becoming more complex and strictly monitored. This is also accompanied by an increasing contribution of accounting to firmsŌĆÖ managerial actions.
Problematic consequence
Due to the limitation of scope, it can promote a limited conception of the responsibilities in constructing new knowledge, accounting being heavily based on pre-established and factual standards. Also when accountants argue, technocratic authority can deny any other perspectives. Although technocratism encourage a mechanical, quantitative, and factual way of thinking, this can lead to an elimination of all grey area which can have detrimental effect on firmsŌĆÖ financial/managerial decisions.
Pragmatism
Pragmatism is a philosophical tradition that views language and thought as tools for prediction, problem solving, and action, rather than describing, representing, or mirroring reality. Pragmatists contend that most philosophical topicsŌĆ ...
Unlike technocrats, pragmatic accountants are rather liberal and accept various possible means when a controversy can be resolved. Matthew Gill argues thatŌĆśAccountantsŌĆÖ training tends to establish a distinction between technical knowledge that can be transmitted in a training centreŌĆÖs classroom, and a capacity for judgement that can only be acquired on the job. Additionally (and ironically), the more complex and technocratic accounting regulation becomes, the more pragmatically accountants must approach their work in order to get anything done.ŌĆÖPragmatic accountants also argues that there needs to be a balance between being fair and allowing the business to operate without too many disruptions.
Strategic pragmatism
Technocratism and strategic pragmatism donŌĆÖt always contradict each other. Especially in risk assessment, risk bridges the gap between technicality and pragmatic strategy by making strategy a technical matter.Niklas Luhmann
Niklas Luhmann (; ; December 8, 1927 ŌĆō November 11, 1998) was a German sociologist, philosopher of social science, and systems theorist.
Niklas Luhmann is one of the most influential German sociologists of the 20th century. His thinking was ...
states thatŌĆśThe individualism of risk-calculating merchants, learning from experience, attentive to news, making decisions on the basis of a well-judged mix of trust and distrustŌĆ”ŌĆÖThis discussion extends to the technocratic project of making things quantifiable by calculating and evaluating the possibilities of probable consequences.
Ethics in accounting
The nature of accounting establishes a unique position of trust in relation to the clients, employers and general public, who count on accountants' professional judgment and advice in making financial/managerial decisions.'They have the responsibility to ensure that their duties are performed in conformity with the ethical values of honesty, integrity, objectivity, due care, confidentiality, and the commitment to the public interest before oneŌĆÖs own.'Theories of ethics

Utilitarianism
In ethical philosophy, utilitarianism is a family of normative ethical theories that prescribe actions that maximize happiness and well-being for the affected individuals. In other words, utilitarian ideas encourage actions that lead to the ...
The doctrine that an action is right in so far as it promotes happiness, and that the greatest happiness of the greatest number should be the guiding principle of conduct.
Jeremy Bentham
Jeremy Bentham (; 4 February Dual dating, 1747/8 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S. 5 February 1748 Old Style and New Style dates, N.S.ŌĆō 6 June 1832) was an English philosopher, jurist, and social reformer regarded as the founder of mo ...
, the founder of the idea, argues that the more happiness there are in the decision, the better decision it is. However, happiness is an unquantifiable concept. John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill (20 May 1806 ŌĆō 7 May 1873) was an English philosopher, political economist, politician and civil servant. One of the most influential thinkers in the history of liberalism and social liberalism, he contributed widely to s ...
supported the idea of utilitarianism but he developed an idea into more detailed one. He believes that there exists a different levels of happiness. It is better to be a human being dissatisfied than a pig satisfied; better to be Socrates dissatisfied than a fool satisfied. And if the fool, or the pig, is of a different opinion, it is only because they only know their own side of the question.
Theory of rights
The theory of rights derives from the belief that people have certain rights as they are being born as human beings which must be respected. Hence, according to this theory, an ethical decision is one that considers the rights of others. On the other hand, a decision is unethical to the extent that it violates another personŌĆÖs rights. Generally, there are two categories of rights: (1) natural rights- rights that exist independently of any legal obligations, often known as human rights and (2) Legal rights and contractual rights- rights that are respected due to social agreement. Amongst natural rights, the right of truth is the most significant in the function of accounting. The clients who request financial statements have the right to be provided with truthful and accurate financial information in order to make choices in constructing financial strategies. This right enforces a moral obligation on the accountants to produce legitimate and objective/true financial statements. On the other hand, legal and contractual rights are well-regarded in the relationship between accountants and employers and between accountants and clients. These contractual relationships mean that employers and clients have a legal right to expect professional and competent service from the accountants.Accounting scandals
Enron
Enron
Enron Corporation was an American Energy development, energy, Commodity, commodities, and services company based in Houston, Texas. It was led by Kenneth Lay and developed in 1985 via a merger between Houston Natural Gas and InterNorth, both re ...
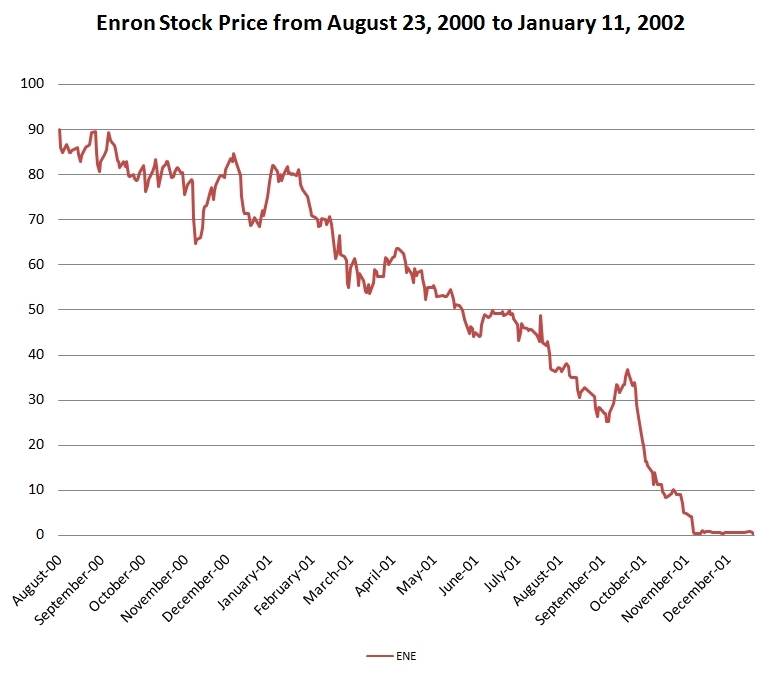
's bankruptcy in December 2001 provides a significant example of the issues of trust in accounting.
= Golden era of Enron
= In 1985, Enron was formed byKenneth Lay
Kenneth Lee Lay (April 15, 1942 ŌĆō July 5, 2006) was an American businessman and political donor who was the founder, chief executive officer and chairman of Enron. He was heavily involved in Enron scandal, Enron's accounting scandal that unr ...
merging the natural gas pipeline companies of Houston Natural Gas and InterNorth. From 1990s to 1998, Enron's stock increased 311% percent which was only slightly higher than the average growth. Then the stock increased by 56% in 1999 and a further 87% in 2000. By December 31, 2000, Enron's stock was valued at $83.13. In addition, Enron was rated the most innovative large company in America in ''Fortune''s Most Admired Companies survey.

= Downfall
= * August 22, 2001 ŌĆō Sherron Watkins gives Kenneth Lay a six-page letter further explaining Enron's accounting issues. * October 16, 2001 ŌĆō Enron announces a third quarter loss of $618 million. * October 31, 2001 ŌĆō The SEC opens a formal investigation into Enron's transactions. * November 9, 2001 ŌĆō Enron andDynegy
Dynegy Inc. is an electric company based in Houston, Texas. It owns and operates a number of power stations in the U.S., all of which are powered by fossil fuels. Dynegy was acquired by Vistra Corp on April 9, 2018. The company is located at 601 ...
announce the $7.8 billion merger agreement. It would form Dynegy Corp, in which Dynegy would own 64% and Enron 36%.
* November 28, 2001 ŌĆō Dynegy announces it has terminated merger talks with Enron.
* December 2, 2001 ŌĆō Enron files for Chapter 11 protection, becoming the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history at that time and leaves thousands of workers with worthless stock in their pensions.
See also
* Philosophy of Law * Philosophy of Economics *Utilitarianism
In ethical philosophy, utilitarianism is a family of normative ethical theories that prescribe actions that maximize happiness and well-being for the affected individuals. In other words, utilitarian ideas encourage actions that lead to the ...
* Ethics
Ethics is the philosophy, philosophical study of Morality, moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates Normativity, normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches inclu ...
* International Accounting Standard Board
* International Financial Reporting Standard
* Enron Scandal
The Enron scandal was an accounting scandal sparked by American energy company Enron, Enron Corporation filing for bankruptcy after news of widespread internal fraud became public in October 2001, which led to the dissolution of its accounting ...
* Technocrat
* Pragmatism
Pragmatism is a philosophical tradition that views language and thought as tools for prediction, problem solving, and action, rather than describing, representing, or mirroring reality. Pragmatists contend that most philosophical topicsŌĆ ...
* Jeremy Bentham
Jeremy Bentham (; 4 February Dual dating, 1747/8 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S. 5 February 1748 Old Style and New Style dates, N.S.ŌĆō 6 June 1832) was an English philosopher, jurist, and social reformer regarded as the founder of mo ...
* Human right
Human rights are universally recognized moral principles or norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both national and international laws. These rights are considered inherent and inalienable, meaning t ...
References
{{Library resources box , by=no , onlinebooks=no , others=no , about=yes , label=Accounting Accounting scholarship