Petrified Wood on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
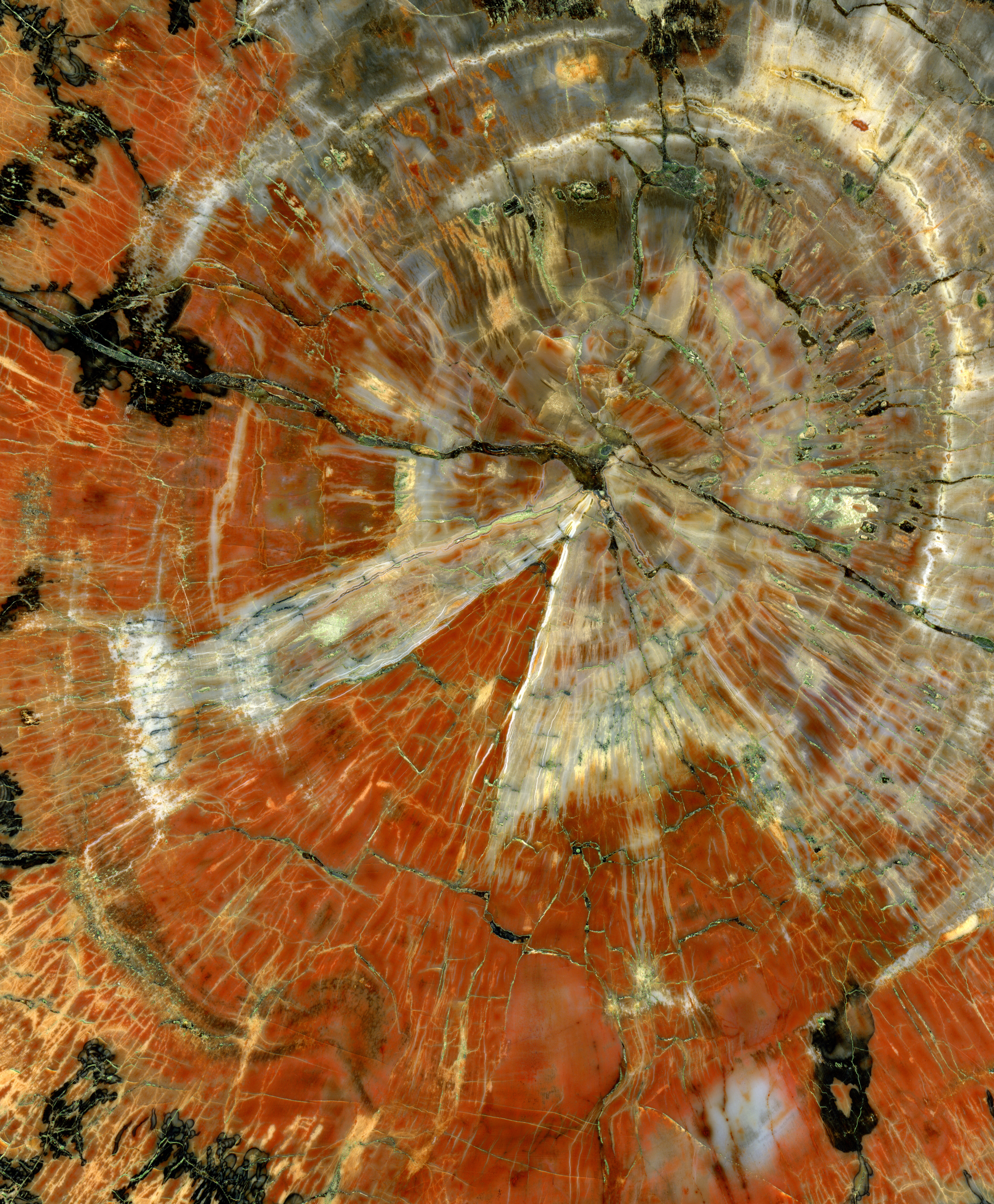 Petrified wood, also known as petrified tree (from
Petrified wood, also known as petrified tree (from
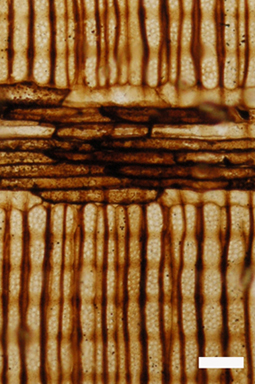

 Petrified wood forms when woody stems of plants are buried in wet sediments saturated with dissolved minerals. The lack of oxygen slows decay of the wood, allowing minerals to replace cell walls and to fill void spaces in the wood.
Wood is composed mostly of holocellulose (
Petrified wood forms when woody stems of plants are buried in wet sediments saturated with dissolved minerals. The lack of oxygen slows decay of the wood, allowing minerals to replace cell walls and to fill void spaces in the wood.
Wood is composed mostly of holocellulose (
 Petrified wood has limited use in jewelry, but is mostly used for decorative pieces such as book ends, table tops, clock faces, or other ornamental objects. A number of Ancestral Puebloan structures near
Petrified wood has limited use in jewelry, but is mostly used for decorative pieces such as book ends, table tops, clock faces, or other ornamental objects. A number of Ancestral Puebloan structures near

 * Egypt – petrified forest in Cairo-Suez road, declared a national protectorate by the ministry of environment, also in the area of
* Egypt – petrified forest in Cairo-Suez road, declared a national protectorate by the ministry of environment, also in the area of
 * Canada – in the
* Canada – in the 
The Petrified forest of Lesvos - Protected Natural Monument
The Mississippi Petrified Forest
Encyclopedia of recreation and leisure in America
{{DEFAULTSORT:Petrified Wood Paleobotany Fossil record of plants Quartz varieties Provincial symbols of Alberta Symbols of Arizona Symbols of Mississippi
 Petrified wood, also known as petrified tree (from
Petrified wood, also known as petrified tree (from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
meaning 'rock' or 'stone'; literally 'wood turned into stone'), is the name given to a special type of '' fossilized wood'', the fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
ized remains of terrestrial vegetation. '' Petrifaction'' is the result of a tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
or tree-like plants having been replaced by stone via a mineralization process that often includes permineralization and replacement. The organic materials making up cell walls have been replicated with mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s (mostly silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
in the form of opal
Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of silica (SiO2·''n''H2O); its water content may range from 3 to 21% by weight, but is usually between 6 and 10%. Due to its amorphous property, it is classified as a mineraloid, unlike crystalline form ...
, chalcedony
Chalcedony ( , or ) is a cryptocrystalline form of silica, composed of very fine intergrowths of quartz and moganite. These are both silica minerals, but they differ in that quartz has a trigonal crystal structure, while moganite is monocli ...
, or quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical f ...
). In some instances, the original structure of the stem tissue may be partially retained. Unlike other plant fossils, which are typically impressions or compressions, petrified wood is a three-dimensional representation of the original organic material.
The petrifaction process occurs underground, when wood becomes buried in water-saturated sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
or volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer ...
. The presence of water reduces the availability of oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
which inhibits aerobic decomposition by bacteria and fungi. Mineral-laden water flowing through the sediments may lead to permineralization, which occurs when minerals precipitate out of solution filling the interiors of cells and other empty spaces. During replacement, the plant's cell walls act as a template for mineralization. There needs to be a balance between the decay of cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wa ...
and lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity a ...
and mineral templating for cellular detail to be preserved with fidelity. Most of the organic matter often decomposes, however some of the lignin may remain. Silica in the form of opal-A, can encrust and permeate wood relatively quickly in hot spring environments. However, petrified wood is most commonly associated with trees that were buried in fine grained sediments of deltas and floodplains or volcanic lahar
A lahar (, from jv, ꦮ꧀ꦭꦲꦂ) is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a river valley.
Lahars are extr ...
s and ash beds. A forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
where such material has petrified becomes known as a petrified forest.
Formation


 Petrified wood forms when woody stems of plants are buried in wet sediments saturated with dissolved minerals. The lack of oxygen slows decay of the wood, allowing minerals to replace cell walls and to fill void spaces in the wood.
Wood is composed mostly of holocellulose (
Petrified wood forms when woody stems of plants are buried in wet sediments saturated with dissolved minerals. The lack of oxygen slows decay of the wood, allowing minerals to replace cell walls and to fill void spaces in the wood.
Wood is composed mostly of holocellulose (cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wa ...
and hemicellulose) and lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity a ...
. Together, these substances make up 95% of the dry composition of wood. Almost half of this is cellulose, which gives wood much of its strength. Cellulose is composed of long chains of polymerized glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
arranged into microfibrils that reinforce the cell walls in the wood. Hemicellulose, a branched polymer of various simple sugars, makes up the majority of the remaining composition of hardwood
Hardwood is wood from dicot trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen. Hardwood (which comes from ...
while lignin, which is a polymer of phenylpropanes, is more abundant in softwood
Scots Pine, a typical and well-known softwood
Softwood is wood from gymnosperm trees such as conifers. The term is opposed to hardwood, which is the wood from angiosperm trees. The main differences between hardwoods and softwoods is that the s ...
. The hemicellulose and lignin encrust and reinforce the cellulose microfibrils.
Dead wood is normally rapidly decomposed by microorganisms, beginning with the holocellulose. The lignin is hydrophobic (water-repelling) and much slower to decay. The rate of decay is affected by temperature and moisture content, but exclusion of oxygen is the most important factor preserving wood tissue: Organisms that decompose lignin must have oxygen for their life processes. As a result, fossil wood older than Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', ...
(about 56 million years old or older) has lost almost all its holocellulose, and only lignin remains. In addition to microbial decomposition, wood buried in an alkaline environment is rapidly broken down by inorganic reactions with the alkali.
Wood is preserved from decomposition by rapid entombment in mud, particularly mud formed from volcanic ash. The wood is then mineralized to transform it to stone. Non-mineralized wood has been recovered from Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ...
formations, particularly '' Callixylon'' from Berea Sandstone, but this is very unusual. The petrified wood is later exposed by erosion of surrounding sediments. Non-mineralized fossil wood is rapidly destroyed when exposed by erosion, but petrified wood is quite durable.
Some 40 minerals have been identified in petrified wood, but silica minerals are by far the most important. Calcite
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratc ...
and pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), lust ...
are much less common, and others are quite rare. Silica binds to the cellulose in cell walls via hydrogen bonding and forms a kind of template. Additional silica then replaces the cellulose as it decomposes, so that cell walls are often preserved in great detail. Thus silicification begins within the cell walls, and the spaces within and between cells are filled with silica more gradually. Over time, almost all the original organic material is lost; only around 10% remains in the petrified wood. The remaining material is nearly pure silica, with only iron, aluminum, and alkali and alkaline earth elements present in more than trace amounts. Iron, calcium, aluminum are the most common, and one or more of these elements may make up more than 1% of the composition.
Just what form the silica initially takes is still a topic of research. There is evidence of initial deposition as opal
Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of silica (SiO2·''n''H2O); its water content may range from 3 to 21% by weight, but is usually between 6 and 10%. Due to its amorphous property, it is classified as a mineraloid, unlike crystalline form ...
, which then recrystallizes to quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical f ...
over long time periods. On the other hand, there is some evidence that silica is deposited directly as quartz.
Wood can become silicified very rapidly in silica-rich hot springs. While wood petrified in this setting is only a minor part of the geologic record, hot spring deposits are important to paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
s because such deposits sometimes preserve more delicate plant parts in exquisite detail. These Lagerstätte
A Lagerstätte (, from '' Lager'' 'storage, lair' '' Stätte'' 'place'; plural ''Lagerstätten'') is a sedimentary deposit that exhibits extraordinary fossils with exceptional preservation—sometimes including preserved soft tissues. These f ...
deposits include the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ...
Rhynie Chert
The Rhynie chert is a Lower Devonian sedimentary deposit exhibiting extraordinary fossil detail or completeness (a Lagerstätte). It is exposed near the village of Rhynie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland; a second unit, the Windyfield chert, is located ...
and East Kirkton Limestone
The East Kirkton Limestone is a rock unit in the West Lothian Oil-Shale Formation in Scotland. It preserves fossils of the Carboniferous period. The limestone outcrops at East Kirkton Quarry.
See also
* '' Kirktonecta''
* List of fossiliferous ...
beds, which record early stages in the evolution of land plants.
Most of the color in petrified wood comes from trace metals. Of these, iron is the most important, and it can produce a range of hues depending on its oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. C ...
. Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hard ...
produces bright green petrified wood. Variations in color likely reflect different episodes of mineralization. In some cases, variations may come from chromatographic separation of trace metals.
Wood can also be petrified by calcite
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratc ...
, as occurs in concretions in coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
beds. Wood petrified by calcite tends to retain more of its original organic material. Petrification begins with deposition of goethite in the cell walls, followed by deposition of calcite in the void spaces. Carbonized wood is resistant to silicification and is usually petrified by other minerals. Wood petrified by minerals other than silica minerals tends to accumulate heavy metals, such as uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
, selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, ...
, and germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors ...
, with uranium most common in wood high in lignin and germanium most common in wood preserved in coal beds. Boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the '' boron group'' it has t ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, and phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
are anomalously low in fossil wood, suggesting they are leached away or scavenged by microorganisms.
Less commonly, the replacement minerals in petrified wood are chalcocite
Chalcocite (), copper(I) sulfide (Cu2S), is an important copper ore mineral. It is opaque and dark gray to black, with a metallic luster. It has a hardness of 2.5–3 on the Mohs scale. It is a sulfide with a monoclinic crystal system.
...
or other sulfide minerals
The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S2−) or disulfide (S22−) as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, ...
. These have been mined as copper ore at locations such as the Nacimiento Mine near Cuba, New Mexico.
Simulated petrified wood
Scientists have attempted to duplicate the process of petrification of wood, both to better understand the natural petrification process and for its possible use as a ceramic material. Early attempts used sodium metasilicate as a source of silica, but tetraethyl orthosilicate has proven more promising.Uses
 Petrified wood has limited use in jewelry, but is mostly used for decorative pieces such as book ends, table tops, clock faces, or other ornamental objects. A number of Ancestral Puebloan structures near
Petrified wood has limited use in jewelry, but is mostly used for decorative pieces such as book ends, table tops, clock faces, or other ornamental objects. A number of Ancestral Puebloan structures near Petrified Forest National Park
Petrified Forest National Park is an American national park in Navajo County, Arizona, Navajo and Apache County, Arizona, Apache counties in northeastern Arizona. Named for its large deposits of petrified wood, the park covers about , encompassin ...
were constructed of petrified wood, including the Agate House Pueblo. Petrified wood is also used in New Age healing.
Occurrences
Petrified wood is found worldwide in sedimentary beds ranging in age from theDevonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, wh ...
(about 390 million years ago), when woody plants first appeared on dry land, to nearly the present. Petrified "forests" tend to be either entire ecosystems buried by volcanic eruptions, in which trunks often remain in their growth positions, or accumulations of drift wood in fluvial environments. Amethyst Ridge at Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowst ...
shows 27 successive forest ecosystems buried by eruptions, while Petrified Forest National Park is a particularly fine example of fluvial accumulations of driftwood.
Volcanic ash is particularly suitable for preservation of wood, because large quantities of silica are released as the ash weathers. The presence of petrified wood in a sedimentary bed is often an indication of the presence of weathered volcanic ash. Petrified wood can also form in arkosic sediments, rich in feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) felds ...
and other minerals that release silica as they break down. The warm supermonsoon climates of the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferou ...
through Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
periods seem to have favored this process. Preservation of petrified forests in volcanic ash beds is less affected by climate and preserves a greater diversity of species.
Areas with a large number of petrified trees include:
Africa

 * Egypt – petrified forest in Cairo-Suez road, declared a national protectorate by the ministry of environment, also in the area of
* Egypt – petrified forest in Cairo-Suez road, declared a national protectorate by the ministry of environment, also in the area of New Cairo
New Cairo ( ar, القاهرة الجديدة ' is an Egyptian city covering an area of about on the southeastern edge of Cairo Governorate, 25 kilometres (15 mi) from Maadi. New Cairo is one of the new cities which have been built in ...
at the Extension of Nasr City
Nasr City ( ar, مدينة نصر ) is a district of Cairo, Egypt. It is located to the east of the Cairo Governorate and consists mostly of condominia. It was established in the 1960s as an extension to neighboring settlement of Heliopol ...
, El Qattamiyya, near El Maadi district, and Al Farafra oasis.
* Libya – Great Sand Sea – Hundreds of square miles of petrified trunks, branches and other debris mixed with Stone Age artifacts
* Madagascar – Northwest Coast
* Namibia – petrified forest of Damaraland
* Sudan – petrified forest north of El-Kurru
El-Kurru was the first of the three royal cemeteries used by the Kushite royals of Napata, also referred to as Egypt's 25th Dynasty, and is home to some of the royal Nubian Pyramids. It is located between the 3rd and 4th cataracts of the Nile ab ...
Asia
* China – in the Junggar Basin ofXinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
, northwest China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
government has issued a crackdown on collecting of this material.
* India – protected geological sites known for petrified wood are the National Fossil Wood Park, Tiruvakkarai (20-million-year-old fossils) and the Akal Wood Fossil Park (180-million-year-old fossils). Petrified wood has also been discovered in Dholavira
Dholavira ( gu, ધોળાવીરા) is an archaeological site at Khadirbet in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch District, in the state of Gujarat in western India, which has taken its name from a modern-day village south of it. This village is ...
in Kutch, Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, dating back to 187–176 million years.
* Japan - there is a fossilized forest preserved at Sendai City Tomizawa Site Museum
* Indonesia – petrified wood covers several area in Banten
Banten ( id, Banten; Sundanese: , romanized ''Banten'') is the westernmost province on the island of Java, Indonesia. Its capital city is Serang. The province borders West Java and the Special Capital Region of Jakarta on the east, the Ja ...
and also in some part of Mount Halimun Salak National Park.
* Israel – several examples of petrified wood occur in the HaMakhtesh HaGadol in the Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its sout ...
desert.
* Pakistan - Sindh - Dadu - Petrified Forest at Khirthar National Park
* Saudi Arabia – petrified forest north of Riyadh
* Thailand – Bantak Petrified Forest Park in Ban Tak District has the longest petrified log in the world, officially measuring 69.7 metres.
Oceania
* Australia – has deposits of petrified and opalized wood.Chinchilla, Queensland
Chinchilla is a rural town and locality in the Western Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , the locality of Chinchilla had a population of 6,612 people.
Chinchilla is known as the 'Melon Capital of Australia', and plays host to a Melo ...
is famous for its 'Chinchilla Red'.
* New Zealand:
** Curio Bay on The Catlins coast contains many petrified wood examples.
** Fossil Forest, Takapuna, Auckland, New Zealand
Europe
* Belgium – Geosite Goudberg near Hoegaarden. * Czech Republic,Nová Paka
Nová Paka (, german: Neupaka) is a town in Jičín District in the Hradec Králové Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 8,900 inhabitants.
Administrative parts
Villages of Heřmanice, Kumburský Újezd, Podlevín, Přibyslav, Pustá Prose ...
– The most famous locality on Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
–Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferou ...
rocks in the Czech Republic.
* France – petrified forest in the village of Champclauson
* Georgia – Goderdzi Petrified Forest Natural Monument.
* Germany – the museum of natural history in Chemnitz
Chemnitz (; from 1953 to 1990: Karl-Marx-Stadt , ) is the third-largest city in the German state of Saxony after Leipzig and Dresden. It is the 28th largest city of Germany as well as the fourth largest city in the area of former East Germany ...
has a collection of petrified trees, from the in situ Chemnitz petrified forest, found in the town in 1737.
* Greece – Petrified forest of Lesvos, at the western tip of the island of Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( el, Λέσβος, Lésvos ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece. It is separated from Asia Minor by the nar ...
, is possibly the largest of the petrified forests, covering an area of over and declared a National Monument in 1985. Large, upright trunks complete with root systems can be found, as well as trunks up to 22 m in length.
* Italy:
** , petrified forest near Avigliano Umbro, Umbria
it, Umbro (man) it, Umbra (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, ...
(Central Italy), age Piacenzian
The Piacenzian is in the international geologic time scale the upper stage or latest age of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 3.6 ± 0.005 Ma and 2.588 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). The Piacenzian is after the Zanclean and is followed ...
.
** , petrified forest near Soddì ( Province of Oristano, Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
), age Chattian
The Chattian is, in the geologic timescale, the younger of two ages or upper of two stages of the Oligocene Epoch/Series. It spans the time between . The Chattian is preceded by the Rupelian and is followed by the Aquitanian (the lowest stage ...
– Aquitanian.
* Norway-Fossilized Tropical Forest in Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group rang ...
*Ukraine – petrified araucaria
''Araucaria'' (; original pronunciation: .ɾawˈka. ɾja is a genus of evergreen coniferous trees in the family Araucariaceae. There are 20 extant species in New Caledonia (where 14 species are endemic, see New Caledonian ''Araucaria ...
trunks near Druzhkivka
Druzhkivka ( uk, Дружківка, ; russian: Дружковка, Druzhkovka) is a city of oblast significance in Donetsk Oblast (province) of Ukraine. Population: ; 64,557 (2001). The area of the city is 46 km².
Druzhkivka is a city lo ...
* United Kingdom
** Fossil Grove, Glasgow, Scotland
** Fossil Forest, Dorset, England
North America
 * Canada – in the
* Canada – in the badlands
Badlands are a type of dry terrain where softer sedimentary rocks and clay-rich soils have been extensively eroded."Badlands" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 2, p. 47. They are characterized by steep slopes, mi ...
of southern Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest T ...
; petrified wood is the provincial stone of Alberta. Axel Heiberg Island
Axel Heiberg Island ( iu, ᐅᒥᖕᒪᑦ ᓄᓈᑦ, ) is an uninhabited island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located in the Arctic Ocean, it is the 32nd largest island in the world and Canada's seventh largest island. Accordin ...
in Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the '' Nunavut Act'' and the '' Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act'' ...
has a large petrified forest. In and around the North Saskatchewan river, around the Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city an ...
area. Blanche Brook, in Stephenville, Newfoundland, has 305-million-year-old examples.
* United States – petrified wood sites include:
** Petrified Wood Park in Lemmon, South Dakota
Lemmon is a town in Perkins County, South Dakota, United States. The population was 1,160 at the 2020 census.
Lemmon is named after George Ed Lemmon, a cattleman, who founded the town in 1906.
The City of Lemmon received the South Dakota Commu ...
** Ginkgo/Wanapum State Park
Ginkgo Petrified Forest State Park/Wanapum Recreational Area is a geologic preserve and public recreation area covering on the western shoreline of the Columbia River's Wanapum Reservoir at Vantage, Washington. Petrified wood was discovered in ...
in Washington state
Washington (), officially the State of Washington, is a U.S. state, state in the Northwestern United States, Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. Named for George Washington—the first President of the United States, U.S. p ...
** Petrified Forest National Park
Petrified Forest National Park is an American national park in Navajo County, Arizona, Navajo and Apache County, Arizona, Apache counties in northeastern Arizona. Named for its large deposits of petrified wood, the park covers about , encompassin ...
in Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
** Petrified Forest
Petrified wood, also known as petrified tree (from Ancient Greek meaning 'rock' or 'stone'; literally 'wood turned into stone'), is the name given to a special type of '' fossilized wood'', the fossilized remains of terrestrial vegetation. ...
in California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
** Mississippi Petrified Forest in Flora, Mississippi
** Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument near Florissant, Colorado
** Yellowstone Petrified Forest and Gallatin Petrified Forest, Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowst ...
, Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to t ...
** The south unit of Theodore Roosevelt National Park
Theodore Roosevelt National Park is an American national park of the badlands in western North Dakota comprising three geographically separated areas. Honoring U.S. President Theodore Roosevelt, it is the only American national park named direc ...
outside Medora, North Dakota
Medora is a city in Billings County, North Dakota, United States. The only incorporated place in Billings County, it is also the county seat. Much of the surrounding area is part of either Little Missouri National Grassland or Theodore Rooseve ...
** Gilboa Fossil Forest in New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
** Black Hills Petrified Forest in South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large po ...
** Escalante Petrified Forest State Park in Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its ...
** Agate Desert in the Upper Rogue River Valley near Medford, Oregon
Medford is a city in and the county seat of Jackson County, Oregon, in the United States. As of the 2020 United States Census on April 1, 2020, the city had a total population of 85,824 and a metropolitan area population of 223,259, making the Me ...
** Fossil Forest in the Catskill region near Cairo, New York
Cairo is a town in Greene County, New York, United States. The population was 6,644 at the 2020 census. The town is in the southern part of the county, partly in the Catskill Park. The town contains a hamlet, also named Cairo.
History
The fi ...
** Valley of Fire State Park
Valley of Fire State Park is a public recreation and nature preservation area covering nearly located south of Overton, Nevada. The state park derives its name from red sandstone formations, the Aztec Sandstone, which formed from shifting s ...
in Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
** Bisti Badlands in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
South America
* Argentina – the Sarmiento Petrified Forest and Jaramillo Petrified Forest in Santa Cruz Province in the ArgentinePatagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and g ...
have many trees that measure more than in diameter and long.
* Brazil:
** in the geopark
A geopark is a protected area with internationally significant geology within which sustainable development is sought and which includes tourism, conservation, education and research concerning not just geology but other relevant sciences.
In 20 ...
of Paleorrota, there is a vast area with petrified trees.
** In the Heritage forest
** ('Fossil Trees Natural Monument') in Tocantins
Tocantins () is one of the 26 states of Brazil. It is the newest state, formed in 1988 and encompassing what had formerly been the northern two-fifths of the state of Goiás. Tocantins covers and had an estimated population of 1,496,880 in 20 ...
: petrified forests of dicksoniaceae (specifically '' Psaronius'' and '' Tietea singularis'') and arthropitys
** Petrified forests of dicksoniaceae (specifically ''Psaronius'' and ''Tietea singularis'') and arthropitys can also be found in the state of São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaW ...
** near Rio Poti, Piauí
Piaui (, ) is one of the states of Brazil, located in the country's Northeast Region. The state has 1.6% of the Brazilian population and produces 0.7% of the Brazilian GDP.
Piaui has the shortest coastline of any coastal Brazilian state at 66& ...
, Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
(around 280–270 million years ago).
* Ecuador – Puyango Petrified Forest – One of the largest collections of petrified wood in the world.
See also
*Amethyst Mountain
Amethyst Mountain, el. is the highest peak and central part of a northwest – southeast trending ridge that lies between the Lamar River to the northeast and Deep Creek to the southwest within Park County, Wyoming. From northwest to southeast, ...
* ''Araucarioxylon arizonicum
''Araucarioxylon arizonicum'' is an extinct species of conifer that is the state fossil of Arizona. The species is known from massive tree trunks that weather out of the Chinle Formation in desert badlands of northern Arizona and adjacent Ne ...
''
* Fossil wood
* Jet (lignite)
* '' Palmoxylon'' (petrified palmwood)
* Submerged forest
A submerged forest is the ''in situ'' remains of trees, especially tree stumps, that lie submerged beneath a bay, sea, ocean, lake, or other body of water. These remains have usually been buried in mud, peat, or sand for several thousand years b ...
* Wood opal
Wood opal is a form of petrified wood which has developed an opalescent sheen or, more rarely, where the wood has been completely replaced by opal. Other names for this opalized sheen-like wood are opalized wood and opalized petrified wood. It is ...
References
External links
The Petrified forest of Lesvos - Protected Natural Monument
The Mississippi Petrified Forest
Encyclopedia of recreation and leisure in America
{{DEFAULTSORT:Petrified Wood Paleobotany Fossil record of plants Quartz varieties Provincial symbols of Alberta Symbols of Arizona Symbols of Mississippi