Peter I Of Russia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the
 This arrangement was brought before the people of Moscow, as ancient tradition demanded, and was ratified. Sophia, one of Alexis' daughters from his first marriage, led a rebellion of the Streltsy (Russia's elite military corps) in April–May 1682. In the subsequent conflict, some of Peter's relatives and friends were murdered, including Matveev, and Peter witnessed some of these acts of political violence.
The Streltsy made it possible for Sophia, the Miloslavskys (the clan of
This arrangement was brought before the people of Moscow, as ancient tradition demanded, and was ratified. Sophia, one of Alexis' daughters from his first marriage, led a rebellion of the Streltsy (Russia's elite military corps) in April–May 1682. In the subsequent conflict, some of Peter's relatives and friends were murdered, including Matveev, and Peter witnessed some of these acts of political violence.
The Streltsy made it possible for Sophia, the Miloslavskys (the clan of  Still, Peter could not acquire actual control over Russian affairs. Power was instead exercised by his mother, Natalya Naryshkina. It was only when Natalya died in 1694 that Peter, then aged 22, became an independent sovereign. Formally, Ivan V was a co-ruler with Peter, though being ineffective. Peter became the sole ruler when Ivan died in 1696 without male offspring, two years later.
Peter grew to be extremely tall as an adult, especially for the time period, reportedly standing . Peter, however, lacked the overall proportional heft and bulk generally found in a man that size. Both his hands and feet were small, and his shoulders were narrow for his height; likewise, his head was small for his tall body. Added to this were Peter's noticeable facial tics, and he may have suffered from '' petit mal seizures'', a form of epilepsy.
During his youth, Peter befriended
Still, Peter could not acquire actual control over Russian affairs. Power was instead exercised by his mother, Natalya Naryshkina. It was only when Natalya died in 1694 that Peter, then aged 22, became an independent sovereign. Formally, Ivan V was a co-ruler with Peter, though being ineffective. Peter became the sole ruler when Ivan died in 1696 without male offspring, two years later.
Peter grew to be extremely tall as an adult, especially for the time period, reportedly standing . Peter, however, lacked the overall proportional heft and bulk generally found in a man that size. Both his hands and feet were small, and his shoulders were narrow for his height; likewise, his head was small for his tall body. Added to this were Peter's noticeable facial tics, and he may have suffered from '' petit mal seizures'', a form of epilepsy.
During his youth, Peter befriended
 Peter implemented sweeping
Peter implemented sweeping
 Peter knew that Russia could not face the Ottoman Empire alone. In 1697, he traveled "incognito" to Western Europe on an 18-month journey with a large Russian delegation–the so-called "Grand Embassy". He used a fake name, allowing him to escape social and diplomatic events, but since he was far taller than most others, he did not fool anyone of importance. One goal was to seek the aid of European monarchs, but Peter's hopes were dashed. France was a traditional ally of the Ottoman Sultan, and
Peter knew that Russia could not face the Ottoman Empire alone. In 1697, he traveled "incognito" to Western Europe on an 18-month journey with a large Russian delegation–the so-called "Grand Embassy". He used a fake name, allowing him to escape social and diplomatic events, but since he was far taller than most others, he did not fool anyone of importance. One goal was to seek the aid of European monarchs, but Peter's hopes were dashed. France was a traditional ally of the Ottoman Sultan, and  In England, Peter met with King William III, visited
In England, Peter met with King William III, visited
 Russia was ill-prepared to fight the Swedes, and their first attempt at seizing the Baltic coast ended in disaster at the Battle of Narva in 1700. In the conflict, the forces of Charles XII, rather than employ a slow methodical siege, attacked immediately using a blinding snowstorm to their advantage. After the battle, Charles XII decided to concentrate his forces against the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which gave Peter time to reorganize the Russian army.
While the Poles fought the Swedes, Peter founded the city of
Russia was ill-prepared to fight the Swedes, and their first attempt at seizing the Baltic coast ended in disaster at the Battle of Narva in 1700. In the conflict, the forces of Charles XII, rather than employ a slow methodical siege, attacked immediately using a blinding snowstorm to their advantage. After the battle, Charles XII decided to concentrate his forces against the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which gave Peter time to reorganize the Russian army.
While the Poles fought the Swedes, Peter founded the city of  Following several defeats, Polish King
Following several defeats, Polish King  Peter, overestimating the support he would receive from his Balkan allies, attacked the Ottoman Empire, initiating the Russo-Turkish War of 1710. Peter's campaign in the Ottoman Empire was disastrous, and in the ensuing
Peter, overestimating the support he would receive from his Balkan allies, attacked the Ottoman Empire, initiating the Russo-Turkish War of 1710. Peter's campaign in the Ottoman Empire was disastrous, and in the ensuing  Peter's northern armies took the Swedish province of
Peter's northern armies took the Swedish province of
 Peter's last years were marked by further reform in Russia. On 22 October 1721, soon after peace was made with Sweden, he was officially proclaimed ''Emperor of All Russia''. Some proposed that he take the title ''Emperor of the East'', but he refused. Gavrila Golovkin, the State Chancellor, was the first to add "the Great, Father of His Country, Emperor of All the Russias" to Peter's traditional title Tsar following a speech by the archbishop of Pskov in 1721. Peter's imperial title was recognized by Augustus II of Poland, Frederick William I of Prussia, and Frederick I of Sweden, but not by the other European monarchs. In the minds of many, the word ''emperor'' connoted superiority or pre-eminence over kings. Several rulers feared that Peter would claim authority over them, just as the Holy Roman Emperor had claimed suzerainty over all Christian nations.
In 1717, Alexander Bekovich-Cherkassky led the first Russian military expedition into Central Asia against the Khanate of Khiva. The expedition ended in complete disaster when the entire expeditionary force was slaughtered.
In 1718, Peter investigated why the formerly Swedish province of Livonia was so orderly. He discovered that the Swedes spent as much administering Livonia (300 times smaller than his empire) as he spent on the entire Russian bureaucracy. He was forced to dismantle the province's government.
Peter's last years were marked by further reform in Russia. On 22 October 1721, soon after peace was made with Sweden, he was officially proclaimed ''Emperor of All Russia''. Some proposed that he take the title ''Emperor of the East'', but he refused. Gavrila Golovkin, the State Chancellor, was the first to add "the Great, Father of His Country, Emperor of All the Russias" to Peter's traditional title Tsar following a speech by the archbishop of Pskov in 1721. Peter's imperial title was recognized by Augustus II of Poland, Frederick William I of Prussia, and Frederick I of Sweden, but not by the other European monarchs. In the minds of many, the word ''emperor'' connoted superiority or pre-eminence over kings. Several rulers feared that Peter would claim authority over them, just as the Holy Roman Emperor had claimed suzerainty over all Christian nations.
In 1717, Alexander Bekovich-Cherkassky led the first Russian military expedition into Central Asia against the Khanate of Khiva. The expedition ended in complete disaster when the entire expeditionary force was slaughtered.
In 1718, Peter investigated why the formerly Swedish province of Livonia was so orderly. He discovered that the Swedes spent as much administering Livonia (300 times smaller than his empire) as he spent on the entire Russian bureaucracy. He was forced to dismantle the province's government.
 After 1718, Peter established colleges in place of the old central agencies of government, including foreign affairs, war, navy, expense, income, justice, and inspection. Later others were added. Each college consisted of a president, a vice-president, a number of councilors and assessors, and a procurator. Some foreigners were included in various colleges but not as president. Peter believed he did not have enough loyal and talented persons to put in full charge of the various departments. Peter preferred to rely on groups of individuals who would keep check on one another. Decisions depended on the majority vote.
In 1722, Peter created a new order of precedence known as the Table of Ranks. Formerly, precedence had been determined by birth. To deprive the Boyars of their high positions, Peter directed that precedence should be determined by merit and service to the Emperor. The Table of Ranks continued to remain in effect until the Russian monarchy was February Revolution, overthrown in 1917.
Peter decided that all of the children of the nobility should have some early education, especially in the areas of sciences. Therefore, on 28 February 1714, he issued a decree calling for compulsory education, which dictated that all Russian 10- to 15-year-old children of the nobility, government clerks, and lesser-ranked officials must learn basic mathematics and geometry, and should be tested on the subjects at the end of their studies.
The once powerful Persian Safavid Empire to the south was in deep decline. Taking advantage of the profitable situation, Peter launched the Russo-Persian War (1722-1723), Russo-Persian War of 1722–1723, otherwise known as "The Persian Expedition of Peter the Great", which drastically increased Russian influence for the first time in the Caucasus and
After 1718, Peter established colleges in place of the old central agencies of government, including foreign affairs, war, navy, expense, income, justice, and inspection. Later others were added. Each college consisted of a president, a vice-president, a number of councilors and assessors, and a procurator. Some foreigners were included in various colleges but not as president. Peter believed he did not have enough loyal and talented persons to put in full charge of the various departments. Peter preferred to rely on groups of individuals who would keep check on one another. Decisions depended on the majority vote.
In 1722, Peter created a new order of precedence known as the Table of Ranks. Formerly, precedence had been determined by birth. To deprive the Boyars of their high positions, Peter directed that precedence should be determined by merit and service to the Emperor. The Table of Ranks continued to remain in effect until the Russian monarchy was February Revolution, overthrown in 1917.
Peter decided that all of the children of the nobility should have some early education, especially in the areas of sciences. Therefore, on 28 February 1714, he issued a decree calling for compulsory education, which dictated that all Russian 10- to 15-year-old children of the nobility, government clerks, and lesser-ranked officials must learn basic mathematics and geometry, and should be tested on the subjects at the end of their studies.
The once powerful Persian Safavid Empire to the south was in deep decline. Taking advantage of the profitable situation, Peter launched the Russo-Persian War (1722-1723), Russo-Persian War of 1722–1723, otherwise known as "The Persian Expedition of Peter the Great", which drastically increased Russian influence for the first time in the Caucasus and
 In the winter of 1723, Peter, whose overall health was never robust, began having problems with his urinary tract and Urinary bladder, bladder. In the summer of 1724, a team of doctors performed surgery releasing upwards of four pounds of blocked urine. Peter remained bedridden until late autumn. In the first week of October, restless and certain he was cured, Peter began a lengthy inspection tour of various projects. According to legend, in November, at Lakhta, Saint Petersburg, Lakhta along the Finnish Gulf to inspect some ironworks, Peter saw a group of soldiers drowning near shore and, wading out into near-waist deep water, came to their rescue.
This icy water rescue is said to have exacerbated Peter's bladder problems and caused his death. The story, however, has been viewed with skepticism by some historians, pointing out that the German chronicler Jacob von Staehlin is the only source for the story, and it seems unlikely that no one else would have documented such an act of heroism. This, plus the interval of time between these actions and Peter's death seems to preclude any direct link.
In early January 1725, Peter was struck once again with uremia. Legend has it that before lapsing into unconsciousness Peter asked for a paper and pen and scrawled an unfinished note that read: ''"Leave all to ..."'' and then, exhausted by the effort, asked for his daughter Anna to be summoned.
Peter died between four and five in the morning 8 February 1725. An autopsy revealed his bladder to be infected with gangrene. He was fifty-two years, seven months old when he died, having reigned forty-two years. He is interred in Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral, Saint Petersburg, Russia.
In the winter of 1723, Peter, whose overall health was never robust, began having problems with his urinary tract and Urinary bladder, bladder. In the summer of 1724, a team of doctors performed surgery releasing upwards of four pounds of blocked urine. Peter remained bedridden until late autumn. In the first week of October, restless and certain he was cured, Peter began a lengthy inspection tour of various projects. According to legend, in November, at Lakhta, Saint Petersburg, Lakhta along the Finnish Gulf to inspect some ironworks, Peter saw a group of soldiers drowning near shore and, wading out into near-waist deep water, came to their rescue.
This icy water rescue is said to have exacerbated Peter's bladder problems and caused his death. The story, however, has been viewed with skepticism by some historians, pointing out that the German chronicler Jacob von Staehlin is the only source for the story, and it seems unlikely that no one else would have documented such an act of heroism. This, plus the interval of time between these actions and Peter's death seems to preclude any direct link.
In early January 1725, Peter was struck once again with uremia. Legend has it that before lapsing into unconsciousness Peter asked for a paper and pen and scrawled an unfinished note that read: ''"Leave all to ..."'' and then, exhausted by the effort, asked for his daughter Anna to be summoned.
Peter died between four and five in the morning 8 February 1725. An autopsy revealed his bladder to be infected with gangrene. He was fifty-two years, seven months old when he died, having reigned forty-two years. He is interred in Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral, Saint Petersburg, Russia.
 Peter founded The All-Joking, All-Drunken Synod of Fools and Jesters, an organization that mocked the Orthodox and Catholic Church when he was eighteen. In January 1695, Peter refused to partake in a traditional Russian Orthodox ceremony of the Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany Ceremony, and would often schedule events for The All-Joking, All-Drunken Synod of Fools and Jesters to directly conflict with the Church.
Peter was brought up in the Russian Orthodox faith, but he had low regard for the Church hierarchy, which he kept under tight governmental control. The traditional leader of the Church was the List of Metropolitans and Patriarchs of Moscow, Patriarch of Moscow. In 1700, when the office fell vacant, Peter refused to name a replacement, allowing the Patriarch's Coadjutor (or deputy) to discharge the duties of the office. Peter could not tolerate the patriarch exercising power superior to the Tsar, as indeed had happened in the case of Patriarch Philaret of Moscow, Philaret (1619–1633) and Patriarch Nikon of Moscow, Nikon (1652–66). The Church reform of Peter the Great therefore abolished the Patriarchate, replacing it with a Holy Synod that was under the control of a Procurator_(Russia), Procurator, and the Tsar appointed all bishops.
In 1721, Peter followed the advice of Theophan Prokopovich in designing the Holy Synod as a council of ten clergymen. For leadership in the church, Peter turned increasingly to Ukrainians, who were more open to reform, but were not well loved by the Russian clergy. Peter implemented a law that stipulated that no Russian man could join a monastery before the age of fifty. He felt that too many able Russian men were being wasted on clerical work when they could be joining his new and improved army.
A clerical career was not a route chosen by upper-class society. Most parish priests were sons of priests and were very poorly educated and paid. The monks in the monasteries had a slightly higher status; they were not allowed to marry. Politically, the church was impotent.
Peter founded The All-Joking, All-Drunken Synod of Fools and Jesters, an organization that mocked the Orthodox and Catholic Church when he was eighteen. In January 1695, Peter refused to partake in a traditional Russian Orthodox ceremony of the Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany Ceremony, and would often schedule events for The All-Joking, All-Drunken Synod of Fools and Jesters to directly conflict with the Church.
Peter was brought up in the Russian Orthodox faith, but he had low regard for the Church hierarchy, which he kept under tight governmental control. The traditional leader of the Church was the List of Metropolitans and Patriarchs of Moscow, Patriarch of Moscow. In 1700, when the office fell vacant, Peter refused to name a replacement, allowing the Patriarch's Coadjutor (or deputy) to discharge the duties of the office. Peter could not tolerate the patriarch exercising power superior to the Tsar, as indeed had happened in the case of Patriarch Philaret of Moscow, Philaret (1619–1633) and Patriarch Nikon of Moscow, Nikon (1652–66). The Church reform of Peter the Great therefore abolished the Patriarchate, replacing it with a Holy Synod that was under the control of a Procurator_(Russia), Procurator, and the Tsar appointed all bishops.
In 1721, Peter followed the advice of Theophan Prokopovich in designing the Holy Synod as a council of ten clergymen. For leadership in the church, Peter turned increasingly to Ukrainians, who were more open to reform, but were not well loved by the Russian clergy. Peter implemented a law that stipulated that no Russian man could join a monastery before the age of fifty. He felt that too many able Russian men were being wasted on clerical work when they could be joining his new and improved army.
A clerical career was not a route chosen by upper-class society. Most parish priests were sons of priests and were very poorly educated and paid. The monks in the monasteries had a slightly higher status; they were not allowed to marry. Politically, the church was impotent.
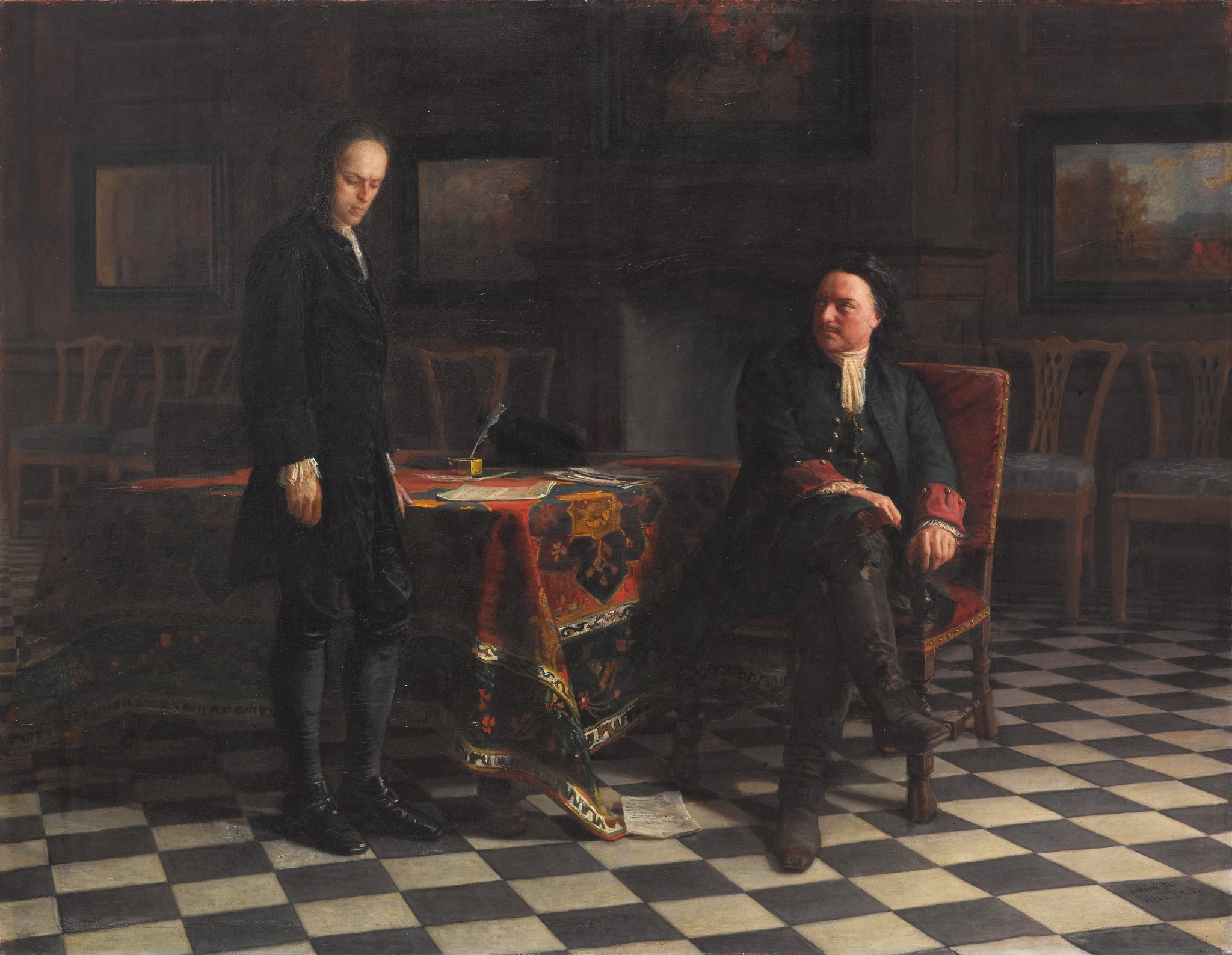 Peter the Great had two wives, with whom he had fourteen children, three of whom survived to adulthood. Peter's mother selected his first wife,
Peter the Great had two wives, with whom he had fourteen children, three of whom survived to adulthood. Peter's mother selected his first wife,
 Peter's legacy has always been a major concern of Russian intellectuals. Riasanovsky points to a "paradoxical dichotomy" in the black and white images such as God/Antichrist, educator/ignoramus, architect of Russia's greatness/destroyer of national culture, father of his country/scourge of the common man. Voltaire's 1759 biography gave 18th-century Russians a man of the Enlightenment, while Alexander Pushkin's "The Bronze Horseman (poem), The Bronze Horseman" poem of 1833 gave a powerful romantic image of a creator-god. Slavophiles in mid-19th century deplored Peter's westernization of Russia. Western writers and political analysts recounted "The Testimony" or secret will of Peter the Great. It supposedly revealed his grand evil plot for Russia to control the world via conquest of Constantinople, Afghanistan and India. It was a forgery made in Paris at Napoleon's command when he started his invasion of Russia in 1812. Nevertheless, it is still quoted in foreign policy circles. The Communists executed the last Romanovs, and their historians such as Mikhail Pokrovsky presented strongly negative views of the entire dynasty. Stalin however admired how Peter strengthened the state, and wartime, diplomacy, industry, higher education, and government administration. Stalin wrote in 1928, "when Peter the Great, who had to deal with more developed countries in the West, feverishly built works in factories for supplying the army and strengthening the country's defenses, this was an original attempt to leap out of the framework of backwardness." As a result, Soviet historiography emphasizes both the positive achievement and the negative factor of oppressing the common people.
After the fall of Communism in 1991, scholars and the general public in Russia and the West gave fresh attention to Peter and his role in Russian history. His reign is now seen as the decisive formative event in the Russian imperial past. Many new ideas have merged, such as whether he strengthened the autocratic state or whether the tsarist regime was not statist enough given its small bureaucracy. Modernization models have become contested ground. Historian Ia. Vodarsky said in 1993 that Peter, "did not lead the country on the path of accelerated economic, political and social development, did not force it to 'achieve a leap' through several stages.... On the contrary, these actions to the greatest degree put a brake on Russia's progress and created conditions for holding it back for one and a half centuries!" The autocratic powers that Stalin admired appeared as a liability to Evgeny Anisimov, who complained that Peter was, "the creator of the administrative command system and the true ancestor of Stalin."
According to ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'', "He did not completely bridge the gulf between Russia and the Western countries, but he achieved considerable progress in development of the national economy and trade, education, science and culture, and foreign policy. Russia became a great power, without whose concurrence no important European problem could thenceforth be settled. His internal reforms achieved progress to an extent that no earlier innovator could have envisaged."
While the cultural turn in historiography has downplayed diplomatic, economic and constitutional issues, new cultural roles have been found for Peter, for example in architecture and dress. James Cracraft argues:
:The Petrine revolution in Russia—subsuming in this phrase the many military, naval, governmental, educational, architectural, linguistic, and other internal reforms enacted by Peter’s regime to promote Russia’s rise as a major European power—was essentially a cultural revolution, one that profoundly impacted both the basic constitution of the Russian Empire and, perforce, its subsequent development.
Peter's legacy has always been a major concern of Russian intellectuals. Riasanovsky points to a "paradoxical dichotomy" in the black and white images such as God/Antichrist, educator/ignoramus, architect of Russia's greatness/destroyer of national culture, father of his country/scourge of the common man. Voltaire's 1759 biography gave 18th-century Russians a man of the Enlightenment, while Alexander Pushkin's "The Bronze Horseman (poem), The Bronze Horseman" poem of 1833 gave a powerful romantic image of a creator-god. Slavophiles in mid-19th century deplored Peter's westernization of Russia. Western writers and political analysts recounted "The Testimony" or secret will of Peter the Great. It supposedly revealed his grand evil plot for Russia to control the world via conquest of Constantinople, Afghanistan and India. It was a forgery made in Paris at Napoleon's command when he started his invasion of Russia in 1812. Nevertheless, it is still quoted in foreign policy circles. The Communists executed the last Romanovs, and their historians such as Mikhail Pokrovsky presented strongly negative views of the entire dynasty. Stalin however admired how Peter strengthened the state, and wartime, diplomacy, industry, higher education, and government administration. Stalin wrote in 1928, "when Peter the Great, who had to deal with more developed countries in the West, feverishly built works in factories for supplying the army and strengthening the country's defenses, this was an original attempt to leap out of the framework of backwardness." As a result, Soviet historiography emphasizes both the positive achievement and the negative factor of oppressing the common people.
After the fall of Communism in 1991, scholars and the general public in Russia and the West gave fresh attention to Peter and his role in Russian history. His reign is now seen as the decisive formative event in the Russian imperial past. Many new ideas have merged, such as whether he strengthened the autocratic state or whether the tsarist regime was not statist enough given its small bureaucracy. Modernization models have become contested ground. Historian Ia. Vodarsky said in 1993 that Peter, "did not lead the country on the path of accelerated economic, political and social development, did not force it to 'achieve a leap' through several stages.... On the contrary, these actions to the greatest degree put a brake on Russia's progress and created conditions for holding it back for one and a half centuries!" The autocratic powers that Stalin admired appeared as a liability to Evgeny Anisimov, who complained that Peter was, "the creator of the administrative command system and the true ancestor of Stalin."
According to ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'', "He did not completely bridge the gulf between Russia and the Western countries, but he achieved considerable progress in development of the national economy and trade, education, science and culture, and foreign policy. Russia became a great power, without whose concurrence no important European problem could thenceforth be settled. His internal reforms achieved progress to an extent that no earlier innovator could have envisaged."
While the cultural turn in historiography has downplayed diplomatic, economic and constitutional issues, new cultural roles have been found for Peter, for example in architecture and dress. James Cracraft argues:
:The Petrine revolution in Russia—subsuming in this phrase the many military, naval, governmental, educational, architectural, linguistic, and other internal reforms enacted by Peter’s regime to promote Russia’s rise as a major European power—was essentially a cultural revolution, one that profoundly impacted both the basic constitution of the Russian Empire and, perforce, its subsequent development.
Civilization 6 Leader and Civilization Breakdown - Montezuma to Shaka
GameRant. Retrieved 15 December 2020.
online
* * * * *
online
* * * * , a popular biography
online
* * * * * *
online
* * * ; Historiography and memory * Brown, Peter B. "Towards a Psychohistory of Peter the Great: Trauma, Modeling, and Coping in Peter's Personality." ''Russian History'' 35#1-2 (2008): 19–44. * Brown, Peter B. "Gazing Anew at Poltava: Perspectives from the Military Revolution Controversy, Comparative History, and Decision-Making Doctrines." ''Harvard Ukrainian Studies'' 31.1/4 (2009): 107–133
online
* Cracraft, James. "Kliuchevskii on Peter the Great." ''Canadian-American Slavic Studies'' 20.4 (1986): 367–381. * Daqiu, Zhu. "Cultural Memory and the Image of Peter the Great in Russian Literature." ''Russian Literature & Arts'' 2 (2014): 19+. * Gasiorowska, Xenia. ''The image of Peter the Great in Russian fiction'' (1979
online
* Platt, Kevin M. F. ''Terror and Greatness: Ivan and Peter as Russian Myths'' (2011) * Raef, Mark, ed. ''Peter the Great, Reformer or Revolutionary?'' (1963) excerpts from scholars and primary source
online
* Resis, Albert. "Russophobia and the" Testament" of Peter the Great, 1812–1980." ''Slavic Review'' 44.4 (1985): 681-69
online
* Riasanovsky, Nicholas V. ''The Image of Peter the Great in Russian History and Thought'' (1985). * Waugh, Daniel Clarke. "We have never been modern: Approaches to the study of Russia in the age of Peter the Great." ''Jahrbücher für Geschichte Osteuropas H.'' 3 (2001): 321-34
online in English
* * Zitser, Ernest A. "The Difference that Peter I Made." in ''The Oxford Handbook of Modern Russian History.'' ed. by Simon Dixon (2013
online
online
* * Bushkovitch, Paul. ''Peter the Great: The Struggle for Power, 1671–1725'' (2001
online
* Cracraft, James. ''The Revolution of Peter the Great'' (2003
online
* Duffy, Christopher. ''Russia's Military Way to the West: Origins and Nature of Russian Military Power 1700-1800'' (Routledge, 2015) pp 9–41 * Graham, Stephen. ''Peter The Great'' (1929
online
* Kamenskii, Aleksandr. ''The Russian Empire in the Eighteenth Century: Searching for a Place in the World''(1997) pp 39–164. * Kluchevsky, V.O. ''A history of Russia'' vol 4 (1926
online
pp 1–230. ** Cracraft, James. "Kliuchevskii on Peter the Great." ''Canadian-American Slavic Studies'' 20.4 (1986): 367–381. * Oliva, Lawrence Jay. ed. ''Russia in the era of Peter the Great'' (1969), excerpts from primary and secondary source
two week borrowing
* Pares, Bernard. ''A History Of Russia'' (1947) pp 193–225
online
* Schimmelpenninck van der Oye, David, and Bruce W. Menning, eds. ''Reforming the Tsar's Army – Military Innovation in Imperial Russia from Peter the Great to the Revolution'' (Cambridge UP, 2004) 361 pp. scholarly essays * Sumner, B. H. ''Peter the Great and the emergence of Russia'' (1950), brief history by schola
online
Peter the Great, a Tsar who Loved Science by Philippe Testard-Vaillant
{{DEFAULTSORT:Peter 01 Of Russia Peter the Great, 1672 births 1725 deaths 17th-century Russian monarchs 18th-century Russian monarchs Russian tsars Russian emperors House of Romanov Russian city founders Royalty from Moscow Russian inventors Russian folklore characters Characters in Bylina Eastern Orthodox monarchs Modern child rulers Burials at Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral, Saint Petersburg Russian military personnel of the Great Northern War Members of the French Academy of Sciences Filicides People of the Regency of Philippe d'Orléans People of the Russo-Persian Wars Netherlands–Russia relations Russian tsareviches Russian people of Tatar descent Deaths from gangrene Russian expatriates in the Netherlands Russian expatriates in the United Kingdom Infectious disease deaths in Russia Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Poland) Children of Alexis of Russia
Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
from to 1721 and subsequently the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
until his death in 1725, jointly ruling with his elder half-brother, Ivan V until 1696. He is primarily credited with the modernisation of the country, transforming it into a European power.
Through a number of successful wars, he captured ports at Azov
Azov (russian: Азов), previously known as Azak,
is a town in Rostov Oblast, Russia, situated on the Don River just from the Sea of Azov, which derives its name from the town. Population:
History
Early settlements in the vicinity
The mout ...
and the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
, laying the groundwork for the Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution of 1917. It developed from ...
, ending uncontested Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
supremacy in the Baltic and beginning the Tsardom's expansion into a much larger empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
that became a major European power. He led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist and medieval social and political systems with ones that were modern, scientific, Westernised and based on the Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
. Peter's reforms had a lasting impact on Russia, and many institutions of the Russian government trace their origins to his reign. He adopted the title of Emperor in place of the old title of Tsar in 1721, and founded and developed the city of Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, which remained the capital of Russia until 1918.
The first Russian university— Saint Petersburg State University—was founded a year before his death, in 1724. The second one, Moscow State University
M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (MSU; russian: Московский государственный университет имени М. В. Ломоносова) is a public research university in Moscow, Russia and the most prestigious ...
, was founded 30 years after his death, during the reign of his daughter Elizabeth
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
.
Title
The imperial title of Peter the Great was the following:By the grace of God By the Grace of God ( la, Dei Gratia, abbreviated D.G.) is a formulaic phrase used especially in Christian monarchies as an introductory part of the full styles of a monarch. For example in England and later the United Kingdom, the phrase was fo ..., the most excellent and great sovereign emperor Pyotr Alekseevich the ruler of all the Russias: ofMoscow Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ..., of Kiev, ofVladimir Vladimir may refer to: Names * Vladimir (name) for the Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Macedonian, Romanian, Russian, Serbian, Slovak and Slovenian spellings of a Slavic name * Uladzimir for the Belarusian version of the name * Volodymyr for the Ukr ..., of Novgorod, Tsar ofKazan Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering an ..., Tsar ofAstrakhan Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the ...and Tsar ofSiberia Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ..., sovereign of Pskov, great prince ofSmolensk Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest ..., ofTver Tver ( rus, Тверь, p=tvʲerʲ) is a city and the administrative centre of Tver Oblast, Russia. It is northwest of Moscow. Population: Tver was formerly the capital of a powerful medieval state and a model provincial town in the Russian ..., ofYugorsk Yugorsk (russian: Югорск) is a town in Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug, Russia, located in the northwestern part of the East-West lowland, from Khanty-Mansiysk. Population: Geography The relief in the town is flat. The town is surround ..., ofPerm Perm or PERM may refer to: Places *Perm, Russia, a city in Russia ** Permsky District, the district **Perm Krai, a federal subject of Russia since 2005 **Perm Oblast, a former federal subject of Russia 1938–2005 **Perm Governorate, an administra ..., of Vyatka, ofBulgaria Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...and others, sovereign and great prince of the Novgorod Lower lands, ofChernigov Chernihiv ( uk, Черні́гів, , russian: Черни́гов, ; pl, Czernihów, ; la, Czernihovia), is a city and municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative center of Chernihiv Oblast and Chernihiv Raion within t ..., ofRyazan Ryazan ( rus, Рязань, p=rʲɪˈzanʲ, a=ru-Ryazan.ogg) is the largest city and administrative center of Ryazan Oblast, Russia. The city is located on the banks of the Oka River in Central Russia, southeast of Moscow. As of the 2010 Cens ..., ofRostov Rostov ( rus, Росто́в, p=rɐˈstof) is a town in Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, one of the oldest in the country and a tourist center of the Golden Ring. It is located on the shores of Lake Nero, northeast of Moscow. Population: While ..., ofYaroslavl Yaroslavl ( rus, Ярослáвль, p=jɪrɐˈsɫavlʲ) is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historic part of the city is a World Heritage Site, and is located at the confluenc ..., ofBelozersk Belozersk (russian: Белозе́рск), known as Beloozero (russian: Белоозеро, label=none) until 1777, is a town and the administrative center of Belozersky District in Vologda Oblast, Russia, located on the southern bank of Lake Be ..., of Udora, of Kondia and the sovereign of all the northern lands, and the sovereign of the Iverian lands, of the Kartlian and Georgian Kings, of the Kabardin lands, of theCircassia Circassia (; also known as Cherkessia in some sources; ady, Адыгэ Хэку, Адыгей, lit=, translit=Adıgə Xəku, Adıgey; ; ota, چرکسستان, Çerkezistan; ) was a country and a historical region in the along the northeast ...n andMountain A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually highe ...princes and many other states and lands western and eastern here and there and the successor and sovereign and ruler.
Early life
Peter was named afterthe apostle
''The Apostle'' is a 1997 American drama film written and directed by Robert Duvall, who stars in the title role. John Beasley, Farrah Fawcett, Walton Goggins, Billy Bob Thornton, June Carter Cash, Miranda Richardson, and Billy Joe Shaver also a ...
, and described as a newborn as "with good health, his mother
''His Mother'' is a 1912 American silent film produced by Kalem Company. It was directed by Sidney Olcott with Gene Gauntier and Jack J. Clark in the leading roles. It was one of more than a dozen films produced by the Kalem Company filmed in Ir ...
's black, vaguely Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
eyes, and a tuft of auburn hair". He was educated from an early age by several tutors commissioned by his father, in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
Alexis of Russia
Aleksey Mikhaylovich ( rus, Алексе́й Миха́йлович, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsʲej mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪtɕ; – ) was the Tsar of Russia from 1645 until his death in 1676. While finding success in foreign affairs, his reign saw several wars ...
, most notably Nikita Zotov, Patrick Gordon
Patrick Leopold Gordon of Auchleuchries (31 March 1635 – 29 November 1699) was a general and rear admiral in Russia, of Scottish origin. He was descended from a family of Aberdeenshire, holders of the estate of Auchleuchries, near Ellon. The ...
, and Paul Menesius. On 29 January 1676, Alexis died, leaving the sovereignty to Peter's elder half-brother, the weak and sickly Feodor III of Russia
Fyodor III Alekséyevich (in Russian: ''Фёдор III Алексеевич'') or Feodor III Alekséyevich (9 June 1661 – 7 May 1682) was the Tsar of Russia between 1676 and 1682. While disabled and paralyzed from birth, he managed to pass ref ...
. Throughout this period, the government was largely run by Artamon Matveev, an enlightened friend of Alexis, the political head of the Naryshkin family
The House of Naryshkin (russian: Нарышкины) is a noble Moscow boyar family of Crimean Tatar descent, going back to a certain Mordko Kurbat Naryshko, a Crimean Tatar, who moved to Moscow in the 15th century.Sergei O. Prokofieff, ''The Spir ...
and one of Peter's greatest childhood benefactors.
This position changed when Feodor died in 1682. As Feodor did not leave any children, a dispute arose between the Miloslavsky family (Maria Miloslavskaya
Maria Ilyinichna Miloslavskaya (, 1 April 1624 – 18 August 1669) was a Russian tsaritsa as the first spouse of tsar Alexis of Russia. She was the mother of tsar Feodor III of Russia, tsar Ivan V of Russia, and the princess regent Sophia Alekse ...
was the first wife of Alexis I) and Naryshkin family (Natalya Naryshkina
Natalya Kirillovna Naryshkina (russian: Ната́лья Кири́лловна Нары́шкина; 1 September 1651 – 4 February 1694) was the Tsaritsa of Russia from 1671–1676 as the second spouse of Tsar Alexis I of Russia, and re ...
was his second) over who should inherit the throne. Peter's other half-brother, Ivan V of Russia
Ivan V Alekseyevich (russian: Иван V Алексеевич; – ) was Tsar of Russia between 1682 and 1696, jointly ruling with his younger half-brother Peter I. Ivan was the youngest son of Alexis I of Russia by his first wife, Maria ...
, was next in line, but was chronically ill and of infirm mind. Consequently, the Boyar Duma
A duma (russian: дума) is a Russian assembly with advisory or legislative functions.
The term ''boyar duma'' is used to refer to advisory councils in Russia from the 10th to 17th centuries. Starting in the 18th century, city dumas were for ...
(a council of Russian nobles) chose the 10-year-old Peter to become Tsar, with his mother as regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
.
 This arrangement was brought before the people of Moscow, as ancient tradition demanded, and was ratified. Sophia, one of Alexis' daughters from his first marriage, led a rebellion of the Streltsy (Russia's elite military corps) in April–May 1682. In the subsequent conflict, some of Peter's relatives and friends were murdered, including Matveev, and Peter witnessed some of these acts of political violence.
The Streltsy made it possible for Sophia, the Miloslavskys (the clan of
This arrangement was brought before the people of Moscow, as ancient tradition demanded, and was ratified. Sophia, one of Alexis' daughters from his first marriage, led a rebellion of the Streltsy (Russia's elite military corps) in April–May 1682. In the subsequent conflict, some of Peter's relatives and friends were murdered, including Matveev, and Peter witnessed some of these acts of political violence.
The Streltsy made it possible for Sophia, the Miloslavskys (the clan of Ivan
Ivan () is a Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John) from Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. The earliest person known to bear the name was Bulgari ...
) and their allies to insist that Peter and Ivan be proclaimed joint Tsars, with Ivan being acclaimed as the senior. Sophia then acted as regent during the minority of the sovereigns and exercised all power. For seven years, she ruled as an autocrat. A large hole was cut in the back of the dual-seated throne used by Ivan and Peter. Sophia would sit behind the throne and listen as Peter conversed with nobles, while feeding him information and giving him responses to questions and problems. This throne can be seen in the Kremlin Armoury
The Kremlin Armoury,Officially called the "Armou/ory Chamber" but also known as the cannon yard, the "Armou/ory Palace", the "Moscow Armou/ory", the "Armou/ory Museum", and the "Moscow Armou/ory Museum" but different from the Kremlin Arsenal. ( ...
in Moscow.
Peter was not particularly concerned that others ruled in his name. He engaged in such pastimes as shipbuilding and sailing, as well as mock battles with his toy army. Peter's mother sought to force him to adopt a more conventional approach and arranged his marriage to Eudoxia Lopukhina
Tsarina Eudoxia Fyodorovna Lopukhina ( rus, Евдоки́я Фёдоровна Лопухина́, Yevdokíya Fyodorovna Lopukhiná; in Moscow – in Moscow) was a Russian Tsaritsa as the first wife of Peter I of Russia, and the last ethnic ...
in 1689. The marriage was a failure, and ten years later Peter forced his wife to become a nun and thus freed himself from the union.
By the summer of 1689, Peter, then age 17, planned to take power from his half-sister Sophia, whose position had been weakened by two unsuccessful Crimean campaigns against the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
in an attempt to stop devastating Crimean Tatar raids into Russia's southern lands. When she learned of his designs, Sophia conspired with some leaders of the Streltsy, who continually aroused disorder and dissent. Peter, warned by others from the Streltsy, escaped in the middle of the night to the impenetrable monastery of Troitse-Sergiyeva Lavra
The Trinity Lavra of St. Sergius (russian: Тро́ице-Се́ргиева ла́вра) is the most important Russian monastery and the spiritual centre of the Russian Orthodox Church. The monastery is situated in the town of Sergiyev Pos ...
; there he slowly gathered adherents who perceived he would win the power struggle. Sophia was eventually overthrown, with Peter I and Ivan V continuing to act as co-tsars. Peter forced Sophia to enter a convent, where she gave up her name and her position as a member of the royal family.
 Still, Peter could not acquire actual control over Russian affairs. Power was instead exercised by his mother, Natalya Naryshkina. It was only when Natalya died in 1694 that Peter, then aged 22, became an independent sovereign. Formally, Ivan V was a co-ruler with Peter, though being ineffective. Peter became the sole ruler when Ivan died in 1696 without male offspring, two years later.
Peter grew to be extremely tall as an adult, especially for the time period, reportedly standing . Peter, however, lacked the overall proportional heft and bulk generally found in a man that size. Both his hands and feet were small, and his shoulders were narrow for his height; likewise, his head was small for his tall body. Added to this were Peter's noticeable facial tics, and he may have suffered from '' petit mal seizures'', a form of epilepsy.
During his youth, Peter befriended
Still, Peter could not acquire actual control over Russian affairs. Power was instead exercised by his mother, Natalya Naryshkina. It was only when Natalya died in 1694 that Peter, then aged 22, became an independent sovereign. Formally, Ivan V was a co-ruler with Peter, though being ineffective. Peter became the sole ruler when Ivan died in 1696 without male offspring, two years later.
Peter grew to be extremely tall as an adult, especially for the time period, reportedly standing . Peter, however, lacked the overall proportional heft and bulk generally found in a man that size. Both his hands and feet were small, and his shoulders were narrow for his height; likewise, his head was small for his tall body. Added to this were Peter's noticeable facial tics, and he may have suffered from '' petit mal seizures'', a form of epilepsy.
During his youth, Peter befriended Patrick Gordon
Patrick Leopold Gordon of Auchleuchries (31 March 1635 – 29 November 1699) was a general and rear admiral in Russia, of Scottish origin. He was descended from a family of Aberdeenshire, holders of the estate of Auchleuchries, near Ellon. The ...
, Franz Lefort Franz may refer to:
People
* Franz (given name)
Franz is a German name and cognate of the given name Francis. Notable people named Franz include:
Nobility
Austria-Hungary
* Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor (1708–1765)
* Francis II, Holy ...
and several other foreigners in Russian service and was a frequent guest in Moscow's German Quarter
German Quarter (russian: Неме́цкая слобода́, ''Nemetskaya sloboda''), also known as the Kukuy Quarter (), was a neighborhood in the northeast of Moscow, located on the right bank of the Yauza River east of Kukuy Creek (h ...
, where he met his Dutch mistress Anna Mons.
Reign
 Peter implemented sweeping
Peter implemented sweeping reforms
Reform ( lat, reformo) means the improvement or amendment of what is wrong, corrupt, unsatisfactory, etc. The use of the word in this way emerges in the late 18th century and is believed to originate from Christopher Wyvill's Association movement ...
aimed at modernizing Russia. Heavily influenced by his advisors from Western Europe, Peter reorganized the Russian army along modern lines and dreamed of making Russia a maritime power
A maritime power is a nation with a very strong navy, which often is also a great power, or at least a regional power. A maritime power is able to easily control their coast, and exert influence upon both nearby and far countries. A nation that dom ...
. He faced much opposition to these policies at home but brutally suppressed rebellions against his authority, including by the Streltsy, Bashkirs
, native_name_lang = bak
, flag = File:Bashkirs of Baymak rayon.jpg
, flag_caption = Bashkirs of Baymak in traditional dress
, image =
, caption =
, population = approx. 2 million
, popplace ...
, Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the ...
, and the greatest civil uprising of his reign, the Bulavin Rebellion
The Bulavin Rebellion or Astrakhan Revolt (; Восстание Булавина, ''Vosstaniye Bulavina'') was a war which took place in the years 1707 and 1708 between the Don Cossacks and the Tsardom of Russia. Kondraty Bulavin, a democraticall ...
.
Peter implemented social modernization in an absolute manner by introducing French and western dress to his court and requiring courtiers, state officials, and the military to shave their beards and adopt modern clothing styles. One means of achieving this end was the introduction of taxes for long beards and robes in September 1698.
In his process to westernize Russia, he wanted members of his family to marry other European royalty. In the past, his ancestors had been snubbed at the idea, but now, it was proving fruitful. He negotiated with Frederick William, Duke of Courland
Frederick William (german: Friedrich Wilhelm; 19 July 1692 – 21 January 1711) was Duke of Courland and Semigallia from 1698 to 1711. Frederick Wilhelm was the son of Friedrich Kasimir Kettler, Duke of Courland and Semigallia and Princess Eli ...
to marry his niece, Anna Ivanovna
Anna Ioannovna (russian: Анна Иоанновна; ), also russified as Anna Ivanovna and sometimes anglicized as Anne, served as regent of the duchy of Courland from 1711 until 1730 and then ruled as Empress of Russia from 1730 to 1740. Much ...
. He used the wedding in order to launch his new capital, St Petersburg, where he had already ordered building projects of westernized palaces and buildings. Peter hired Italian and German architects to design it.
As part of his reforms, Peter started an industrialization effort that was slow but eventually successful. Russian manufacturing and main exports were based on the mining and lumber industries. For example, by the end of the century Russia came to export more iron than any other country in the world.
To improve his nation's position on the seas, Peter sought more maritime outlets. His only outlet at the time was the White Sea
The White Sea (russian: Белое море, ''Béloye móre''; Karelian and fi, Vienanmeri, lit. Dvina Sea; yrk, Сэрако ямʼ, ''Serako yam'') is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is s ...
at Arkhangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ; rus, Арха́нгельск, p=ɐrˈxanɡʲɪlʲsk), also known in English as Archangel and Archangelsk, is a city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near ...
. The Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
was at the time controlled by Sweden in the north, while the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
and the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
were controlled by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
and Safavid Empire respectively in the south.
Peter attempted to acquire control of the Black Sea, which would require expelling the Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
from the surrounding areas. As part of an agreement with in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
that ceded Kiev to Russia, Peter was forced to wage war against the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
n Khan and against the Khan's overlord, the Ottoman Sultan. Peter's primary objective became the capture of the Ottoman fortress of Azov
Azov (russian: Азов), previously known as Azak,
is a town in Rostov Oblast, Russia, situated on the Don River just from the Sea of Azov, which derives its name from the town. Population:
History
Early settlements in the vicinity
The mout ...
, near the Don River
The Don ( rus, Дон, p=don) is the fifth-longest river in Europe. Flowing from Central Russia to the Sea of Azov in Southern Russia, it is one of Russia's largest rivers and played an important role for traders from the Byzantine Empire.
Its ...
. In the summer of 1695 Peter organized the Azov campaigns
Azov (russian: Азов), previously known as Azak,
is a town in Rostov Oblast, Russia, situated on the Don River just from the Sea of Azov, which derives its name from the town. Population:
History
Early settlements in the vicinity
The mout ...
to take the fortress, but his attempts ended in failure.
Peter returned to Moscow in November 1695 and began building a large navy. He launched about thirty ships against the Ottomans in 1696, capturing Azov in July of that year. On 12 September 1698, Peter officially founded the first Russian Navy base, Taganrog
Taganrog ( rus, Таганрог, p=təɡɐnˈrok) is a port city in Rostov Oblast, Russia, on the north shore of the Taganrog Bay in the Sea of Azov, several kilometers west of the mouth of the Don River. Population:
History of Taganrog
Th ...
on the Sea of Azov.
Grand Embassy
 Peter knew that Russia could not face the Ottoman Empire alone. In 1697, he traveled "incognito" to Western Europe on an 18-month journey with a large Russian delegation–the so-called "Grand Embassy". He used a fake name, allowing him to escape social and diplomatic events, but since he was far taller than most others, he did not fool anyone of importance. One goal was to seek the aid of European monarchs, but Peter's hopes were dashed. France was a traditional ally of the Ottoman Sultan, and
Peter knew that Russia could not face the Ottoman Empire alone. In 1697, he traveled "incognito" to Western Europe on an 18-month journey with a large Russian delegation–the so-called "Grand Embassy". He used a fake name, allowing him to escape social and diplomatic events, but since he was far taller than most others, he did not fool anyone of importance. One goal was to seek the aid of European monarchs, but Peter's hopes were dashed. France was a traditional ally of the Ottoman Sultan, and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
was eager to maintain peace in the east while conducting its own wars in the west. Peter, furthermore, had chosen an inopportune moment: the Europeans at the time were more concerned about the War of Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phili ...
over who would succeed the childless King Charles II of Spain
Charles II of Spain (''Spanish: Carlos II,'' 6 November 1661 – 1 November 1700), known as the Bewitched (''Spanish: El Hechizado''), was the last Habsburg ruler of the Spanish Empire. Best remembered for his physical disabilities and the War ...
than about fighting the Ottoman Sultan.
The "Grand Embassy" continued nevertheless. While visiting the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Peter learned much about life in Western Europe. He studied shipbuilding in Zaandam
Zaandam () is a city in the province of North Holland, Netherlands. It is the main city of the municipality of Zaanstad, and received city rights in 1811. It is located on the river Zaan, just north of Amsterdam.
The statistical district Zaand ...
(the house he lived in is now a museum, the Czar Peter House) and Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
, where he visited, among others, the upper-class De Wilde family. Jacob de Wilde, a collector-general with the Admiralty of Amsterdam
The Admiralty of Amsterdam was the largest of the five Dutch admiralties at the time of the Dutch Republic. The administration of the various admiralties was strongly influenced by provincial interests. The territory for which Amsterdam ...
, had a well-known collection of art and coins, and De Wilde's daughter Maria de Wilde made an engraving of the meeting between Peter and her father, providing visual evidence of "the beginning of the West European classical tradition in Russia". According to Roger Tavernier, Peter the Great later acquired De Wilde's collection.
Thanks to the mediation of Nicolaes Witsen
Nicolaes Witsen (8 May 1641 – 10 August 1717; modern Dutch: ''Nicolaas Witsen'') was a Dutch statesman who was mayor of Amsterdam thirteen times, between 1682 and 1706. In 1693 he became administrator of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). I ...
, mayor of Amsterdam and an expert on Russia, the Tsar was given the opportunity to gain practical experience in the largest shipyard in the world, belonging to the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
, for a period of four months. The Tsar helped with the construction of an East Indiaman ship specially laid down for him: ''Peter and Paul''. During his stay the Tsar engaged many skilled workers such as builders of locks, fortresses, shipwrights, and seamen—including Cornelis Cruys
Cornelius Cruys ( no, Niels Creutz, i=no, russian: Корнелий Крюйс, i=no; 14 June 1655 – 14 June 1727) was a Norwegian–Dutch admiral of the Imperial Russian Navy, and the first commander of the Russian Baltic Fleet.
Early ...
, a vice-admiral who became, under Franz Lefort Franz may refer to:
People
* Franz (given name)
Franz is a German name and cognate of the given name Francis. Notable people named Franz include:
Nobility
Austria-Hungary
* Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor (1708–1765)
* Francis II, Holy ...
, the Tsar's advisor in maritime affairs. Peter later put his knowledge of shipbuilding to use in helping build Russia's navy. Peter paid a visit to surgeon Frederik Ruysch
Frederik Ruysch (; March 28, 1638 – February 22, 1731) was a Dutch botanist and anatomist. He is known for developing techniques for preserving anatomical specimens, which he used to create dioramas or scenes incorporating human parts. His ana ...
, who taught him how to draw teeth and catch butterflies, and to Ludolf Bakhuysen, a painter of seascapes. Jan van der Heyden
Jan van der Heyden (5 March 1637, Gorinchem – 28 March 1712, Amsterdam) was a Dutch Baroque-era painter, glass painter, draughtsman and printmaker. Van der Heyden was one of the first Dutch painters to specialize in townscapes and became ...
, the inventor of the fire hose, received Peter, who was keen to learn and pass on his knowledge to his countrymen. On 16 January 1698 Peter organized a farewell party and invited Johan Huydecoper van Maarsseveen, who had to sit between Lefort and the Tsar and drink.
 In England, Peter met with King William III, visited
In England, Peter met with King William III, visited Greenwich
Greenwich ( , ,) is a town in south-east London, England, within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It is situated east-southeast of Charing Cross.
Greenwich is notable for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Greenwich ...
and Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
, posed for Sir Godfrey Kneller, and saw a Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
Fleet Review
A fleet review or naval review is an event where a gathering of ships from a particular navy is paraded and reviewed by an incumbent head of state and/or other official civilian and military dignitaries. A number of national navies continue to ...
at Deptford
Deptford is an area on the south bank of the River Thames in southeast London, within the London Borough of Lewisham. It is named after a Ford (crossing), ford of the River Ravensbourne. From the mid 16th century to the late 19th it was home ...
. He studied the English techniques of city-building he would later use to great effect at Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
.
The Embassy next went to Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
, Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label= Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth ...
, Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and List of cities in the Czech Republic, largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 milli ...
and Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
. Peter spoke with Augustus II the Strong
Augustus II; german: August der Starke; lt, Augustas II; in Saxony also known as Frederick Augustus I – Friedrich August I (12 May 16701 February 1733), most commonly known as Augustus the Strong, was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as K ...
and Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor.
Peter's visit was cut short in 1698, when he was forced to rush home by a rebellion of the Streltsy. The rebellion was easily crushed before Peter returned home from England; of the Tsar's troops, only one was killed. Peter nevertheless acted ruthlessly towards the mutineers. Over one thousand two hundred of the rebels were tortured and executed, and Peter ordered that their bodies be publicly exhibited as a warning to future conspirators. The Streltsy were disbanded, some of the rebels were deported to Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
, and the individual they sought to put on the Throne —
Peter's half-sister Sophia — was forced to become a nun.
In 1698, Peter sent a delegation to Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, under boyar Boris Sheremetev
Count Boris Petrovich Sheremetev (russian: Граф Бори́с Петро́вич Шереме́тев, tr. ; – ) was an Imperial Russian diplomat and general field marshal during the Great Northern War. He became the first Russian count i ...
, to observe the training and abilities of the Knights of Malta and their fleet
Fleet may refer to:
Vehicles
*Fishing fleet
*Naval fleet
*Fleet vehicles, a pool of motor vehicles
*Fleet Aircraft, the aircraft manufacturing company
Places
Canada
* Fleet, Alberta, Canada, a hamlet
England
* The Fleet Lagoon, at Chesil Beach ...
. Sheremetev investigated the possibility of future joint ventures with the Knights, including action against the Turks and the possibility of a future Russian naval base.
Peter's visits to the West impressed upon him the notion that European customs were in several respects superior to Russian traditions. He commanded all of his courtiers and officials to wear European clothing and cut off their long beards, causing his Boyars, who were very fond of their beards, great upset. Boyars who sought to retain their beards were required to pay an annual beard tax of one hundred rubles
The ruble (American English) or rouble (Commonwealth English) (; rus, рубль, p=rublʲ) is the currency unit of Belarus and Russia. Historically, it was the currency of the Russian Empire and of the Soviet Union.
, currencies named ''rub ...
. Peter also sought to end arranged marriages, which were the norm among the Russian nobility, because he thought such a practice was barbaric and led to domestic violence, since the partners usually resented each other.
In 1699, Peter changed the date of the celebration of the new year from 1 September to 1 January. Traditionally, the years were reckoned from the purported creation of the World, but after Peter's reforms, they were to be counted from the birth of Christ
The nativity of Jesus, nativity of Christ, birth of Jesus or birth of Christ is described in the biblical gospels of Luke and Matthew. The two accounts agree that Jesus was born in Bethlehem in Judaea, his mother Mary was engaged to a man n ...
. Thus, in the year 7207 of the old Russian calendar, Peter proclaimed that the Julian Calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
was in effect and the year was 1700.
Great Northern War
Peter made a temporary peace with the Ottoman Empire that allowed him to keep the captured fort of Azov, and turned his attention to Russian maritime supremacy. He sought to acquire control of the Baltic Sea, which had been taken by theSwedish Empire
The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries ( sv, Stormaktstiden, "the Era of Great Power"). The beginning of the empire is usually ta ...
a half-century earlier. Peter declared war on Sweden, which was at the time led by the young King Charles XII
Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII ( sv, Karl XII) or Carolus Rex (17 June 1682 – 30 November 1718 O.S.), was King of Sweden (including current Finland) from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of ...
. Sweden was also opposed by Denmark–Norway, Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
.
 Russia was ill-prepared to fight the Swedes, and their first attempt at seizing the Baltic coast ended in disaster at the Battle of Narva in 1700. In the conflict, the forces of Charles XII, rather than employ a slow methodical siege, attacked immediately using a blinding snowstorm to their advantage. After the battle, Charles XII decided to concentrate his forces against the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which gave Peter time to reorganize the Russian army.
While the Poles fought the Swedes, Peter founded the city of
Russia was ill-prepared to fight the Swedes, and their first attempt at seizing the Baltic coast ended in disaster at the Battle of Narva in 1700. In the conflict, the forces of Charles XII, rather than employ a slow methodical siege, attacked immediately using a blinding snowstorm to their advantage. After the battle, Charles XII decided to concentrate his forces against the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which gave Peter time to reorganize the Russian army.
While the Poles fought the Swedes, Peter founded the city of Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
in 1703, in Ingermanland (a province of the Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries ( sv, Stormaktstiden, "the Era of Great Power"). The beginning of the empire is usually ta ...
that he had captured). It was named after his patron saint Saint Peter
) (Simeon, Simon)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire
, death_date = Between AD 64–68
, death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire
, parents = John (or Jonah; Jona)
, occupat ...
. He forbade the building of stone edifices outside Saint Petersburg, which he intended to become Russia's capital, so that all stonemasons could participate in the construction of the new city. Peter moved the capital to St. Petersburg in 1703. While the city was being built he lived in a three-room log cabin with Catherine, where she did the cooking and caring for the children, and he tended a garden as though they were an ordinary couple. Between 1713 and 1728, and from 1732 to 1918, Saint Petersburg was the capital of imperial Russia.
 Following several defeats, Polish King
Following several defeats, Polish King Augustus II the Strong
Augustus II; german: August der Starke; lt, Augustas II; in Saxony also known as Frederick Augustus I – Friedrich August I (12 May 16701 February 1733), most commonly known as Augustus the Strong, was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as K ...
abdicated in 1706. Swedish king Charles XII turned his attention to Russia, invading it in 1708. After crossing into Russia, Charles defeated Peter at Golovchin in July. In the Battle of Lesnaya, Charles suffered his first loss after Peter crushed a group of Swedish reinforcements marching from Riga. Deprived of this aid, Charles was forced to abandon his proposed march on Moscow.
Charles XII refused to retreat to Poland or back to Sweden and instead invaded Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. Peter withdrew his army southward, employing scorched earth, destroying along the way anything that could assist the Swedes. Deprived of local supplies, the Swedish army was forced to halt its advance in the winter of 1708–1709. In the summer of 1709, they resumed their efforts to capture Russian-ruled Ukraine, culminating in the Battle of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava; russian: Полта́вская би́тва; uk, Полта́вська би́тва (8 July 1709) was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. A Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeat ...
on 27 June. The battle was a decisive defeat for the Swedish forces, ending Charles' campaign in Ukraine and forcing him south to seek refuge in the Ottoman Empire. Russia had defeated what was considered to be one of the world's best militaries, and the victory overturned the view that Russia was militarily incompetent. In Poland, Augustus II was restored as King.
 Peter, overestimating the support he would receive from his Balkan allies, attacked the Ottoman Empire, initiating the Russo-Turkish War of 1710. Peter's campaign in the Ottoman Empire was disastrous, and in the ensuing
Peter, overestimating the support he would receive from his Balkan allies, attacked the Ottoman Empire, initiating the Russo-Turkish War of 1710. Peter's campaign in the Ottoman Empire was disastrous, and in the ensuing Treaty of the Pruth
The Treaty of the Pruth was signed on the banks of the river Prut between the Ottoman Empire and the Tsardom of Russia on 23 July 1711 ending the Russo-Turkish War of 1710–1711. The treaty was a political victory for the Ottoman Empire.
The ...
, Peter was forced to return the Black Sea ports he had seized in 1697. In return, the Sultan expelled Charles XII.
The Ottomans called him ''Mad Peter'' (), for his willingness to sacrifice large numbers of his troops in wartime.
Normally, the Boyar Duma would have exercised power during his absence. Peter, however, mistrusted the boyars; he instead abolished the Duma and created a Senate of ten members. The Senate was founded as the highest state institution to supervise all judicial, financial and administrative affairs. Originally established only for the time of the monarch's absence, the Senate became a permanent body after his return. A special high official, the Ober-Procurator, served as the link between the ruler and the senate and acted, in Peter own words, as "the sovereign's eye". Without his signature no Senate decision could go into effect; the Senate became one of the most important institutions of Imperial Russia.
 Peter's northern armies took the Swedish province of
Peter's northern armies took the Swedish province of Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Ли ...
(the northern half of modern Latvia, and the southern half of modern Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
), driving the Swedes into Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
. In 1714 the Russian fleet won the Battle of Gangut
The Battle of Gangut (russian: Гангутское сражение, fi, Riilahden taistelu, Finland Swedish: ''Slaget vid Rilax'', sv, Sjöslaget vid Hangöudd) took place on 27 July Jul./ 7 August 1714 Greg. during the Great Northern War ...
. Most of Finland was occupied by the Russians.
In 1716 and 1717, the Tsar revisited the Netherlands and went to see Herman Boerhaave
Herman Boerhaave (, 31 December 1668 – 23 September 1738Underwood, E. Ashworth. "Boerhaave After Three Hundred Years." ''The British Medical Journal'' 4, no. 5634 (1968): 820–25. https://www.jstor.org/stable/20395297.) was a Dutch botanist, ...
. He continued his travel to the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
and France, where he obtained many books and proposed a marriage between his daughter and King Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached ...
. Peter obtained the assistance of the Electorate of Hanover and the Kingdom of Prussia.
The Tsar's navy was powerful enough that the Russians could penetrate Sweden. Still, Charles XII refused to yield, and not until his death in battle in 1718 did peace become feasible. After the battle near Åland, Sweden made peace with all powers but Russia by 1720. In 1721, the Treaty of Nystad ended the Great Northern War. Russia acquired Ingria, Reval Governorate, Estonia, Riga Governorate, Livonia, and a substantial portion of Old Finland, Karelia. In turn, Russia paid two million Riksdaler and surrendered most of Finland. The Tsar retained some Finnish lands close to Saint Petersburg, which he had made his capital in 1712.
Later years
 Peter's last years were marked by further reform in Russia. On 22 October 1721, soon after peace was made with Sweden, he was officially proclaimed ''Emperor of All Russia''. Some proposed that he take the title ''Emperor of the East'', but he refused. Gavrila Golovkin, the State Chancellor, was the first to add "the Great, Father of His Country, Emperor of All the Russias" to Peter's traditional title Tsar following a speech by the archbishop of Pskov in 1721. Peter's imperial title was recognized by Augustus II of Poland, Frederick William I of Prussia, and Frederick I of Sweden, but not by the other European monarchs. In the minds of many, the word ''emperor'' connoted superiority or pre-eminence over kings. Several rulers feared that Peter would claim authority over them, just as the Holy Roman Emperor had claimed suzerainty over all Christian nations.
In 1717, Alexander Bekovich-Cherkassky led the first Russian military expedition into Central Asia against the Khanate of Khiva. The expedition ended in complete disaster when the entire expeditionary force was slaughtered.
In 1718, Peter investigated why the formerly Swedish province of Livonia was so orderly. He discovered that the Swedes spent as much administering Livonia (300 times smaller than his empire) as he spent on the entire Russian bureaucracy. He was forced to dismantle the province's government.
Peter's last years were marked by further reform in Russia. On 22 October 1721, soon after peace was made with Sweden, he was officially proclaimed ''Emperor of All Russia''. Some proposed that he take the title ''Emperor of the East'', but he refused. Gavrila Golovkin, the State Chancellor, was the first to add "the Great, Father of His Country, Emperor of All the Russias" to Peter's traditional title Tsar following a speech by the archbishop of Pskov in 1721. Peter's imperial title was recognized by Augustus II of Poland, Frederick William I of Prussia, and Frederick I of Sweden, but not by the other European monarchs. In the minds of many, the word ''emperor'' connoted superiority or pre-eminence over kings. Several rulers feared that Peter would claim authority over them, just as the Holy Roman Emperor had claimed suzerainty over all Christian nations.
In 1717, Alexander Bekovich-Cherkassky led the first Russian military expedition into Central Asia against the Khanate of Khiva. The expedition ended in complete disaster when the entire expeditionary force was slaughtered.
In 1718, Peter investigated why the formerly Swedish province of Livonia was so orderly. He discovered that the Swedes spent as much administering Livonia (300 times smaller than his empire) as he spent on the entire Russian bureaucracy. He was forced to dismantle the province's government.

 After 1718, Peter established colleges in place of the old central agencies of government, including foreign affairs, war, navy, expense, income, justice, and inspection. Later others were added. Each college consisted of a president, a vice-president, a number of councilors and assessors, and a procurator. Some foreigners were included in various colleges but not as president. Peter believed he did not have enough loyal and talented persons to put in full charge of the various departments. Peter preferred to rely on groups of individuals who would keep check on one another. Decisions depended on the majority vote.
In 1722, Peter created a new order of precedence known as the Table of Ranks. Formerly, precedence had been determined by birth. To deprive the Boyars of their high positions, Peter directed that precedence should be determined by merit and service to the Emperor. The Table of Ranks continued to remain in effect until the Russian monarchy was February Revolution, overthrown in 1917.
Peter decided that all of the children of the nobility should have some early education, especially in the areas of sciences. Therefore, on 28 February 1714, he issued a decree calling for compulsory education, which dictated that all Russian 10- to 15-year-old children of the nobility, government clerks, and lesser-ranked officials must learn basic mathematics and geometry, and should be tested on the subjects at the end of their studies.
The once powerful Persian Safavid Empire to the south was in deep decline. Taking advantage of the profitable situation, Peter launched the Russo-Persian War (1722-1723), Russo-Persian War of 1722–1723, otherwise known as "The Persian Expedition of Peter the Great", which drastically increased Russian influence for the first time in the Caucasus and
After 1718, Peter established colleges in place of the old central agencies of government, including foreign affairs, war, navy, expense, income, justice, and inspection. Later others were added. Each college consisted of a president, a vice-president, a number of councilors and assessors, and a procurator. Some foreigners were included in various colleges but not as president. Peter believed he did not have enough loyal and talented persons to put in full charge of the various departments. Peter preferred to rely on groups of individuals who would keep check on one another. Decisions depended on the majority vote.
In 1722, Peter created a new order of precedence known as the Table of Ranks. Formerly, precedence had been determined by birth. To deprive the Boyars of their high positions, Peter directed that precedence should be determined by merit and service to the Emperor. The Table of Ranks continued to remain in effect until the Russian monarchy was February Revolution, overthrown in 1917.
Peter decided that all of the children of the nobility should have some early education, especially in the areas of sciences. Therefore, on 28 February 1714, he issued a decree calling for compulsory education, which dictated that all Russian 10- to 15-year-old children of the nobility, government clerks, and lesser-ranked officials must learn basic mathematics and geometry, and should be tested on the subjects at the end of their studies.
The once powerful Persian Safavid Empire to the south was in deep decline. Taking advantage of the profitable situation, Peter launched the Russo-Persian War (1722-1723), Russo-Persian War of 1722–1723, otherwise known as "The Persian Expedition of Peter the Great", which drastically increased Russian influence for the first time in the Caucasus and Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
region, and prevented the Ottoman Empire from making territorial gains in the region. After considerable success and the capture of many provinces and cities in the Caucasus and northern mainland Persia, the Safavids were forced to hand over territory to Russia, comprising Derbent, Shirvan, Gilan Province, Gilan, Mazandaran Province, Mazandaran, Baku, and Astrabad. However, within twelve years all the territories would be ceded back to Persia, now led by the charismatic military genius Nader Shah, as part of the Treaty of Resht, Treaties of Resht and Treaty of Ganja, Ganja respectively, and the Russo-Persian alliance against the Ottoman Empire, which was the common enemy of both.
Peter introduced new taxes to fund improvements in Saint Petersburg. He abolished the land tax and household tax and replaced them with a Tax per head, poll tax. The taxes on land and on households were payable only by individuals who owned property or maintained families; the new head taxes, however, were payable by serfs and paupers. In 1725 the construction of Peterhof Palace, Peterhof, a palace near Saint Petersburg, was completed. Peterhof (Dutch language, Dutch for "Peter's Court") was a grand residence, becoming known as the "Russian Palace of Versailles, Versailles".
Illness and death
 In the winter of 1723, Peter, whose overall health was never robust, began having problems with his urinary tract and Urinary bladder, bladder. In the summer of 1724, a team of doctors performed surgery releasing upwards of four pounds of blocked urine. Peter remained bedridden until late autumn. In the first week of October, restless and certain he was cured, Peter began a lengthy inspection tour of various projects. According to legend, in November, at Lakhta, Saint Petersburg, Lakhta along the Finnish Gulf to inspect some ironworks, Peter saw a group of soldiers drowning near shore and, wading out into near-waist deep water, came to their rescue.
This icy water rescue is said to have exacerbated Peter's bladder problems and caused his death. The story, however, has been viewed with skepticism by some historians, pointing out that the German chronicler Jacob von Staehlin is the only source for the story, and it seems unlikely that no one else would have documented such an act of heroism. This, plus the interval of time between these actions and Peter's death seems to preclude any direct link.
In early January 1725, Peter was struck once again with uremia. Legend has it that before lapsing into unconsciousness Peter asked for a paper and pen and scrawled an unfinished note that read: ''"Leave all to ..."'' and then, exhausted by the effort, asked for his daughter Anna to be summoned.
Peter died between four and five in the morning 8 February 1725. An autopsy revealed his bladder to be infected with gangrene. He was fifty-two years, seven months old when he died, having reigned forty-two years. He is interred in Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral, Saint Petersburg, Russia.
In the winter of 1723, Peter, whose overall health was never robust, began having problems with his urinary tract and Urinary bladder, bladder. In the summer of 1724, a team of doctors performed surgery releasing upwards of four pounds of blocked urine. Peter remained bedridden until late autumn. In the first week of October, restless and certain he was cured, Peter began a lengthy inspection tour of various projects. According to legend, in November, at Lakhta, Saint Petersburg, Lakhta along the Finnish Gulf to inspect some ironworks, Peter saw a group of soldiers drowning near shore and, wading out into near-waist deep water, came to their rescue.
This icy water rescue is said to have exacerbated Peter's bladder problems and caused his death. The story, however, has been viewed with skepticism by some historians, pointing out that the German chronicler Jacob von Staehlin is the only source for the story, and it seems unlikely that no one else would have documented such an act of heroism. This, plus the interval of time between these actions and Peter's death seems to preclude any direct link.
In early January 1725, Peter was struck once again with uremia. Legend has it that before lapsing into unconsciousness Peter asked for a paper and pen and scrawled an unfinished note that read: ''"Leave all to ..."'' and then, exhausted by the effort, asked for his daughter Anna to be summoned.
Peter died between four and five in the morning 8 February 1725. An autopsy revealed his bladder to be infected with gangrene. He was fifty-two years, seven months old when he died, having reigned forty-two years. He is interred in Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral, Saint Petersburg, Russia.
Religion
 Peter founded The All-Joking, All-Drunken Synod of Fools and Jesters, an organization that mocked the Orthodox and Catholic Church when he was eighteen. In January 1695, Peter refused to partake in a traditional Russian Orthodox ceremony of the Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany Ceremony, and would often schedule events for The All-Joking, All-Drunken Synod of Fools and Jesters to directly conflict with the Church.
Peter was brought up in the Russian Orthodox faith, but he had low regard for the Church hierarchy, which he kept under tight governmental control. The traditional leader of the Church was the List of Metropolitans and Patriarchs of Moscow, Patriarch of Moscow. In 1700, when the office fell vacant, Peter refused to name a replacement, allowing the Patriarch's Coadjutor (or deputy) to discharge the duties of the office. Peter could not tolerate the patriarch exercising power superior to the Tsar, as indeed had happened in the case of Patriarch Philaret of Moscow, Philaret (1619–1633) and Patriarch Nikon of Moscow, Nikon (1652–66). The Church reform of Peter the Great therefore abolished the Patriarchate, replacing it with a Holy Synod that was under the control of a Procurator_(Russia), Procurator, and the Tsar appointed all bishops.
In 1721, Peter followed the advice of Theophan Prokopovich in designing the Holy Synod as a council of ten clergymen. For leadership in the church, Peter turned increasingly to Ukrainians, who were more open to reform, but were not well loved by the Russian clergy. Peter implemented a law that stipulated that no Russian man could join a monastery before the age of fifty. He felt that too many able Russian men were being wasted on clerical work when they could be joining his new and improved army.
A clerical career was not a route chosen by upper-class society. Most parish priests were sons of priests and were very poorly educated and paid. The monks in the monasteries had a slightly higher status; they were not allowed to marry. Politically, the church was impotent.
Peter founded The All-Joking, All-Drunken Synod of Fools and Jesters, an organization that mocked the Orthodox and Catholic Church when he was eighteen. In January 1695, Peter refused to partake in a traditional Russian Orthodox ceremony of the Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany Ceremony, and would often schedule events for The All-Joking, All-Drunken Synod of Fools and Jesters to directly conflict with the Church.
Peter was brought up in the Russian Orthodox faith, but he had low regard for the Church hierarchy, which he kept under tight governmental control. The traditional leader of the Church was the List of Metropolitans and Patriarchs of Moscow, Patriarch of Moscow. In 1700, when the office fell vacant, Peter refused to name a replacement, allowing the Patriarch's Coadjutor (or deputy) to discharge the duties of the office. Peter could not tolerate the patriarch exercising power superior to the Tsar, as indeed had happened in the case of Patriarch Philaret of Moscow, Philaret (1619–1633) and Patriarch Nikon of Moscow, Nikon (1652–66). The Church reform of Peter the Great therefore abolished the Patriarchate, replacing it with a Holy Synod that was under the control of a Procurator_(Russia), Procurator, and the Tsar appointed all bishops.
In 1721, Peter followed the advice of Theophan Prokopovich in designing the Holy Synod as a council of ten clergymen. For leadership in the church, Peter turned increasingly to Ukrainians, who were more open to reform, but were not well loved by the Russian clergy. Peter implemented a law that stipulated that no Russian man could join a monastery before the age of fifty. He felt that too many able Russian men were being wasted on clerical work when they could be joining his new and improved army.
A clerical career was not a route chosen by upper-class society. Most parish priests were sons of priests and were very poorly educated and paid. The monks in the monasteries had a slightly higher status; they were not allowed to marry. Politically, the church was impotent.
Marriages and family
 Peter the Great had two wives, with whom he had fourteen children, three of whom survived to adulthood. Peter's mother selected his first wife,
Peter the Great had two wives, with whom he had fourteen children, three of whom survived to adulthood. Peter's mother selected his first wife, Eudoxia Lopukhina
Tsarina Eudoxia Fyodorovna Lopukhina ( rus, Евдоки́я Фёдоровна Лопухина́, Yevdokíya Fyodorovna Lopukhiná; in Moscow – in Moscow) was a Russian Tsaritsa as the first wife of Peter I of Russia, and the last ethnic ...
, with the advice of other nobles in 1689. This was consistent with previous Romanov tradition by choosing a daughter of a minor noble. This was done to prevent fighting between the stronger noble houses and to bring fresh blood into the family. He also had a mistress from Holland, Anna Mons.
Upon his return from his European tour in 1698, Peter sought to end his unhappy marriage. He divorced the Tsaritsa and forced her to join a convent. The Tsaritsa had borne Peter three children, although only one, Alexei Petrovich, Tsarevich of Russia, had survived past his childhood.
He took Marta Helena Skowrońska, a Polish-Lithuanian peasant, as a mistress some time between 1702 and 1704. Marta converted to the Russian Orthodox Church and took the name Catherine. Though no record exists, Catherine and Peter are described as having married secretly between 23 Oct and 1 December 1707 in St. Petersburg. Peter valued Catherine and married her again (this time officially) at Saint Isaac's Cathedral in Saint Petersburg on 19 February 1712.
His eldest child and heir, Alexei, was suspected of being involved in a plot to overthrow the Emperor. Alexei was tried and confessed under torture during questioning conducted by a secular court. He was convicted and sentenced to be executed. The sentence could be carried out only with Peter's signed authorization, and Alexei died in prison, as Peter hesitated before making the decision. Alexei's death most likely resulted from injuries suffered during his torture. Alexei's mother Eudoxia had also been punished; she was dragged from her home, tried on false charges of adultery, publicly flogged, and finally confined in monasteries while forbidden to be talked to.
In 1724, Peter had his second wife, Catherine I of Russia, Catherine, crowned as Empress, although he remained Russia's actual ruler. All of Peter's male children had died.
Issue
By his two wives, he had fourteen children. These included three sons named ''Pavel'' and three sons named ''Peter'', all of whom died in infancy. Only three of his children survived to adulthood: Alexei, Anna Petrovna, and Elizabeth. He had only two grandchildren: Peter II and Peter III.Mistresses and illegitimate children
* Maria Cantemir, Princess Maria Cantemir of Moldavia (1700 – 1754), daughter of Dimitrie Cantemir **Unnamed son (1722 – 1723) – who died prematurely. According to other sources, the baby was stilborn. * Mary Hamilton (lady in waiting), Lady Mary Hamilton, Catherina I's lady in waiting of Scottish descent. ** miscarriage (1715) ** Unnamed child (1717 – 1718) ** Unnamed childLegacy

 Peter's legacy has always been a major concern of Russian intellectuals. Riasanovsky points to a "paradoxical dichotomy" in the black and white images such as God/Antichrist, educator/ignoramus, architect of Russia's greatness/destroyer of national culture, father of his country/scourge of the common man. Voltaire's 1759 biography gave 18th-century Russians a man of the Enlightenment, while Alexander Pushkin's "The Bronze Horseman (poem), The Bronze Horseman" poem of 1833 gave a powerful romantic image of a creator-god. Slavophiles in mid-19th century deplored Peter's westernization of Russia. Western writers and political analysts recounted "The Testimony" or secret will of Peter the Great. It supposedly revealed his grand evil plot for Russia to control the world via conquest of Constantinople, Afghanistan and India. It was a forgery made in Paris at Napoleon's command when he started his invasion of Russia in 1812. Nevertheless, it is still quoted in foreign policy circles. The Communists executed the last Romanovs, and their historians such as Mikhail Pokrovsky presented strongly negative views of the entire dynasty. Stalin however admired how Peter strengthened the state, and wartime, diplomacy, industry, higher education, and government administration. Stalin wrote in 1928, "when Peter the Great, who had to deal with more developed countries in the West, feverishly built works in factories for supplying the army and strengthening the country's defenses, this was an original attempt to leap out of the framework of backwardness." As a result, Soviet historiography emphasizes both the positive achievement and the negative factor of oppressing the common people.
After the fall of Communism in 1991, scholars and the general public in Russia and the West gave fresh attention to Peter and his role in Russian history. His reign is now seen as the decisive formative event in the Russian imperial past. Many new ideas have merged, such as whether he strengthened the autocratic state or whether the tsarist regime was not statist enough given its small bureaucracy. Modernization models have become contested ground. Historian Ia. Vodarsky said in 1993 that Peter, "did not lead the country on the path of accelerated economic, political and social development, did not force it to 'achieve a leap' through several stages.... On the contrary, these actions to the greatest degree put a brake on Russia's progress and created conditions for holding it back for one and a half centuries!" The autocratic powers that Stalin admired appeared as a liability to Evgeny Anisimov, who complained that Peter was, "the creator of the administrative command system and the true ancestor of Stalin."
According to ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'', "He did not completely bridge the gulf between Russia and the Western countries, but he achieved considerable progress in development of the national economy and trade, education, science and culture, and foreign policy. Russia became a great power, without whose concurrence no important European problem could thenceforth be settled. His internal reforms achieved progress to an extent that no earlier innovator could have envisaged."
While the cultural turn in historiography has downplayed diplomatic, economic and constitutional issues, new cultural roles have been found for Peter, for example in architecture and dress. James Cracraft argues:
:The Petrine revolution in Russia—subsuming in this phrase the many military, naval, governmental, educational, architectural, linguistic, and other internal reforms enacted by Peter’s regime to promote Russia’s rise as a major European power—was essentially a cultural revolution, one that profoundly impacted both the basic constitution of the Russian Empire and, perforce, its subsequent development.
Peter's legacy has always been a major concern of Russian intellectuals. Riasanovsky points to a "paradoxical dichotomy" in the black and white images such as God/Antichrist, educator/ignoramus, architect of Russia's greatness/destroyer of national culture, father of his country/scourge of the common man. Voltaire's 1759 biography gave 18th-century Russians a man of the Enlightenment, while Alexander Pushkin's "The Bronze Horseman (poem), The Bronze Horseman" poem of 1833 gave a powerful romantic image of a creator-god. Slavophiles in mid-19th century deplored Peter's westernization of Russia. Western writers and political analysts recounted "The Testimony" or secret will of Peter the Great. It supposedly revealed his grand evil plot for Russia to control the world via conquest of Constantinople, Afghanistan and India. It was a forgery made in Paris at Napoleon's command when he started his invasion of Russia in 1812. Nevertheless, it is still quoted in foreign policy circles. The Communists executed the last Romanovs, and their historians such as Mikhail Pokrovsky presented strongly negative views of the entire dynasty. Stalin however admired how Peter strengthened the state, and wartime, diplomacy, industry, higher education, and government administration. Stalin wrote in 1928, "when Peter the Great, who had to deal with more developed countries in the West, feverishly built works in factories for supplying the army and strengthening the country's defenses, this was an original attempt to leap out of the framework of backwardness." As a result, Soviet historiography emphasizes both the positive achievement and the negative factor of oppressing the common people.
After the fall of Communism in 1991, scholars and the general public in Russia and the West gave fresh attention to Peter and his role in Russian history. His reign is now seen as the decisive formative event in the Russian imperial past. Many new ideas have merged, such as whether he strengthened the autocratic state or whether the tsarist regime was not statist enough given its small bureaucracy. Modernization models have become contested ground. Historian Ia. Vodarsky said in 1993 that Peter, "did not lead the country on the path of accelerated economic, political and social development, did not force it to 'achieve a leap' through several stages.... On the contrary, these actions to the greatest degree put a brake on Russia's progress and created conditions for holding it back for one and a half centuries!" The autocratic powers that Stalin admired appeared as a liability to Evgeny Anisimov, who complained that Peter was, "the creator of the administrative command system and the true ancestor of Stalin."
According to ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'', "He did not completely bridge the gulf between Russia and the Western countries, but he achieved considerable progress in development of the national economy and trade, education, science and culture, and foreign policy. Russia became a great power, without whose concurrence no important European problem could thenceforth be settled. His internal reforms achieved progress to an extent that no earlier innovator could have envisaged."
While the cultural turn in historiography has downplayed diplomatic, economic and constitutional issues, new cultural roles have been found for Peter, for example in architecture and dress. James Cracraft argues:
:The Petrine revolution in Russia—subsuming in this phrase the many military, naval, governmental, educational, architectural, linguistic, and other internal reforms enacted by Peter’s regime to promote Russia’s rise as a major European power—was essentially a cultural revolution, one that profoundly impacted both the basic constitution of the Russian Empire and, perforce, its subsequent development.
Popular culture
Peter has been featured in many histories, novels, plays, films, monuments and paintings. They include the poems ''The Bronze Horseman (poem), The Bronze Horseman'', ''Poltava (poem), Poltava'' and the unfinished novel ''The Moor of Peter the Great'', all by Alexander Pushkin. The former dealt with The Bronze Horseman, an equestrian statue raised in Peter's honour. Aleksey Nikolayevich Tolstoy wrote a biographical historical novel about him, named ''Pëtr I'', in the 1930s. * The 1922 German silent film ''Peter the Great (1922 film), Peter the Great'' directed by Dimitri Buchowetzki and starring Emil Jannings as Peter * The 1937–1938 Soviet Union (Russia) film ''Peter the First'' * The 1976 film ''Skaz pro to, kak tsar Pyotr arapa zhenil'' (''How Tsar Peter the Great Married Off His Moor''), starring Aleksey Petrenko as Peter, and Vladimir Vysotsky as Abram Petrovich Gannibal, shows Peter's attempt to build the Baltic Fleet. * The 2007 film ''The Sovereign's Servant'' depicts the unsavoury brutal side of Peter during the campaign. * Peter was played by Jan Niklas and Maximilian Schell in the 1986 NBC miniseries ''Peter the Great (TV series), Peter the Great''. * A character based on Peter plays a major role in ''The Age of Unreason'', a series of four alternate history novels written by American science fiction and fantasy author Gregory Keyes. * Peter is one of many supporting characters in Neal Stephenson's ''Baroque Cycle'' – mainly featuring in the third novel, ''The System of the World''. * Peter was portrayed on BBC Radio 4 by Isaac Rouse as a boy, Will Howard as a young adult and Elliot Cowan as an adult in the radio plays ''Peter the Great: The Gamblers'' and ''Peter the Great: The Queen of Spades'', written by Mike Walker (radio dramatist), Mike Walker and which were the last two plays in the first series of ''Tsar''. The plays were broadcast on 25 September and 2 October 2016. * A verse in the ''Godiva's Hymn, Engineers' Drinking Song'' references Peter the Great:* Peter was played by Jason Isaacs in the 2020 'antihistory' Hulu series The Great (TV series), ''The Great''. * Peter is featured as the leader of the Russian civilization in the computer game ''Sid Meier's Civilization VI''.There was a man named Peter the Great who was a Russian Tzar; When remodeling his the castle put the throne behind the bar; He lined the walls with vodka, rum, and 40 kinds of beers; And advanced the Russian culture by 120 years!
GameRant. Retrieved 15 December 2020.
See also
* Government reform of Peter the Great * History of the administrative division of Russia * Russian battlecruiser Pyotr Velikiy, Russian battlecruiser ''Pyotr Velikiy'', a Russian Navy battle cruiser named after Peter the Great * History of Russia (1721–96) * Rulers of Russia family tree * Peter the Great Statue * , on the modernization of the Russian military under Peter the Great * List of people known as "the Great"Notes
References
Sources
* Anisimov, Evgenii V. (2015) ''The Reforms of Peter the Great: Progress Through Violence in Russia'' (Routledge) * *online
* * * * *
online
* * * * , a popular biography
online
* * * * * *
online
* * * ; Historiography and memory * Brown, Peter B. "Towards a Psychohistory of Peter the Great: Trauma, Modeling, and Coping in Peter's Personality." ''Russian History'' 35#1-2 (2008): 19–44. * Brown, Peter B. "Gazing Anew at Poltava: Perspectives from the Military Revolution Controversy, Comparative History, and Decision-Making Doctrines." ''Harvard Ukrainian Studies'' 31.1/4 (2009): 107–133
online
* Cracraft, James. "Kliuchevskii on Peter the Great." ''Canadian-American Slavic Studies'' 20.4 (1986): 367–381. * Daqiu, Zhu. "Cultural Memory and the Image of Peter the Great in Russian Literature." ''Russian Literature & Arts'' 2 (2014): 19+. * Gasiorowska, Xenia. ''The image of Peter the Great in Russian fiction'' (1979
online
* Platt, Kevin M. F. ''Terror and Greatness: Ivan and Peter as Russian Myths'' (2011) * Raef, Mark, ed. ''Peter the Great, Reformer or Revolutionary?'' (1963) excerpts from scholars and primary source
online
* Resis, Albert. "Russophobia and the" Testament" of Peter the Great, 1812–1980." ''Slavic Review'' 44.4 (1985): 681-69
online
* Riasanovsky, Nicholas V. ''The Image of Peter the Great in Russian History and Thought'' (1985). * Waugh, Daniel Clarke. "We have never been modern: Approaches to the study of Russia in the age of Peter the Great." ''Jahrbücher für Geschichte Osteuropas H.'' 3 (2001): 321-34
online in English
* * Zitser, Ernest A. "The Difference that Peter I Made." in ''The Oxford Handbook of Modern Russian History.'' ed. by Simon Dixon (2013
online
Further reading
* Anderson, M.S. "Russia under Peter the Great and the changed relations of East and West." in J.S. Bromley, ed., ''The New Cambridge Modern History: VI: 1688-1715'' (1970) pp. 716–40. * Anisimov, Evgenii V. ''The Reforms of Peter the Great: Progress through Coercion in Russia'' (1993online
* * Bushkovitch, Paul. ''Peter the Great: The Struggle for Power, 1671–1725'' (2001
online
* Cracraft, James. ''The Revolution of Peter the Great'' (2003
online
* Duffy, Christopher. ''Russia's Military Way to the West: Origins and Nature of Russian Military Power 1700-1800'' (Routledge, 2015) pp 9–41 * Graham, Stephen. ''Peter The Great'' (1929
online
* Kamenskii, Aleksandr. ''The Russian Empire in the Eighteenth Century: Searching for a Place in the World''(1997) pp 39–164. * Kluchevsky, V.O. ''A history of Russia'' vol 4 (1926
online
pp 1–230. ** Cracraft, James. "Kliuchevskii on Peter the Great." ''Canadian-American Slavic Studies'' 20.4 (1986): 367–381. * Oliva, Lawrence Jay. ed. ''Russia in the era of Peter the Great'' (1969), excerpts from primary and secondary source
two week borrowing
* Pares, Bernard. ''A History Of Russia'' (1947) pp 193–225
online
* Schimmelpenninck van der Oye, David, and Bruce W. Menning, eds. ''Reforming the Tsar's Army – Military Innovation in Imperial Russia from Peter the Great to the Revolution'' (Cambridge UP, 2004) 361 pp. scholarly essays * Sumner, B. H. ''Peter the Great and the emergence of Russia'' (1950), brief history by schola
online
External links
* – Historical reconstruction ''The Romanovs''. StarMedia. Babich-Design (Russia, 2013)Peter the Great, a Tsar who Loved Science by Philippe Testard-Vaillant
{{DEFAULTSORT:Peter 01 Of Russia Peter the Great, 1672 births 1725 deaths 17th-century Russian monarchs 18th-century Russian monarchs Russian tsars Russian emperors House of Romanov Russian city founders Royalty from Moscow Russian inventors Russian folklore characters Characters in Bylina Eastern Orthodox monarchs Modern child rulers Burials at Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral, Saint Petersburg Russian military personnel of the Great Northern War Members of the French Academy of Sciences Filicides People of the Regency of Philippe d'Orléans People of the Russo-Persian Wars Netherlands–Russia relations Russian tsareviches Russian people of Tatar descent Deaths from gangrene Russian expatriates in the Netherlands Russian expatriates in the United Kingdom Infectious disease deaths in Russia Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Poland) Children of Alexis of Russia