perimetry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A visual field test is an eye examination that can detect dysfunction in central and
 ; Tangent screen
: The simplest form of perimetry uses a white tangent screen. Vision is tested by presenting different sized pins attached to a black wand, which may be moved, against a black background. This test stimulus (pins) may be white or colored.
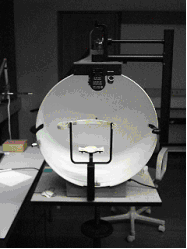
; Goldmann perimeter
: The Goldmann perimeter is a hollow white spherical bowl positioned a set distance in front of the patient. An examiner presents a test light of variable size and intensity. The light may move towards the center from the perimeter (kinetic perimetry), or it may remain in one location (static perimetry). The Goldmann method is able to test the entire range of peripheral vision and has been used for years to follow vision changes in
; Tangent screen
: The simplest form of perimetry uses a white tangent screen. Vision is tested by presenting different sized pins attached to a black wand, which may be moved, against a black background. This test stimulus (pins) may be white or colored.
; Goldmann perimeter
: The Goldmann perimeter is a hollow white spherical bowl positioned a set distance in front of the patient. An examiner presents a test light of variable size and intensity. The light may move towards the center from the perimeter (kinetic perimetry), or it may remain in one location (static perimetry). The Goldmann method is able to test the entire range of peripheral vision and has been used for years to follow vision changes in
"Amsler Grid" Test
from Ossibus Software {{Authority control Diagnostic ophthalmology
peripheral vision
Peripheral vision, or ''indirect vision'', is vision as it occurs outside the point of fixation, i.e. away from the center of gaze or, when viewed at large angles, in (or out of) the "corner of one's eye". The vast majority of the area in the ...
which may be caused by various medical conditions such as glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye rem ...
, stroke, pituitary disease
A pituitary disease is a disorder primarily affecting the pituitary gland.
__TOC__ Table
The main disorders involving the pituitary gland are:
Overproduction or underproduction of a pituitary hormone will affect the respective end-organ. For exa ...
, brain tumour
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and seconda ...
s or other neurological deficits. Visual field testing can be performed clinically by keeping the subject's gaze fixed while presenting objects at various places within their visual field
The visual field is the "spatial array of visual sensations available to observation in introspectionist psychological experiments". Or simply, visual field can be defined as the entire area that can be seen when an eye is fixed straight at a point ...
. Simple manual equipment can be used such as in the tangent screen test or the Amsler grid
The Amsler grid, used since 1945, is a grid of horizontal and vertical lines used to monitor a person's central visual field. The grid was developed by Marc Amsler, a Swiss ophthalmologist. It is a diagnostic tool that aids in the detection of ...
. When dedicated machinery is used it is called a perimeter.
The exam may be performed by a technician in one of several ways. The test may be performed by a technician directly, with the assistance of a machine, or completely by an automated machine. Machine-based tests aid diagnostics by allowing a detailed printout of the patient's visual field.
Other names for this test may include perimetry, Tangent screen exam, Automated perimetry exam, Goldmann visual field exam, or brand names such as Henson 9000 Perimeter, Humphrey Field Analyzer, Octopus Perimeter, Oculus Easyfield perimeter, Olleyes VisuALL, Optopol PTS perimeter, etc.
Examination methods
Techniques used to perform this test include the confrontation visual field examination (Donders' test). The examiner will ask the patient to cover one eye and stare at the examiner. Ideally, when the patient covers their right eye, the examiner covers their left eye and vice versa. The examiner will then move his hand out of the patient's visual field and then bring it back in. Commonly the examiner will use a slowly wagging finger or a hat pin for this. The patient signals the examiner when his hand comes back into view. This is frequently done by an examiner as a simple and preliminary test.Perimetry
Perimetry or campimetry is one way to systematically test the visual field. It is the systematic measurement of differential light sensitivity in thevisual field
The visual field is the "spatial array of visual sensations available to observation in introspectionist psychological experiments". Or simply, visual field can be defined as the entire area that can be seen when an eye is fixed straight at a point ...
by the detection of the presence of test targets on a defined background. Perimetry more carefully maps and quantifies the visual field, especially at the extreme periphery of the visual field. The name comes from the method of testing the ''perimeter'' of the visual field.
Automated perimeters are used widely, and applications include: diagnosing disease, job selection, visual competence assessment, school or community screenings, military selection, and disability classifications.
Types
 ; Tangent screen
: The simplest form of perimetry uses a white tangent screen. Vision is tested by presenting different sized pins attached to a black wand, which may be moved, against a black background. This test stimulus (pins) may be white or colored.
; Goldmann perimeter
: The Goldmann perimeter is a hollow white spherical bowl positioned a set distance in front of the patient. An examiner presents a test light of variable size and intensity. The light may move towards the center from the perimeter (kinetic perimetry), or it may remain in one location (static perimetry). The Goldmann method is able to test the entire range of peripheral vision and has been used for years to follow vision changes in
; Tangent screen
: The simplest form of perimetry uses a white tangent screen. Vision is tested by presenting different sized pins attached to a black wand, which may be moved, against a black background. This test stimulus (pins) may be white or colored.
; Goldmann perimeter
: The Goldmann perimeter is a hollow white spherical bowl positioned a set distance in front of the patient. An examiner presents a test light of variable size and intensity. The light may move towards the center from the perimeter (kinetic perimetry), or it may remain in one location (static perimetry). The Goldmann method is able to test the entire range of peripheral vision and has been used for years to follow vision changes in glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye rem ...
patients. However, now automated perimetry is more commonly used.
; Automated perimetry
: Automated perimetry uses a mobile stimulus moved by a perimetry machine. The patient indicates whether he sees the light by pushing a button. The use of a white background and lights of incremental brightness is called "white-on-white" perimetry. This type of perimetry is the most commonly used in clinical practice, and in research trials where loss of visual field must be measured. However, the sensitivity of white-on-white perimetry is low, and the variability is relatively high; as many as 25–50 percent of the photoreceptor cells may be lost before changes in visual field acuity are detected. This method is commonly used for early detection of blind spots. The patient sits in front of an (artificial) small concave dome in a small machine with a target in the center. The chin rests on the machine and the eye that is not being tested is covered. A button is given to the patient to be used during the exam. The patient is set in front of the dome and asked to focus on the target at the center. A computer then shines lights on the inside dome and the patient clicks the button whenever a light is seen. The computer then automatically maps and calculates the patient's visual field.
; Microperimetry
: Microperimetry
Microperimetry, sometimes called fundus-controlled perimetry, is a type of visual field test which uses one of several technologies to create a "retinal sensitivity map" of the quantity of light perceived in specific parts of the retina in people ...
assesses the macular function in a similar way to perimetry. However, fundus imaging is performed at the same time. This allows for fundus tracking to ensure accurate stimulus placement. Thus, microperimetry provides enhances the retest reliability, enables precise structure-function correlation, and allows for examination of patients with unstable fixation.
Methods of stimulus presentation
Static perimetry
Static perimetry tests different locations throughout the field one at a time. First, a dim light is presented at a particular location. If the patient does not see the light, it is made gradually brighter until it is seen. The minimum brightness required for the detection of a light stimulus is called the "threshold" sensitivity level of that location. This procedure is then repeated at several other locations, until the entire visual field is tested. Threshold static perimetry is generally done using automated equipment. It is used for rapid screening and follow-up of diseases involving deficits such as scotomas, loss ofperipheral vision
Peripheral vision, or ''indirect vision'', is vision as it occurs outside the point of fixation, i.e. away from the center of gaze or, when viewed at large angles, in (or out of) the "corner of one's eye". The vast majority of the area in the ...
and more subtle vision loss. Perimetry testing is important in the screening, diagnosing, and monitoring of various eye, retinal, optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from ...
and brain disorders.
Kinetic perimetry
Kinetic perimetry uses a mobile stimulus moved by an examiner (perimetrist) such as in Goldmann kinetic perimetry. First, a single test light of constant size and brightness is used. The test light is moved towards the center of vision from the periphery until it is first detected by the patient. This is repeated by approaching the center of vision from different directions. Repeating this enough will establish a boundary of vision for that target. The procedure is repeated using different test lights that are larger or brighter than the original test light. In this way, kinetic perimetry is useful for mapping visual field sensitivity boundaries. It may be a good alternative for patients that have difficulty with automated perimetry, either due to difficulty maintaining constant gaze, or due to cognitive impairment.Stimulus settings and photoreceptor-specific perimetry
Photopic perimetry
The most commonly performed perimetry test uses white stimuli on a bright white background (photopic white-on-white testing). This tests isolated L- and M-cone function and is applied in the setting of glaucoma.Scotopic perimetry
Following 30 minutes of dark-adaptation, it is possible to selectively test rod function using short-wavelength (blue) stimuli on a dark background. Today, it is also possible to perform this type of examination in eyes with unstable fixation using scotopic microperimetry.See also
*Bitemporal hemianopsia
Bitemporal hemianopsia, is the medical description of a type of partial blindness where vision is missing in the outer half of both the right and left visual field. It is usually associated with lesions of the optic chiasm, the area where the opt ...
(loss of peripheral vision).
References
External links
"Amsler Grid" Test
from Ossibus Software {{Authority control Diagnostic ophthalmology