Pedro I of Brazil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
'' Dom'' Pedro I (12 October 1798 – 24 September 1834), known in Brazil and in Portugal as "the Liberator" () or "the Soldier King" () in Portugal, was the founder and first ruler of the
 Pedro was born at 08:00 on 12 October 1798 in the Queluz Royal Palace near
Pedro was born at 08:00 on 12 October 1798 in the Queluz Royal Palace near
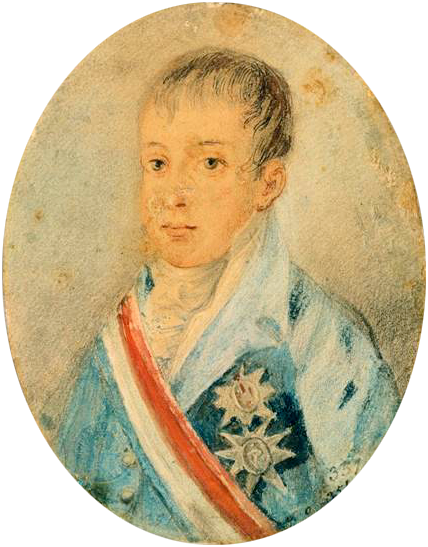 In late November 1807, when Pedro was nine, the royal family escaped from Portugal as an invading French army sent by
In late November 1807, when Pedro was nine, the royal family escaped from Portugal as an invading French army sent by
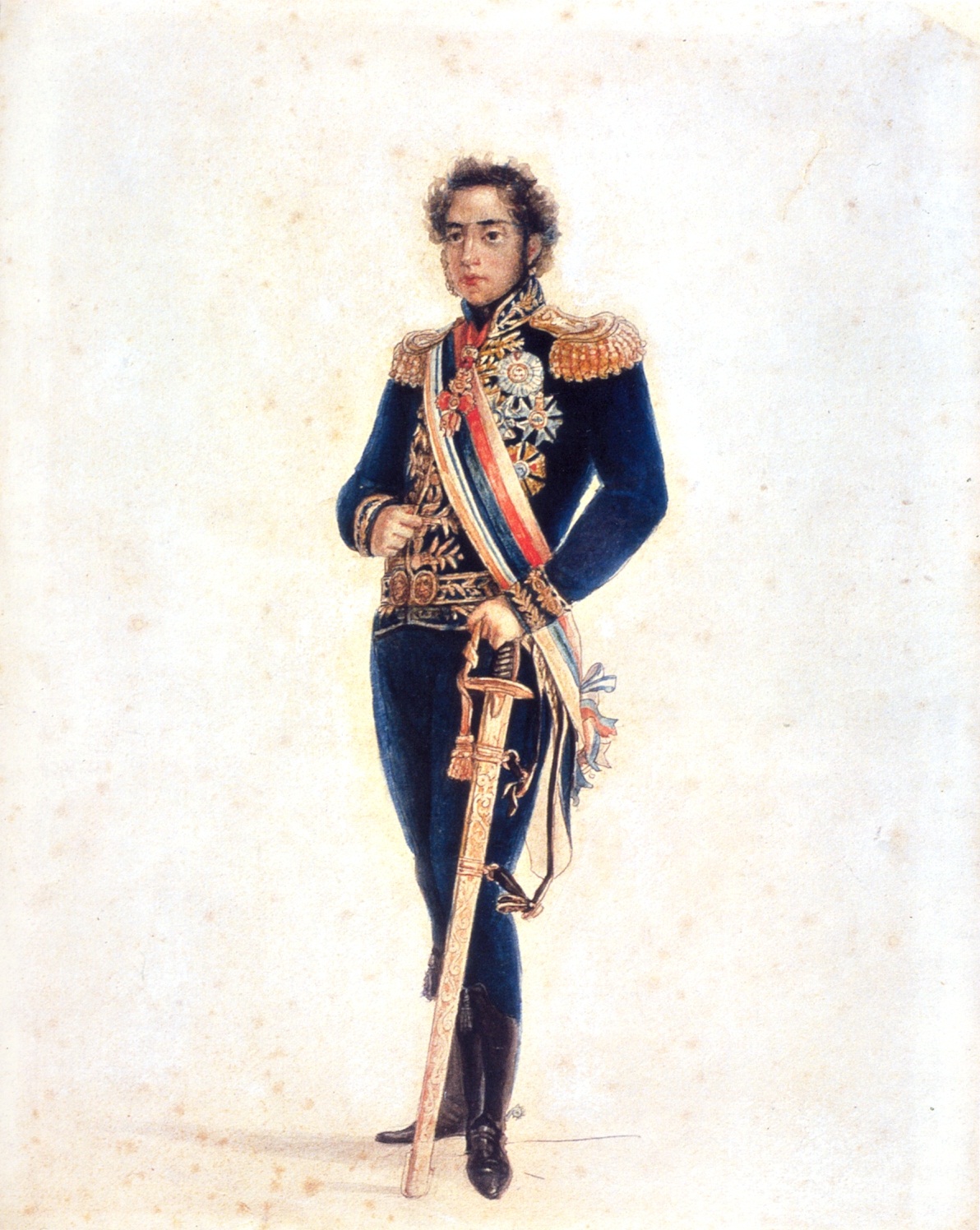 The prince found fulfillment in activities that required physical skills, rather than in the classroom. At his father's Santa Cruz farm, Pedro trained unbroken horses, and became a fine horseman and an excellent
The prince found fulfillment in activities that required physical skills, rather than in the classroom. At his father's Santa Cruz farm, Pedro trained unbroken horses, and became a fine horseman and an excellent
 On 17 October 1820, news arrived that the military garrisons in Portugal had mutinied, leading to what became known as the Liberal Revolution of 1820. The military formed a provisional government, supplanting the regency appointed by John VI, and summoned the ''Cortes''—the centuries-old Portuguese parliament, this time democratically elected with the aim of creating a national Constitution. Pedro was surprised when his father not only asked for his advice, but also decided to send him to Portugal to rule as regent on his behalf and to placate the revolutionaries. The prince was never educated to rule and had previously been allowed no participation in state affairs. The role that was his by birthright was instead filled by his elder sister Dona Maria Teresa: John VI had relied on her for advice, and it was she who had been given membership in the
On 17 October 1820, news arrived that the military garrisons in Portugal had mutinied, leading to what became known as the Liberal Revolution of 1820. The military formed a provisional government, supplanting the regency appointed by John VI, and summoned the ''Cortes''—the centuries-old Portuguese parliament, this time democratically elected with the aim of creating a national Constitution. Pedro was surprised when his father not only asked for his advice, but also decided to send him to Portugal to rule as regent on his behalf and to placate the revolutionaries. The prince was never educated to rule and had previously been allowed no participation in state affairs. The role that was his by birthright was instead filled by his elder sister Dona Maria Teresa: John VI had relied on her for advice, and it was she who had been given membership in the
 At the outset of his regency, Pedro promulgated decrees that guaranteed personal and property rights. He also reduced government expenditure and taxes. Even the revolutionaries arrested in the Merchants' Exchange incident were set free. On 5 June 1821, army troops under Portuguese lieutenant general Jorge Avilez (later Count of Avilez) mutinied, demanding that Pedro should take an oath to uphold the Portuguese Constitution after it was enacted. The prince rode out alone to intervene with the mutineers. He calmly and resourcefully negotiated, winning the respect of the troops and succeeding in reducing the impact of their more unacceptable demands. The mutiny was a thinly veiled military coup d'état that sought to turn Pedro into a mere figurehead and transfer power to Avilez. The prince accepted the unsatisfactory outcome, but he also warned that it was the last time he would yield under pressure.
The continuing crisis reached a point of no return when the ''Cortes'' dissolved the central government in Rio de Janeiro and ordered Pedro's return. This was perceived by Brazilians as an attempt to subordinate their country again to Portugal—Brazil had not been a colony since 1815 and had the status of a kingdom. On 9 January 1822, Pedro was presented with a petition containing 8,000 signatures that begged him not to leave. He replied, "Since it is for the good of all and the general happiness of the Nation, I am willing. Tell the people that I am staying." The date became known as the '' Dia do Fico''. Avilez again mutinied and tried to force Pedro's return to Portugal. This time the prince fought back, rallying the Brazilian troops (which had not joined the Portuguese in previous mutinies), militia units and armed civilians. Outnumbered, Avilez surrendered and was expelled from Brazil along with his troops.
During the next few months, Pedro attempted to maintain a semblance of unity with Portugal, but the final rupture was impending. Aided by an able minister,
At the outset of his regency, Pedro promulgated decrees that guaranteed personal and property rights. He also reduced government expenditure and taxes. Even the revolutionaries arrested in the Merchants' Exchange incident were set free. On 5 June 1821, army troops under Portuguese lieutenant general Jorge Avilez (later Count of Avilez) mutinied, demanding that Pedro should take an oath to uphold the Portuguese Constitution after it was enacted. The prince rode out alone to intervene with the mutineers. He calmly and resourcefully negotiated, winning the respect of the troops and succeeding in reducing the impact of their more unacceptable demands. The mutiny was a thinly veiled military coup d'état that sought to turn Pedro into a mere figurehead and transfer power to Avilez. The prince accepted the unsatisfactory outcome, but he also warned that it was the last time he would yield under pressure.
The continuing crisis reached a point of no return when the ''Cortes'' dissolved the central government in Rio de Janeiro and ordered Pedro's return. This was perceived by Brazilians as an attempt to subordinate their country again to Portugal—Brazil had not been a colony since 1815 and had the status of a kingdom. On 9 January 1822, Pedro was presented with a petition containing 8,000 signatures that begged him not to leave. He replied, "Since it is for the good of all and the general happiness of the Nation, I am willing. Tell the people that I am staying." The date became known as the '' Dia do Fico''. Avilez again mutinied and tried to force Pedro's return to Portugal. This time the prince fought back, rallying the Brazilian troops (which had not joined the Portuguese in previous mutinies), militia units and armed civilians. Outnumbered, Avilez surrendered and was expelled from Brazil along with his troops.
During the next few months, Pedro attempted to maintain a semblance of unity with Portugal, but the final rupture was impending. Aided by an able minister,
 After his wife's death, Pedro I realized how miserably he had treated her, and his relationship with Domitila began to crumble. Maria Leopoldina, unlike his mistress, was popular, honest and loved him without expecting anything in return. The Emperor greatly missed her, and even his obsession with Domitila failed to overcome his sense of loss and regret. One day Domitila found him weeping on the floor and embracing a portrait of his deceased wife, whose sad-looking ghost Pedro I claimed to have seen. Later on, the Emperor left the bed he shared with Domitila and shouted: "Get off of me! I know I live an unworthy life of a sovereign. The thought of the Empress does not leave me." He did not forget his children, orphaned of their mother, and was observed on more than one occasion holding his son, the young Pedro, in his arms and saying: "Poor boy, you are the most unhappy prince in the world."
At the insistence of Pedro I, Domitila departed from Rio de Janeiro on 27 June 1828. He had resolved to marry again and to become a better person. He even tried to persuade his father-in-law of his sincerity, by claiming in a letter "that all my wickedness is over, that I shall not again fall into those errors into which I have fallen, which I regret and have asked God for forgiveness". Francis I was less than convinced. The Austrian emperor, deeply offended by the conduct his daughter endured, withdrew his support for Brazilian concerns and frustrated Pedro I's Portuguese interests. Because of Pedro I's bad reputation in Europe, owing to his past behavior, princesses from several nations declined his proposals of marriage one after another. His pride thus wounded, he allowed his mistress to return, which she did on 29 April 1829 after having been away nearly a year.
However, once he learned that a betrothal had finally been arranged, the Emperor ended his relationship to Domitila. She returned to her native province of São Paulo on 27 August, where she remained. Days earlier, on 2 August, the Emperor had been married by proxy to Amélie of Leuchtenberg. He was stunned by her beauty after meeting her in person. The vows previously made by proxy were ratified in a Nuptial Mass on 17 October. Amélie was kind and loving to his children and provided a much needed sense of normality to both his family and the general public. After Domitila's banishment from court, the vow the Emperor made to alter his behavior proved to be sincere. He had no more affairs and remained faithful to his spouse. In an attempt to mitigate and move beyond other past misdeeds, he made peace with José Bonifácio, his former minister and mentor.
After his wife's death, Pedro I realized how miserably he had treated her, and his relationship with Domitila began to crumble. Maria Leopoldina, unlike his mistress, was popular, honest and loved him without expecting anything in return. The Emperor greatly missed her, and even his obsession with Domitila failed to overcome his sense of loss and regret. One day Domitila found him weeping on the floor and embracing a portrait of his deceased wife, whose sad-looking ghost Pedro I claimed to have seen. Later on, the Emperor left the bed he shared with Domitila and shouted: "Get off of me! I know I live an unworthy life of a sovereign. The thought of the Empress does not leave me." He did not forget his children, orphaned of their mother, and was observed on more than one occasion holding his son, the young Pedro, in his arms and saying: "Poor boy, you are the most unhappy prince in the world."
At the insistence of Pedro I, Domitila departed from Rio de Janeiro on 27 June 1828. He had resolved to marry again and to become a better person. He even tried to persuade his father-in-law of his sincerity, by claiming in a letter "that all my wickedness is over, that I shall not again fall into those errors into which I have fallen, which I regret and have asked God for forgiveness". Francis I was less than convinced. The Austrian emperor, deeply offended by the conduct his daughter endured, withdrew his support for Brazilian concerns and frustrated Pedro I's Portuguese interests. Because of Pedro I's bad reputation in Europe, owing to his past behavior, princesses from several nations declined his proposals of marriage one after another. His pride thus wounded, he allowed his mistress to return, which she did on 29 April 1829 after having been away nearly a year.
However, once he learned that a betrothal had finally been arranged, the Emperor ended his relationship to Domitila. She returned to her native province of São Paulo on 27 August, where she remained. Days earlier, on 2 August, the Emperor had been married by proxy to Amélie of Leuchtenberg. He was stunned by her beauty after meeting her in person. The vows previously made by proxy were ratified in a Nuptial Mass on 17 October. Amélie was kind and loving to his children and provided a much needed sense of normality to both his family and the general public. After Domitila's banishment from court, the vow the Emperor made to alter his behavior proved to be sincere. He had no more affairs and remained faithful to his spouse. In an attempt to mitigate and move beyond other past misdeeds, he made peace with José Bonifácio, his former minister and mentor.
 Since the days of the Constituent Assembly in 1823, and with renewed vigor in 1826 with the opening of the General Assembly (the Brazilian parliament), there had been an ideological struggle over the balance of powers wielded by the emperor and legislature in governance. On one side were those who shared Pedro I's views, politicians who believed that the monarch should be free to choose ministers, national policies and the direction of government. In opposition were those, then known as the Liberal Party, who believed that cabinets should have the power to set the government's course and should consist of deputies drawn from the majority party who were accountable to the parliament. Strictly speaking, both the party that supported Pedro I's government and the Liberal Party advocated
Since the days of the Constituent Assembly in 1823, and with renewed vigor in 1826 with the opening of the General Assembly (the Brazilian parliament), there had been an ideological struggle over the balance of powers wielded by the emperor and legislature in governance. On one side were those who shared Pedro I's views, politicians who believed that the monarch should be free to choose ministers, national policies and the direction of government. In opposition were those, then known as the Liberal Party, who believed that cabinets should have the power to set the government's course and should consist of deputies drawn from the majority party who were accountable to the parliament. Strictly speaking, both the party that supported Pedro I's government and the Liberal Party advocated
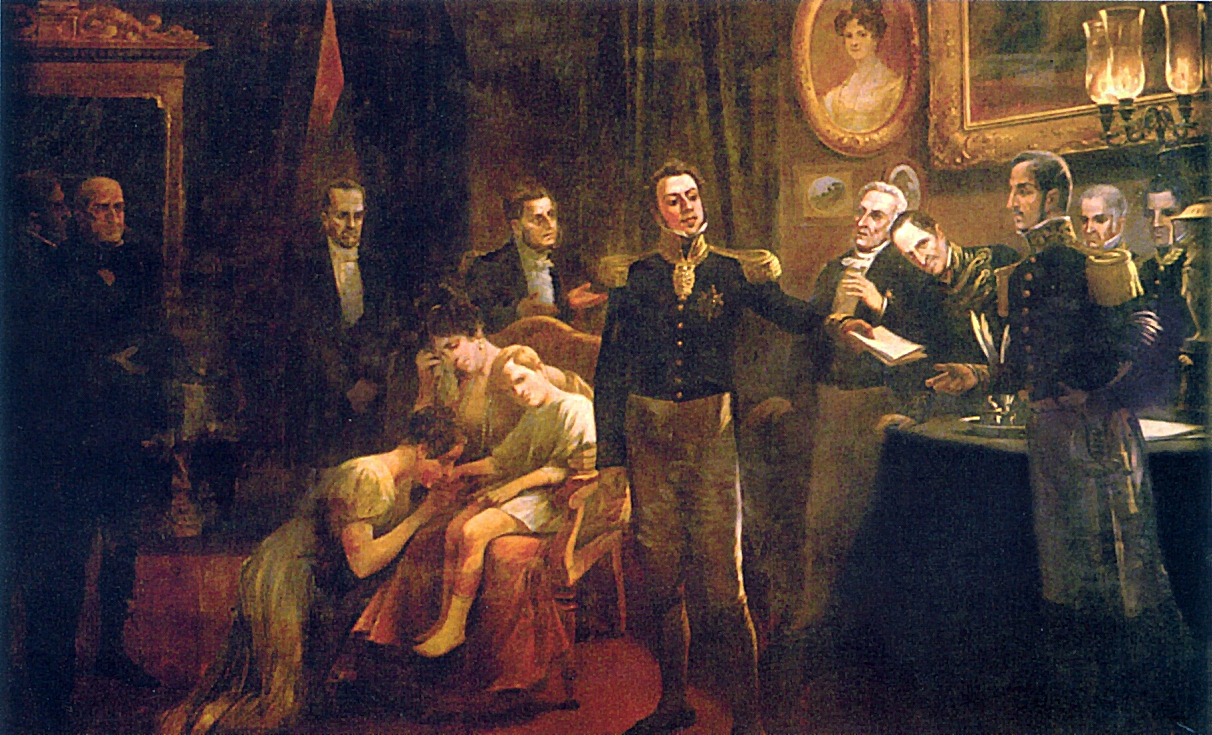 The Emperor's efforts to appease the Liberal Party resulted in very important changes. He supported an 1827 law that established ministerial responsibility. On 19 March 1831, he named a cabinet formed by politicians drawn from the opposition, allowing a greater role for the parliament in the government. Lastly, he offered positions in Europe to Francisco Gomes and another Portuguese-born friend to extinguish rumors of a "secret cabinet". To his dismay, his palliative measures did not stop the continuous attacks from the Liberal side upon his government and his foreign birth. Frustrated by their intransigence, he became unwilling to deal with his deteriorating political situation.
Meanwhile, Portuguese exiles campaigned to convince him to give up on Brazil and instead devote his energies to the fight for his daughter's claim to Portugal's crown. According to Roderick J. Barman, " nan emergency the Emperor's abilities shone forth—he became cool in nerve, resourceful and steadfast in action. Life as a constitutional monarch, full of tedium, caution, and conciliation, ran against the essence of his character." On the other hand, the historian remarked, he "found in his daughter's case everything that appealed most to his character. By going to Portugal he could champion the oppressed, display his chivalry and self-denial, uphold constitutional rule, and enjoy the freedom of action he craved."
The idea of abdicating and returning to Portugal took root in his mind, and, beginning in early 1829, he talked about it frequently. An opportunity soon appeared to act upon the notion. Radicals within the Liberal Party rallied street gangs to harass the Portuguese community in Rio de Janeiro. On 11 March 1831, in what became known as the Night of the Bottle Fight (), the Portuguese retaliated and turmoil gripped the streets of the national capital. On 5 April, Pedro I fired the Liberal cabinet, which had only been in power since 19 March, for its incompetence in restoring order. A large crowd, incited by the radicals, gathered in Rio de Janeiro downtown on the afternoon of 6 April and demanded the immediate restoration of the fallen cabinet. The Emperor's reply was: "I will do everything for the people and nothing ompelledby the people." Sometime after nightfall, army troops, including his guard, deserted him and joined the protests. Only then did he realize how isolated and detached from Brazilian affairs he had become, and to everyone's surprise, he abdicated at approximately 03:00 on 7 April. Upon delivering the abdication document to a messenger, he said: "Here you have my act of abdication, I'm returning to Europe and leaving a country that I loved very much, and still love."
The Emperor's efforts to appease the Liberal Party resulted in very important changes. He supported an 1827 law that established ministerial responsibility. On 19 March 1831, he named a cabinet formed by politicians drawn from the opposition, allowing a greater role for the parliament in the government. Lastly, he offered positions in Europe to Francisco Gomes and another Portuguese-born friend to extinguish rumors of a "secret cabinet". To his dismay, his palliative measures did not stop the continuous attacks from the Liberal side upon his government and his foreign birth. Frustrated by their intransigence, he became unwilling to deal with his deteriorating political situation.
Meanwhile, Portuguese exiles campaigned to convince him to give up on Brazil and instead devote his energies to the fight for his daughter's claim to Portugal's crown. According to Roderick J. Barman, " nan emergency the Emperor's abilities shone forth—he became cool in nerve, resourceful and steadfast in action. Life as a constitutional monarch, full of tedium, caution, and conciliation, ran against the essence of his character." On the other hand, the historian remarked, he "found in his daughter's case everything that appealed most to his character. By going to Portugal he could champion the oppressed, display his chivalry and self-denial, uphold constitutional rule, and enjoy the freedom of action he craved."
The idea of abdicating and returning to Portugal took root in his mind, and, beginning in early 1829, he talked about it frequently. An opportunity soon appeared to act upon the notion. Radicals within the Liberal Party rallied street gangs to harass the Portuguese community in Rio de Janeiro. On 11 March 1831, in what became known as the Night of the Bottle Fight (), the Portuguese retaliated and turmoil gripped the streets of the national capital. On 5 April, Pedro I fired the Liberal cabinet, which had only been in power since 19 March, for its incompetence in restoring order. A large crowd, incited by the radicals, gathered in Rio de Janeiro downtown on the afternoon of 6 April and demanded the immediate restoration of the fallen cabinet. The Emperor's reply was: "I will do everything for the people and nothing ompelledby the people." Sometime after nightfall, army troops, including his guard, deserted him and joined the protests. Only then did he realize how isolated and detached from Brazilian affairs he had become, and to everyone's surprise, he abdicated at approximately 03:00 on 7 April. Upon delivering the abdication document to a messenger, he said: "Here you have my act of abdication, I'm returning to Europe and leaving a country that I loved very much, and still love."
 At dawn on the morning of 7 April, Pedro, his wife, and others, including his daughter Maria II and his sister Ana de Jesus, were taken on board the British warship HMS ''Warspite''. The vessel remained at anchor off Rio de Janeiro, and, on 13 April, the former emperor transferred to and departed for Europe aboard HMS ''Volage''. He arrived in Cherbourg-Octeville, France, on 10 June. During the next few months, he shuttled between France and Great Britain. He was warmly welcomed, but received no actual support from either government to restore his daughter's throne. Finding himself in an awkward situation because he held no official status in either the Brazilian Imperial House or in the Portuguese Royal House, Pedro assumed the title of Duke of Braganza on 15 June, a position that once had been his as heir-apparent to Portugal's crown. Although the title should have belonged to Maria II's heir-apparent, which he certainly was not, his claim was met with general recognition. On 1 December, his only daughter by Amélie, Maria Amélia, was born in Paris.
He did not forget his children left in Brazil. He wrote poignant letters to each of them, conveying how greatly he missed them and repeatedly asking them to seriously attend to their educations. Shortly before his abdication, Pedro had told his son and successor: "I intend that my brother Miguel and I will be the last badly educated of the Braganza family". Charles Napier, a naval commander who fought under Pedro's banner in the 1830s, remarked that "his good qualities were his own; his bad owing to want of education; and no man was more sensible of that defect than himself." His letters to Pedro II were often couched in language beyond the boy's reading level, and historians have assumed such passages were chiefly intended as advice that the young monarch might eventually consult upon reaching adulthood.
While in Paris, the Duke of Braganza met and befriended Gilbert du Motier, Marquis of Lafayette, a veteran of the
At dawn on the morning of 7 April, Pedro, his wife, and others, including his daughter Maria II and his sister Ana de Jesus, were taken on board the British warship HMS ''Warspite''. The vessel remained at anchor off Rio de Janeiro, and, on 13 April, the former emperor transferred to and departed for Europe aboard HMS ''Volage''. He arrived in Cherbourg-Octeville, France, on 10 June. During the next few months, he shuttled between France and Great Britain. He was warmly welcomed, but received no actual support from either government to restore his daughter's throne. Finding himself in an awkward situation because he held no official status in either the Brazilian Imperial House or in the Portuguese Royal House, Pedro assumed the title of Duke of Braganza on 15 June, a position that once had been his as heir-apparent to Portugal's crown. Although the title should have belonged to Maria II's heir-apparent, which he certainly was not, his claim was met with general recognition. On 1 December, his only daughter by Amélie, Maria Amélia, was born in Paris.
He did not forget his children left in Brazil. He wrote poignant letters to each of them, conveying how greatly he missed them and repeatedly asking them to seriously attend to their educations. Shortly before his abdication, Pedro had told his son and successor: "I intend that my brother Miguel and I will be the last badly educated of the Braganza family". Charles Napier, a naval commander who fought under Pedro's banner in the 1830s, remarked that "his good qualities were his own; his bad owing to want of education; and no man was more sensible of that defect than himself." His letters to Pedro II were often couched in language beyond the boy's reading level, and historians have assumed such passages were chiefly intended as advice that the young monarch might eventually consult upon reaching adulthood.
While in Paris, the Duke of Braganza met and befriended Gilbert du Motier, Marquis of Lafayette, a veteran of the
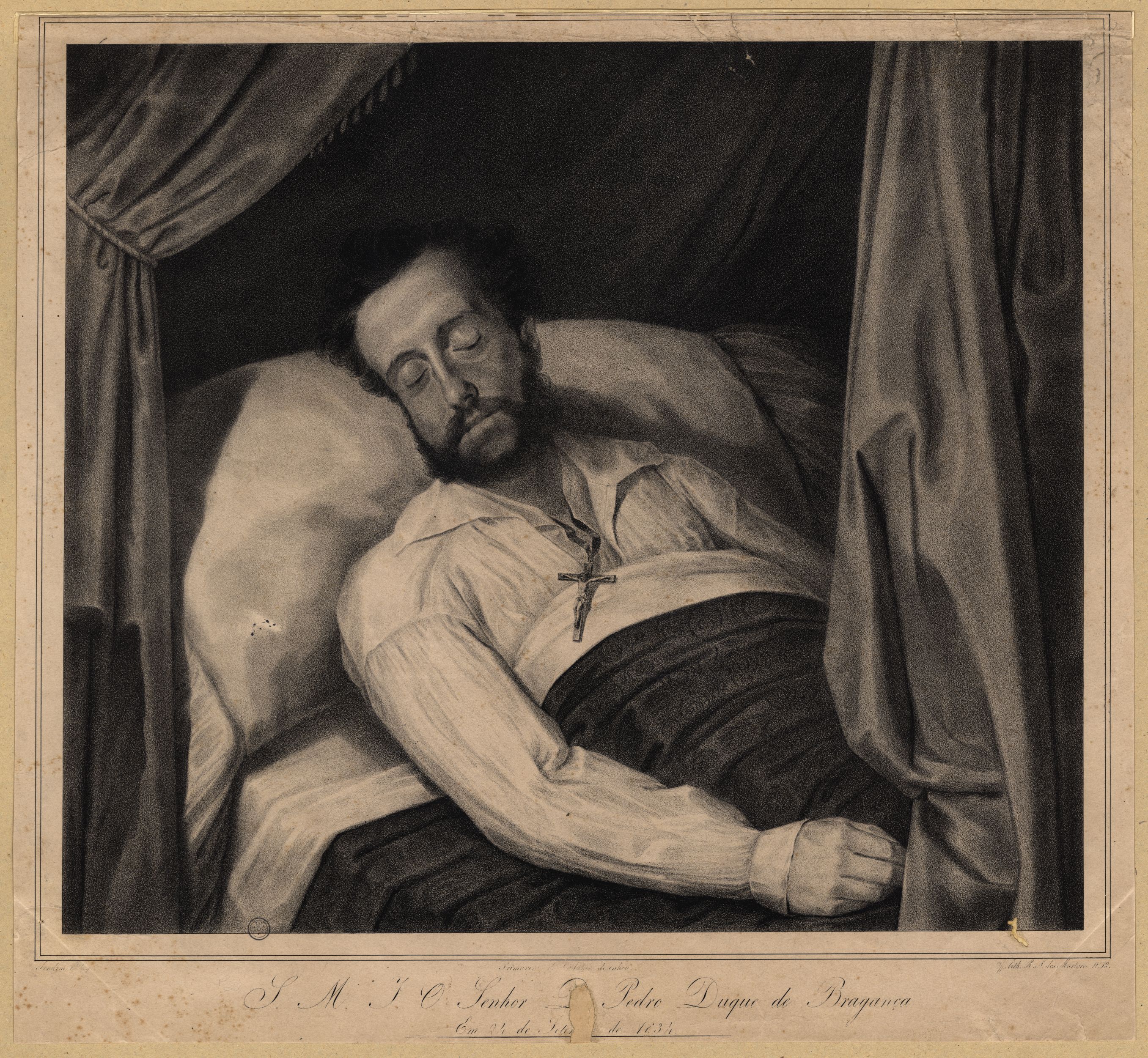 In early 1833, while besieged in Porto, Pedro received news from Brazil of his daughter Paula's impending death. Months later, in September, he met with Antônio Carlos de Andrada, a brother of Bonifácio who had come from Brazil. As a representative of the Restorationist Party, Antônio Carlos asked the Duke of Braganza to return to Brazil and rule his former empire as regent during his son's minority. Pedro realized that the Restorationists wanted to use him as a tool to facilitate their own rise to power, and frustrated Antônio Carlos by making several demands, to ascertain whether the Brazilian people, and not merely a faction, truly wanted him back. He insisted that any request to return as regent be constitutionally valid. The people's will would have to be conveyed through their local representatives and his appointment approved by the General Assembly. Only then, and "upon the presentation of a petition to him in Portugal by an official delegation of the Brazilian parliament" would he consider accepting.
During the war, the Duke of Braganza mounted cannons, dug trenches, tended the wounded, ate among the rank and file and fought under heavy fire as men next to him were shot or blown to pieces. His cause was nearly lost until he took the risky step of dividing his forces and sending a portion to launch an amphibious attack on southern Portugal. The
In early 1833, while besieged in Porto, Pedro received news from Brazil of his daughter Paula's impending death. Months later, in September, he met with Antônio Carlos de Andrada, a brother of Bonifácio who had come from Brazil. As a representative of the Restorationist Party, Antônio Carlos asked the Duke of Braganza to return to Brazil and rule his former empire as regent during his son's minority. Pedro realized that the Restorationists wanted to use him as a tool to facilitate their own rise to power, and frustrated Antônio Carlos by making several demands, to ascertain whether the Brazilian people, and not merely a faction, truly wanted him back. He insisted that any request to return as regent be constitutionally valid. The people's will would have to be conveyed through their local representatives and his appointment approved by the General Assembly. Only then, and "upon the presentation of a petition to him in Portugal by an official delegation of the Brazilian parliament" would he consider accepting.
During the war, the Duke of Braganza mounted cannons, dug trenches, tended the wounded, ate among the rank and file and fought under heavy fire as men next to him were shot or blown to pieces. His cause was nearly lost until he took the risky step of dividing his forces and sending a portion to launch an amphibious attack on southern Portugal. The

 Emperor Pedro I was Grand Master of the following Brazilian Orders:
* Order of Christ
* Order of Aviz
* Order of Saint James of the Sword
* Order of the Southern Cross
* Order of Pedro I
* Order of the Rose
As King Pedro IV, he was Grand Master of the following Portuguese Orders:
* Order of Christ
* Order of Saint Benedict of Aviz
* Order of Saint James of the Sword
* Order of the Tower and Sword
* Order of the Immaculate Conception of Vila Viçosa
After having abdicated the Portuguese crown:
* Grand Cross of the Portuguese Order of the Tower and of the Sword, of Valor, Loyalty and Merit on 20 September 1834
He was a recipient of the following foreign honors:
* Knight of the Spanish
Emperor Pedro I was Grand Master of the following Brazilian Orders:
* Order of Christ
* Order of Aviz
* Order of Saint James of the Sword
* Order of the Southern Cross
* Order of Pedro I
* Order of the Rose
As King Pedro IV, he was Grand Master of the following Portuguese Orders:
* Order of Christ
* Order of Saint Benedict of Aviz
* Order of Saint James of the Sword
* Order of the Tower and Sword
* Order of the Immaculate Conception of Vila Viçosa
After having abdicated the Portuguese crown:
* Grand Cross of the Portuguese Order of the Tower and of the Sword, of Valor, Loyalty and Merit on 20 September 1834
He was a recipient of the following foreign honors:
* Knight of the Spanish
Empire of Brazil
The Empire of Brazil was a 19th-century state that broadly comprised the territories which form modern Brazil and Uruguay until the latter achieved independence in 1828. The empire's government was a Representative democracy, representative Par ...
from 1822 to 1831 (under the name of Pedro I) and King of Portugal
This is a list of Portuguese monarchs who ruled from the establishment of the Kingdom of Portugal, in 1139, to the deposition of the Portuguese monarchy and creation of the Portugal, Portuguese Republic with the 5 October 1910 revolution.
Thro ...
in 1826 (under the name of Pedro IV).
Born in Lisbon
Lisbon ( ; ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 567,131, as of 2023, within its administrative limits and 3,028,000 within the Lisbon Metropolitan Area, metropolis, as of 2025. Lisbon is mainlan ...
, Pedro was the fourth child of King Dom John VI of Portugal
'' Dom'' John VI (; 13 May 1767 – 10 March 1826), known as "the Clement" (), was King of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves from 1816 to 1825, and after the recognition of Brazil's independence, titular Emperor of Brazil ...
and Queen Carlota Joaquina, and thus a member of the House of Braganza
The Most Serene House of Braganza (), also known as the Brigantine dynasty (''dinastia Brigantina''), is a dynasty of emperors, kings, princes, and dukes of Portuguese people, Portuguese origin which reigned in Europe and the Americas.
The hous ...
. When the country was invaded by French troops in 1807, he and his family fled to Portugal's largest and wealthiest colony, Brazil.
The outbreak of the Liberal Revolution of 1820 in Lisbon compelled Pedro I's father to return to Portugal in April 1821, leaving him to rule Brazil as regent. He had to deal with challenges from revolutionaries and insubordination by Portuguese troops, all of which he subdued. The Portuguese government's threat to revoke the political autonomy that Brazil had enjoyed since 1808 was met with widespread discontent in Brazil. Pedro I chose the Brazilian side and declared Brazil's independence from Portugal on 7 September 1822. On 12 October, he was acclaimed Brazilian emperor and by March 1824 had defeated all armies loyal to Portugal. A few months later, Pedro I crushed the short-lived Confederation of the Equator, a failed secession attempt by provincial rebels in Brazil's northeast.
A secessionist rebellion in the southern province of Cisplatina in early 1825, and the subsequent attempt by the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata
The United Provinces of the Río de la Plata (), earlier known as the United Provinces of South America (), was a name adopted in 1816 by the Congress of Tucumán for the region of South America that declared independence in 1816, with the Sove ...
to annex it, led the Empire into the Cisplatine War
The Cisplatine War was an armed conflict fought in the 1820s between the Empire of Brazil and the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata over control of Brazil's Cisplatina province. It was fought in the aftermath of the United Provinces' an ...
. In March 1826, Pedro I briefly became king of Portugal before abdicating in favor of his eldest daughter, Dona Maria II. The situation worsened in 1828 when the war in the south resulted in Brazil's loss of Cisplatina. During the same year in Lisbon, Maria II's throne was usurped by Prince Dom Miguel, Pedro I's younger brother. The Emperor's concurrent and scandalous sexual affair with Domitila de Castro tarnished his reputation. Other difficulties arose in the Brazilian parliament, where a struggle over whether the government would be chosen by the monarch or by the legislature dominated political debates from 1826 to 1831. Unable to deal with problems in both Brazil and Portugal simultaneously, on 7 April 1831 Pedro I abdicated in favor of his son Dom Pedro II, and sailed for Europe.
Pedro I invaded Portugal at the head of an army in July 1832. Faced at first with what seemed a national civil war, he soon became involved in a wider conflict that enveloped the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
in a struggle between proponents of liberalism and those seeking a return to absolutism. Pedro I died of tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
in September 1834, just a few months after he and the liberals had emerged victorious. He was hailed by both contemporaries and posterity as a key figure who helped spread the liberal ideals that allowed Brazil and Portugal to move from absolutist regimes to representative forms of government.
Early years
Birth
 Pedro was born at 08:00 on 12 October 1798 in the Queluz Royal Palace near
Pedro was born at 08:00 on 12 October 1798 in the Queluz Royal Palace near Lisbon
Lisbon ( ; ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 567,131, as of 2023, within its administrative limits and 3,028,000 within the Lisbon Metropolitan Area, metropolis, as of 2025. Lisbon is mainlan ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
. He was named after St. Peter of Alcantara, and his full name was Pedro de Alcântara Francisco António João Carlos Xavier de Paula Miguel Rafael Joaquim José Gonzaga Pascoal Cipriano Serafim. He was referred to using the honorific " Dom" (Lord
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power (social and political), power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the Peerage o ...
) from birth.
Through his father, Prince Dom John (later King Dom John VI), Pedro was a member of the House of Braganza
The Most Serene House of Braganza (), also known as the Brigantine dynasty (''dinastia Brigantina''), is a dynasty of emperors, kings, princes, and dukes of Portuguese people, Portuguese origin which reigned in Europe and the Americas.
The hous ...
(Portuguese: ''Bragança'') and a grandson of King Dom Peter III and Queen Dona (Lady) Maria I of Portugal, who were uncle and niece as well as husband and wife. His mother, Doña Carlota Joaquina, was the daughter of King Don Charles IV of Spain. Pedro's parents had an unhappy marriage. Carlota Joaquina was an ambitious woman, who always sought to advance Spain's interests, even to the detriment of Portugal's. Reputedly unfaithful to her husband, she went as far as to plot his overthrow in league with dissatisfied Portuguese nobles.
As the second eldest son (though the fourth child), Pedro became his father's heir apparent and Prince of Beira
Prince of Beira (, feminine: ''Princesa da Beira'') is a title traditionally granted to the heir apparent to the King of Portugal, throne of Portugal. The title's original use that it be granted on the eldest daughter of the reigning monarch of P ...
upon the death of his elder brother Francisco António in 1801. Prince Dom John had been acting as regent on behalf of his mother, Queen Maria I, after she was declared incurably insane in 1792. By 1802, Pedro's parents were estranged; John lived in the Mafra Palace and Carlota Joaquina in Ramalhão Palace. Pedro and his siblings resided in the Queluz Palace with their grandmother Maria I, far from their parents, whom they saw only during state occasions at Queluz.
Education
 In late November 1807, when Pedro was nine, the royal family escaped from Portugal as an invading French army sent by
In late November 1807, when Pedro was nine, the royal family escaped from Portugal as an invading French army sent by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
approached Lisbon. Pedro and his family arrived in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the List of cities in Brazil by population, second-most-populous city in Brazil (after São Paulo) and the Largest cities in the America ...
, then capital of Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
, Portugal's largest and wealthiest colony, in March 1808. During the voyage, Pedro read Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most fa ...
's ''Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; or ) is a Latin Epic poetry, epic poem that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Troy, Trojan who fled the Trojan War#Sack of Troy, fall of Troy and travelled to Italy, where he became the ancestor of the Ancient Rome ...
'' and conversed with the ship's crew, picking up navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the motion, movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navig ...
al skills. In Brazil, after a brief stay in the City Palace, Pedro settled with his younger brother Miguel and their father in the Palace of São Cristóvão (Saint Christopher). Although never on intimate terms with his father, Pedro loved him and resented the constant humiliation his father suffered at the hands of Carlota Joaquina due to her extramarital affairs. As an adult, Pedro would openly call his mother, for whom he held only feelings of contempt, a "bitch". The early experiences of betrayal, coldness and neglect had a great impact on the formation of Pedro's character.
A modicum of stability during his childhood was provided by his ''aia'' (governess), Maria Genoveva do Rêgo e Matos, whom he loved as a mother, and by his ''aio'' (supervisor) friar António de Arrábida, who became his mentor. Both were in charge of Pedro's upbringing and attempted to furnish him with a suitable education. His instruction encompassed a broad array of subjects that included mathematics, political economy
Political or comparative economy is a branch of political science and economics studying economic systems (e.g. Marketplace, markets and national economies) and their governance by political systems (e.g. law, institutions, and government). Wi ...
, logic, history and geography. He learned to speak and write not only in Portuguese, but also Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and French. He could translate from English and understood German. Even later on, as an emperor, Pedro would devote at least two hours of each day to study and reading.
Despite the breadth of Pedro's instruction, his education proved lacking. Historian Octávio Tarquínio de Sousa said that Pedro "was without a shadow of doubt intelligent, quick-witted, ndperspicacious." However, historian Roderick J. Barman relates that he was by nature "too ebullient, too erratic, and too emotional". He remained impulsive and never learned to exercise self-control or to assess the consequences of his decisions and adapt his outlook to changes in situations. His father never allowed anyone to discipline him. While Pedro's schedule dictated two hours of study each day, he sometimes circumvented the routine by dismissing his instructors in favor of activities that he found more interesting.
First marriage
 The prince found fulfillment in activities that required physical skills, rather than in the classroom. At his father's Santa Cruz farm, Pedro trained unbroken horses, and became a fine horseman and an excellent
The prince found fulfillment in activities that required physical skills, rather than in the classroom. At his father's Santa Cruz farm, Pedro trained unbroken horses, and became a fine horseman and an excellent farrier
A farrier is a specialist in equine hoof care, including the trimming and balancing of horses' hooves and the placing of shoes on their hooves, if necessary. A farrier combines some blacksmith's skills (fabricating, adapting, and adju ...
. He and his brother Miguel enjoyed mounted hunts over unfamiliar ground, through forests, and even at night or in inclement weather. He displayed a talent for drawing and handicrafts, applying himself to wood carving and furniture making. In addition, he had a taste for music, and under the guidance of Marcos Portugal the prince became an able composer (later creating Brazil's Independence Anthem). He had a good singing voice, and was proficient with several musical instruments (including piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ...
, flute
The flute is a member of a family of musical instruments in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, producing sound with a vibrating column of air. Flutes produce sound when the player's air flows across an opening. In th ...
and guitar
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted (with Fretless guitar, some exceptions) and typically has six or Twelve-string guitar, twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming ...
), playing popular songs and dances. Pedro was a simple man, both in habits and in dealing with others. Except on solemn occasions when he donned court dress, his daily attire consisted of white cotton trousers, striped cotton jacket and a broad-brimmed straw hat, or a frock coat and a top hat in more formal situations. He would frequently take time to engage in conversation with people on the street, noting their concerns.
Pedro's character was marked by an energetic drive that bordered on hyperactivity. He was impetuous with a tendency to be domineering and short-tempered. Easily bored or distracted, he entertained himself with dalliances with women in addition to his hunting and equestrian activities. His restless spirit compelled him to search for adventure, and, sometimes in disguise as a traveler, he frequented taverns in Rio de Janeiro's disreputable districts. He rarely drank alcohol, but was an incorrigible womanizer. His earliest known lasting affair was with a French dancer called Noémi Thierry, who had a stillborn child by him. Pedro's father, who had ascended the throne as John VI, sent Thierry away to avoid jeopardizing the prince's betrothal to Archduchess Maria Leopoldina, daughter of Emperor Francis I of Austria (formerly Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor
Francis II and I (; 12 February 1768 – 2 March 1835) was the last Holy Roman Emperor as Francis II from 1792 to 1806, and the first Emperor of Austria as Francis I from 1804 to 1835. He was also King of Hungary, List of rulers of Croatia, Croa ...
).
On 13 May 1817, Pedro was married by proxy to Maria Leopoldina. When she arrived in Rio de Janeiro on 5 November, she immediately fell in love with Pedro, who was far more charming and attractive than she had been led to expect. After "years under a tropical sun, his complexion was still light, his cheeks rosy." The 19-year-old prince was handsome and a little above average in height, with bright dark eyes and dark brown hair. "His good appearance", said historian Neill Macaulay, "owed much to his bearing, proud and erect even at an awkward age, and his grooming, which was impeccable. Habitually neat and clean, he had taken to the Brazilian custom of bathing often." The Nuptial Mass, with the ratification of the vows previously taken by proxy, occurred the following day. Seven children resulted from this marriage: Maria (later Queen Dona Maria II of Portugal), Miguel, João
João is a given name of Portuguese origin. It is equivalent to the given name John. The diminutive is Joãozinho and the feminine is Joana. It is widespread in Portuguese-speaking countries. Notable people with the name are enumerated in t ...
, Januária, Paula, Francisca and Pedro (later Emperor Dom Pedro II of Brazil).
Independence of Brazil
Liberal Revolution of 1820
 On 17 October 1820, news arrived that the military garrisons in Portugal had mutinied, leading to what became known as the Liberal Revolution of 1820. The military formed a provisional government, supplanting the regency appointed by John VI, and summoned the ''Cortes''—the centuries-old Portuguese parliament, this time democratically elected with the aim of creating a national Constitution. Pedro was surprised when his father not only asked for his advice, but also decided to send him to Portugal to rule as regent on his behalf and to placate the revolutionaries. The prince was never educated to rule and had previously been allowed no participation in state affairs. The role that was his by birthright was instead filled by his elder sister Dona Maria Teresa: John VI had relied on her for advice, and it was she who had been given membership in the
On 17 October 1820, news arrived that the military garrisons in Portugal had mutinied, leading to what became known as the Liberal Revolution of 1820. The military formed a provisional government, supplanting the regency appointed by John VI, and summoned the ''Cortes''—the centuries-old Portuguese parliament, this time democratically elected with the aim of creating a national Constitution. Pedro was surprised when his father not only asked for his advice, but also decided to send him to Portugal to rule as regent on his behalf and to placate the revolutionaries. The prince was never educated to rule and had previously been allowed no participation in state affairs. The role that was his by birthright was instead filled by his elder sister Dona Maria Teresa: John VI had relied on her for advice, and it was she who had been given membership in the Council of State
A council of state is a governmental body in a country, or a subdivision of a country, with a function that varies by jurisdiction. It may be the formal name for the cabinet or it may refer to a non-executive advisory body associated with a head ...
.
Pedro was regarded with suspicion by his father and by the king's close advisers, all of whom clung to the principles of absolute monarchy. By contrast, the prince was a well-known, staunch supporter of liberalism
Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality, the right to private property, and equality before the law. ...
and of constitutional representative monarchy. He had read the works of Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778), known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' Voltaire (, ; ), was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, philosopher (''philosophe''), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit ...
, Benjamin Constant, Gaetano Filangieri and Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January ew Style, NS1729 – 9 July 1797) was an Anglo-Irish Politician, statesman, journalist, writer, literary critic, philosopher, and parliamentary orator who is regarded as the founder of the Social philosophy, soc ...
. Even his wife Maria Leopoldina remarked, "My husband, God help us, loves the new ideas." John VI postponed Pedro's departure for as long as possible, fearing that once he was in Portugal, he would be acclaimed king by the revolutionaries.
On 26 February 1821, Portuguese troops stationed in Rio de Janeiro mutinied. Neither John VI nor his government made any move against the mutinous units. Pedro decided to act on his own and rode to meet the rebels. He negotiated with them and convinced his father to accept their demands, which included naming a new cabinet and making an oath of obedience to the forthcoming Portuguese Constitution. On 21 April, the parish electors of Rio de Janeiro met at the Merchants' Exchange to elect their representatives to the ''Cortes''. A small group of agitators seized the meeting and formed a revolutionary government. Again, John VI and his ministers remained passive, and the monarch was about to accept the revolutionaries' demands when Pedro took the initiative and sent army troops to re-establish order. Under pressure from the ''Cortes'', John VI and his family departed for Portugal on 26 April, leaving behind Pedro and Maria Leopoldina. Two days before he embarked, the King warned his son: "Pedro, if Brazil breaks away, let it rather do so for you, who will respect me, than for one of those adventurers."
Independence or Death
 At the outset of his regency, Pedro promulgated decrees that guaranteed personal and property rights. He also reduced government expenditure and taxes. Even the revolutionaries arrested in the Merchants' Exchange incident were set free. On 5 June 1821, army troops under Portuguese lieutenant general Jorge Avilez (later Count of Avilez) mutinied, demanding that Pedro should take an oath to uphold the Portuguese Constitution after it was enacted. The prince rode out alone to intervene with the mutineers. He calmly and resourcefully negotiated, winning the respect of the troops and succeeding in reducing the impact of their more unacceptable demands. The mutiny was a thinly veiled military coup d'état that sought to turn Pedro into a mere figurehead and transfer power to Avilez. The prince accepted the unsatisfactory outcome, but he also warned that it was the last time he would yield under pressure.
The continuing crisis reached a point of no return when the ''Cortes'' dissolved the central government in Rio de Janeiro and ordered Pedro's return. This was perceived by Brazilians as an attempt to subordinate their country again to Portugal—Brazil had not been a colony since 1815 and had the status of a kingdom. On 9 January 1822, Pedro was presented with a petition containing 8,000 signatures that begged him not to leave. He replied, "Since it is for the good of all and the general happiness of the Nation, I am willing. Tell the people that I am staying." The date became known as the '' Dia do Fico''. Avilez again mutinied and tried to force Pedro's return to Portugal. This time the prince fought back, rallying the Brazilian troops (which had not joined the Portuguese in previous mutinies), militia units and armed civilians. Outnumbered, Avilez surrendered and was expelled from Brazil along with his troops.
During the next few months, Pedro attempted to maintain a semblance of unity with Portugal, but the final rupture was impending. Aided by an able minister,
At the outset of his regency, Pedro promulgated decrees that guaranteed personal and property rights. He also reduced government expenditure and taxes. Even the revolutionaries arrested in the Merchants' Exchange incident were set free. On 5 June 1821, army troops under Portuguese lieutenant general Jorge Avilez (later Count of Avilez) mutinied, demanding that Pedro should take an oath to uphold the Portuguese Constitution after it was enacted. The prince rode out alone to intervene with the mutineers. He calmly and resourcefully negotiated, winning the respect of the troops and succeeding in reducing the impact of their more unacceptable demands. The mutiny was a thinly veiled military coup d'état that sought to turn Pedro into a mere figurehead and transfer power to Avilez. The prince accepted the unsatisfactory outcome, but he also warned that it was the last time he would yield under pressure.
The continuing crisis reached a point of no return when the ''Cortes'' dissolved the central government in Rio de Janeiro and ordered Pedro's return. This was perceived by Brazilians as an attempt to subordinate their country again to Portugal—Brazil had not been a colony since 1815 and had the status of a kingdom. On 9 January 1822, Pedro was presented with a petition containing 8,000 signatures that begged him not to leave. He replied, "Since it is for the good of all and the general happiness of the Nation, I am willing. Tell the people that I am staying." The date became known as the '' Dia do Fico''. Avilez again mutinied and tried to force Pedro's return to Portugal. This time the prince fought back, rallying the Brazilian troops (which had not joined the Portuguese in previous mutinies), militia units and armed civilians. Outnumbered, Avilez surrendered and was expelled from Brazil along with his troops.
During the next few months, Pedro attempted to maintain a semblance of unity with Portugal, but the final rupture was impending. Aided by an able minister, José Bonifácio de Andrada
José is a predominantly Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese form of the given name Joseph. While spelled alike, this name is pronounced very differently in each of the two languages: Spanish ; Portuguese (or ).
In French, the name ''J ...
, he searched for support outside Rio de Janeiro. The prince traveled to Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil, being the fourth largest state by area and the second largest in number of inhabitants with a population of 20,539,989 according to the 2022 Brazilian census, 2022 census. Located in ...
in April and on to São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
in August. He was welcomed warmly in both Brazilian provinces, and the visits reinforced his authority. While returning from São Paulo, he received news sent on 7 September that the ''Cortes'' would not accept self-governance
Self-governance, self-government, self-sovereignty or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority (sociology), authority. It may refer to pers ...
in Brazil and would punish all who disobeyed its orders. "Never one to eschew the most dramatic action on the immediate impulse", said Barman about the prince, he "required no more time for decision than the reading of the letters demanded." Pedro mounted his bay mare and, in front of his entourage and his Guard of Honor, said: "Friends, the Portuguese ''Cortes'' wished to enslave and persecute us. As of today our bonds are ended. By my blood, by my honor, by my God, I swear to bring about the independence of Brazil. Brazilians, let our watchword from this day forth be 'Independence or Death!
Constitutional Emperor
The prince was acclaimed Emperor Dom Pedro I on his 24th birthday, which coincided with the inauguration of theEmpire of Brazil
The Empire of Brazil was a 19th-century state that broadly comprised the territories which form modern Brazil and Uruguay until the latter achieved independence in 1828. The empire's government was a Representative democracy, representative Par ...
on 12 October. He was crowned on 1 December in what is today known as the Old Cathedral of Rio de Janeiro. His ascendancy did not immediately extend throughout Brazil's territories. He had to force the submission of several provinces in the northern, northeastern and southern regions, and the last Portuguese holdout units only surrendered in early 1824. Meanwhile, Pedro I's relationship with Bonifácio deteriorated. The situation came to a head when Pedro I, on the grounds of inappropriate conduct, dismissed Bonifácio. Bonifácio had used his position to harass, prosecute, arrest and even exile his political enemies. For months Bonifácio's enemies had worked to win over the Emperor. While Pedro I was still Prince Regent, they had given him the title "Perpetual Defender of Brazil" on 13 May 1822. They also inducted him into Freemasonry on 2 August and later made him grand master on 7 October, replacing Bonifácio in that position.
The crisis between the monarch and his former minister was felt immediately within the Constituent and Legislative General Assembly, which had been elected for the purpose of drafting a Constitution. A member of the Constituent Assembly, Bonifácio resorted to demagoguery, alleging the existence of a major Portuguese conspiracy against Brazilian interests—insinuating that Pedro I, who had been born in Portugal, was implicated. The Emperor became outraged by the invective directed at the loyalty of citizens who were of Portuguese birth and the hints that he was himself conflicted in his allegiance to Brazil. On 12 November 1823, Pedro I ordered the dissolution of the Constituent Assembly and called for new elections. On the following day, he placed a newly established native Council of State
A council of state is a governmental body in a country, or a subdivision of a country, with a function that varies by jurisdiction. It may be the formal name for the cabinet or it may refer to a non-executive advisory body associated with a head ...
in charge of composing a constitutional draft. Copies of the draft were sent to all town councils, and the vast majority voted in favor of its instant adoption as the Constitution of the Empire.
As a result of the highly centralized State created by the Constitution, rebellious elements in Ceará
Ceará (, ) is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, northeastern part of the country, on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. It is the List of Brazilian states by population, eighth-largest Brazilian State by ...
, Paraíba
Paraíba ( , ; ) is a states of Brazil, state of Brazil. It is located in the Brazilian Northeast, and it is bordered by Rio Grande do Norte to the north, Ceará to the west, Pernambuco to the south and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Paraíba i ...
and Pernambuco
Pernambuco ( , , ) is a States of Brazil, state of Brazil located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast region of the country. With an estimated population of 9.5 million people as of 2024, it is the List of Brazilian states by population, ...
attempted to secede from Brazil and unite in what became known as the Confederation of the Equator. Pedro I unsuccessfully sought to avoid bloodshed by offering to placate the rebels. Angry, he said: "What did the insults from Pernambuco require? Surely a punishment, and such a punishment that it will serve as an example for the future." The rebels were never able to secure control over their provinces, and were easily suppressed. By late 1824, the rebellion was over. Sixteen rebels were tried and executed, while all others were pardoned by the Emperor.
Crises within and without
Portuguese dynastic affair
After long negotiations, Portugal signed a treaty with Brazil on 29 August 1825 in which it recognized Brazilian independence. Except for the recognition of independence, the treaty provisions were at Brazil's expense, including a demand for reparations to be paid to Portugal, with no other requirements of Portugal. Compensation was to be paid to all Portuguese citizens residing in Brazil for the losses they had experienced, such as properties which had been confiscated. John VI was also given the right to style himself emperor of Brazil. More humiliating was that the treaty implied that independence had been granted as a beneficent act of John VI, rather than having been compelled by the Brazilians through force of arms. Even worse, Great Britain was rewarded for its role in advancing the negotiations by the signing of a separate treaty in which its favorable commercial rights were renewed and by the signing of a convention in which Brazil agreed to abolish slave trade with Africa within four years. Both accords were severely harmful to Brazilian economic interests. A few months later, the Emperor received word that his father had died on 10 March 1826, and that he had succeeded his father on the Portuguese throne as King Dom Pedro IV. Aware that a reunion of Brazil and Portugal would be unacceptable to the people of both nations, he hastily abdicated the crown of Portugal on 2 May in favor of his eldest daughter, who became Queen Dona Maria II. His abdication was conditional: Portugal was required to accept the Constitution which he had drafted and Maria II was to marry his brother Miguel. Regardless of the abdication, Pedro I continued to act as an absentee king of Portugal and interceded in its diplomatic matters, as well as in internal affairs, such as making appointments. (Although Maria II had already been recognized as queen, all Portuguese coins for the period 1826-1828 bear the name and image of Pedro IV.) He found it difficult, at the very least, to keep his position as Brazilian emperor separate from his obligations to protect his daughter's interests in Portugal. On 3 March 1828, when his plans appeared to be secure, he finalized his earlier conditional abdication from the Portuguese throne with an additional decree. Miguel feigned compliance with Pedro I's plans. As soon as he was declared regent in early 1828, and backed by Carlota Joaquina, he abrogated the Constitution and, supported by those Portuguese in favor of absolutism, was acclaimed King Dom Miguel I. As painful as was his beloved brother's betrayal, Pedro I also endured the defection of his surviving sisters, Maria Teresa, Maria Francisca, Isabel Maria and Maria da Assunção, to Miguel I's faction. Only his youngest sister, Ana de Jesus, remained faithful to him, and she later traveled to Rio de Janeiro to be close to him. Consumed by hatred and beginning to believe rumors that Miguel I had murdered their father, Pedro I turned his focus on Portugal and tried in vain to garner international support for Maria II's rights.War and widowhood
Backed by theUnited Provinces of the Río de la Plata
The United Provinces of the Río de la Plata (), earlier known as the United Provinces of South America (), was a name adopted in 1816 by the Congress of Tucumán for the region of South America that declared independence in 1816, with the Sove ...
(present-day Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
), a small band declared Brazil's southernmost province of Cisplatina to be independent in April 1825. The Brazilian government at first perceived the secession attempt as a minor uprising. It took months before a greater threat posed by the involvement of the United Provinces, which expected to annex Cisplatina, caused serious concern. In retaliation, the Empire declared war in December, triggering the Cisplatine War
The Cisplatine War was an armed conflict fought in the 1820s between the Empire of Brazil and the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata over control of Brazil's Cisplatina province. It was fought in the aftermath of the United Provinces' an ...
. The Emperor traveled to Bahia
Bahia () is one of the 26 Federative units of Brazil, states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo (state), São Paulo, Mina ...
province (located in northeastern Brazil) in February 1826, taking along his wife and daughter Maria. The Emperor was warmly welcomed by the inhabitants of Bahia. The trip was planned to generate support for the war-effort.
The imperial entourage included Domitila de Castro (then-Viscountess and later Marchioness of Santos), who had been Pedro I's mistress since their first meeting in 1822. Although he had never been faithful to Maria Leopoldina, he had previously been careful to conceal his sexual escapades with other women. However, his infatuation for his new lover "had become both blatant and limitless", while his wife endured slights and became the object of gossip. Pedro I was increasingly rude and mean toward Maria Leopoldina, left her short of funds, prohibited her from leaving the palace and forced her to endure Domitila's presence as her lady-in-waiting
A lady-in-waiting (alternatively written lady in waiting) or court lady is a female personal assistant at a Royal court, court, attending on a royal woman or a high-ranking nobility, noblewoman. Historically, in Europe, a lady-in-waiting was o ...
. In the meantime, his lover took advantage by advancing her interests, as well as those of her family and friends. Those seeking favors or to promote projects increasingly sought her help, bypassing the normal, legal channels.
On 24 November 1826, Pedro I sailed from Rio de Janeiro to São José in the province of Santa Catarina. From there he rode to Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre (, ; , ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Brazilian Federative units of Brazil, state of Rio Grande do Sul. Its population of roughly 1.4 million inhabitants (2022) makes it the List of largest cities in Brazil, 11th-most p ...
, capital of the province of Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, ; ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative units of Brazil#List, fifth-most populous state and the List of Brazilian s ...
, where the main army was stationed. Upon his arrival on 7 December, the Emperor found the military conditions to be much worse than previous reports had led him to expect. He "reacted with his customary energy: he passed a flurry of orders, fired reputed grafters and incompetents, fraternized with the troops, and generally shook up military and civilian administration." He was already on his way back to Rio de Janeiro when he was told that Maria Leopoldina had died following a miscarriage. Unfounded rumors soon spread that purported that she had died after being physically assaulted by Pedro I. Meanwhile, the war continued on with no conclusion in sight. Pedro I relinquished Cisplatina in August 1828, and the province became the independent nation of Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
.
Second marriage
 After his wife's death, Pedro I realized how miserably he had treated her, and his relationship with Domitila began to crumble. Maria Leopoldina, unlike his mistress, was popular, honest and loved him without expecting anything in return. The Emperor greatly missed her, and even his obsession with Domitila failed to overcome his sense of loss and regret. One day Domitila found him weeping on the floor and embracing a portrait of his deceased wife, whose sad-looking ghost Pedro I claimed to have seen. Later on, the Emperor left the bed he shared with Domitila and shouted: "Get off of me! I know I live an unworthy life of a sovereign. The thought of the Empress does not leave me." He did not forget his children, orphaned of their mother, and was observed on more than one occasion holding his son, the young Pedro, in his arms and saying: "Poor boy, you are the most unhappy prince in the world."
At the insistence of Pedro I, Domitila departed from Rio de Janeiro on 27 June 1828. He had resolved to marry again and to become a better person. He even tried to persuade his father-in-law of his sincerity, by claiming in a letter "that all my wickedness is over, that I shall not again fall into those errors into which I have fallen, which I regret and have asked God for forgiveness". Francis I was less than convinced. The Austrian emperor, deeply offended by the conduct his daughter endured, withdrew his support for Brazilian concerns and frustrated Pedro I's Portuguese interests. Because of Pedro I's bad reputation in Europe, owing to his past behavior, princesses from several nations declined his proposals of marriage one after another. His pride thus wounded, he allowed his mistress to return, which she did on 29 April 1829 after having been away nearly a year.
However, once he learned that a betrothal had finally been arranged, the Emperor ended his relationship to Domitila. She returned to her native province of São Paulo on 27 August, where she remained. Days earlier, on 2 August, the Emperor had been married by proxy to Amélie of Leuchtenberg. He was stunned by her beauty after meeting her in person. The vows previously made by proxy were ratified in a Nuptial Mass on 17 October. Amélie was kind and loving to his children and provided a much needed sense of normality to both his family and the general public. After Domitila's banishment from court, the vow the Emperor made to alter his behavior proved to be sincere. He had no more affairs and remained faithful to his spouse. In an attempt to mitigate and move beyond other past misdeeds, he made peace with José Bonifácio, his former minister and mentor.
After his wife's death, Pedro I realized how miserably he had treated her, and his relationship with Domitila began to crumble. Maria Leopoldina, unlike his mistress, was popular, honest and loved him without expecting anything in return. The Emperor greatly missed her, and even his obsession with Domitila failed to overcome his sense of loss and regret. One day Domitila found him weeping on the floor and embracing a portrait of his deceased wife, whose sad-looking ghost Pedro I claimed to have seen. Later on, the Emperor left the bed he shared with Domitila and shouted: "Get off of me! I know I live an unworthy life of a sovereign. The thought of the Empress does not leave me." He did not forget his children, orphaned of their mother, and was observed on more than one occasion holding his son, the young Pedro, in his arms and saying: "Poor boy, you are the most unhappy prince in the world."
At the insistence of Pedro I, Domitila departed from Rio de Janeiro on 27 June 1828. He had resolved to marry again and to become a better person. He even tried to persuade his father-in-law of his sincerity, by claiming in a letter "that all my wickedness is over, that I shall not again fall into those errors into which I have fallen, which I regret and have asked God for forgiveness". Francis I was less than convinced. The Austrian emperor, deeply offended by the conduct his daughter endured, withdrew his support for Brazilian concerns and frustrated Pedro I's Portuguese interests. Because of Pedro I's bad reputation in Europe, owing to his past behavior, princesses from several nations declined his proposals of marriage one after another. His pride thus wounded, he allowed his mistress to return, which she did on 29 April 1829 after having been away nearly a year.
However, once he learned that a betrothal had finally been arranged, the Emperor ended his relationship to Domitila. She returned to her native province of São Paulo on 27 August, where she remained. Days earlier, on 2 August, the Emperor had been married by proxy to Amélie of Leuchtenberg. He was stunned by her beauty after meeting her in person. The vows previously made by proxy were ratified in a Nuptial Mass on 17 October. Amélie was kind and loving to his children and provided a much needed sense of normality to both his family and the general public. After Domitila's banishment from court, the vow the Emperor made to alter his behavior proved to be sincere. He had no more affairs and remained faithful to his spouse. In an attempt to mitigate and move beyond other past misdeeds, he made peace with José Bonifácio, his former minister and mentor.
Between Portugal and Brazil
Endless crises
 Since the days of the Constituent Assembly in 1823, and with renewed vigor in 1826 with the opening of the General Assembly (the Brazilian parliament), there had been an ideological struggle over the balance of powers wielded by the emperor and legislature in governance. On one side were those who shared Pedro I's views, politicians who believed that the monarch should be free to choose ministers, national policies and the direction of government. In opposition were those, then known as the Liberal Party, who believed that cabinets should have the power to set the government's course and should consist of deputies drawn from the majority party who were accountable to the parliament. Strictly speaking, both the party that supported Pedro I's government and the Liberal Party advocated
Since the days of the Constituent Assembly in 1823, and with renewed vigor in 1826 with the opening of the General Assembly (the Brazilian parliament), there had been an ideological struggle over the balance of powers wielded by the emperor and legislature in governance. On one side were those who shared Pedro I's views, politicians who believed that the monarch should be free to choose ministers, national policies and the direction of government. In opposition were those, then known as the Liberal Party, who believed that cabinets should have the power to set the government's course and should consist of deputies drawn from the majority party who were accountable to the parliament. Strictly speaking, both the party that supported Pedro I's government and the Liberal Party advocated Liberalism
Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality, the right to private property, and equality before the law. ...
, and thus constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
.
Regardless of Pedro I's failures as a ruler, he respected the Constitution: he did not tamper with elections or countenance vote rigging, refuse to sign
A sign is an object, quality, event, or entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to its object—for instance, thunder is a sign of storm, or me ...
acts ratified by the government, or impose any restrictions on freedom of speech. Although within his prerogative, he did not dissolve the Chamber of Deputies and call for new elections when it disagreed with his aims or postpone seating the legislature. Liberal newspapers and pamphlets seized on Pedro I's Portuguese birth in support of both valid accusations (e.g., that much of his energy was directed toward affairs concerning Portugal) and false charges (e.g., that he was involved in plots to suppress the Constitution and to reunite Brazil and Portugal). To the Liberals, the Emperor's Portuguese-born friends who were part of the Imperial court, including Francisco Gomes da Silva who was nicknamed "the Buffoon", were part of these conspiracies and formed a " secret cabinet". None of these figures exhibited interest in such issues, and whatever interests they may have shared, there was no palace cabal plotting to abrogate the Constitution or to bring Brazil back under Portugal's control.
Another source of criticism by the Liberals involved Pedro I's abolitionist views. The Emperor had indeed conceived a gradual process for eliminating slavery. However, the constitutional power to enact legislation was in the hands of the Assembly, which was dominated by slave-owning landholders who could thus thwart any attempt at abolition. The Emperor opted to try persuasion by moral example, setting up his estate at Santa Cruz as a model by granting land to his freed slaves there. Pedro I also professed other advanced ideas. When he declared his intention to remain in Brazil on 9 January 1822 and the populace sought to accord him the honor of unhitching the horses and pulling his carriage themselves, the then-Prince Regent refused. His reply was a simultaneous denunciation of the divine right of kings, of nobility's supposedly superior blood and of racism: "It grieves me to see my fellow humans giving a man tributes appropriate for the divinity, I know that my blood is the same color as that of the Negroes."
Abdication
 The Emperor's efforts to appease the Liberal Party resulted in very important changes. He supported an 1827 law that established ministerial responsibility. On 19 March 1831, he named a cabinet formed by politicians drawn from the opposition, allowing a greater role for the parliament in the government. Lastly, he offered positions in Europe to Francisco Gomes and another Portuguese-born friend to extinguish rumors of a "secret cabinet". To his dismay, his palliative measures did not stop the continuous attacks from the Liberal side upon his government and his foreign birth. Frustrated by their intransigence, he became unwilling to deal with his deteriorating political situation.
Meanwhile, Portuguese exiles campaigned to convince him to give up on Brazil and instead devote his energies to the fight for his daughter's claim to Portugal's crown. According to Roderick J. Barman, " nan emergency the Emperor's abilities shone forth—he became cool in nerve, resourceful and steadfast in action. Life as a constitutional monarch, full of tedium, caution, and conciliation, ran against the essence of his character." On the other hand, the historian remarked, he "found in his daughter's case everything that appealed most to his character. By going to Portugal he could champion the oppressed, display his chivalry and self-denial, uphold constitutional rule, and enjoy the freedom of action he craved."
The idea of abdicating and returning to Portugal took root in his mind, and, beginning in early 1829, he talked about it frequently. An opportunity soon appeared to act upon the notion. Radicals within the Liberal Party rallied street gangs to harass the Portuguese community in Rio de Janeiro. On 11 March 1831, in what became known as the Night of the Bottle Fight (), the Portuguese retaliated and turmoil gripped the streets of the national capital. On 5 April, Pedro I fired the Liberal cabinet, which had only been in power since 19 March, for its incompetence in restoring order. A large crowd, incited by the radicals, gathered in Rio de Janeiro downtown on the afternoon of 6 April and demanded the immediate restoration of the fallen cabinet. The Emperor's reply was: "I will do everything for the people and nothing ompelledby the people." Sometime after nightfall, army troops, including his guard, deserted him and joined the protests. Only then did he realize how isolated and detached from Brazilian affairs he had become, and to everyone's surprise, he abdicated at approximately 03:00 on 7 April. Upon delivering the abdication document to a messenger, he said: "Here you have my act of abdication, I'm returning to Europe and leaving a country that I loved very much, and still love."
The Emperor's efforts to appease the Liberal Party resulted in very important changes. He supported an 1827 law that established ministerial responsibility. On 19 March 1831, he named a cabinet formed by politicians drawn from the opposition, allowing a greater role for the parliament in the government. Lastly, he offered positions in Europe to Francisco Gomes and another Portuguese-born friend to extinguish rumors of a "secret cabinet". To his dismay, his palliative measures did not stop the continuous attacks from the Liberal side upon his government and his foreign birth. Frustrated by their intransigence, he became unwilling to deal with his deteriorating political situation.
Meanwhile, Portuguese exiles campaigned to convince him to give up on Brazil and instead devote his energies to the fight for his daughter's claim to Portugal's crown. According to Roderick J. Barman, " nan emergency the Emperor's abilities shone forth—he became cool in nerve, resourceful and steadfast in action. Life as a constitutional monarch, full of tedium, caution, and conciliation, ran against the essence of his character." On the other hand, the historian remarked, he "found in his daughter's case everything that appealed most to his character. By going to Portugal he could champion the oppressed, display his chivalry and self-denial, uphold constitutional rule, and enjoy the freedom of action he craved."
The idea of abdicating and returning to Portugal took root in his mind, and, beginning in early 1829, he talked about it frequently. An opportunity soon appeared to act upon the notion. Radicals within the Liberal Party rallied street gangs to harass the Portuguese community in Rio de Janeiro. On 11 March 1831, in what became known as the Night of the Bottle Fight (), the Portuguese retaliated and turmoil gripped the streets of the national capital. On 5 April, Pedro I fired the Liberal cabinet, which had only been in power since 19 March, for its incompetence in restoring order. A large crowd, incited by the radicals, gathered in Rio de Janeiro downtown on the afternoon of 6 April and demanded the immediate restoration of the fallen cabinet. The Emperor's reply was: "I will do everything for the people and nothing ompelledby the people." Sometime after nightfall, army troops, including his guard, deserted him and joined the protests. Only then did he realize how isolated and detached from Brazilian affairs he had become, and to everyone's surprise, he abdicated at approximately 03:00 on 7 April. Upon delivering the abdication document to a messenger, he said: "Here you have my act of abdication, I'm returning to Europe and leaving a country that I loved very much, and still love."
Return to Europe
Portuguese Civil War
 At dawn on the morning of 7 April, Pedro, his wife, and others, including his daughter Maria II and his sister Ana de Jesus, were taken on board the British warship HMS ''Warspite''. The vessel remained at anchor off Rio de Janeiro, and, on 13 April, the former emperor transferred to and departed for Europe aboard HMS ''Volage''. He arrived in Cherbourg-Octeville, France, on 10 June. During the next few months, he shuttled between France and Great Britain. He was warmly welcomed, but received no actual support from either government to restore his daughter's throne. Finding himself in an awkward situation because he held no official status in either the Brazilian Imperial House or in the Portuguese Royal House, Pedro assumed the title of Duke of Braganza on 15 June, a position that once had been his as heir-apparent to Portugal's crown. Although the title should have belonged to Maria II's heir-apparent, which he certainly was not, his claim was met with general recognition. On 1 December, his only daughter by Amélie, Maria Amélia, was born in Paris.
He did not forget his children left in Brazil. He wrote poignant letters to each of them, conveying how greatly he missed them and repeatedly asking them to seriously attend to their educations. Shortly before his abdication, Pedro had told his son and successor: "I intend that my brother Miguel and I will be the last badly educated of the Braganza family". Charles Napier, a naval commander who fought under Pedro's banner in the 1830s, remarked that "his good qualities were his own; his bad owing to want of education; and no man was more sensible of that defect than himself." His letters to Pedro II were often couched in language beyond the boy's reading level, and historians have assumed such passages were chiefly intended as advice that the young monarch might eventually consult upon reaching adulthood.
While in Paris, the Duke of Braganza met and befriended Gilbert du Motier, Marquis of Lafayette, a veteran of the
At dawn on the morning of 7 April, Pedro, his wife, and others, including his daughter Maria II and his sister Ana de Jesus, were taken on board the British warship HMS ''Warspite''. The vessel remained at anchor off Rio de Janeiro, and, on 13 April, the former emperor transferred to and departed for Europe aboard HMS ''Volage''. He arrived in Cherbourg-Octeville, France, on 10 June. During the next few months, he shuttled between France and Great Britain. He was warmly welcomed, but received no actual support from either government to restore his daughter's throne. Finding himself in an awkward situation because he held no official status in either the Brazilian Imperial House or in the Portuguese Royal House, Pedro assumed the title of Duke of Braganza on 15 June, a position that once had been his as heir-apparent to Portugal's crown. Although the title should have belonged to Maria II's heir-apparent, which he certainly was not, his claim was met with general recognition. On 1 December, his only daughter by Amélie, Maria Amélia, was born in Paris.
He did not forget his children left in Brazil. He wrote poignant letters to each of them, conveying how greatly he missed them and repeatedly asking them to seriously attend to their educations. Shortly before his abdication, Pedro had told his son and successor: "I intend that my brother Miguel and I will be the last badly educated of the Braganza family". Charles Napier, a naval commander who fought under Pedro's banner in the 1830s, remarked that "his good qualities were his own; his bad owing to want of education; and no man was more sensible of that defect than himself." His letters to Pedro II were often couched in language beyond the boy's reading level, and historians have assumed such passages were chiefly intended as advice that the young monarch might eventually consult upon reaching adulthood.
While in Paris, the Duke of Braganza met and befriended Gilbert du Motier, Marquis of Lafayette, a veteran of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
who became one of his staunchest supporters. With limited funds, Pedro organized a small army composed of Portuguese liberals, like Almeida Garrett and Alexandre Herculano, foreign mercenaries and volunteers such as Lafayette's grandson, Adrien Jules de Lasteyrie. On 25 January 1832, Pedro bade farewell to his family, Lafayette and around two hundred well-wishers. He knelt before Maria II and said: "My lady, here is a Portuguese general who will uphold your rights and restore your crown." In tears, his daughter embraced him. Pedro and his army sailed to the Atlantic archipelago of the Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atl ...
, the only Portuguese territory that had remained loyal to his daughter. After a few months of final preparations they embarked for mainland Portugal, entering the city of Porto
Porto (), also known in English language, English as Oporto, is the List of cities in Portugal, second largest city in Portugal, after Lisbon. It is the capital of the Porto District and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto c ...
unopposed on 9 July. His brother's troops moved to encircle the city, beginning a siege that lasted for more than a year.
Death
 In early 1833, while besieged in Porto, Pedro received news from Brazil of his daughter Paula's impending death. Months later, in September, he met with Antônio Carlos de Andrada, a brother of Bonifácio who had come from Brazil. As a representative of the Restorationist Party, Antônio Carlos asked the Duke of Braganza to return to Brazil and rule his former empire as regent during his son's minority. Pedro realized that the Restorationists wanted to use him as a tool to facilitate their own rise to power, and frustrated Antônio Carlos by making several demands, to ascertain whether the Brazilian people, and not merely a faction, truly wanted him back. He insisted that any request to return as regent be constitutionally valid. The people's will would have to be conveyed through their local representatives and his appointment approved by the General Assembly. Only then, and "upon the presentation of a petition to him in Portugal by an official delegation of the Brazilian parliament" would he consider accepting.
During the war, the Duke of Braganza mounted cannons, dug trenches, tended the wounded, ate among the rank and file and fought under heavy fire as men next to him were shot or blown to pieces. His cause was nearly lost until he took the risky step of dividing his forces and sending a portion to launch an amphibious attack on southern Portugal. The
In early 1833, while besieged in Porto, Pedro received news from Brazil of his daughter Paula's impending death. Months later, in September, he met with Antônio Carlos de Andrada, a brother of Bonifácio who had come from Brazil. As a representative of the Restorationist Party, Antônio Carlos asked the Duke of Braganza to return to Brazil and rule his former empire as regent during his son's minority. Pedro realized that the Restorationists wanted to use him as a tool to facilitate their own rise to power, and frustrated Antônio Carlos by making several demands, to ascertain whether the Brazilian people, and not merely a faction, truly wanted him back. He insisted that any request to return as regent be constitutionally valid. The people's will would have to be conveyed through their local representatives and his appointment approved by the General Assembly. Only then, and "upon the presentation of a petition to him in Portugal by an official delegation of the Brazilian parliament" would he consider accepting.
During the war, the Duke of Braganza mounted cannons, dug trenches, tended the wounded, ate among the rank and file and fought under heavy fire as men next to him were shot or blown to pieces. His cause was nearly lost until he took the risky step of dividing his forces and sending a portion to launch an amphibious attack on southern Portugal. The Algarve
The Algarve (, , ) is the southernmost NUTS statistical regions of Portugal, NUTS II region of continental Portugal. It has an area of with 467,495 permanent inhabitants and incorporates 16 municipalities (concelho, ''concelhos'' or ''município ...
region fell to the expedition, which then marched north straight for Lisbon, which capitulated on 24 July. Pedro proceeded to subdue the remainder of the country, but just when the conflict looked to be winding down to a conclusion, his Spanish uncle Don Carlos, who was attempting to seize the crown of his niece Doña Isabella II, intervened. In this wider conflict that engulfed the entire Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
, the First Carlist War
The First Carlist War was a civil war in Spain from 1833 to 1840, the first of three Carlist Wars. It was fought between two factions over the succession to the throne and the nature of the Monarchy of Spain, Spanish monarchy: the conservative a ...
, the Duke of Braganza allied with liberal Spanish armies loyal to Isabella II and defeated both Miguel I and Carlos. A peace accord was reached on 26 May 1834.
Except for bouts of epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
that manifested in seizures
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
every few years, Pedro had always enjoyed robust health. The war, however, undermined his constitution and by 1834 he was dying of tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
. He was confined to his bed in Queluz Royal Palace from 10 September. Pedro dictated an open letter to the Brazilians, in which he begged that a gradual abolition of slavery be adopted. He warned them: "Slavery is an evil, and an attack against the rights and dignity of the human species, but its consequences are less harmful to those who suffer in captivity than to the Nation whose laws allow slavery. It is a cancer that devours its morality." After a long and painful illness, Pedro died at 14:30 on 24 September 1834. As he had requested, his heart was placed in Porto's Lapa Church and his body was interred in the Royal Pantheon of the House of Braganza. The news of his death arrived in Rio de Janeiro on 20 November, but his children were informed only after 2 December. Bonifácio, who had been removed from his position as their guardian, wrote to Pedro II and his sisters: "Dom Pedro did not die. Only ordinary men die, not heroes."
Legacy
Upon the death of Pedro I, the then-powerful Restorationist Party vanished overnight. A fair assessment of the former monarch became possible once the threat of his return to power was removed. Evaristo da Veiga, one of his worst critics as well as a leader in the Liberal Party, left a statement which, according to historian Octávio Tarquínio de Sousa, became the prevailing view thereafter: "the former emperor of Brazil was not a prince of ordinary measure ... and Providence has made him a powerful instrument of liberation, both in Brazil and in Portugal. If we raziliansexist as a body in a free Nation, if our land was not ripped apart into small enemy republics, where only anarchy and military spirit predominated, we owe much to the resolution he took in remaining among us, in making the first shout for our Independence." He continued: "Portugal, if it was freed from the darkest and demeaning tyranny ... if it enjoys the benefits brought by representative government to learned peoples, it owes it to D m Pedro de Alcântara, whose fatigues, sufferings and sacrifices for the Portuguese cause has earned him in high degree the tribute of national gratitude." John Armitage, who lived in Brazil during the latter half of Pedro I's reign, remarked that "even the errors of the Monarch have been attended with great benefit through their influence on the affairs of the mother country. Had he governed with more wisdom it would have been well for the land of his adoption, yet, perhaps, unfortunate for humanity." Armitage added that like "the late Emperor of the French, he was also a child of destiny, or rather, an instrument in the hands of an all-seeing and beneficent Providence for the furtherance of great and inscrutable ends. In the old as in the new world he was henceforth fated to become the instrument of further revolutions, and ere the close of his brilliant but ephemeral career in the land of his fathers, to atone amply for the errors and follies of his former life, by his chivalrous and heroic devotion in the cause of civil and religious freedom." In 1972, on the 150th anniversary of Brazilian independence, Pedro I's remains (though not his heart) were brought to Brazil—as he had requested in his will—accompanied by much fanfare and with honors due to a head of state. His remains were reinterred in the Monument to the Independence of Brazil, along with those of Maria Leopoldina and Amélie, in the city of São Paulo. Years later, Neill Macaulay said that " iticism of Dom Pedro was freely expressed and often vehement; it prompted him to abdicate two thrones. His tolerance of public criticism and his willingness to relinquish power set Dom Pedro apart from his absolutist predecessors and from the rulers of today's coercive states, whose lifetime tenure is as secure as that of the kings of old." Macaulay affirmed that " ccessful liberal leaders like Dom Pedro may be honored with an occasional stone or bronze monument, but their portraits, four stories high, do not shape public buildings; their pictures are not borne in parades of hundreds of thousands of uniformed marchers; no '-isms' attach to their names." As part of Brazil's 200-year independence celebrations in 2022, the embalmed heart of Pedro I received military honors upon arrival inBrasília
Brasília ( ; ) is the capital city, capital of Brazil and Federal District (Brazil), Federal District. Located in the Brazilian highlands in the country's Central-West Region, Brazil, Central-West region, it was founded by President Juscelino ...
and was put on public display at the foreign ministry. It was then returned to Portugal after Brazil's independence day.
Titles and honors
Titles and styles
* 12 October 1798 – 11 June 1801: ''His Highness'' The ''Most Serene'' Infante Dom Pedro, Grand Prior of Crato * 11 June 1801 – 20 March 1816: ''His Royal Highness'' The Prince of Beira * 20 March 1816 – 9 January 1817: ''His Royal Highness'' The Prince of Brazil * 9 January 1817 – 10 March 1826: ''His Royal Highness'' The Prince Royal (in Portugal) * 12 October 1822 – 7 April 1831: ''His Imperial Majesty'' The Emperor of Brazil * 10 March 1826 – 2 May 1826: ''His Most Faithful Majesty'' The King of Portugal * 15 June 1831 – 24 September 1834: ''His Imperial Majesty'' The Duke of Braganza As Brazilian emperor his full style and title were: "His Imperial Majesty Dom Pedro I, Constitutional Emperor and Perpetual Defender of Brazil". As Portuguese king his full style and title were: "His Most Faithful Majesty Dom Pedro IV, King of Portugal and the Algarves, of either side of the sea in Africa, Lord of Guinea and of Conquest, Navigation and Commerce of Ethiopia, Arabia, Persia and India, etc."Nobility
As heir-apparent to the Portuguese crown: * Duke of Braganza * Duke of Barcelos * Duke of Guimarães * Marquis of Vila Viçosa * Count of Ourém * Count of Barcelos * Count of Faria and Neiva * Count of Arraiolos * Count of GuimarãesHonors

 Emperor Pedro I was Grand Master of the following Brazilian Orders:
* Order of Christ
* Order of Aviz
* Order of Saint James of the Sword
* Order of the Southern Cross
* Order of Pedro I
* Order of the Rose
As King Pedro IV, he was Grand Master of the following Portuguese Orders:
* Order of Christ
* Order of Saint Benedict of Aviz
* Order of Saint James of the Sword
* Order of the Tower and Sword
* Order of the Immaculate Conception of Vila Viçosa
After having abdicated the Portuguese crown:
* Grand Cross of the Portuguese Order of the Tower and of the Sword, of Valor, Loyalty and Merit on 20 September 1834
He was a recipient of the following foreign honors:
* Knight of the Spanish
Emperor Pedro I was Grand Master of the following Brazilian Orders:
* Order of Christ
* Order of Aviz
* Order of Saint James of the Sword
* Order of the Southern Cross
* Order of Pedro I
* Order of the Rose
As King Pedro IV, he was Grand Master of the following Portuguese Orders:
* Order of Christ
* Order of Saint Benedict of Aviz
* Order of Saint James of the Sword
* Order of the Tower and Sword
* Order of the Immaculate Conception of Vila Viçosa
After having abdicated the Portuguese crown:
* Grand Cross of the Portuguese Order of the Tower and of the Sword, of Valor, Loyalty and Merit on 20 September 1834
He was a recipient of the following foreign honors:
* Knight of the Spanish Order of the Golden Fleece
The Distinguished Order of the Golden Fleece (, ) is a Catholic order of chivalry founded in 1430 in Brugge by Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, to celebrate his marriage to Isabella of Portugal, Duchess of Burgundy, Isabella of Portugal. T ...
* Grand Cross of the Spanish Order of Charles III
* Grand Cross of the Spanish Order of Isabella the Catholic
The Royal Order of Isabella the Catholic (; Abbreviation, Abbr.: OYC) is a knighthood and one of the three preeminent Order of merit, orders of merit bestowed by the Kingdom of Spain, alongside the Order of Charles III (established in 1771) and ...
* Grand Cross of the French Order of Saint Louis
The Royal and Military Order of Saint Louis () is a dynastic order of chivalry founded 5 April 1693 by King Louis XIV, named after Saint Louis (King Louis IX of France). It was intended as a reward for exceptional officers, notable as the fi ...
* Knight of the French Order of the Holy Spirit
The Order of the Holy Spirit (; sometimes translated into English as the Order of the Holy Ghost) is a French order of chivalry founded by Henry III of France in 1578. Today, it is a dynastic order under the House of France.
It should not be c ...
* Knight of the French Order of Saint Michael
The Order of Saint Michael () is a French dynastic order of chivalry, founded by King Louis XI of France on 1 August 1469, in response to the Order of the Golden Fleece founded by Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, Louis' chief competitor fo ...
* Grand Cross of the Austro-Hungarian Order of Saint Stephen
Genealogy
Ancestry
The ancestry of Emperor Pedro I:Issue
See also
* Hino da Independência and Hino da Carta, both composed by Pedro I. * Dom Pedro aquamarine, named after the Emperor and his son Pedro II, is the world's largest cut aquamarine gem. * Equestrian statue of Pedro I, erected in Rio de Janeiro in Pedro's honor in 1862.Endnotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pedro 01 Of Brazil 1798 births 1834 deaths 18th-century Portuguese people 19th-century Brazilian people 19th-century Portuguese monarchs Brazilian abolitionists Brazilian nobility Brazilian people of Portuguese descent Brazilian people of Spanish descent Brazilian revolutionaries 19th-century deaths from tuberculosis Dukes of Braganza Brazilian emperors 3 3 3 House of Braganza Tuberculosis deaths in Portugal Knights Grand Cross of the Order of Isabella the Catholic Grand Crosses of the Order of Saint Louis Knights of the Golden Fleece of Spain National anthem writers Nobility from Lisbon People of the Cisplatine War People of the Latin American wars of independence People of the Liberal Wars Portuguese infantes Princes of Beira Princes Royal of Portugal Regents of Brazil Royalty and nobility with epilepsy Brazilian Freemasons Brazilian monarchists Monarchs who abdicated Grand Crosses of the Order of Saint Stephen of Hungary Royal reburials 19th-century regents