Particle Detector on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In experimental and applied
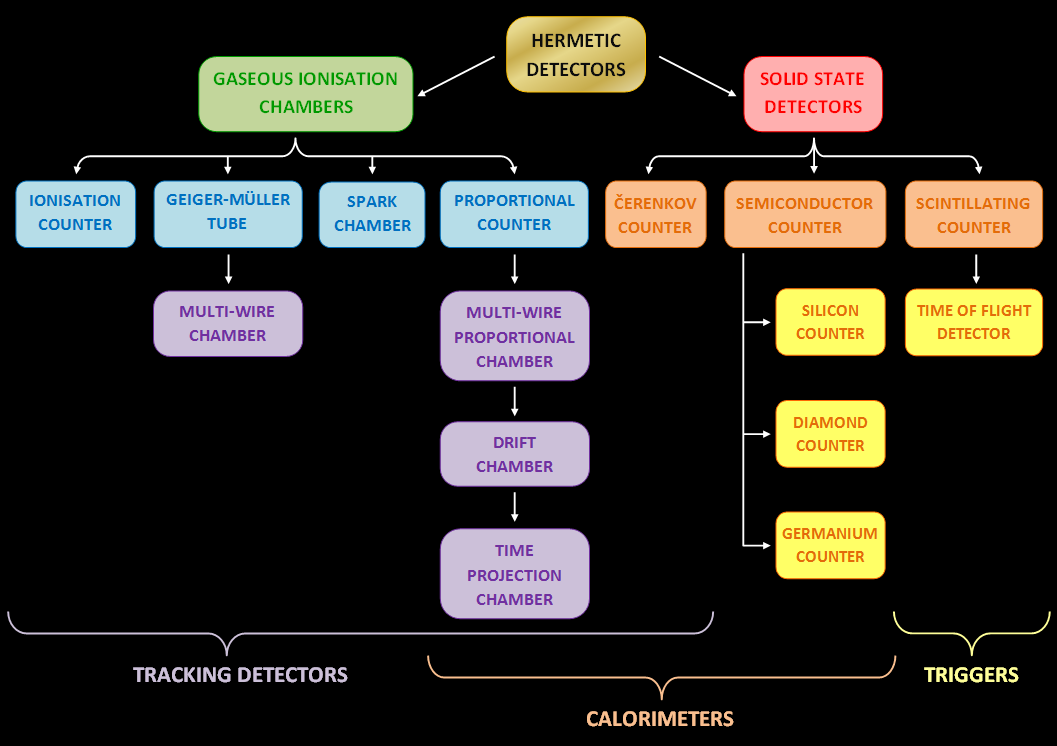 Many of the detectors invented and used so far are ionization detectors (of which
Many of the detectors invented and used so far are ionization detectors (of which  Historical examples
*
Historical examples
*
*** Delphi
*** L3 *** Opal
**for the SPS *** The COMPASS Experiment *
Gargamelle
*
NA61/SHINE
*At
CDF
*
D0
**
STAR
*At
PeP-II
***
SLC
*
*At
VEPP-2M
an
VEPP-2000
*** ND *** SND ***CMD **for th
VEPP-4
*
*Others
MECO
from
particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
, nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the ...
, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from ...
s, such as those produced by nuclear decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams.
Large accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle ...
. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle.
Examples and types
 Many of the detectors invented and used so far are ionization detectors (of which
Many of the detectors invented and used so far are ionization detectors (of which gaseous ionization detector
Gaseous ionization detectors are radiation detection instruments used in particle physics to detect the presence of ionizing particles, and in radiation protection applications to measure ionizing radiation.
They use the ionising effect of radia ...
s and semiconductor detector
A semiconductor detector in ionizing radiation detection physics is a device that uses a semiconductor (usually silicon or germanium) to measure the effect of incident charged particles or photons.
Semiconductor detectors find broad applicat ...
s are most typical) and scintillation detectors; but other, completely different principles have also been applied, like Čerenkov light and transition radiation.
 Historical examples
*
Historical examples
*Bubble chamber
A bubble chamber is a vessel filled with a superheated transparent liquid (most often liquid hydrogen) used to detect electrically charged particles moving through it. It was invented in 1952 by Donald A. Glaser, for which he was awarded the 1 ...
* Wilson cloud chamber (diffusion chamber)
* Photographic plate
;Detectors for radiation protection
The following types of particle detector are widely used for radiation protection, and are commercially produced in large quantities for general use within the nuclear, medical, and environmental fields.
*Dosimeter
A radiation dosimeter is a device that measures dose uptake of external ionizing radiation. It is worn by the person being monitored when used as a personal dosimeter, and is a record of the radiation dose received. Modern electronic personal d ...
*Electroscope
The electroscope is an early scientific instrument used to detect the presence of electric charge on a body. It detects charge by the movement of a test object due to the Coulomb electrostatic force on it. The amount of charge on an object is ...
(when used as a portable dosimeter)
*Gaseous ionization detector
Gaseous ionization detectors are radiation detection instruments used in particle physics to detect the presence of ionizing particles, and in radiation protection applications to measure ionizing radiation.
They use the ionising effect of radia ...
** Geiger counter
**Ionization chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest type of gas-filled radiation detector, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of certain types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, and beta particles. Conventionally, the term ...
**Proportional counter The proportional counter is a type of gaseous ionization detector device used to measure particles of ionizing radiation. The key feature is its ability to measure the energy of incident radiation, by producing a detector output pulse that is ''pro ...
* Scintillation counter
*Semiconductor detector
A semiconductor detector in ionizing radiation detection physics is a device that uses a semiconductor (usually silicon or germanium) to measure the effect of incident charged particles or photons.
Semiconductor detectors find broad applicat ...
Commonly used detectors for particle and nuclear physics
*Gaseous ionization detector
Gaseous ionization detectors are radiation detection instruments used in particle physics to detect the presence of ionizing particles, and in radiation protection applications to measure ionizing radiation.
They use the ionising effect of radia ...
**Ionization chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest type of gas-filled radiation detector, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of certain types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, and beta particles. Conventionally, the term ...
**Proportional counter The proportional counter is a type of gaseous ionization detector device used to measure particles of ionizing radiation. The key feature is its ability to measure the energy of incident radiation, by producing a detector output pulse that is ''pro ...
***Multiwire proportional chamber
A wire chamber or multi-wire proportional chamber is a type of proportional counter that detects charged particles and photons and can give positional information on their trajectory, by tracking the trails of gaseous ionization. was located via ...
***Drift chamber
A wire chamber or multi-wire proportional chamber is a type of proportional counter that detects charged particles and photons and can give positional information on their trajectory, by tracking the trails of gaseous ionization. was located via ...
***Time projection chamber
In physics, a time projection chamber (TPC) is a type of particle detector that uses a combination of electric fields and magnetic fields together with a sensitive volume of gas or liquid to perform a three-dimensional reconstruction of a particl ...
***Micropattern gaseous detector
Micropattern gaseous detectors (MPGDs) are a group of gaseous ionization detectors
Gaseous ionization detectors are radiation detection instruments used in particle physics to detect the presence of ionizing particles, and in radiation protecti ...
** Geiger–Müller tube
**Spark chamber {{short description, Charged particle detector
A spark chamber is a particle detector: a device used in particle physics for detecting electrically charged particles. They were most widely used as research tools from the 1930s to the 1960s and have ...
*Solid-state detectors:
**Semiconductor detector
A semiconductor detector in ionizing radiation detection physics is a device that uses a semiconductor (usually silicon or germanium) to measure the effect of incident charged particles or photons.
Semiconductor detectors find broad applicat ...
and variants including CCDs
***Silicon Vertex Detector
** Solid-state nuclear track detector
** Cherenkov detector
*** Ring-imaging Cherenkov detector (RICH)
** Scintillation counter and associated photomultiplier A photomultiplier is a device that converts incident photons into an electrical signal.
Kinds of photomultiplier include:
* Photomultiplier tube, a vacuum tube converting incident photons into an electric signal. Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs for sh ...
, photodiode, or avalanche photodiode
An avalanche photodiode (APD) is a highly sensitive semiconductor photodiode detector that exploits the photoelectric effect to convert light into electricity. From a functional standpoint, they can be regarded as the semiconductor analog of phot ...
*** Lucas cell
*** Time-of-flight detector
** Transition radiation detector
*Calorimeter
A calorimeter is an object used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal micro calorimeters, titration calorimete ...
* Microchannel plate detector
*Neutron detector
Neutron detection is the effective detection of neutrons entering a well-positioned detector. There are two key aspects to effective neutron detection: hardware and software. Detection hardware refers to the kind of neutron detector used (the most ...
Modern detectors
Modern detectors in particle physics combine several of the above elements in layers much like anonion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onio ...
.
Research particle detectors
Detectors designed for modern accelerators are huge, both in size and in cost. The term '' counter'' is often used instead of ''detector'' when the detector counts the particles but does not resolve its energy or ionization. Particle detectors can also usually track ionizing radiation (high energyphoton
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
s or even visible light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
). If their main purpose is radiation measurement, they are called ''radiation detectors'', but as photons are also (massless) particles, the term ''particle detector'' is still correct.
At colliders
*At CERN **for the LHC ***CMS
CMS may refer to:
Computing
* Call management system
* CMS-2 (programming language), used by the United States Navy
* Code Morphing Software, a technology used by Transmeta
* Collection management system for a museum collection
* Color manag ...
***ATLAS
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
*** ALICE
***LHCb
The LHCb (Large Hadron Collider beauty) experiment is one of eight particle physics detector experiments collecting data at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. LHCb is a specialized b-physics experiment, designed primarily to measure the paramet ...
**for the LEP
*** Aleph*** Delphi
*** L3 *** Opal
**for the SPS *** The COMPASS Experiment *
Gargamelle
*
NA61/SHINE
*At
Fermilab
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), located just outside Batavia, Illinois, near Chicago, is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory specializing in high-energy particle physics. Since 2007, Fermilab has been opera ...
**for the Tevatron
The Tevatron was a circular particle accelerator (active until 2011) in the United States, at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (also known as ''Fermilab''), east of Batavia, Illinois, and is the second highest energy particle collider ...
*CDF
*
D0
**
Mu2e
Mu2e, or the Muon-to-Electron Conversion Experiment, is a particle physics experiment at Fermilab in the US. The goal of the experiment is to identify physics beyond the Standard Model, namely, the conversion of muons to electrons without the e ...
*At DESY
**for HERA
*** H1
*** HERA-B
***HERMES
Hermes (; grc-gre, wikt:Ἑρμῆς, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travelle ...
***ZEUS
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label= genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label= genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek reli ...
*At BNL
**for the RHIC
*** PHENIX
*** Phobos
*STAR
*At
SLAC
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center,
is a United States Department of Energy National Laboratory operated by Stanford University under the programmatic direction of the U.S. Departme ...
**for thPeP-II
***
BaBar
Babar ( ur, ), also variously spelled as Baber, Babur, and Babor is a male given name of Pashto, and Persian origin, and a popular male given name in Pakistan. It is generally taken in reference to the Persian ''babr'' (Persian: ببر), meaning ...
**for thSLC
*
*At
Cornell
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to teach a ...
**for CESR
***CLEO Cleo may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Cleo'' (magazine), an Australian magazine established in 1972, now active in Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand
* Cleo (group), a South Korean girl group formed in 1999
* ''Cleo'' (play), by Lawren ...
*** CUSB
*At BINP
**for thVEPP-2M
an
VEPP-2000
*** ND *** SND ***CMD **for th
VEPP-4
*
*Others
MECO
from
UC Irvine
UC may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* '' University Challenge'', a popular British quiz programme airing on BBC Two
** ''University Challenge (New Zealand)'', the New Zealand version of the British programme
* Universal Century, one of the t ...
Under construction
*For International Linear Collider (ILC) **CALICE
Calice may refer to:
* CALICE (Calorimeter for Linear Collider Experiment), a research and development organization
* , an Austrian nobility, Austrian noble family
* Calice Becker (fl. 1990–2014), French perfumer
* Calice, an alternative name fo ...
(Calorimeter for Linear Collider Experiment)
Without colliders
* Antarctic Muon And Neutrino Detector Array (AMANDA) *Cryogenic Dark Matter Search
The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) is a series of experiments designed to directly detect particle dark matter in the form of Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (or WIMPs). Using an array of semiconductor detectors at millikelvin temperatur ...
(CDMS)
*Super-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a Neutrino detector, neutrino observatory located Kamioka Observatory, under Mount Ikeno ...
*XENON
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
On spacecraft
*Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS-02) is a particle physics experiment module that is mounted on the International Space Station (ISS).Kristine Rainey (April 2, 2013)Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS): How It Works NASA. Retrieved June 2, 20 ...
(AMS)
*JEDI
Jedi (), Jedi Knights, or collectively the Jedi Order are the main heroic protagonists of many works of the '' Star Wars'' franchise. Working symbiotically alongside the Old Galactic Republic, and later supporting the Rebel Alliance, the Jedi ...
(Jupiter Energetic-particle Detector Instrument)
Theoretical Models of Particle Detectors
Beyond their experimental implementations, theoretical models of particle detectors are also of great importance to theoretical physics. These models consider localized non-relativistic quantum systems coupled to a quantum field. They receive the name of particle detectors because when the non-relativistic quantum system is measured in an excited state, one can claim to have detected a particle. The first instance of particle detector models in the literature dates from the 80's, where a particle in a box was introduced by W. G. Unruh in order to probe a quantum field around a black hole. Shortly after,Bryce DeWitt
Bryce Seligman DeWitt (January 8, 1923 – September 23, 2004), was an American theoretical physicist noted for his work in gravitation and quantum field theory.
Life
He was born Carl Bryce Seligman, but he and his three brothers, including th ...
proposed a simplification of the model, giving rise to the Unruh-DeWitt detector model.
Beyond their applications to theoretical physics, particle detector models are related to experimental fields such as quantum optics
Quantum optics is a branch of atomic, molecular, and optical physics dealing with how individual quanta of light, known as photons, interact with atoms and molecules. It includes the study of the particle-like properties of photons. Photons have ...
, where atoms can be used as detectors for the quantum electromagnetic field via the light-matter interaction. From a conceptual side, particle detectors also allow one to formally define the concept of particles without relying on asymptotic states, or representations of a quantum field theory. As M. Scully puts it, from an operational viewpoint one can state that "a particle is what a particle detector detects", which in essence defines a particle as the detection of excitations of a quantum field.
See also
*Counting efficiency In the measurement of ionising radiation the counting efficiency is the ratio between the number of particles or photons counted with a radiation counter and the number of particles or photons of the same type and energy emitted by the radiation s ...
*List of particles
This is a list of known and hypothesized particles.
Elementary particles
Elementary particles are particles with no measurable internal structure; that is, it is unknown whether they are composed of other particles. They are the fundamental ob ...
* Tail-pulse generator
References
* * *Further reading
;Filmstrips *"''Radiation detectors''". H. M. Stone Productions, Schloat. Tarrytown, N.Y., Prentice-Hall Media, 1972. ;General Information * {{Authority control Ionising radiation detectors