Paris Peace Conference (1919ŌĆō1920) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Paris Peace Conference was a set of formal and informal diplomatic meetings in 1919 and 1920 after the end of
 A central issue of the conference was the disposition of the overseas colonies of Germany (Austria-Hungary did not have major colonies, and the Ottoman Empire was a separate issue).
Some British dominions wanted their reward for their sacrifice. Australia wanted
A central issue of the conference was the disposition of the overseas colonies of Germany (Austria-Hungary did not have major colonies, and the Ottoman Empire was a separate issue).
Some British dominions wanted their reward for their sacrifice. Australia wanted
 The maintenance of the unity, territories, and interests of the British Empire was an overarching concern for the British delegates to the conference. Still, they entered the conference with more specific goals with this order of priority:
* Ensure colonial claims of Germany were redacted (taken or given to victory colonies)
* Germany was ensued with 30 billion dollars of debt, concerning interest
* Ensuring the security of France
* Removing the threat of the German High Seas Fleet
* Settling territorial contentions
* Supporting the League of Nations
The Racial Equality Proposal put forth by the Japanese did not directly conflict with any core British interest, but as the conference progressed, its full implications on immigration to the
The maintenance of the unity, territories, and interests of the British Empire was an overarching concern for the British delegates to the conference. Still, they entered the conference with more specific goals with this order of priority:
* Ensure colonial claims of Germany were redacted (taken or given to victory colonies)
* Germany was ensued with 30 billion dollars of debt, concerning interest
* Ensuring the security of France
* Removing the threat of the German High Seas Fleet
* Settling territorial contentions
* Supporting the League of Nations
The Racial Equality Proposal put forth by the Japanese did not directly conflict with any core British interest, but as the conference progressed, its full implications on immigration to the
 The dominion governments were not originally given separate invitations to the conference and had been expected to send representatives as part of the British delegation.
Convinced that Canada had become a nation on the battlefields of Europe, Prime Minister Sir Robert Borden demanded that it have a separate seat at the conference. That was initially opposed not only by Britain but also by the United States, which saw any Dominion delegation as an extra British vote. Borden responded by pointing out that since Canada had lost nearly 60,000 men, a far larger proportion of its men than the 50,000 American men lost, it had at least the right to the representation of a "minor" power. Lloyd George eventually relented and persuaded the reluctant Americans to accept the presence of delegations from Canada,
The dominion governments were not originally given separate invitations to the conference and had been expected to send representatives as part of the British delegation.
Convinced that Canada had become a nation on the battlefields of Europe, Prime Minister Sir Robert Borden demanded that it have a separate seat at the conference. That was initially opposed not only by Britain but also by the United States, which saw any Dominion delegation as an extra British vote. Borden responded by pointing out that since Canada had lost nearly 60,000 men, a far larger proportion of its men than the 50,000 American men lost, it had at least the right to the representation of a "minor" power. Lloyd George eventually relented and persuaded the reluctant Americans to accept the presence of delegations from Canada,
 French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau controlled his delegation, and his chief goal was to weaken Germany militarily, strategically, and economically. Having personally witnessed two German attacks on French soil in the last 40 years, he was adamant for Germany not to be permitted to attack France again. Particularly, Clemenceau sought an American and British joint guarantee of French security in the event of another German attack.
Clemenceau also expressed skepticism and frustration with Wilson's
French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau controlled his delegation, and his chief goal was to weaken Germany militarily, strategically, and economically. Having personally witnessed two German attacks on French soil in the last 40 years, he was adamant for Germany not to be permitted to attack France again. Particularly, Clemenceau sought an American and British joint guarantee of French security in the event of another German attack.
Clemenceau also expressed skepticism and frustration with Wilson's
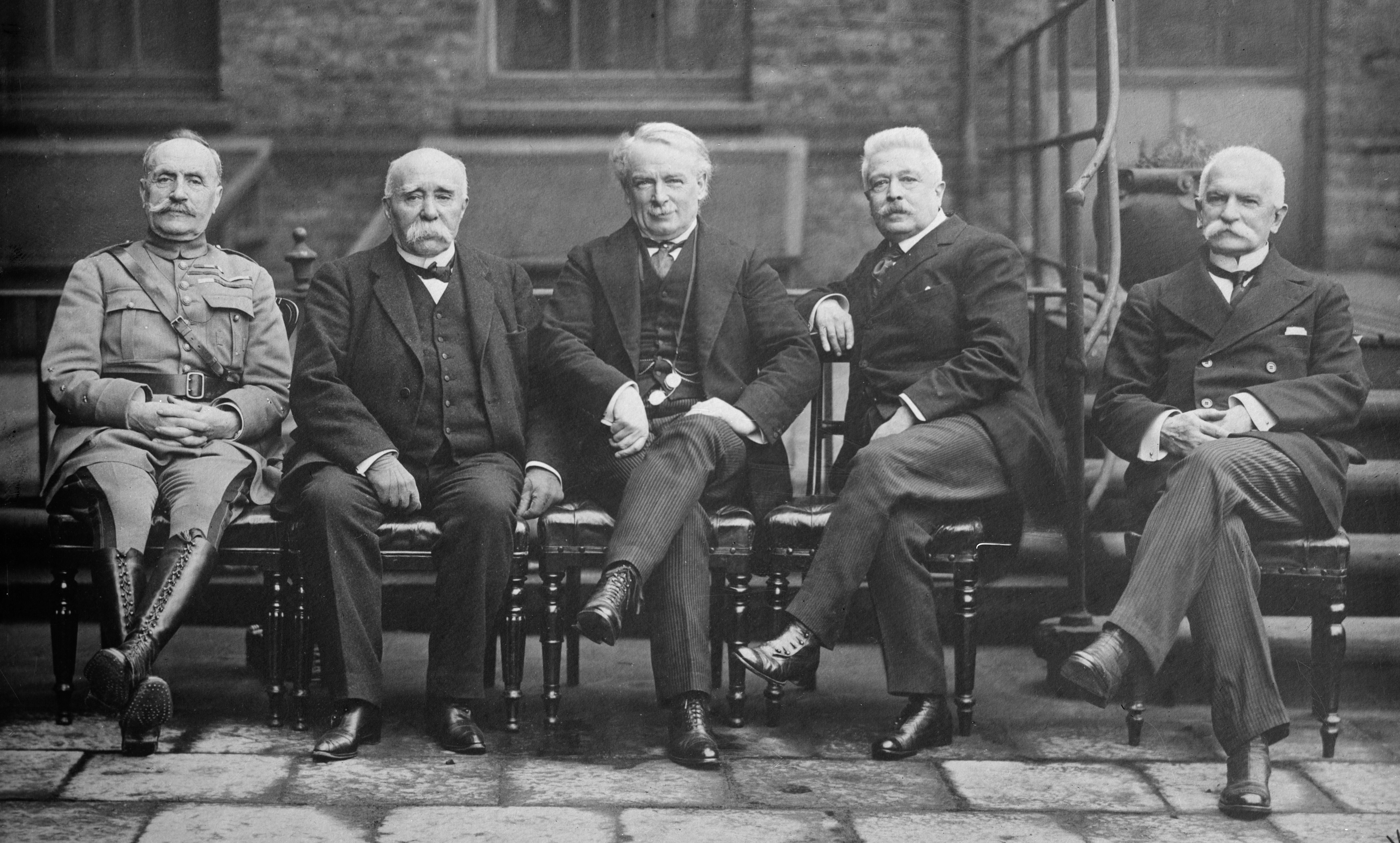 In 1914, Italy remained neutral despite the Triple Alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary. In 1915, it joined the Allies to gain the territories promised by the
In 1914, Italy remained neutral despite the Triple Alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary. In 1915, it joined the Allies to gain the territories promised by the

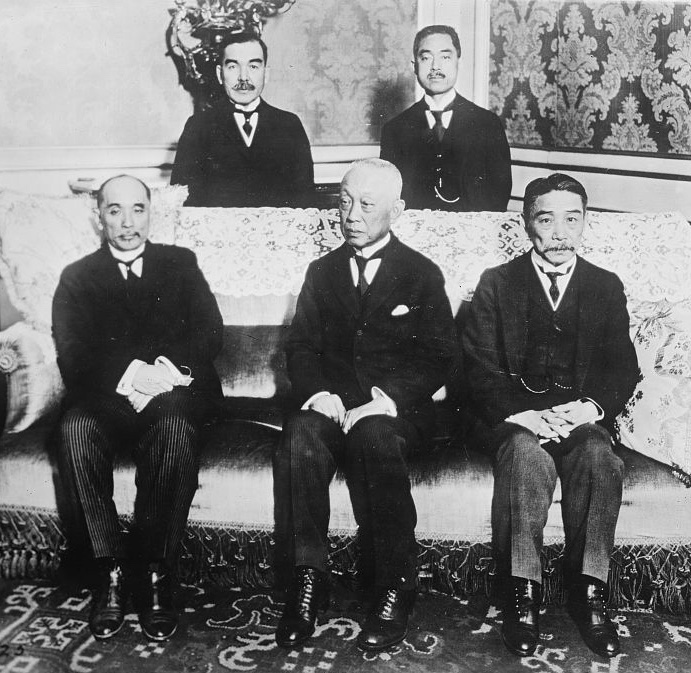 Japan sent a large delegation, headed by the former Prime Minister, Marquis
Japan sent a large delegation, headed by the former Prime Minister, Marquis
 Until Wilson's arrival in Europe in December 1918, no sitting American president had ever visited the continent. Wilson's 1918
Until Wilson's arrival in Europe in December 1918, no sitting American president had ever visited the continent. Wilson's 1918
 Ukraine had its best opportunity to win recognition and support from foreign powers at the conference. At a meeting of the Big Five on 16 January, Lloyd George called Ukrainian leader Symon Petliura an adventurer and dismissed Ukraine as an anti-Bolshevik stronghold. Sir Eyre Crowe, British Undersecretary of State for Foreign Affairs, spoke against a union of East Galicia and Poland. The British cabinet never decided whether to support a united or dismembered Russia. The United States was sympathetic to a strong, united Russia, as a counterpoise to Japan, but Britain feared a threat to India. Petliura appointed Count Tyshkevich as his representative to the Vatican, and Pope Benedict XV recognized Ukrainian independence, but Ukraine was effectively ignored.
Ukraine had its best opportunity to win recognition and support from foreign powers at the conference. At a meeting of the Big Five on 16 January, Lloyd George called Ukrainian leader Symon Petliura an adventurer and dismissed Ukraine as an anti-Bolshevik stronghold. Sir Eyre Crowe, British Undersecretary of State for Foreign Affairs, spoke against a union of East Galicia and Poland. The British cabinet never decided whether to support a united or dismembered Russia. The United States was sympathetic to a strong, united Russia, as a counterpoise to Japan, but Britain feared a threat to India. Petliura appointed Count Tyshkevich as his representative to the Vatican, and Pope Benedict XV recognized Ukrainian independence, but Ukraine was effectively ignored.
 The three South Caucasian republics of
The three South Caucasian republics of

 The February 1919 statement included the following main points: recognition of Jewish "title" over the land, a declaration of the borders (significantly larger than in the prior Sykes-Picot agreement), and League of Nations sovereignty under British mandate.Statement of the Zionist Organization regarding Palestine
The February 1919 statement included the following main points: recognition of Jewish "title" over the land, a declaration of the borders (significantly larger than in the prior Sykes-Picot agreement), and League of Nations sovereignty under British mandate.Statement of the Zionist Organization regarding Palestine
, 3 February 1919 An offshoot of the conference was convened at San Remo in 1920, leading to the creation of the

Writing the Great War ŌĆō The Historiography of World War I from 1918 to the Present
' (2020); full coverage for major countries. * Cooper, John Milton. ''Woodrow Wilson: A Biography'' (2009), scholarly biography; pp 439ŌĆō53
excerpt and text search
* Dillon, Emile Joseph. ''The Inside Story of the Peace Conference'', (1920
online
* Dockrill, Michael, and John Fisher. ''The Paris Peace Conference, 1919: Peace Without Victory?'' (Springer, 2016). * Ferguson, Niall. ''The Pity of War: Explaining World War One'' (1999), economics issues at Paris pp 395ŌĆō432 * Doumanis, Nicholas, ed. ''The Oxford Handbook of European History, 1914ŌĆō1945'' (2016) ch 9. * David Fromkin, Fromkin, David. ''A Peace to End All Peace, The Fall of the Ottoman Empire and the Creation of the Modern Middle East'', Macmillan 1989. * Gelfand, Lawrence Emerson. ''The Inquiry: American Preparations for Peace, 1917ŌĆō1919'' (Yale UP, 1963). * Ginneken, Anique H.M. van. ''Historical Dictionary of the League of Nations'' (2006)\ * Greene, Theodore, ed. ''Wilson at Versailles'' (1949) short excerpts from scholarly studies
online free
* Henderson, W. O. "The Peace Settlement, 1919" ''History'' 26.101 (1941): 60ŌĆō6
online
historiography * Henig, Ruth. ''Versailles and After: 1919ŌĆō1933'' (2nd ed. 1995), 100 pages; brief introduction by scholar * * Keynes, John Maynard, ''The Economic Consequences of the Peace'' (1920) famous criticism by leading economis
full text online
* Dimitri Kitsikis, ''Le r├┤le des experts ├Ā la Conf├®rence de la Paix de 1919'', Ottawa, ├®ditions de l'universit├® d'Ottawa, 1972. * Dimitri Kitsikis, ''Propagande et pressions en politique internationale. La Gr├©ce et ses revendications ├Ā la Conf├®rence de la Paix, 1919ŌĆō1920'', Paris, Presses universitaires de France, 1963. * Knock, Thomas J. ''To End All Wars: Woodrow Wilson and the Quest for a New World Order'' (1995) * Lederer, Ivo J., ed. ''The Versailles SettlementŌĆöWas It Foredoomed to Failure?'' (1960) short excerpts from scholars * Lentin, Antony. ''Guilt at Versailles: Lloyd George and the Pre-history of Appeasement'' (1985) * Lentin, Antony. ''Lloyd George and the Lost Peace: From Versailles to Hitler, 1919ŌĆō1940'' (2004) * * Macalister-Smith, Peter, Schwietzke, Joachim: ''Diplomatic Conferences and Congresses. A Bibliographical Compendium of State Practice 1642 to 1919'', W. Neugebauer, Graz, Feldkirch 2017, . * MacMillan, Margaret. ''Peacemakers: The Paris Peace Conference of 1919 and Its Attempt to End War'' (2001), also published as ''Paris 1919: Six Months That Changed the World'' (2003); influential survey * * * Paxton, Robert O., and Julie Hessler. ''Europe in the Twentieth Century'' (2011) pp 141ŌĆō78 * Marks, Sally. ''The Illusion of Peace: International Relations in Europe 1918ŌĆō1933'' (2nd ed. 2003) * Marks, Sally. "Mistakes and Myths: The Allies, Germany, and the Versailles Treaty, 1918ŌĆō1921." ''Journal of Modern History'' 85.3 (2013): 632ŌĆō659
online
* Mayer, Arno J., ''Politics and Diplomacy of Peacemaking: Containment and Counter-revolution at Versailles, 1918ŌĆō1919'' (1967), leftist * Newton, Douglas. ''British Policy and the Weimar Republic, 1918ŌĆō1919'' (1997). 484 pgs. * * Roberts, Priscilla. "Wilson, Europe's Colonial Empires, and the Issue of Imperialism", in Ross A. Kennedy, ed., ''A Companion to Woodrow Wilson'' (2013) pp: 492ŌĆō517. * Schwabe, Klaus. ''Woodrow Wilson, Revolutionary Germany, and Peacemaking, 1918ŌĆō1919: Missionary Diplomacy and the Realities of Power'' (1985) * Sharp, Alan. ''The Versailles Settlement: Peacemaking after the First World War, 1919ŌĆō1923'' (2nd ed. 2008) * * Naoko Shimazu (1998), ''Japan, Race and Equality'', Routledge, * Steiner, Zara. ''The Lights that Failed: European International History 1919ŌĆō1933'' (Oxford History of Modern Europe) (2007), pp 15ŌĆō79; major scholarly work * * Walworth, Arthur. ''Wilson and His Peacemakers: American Diplomacy at the Paris Peace Conference, 1919'' (1986) 618pp * ; 904pp; full scale scholarly biography; winner of Pulitzer Prize
online free; 2nd ed. 1965
* Watson, David Robin. ''George Clemenceau: A Political Biography'' (1976) 463 pgs. * Xu, Guoqi. ''Asia and the Great War ŌĆō A Shared History'' (Oxford UP, 2016
online
Seating Plan of the Paris Peace Conference ŌĆō UK Parliament Living Heritage
Frances Stevenson ŌĆō Paris Peace Conference Diary ŌĆō UK Parliament Living Heritage
Frances Stevenson ŌĆō Paris Peace Conference ID Card ŌĆō UK Parliament Living Heritage
* Sharp, Alan
The Paris Peace Conference and its Consequences
in
1914ŌĆō1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
Excerpts from the NFB documentary ''Paris 1919''
Sampling of maps
used by the American delegates held by th
American Geographical Society Library
UW Milwaukee {{DEFAULTSORT:Paris Peace Conference (1919-1920) Paris Peace Conference (1919ŌĆō1920), 1919 in international relations 1920 in international relations 1919 conferences 1920 conferences Georges Clemenceau Presidency of Woodrow Wilson Conferences in Paris, Peace 1919 in Paris 1920 in Paris 20th-century diplomatic conferences Diplomatic conferences in France David Lloyd George Eleftherios Venizelos
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 ŌĆō 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, in which the victorious Allies set the peace terms for the defeated Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914ŌĆō1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
. Dominated by the leaders of Britain, France, the United States and Italy, the conference resulted in five treaties that rearranged the maps of Europe and parts of Asia, Africa and the Pacific Islands, and also imposed financial penalties. Germany, Austria-Hungary, Turkey and the other losing nations were not given a voice in the deliberations; this later gave rise to political resentments that lasted decades. The arrangements made by this conference are considered one of the greatest watersheds of 20th century geopolitical history which would lead to World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 ŌĆō 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
The conference involved diplomats from 32 countries and nationalities. Its major decisions were the creation of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919ŌĆō1920), Paris Peace ...
and the five peace treaties with the defeated states. Main arrangements agreed upon in the treaties were, among others, the transition of German and Ottoman overseas possessions as " mandates" from the hands of these countries chiefly into the hands of Britain and France; the imposition of reparations upon Germany; and the drawing of new national boundaries, sometimes involving plebiscites, to reflect ethnic boundaries more closely.
US President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
in 1917 commissioned a group of about 150 academics to research topics likely to arise in diplomatic talks on the European stage, and to develop a set of principles to be used for the peace negotiations to end World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 ŌĆō 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. The results of this research were summarized in the so-called Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms to the United States Congress ...
document that became the basis for the terms of the German surrender during the conference, as it had earlier been the basis of the German government's negotiations in the Armistice of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed in a railroad car, in the Compi├©gne Forest near the town of Compi├©gne, that ended fighting on land, at sea, and in the air in World War I between the Entente and their las ...
.
The main result of the conference was the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
with Germany; Article 231 of that treaty placed the responsibility for the war on "the aggression of Germany and her allies". That provision proved very humiliating for German leaders, armies and citizens alike, and set the stage for the expensive reparations that Germany was intended to pay, only a small portion of which had been delivered when it stopped paying after 1931. The five great powers at that time, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and the United States, controlled the Conference. The " Big Four" leaders were French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau, British Prime Minister David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor (17 January 1863 ŌĆō 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. A Liberal Party (United Kingdom), Liberal Party politician from Wales, he was known for leadi ...
, US President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
, and Italian Prime Minister Vittorio Emanuele Orlando. Together with teams of diplomats and jurist
A jurist is a person with expert knowledge of law; someone who analyzes and comments on law. This person is usually a specialist legal scholar, mostly (but not always) with a formal education in law (a law degree) and often a Lawyer, legal prac ...
s, they met informally 145 times and agreed upon all major decisions before they were ratified. Ren├® Albrecht-Carri├®, ''Diplomatic History of Europe Since the Congress of Vienna'' (1958) p. 363
The conference began on 18 January 1919. With respect to its end, Professor Michael Neiberg noted, "Although the senior statesmen stopped working personally on the conference in June 1919, the formal peace process did not really end until July 1923, when the Treaty of Lausanne was signed." The entire process is often referred to as the "Versailles Conference", although only the signing of the first treaty took place in the historic palace; the negotiations occurred at the Quai d'Orsay in Paris.
Overview and direct results
The Conference formally opened on 18 January 1919 at the Quai d'Orsay in Paris. This date was symbolic, as it was the anniversary of the proclamation ofWilliam I William I may refer to:
Kings
* William the Conqueror (ŌĆō1087), also known as William I, King of England
* William I of Sicily (died 1166)
* William I of Scotland (died 1214), known as William the Lion
* William I of the Netherlands and Luxembour ...
as German Emperor
The German Emperor (, ) was the official title of the head of state and Hereditary monarchy, hereditary ruler of the German Empire. A specifically chosen term, it was introduced with the 1 January 1871 constitution and lasted until the abdicati ...
in 1871, in the Hall of Mirrors
The Hall of Mirrors () is a grand Baroque architecture, Baroque style gallery and one of the most emblematic rooms in the royal Palace of Versailles near Paris, France. The grandiose ensemble of the hall and its adjoining salons was intended to ...
at the Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in Franc ...
, shortly before the end of the Siege of Paris ŌĆō a day itself imbued with significance in Germany, as the anniversary of the establishment of the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
in 1701.
The Delegates from 27 nations (delegates representing 5 nationalities were for the most part ignored) were assigned to 52 commissions, which held 1,646 sessions to prepare reports, with the help of many experts, on topics ranging from prisoners of war to undersea cables, to international aviation, to responsibility for the war. Key recommendations were folded into the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
with Germany, which had 15 chapters and 440 clauses, as well as treaties for the other defeated nations.
The five major powers, France, Britain, Italy, the U.S., and Japan, controlled the Conference. Amongst the "Big Five", in practice Japan only sent a former prime minister and played a small role; and the " Big Four" leaders dominated the conference.
The four met together informally 145 times and made all the major decisions, which were then ratified by other attendees. The open meetings of all the delegations approved the decisions made by the Big Four. The conference came to an end on 21 January 1920, with the inaugural General Assembly of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919ŌĆō1920), Paris Peace ...
.
Five major peace treaties were prepared at the Paris Peace Conference, with, in parentheses, the affected countries:
* the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
, 28 June 1919 (Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
)
* the Treaty of Saint-Germain, 10 September 1919 (Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
)
* the Treaty of Neuilly, 27 November 1919 (Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
)
* the Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon (; ; ; ), often referred to in Hungary as the Peace Dictate of Trianon or Dictate of Trianon, was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference (1919ŌĆō1920), Paris Peace Conference. It was signed on the one side by Hungary ...
, 4 June 1920 (Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
)
* the Treaty of S├©vres
The Treaty of S├©vres () was a 1920 treaty signed between some of the Allies of World War I and the Ottoman Empire, but not ratified. The treaty would have required the cession of large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, ...
, 10 August 1920; subsequently revised by the Treaty of Lausanne, 24 July 1923 (Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
/Republic of Turkey).
The major decisions were the establishment of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919ŌĆō1920), Paris Peace ...
; the five peace treaties with defeated enemies; the awarding of German and Ottoman overseas possessions as "mandates", chiefly to members of the British Empire and to France; reparations imposed on Germany; and the drawing of new national boundaries, sometimes with plebiscites, to better reflect the forces of nationalism. The main result was the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
, with Germany, which in section 231 assigned the liability for damaged caused to the Allies by "the aggression of Germany and her allies" to the defeated Central Powers. This provision proved humiliating for Germany and set the stage for significant reparations Germany was supposed to pay. Germany paid only a small portion, before reparations ended in 1931. According to British historian AJP Taylor, the treaty seemed to Germans "wicked, unfair" and "dictation, a slave treaty" but one which they would repudiate at some stage if it "did not fall to pieces of its own absurdity."
As the conference's decisions were enacted unilaterally and largely on the whims of the Big Four, Paris was effectively the center of a world government
World government is the concept of a single political authority governing all of Earth and humanity. It is conceived in a variety of forms, from tyrannical to democratic, which reflects its wide array of proponents and detractors.
There has ...
during the conference, which deliberated over and implemented the sweeping changes to the political geography
Political geography is concerned with the study of both the spatially uneven outcomes of political processes and the ways in which political processes are themselves affected by spatial structures. Conventionally, for the purposes of analysis, ...
of Europe. Most famously, the Treaty of Versailles itself weakened the German military and placed liability for the war and substantial reparations on Germany's shoulders, and the later humiliation and resentment in Germany is often considered to be one of the direct causes of Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party ( or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor ...
's electoral successes and one of the indirect causes of World War II
The causes of World War II have been given considerable attention by historians. The immediate precipitating event was the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany on September 1, 1939, and the subsequent declarations of war on Germany made by Unit ...
.
The League of Nations proved controversial in the United States since critics said it subverted the powers of the US Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
to declare war. The US Senate
The United States Senate is a chamber of the bicameral United States Congress; it is the upper house, with the U.S. House of Representatives being the lower house. Together, the Senate and House have the authority under Article One of the ...
did not ratify any of the peace treaties and so the United States never joined the League. Instead, the 1921ŌĆō1923 Harding administration concluded new treaties with Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, and Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
. The German Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
was not invited to attend the conference at Versailles. Representatives of White Russia but not Communist Russia were at the conference. Numerous other nations sent delegations to appeal for various unsuccessful additions to the treaties, and parties lobbied for causes ranging from independence for the countries of the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
to Japan's unsuccessful proposal for racial equality to the other great powers.
Mandates
 A central issue of the conference was the disposition of the overseas colonies of Germany (Austria-Hungary did not have major colonies, and the Ottoman Empire was a separate issue).
Some British dominions wanted their reward for their sacrifice. Australia wanted
A central issue of the conference was the disposition of the overseas colonies of Germany (Austria-Hungary did not have major colonies, and the Ottoman Empire was a separate issue).
Some British dominions wanted their reward for their sacrifice. Australia wanted New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
, New Zealand wanted Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and known until 1997 as Western Samoa, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu), two smaller, inhabited ...
, and South Africa wanted South West Africa
South West Africa was a territory under Union of South Africa, South African administration from 1915 to 1990. Renamed ''Namibia'' by the United Nations in 1968, Independence of Namibia, it became independent under this name on 21 March 1990. ...
. Wilson wanted the League to administer all German colonies until they were ready for independence. Lloyd George realized he needed to support his dominions and so he proposed a compromise: there would be three types of mandates.
Mandates for the Turkish provinces were one category and would be divided up between Britain and France. The second category, of New Guinea, Samoa, and South West Africa, were located so close to responsible supervisors that the mandates could hardly be given to anyone except Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. Finally, the African colonies would need the careful supervision as "Class B" mandates, which could be provided only by experienced colonial powers: Britain, France, and Belgium although Italy and Portugal received small amounts of territory. Wilson and the others finally went along with the solution. The dominions received " Class C Mandates" to the colonies that they wanted. Japan obtained mandates over German possessions north of the Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
.
Wilson wanted no mandates for the United States, but his main advisor, Colonel House, was deeply involved in awarding the others. Wilson was especially offended by Australian demands and had some memorable clashes with Billy Hughes
William Morris Hughes (25 September 1862 ŌĆō 28 October 1952) was an Australian politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Australia from 1915 to 1923. He led the nation during World War I, and his influence on national politics s ...
(the Australian Prime Minister), this the most famous:
:
British approach
 The maintenance of the unity, territories, and interests of the British Empire was an overarching concern for the British delegates to the conference. Still, they entered the conference with more specific goals with this order of priority:
* Ensure colonial claims of Germany were redacted (taken or given to victory colonies)
* Germany was ensued with 30 billion dollars of debt, concerning interest
* Ensuring the security of France
* Removing the threat of the German High Seas Fleet
* Settling territorial contentions
* Supporting the League of Nations
The Racial Equality Proposal put forth by the Japanese did not directly conflict with any core British interest, but as the conference progressed, its full implications on immigration to the
The maintenance of the unity, territories, and interests of the British Empire was an overarching concern for the British delegates to the conference. Still, they entered the conference with more specific goals with this order of priority:
* Ensure colonial claims of Germany were redacted (taken or given to victory colonies)
* Germany was ensued with 30 billion dollars of debt, concerning interest
* Ensuring the security of France
* Removing the threat of the German High Seas Fleet
* Settling territorial contentions
* Supporting the League of Nations
The Racial Equality Proposal put forth by the Japanese did not directly conflict with any core British interest, but as the conference progressed, its full implications on immigration to the British dominions
A dominion was any of several largely self-governance, self-governing countries of the British Empire, once known collectively as the ''British Commonwealth of Nations''. Progressing from colonies, their degrees of self-governing colony, colon ...
, with Australia taking particular exception, became a major point of contention within the delegation.
Ultimately, the British delegation did not treat that proposal as a fundamental aim of the conference; they were willing to sacrifice the Racial Equality Proposal to placate the Australian delegation and thus help to satisfy their overarching aim of preserving the unity of the British Empire.
Britain had reluctantly consented to the attendance of separate delegations from British dominions, but the British managed to rebuff attempts by the envoys of the newly proclaimed Irish Republic
The Irish Republic ( or ) was a Revolutionary republic, revolutionary state that Irish Declaration of Independence, declared its independence from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in January 1919. The Republic claimed jurisdict ...
to put a case to the conference for Irish self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
, diplomatic recognition, and membership in the proposed League of Nations. The Irish envoys' final "Demand for Recognition" in a letter to Clemenceau, the conference chairman, was not answered. Britain had been planning to renege on the Government of Ireland Act 1914
The Government of Ireland Act 1914 ( 4 & 5 Geo. 5. c. 90), also known as the Home Rule Act, and before enactment as the Third Home Rule Bill, was an Act passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom intended to provide home rule (self-gover ...
and instead to replace it with a new Government of Ireland Bill which would partition Ireland into two Irish Home Rule states (which eventually was passed as the Government of Ireland Act 1920). The planned two states would both be within the United Kingdom and so neither would have dominion status.
David Lloyd George commented that he did "not do badly" at the peace conference "considering I was seated between Jesus Christ
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
and Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 ŌĆō 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
." This was a reference to the great idealism of Wilson, who desired merely to punish Germany, and the stark realism of Clemenceau, who was determined to see Germany effectively destroyed.
Eastern Mediterranean
Like the other main Allied powers, the British public was more inclined to punish Germany and Austria. Britain's relationship with theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
was not a topic in the 1918 general election. There was an indecision among British decision makers over defanging and demobilizing the Ottoman army, the fate to be assigned to leading Committee of Union and Progress
The Ottoman Committee of Union and Progress (CUP, also translated as the Society of Union and Progress; , French language, French: ''Union et Progr├©s'') was a revolutionary group, secret society, and political party, active between 1889 and 1926 ...
members, and the future of the Turkish straits. Per Taner Ak├¦am, the considerations of British envoys to Versailles were:
# Securing Britain's link to India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
# Avoiding friction with France
# The long-standing policy of supporting the Ottoman Empire was no longer sensible
# An Eastern Mediterranean ally had to fill the security vacuum the Ottoman Empire left to contain a resurgent Russian threat
A strong Greece, Armenia, and fortified Palestine were all reflections of this sentiment.
Dominion representation
 The dominion governments were not originally given separate invitations to the conference and had been expected to send representatives as part of the British delegation.
Convinced that Canada had become a nation on the battlefields of Europe, Prime Minister Sir Robert Borden demanded that it have a separate seat at the conference. That was initially opposed not only by Britain but also by the United States, which saw any Dominion delegation as an extra British vote. Borden responded by pointing out that since Canada had lost nearly 60,000 men, a far larger proportion of its men than the 50,000 American men lost, it had at least the right to the representation of a "minor" power. Lloyd George eventually relented and persuaded the reluctant Americans to accept the presence of delegations from Canada,
The dominion governments were not originally given separate invitations to the conference and had been expected to send representatives as part of the British delegation.
Convinced that Canada had become a nation on the battlefields of Europe, Prime Minister Sir Robert Borden demanded that it have a separate seat at the conference. That was initially opposed not only by Britain but also by the United States, which saw any Dominion delegation as an extra British vote. Borden responded by pointing out that since Canada had lost nearly 60,000 men, a far larger proportion of its men than the 50,000 American men lost, it had at least the right to the representation of a "minor" power. Lloyd George eventually relented and persuaded the reluctant Americans to accept the presence of delegations from Canada, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, Australia, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
, New Zealand, and South Africa, and that those countries receive their seats in the League of Nations.
Canada, despite its huge losses in the war, did not ask for either reparations or mandates.
The Australian delegation, led by Australian Prime Minister Billy Hughes
William Morris Hughes (25 September 1862 ŌĆō 28 October 1952) was an Australian politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Australia from 1915 to 1923. He led the nation during World War I, and his influence on national politics s ...
fought greatly for its demands: reparations, the annexation of German New Guinea
German New Guinea () consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups, and was part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , became a German protectorate in 188 ...
, and the rejection of the Racial Equality Proposal. He said that he had no objection to the proposal if it was stated in unambiguous terms that it did not confer any right to enter Australia. He was concerned by the increasing power of Japan. Within months of the declaration of war in 1914, Japan, Australia, and New Zealand had seized all of Germany's possessions in the Far East and the Pacific Ocean. The British had given their blessing for Japan to occupy German possessions, but Hughes was alarmed by that policy.
French approach
 French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau controlled his delegation, and his chief goal was to weaken Germany militarily, strategically, and economically. Having personally witnessed two German attacks on French soil in the last 40 years, he was adamant for Germany not to be permitted to attack France again. Particularly, Clemenceau sought an American and British joint guarantee of French security in the event of another German attack.
Clemenceau also expressed skepticism and frustration with Wilson's
French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau controlled his delegation, and his chief goal was to weaken Germany militarily, strategically, and economically. Having personally witnessed two German attacks on French soil in the last 40 years, he was adamant for Germany not to be permitted to attack France again. Particularly, Clemenceau sought an American and British joint guarantee of French security in the event of another German attack.
Clemenceau also expressed skepticism and frustration with Wilson's Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms to the United States Congress ...
and complained: "Mr. Wilson bores me with his fourteen points. Why, God Almighty has only ten!" Wilson gained some favour by signing a mutual defense treaty with France, but he did not present it to his country's government for ratification and so it never took effect.
Another possible French policy was to seek a rapprochement with Germany. In May 1919 the diplomat Ren├® Massigli was sent on several secret missions to Berlin. During his visits, he offered, on behalf of his government, to revise the territorial and economic clauses of the upcoming peace treaty. Massigli spoke of the desirability of "practical, verbal discussions" between French and German officials that would lead to a "Franco-German collaboration."
Massigli told the Germans that the French thought of the "Anglo-Saxon powers" (the United States and the British Empire) as the major threat to France in the post-war world. He argued that both France and Germany had a joint interest in opposing "Anglo-Saxon domination" of the world, and he warned that the "deepening of opposition" between the French and the Germans "would lead to the ruin of both countries, to the advantage of the Anglo-Saxon powers."Trachtenberg (1979), p. 43.
The Germans rejected Massigli's offers because they believed that the intention was to trick them into accepting the Treaty of Versailles unchanged; also, the German Foreign Minister, Count Ulrich von Brockdorff-Rantzau, thought that the United States was more likely to reduce the severity of the penalties than France was. (Lloyd George was the one who eventually pushed for better terms for Germany.)
Italian approach
 In 1914, Italy remained neutral despite the Triple Alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary. In 1915, it joined the Allies to gain the territories promised by the
In 1914, Italy remained neutral despite the Triple Alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary. In 1915, it joined the Allies to gain the territories promised by the Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It was built upon th ...
in the secret Treaty of London: Trentino
Trentino (), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento (; ; ), is an Autonomous province#Italy, autonomous province of Italy in the Northern Italy, country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the Regions of Italy, region of Tren ...
, the Tyrol
Tyrol ( ; historically the Tyrole; ; ) is a historical region in the Alps of Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary, f ...
as far as Brenner, Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
, Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
, most of the Dalmatian Coast (except Fiume
Rijeka (;
Fiume ( łfju╦Éme in Italian and in Fiuman Venetian) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and in 2021 had a po ...
), Valona, a protectorate over Albania, Antalya
Antalya is the fifth-most populous city in Turkey and the capital of Antalya Province. Recognized as the "capital of tourism" in Turkey and a pivotal part of the Turkish Riviera, Antalya sits on Anatolia's southwest coast, flanked by the Tau ...
(in Turkey), and possibly colonies in Africa.
Italian Prime Minister Vittorio Emanuele Orlando tried to obtain full implementation of the Treaty of London, as agreed by France and Britain before the war. He had popular support because of the loss of 700,000 soldiers and a budget deficit of 12,000,000,000 Italian lire during the war made both the government and people feel entitled to all of those territories and even others not mentioned in the Treaty of London, particularly Fiume, which many Italians believed should be annexed to Italy because of the city's Italian population.
Orlando, unable to speak English, conducted negotiations jointly with his Foreign Minister Sidney Sonnino, a Protestant of British origins who spoke the language. Together, they worked primarily to secure the partition of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
. At the conference, Italy gained Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
, Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
, Trentino
Trentino (), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento (; ; ), is an Autonomous province#Italy, autonomous province of Italy in the Northern Italy, country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the Regions of Italy, region of Tren ...
, and South Tyrol
South Tyrol ( , ; ; ), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano ŌĆō South Tyrol, is an autonomous administrative division, autonomous provinces of Italy, province in northern Italy. Together with Trentino, South Tyrol forms the autonomo ...
. Most of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
was given to the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. Fiume remained disputed territory, causing a nationalist outrage.H. James Burgwyn, ''Legend of the Mutilated Victory: Italy, the Great War and the Paris Peace Conference, 1915ŌĆō1919'' (1993)
Orlando obtained other results, such as the permanent membership of Italy in the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919ŌĆō1920), Paris Peace ...
and the promise by the Allies to transfer British Jubaland
Jubaland (; ; ), or the Juba Valley (), is a States and regions of Somalia, Federal Member State in southern Somalia. Its eastern border lies no more than east of the Jubba River, stretching from Dolow to the Indian Ocean, while its western si ...
and the French Aozou strip to Italian colonies. Protectorates over Albania and Antalya were also recognized, but nationalists considered the war to be a mutilated victory
Mutilated victory () is a term coined by Gabriele D'Annunzio at the end of World War I, used by a part of Italian nationalists to denounce the partial infringement (and request the full application) of the 1915 pact of London concerning territori ...
, and Orlando was ultimately forced to abandon the conference and to resign. Francesco Saverio Nitti
Francesco Saverio Vincenzo de Paola Nitti (; 19 July 1868 ŌĆō 20 February 1953) was an Italian economist and statesman. A member of the Italian Radical Party, Nitti served as Prime Minister of Italy between 1919 and 1920. An opponent of the ...
took his place and signed the treaties.
There was a general disappointment in Italy, which the nationalists and fascists used to build the idea that Italy was betrayed by the Allies and refused what had been promised. That was a cause for the general rise of Italian fascism. Orlando refused to see the war as a mutilated victory and replied to nationalists calling for a greater expansion, "Italy today is a great state... on par with the great historic and contemporary states. This is, for me, our main and principal expansion."
Japanese approach

 Japan sent a large delegation, headed by the former Prime Minister, Marquis
Japan sent a large delegation, headed by the former Prime Minister, Marquis Saionji Kinmochi
Kazoku, Prince was a Japanese politician who served as Prime Minister of Japan, prime minister of Japan from 1906 to 1908, and from 1911 to 1912. As the last surviving member of the ''genr┼Ź'', the group of senior statesmen who had directed pol ...
. It was originally one of the "big five" but relinquished that role because of its slight interest in European affairs. Instead, it focused on two demands: the inclusion of its Racial Equality Proposal in the League's Covenant and Japanese territorial claims with respect to former German colonies: Shantung (including Kiaochow) and the Pacific islands north of the Equator, the Marshall Islands, Micronesia, the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands ( ; ), also simply the Marianas, are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st pa ...
, and the Carolines.Macmillan, ch. 23
The former Foreign Minister Baron Makino Nobuaki
Count , was a Japanese politician and imperial court official. As Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal of Japan, Makino served as Emperor Hirohito's chief counselor on the monarch's position in Japanese society and policymaking.
After victory in W ...
was ''de facto'' chief. Saionji's role was symbolic and limited because of his history of ill-health. The Japanese delegation became unhappy after it had received only half of the rights of Germany, and it then walked out of the conference.
Racial equality proposal
During the negotiations, the leader of the Japanese delegation, Saionji Kinmochi, proposed the inclusion of a " racial equality clause" in theCovenant of the League of Nations
The Covenant of the League of Nations was the charter of the League of Nations. It was signed on 28 June 1919 as Part I of the Treaty of Versailles, and became effective together with the rest of the Treaty on 10 January 1920.
Creation
Early ...
on 13 February as an amendment to Article 21:
The equality of nations being a basic principle of the League of Nations, the High Contracting Parties agree to accord as soon as possible to all alien nationals of states, members of the League, equal and just treatment in every respect making no distinction, either in law or in fact, on account of their race or nationality.The clause quickly proved problematic to both the American and British delegations. Though the proposal itself was compatible with Britain's stance of nominal equality for all
British subject
The term "British subject" has several different meanings depending on the time period. Before 1949, it referred to almost all subjects of the British Empire (including the United Kingdom, Dominions, and colonies, but excluding protectorates ...
s as a principle for maintaining imperial unity, there were significant deviations in the stated interests of its dominion
A dominion was any of several largely self-governance, self-governing countries of the British Empire, once known collectively as the ''British Commonwealth of Nations''. Progressing from colonies, their degrees of self-governing colony, colon ...
s, notably Australia and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
. Though both dominions could not vote on the decision individually, they were strongly opposed to the clause and pressured Britain to do likewise. Ultimately, the British delegation succumbed to imperial pressure and abstained from voting for the clause.
Meanwhile, though Wilson was indifferent to the clause, there was fierce resistance to it from the American public, and he ruled as Conference chairman that a unanimous vote was required for the Japanese proposal to pass. Ultimately, on the day of the vote, only 11 of the 17 delegates voted in favor of the proposal. The defeat of the proposal influenced Japan's turn from co-operation with the Western world, into more nationalist and militarist policies and approaches.
Territorial claims
The Japanese claim to Shantung faced strong challenges from the Chinese patriotic student group. In 1914, at the outset of the war, Japan seized the territory that had been granted to Germany in 1897 and seized the German islands in the Pacific north of the equator. In 1917, Japan made secret agreements with Britain, France, and Italy to guarantee their annexation of these territories. With Britain, there was an agreement to support British annexation of thePacific Islands
The Pacific islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean. They are further categorized into three major island groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Depending on the context, the term ''Pacific Islands'' may refer to one of several ...
south of the Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
.Fifield, Russell. "Japanese Policy toward the Shantung Question at the Paris Peace Conference", ''Journal of Modern History'' (1951) 23:3 pp. 265ŌĆō272. , reprint primary Japanese sources.
Despite a generally pro-Chinese view by the American delegation, Article 156 of the Treaty of Versailles transferred German concessions in the Jiaozhou Bay
Jiaozhou Bay (; ; ) is a bay located in the prefecture-level city of Qingdao (Tsingtau), Shandong Province, China.
The bay has historically been romanized as Kiaochow, Kiauchau or Kiao-Chau in English and Kiautschou in German.
Geography ...
, China, to Japan rather than returning sovereign authority to China. The leader of the Chinese delegation, Lu Zhengxiang, demanded a reservation be inserted, before he would sign the treaty. After the reservation was denied, the treaty was signed by all the delegations except that of China. Chinese outrage over that provision led to demonstrations known as the May Fourth Movement
The May Fourth Movement was a Chinese cultural and anti-imperialist political movement which grew out of student protests in Beijing on May 4, 1919. Students gathered in front of Tiananmen to protest the Chinese government's weak response ...
. The Pacific Islands north of the equator became a class C mandate, administered by Japan.
American approach
 Until Wilson's arrival in Europe in December 1918, no sitting American president had ever visited the continent. Wilson's 1918
Until Wilson's arrival in Europe in December 1918, no sitting American president had ever visited the continent. Wilson's 1918 Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms to the United States Congress ...
had helped win many hearts and minds as the war ended, not only in America but all over Europe, including Germany, as well as its allies in and the former subjects of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
.
Wilson's diplomacy and his Fourteen Points had essentially established the conditions for the armistices that had brought an end to World War I. Wilson felt it to be his duty and obligation to the people of the world to be a prominent figure at the peace negotiations. High hopes and expectations were placed on him to deliver what he had promised for the postwar era. In doing so, Wilson ultimately began to lead the foreign policy of the United States
The officially stated goals of the foreign policy of the United States of America, including all the bureaus and offices in the United States Department of State, as mentioned in the ''Foreign Policy Agenda'' of the Department of State, are ...
towards interventionism, a move that has been strongly resisted in some United States circles ever since.
Once Wilson arrived, however, he found "rivalries, and conflicting claims previously submerged." He worked mostly at trying to influence both the French, led by Georges Clemenceau, and the British, led by David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor (17 January 1863 ŌĆō 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. A Liberal Party (United Kingdom), Liberal Party politician from Wales, he was known for leadi ...
, in their treatment of Germany and its allies in Europe and the former Ottoman Empire in the Middle East. Wilson's attempts to gain acceptance of his Fourteen Points ultimately failed; France and Britain each refused to adopt specific points as well as certain core principles.
Several of the Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms to the United States Congress ...
conflicted with the desires of European powers. The United States did not consider it fair or warranted that Article 231 of the Treaty of Versailles declared Germany solely responsible for the war. (The United States did not sign peace treaties with the Central Powers until 1921 under President Warren Harding, when separate documents were signed with Germany, Austria, and Hungary respectively.)
In the Middle East, negotiations were complicated by competing aims and claims, and the new mandate system. The United States expressed a hope to establish a more liberal and diplomatic world as stated in the Fourteen Points, in which democracy, sovereignty, liberty and self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
would be respected. France and Britain, on the other hand, already controlled empires through which they wielded power over their subjects around the world, and aspired to maintain and expand their colonial power rather than relinquish it. Various people, both in Washington and the Middle East, sought American mandates, as they identified the United States as a neutral and non-colonial power. American mandates were considered for Syria, Armenia, and the Ottoman Empire.
In light of the previously secret SykesŌĆōPicot Agreement
The SykesŌĆōPicot Agreement () was a 1916 secret treaty between the United Kingdom and France, with assent from Russia and Italy, to define their mutually agreed spheres of influence and control in an eventual partition of the Ottoman Empire.
T ...
and following the adoption of the mandate system on the Arab provinces of the former Ottoman Empire, the conference heard statements from competing Zionists and Arabs. Wilson then recommended an international commission of inquiry to ascertain the wishes of the local inhabitants. The idea, first accepted by Great Britain and France, was later rejected, but became the purely-American KingŌĆōCrane Commission which toured all Syria and Palestine during the summer of 1919 taking statements and sampling opinion. Its report, presented to Wilson, was kept secret from the public until ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' broke the story in December 1922. A pro-Zionist joint resolution on Palestine was passed by the United States Congress in September 1922.
Though Ottoman intelligentsia were hopeful of the application of Wilsonian idealism in the post-war middle east (especially from point 12 of the Fourteen Points), on 20 March 1919, President Wilson announced his support to detach Istanbul from the Ottoman Empire.
France and Britain tried to appease Wilson by consenting to the establishment of his League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919ŌĆō1920), Paris Peace ...
. However, because isolationist sentiment in the United States was strong, and because some of the articles in the League Charter conflicted with the US Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally including seven articles, the Constitut ...
, the United States never ratified the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
or joined the League that Wilson had helped to create to further peace by diplomacy, rather than war, and the conditions that can breed peace.
Greek approach
Greek Prime MinisterEleftherios Venizelos
Eleftherios Kyriakou Venizelos (, ; ŌĆō 18 March 1936) was a Cretan State, Cretan Greeks, Greek statesman and prominent leader of the Greek national liberation movement. As the leader of the Liberal Party (Greece), Liberal Party, Venizelos ser ...
took part in the conference as Greece's chief representative. Wilson was said to have placed Venizelos first for personal ability among all delegates in Paris.
Venizelos proposed Greek expansion in Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
and Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, which had been part of the defeated Kingdom of Bulgaria
The Tsardom of Bulgaria (), also known as the Third Bulgarian Tsardom (), usually known in English as the Kingdom of Bulgaria, or simply Bulgaria, was a constitutional monarchy in Southeastern Europe, which was established on , when the Bulgaria ...
and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
; Northern Epirus
Northern Epirus (, ; ) is a term used for specific parts of southern Albania which were first claimed by the Kingdom of Greece in the Balkan Wars and later were associated with the Greek minority in Albania and Greece-Albania diplomatic relation ...
, Imvros; and Tenedos
Tenedos (, ''Tenedhos''; ), or Bozcaada in Turkish language, Turkish, is an island of Turkey in the northeastern part of the Aegean Sea. Administratively, the island constitutes the Bozcaada, ├ćanakkale, Bozcaada district of ├ćanakkale Provinc ...
for the realization of the '' Megali Idea''. He also reached the Venizelos-Tittoni agreement with the Italians on the cession of the Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; , ''Dodek├Īnisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger and 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. This island group generally define ...
(apart from Rhodes) to Greece. For the Pontic Greeks
The Pontic Greeks (; or ; , , ), also Pontian Greeks or simply Pontians, are an ethnically Greek group indigenous to the region of Pontus, in northeastern Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). They share a common Pontic Greek culture that is di ...
, he proposed a common Pontic-Armenian state.
As a liberal politician, Venizelos was a strong supporter of the Fourteen Points and the League of Nations.
Chinese approach
The Chinese delegation was led by Lu Zhengxiang, who was accompanied by Wellington Koo and Cao Rulin. Koo demanded Germany's concessions onShandong
Shandong is a coastal Provinces of China, province in East China. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural ...
be returned to China. He also called for an end to imperialist institutions such as extraterritoriality
In international law, extraterritoriality or exterritoriality is the state of being exempted from the jurisdiction of local law, usually as the result of diplomatic negotiations.
Historically, this primarily applied to individuals, as jurisdict ...
, legation
A legation was a diplomatic representative office of lower rank than an embassy. Where an embassy was headed by an ambassador, a legation was headed by a minister. Ambassadors outranked ministers and had precedence at official events. Legation ...
guards, and foreign leaseholds. Despite American support and the ostensible spirit of self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
, the Western powers refused his claims but instead transferred the German concessions to Japan. That sparked widespread student protests in China on 4 May, later known as the May Fourth Movement
The May Fourth Movement was a Chinese cultural and anti-imperialist political movement which grew out of student protests in Beijing on May 4, 1919. Students gathered in front of Tiananmen to protest the Chinese government's weak response ...
, which eventually pressured the government into refusing to sign the Treaty of Versailles. Thus, the Chinese delegation at the conference was the only one not to sign the treaty at the signing ceremony.
Other nations' approach
All-Russian Government (Whites)
While Russia was formally excluded from the Conference although it had fought against the Central Powers for three years. However the Russian Provincial Council (chaired by Prince Lvov), the successor to theRussian Constituent Assembly
The All Russian Constituent Assembly () was a constituent assembly convened in Russia after the February Revolution of 1917. It met for 13 hours, from 4 p.m. to 5 a.m., , whereupon it was dissolved by the Bolshevik-led All-Russian Central Ex ...
and the political arm of the Russian White movement
The White movement,. The old spelling was retained by the Whites to differentiate from the Reds. also known as the Whites, was one of the main factions of the Russian Civil War of 1917ŌĆō1922. It was led mainly by the Right-wing politics, right- ...
attended the conference and was represented by the former tsarist minister Sergey Sazonov,Erik Goldstein ''The First World War Peace Settlements, 1919ŌĆō1925'' p. 49 Routledge (2013) who, if the tsar had not been overthrown, would most likely have attended the conference anyway. The Council maintained the position of an indivisible Russia, but some were prepared to negotiate over the loss of Poland and Finland. The Council suggested all matters relating to territorial claims or demands for autonomy within the former Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
be referred to a new All-Russian Constituent Assembly.
Baltic states
Delegations from the Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, led respectively by Jaan Poska,J─ünis ─īakste
J─ünis Kristaps ─īakste (; 14 September 1859 ŌĆō 14 March 1927) was a Latvian politician and lawyer who served as the first head of an independent Latvian state as the Chairman of the Tautas Padome, People's Council (1918ŌĆō1920), the Speaker o ...
and Augustinas Voldemaras, also participated in the conference, and successfully achieved international recognition of the independence of Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
, Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
.
Ukraine
 Ukraine had its best opportunity to win recognition and support from foreign powers at the conference. At a meeting of the Big Five on 16 January, Lloyd George called Ukrainian leader Symon Petliura an adventurer and dismissed Ukraine as an anti-Bolshevik stronghold. Sir Eyre Crowe, British Undersecretary of State for Foreign Affairs, spoke against a union of East Galicia and Poland. The British cabinet never decided whether to support a united or dismembered Russia. The United States was sympathetic to a strong, united Russia, as a counterpoise to Japan, but Britain feared a threat to India. Petliura appointed Count Tyshkevich as his representative to the Vatican, and Pope Benedict XV recognized Ukrainian independence, but Ukraine was effectively ignored.
Ukraine had its best opportunity to win recognition and support from foreign powers at the conference. At a meeting of the Big Five on 16 January, Lloyd George called Ukrainian leader Symon Petliura an adventurer and dismissed Ukraine as an anti-Bolshevik stronghold. Sir Eyre Crowe, British Undersecretary of State for Foreign Affairs, spoke against a union of East Galicia and Poland. The British cabinet never decided whether to support a united or dismembered Russia. The United States was sympathetic to a strong, united Russia, as a counterpoise to Japan, but Britain feared a threat to India. Petliura appointed Count Tyshkevich as his representative to the Vatican, and Pope Benedict XV recognized Ukrainian independence, but Ukraine was effectively ignored.
Belarus
A delegation of theBelarusian Democratic Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic (BNR; , ), also known as the Belarusian Democratic Republic, was a state proclaimed by the Council of the Belarusian Democratic Republic in its Second Constituent Charter on 9 March 1918 during World War I. The ...
, under Prime Minister Anton ┼üuckievi─Ź, also participated in the conference, and attempted to gain international recognition of the independence of Belarus. On the way to the conference, the delegation was received by Czechoslovak President Tom├Ī┼Ī Masaryk
Tom├Ī┼Ī Garrigue Masaryk (7 March 185014 September 1937) was a Czechoslovaks, Czechoslovak statesman, political activist and philosopher who served as the first List of presidents of Czechoslovakia, president of Czechoslovakia from 191 ...
in Prague. During the conference, ┼üuckievi─Ź had meetings with the exiled foreign minister of Admiral Alexander Kolchak
Admiral Alexander Vasilyevich Kolchak (; ŌĆō 7 February 1920) was a Russian navy officer and polar explorer who led the White movement in the Russian Civil War. As he assumed the title of Supreme Ruler of Russia in 1918, Kolchak headed a mili ...
's Russian government, Sergey Sazonov, and Polish Prime Minister Ignacy Jan Paderewski
Ignacy Jan Paderewski (; r 1859ŌĆō 29 June 1941) was a Polish pianist, composer and statesman who was a spokesman for Polish independence. In 1919, he was the nation's Prime Minister of Poland, prime minister and foreign minister durin ...
.
Minority rights
At the insistence of Wilson, the Big Four required Poland to sign a treaty on 28 June 1919 that guaranteedminority rights
Minority rights are the normal individual rights as applied to members of racial, ethnic, class, religious, linguistic or gender and sexual minorities, and also the collective rights accorded to any minority group.
Civil-rights movements oft ...
in the new nation. Poland signed under protest and made little effort to enforce the specified rights for Germans, Jews, Ukrainians, and other minorities. Similar treaties were signed by Czechoslovakia, Romania, Yugoslavia, Greece, Austria, Hungary, and Bulgaria and later by Latvia, Estonia, and Lithuania. Estonia had already given cultural autonomy to minorities in its declaration of independence. Finland and Germany were not asked to sign a minority treaty.
In Poland, the key provisions were to become fundamental laws, which would override any national legal codes or legislation. The new country pledged to assure "full and complete protection of life and liberty to all individuals... without distinction of birth, nationality, language, race, or religion." Freedom of religion was guaranteed to everyone. Most residents were given citizenship, but there was considerable ambiguity on who was covered. The treaty guaranteed basic civil, political, and cultural rights and required all citizens to be equal before the law and enjoy identical rights of citizens and workers. Polish was to be the national language
'' ''
A national language is a language (or language variant, e.g. dialect) that has some connectionŌĆö de facto or de jureŌĆöwith a nation. The term is applied quite differently in various contexts. One or more languages spoken as first languag ...
, but the treaty provided for minority languages
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally (as of 2019) and ...
to be freely used privately, in commerce, in religion, in the press, at public meetings, and before all courts. Minorities were to be permitted to establish and control at their own expense private charities, churches, social institutions, and schools, without interference from the government, which was required to set up German-language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is a ...
public schools in districts that had been German before the war. All education above the primary level was to be conducted exclusively in the national language. Article 12 was the enforcement clause and gave the Council of the League of Nations the responsibility to monitor and enforce the treaties.
Caucasus
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
, and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
and the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus
The Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus (MRNC), also referred to as the United Republics of the North Caucasus, Mountain Republic, or the Republic of the Mountaineers, was a transcontinental state in Eurasia. It encompassed the entiret ...
all sent a delegation to the conference. Their attempts to gain protection from threats posed by the ongoing Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
largely failed since none of the major powers was interested in taking a mandate over the Caucasian territories. After a series of delays, the three South Caucasian countries ultimately gained ''de facto'' recognition from the Supreme Council of the Allied powers but only after all European troops had been withdrawn from the Caucasus, except for a British contingent in Batumi
Batumi (; ka, ßāæßāÉßāŚßāŻßāøßāś ), historically Batum or Batoum, is the List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), second-largest city of Georgia (country), Georgia and the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Adjara, located on the coast ...
. Georgia was recognized ''de facto'' on 12 January 1920, followed by Azerbaijan the same day and Armenia on 19 January 1920. The Allied leaders decided to limit their assistance to the Caucasian republics to the supply of arms, munitions, and food.
The Armenian delegation included Avetis Aharonian
Avetis Aharonian (; 4 January 1866 – 20 March 1948) was an Armenian politician, writer, public figure and revolutionary, also part of the Armenian national movement.
Biography
Aharonian was born in 1866 in Surmali, Erivan Governorate, R ...
, Hamo Ohanjanyan, and Armen Garo
Garegin or Karekin Pastermadjian (), better known by his ''nom de guerre'' Armen Garo or Armen Karo (į▒ųĆš┤š¦šČ į│šĪųĆųģ; 9 February 1872 – 23 March 1923) was an Armenian activist and politician. Armen Karo was a leading member of the Arme ...
. The Azerbaijani mission was headed by Alimardan bey Topchubashov and included Mammad Hasan Hajinski, Akbar agha Sheykhulislamov, Ahmet A─¤ao─¤lu and Mahammad Amin Rasulzade, first president of Azerbaijan Democratic Republic. The Georgian delegation included Nikolay Chkheidze, Irakli Tsereteli, and Zurab Avalishvili.
Korea
After a failed attempt by the Korean National Association to send a three-man delegation to Paris, a delegation of Koreans from China and Hawaii made it there. It included a representative from theKorean Provisional Government
The Korean Provisional Government (KPG), formally the Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea (), was a Korean government-in-exile based in Republic of China (1912ŌĆō1949), China during Korea under Japanese rule, Japanese rule over K ...
in Shanghai, Kim Kyu-sik. They were aided by the Chinese, who were eager for the opportunity to embarrass Japan at the international forum. Several top Chinese leaders at the time, including Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-senUsually known as Sun Zhongshan () in Chinese; also known by Names of Sun Yat-sen, several other names. (; 12 November 186612 March 1925) was a Chinese physician, revolutionary, statesman, and political philosopher who founded the Republ ...
, told US diplomats that the conference should take up the question of Korean independence. However, the Chinese, already locked in a struggle against the Japanese, could do little else for Korea. Other than China, no nation took the Koreans seriously at the conference because it already had the status of a Japanese colony. The failure of Korean nationalists to gain support from the conference ended their hopes of foreign support.
Palestine
After the conference's decision to separate the former Arab provinces from the Ottoman Empire and to apply the new mandate-system to them, theWorld Zionist Organization
The World Zionist Organization (; ''HaHistadrut HaTzionit Ha'Olamit''), or WZO, is a non-governmental organization that promotes Zionism. It was founded as the Zionist Organization (ZO; 1897ŌĆō1960) at the initiative of Theodor Herzl at the F ...
submitted its draft resolutions for consideration by the conference.

 The February 1919 statement included the following main points: recognition of Jewish "title" over the land, a declaration of the borders (significantly larger than in the prior Sykes-Picot agreement), and League of Nations sovereignty under British mandate.Statement of the Zionist Organization regarding Palestine
The February 1919 statement included the following main points: recognition of Jewish "title" over the land, a declaration of the borders (significantly larger than in the prior Sykes-Picot agreement), and League of Nations sovereignty under British mandate.Statement of the Zionist Organization regarding Palestine, 3 February 1919 An offshoot of the conference was convened at San Remo in 1920, leading to the creation of the
Mandate for Palestine
The Mandate for Palestine was a League of Nations mandate for British Empire, British administration of the territories of Mandatory Palestine, Palestine and Emirate of Transjordan, Transjordanwhich had been Ottoman Syria, part of the Ottoman ...
, which was to come into force in 1923.
Assyrians
Up to 300 000Assyrians
Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from ot ...
died during the Sayfo
The Sayfo (, ), also known as the Seyfo or the Assyrian genocide, was the mass murder and deportation of Assyrian people, Assyrian/Syriac Christians in southeastern Anatolia and Persia's Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan province by Ottoman Army ...
in the years before the conference. Several delegations of Assyrians
Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from ot ...
participated to fulfill wishes of a free Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''m─üt A┼Ī┼Īur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
. The delegations came from different parts of the world. Syriac Orthodox
The Syriac Orthodox Church (), also informally known as the Jacobite Church, is an Oriental Orthodox denomination that originates from the Church of Antioch. The church currently has around 4-5 million followers. The church upholds the Mia ...
Bishop of Syria Aphrem Barsoum (b. 1887), later Patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Roman Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and ...
of the church, has often been depicted as a leader of the "Assyro-Chaldean delegation". An Assyrian delegation from the United States was also present, representing the Assyrian National Association in America. A delegation from Constantinople represented the Assyro-Chaldean National Council, formed in 1919 after Syriac-Orthodox, Chaldean Catholics and Syriac Catholics had united and declared their basic political and national unity under the "Assyro-Chaldean" name. There was also one delegation from Caucasia and one from Persia.
Aromanians
During the Peace Conference, a delegation ofAromanians
The Aromanians () are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgari ...
participated to fulfill autonomist wishes for the Aromanian people in the same vein as the Samarina Republic attempt two years earlier, but failed to accomplish any recognition for the self-rule desires of their people.

Women's approach
An unprecedented aspect of the conference was concerted pressure brought to bear on delegates by a committee of women, who sought to establish and entrench women's fundamental social, economic, and political rights, such as that of suffrage, within the peace framework. Although they were denied seats at the Paris Conference, the leadership of Marguerite de Witt-Schlumberger, the president of the French Union for Women's Suffrage, caused an Inter-Allied Women's Conference (IAWC) to be convened, which met from 10 February to 10 April 1919. The IAWC lobbied Wilson and then the other delegates of the Paris Conference to admit women to its committees, and it was successful in achieving a hearing from the conference's Commissions for International Labour Legislation and then the League of Nations Commission. One key and concrete outcome of the IAWC's work was Article 7 of theCovenant of the League of Nations
The Covenant of the League of Nations was the charter of the League of Nations. It was signed on 28 June 1919 as Part I of the Treaty of Versailles, and became effective together with the rest of the Treaty on 10 January 1920.
Creation
Early ...
: "All positions under or in connection with the League, including the Secretariat, shall be open equally to men and women." More generally, the IAWC placed the issue of women's rights at the center of the new world order that was established in Paris.
Pan-African Congress
The firstPan-African Congress
The Pan-African Congress (PAC) is a regular series of meetings which first took place on the back of the Pan-African Conference held in London in 1900.
The Pan-African Congress first gained a reputation as a peacemaker for decolonization in ...
, supported by W.E.B. Du Bois, unsuccessfully petitioned the Paris Conference to turn Germany's colonies over to an international organization instead of to other colonial powers.
Historical assessments
The remaking of the world map at the conferences gave birth to a number of critical conflict-prone contradictions internationally that would become some of the causes of World War II.''First World War'' ŌĆō Willmott, H. P., Dorling Kindersley, 2003, pp. 292ŌĆō307. The British historianEric Hobsbawm
Eric John Ernest Hobsbawm (; 9 June 1917 ŌĆō 1 October 2012) was a British historian of the rise of industrial capitalism, socialism and nationalism. His best-known works include his tetralogy about what he called the "long 19th century" (''Th ...
claimed:
Hobsbawm and other left-wing historians have argued that Wilson's Fourteen Points, particularly the principle of self-determination, were measures that were primarily against the Bolsheviks and designed, by playing the nationalist card, to tame the revolutionary fever that was sweeping across Europe in the wake of the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
and the end of the war:
The right-wing historian John Lewis Gaddis agreed: "When Woodrow Wilson made the principle of self-determination one of his Fourteen Points his intent had been to undercut the appeal of Bolshevism."
That view has a long history and can be summarised by Ray Stannard Baker
Ray Stannard Baker (April 17, 1870 ŌĆō July 12, 1946) (also known by his pen name David Grayson) was an American journalist, historian, biographer, and writer.
Biography
Baker was born in Lansing, Michigan. After graduating from the Michigan ...
's famous remark: "Paris cannot be understood without Moscow.".
The British historian Antony Lentin viewed Lloyd George's role in Paris as a major success:
Cultural references
* British official artistsWilliam Orpen
Major (United Kingdom), Major Sir William Newenham Montague Orpen, (27 November 1878 ŌĆō 29 September 1931) was an Irish artist who mainly worked in London. Orpen was a fine draughtsman and a popular, commercially successful painter of portrai ...
and Augustus John
Augustus Edwin John (4 January 1878 ŌĆō 31 October 1961) was a Welsh painter, draughtsman, and etcher. For a time he was considered the most important artist at work in Britain: Virginia Woolf remarked that by 1908 the era of John Singer Sarg ...
were present at the Conference.
* ''World's End'' (1940), the first novel in Upton Sinclair
Upton Beall Sinclair Jr. (September 20, 1878 ŌĆō November 25, 1968) was an American author, muckraker journalist, and political activist, and the 1934 California gubernatorial election, 1934 Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party ...
's Pulitzer Prize-winning Lanny Budd series, describes the political machinations and consequences of the Paris Peace Conference through much of the book's second half, with Sinclair's narrative including many historically accurate characters and events.
* The first two books of novelist Robert Goddard's ''The Wide World'' trilogy (''The Ways of the World'' and ''The Corners of the Globe'') are centered around the diplomatic machinations which form the background to the conference.
* ''Paris 1919'' (1973), the third studio album by Welsh musician John Cale
John Davies Cale (born 9 March 1942) is a Welsh musician, composer, and record producer who was a founding member of the American rock band the Velvet Underground. Over his six-decade career, Cale has worked in various styles across rock, dr ...
, is named after the Paris Peace Conference, and its title song explores various aspects of early-20th-century culture and history in Western Europe.
* '' A Dangerous Man: Lawrence After Arabia'' (1992) is a British television film starring Ralph Fiennes
Ralph Nathaniel Twisleton-Wykeham-Fiennes (; born 22 December 1962) is an English actor, film producer, and director. He has received List of awards and nominations received by Ralph Fiennes, various accolades, including a British Academy Film ...
as T. E. Lawrence and Alexander Siddig
Siddig el-Fadil (born 21 November 1965) is a British actor and director, known professionally as Alexander Siddig. Siddig is best known for his roles as Dr. Julian Bashir in the television series '' Star Trek: Deep Space Nine'', former terrori ...
as Emir Faisal, depicting their struggles to secure an independent Arab state at the conference.
* "Paris, May 1919" is a 1993 episode of ''The Young Indiana Jones Chronicles
''The Young Indiana Jones Chronicles'' (sometimes referred to as ''Young Indy'') is an American television series that aired on ABC from March 4, 1992, to July 24, 1993. Filming took place in various locations around the world, with "Old Indy" ...
,'' written by Jonathan Hales and directed by David Hare, in which Indiana Jones
''Indiana Jones'' is an American media franchise consisting of five films and a prequel television series, along with games, comics, and tie-in novels, that depicts the adventures of Indiana Jones (character), Dr. Henry Walton "Indiana" Jones, ...
is shown working as a translator with the American delegation at the Paris Peace Conference.
See also
*Commission of Responsibilities
In-Commission or commissioning may refer to:
Business and contracting
* Commission (remuneration), a form of payment to an agent for services rendered
** Commission (art), the purchase or the creation of a piece of art most often on behalf of anot ...
* Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814ŌĆō1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
* Czech Corridor
* Reparation Commission
* The Inquiry
* Minority Treaties
* Congress of Oppressed Nationalities of the Austro-Hungarian Empire
* Heavenly Twins (Sumner and Cunliffe), The Heavenly Twins
* Armenian National Delegation
References
Sources
* * * * *Further reading
* Albrecht-Carrie, Rene. ''Italy at the Paris Peace Conference'' (1938) * Ambrosius, Lloyd E. ''Woodrow Wilson and the American Diplomatic Tradition: The Treaty Fight in Perspective'' (1990) * Andelman, David A. ''A Shattered Peace: Versailles 1919 and the Price We Pay Today'' (2007) popular history that stresses multiple long-term disasters caused by Treaty. * Bailey; Thomas A. ''Wilson and the Peacemakers: Combining Woodrow Wilson and the Lost Peace and Woodrow Wilson and the Great Betrayal'' (1947) * Birdsall, Paul. ''Versailles twenty years after'' (1941) well balanced older account * Boemeke, Manfred F., ''et al.'', eds. ''The Treaty of Versailles: A Reassessment after 75 Years'' (1998). A major collection of important papers by scholars * Bruce, Scot David, ''Woodrow Wilson's Colonial Emissary: Edward M. House and the Origins of the Mandate System, 1917ŌĆō1919'' (University of Nebraska Press, 2013). * Clements, Kendrick, A. ''Woodrow Wilson: World Statesman'' (1999). * Cornelissen, Christoph, and Arndt Weinrich, eds.Writing the Great War ŌĆō The Historiography of World War I from 1918 to the Present
' (2020); full coverage for major countries. * Cooper, John Milton. ''Woodrow Wilson: A Biography'' (2009), scholarly biography; pp 439ŌĆō53
excerpt and text search
* Dillon, Emile Joseph. ''The Inside Story of the Peace Conference'', (1920
online
* Dockrill, Michael, and John Fisher. ''The Paris Peace Conference, 1919: Peace Without Victory?'' (Springer, 2016). * Ferguson, Niall. ''The Pity of War: Explaining World War One'' (1999), economics issues at Paris pp 395ŌĆō432 * Doumanis, Nicholas, ed. ''The Oxford Handbook of European History, 1914ŌĆō1945'' (2016) ch 9. * David Fromkin, Fromkin, David. ''A Peace to End All Peace, The Fall of the Ottoman Empire and the Creation of the Modern Middle East'', Macmillan 1989. * Gelfand, Lawrence Emerson. ''The Inquiry: American Preparations for Peace, 1917ŌĆō1919'' (Yale UP, 1963). * Ginneken, Anique H.M. van. ''Historical Dictionary of the League of Nations'' (2006)\ * Greene, Theodore, ed. ''Wilson at Versailles'' (1949) short excerpts from scholarly studies
online free
* Henderson, W. O. "The Peace Settlement, 1919" ''History'' 26.101 (1941): 60ŌĆō6
online
historiography * Henig, Ruth. ''Versailles and After: 1919ŌĆō1933'' (2nd ed. 1995), 100 pages; brief introduction by scholar * * Keynes, John Maynard, ''The Economic Consequences of the Peace'' (1920) famous criticism by leading economis
full text online
* Dimitri Kitsikis, ''Le r├┤le des experts ├Ā la Conf├®rence de la Paix de 1919'', Ottawa, ├®ditions de l'universit├® d'Ottawa, 1972. * Dimitri Kitsikis, ''Propagande et pressions en politique internationale. La Gr├©ce et ses revendications ├Ā la Conf├®rence de la Paix, 1919ŌĆō1920'', Paris, Presses universitaires de France, 1963. * Knock, Thomas J. ''To End All Wars: Woodrow Wilson and the Quest for a New World Order'' (1995) * Lederer, Ivo J., ed. ''The Versailles SettlementŌĆöWas It Foredoomed to Failure?'' (1960) short excerpts from scholars * Lentin, Antony. ''Guilt at Versailles: Lloyd George and the Pre-history of Appeasement'' (1985) * Lentin, Antony. ''Lloyd George and the Lost Peace: From Versailles to Hitler, 1919ŌĆō1940'' (2004) * * Macalister-Smith, Peter, Schwietzke, Joachim: ''Diplomatic Conferences and Congresses. A Bibliographical Compendium of State Practice 1642 to 1919'', W. Neugebauer, Graz, Feldkirch 2017, . * MacMillan, Margaret. ''Peacemakers: The Paris Peace Conference of 1919 and Its Attempt to End War'' (2001), also published as ''Paris 1919: Six Months That Changed the World'' (2003); influential survey * * * Paxton, Robert O., and Julie Hessler. ''Europe in the Twentieth Century'' (2011) pp 141ŌĆō78 * Marks, Sally. ''The Illusion of Peace: International Relations in Europe 1918ŌĆō1933'' (2nd ed. 2003) * Marks, Sally. "Mistakes and Myths: The Allies, Germany, and the Versailles Treaty, 1918ŌĆō1921." ''Journal of Modern History'' 85.3 (2013): 632ŌĆō659
online
* Mayer, Arno J., ''Politics and Diplomacy of Peacemaking: Containment and Counter-revolution at Versailles, 1918ŌĆō1919'' (1967), leftist * Newton, Douglas. ''British Policy and the Weimar Republic, 1918ŌĆō1919'' (1997). 484 pgs. * * Roberts, Priscilla. "Wilson, Europe's Colonial Empires, and the Issue of Imperialism", in Ross A. Kennedy, ed., ''A Companion to Woodrow Wilson'' (2013) pp: 492ŌĆō517. * Schwabe, Klaus. ''Woodrow Wilson, Revolutionary Germany, and Peacemaking, 1918ŌĆō1919: Missionary Diplomacy and the Realities of Power'' (1985) * Sharp, Alan. ''The Versailles Settlement: Peacemaking after the First World War, 1919ŌĆō1923'' (2nd ed. 2008) * * Naoko Shimazu (1998), ''Japan, Race and Equality'', Routledge, * Steiner, Zara. ''The Lights that Failed: European International History 1919ŌĆō1933'' (Oxford History of Modern Europe) (2007), pp 15ŌĆō79; major scholarly work * * Walworth, Arthur. ''Wilson and His Peacemakers: American Diplomacy at the Paris Peace Conference, 1919'' (1986) 618pp * ; 904pp; full scale scholarly biography; winner of Pulitzer Prize
online free; 2nd ed. 1965
* Watson, David Robin. ''George Clemenceau: A Political Biography'' (1976) 463 pgs. * Xu, Guoqi. ''Asia and the Great War ŌĆō A Shared History'' (Oxford UP, 2016
online
External links
Seating Plan of the Paris Peace Conference ŌĆō UK Parliament Living Heritage
Frances Stevenson ŌĆō Paris Peace Conference Diary ŌĆō UK Parliament Living Heritage
Frances Stevenson ŌĆō Paris Peace Conference ID Card ŌĆō UK Parliament Living Heritage
* Sharp, Alan
The Paris Peace Conference and its Consequences
in
1914ŌĆō1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War
Excerpts from the NFB documentary ''Paris 1919''
Sampling of maps
used by the American delegates held by th
American Geographical Society Library
UW Milwaukee {{DEFAULTSORT:Paris Peace Conference (1919-1920) Paris Peace Conference (1919ŌĆō1920), 1919 in international relations 1920 in international relations 1919 conferences 1920 conferences Georges Clemenceau Presidency of Woodrow Wilson Conferences in Paris, Peace 1919 in Paris 1920 in Paris 20th-century diplomatic conferences Diplomatic conferences in France David Lloyd George Eleftherios Venizelos