Pachycormiformes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pachycormiformes is an extinct order of marine
 Pachycormiformes are united by "a compound bone (rostrodermethmoid) forming the anterodorsal border of the mouth; a reduced
Pachycormiformes are united by "a compound bone (rostrodermethmoid) forming the anterodorsal border of the mouth; a reduced
ray-finned fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species.
The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or h ...
known from the Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (geology), Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic series (stratigraphy), Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic-J ...
to the end of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
. It only includes a single family, Pachycormidae. They were characterized by having serrated pectoral fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as se ...
s (though more recent studies demonstrated that fin shape diversity in this group was high), reduced pelvic fins and a bony rostrum
Rostrum may refer to:
* Any kind of a platform for a speaker:
**dais
**pulpit
* Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects
* Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ships
* Ros ...
. Their exact relations with other fish are unclear, but they are generally considered to be teleosteomorphs, more closely related to teleosts
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant species of fish. Teleo ...
than to Holostei
Holostei is a group of ray-finned bony fish. It is divided into two major clades, the Halecomorphi, represented by a single living species, the bowfin ('' Amia calva''), as well as the Ginglymodi, the sole living representatives being the gars ...
. Pachycormiformes are morphologically diverse, containing both tuna
A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna (max length: ...
and swordfish
Swordfish (''Xiphias gladius''), also known as broadbills in some countries, are large, highly migratory predatory fish characterized by a long, flat, pointed bill. They are a popular sport fish of the billfish category, though elusive. Swordf ...
-like carnivorous forms, as well as edentulous
Toothlessness, or edentulism, is the condition of having no teeth. In organisms that naturally have teeth, it is the result of tooth loss.
Organisms that never possessed teeth can also be described as edentulous. Examples are the members of the ...
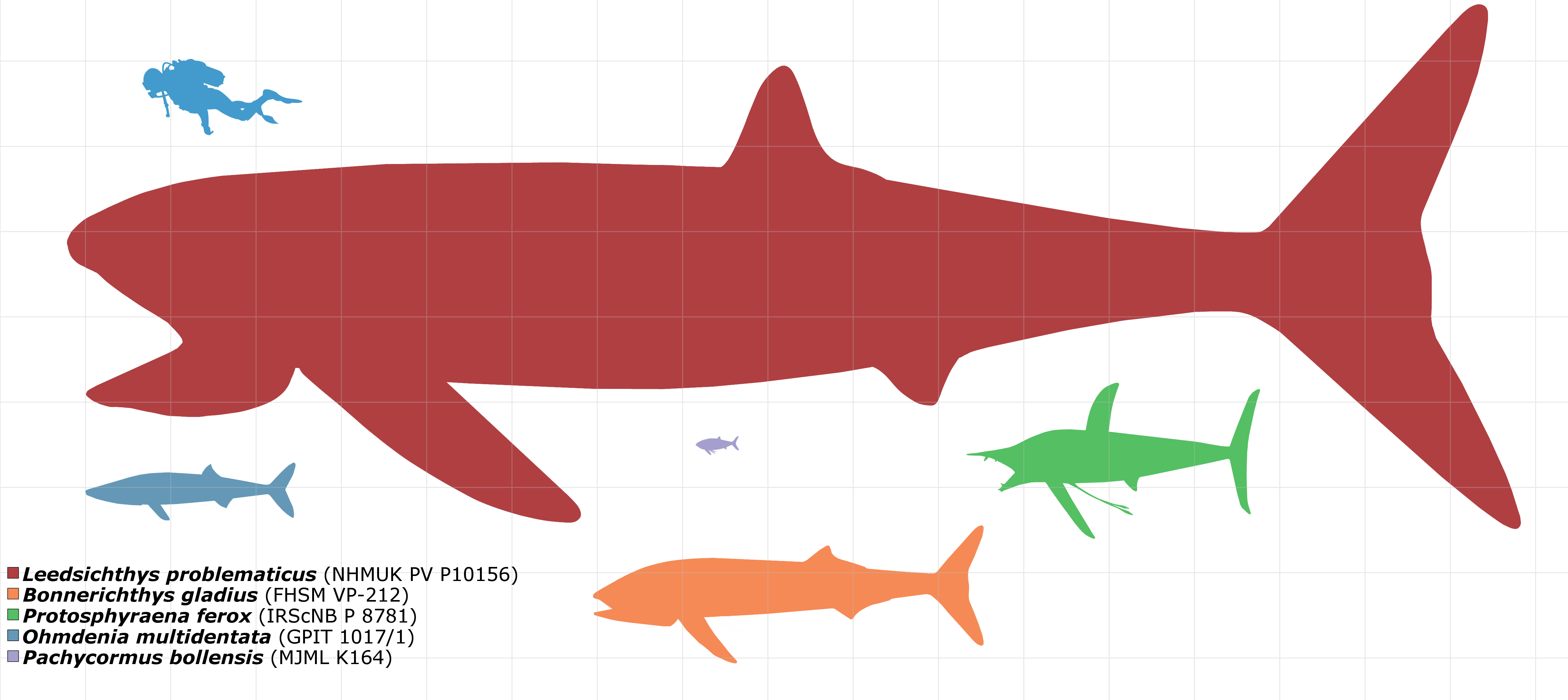
suspension-feeding forms, with the latter including the largest ray finned fish known to have existed, ''Leedsichthys
''Leedsichthys'' is an extinct genus of pachycormid fish that lived in the oceans of the Middle to Late Jurassic.Liston, JJ (2004). An overview of the pachycormiform ''Leedsichthys''. In: Arratia G and Tintori A (eds) Mesozoic Fishes 3 - Syste ...
,'' with an estimated maximum length of 16 metres.
Synapomorphies
 Pachycormiformes are united by "a compound bone (rostrodermethmoid) forming the anterodorsal border of the mouth; a reduced
Pachycormiformes are united by "a compound bone (rostrodermethmoid) forming the anterodorsal border of the mouth; a reduced coronoid process of the mandible
In human anatomy, the mandible's coronoid process (from Greek ''korōnē'', denoting something hooked) is a thin, triangular eminence, which is flattened from side to side and varies in shape and size. Its anterior border is convex and is continuou ...
; absence of supraorbitals associated with a dermosphenotic defining the dorsal margin of the orbit; two large, plate-like suborbital bones posterior to the infraorbitals; long, slender pectoral fins
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as see ...
; asymmetrical branching of pectoral fin lepidotrichia
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as see ...
; considerable overlap of the hypurals by caudal fin rays (hypurostegy); and the presence of distinctive uroneural-like ossifications of the caudal fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as se ...
endoskeleton"
Relationships
Pachycormiformes are generally interpreted as members ofTeleosteomorpha
Neopterygii (from Greek νέος ''neos'' 'new' and πτέρυξ ''pteryx'' 'fin') is a subclass of ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii). Neopterygii includes the Holostei and the Teleostei, of which the latter comprise the vast majority of extant ...
, the group that includes all fish more closely related to modern teleosts
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant species of fish. Teleo ...
than to Holostei
Holostei is a group of ray-finned bony fish. It is divided into two major clades, the Halecomorphi, represented by a single living species, the bowfin ('' Amia calva''), as well as the Ginglymodi, the sole living representatives being the gars ...
(the group containing bowfin
The bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a bony fish, native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being the sole surviving species of the Halecomorp ...
and gars), often they have been considered to be the sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
of the Aspidorhynchiformes.
Gallery
Taxonomy
Taxonomy according to Cooper ''et al.'' (2022): * ''Euthynotus
''Euthynotus'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the early Toarcian stage of the Early Jurassic epoch. It is generally considered the basalmost pachycormiform.
Species
''Euthynotus'' has two species classified withi ...
'' Wagner, 1860
* '' Haasichthys'' Delsate, 1999
* '' Notodectes'' Dolgopol de Saez, 1949
* ''Pseudoasthenocormus
''Pseudoasthenocormus'' is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Pachycormidae. It contains one species, ''P. retrodorsalis''. It lived during the upper Jurassic (Kimmeridgian–Tithonian, about 152–148 million years ago) ...
''
* '' Sauropsis'' Agassiz, 1843
* Hypsocorminae Vetter, 1881
** '' Australopachycormus'' Kear, 2007
** ''Hypsocormus
''Hypsocormus'' (from el, ῠ̔́ψος , 'height' and el, κορμός 'timber log') is an extinct genus of pachycormid fish from the Middle to Late Jurassic of Europe. Fossils have been found in Germany, France and the UK.
The type speci ...
'' Wagner, 1860
** '' Kaykay'' Gouiric-Cavalli & Arratia, 2022
** ''Orthocormus
''Orthocormus'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric pachycormiform bony fish. It is known from three species found in Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) aged plattenkalk deposits in Bavaria, Germany. The species "'' Hypsocormus" tenuirostris'' Woodwar ...
'' Weitzel, 1930
** ''Protosphyraena
''Protosphyraena'' is a fossil genus of swordfish-like marine fish, that thrived worldwide during the Upper Cretaceous Period (Coniacian-Maastrichtian). Though fossil remains of this taxon have been found in both Europe and Asia, it is perhaps ...
'' Leidy, 1857
** '' Simocormus'' Maxwell ''et al.'', 2020
* Asthenocorminae Cooper ''et al.'', 2022
** '' Germanostomus'' Cooper ''et al.'', 2022
** ''Ohmdenia
''Ohmdenia'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived from the Toarcian stage of the Early Jurassic epoch.
''Ohmdenia'' was first described in 1953 by B. Hauff, based on a fossil found in the well-known Posidonia Shale in Holzmad ...
'' Hauff, 1953
** '' Pachycormus''? Agassiz, 1833
** '' Saurostomus'' Agassiz, 1843
** Suspension-feeding clade
*** ''Asthenocormus
''Asthenocormus'' is an extinct genus of pachycormiform ray-finned fish. A member of the edentulous suspension feeding clade within the Pachycormiformes, fossils have been found in the Upper Jurassic plattenkalks of Bavaria, Germany.'
See ...
'' Woodward, 1895
*** ''Bonnerichthys
''Bonnerichthys'' is a genus of fossil fishes within the family Pachycormidae that lived during the Late Cretaceous Period Fossil remains of this taxon were first described from the Smoky Hill Member of the Niobrara Chalk Formation of Kansas ( ...
'' Friedman ''et al.'', 2010
*** ''Leedsichthys
''Leedsichthys'' is an extinct genus of pachycormid fish that lived in the oceans of the Middle to Late Jurassic.Liston, JJ (2004). An overview of the pachycormiform ''Leedsichthys''. In: Arratia G and Tintori A (eds) Mesozoic Fishes 3 - Syste ...
'' Woodward, 1889
*** '' Martillichthys'' Liston, 2008
*** ''Rhinconichthys
''Rhinconichthys'' is an extinct genus of bony fish which existed during the upper Cretaceous period.
Along with its close cousins the great-white-shark-sized or larger ''Bonnerichthys'' and the immense ''Leedsichthys'', ''Rhinconichthys'' for ...
'' Friedman ''et al.'', 2010
Cladistics according to Friedman ''et al.'' (2010).
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q1227671 Late Triassic first appearances Maastrichtian extinctions Prehistoric ray-finned fish orders