PC Speaker on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A PC speaker is a

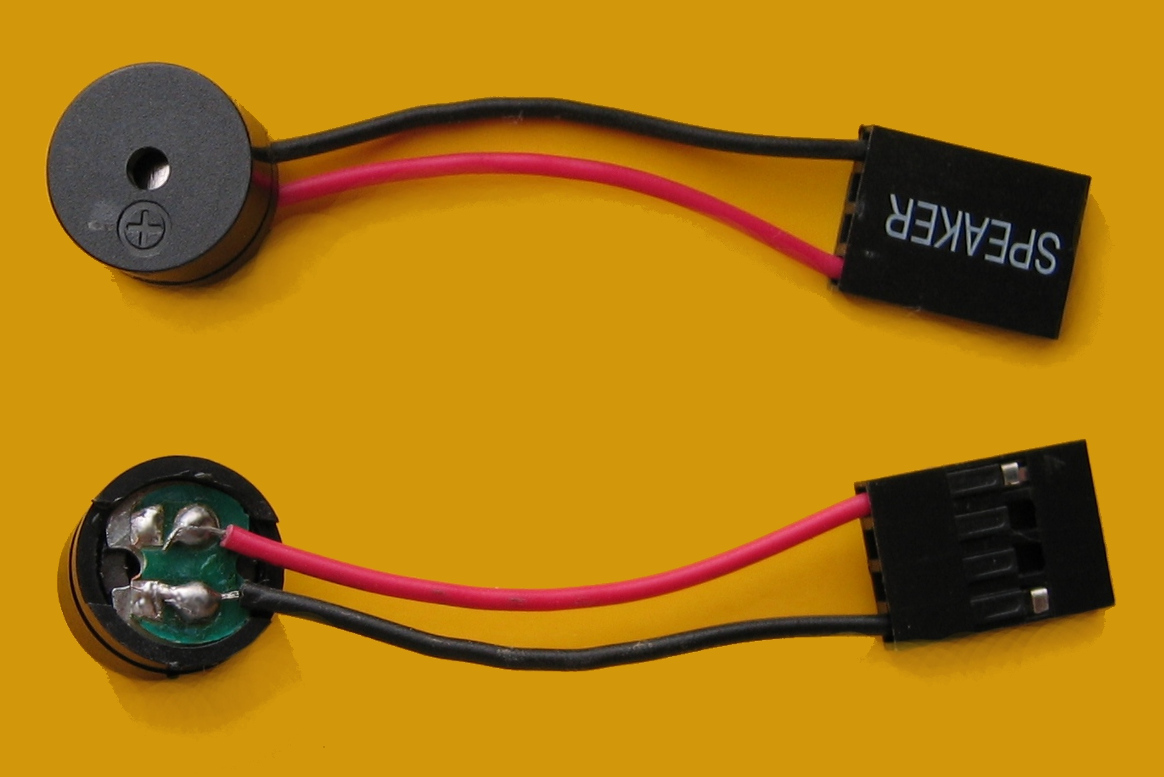 In some applications, the PC speaker is affixed directly to the computer's motherboard; in others, including the first IBM Personal Computer, the speaker is attached by wire to a connector on the motherboard. Some PC cases come with a PC speaker preinstalled. A wired PC speaker connector may have a two-, three-, or four-pin configuration, and either two or three wires. The female connector of the speaker connects to
In some applications, the PC speaker is affixed directly to the computer's motherboard; in others, including the first IBM Personal Computer, the speaker is attached by wire to a connector on the motherboard. Some PC cases come with a PC speaker preinstalled. A wired PC speaker connector may have a two-, three-, or four-pin configuration, and either two or three wires. The female connector of the speaker connects to
Smacky
Open-source C++ software for playing (monophonic) music on the PC speaker.
Site for old PC without sound cards
by Mark Feldman for ''PC-GPE''. *Programming the PC Speaker, by Phil Inch
(includes a very detailed explanation of how to play back PCM audio on the PC speaker, and why it works)
A freeware to use the PC speaker to make music (superseded b
BaWaMI
by Frank Buß. APIs for beeping.
Commandline PC speaker program for Linux
https://web.archive.org/web/20030820082835/http://ftp.falsehope.com/pub/beep/ FTP]
Practical article on implementing a Linux Kernel Driver
Timing on the PC family under DOS
(Sections 7.5, 7.29, 7.30, and 10.7 – 10.7.4 in particular) {{DEFAULTSORT:Pc Speaker Legacy hardware Loudspeakers Computer-related introductions in 1981
loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or speaker driver) is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A ''speaker system'', also often simply referred to as a "speaker" or ...
built into some IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are similar to the original IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC, IBM Personal Computer XT, XT, and IBM Personal Computer/AT, AT, all from computer giant IBM, that are able to use the same software and expansion cards. Such ...
computers. The first IBM Personal Computer
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team ...
, model 5150, employed a standard 2.25 inch magnetic driven (dynamic) speaker. More recent computers use a tiny moving-iron or piezo speaker instead. The speaker allows software and firmware to provide auditory feedback to a user, such as to report a hardware fault. A PC speaker generates waveforms using the programmable interval timer
In CPU, computing and in embedded systems, a programmable interval timer (PIT) is a Counter (digital), counter that generates an output signal when it reaches a programmed count. The output signal may trigger an interrupt.
Common features
PITs may ...
, an Intel 8253
The Intel 8253 and 8254 are programmable interval timers (PITs), which perform timing and counting functions using three 16-bit counters.
The 825x family was primarily designed for the Intel 8080/ 8085-processors, but were later used in x86 ...
or 8254 chip.
Use cases
BIOS/UEFI error codes
The PC speaker is used during thepower-on self-test
A power-on self-test (POST) is a process performed by firmware or software routines immediately after a computer or other digital electronic device is powered on.
This article mainly deals with POSTs on personal computers, but many other embed ...
(POST) sequence to indicate errors during the boot process. Since it is active before the graphics card, it can be used to communicate "beep codes" related to problems that prevent the much more complex initialization of the graphics card to take place. For example, the Video BIOS usually cannot activate a graphics card unless working RAM is present in the system while beeping the speaker is possible with just ROM and the CPU registers. Usually, different error codes will be signalled by specific beeping patterns, such as e.g. "one beep; pause; three beeps; pause; repeat". These patterns are specific to the BIOS/UEFI manufacturer and are usually documented in the technical manual of the motherboard.
Software
Several programs, including music software, operating systems or games, could playpulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM Stream (comp ...
(PCM) sound through the PC speaker using special ''Pulse-width Modulation'' techniques explained later in this article.
Games
The PC speaker was often used in very innovative ways to create the impression of polyphonic music or sound effects within computer games of its era, such as theLucasArts
Lucasfilm Games (known as LucasArts between 1990 and 2021) is an American video game licensor that is part of Lucasfilm. It was founded in May 1982 by George Lucas as a video game development group alongside his film company; as part of a large ...
series of adventure games from the mid-1980s, using swift arpeggios. Several games such as '' Space Hulk'' and '' Pinball Fantasies'' were noted for their elaborate sound effects; ''Space Hulk'', in particular, even had full speech.
However, because the method used to reproduce PCM was very sensitive to timing issues, these effects either caused noticeable sluggishness on slower PCs or sometimes failed on faster PCs (that is, significantly faster than the program was originally developed for). Also, it was difficult for programs to do much else, even update the display, during the playing of such sounds. Thus, when sound cards (which can output complex sounds independent from the CPU once initiated) became mainstream in the PC market after 1990, they quickly replaced the PC speaker as the preferred output device for sound effects. Most newly-released PC games stopped supporting the speaker during the second half of the 1990s.
Other programs
Several programs, including MP (Module Player, 1989),Scream Tracker
''Scream Tracker'' is a tracker (an integrated multi-track step sequencer
A music sequencer (or audio sequencer or simply sequencer) is a device or application software that can record, edit, or play back music, by handling note and perform ...
, Fast Tracker
FastTracker 2 (also referred to as FastTracker II) is a music tracker created by Fredrik "Mr. H" Huss and Magnus "Vogue" Högdahl, two members of the demogroup Triton (who later founded Starbreeze Studios) which set about releasing their own tra ...
, Impulse Tracker, and even device drivers for Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, w ...
and Microsoft Windows, could play PCM sound through the PC speaker.
Modern Microsoft Windows systems have PC speaker support as a separate device with special capabilities – that is, it cannot be configured as a normal audio output device. Some software uses this special sound channel to produce sounds. For example, Skype
Skype () is a proprietary telecommunications application operated by Skype Technologies, a division of Microsoft, best known for VoIP-based videotelephony, videoconferencing and voice calls. It also has instant messaging, file transfer, deb ...
can use it as a reserve calling signal device for the case where the primary audio output device cannot be heard (for example because the volume is set to the minimum level or the amplifier is turned off).
In the 1990s, a computer virus for Microsoft DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few ope ...
named "Techno" appeared, playing a melody through the PC speaker while printing the word "TECHNO" on the screen until filled.
Pinouts
pin header
A pin header (or simply header) is a form of electrical connector. A male pin header consists of one or more rows of metal pins molded into a plastic base, often apart, though available in many spacings. Male pin headers are cost-effective du ...
s on the motherboard, which are sometimes labeled or .
Pulse-width modulation
The PC speaker is normally meant to reproduce a square wave via only 2 levels of output (two voltage levels, typically 0 V and 5 V), driven by channel 2 of theIntel 8253
The Intel 8253 and 8254 are programmable interval timers (PITs), which perform timing and counting functions using three 16-bit counters.
The 825x family was primarily designed for the Intel 8080/ 8085-processors, but were later used in x86 ...
(PC, XT) or 8254 (AT and later) Programmable Interval Timer
In CPU, computing and in embedded systems, a programmable interval timer (PIT) is a Counter (digital), counter that generates an output signal when it reaches a programmed count. The output signal may trigger an interrupt.
Common features
PITs may ...
operating in mode three (square wave signal). The speaker hardware itself is directly accessible via PC I/O port 61H (61 hexadecimal) via bit 1 and can be physically manipulated for 2 levels of output (i.e. 1-bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represente ...
sound). However, by carefully timing a short pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the n ...
(i.e. going from one output level to the other and then back to the first), and by relying on the speaker's physical filtering properties (limited frequency response, self-inductance, etc.), it is possible to drive the speaker to various intermediate output levels, functioning as a crude digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC, D/A, D2A, or D-to-A) is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
There are several DAC archit ...
. This technique is called pulse-width modulation (PWM) and allows approximate playback of PCM audio. (A more refined version of this technique is used in class D audio amplifiers.)
With the PC speaker this method achieves limited quality playback, but a commercial solution named RealSound used it to provide improved sound on several games.
Obtaining a high fidelity sound output using this technique requires a switching frequency much higher than the audio frequencies meant to be reproduced (typically with a ratio of 10:1 or more), and the output voltage to be bipolar, in order to make better use the output devices' dynamic range and power. On the PC speaker, however, the output voltage is either zero or TTL
TTL may refer to:
Photography
* Through-the-lens metering, a camera feature
* Zenit TTL, an SLR film camera named for its TTL metering capability
Technology
* Time to live, a computer data lifespan-limiting mechanism
* Transistor–transistor lo ...
level (unipolar).
The quality depends on a trade-off between the PWM carrier frequency
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a ...
(effective sample rate
In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous-time signal to a discrete-time signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of "samples".
A sample is a value of the signal at a point in time and/or spa ...
) and the number of output levels (effective bit depth). The clock rate of the PC's programmable interval timer
In CPU, computing and in embedded systems, a programmable interval timer (PIT) is a Counter (digital), counter that generates an output signal when it reaches a programmed count. The output signal may trigger an interrupt.
Common features
PITs may ...
which drives the speaker is fixed at 1,193,180 Hz, and the product of the audio sample rate times the maximum DAC value must equal this.
Typically, a 6-bit DAC with a maximum value of 63 is used at a sample rate of 18,939.4 Hz, producing poor but recognizable audio.
The audio fidelity of this technique is further decreased by the lack of a properly sized dynamic loudspeaker, specially in modern machines and particularly laptops that use a tiny moving-iron speaker (often confused with piezoelectric
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The word '' ...
). The reason for this is that PWM-produced audio requires a low-pass filter before the final output in order to suppress switching noise and high harmonics. A normal dynamic loudspeaker does this naturally, but the tiny metal diaphragm of the moving-iron speaker will let much switching noise pass, as will many direct couplings (though there are exceptions to this, e.g. filtered "speaker in" ports on some motherboards and sound cards).
This use of the PC speaker for complex audio output became less common with the introduction of Sound Blaster
Sound Blaster is a family of sound cards designed by Singaporean technology company Creative Technology (known in the US as Creative Labs). Sound Blaster sound cards were the de facto standard for consumer audio on the IBM PC compatible system pl ...
and other sound card
A sound card (also known as an audio card) is an internal expansion card that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under the control of computer programs. The term ''sound card'' is also applied to external audio ...
s.
See also
*Intel 8253
The Intel 8253 and 8254 are programmable interval timers (PITs), which perform timing and counting functions using three 16-bit counters.
The 825x family was primarily designed for the Intel 8080/ 8085-processors, but were later used in x86 ...
* RealSound
* Loudspeaker enclosure
A loudspeaker enclosure or loudspeaker cabinet is an enclosure (often rectangular box-shaped) in which speaker drivers (e.g., loudspeakers and tweeters) and associated electronic hardware, such as crossover circuits and, in some cases, powe ...
Notes
External links
Smacky
Open-source C++ software for playing (monophonic) music on the PC speaker.
Site for old PC without sound cards
by Mark Feldman for ''PC-GPE''. *Programming the PC Speaker, by Phil Inch
(includes a very detailed explanation of how to play back PCM audio on the PC speaker, and why it works)
A freeware to use the PC speaker to make music (superseded b
BaWaMI
by Frank Buß. APIs for beeping.
Commandline PC speaker program for Linux
https://web.archive.org/web/20030820082835/http://ftp.falsehope.com/pub/beep/ FTP]
Practical article on implementing a Linux Kernel Driver
Timing on the PC family under DOS
(Sections 7.5, 7.29, 7.30, and 10.7 – 10.7.4 in particular) {{DEFAULTSORT:Pc Speaker Legacy hardware Loudspeakers Computer-related introductions in 1981