Prolactin cell on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A prolactin cell (also known as a lactotropic cell, epsilon acidophil, lactotrope, lactotroph, mammatroph, mammotroph) is a
cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a de ...
in the anterior pituitary
The anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is a major Organ (anatomy), organ of the endocrine system. The anterior pituitary is the glandular, Anatomical terms of location#Usage in human anatomy, anterior lobe that t ...
which produces prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin and mammotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secr ...
(a peptide hormone
Peptide hormones are hormones composed of peptide molecules. These hormones influence the endocrine system of animals, including humans. Most hormones are classified as either amino-acid-based hormones (amines, peptides, or proteins) or steroid h ...
) in response to hormonal signals including dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
(which is inhibitory), thyrotropin-releasing hormone
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a hypophysiotropic hormone produced by neurons in the hypothalamus that stimulates the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) as well as prolactin from the anterior pituitary.
TRH has been used ...
and estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
(especially during pregnancy), which are stimulatory. Prolactin is responsible for actions needed for body homeostasis, the development of breasts, and for lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process ...
. The inhibitory effects of dopamine override the stimulatory effects of TRH in non-pregnant, non-lactating sexually mature females. Depending on the sex of the individual, prolactin cells account for 20% - 50% of all cells in the anterior pituitary gland. Other regulators include oxytocin
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Present in animals since early stages of evolution, in humans it plays roles in behavior that include Human bonding, ...
and progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the ma ...
.
Males and non-pregnant, non-lactating females typically have low levels of prolactin. The number for prolactin cells in a pregnant female will increase to allow for breast tissue development. Prolactin is involved in the maturation of mammary gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, human ...
s and their secretion of milk in association with oxytocin, estrogen, progesterone, glucocorticoids, and others. Prolactin has numerous other effects in both sexes.
Function
When prolactin cells are observed in vitro, they are responsible for firing spontaneous action potentials, causing Ca2+ to follow the action potential pathway and allows for the exocytotic pathway, prolactin gene transcription, and hormone synthesis to remain active throughout. Prolactin gene transcription is responsible for the production of prolactin. Prolactin is involved in the maturation ofmammary glands
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, human ...
and their secretion of milk in association with oxytocin, estrogen, progesterone, glucocorticoids, and others. Prolactin has numerous other effects in both sexes.
Conditions
Prolactin cells areacidophilic
Acidophiles or acidophilic organisms are those that thrive under highly acidic conditions (usually at pH 5.0 or below). These organisms can be found in different branches of the tree of life, including Archaea, Bacteria,Becker, A.Types of Bacteri ...
by hematoxylin & eosin stains and, If these cells undergo neoplastic
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
transformation, they will give rise to a prolactinoma
A prolactinoma is a tumor (adenoma) of the pituitary gland that produces the hormone prolactin. It is the most common type of functioning pituitary tumor. Symptoms of prolactinoma are due to abnormally high levels of prolactin in the blood ( hyp ...
, a prolactin-secreting pituitary adenoma
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.
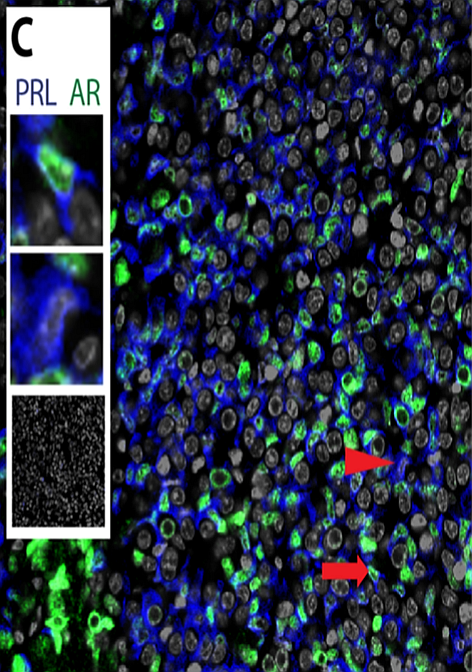 In men, prolactinoma could also cause erectile dysfunction, enlarged breast tissue, small muscles or a decrease in the amount of body hair. In women, this could cause breast discharge, irregular menstrual cycles, painful intercourse, acne, or an increase in the amount of body hair.
In men, prolactinoma could also cause erectile dysfunction, enlarged breast tissue, small muscles or a decrease in the amount of body hair. In women, this could cause breast discharge, irregular menstrual cycles, painful intercourse, acne, or an increase in the amount of body hair.
Prolactinoma
A prolactinoma is a tumor (adenoma) of the pituitary gland that produces the hormone prolactin. It is the most common type of functioning pituitary tumor. Symptoms of prolactinoma are due to abnormally high levels of prolactin in the blood ( hyp ...
is a tumor of the pituitary gland that is typically non-cancerous. This disorder is more common in females than males. Although the tumor itself may not cause symptoms, the tumor can cause an increased production of prolactin and decreased levels of estrogen and testosterone.
Symptoms of both sexes could include osteoporosis, infertility, or a decrease in sexual desire.
 In men, prolactinoma could also cause erectile dysfunction, enlarged breast tissue, small muscles or a decrease in the amount of body hair. In women, this could cause breast discharge, irregular menstrual cycles, painful intercourse, acne, or an increase in the amount of body hair.
In men, prolactinoma could also cause erectile dysfunction, enlarged breast tissue, small muscles or a decrease in the amount of body hair. In women, this could cause breast discharge, irregular menstrual cycles, painful intercourse, acne, or an increase in the amount of body hair.
See also
* Hypothalamic–pituitary–prolactin axis *List of distinct cell types in the adult human body
The list of human cell types provides an enumeration and description of the various specialized cells found within the human body, highlighting their distinct functions, characteristics, and contributions to overall physiological processes. Cell ...
References
Peptide hormone secreting cells Human cells Human female endocrine system {{Cell-biology-stub