Portable Pixmap Format on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Netpbm (formerly Pbmplus) is an
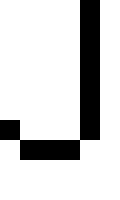 P1
# This is an example bitmap of the letter "J"
6 10
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
1 0 0 0 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
The string ''P1'' identifies the file format. The
P1
# This is an example bitmap of the letter "J"
6 10
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
1 0 0 0 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
The string ''P1'' identifies the file format. The
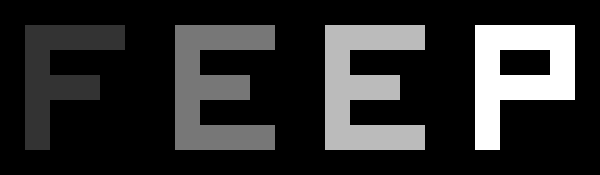 P2
# Shows the word "FEEP"
24 7
15
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 3 3 3 3 0 0 7 7 7 7 0 0 11 11 11 11 0 0 15 15 15 15 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 11 0 0 0 0 0 15 0 0 15 0
0 3 3 3 0 0 0 7 7 7 0 0 0 11 11 11 0 0 0 15 15 15 15 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 11 0 0 0 0 0 15 0 0 0 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 7 7 7 0 0 11 11 11 11 0 0 15 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
P2
# Shows the word "FEEP"
24 7
15
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 3 3 3 3 0 0 7 7 7 7 0 0 11 11 11 11 0 0 15 15 15 15 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 11 0 0 0 0 0 15 0 0 15 0
0 3 3 3 0 0 0 7 7 7 0 0 0 11 11 11 0 0 0 15 15 15 15 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 11 0 0 0 0 0 15 0 0 0 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 7 7 7 0 0 11 11 11 11 0 0 15 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
File:Bmp_format2.svg, frameless,
rect 50 50 100 100 0,0: blue 0000FF FF
rect 100 50 150 100 0,1: green 00FF00 FF
rect 150 50 200 100 0,2: red FF0000 FF
rect 200 50 250 100 0,3: white FFFFFF FF
rect 50 100 100 150 1,0: blue 0000FF 7F, half transparent
rect 100 100 150 150 1,1: green 00FF00 7F, half transparent
rect 150 100 200 150 1,2: red FF0000 7F, half transparent
rect 200 100 250 150 1,3: white FFFFFF 7F, half transparent
default BMP file format#Example 2
desc top-left
P7
WIDTH 4
HEIGHT 2
DEPTH 4
MAXVAL 255
TUPLTYPE RGB_ALPHA
ENDHDR
pfm: the PFM graphic image file format as understood by the Netpbm
{{Graphics file formats Free graphics software Free software programmed in C Free software programmed in Perl Graphics file formats Graphics libraries Image processing software Unix programming tools
open-source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use and view the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentrali ...
package of graphics programs and a programming library. It is used primarily in Unix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, a ...
, where it is found in all major open-source operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
distributions, but also works on Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
, macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
, and other operating systems.
File formats
Several graphics formats are used and defined by the Netpbm project: * portable bitmap format (PBM) * portable graymap format (PGM) * portable pixmap format (PPM) PBM, PGM and PPM, sometimes collectively referred to as the portable anymap format (PNM) areimage file format
An image file format is a file format for a digital image. There are many formats that can be used, such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Most formats up until 2022 were for storing 2D images, not 3D ones. The data stored in an image file format may be co ...
s designed to be easily exchanged between platforms. The magic number at the beginning of a file determines the type. PNM files use a magic number of an ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
"P" followed by a number defining the file type.
The PBM format was invented by Jef Poskanzer
Jeffrey A. Poskanzer is a computer programmer. He was the first person to post a weekly FAQ to Usenet. He developed the portable pixmap file format and pbmplus (the precursor to the Netpbm package) to manipulate it. He has also worked on the team ...
in the 1980s. The format allowed monochrome bitmaps to be transmitted within an email message as plain ASCII text, so that it would survive any changes in text formatting. The first library to handle the PBM format was released in 1988 under the name Pbmplus, containing tools to convert between PBM and other graphics formats. By the end of 1988, Poskanzer had developed the PGM and PPM formats along with their associated tools and added them to Pbmplus. The final release of Pbmplus was December 10, 1991.
The Netpbm library was released in 1993 to replace the then-unmaintained Pbmplus. It repackaged the original library and incorporated fixes created by other developers.
Description
Each file starts with a two-byte magic number in ASCII that identifies the file type (PBM, PGM, or PPM) and its encoding (ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
/"plain" or binary/"raw"). The magic number is a capital P followed by a single-digit number.
The Netpbm library supports an additional PAM file format with a magic number of P7.
PNM files can be created as both plain text and raw binary. The ASCII ("plain") formats allow for human readability and easy transfer to other platforms, whereas the binary ("raw") formats are easier to parse by programs and more efficient in file size. In the binary formats, PBM uses 1 bit per pixel, PGM uses 8 or 16 bits per pixel, and PPM uses 24 or 48 bits per pixel: 8/16 for red, 8/16 for green, 8/16 for blue. Application support for the 16 bit variants is rare. In either form, the header remains in ASCII format and the arguments are separated by a whitespace.
PGM and PPM documentation defines that gray and color values use the BT.709 color space and gamma
Gamma (; uppercase , lowercase ; ) is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter normally repr ...
transfer function. However, depending on the application, the used color space may be sRGB
sRGB (standard RGB) is a colorspace, for use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was initially proposed by HP and Microsoft in 1996 and became an official standard of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 6 ...
, linear or some other color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital represe ...
. There is no metadata in the file to indicate which color space is being used.
PBM example
A simple example of the PBM format is as follows: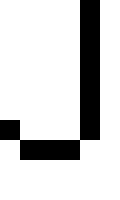 P1
# This is an example bitmap of the letter "J"
6 10
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
1 0 0 0 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
The string ''P1'' identifies the file format. The
P1
# This is an example bitmap of the letter "J"
6 10
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
1 0 0 0 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
The string ''P1'' identifies the file format. The number sign
The symbol is known as the number sign, hash, (or in North America) the pound sign. The symbol has historically been used for a wide range of purposes including the designation of an ordinal number and as a Typographic ligature, ligatured abbre ...
introduces a comment. The next two numbers give the width and the height. The following matrix gives the pixel values. As the PBM format is monochromatic and only supports two shades, namely, black and white, the image is described in only ones and zeros. This is known as a bitmap
In computing, a bitmap (also called raster) graphic is an image formed from rows of different colored pixels. A GIF is an example of a graphics image file that uses a bitmap.
As a noun, the term "bitmap" is very often used to refer to a partic ...
.
The matrix cells do not need to be aligned; the format ignores whitespace and line feeds in the data section. The following displays the same image:
P1
# This is an example bitmap of the letter "J"
6 10
000010000010000010000010000010000010100010011100000000000000
A value of 0 signifies a white pixel, and a 1 signifies a black pixel. This differs from the other formats, where higher values signify brighter pixels.
The P4 binary format of the same image represents each pixel with a single bit. The width of the row in pixels is given in the header, packed to the length of 8 pixels or a byte. The first pixel in a row is the most significant bit. The extra bits used to make the length equal to a byte are ignored. The following formula can be used to calculate the number of required bytes . Using the example above a grid would take 10 bytes.
P4
# This is an example binary format of the letter "J" with each byte in decimal notation
6 10
8 8 8 8 8 8 136 112 0 0
PGM example
The PGM and PPM formats have an additional parameter for the maximum value (numbers of grey between black and white) after the X and Y dimensions and before the actual pixel data. Black is 0 and max value is white.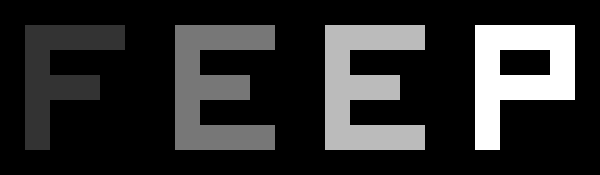 P2
# Shows the word "FEEP"
24 7
15
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 3 3 3 3 0 0 7 7 7 7 0 0 11 11 11 11 0 0 15 15 15 15 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 11 0 0 0 0 0 15 0 0 15 0
0 3 3 3 0 0 0 7 7 7 0 0 0 11 11 11 0 0 0 15 15 15 15 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 11 0 0 0 0 0 15 0 0 0 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 7 7 7 0 0 11 11 11 11 0 0 15 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
P2
# Shows the word "FEEP"
24 7
15
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 3 3 3 3 0 0 7 7 7 7 0 0 11 11 11 11 0 0 15 15 15 15 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 11 0 0 0 0 0 15 0 0 15 0
0 3 3 3 0 0 0 7 7 7 0 0 0 11 11 11 0 0 0 15 15 15 15 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 11 0 0 0 0 0 15 0 0 0 0
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 7 7 7 7 0 0 11 11 11 11 0 0 15 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
PPM example
This is an example of a color RGB image stored in PPM format. (Not shown are the newline character(s) at the end of each line.) P3 # "P3" means this is a RGB color image in ASCII # "3 2" is the width and height of the image in pixels # "255" is the maximum value for each color # This, up through the "255" line below are the header. # Everything after that is the image data: RGB triplets. # In order: red, green, blue, yellow, white, and black. 3 2 255 255 0 0 0 255 0 0 0 255 255 255 0 255 255 255 0 0 0 The P6 binary format of the same image represents each color component of each pixel with one byte (thus three bytes per pixel) in the order red, green, then blue. The file is smaller, but the color information is more difficult to read by humans. The binary image information comes after the header (which ends with a whitespace). In the binary format, last headerline must be like "255\n", with data immediately following it; any comment added after 255 will be taken as the start of image data, and the image will be skewed to the right (at least when opened by the image-manipulation program GIMP (December 2022)). The PPM format is not compressed, and thus requires more space and bandwidth than a compressed format would. For example, the above 192×128 PNG (Portable Network Graphics
Portable Network Graphics (PNG, officially pronounced , colloquially pronounced ) is a raster graphics, raster-graphics file graphics file format, format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was developed as an improved, non-patented ...
) image has a file size of 166 bytes. When converted to a 192×128 PPM image, the file size is 73,848 bytes. Filesize reduction factor 100 or so when converting to png is typical if the image is a line drawing; if the image is a photo, it is best converted to jpeg, which yields a greater filesize reduction.
PPM is generally used as an intermediate format for image work before converting to a more efficient format like PNG without any loss of information in the intermediate step.
The image shown above using only 0 or the maximal value for the red, green and blue channels can be encoded as follows:P3 # The same image with width 3 and height 2, # using 0 or 1 per color (red, green, blue) 3 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0White space (including line ends) and comment lines are syntactically equivalent to a single space within the PNM headers. For the plain formats (P1, P2 and P3) this is also true of the pixmap lines:
P3 3 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
Extensions
16-bit
The original definition of the PGM and the PPM binary formats (the P5 and P6 formats) did not allow bit depths greater than 8 bits. While the ASCII format can accommodate greater bit depths, it increases file sizes and slows read and write operations. Many programmers have extended the format to allow higher bit depths. When using higher bit depths, theendianness
file:Gullivers_travels.jpg, ''Gulliver's Travels'' by Jonathan Swift, the novel from which the term was coined
In computing, endianness is the order in which bytes within a word (data type), word of digital data are transmitted over a data comm ...
of the file matters. Various implementations have not agreed on which byte order to use, and some connected the 16-bit endianness to the pixel packing order. The PGM and PPM documentation says the most significant byte is first and the Netpbm implementation uses big-endian byte order.
32-bit
The PFM (Portable Floatmap) is the unofficial four byte IEEE 754 single precision floating point extension. # The first line is either the ASCII text "PF", for a color file, or "Pf", for a grey-scale file. # The next ASCII text line contains the width and height, separated by the space character hex 20 or sometimes with hex 0A (resulting in four lines). After each line a white space character hex 0A is written and not the Windows/DOS CR/LF combination. # The third ASCII text line holds a nonzero decimal number that indicates little-endian floats for the pixel data when negative and big-endian floats when positive. The absolute value of the number indicates the range. So the third line containing -1.0 indicates little-endian format in range zero to one. (No comments may follow.) After the header the file, each pixel is specified with a floating point number from left-to-right, bottom-to-top. Some programs suggest PF4 as an additional extension for the RGBA format. PFM is supported by the programsPhotoshop
Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor developed and published by Adobe for Windows and macOS. It was created in 1987 by Thomas and John Knoll. It is the most used tool for professional digital art, especially in raster graphics editin ...
, GIMP
Gimp or GIMP may refer to:
Clothing
* Bondage suit, also called a gimp suit, a type of suit used in BDSM
* Bondage mask, also called a gimp mask, often worn in conjunction with a gimp suit
Embroidery and crafts
* Gimp (thread), an ornamental tr ...
, and ImageMagick
ImageMagick, invoked from the command line as magick, is a free and open-source cross-platform software suite for displaying, creating, converting, modifying, and editing raster images. ImageMagick was created by John Cristy in 1987, and it ...
. It is also supported by the ''de facto'' reference implementation netpbm.
Programs
The Netpbm package contains over 350 programs, most of which have "pbm", "pgm", "ppm", "pam", or "pnm" in their names. For example, one might usepamscale to shrink an image by 10%, pamcomp to overlay one image on top of another, pbmtext to create an image of text, or reduce the number of colors in an image with pnmquant.
The programs are designed to be minimal building blocks that can be used in various combinations to do other things. The Netpbm package can, for example, use two successive conversion programs to turn a color picture in the GIF format into a .bmp file:
giftopnm somepic.gif > somepic.ppm
ppmtobmp somepic.ppm > somepic.bmp
This kind of operation is commonly done as a pipeline
A pipeline is a system of Pipe (fluid conveyance), pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries ...
to save execution time and to avoid creating a temporary file:
giftopnm somepic.gif , ppmtobmp > somepic.bmp
The Netpbm programs are frequently used as intermediates to convert between obscure formats. For instance, there may be no tool to convert an X11 window dump (XWD
In the X Window System, the program xwd (X Window dump) captures the content of a screen or of a window and optionally saves it into a file.
xwd runs in one of two ways: if a user specifies the whole screen or the name or identifier of a wi ...
format) directly to a Macintosh PICT
PICT is a graphics file format introduced on the original Apple Macintosh computer as its standard metafile format. It allows the interchange of graphics (both bitmapped and vector), and some limited text support, between Mac applications, an ...
file, but one can do this by running xwdtopnm, then ppmtopict. (Tools which say that they output PNM output either PBM, PGM, or PPM. Tools importing PNM will read any of the three formats.) As a more complex example, Netpbm tools can convert 48×48 XBM to ''Ikon'' and eventually X-Face
An X-Face is a small bitmap (48 × 48 pixels, black and white) image which is added to a Usenet posting or e-mail message, typically showing a picture of the author's face. The image data is included in the posting as encoded text, and attached ...
.
History
The PBM (black and white) format was invented byJef Poskanzer
Jeffrey A. Poskanzer is a computer programmer. He was the first person to post a weekly FAQ to Usenet. He developed the portable pixmap file format and pbmplus (the precursor to the Netpbm package) to manipulate it. He has also worked on the team ...
in the mid-1980s. At the time, there was no standard, reliable way to send binary files in email, and attempting to send anything other than 7-bit ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
in email often resulted in data corruption
Data corruption refers to errors in computer data that occur during writing, reading, storage, transmission, or processing, which introduce unintended changes to the original data. Computer, transmission, and storage systems use a number of meas ...
. PBM was designed to allow images to be sent via email without being corrupted. Poskanzer released the forerunner of Netpbm, called Pbmplus in 1988. By the end of 1988, Poskanzer had developed the PGM (greyscale) and PPM (color) formats and released them with Pbmplus.
The last release of Pbmplus was on December 10, 1991. Poskanzer never released any further updates, and in 1993, Netpbm was developed to replace it. At first, it was nothing more than a renamed release of Pbmplus, but updates continued to occur until 1995 when the package again became abandoned. In 1999, the Netpbm package was picked up by its present maintainer, Bryan Henderson.
In 2000, PAM was added to the file formats of the Netpbm library allowing an alpha channel.
The name Netpbm came from the program developers collaborating over the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
, which was notable at the time; the NetBSD
NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was fork (software development), forked. It continues to ...
operating system and NetHack
''NetHack'' is an open source single-player roguelike video game, first released in 1987 and maintained by the NetHack DevTeam. The game is a fork of the 1984 game ''Hack'', itself inspired by the 1980 game '' Rogue''. The player takes the role ...
game got their names similarly. (Unlike with the later, more widespread Portable Network Graphics
Portable Network Graphics (PNG, officially pronounced , colloquially pronounced ) is a raster graphics, raster-graphics file graphics file format, format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was developed as an improved, non-patented ...
(PNG) format, the "net" in the name is not actually in reference to the image itself being optimized for transfer over a network.)
PAM graphics format
Portable Arbitrary Map (PAM) is an extension of the older binary P4...P6 graphics formats, introduced with netpbm version 9.7 (August 2000). PAM generalises all features of PBM, PGM, and PPM, and provides for extensions. PAM defines two new attributes; ''depth'' and ''tuple'' type: #The ''depth'' attribute defines the number of channels in the image, such as 1 for greyscale images and 3 for RGB images. #The ''tuple type'' attribute specifies what kind of image the PAM file represents, thus enabling it to stand for the older Netpbm formats, as well as to be extended to new uses, e.g., transparency. PAM is supported byXnView
XnView is an image organizer and general-purpose file manager used for viewing, converting, organizing and editing raster images, as well as general purpose file management. It comes with built-in hex inspection, batch renaming, image scan ...
and FFmpeg
FFmpeg is a free and open-source software project consisting of a suite of libraries and programs for handling video, audio, and other multimedia files and streams. At its core is the command-line ffmpeg tool itself, designed for processing vide ...
. As specified the TUPLTYPE is optional; however, FFmpeg requires it.
Differences from the older formats
The header for the PAM file format begins with P7, and (unlike in the other formats) ends in an explicit close: "ENDHDR" followed by a whitespace. Line ends in a PAM header are significant; for PNM, line ends are whitespace. There is no plain (human-readable,ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
-based) version of PAM. PAM files are always binary, and attempts to use the switch -plain with Netpbm programs that produce PAM output results in an error message.
For the black-and-white version of PAM (depth 1, tuple type BLACKANDWHITE), corresponding to PBM, PAM uses one byte per pixel, instead of PBM's use of one bit per pixel (packing eight pixels in one byte). Also, the value 1 in such a PAM image stands for white ("light on"), as opposed to black in PBM ("ink on").
Transparency
All of the basic tuple types (BLACKANDWHITE, GRAYSCALE, and RGB) have a variant with an opacity channel. The tuple type is created by appending "_ALPHA" as a suffix to the base tuple type. For example, an image with a tuple type of GRAYSCALE is equivalent to PGM (portable graymap). GRAYSCALE_ALPHA with transparency is not directly possible in PGM. The specification permits MAXVAL 1 for GRAYSCALE, but it would have the same effect as BLACKANDWHITE. Anexample
Example may refer to:
* ''exempli gratia'' (e.g.), usually read out in English as "for example"
* .example, reserved as a domain name that may not be installed as a top-level domain of the Internet
** example.com, example.net, example.org, an ...
in the BMP article shows an RGBA
RGBA stands for red green blue alpha. While it is sometimes described as a color space, it is actually a three-channel RGB color model supplemented with a fourth ''alpha channel''. Alpha indicates how opaque each pixel is and allows an image to ...
image with 4×2=8 blue, green, red, and white pixels; half transparent (0x7F) in the first lower row, opaque (0xFF) in the second upper row; hex. FF00007F 00FF007F 0000FF7F FFFFFF7F FF0000FF 00FF00FF 0000FFFF FFFFFFFF in BGRA order. For PAM, this bitmap has to be given in RGBA order, swapping the 1st and 3rd byte in each pixel. BMP rows are typically arranged bottom-up, for PAM and PNM rows are given top-down (i.e. for this example 0000FFFF 00FF00FF FF0000FF FFFFFFFF 0000FF7F 00FF007F FF00007F FFFFFF7F). The PAM header for this example could be:
Extensions
PAM's tuple-type mechanism allows for many extensions. In theory, PAM can be extended to represent color models such as CMYK. The format is not even limited to graphics, its definition allows it to be used for arbitrary three-dimensional matrices of unsigned integers. Some programs of the Netpbm package, for example pamsummcol, function as crude matrix arithmetic processors and use the PAM format this way.Licensing
Netpbm consists of hundreds of different tools, each offered with a public copyright license of its own. An analysis byDebian
Debian () is a free and open-source software, free and open source Linux distribution, developed by the Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock in August 1993. Debian is one of the oldest operating systems based on the Linux kerne ...
developer Steve McIntyre from 2001 suggests mostly free software licenses, one non-commercial license (non-free) and a dozen without any license offered (thus also non-free). As mentioned in the analysis, it obviously doesn't cover changes since.
See also
* GD Graphics Library *GraphicsMagick
GraphicsMagick is a fork of ImageMagick, emphasizing stability of both programming API and command-line options. It was branched off ImageMagick's version 5.5.2 in 2002 after irreconcilable differences emerged in the developers' group.
In additi ...
* ImageMagick
ImageMagick, invoked from the command line as magick, is a free and open-source cross-platform software suite for displaying, creating, converting, modifying, and editing raster images. ImageMagick was created by John Cristy in 1987, and it ...
* List of Unix commands
This is a list of the shell commands of the most recent version of the Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) IEEE Std 1003.1-2024 which is part of the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). These commands are implemented in many shells on moder ...
* X PixMap
X PixMap (XPM) is an Image file formats, image file format used by the X Window System, created in 1989 by Daniel Dardailler and Colas Nahaboo working at Groupe Bull, Bull Research Center at Sophia Antipolis, France, and later enhanced by Arnaud L ...
(comparison of PBM and XPM)
* X BitMap
In computer graphics, the X Window System used X BitMap (XBM), a plain text binary image format, for storing cursor and icon bitmaps used in the X GUI. The XBM format is superseded by XPM, which first appeared for X11 in 1989.
Format
XBM fil ...
References
External links
*pfm: the PFM graphic image file format as understood by the Netpbm
{{Graphics file formats Free graphics software Free software programmed in C Free software programmed in Perl Graphics file formats Graphics libraries Image processing software Unix programming tools