Passive Dynamics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Passive dynamics refers to the dynamical behavior of
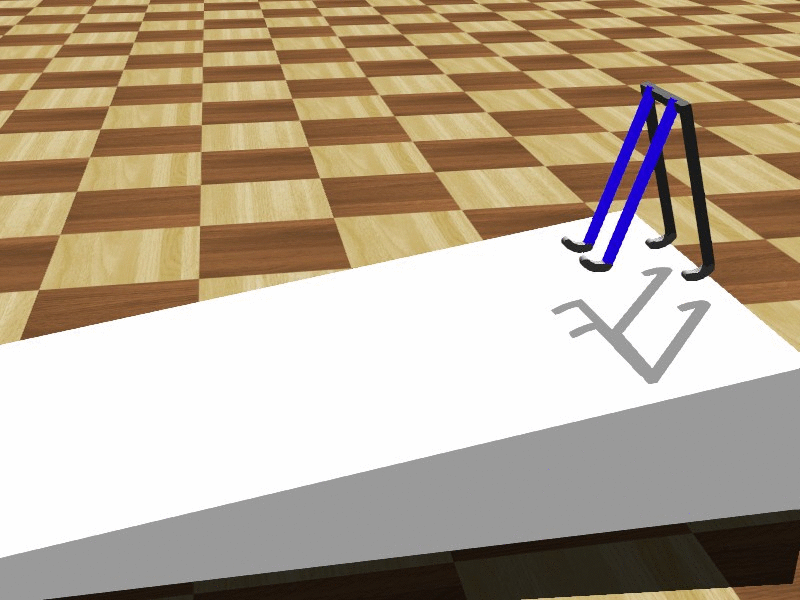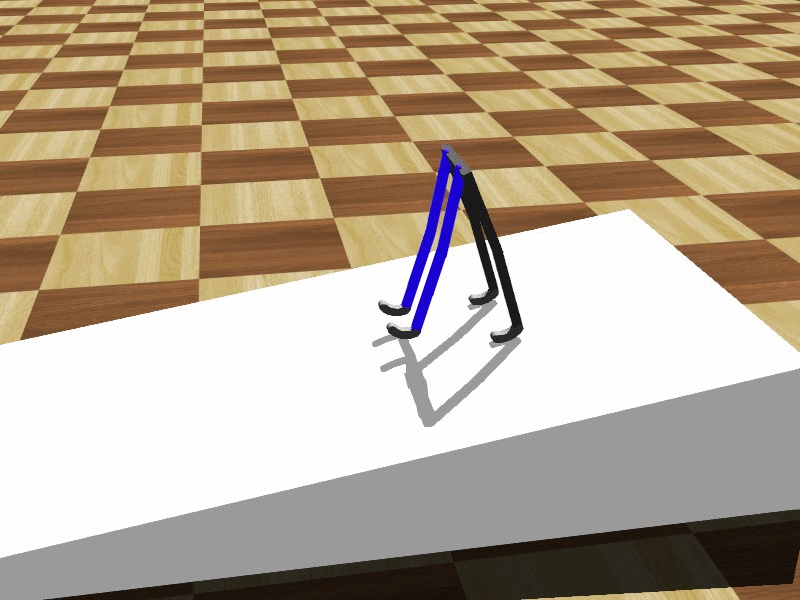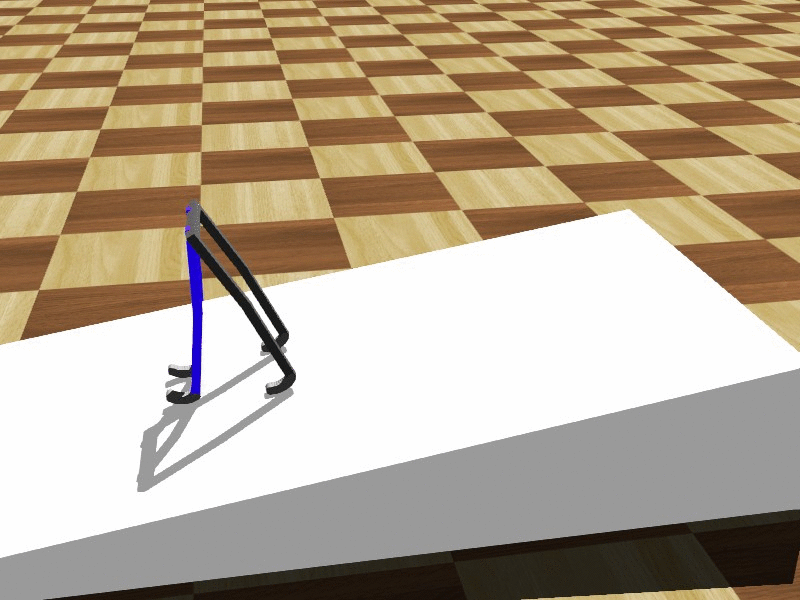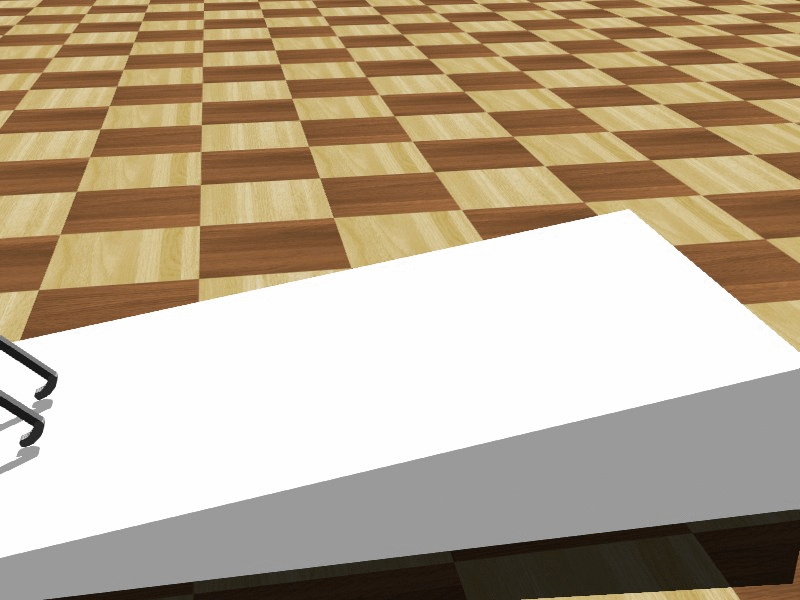 Tad McGeer's 1990 paper "Passive Walking with Knees" provides an excellent overview on the advantages of knees for walking legs. He clearly demonstrates that knees have many practical advantages for walking systems. Knees, according to McGeer, solve the problem of feet colliding with the ground when the leg swings forward, and also offers more stability in some settings.
Passive dynamics is a valuable addition to the field of controls because it approaches the control of a system as a combination of mechanical and electrical elements. While control methods have always been based on the mechanical actions (physics) of a system, passive dynamics utilizes the discovery of morphological computation. Morphological computation is the ability of the mechanical system to accomplish control functions.
Tad McGeer's 1990 paper "Passive Walking with Knees" provides an excellent overview on the advantages of knees for walking legs. He clearly demonstrates that knees have many practical advantages for walking systems. Knees, according to McGeer, solve the problem of feet colliding with the ground when the leg swings forward, and also offers more stability in some settings.
Passive dynamics is a valuable addition to the field of controls because it approaches the control of a system as a combination of mechanical and electrical elements. While control methods have always been based on the mechanical actions (physics) of a system, passive dynamics utilizes the discovery of morphological computation. Morphological computation is the ability of the mechanical system to accomplish control functions.
Cornell Biorobotics and Locomotion Lab
— videos and papers on passive dynamic walkers, including McGeer's originals, the Cornell Efficient Walker, and the Cornell Ranger
Droid Logic
— simulations of passive dynamic walkers and runners created using evolutionary robotics
MIT Leg Lab
— walking and running robots that utilize natural dynamics
— the Cornell Efficient Walker, its passive predecessor, and additional references Robot kinematics 1980s in robotics
actuator
An actuator is a machine element, component of a machine that produces force, torque, or Displacement (geometry), displacement, when an electrical, Pneumatics, pneumatic or Hydraulic fluid, hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system (called an ...
s, robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
s, or organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s when not drawing energy from a supply (e.g., batteries, fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work (physics), work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chem ...
, ATP). Depending on the application, considering or altering the passive dynamics of a powered system can have drastic effects on performance, particularly energy economy, stability
Stability may refer to:
Mathematics
*Stability theory, the study of the stability of solutions to differential equations and dynamical systems
** Asymptotic stability
** Exponential stability
** Linear stability
**Lyapunov stability
** Marginal s ...
, and task bandwidth. Devices using no power source are considered "passive", and their behavior is fully described by their passive dynamics.
In some fields of robotics ( legged robotics in particular), design and more relaxed control of passive dynamics has become a complementary (or even alternative) approach to joint-positioning control methods developed through the 20th century. Additionally, the passive dynamics of animals have been of interest to biomechanists and integrative biologists, as these dynamics often underlie biological motions and couple with neuromechanical control.
Particularly relevant fields for investigating and engineering passive dynamics include legged locomotion and manipulation.
History
The term and its principles were developed by Tad McGeer in the late 1980s. While atSimon Fraser University
Simon Fraser University (SFU) is a Public university, public research university in British Columbia, Canada. It maintains three campuses in Greater Vancouver, respectively located in Burnaby (main campus), Surrey, British Columbia, Surrey, and ...
in Burnaby
Burnaby is a city in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia, Canada. Located in the centre of the Burrard Peninsula, it neighbours the City of Vancouver to the west, the District of North Vancouver across the confluence of the Burrard In ...
, British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, McGeer showed that a human-like frame can walk itself down a slope without requiring muscles or motors. Unlike traditional robots, which expend energy by using motors to control every motion, McGeer's early passive-dynamic machines relied only on gravity and the natural swinging of their limbs to move forward down a slope.
Models
The original model for passive dynamics is based on human and animal leg motions. Completely actuated systems, such as the legs of theHonda Asimo
commonly known as just Honda, is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate automotive manufacturer headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Founded in October 1946 by Soichiro Honda, Honda has bee ...
robot, are not very efficient because each joint has a motor and control assembly. Human-like gaits are far more efficient because movement is sustained by the natural swing of the legs instead of motors placed at each joint.  Tad McGeer's 1990 paper "Passive Walking with Knees" provides an excellent overview on the advantages of knees for walking legs. He clearly demonstrates that knees have many practical advantages for walking systems. Knees, according to McGeer, solve the problem of feet colliding with the ground when the leg swings forward, and also offers more stability in some settings.
Passive dynamics is a valuable addition to the field of controls because it approaches the control of a system as a combination of mechanical and electrical elements. While control methods have always been based on the mechanical actions (physics) of a system, passive dynamics utilizes the discovery of morphological computation. Morphological computation is the ability of the mechanical system to accomplish control functions.
Tad McGeer's 1990 paper "Passive Walking with Knees" provides an excellent overview on the advantages of knees for walking legs. He clearly demonstrates that knees have many practical advantages for walking systems. Knees, according to McGeer, solve the problem of feet colliding with the ground when the leg swings forward, and also offers more stability in some settings.
Passive dynamics is a valuable addition to the field of controls because it approaches the control of a system as a combination of mechanical and electrical elements. While control methods have always been based on the mechanical actions (physics) of a system, passive dynamics utilizes the discovery of morphological computation. Morphological computation is the ability of the mechanical system to accomplish control functions.
Applying passive dynamics
Adding actuation to passive dynamic walkers result in highly efficient robotic walkers. Such walkers can be implemented at lower mass and use less energy because they walk effectively with only a couple of motors. This combination results in a superior "specific cost of transport". Energy efficiency in level-ground transport is quantified in terms of the dimensionless "specific cost of transport", which is the amount of energy required to carry a unit weight a unit distance. Passive dynamic walkers such as the Cornell Efficient Biped have the same specific cost of transport as humans, 0.20. Not incidentally, passive dynamic walkers have human-like gaits. By comparison, Honda's bipedASIMO
ASIMO (Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility) is a humanoid robot created by Honda in 2000.
In 2002, there were 20 units of the first ASIMO model produced; three different ASIMO models subsequently followed. As of February 2009, there were over ...
, which does not utilize the passive dynamics of its own limbs, has a specific cost of transport of 3.23.
The current distance record for walking robots, 65.17 km, is held by the passive dynamics based Cornell Ranger.
Passive dynamics have recently found a role in the design and control of prosthetics
In medicine, a prosthesis (: prostheses; from ), or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through physical trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth (congenital disorder). Prosthe ...
. Since passive dynamics provides the mathematical models of efficient motion, it is an appropriate avenue to develop efficient limbs that require less energy for amputees. Andrew Hansen, Steven Gard and others have done extensive research in developing better foot prosthetics by utilizing passive dynamics.
Passive walking biped robots exhibit different kinds of chaotic behaviors e.g., bifurcation
Bifurcation or bifurcated may refer to:
Science and technology
* Bifurcation theory, the study of sudden changes in dynamical systems
** Bifurcation, of an incompressible flow, modeled by squeeze mapping the fluid flow
* River bifurcation, the for ...
, intermittency
In dynamical systems, intermittency is the irregular alternation of phases of apparently periodic and chaotic dynamics ( Pomeau–Manneville dynamics), or different forms of chaotic dynamics (crisis-induced intermittency).
Experimentally ...
and crisis
A crisis (: crises; : critical) is any event or period that will lead to an unstable and dangerous situation affecting an individual, group, or all of society. Crises are negative changes in the human or environmental affairs, especially when ...
.
See also
*Underactuation Underactuation is a technical term used in robotics and control theory to describe mechanical systems that cannot be commanded to follow arbitrary trajectories in configuration space. This condition can occur for a number of reasons, the simples ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * and *{{cite journal , author=Chandana Paul , title = Morphology and Computation , journal = Proceedings of the International Conference on the Simulation of Adaptive Behaviour , year = 2004 , pages = 33–38External links
Cornell Biorobotics and Locomotion Lab
— videos and papers on passive dynamic walkers, including McGeer's originals, the Cornell Efficient Walker, and the Cornell Ranger
Droid Logic
— simulations of passive dynamic walkers and runners created using evolutionary robotics
MIT Leg Lab
— walking and running robots that utilize natural dynamics
— the Cornell Efficient Walker, its passive predecessor, and additional references Robot kinematics 1980s in robotics