Palisade (pathology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
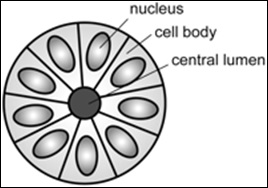
 A ''rosette'' is a cell formation in a halo or spoke-and-wheel arrangement, surrounding a central core or hub. The central hub may consist of an empty-appearing lumen or a space filled with cytoplasmic processes. The cytoplasm of each of the cells in the rosette is often wedge-shaped with the apex directed toward the central core: the nuclei of the cells participating
in the rosette are peripherally positioned and form a ring or halo around the hub.
A ''rosette'' is a cell formation in a halo or spoke-and-wheel arrangement, surrounding a central core or hub. The central hub may consist of an empty-appearing lumen or a space filled with cytoplasmic processes. The cytoplasm of each of the cells in the rosette is often wedge-shaped with the apex directed toward the central core: the nuclei of the cells participating
in the rosette are peripherally positioned and form a ring or halo around the hub.
from The Free Dictionary. Retrieved 6 January 2010.) have been described as a form of palisading. Unlike the center of the
File:Structure of a Flexner–Wintersteiner rosette.jpg, Structure of a Flexner–Wintersteiner rosette
Flexner–Wintersteiner rosettes were first described in 1891 by Simon Flexner, a professor of experimental pathology at the
 A ''Homer-Wright pseudorosette'' is a type of pseudorosette in which differentiated tumor cells surround the neuropil. Examples of tumors containing these are
A ''Homer-Wright pseudorosette'' is a type of pseudorosette in which differentiated tumor cells surround the neuropil. Examples of tumors containing these are
File:Structure of a Homer Wright pseudorosette.jpg, Structure of a Homer-Wright pseudorosette
File:Micrograph of perivascular pseudorosettes.jpg, Micrograph of perivascular pseudorosettes
File:Structure of a perivascular pseudorosette.jpg, Structure of a perivascular pseudorosette
File:Micrograph of pineocytomatous-neurocytic pseudorosettes.jpg, Micrograph of pineocytomatous/neurocytic pseudorosettes
File:Structure of pineocytomatous-neurocytic pseudorosettes.jpg, Structure of pineocytomatous/neurocytic pseudorosettes
 Palisades that are generally longer than a rosette or pseudorosette can be seen in neural tumors such as
Palisades that are generally longer than a rosette or pseudorosette can be seen in neural tumors such as
File:GBM pseudopalisading necrosis.jpg, Pseudopalisades seen around necroses in
 In
In histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: 'tissue', 'suffering', and '' -logia'' 'study of') is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopatholog ...
, a palisade is a single layer of relatively long cells, arranged loosely perpendicular to a surface and parallel to each other. A rosette is a palisade in a halo or spoke-and-wheel arrangement, surrounding a central core or hub. A pseudorosette is a perivascular radial arrangement of neoplastic
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
cells around a small blood vessel. Rosettes are characteristic of tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s.
Rosette

 A ''rosette'' is a cell formation in a halo or spoke-and-wheel arrangement, surrounding a central core or hub. The central hub may consist of an empty-appearing lumen or a space filled with cytoplasmic processes. The cytoplasm of each of the cells in the rosette is often wedge-shaped with the apex directed toward the central core: the nuclei of the cells participating
in the rosette are peripherally positioned and form a ring or halo around the hub.
A ''rosette'' is a cell formation in a halo or spoke-and-wheel arrangement, surrounding a central core or hub. The central hub may consist of an empty-appearing lumen or a space filled with cytoplasmic processes. The cytoplasm of each of the cells in the rosette is often wedge-shaped with the apex directed toward the central core: the nuclei of the cells participating
in the rosette are peripherally positioned and form a ring or halo around the hub.
Pathogenesis
Rosettes may be considered primary or secondary manifestations of tumor architecture. Primary rosettes form as a characteristic growth pattern of a given tumor type whereas secondary rosettes result from the influence of external factors on tumor growth. For example, regressive cell swelling may centripetally displace the cytoplasm as the nucleus is squeezed to the periphery, forming a secondary rosette. Although the presence of primary rosettes may suggest a given diagnosis, usually this finding alone is not considered absolutelypathognomonic
Pathognomonic (synonym ''pathognomic'') is a term, often used in medicine, that means "characteristic for a particular disease". A pathognomonic sign is a particular sign whose presence means that a particular disease is present beyond any doubt. ...
for one specific tumor type.
Loss or gain of genetic information is the main cause of rosette and pseudorosette formation. The cell populations exhibiting neuronal differentiation are believed to secrete surface glycoproteins and glycolipids which mediate cell-to-cell recognition and adhesion. One hypothesis is that these sticky cell surface markers cause the developing cell bodies to cluster or aggregate and their primitive neurites to tangle. As the cells grow, the neurite tangle remains centrally located and the cell bodies are squeezed to the periphery, thus explaining the rosette pattern. Depending upon their location, ependyma
The ependyma is the thin neuroepithelial ( simple columnar ciliated epithelium) lining of the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. The ependyma is one of the four types of neuroglia in the central nervous s ...
l cells may display 2 cell poles. A luminal pole projects to the ependymal lining of a ventricle and a "submesenchymal pole" projects toward the surface of the brain demonstrating glial processes and peripherally situated footplates. Frieda and Pollak conceptualize the architecture of ependymoma
An ependymoma is a tumor that arises from the ependyma, a tissue of the central nervous system. Usually, in pediatric cases the location is intracranial, while in adults it is spinal. The common location of intracranial ependymomas is the floor ...
s as a primitive neural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural folds become elevated, ...
turned inside out with the submesenchymal poles converging toward a central vessel, thus forming a pseudorosette rather than projecting centrifugally toward the pia.
Causes
True rosettes are mainly found in neuropathologic disorder. Other conditions where they are present includeosteosarcoma
An osteosarcoma (OS) or osteogenic sarcoma (OGS) is a cancerous tumor in a bone. Specifically, it is an aggressive malignant neoplasm that arises from primitive transformed cells of mesenchyme, mesenchymal origin (and thus a sarcoma) and that exhi ...
, non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredn ...
, fibromyxoid sarcoma, medullary thyroid carcinoma
Medullary thyroid cancer is a form of thyroid carcinoma which originates from the parafollicular cells (C cells), which produce the hormone calcitonin.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, ...
, embryonal tumor with abundant neuropil and true rosettes (ETANTR), rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly aggressive form of cancer that develops from mesenchymal cells that have failed to fully differentiate into myocytes of skeletal muscle. Cells of the neoplasm, tumor are identified as rhabdomyoblasts.
The four ...
, chronic cholestasis
Cholestasis is a condition where the flow of bile from the liver to the duodenum is impaired. The two basic distinctions are:
* obstructive type of cholestasis, where there is a mechanical blockage in the duct system that can occur from a gallston ...
and chronic active hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite ...
, tobacco rosette: complex viral disease, malaria, adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ; AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or ...
in colon and rectum, hyalinizing spindle cell fused with giant rosette, and endometrial stromal sarcoma with hyalinizing giant rosettes.
Flexner–Wintersteiner rosette
Flexner–Wintersteiner rosettes, a spoke-and-wheel shaped cell formation seen inretinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and 80% of retinoblastoma cas ...
and certain other ophthalmic tumors,Definition of 'rosette'from The Free Dictionary. Retrieved 6 January 2010.) have been described as a form of palisading. Unlike the center of the
Homer-Wright rosette
In histopathology, a palisade is a single layer of relatively long cells, arranged loosely perpendicular to a surface and parallel to each other. A rosette is a palisade in a halo or spoke-and-wheel arrangement, surrounding a central core or hub. ...
, the central lumen is devoid of fiber-rich neuropil. The defining feature of this rosette is the central extension of cytoplasmic projections of the surrounding cells. Like the Homer Wright rosette, the Flexner–Wintersteiner rosette represents a specific form of tumor differentiation.McLean IW, Burnier MN, Zimmerman LE, et al. Tumors of the retina. In: Atlas of tumor pathology: tumors of the eye and ocular adnexa. Washington, DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1994:97–154 Electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing i ...
reveals that the tumor cells forming the Flexner–Wintersteiner rosette have ultrastructural features of primitive photoreceptor cells. Furthermore, the rosette lumen shows similar staining patterns as in rods and cones, suggesting that Flexner–Wintersteiner rosettes represent a specific form of retinal differentiation. In addition to being a characteristic finding in retinoblastomas, Flexner–Wintersteiner rosettes may also be found in pinealoblastoma
Pineoblastoma is a malignant tumor of the pineal gland. A pineoblastoma is a supratentorial midline primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Pineoblastoma can present at any age, but is most common in young children. They account for 0.001% of all prima ...
s and medulloepitheliomas.
University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (Penn or UPenn) is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. One of nine colonial colleges, it was chartered in 1755 through the efforts of f ...
. Flexner noted characteristic clusters of cells in an infantile eye tumor which he called retinoepithelioma. In 1897, Austrian ophthalmologist Hugo Wintersteiner confirmed Flexner's observations and noted that the cell clusters resembled rods and cones. These characteristic rosette formations were subsequently recognized as important features of retinoblastomas.
Pseudorosette
A ''pseudorosette'' is a perivascular radial arrangement of neoplastic cells around a small blood vessel. Pseudorosettes are present inneuroblastoma
Neuroblastoma (NB) is a type of cancer that forms in certain types of nerve tissue. It most frequently starts from one of the adrenal glands but can also develop in the head, neck, chest, abdomen, or Vertebral column, spine. Symptoms may include ...
, medulloblastoma
Medulloblastoma is a common type of primary brain cancer in children. It originates in the part of the brain that is towards the back and the bottom, on the floor of the skull, in the cerebellum, or posterior fossa.
The brain is divided into two ...
, malignant melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
, ependymoma
An ependymoma is a tumor that arises from the ependyma, a tissue of the central nervous system. Usually, in pediatric cases the location is intracranial, while in adults it is spinal. The common location of intracranial ependymomas is the floor ...
, Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about three people per million members of the population. It is also known as cutaneous APUDoma, Primary tumor, primary neuroendocrine tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma ...
, neuroendocrine tumor
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lu ...
of the skin, seborrheic keratosis
A seborrheic keratosis is a non-cancerous ( benign) skin tumour that originates from cells, namely keratinocytes, in the outer layer of the skin called the epidermis. Like liver spots, seborrheic keratoses are seen more often as people age.
The ...
, dendritic cell neurofibroma
A neurofibroma is a benign nerve-sheath tumor in the peripheral nervous system. In 90% of cases, they are found as stand-alone tumors (solitary neurofibroma, solitary nerve sheath tumor or sporadic neurofibroma), while the remainder are found in ...
, astroblastoma, large cell neuroendocrine tumor of the cervix, clear cell ependymoma of the spinal cord, celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
, nasal tumor of olfactory origin, rosette-forming glioneural tumor (RGNT), oncocytoma
An oncocytoma is a tumor made up of oncocytes, epithelial cell (biology), cells characterized by an excessive amount of mitochondria, resulting in an abundant acidophilic, granular cytoplasm. The cells and the tumor that they compose are often be ...
, Wilm's tumor
Wilms' tumor or Wilms tumor, also known as nephroblastoma, is a cancer of the kidneys that typically occurs in children (rarely in adults), and occurs most commonly as a renal tumor in child patients. It is named after Max Wilms, the German surg ...
, and pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of the adrenal medulla composed of chromaffin cells and is part of the paraganglioma (PGL) family of tumors, being defined as an intra-adrenal PGL. These neuroendocrine tumors can be sympathetic, where they relea ...
of the urinary bladder.
Homer-Wright pseudorosette
 A ''Homer-Wright pseudorosette'' is a type of pseudorosette in which differentiated tumor cells surround the neuropil. Examples of tumors containing these are
A ''Homer-Wright pseudorosette'' is a type of pseudorosette in which differentiated tumor cells surround the neuropil. Examples of tumors containing these are neuroblastoma
Neuroblastoma (NB) is a type of cancer that forms in certain types of nerve tissue. It most frequently starts from one of the adrenal glands but can also develop in the head, neck, chest, abdomen, or Vertebral column, spine. Symptoms may include ...
, medulloblastoma
Medulloblastoma is a common type of primary brain cancer in children. It originates in the part of the brain that is towards the back and the bottom, on the floor of the skull, in the cerebellum, or posterior fossa.
The brain is divided into two ...
, pinealoblastoma
Pineoblastoma is a malignant tumor of the pineal gland. A pineoblastoma is a supratentorial midline primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Pineoblastoma can present at any age, but is most common in young children. They account for 0.001% of all prima ...
, and primitive neuroectodermal tumor
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor is a malignant (cancerous) neural crest tumor. It is a rare tumor, usually occurring in children and young adults under 25 years of age. The overall 5 year survival rate is about 53%.
It gets its name because the ...
s of bone. Homer-Wright rosettes are considered "pseudo" in the sense that they are not true rosettes. Unlike Flexner–Wintersteiner rosettes, which contain an empty lumen, Homer-Wright rosettes contain abundant fibrillary material. They are named for James Homer Wright
James Homer Wright (April 8, 1869 – January 3, 1928) was an early and influential American pathologist, who was chief of pathology at Massachusetts General Hospital from 1896 to 1926. Wright was born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
In 1915, he jo ...
.
Perivascular pseudorosette
A perivascular pseudorosette consists of a spoke-wheel arrangement of cells with tapered cellular processes radiates around a wall of a centrally placed vessel. The modifier “pseudo” differentiates this pattern from the Homer Wright and Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes, perhaps because the central structure is not actually formed by the tumor itself, but instead represents a native, non-neoplastic element. Also, some early investigators argued about the definition of a central lumen, choosing “pseudo” to indicate that the hub was not a true lumen but contained structures. Nevertheless, this pattern remains extremely diagnostically useful and the modifier unnecessarily leads to confusion. Perivascular pseudorosettes are encountered in most ependymomas regardless of grade or variant. As such, they are significantly more sensitive for the diagnosis of ependymomas than true ependymal rosettes. Unfortunately, perivascular pseudorosettes are also less specific in that they are also encountered in medulloblastomas, PNETs, central neurocytomas, and less often in glioblastomas, and a rare pediatric tumor, monomorphous pilomyxoid astrocytomas.Pineocytomatous/neurocytic pseudorosettes
Histologic features of these two tumors are virtually identical, including their tendency to form neuropil-rich rosettes, referred to as pineocytomatous/neurocytic rosettes in central neurocytoma. Both are quite similar to the Homer-Wright rosette, but they are generally larger and more irregular in contour. The cells of the pineocytomatous/neurocytic rosettes are also considered to be much more differentiated than the cells forming Homer-Wright rosettes in that the nuclei are slightly larger, more rounded, much less mitotically active, and paler or less hyperchromatic. In rare cases, these rosettes may aggregate in a sheet of back-to-back clusters resembling fieldstone pavement.Clinical significance of rosettes and pseudorosettes
The neuropathologic diagnosis of brain tumors entails the microscopic examination of conventional formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue samples surgically removed from a radiographically defined lesion. Pathologists rely on visual clues such as pattern recognition when examining the stained tissue with a microscope, much as radiologists rely on grayscale patterns of densities and intensities on images. Some histologic patterns of cellular architecture are distinctive if not pathognomonic whereas others are less specific, but nevertheless considerably narrow the differential diagnosis. The precise biologic bases for some of the observed microscopic patterns are poorly understood though their recognition is nonetheless useful. Rosettes are a commonly encountered neuropathologic histologic architectural pattern seen within certain tumors is the rosette. Although more advanced methods of tissue examination have been developed, such as histochemical and immunohistochemical profiling, genetic analysis, and electron microscopy, the microscopic review ofH&E stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin–eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diag ...
ed material remains a critical component of tumor diagnosis.
Immunohistochemical evidence of neuronal differentiation is found in nearly all cases with neuronal markers such as synaptophysin, neuronspecific enolase, and neurofilament protein. Some medulloblastomas may also display other forms of differentiation as demonstrated by the presence of the astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein. Skeletal muscle and melanocytic differentiation are considerably less common and define the medullomyoblastoma and melanotic medulloblastoma variants, respectively.
Long palisades
 Palisades that are generally longer than a rosette or pseudorosette can be seen in neural tumors such as
Palisades that are generally longer than a rosette or pseudorosette can be seen in neural tumors such as Schwannoma
A schwannoma (or neurilemmoma) is a usually benign nerve sheath tumor composed of Schwann cells, which normally produce the insulating myelin sheath covering peripheral nerves.
Schwannomas are homogeneous tumors, consisting only of Schwann cells ...
, as well as in ameloblastoma
Ameloblastoma is a rare, benign or cancerous tumor of odontogenic epithelium ( ameloblasts, or outside portion, of the teeth during development) much more commonly appearing in the lower jaw than the upper jaw. It was recognized in 1827 by Cusa ...
s. They can also be seen in nodular basal-cell carcinoma
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), also known as basal-cell cancer, basalioma, or rodent ulcer, is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a painless, raised area of skin, which may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it. ...
s.Initially copied from:
Visually similar findings
Pseudopalisading, a visually similar finding, is the formation of hypercellular zones that typically surroundsnecrotic
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who is ...
tissue.
glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nons ...
.
References
{{reflist Cellular processes