Ottawa is the
capital city
A capital city, or just capital, is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state (polity), state, province, department (administrative division), department, or other administrative division, subnational division, usually as its ...
of
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
. It is located in the
southern portion of the province of
Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, at the confluence of the
Ottawa River
The Ottawa River (, ) is a river in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. It is named after the Algonquin word "to trade", as it was the major trade route of Eastern Canada at the time. For most of its length, it defines the border betw ...
and the
Rideau River. Ottawa borders
Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core of the Ottawa–Gatineau
census metropolitan area
The census geographic units of Canada are the census subdivisions defined and used by Canada's federal government statistics bureau Statistics Canada to conduct the country's quinquennial census. These areas exist solely for the purposes of stat ...
(CMA) and the
National Capital Region (NCR). Ottawa had a city population of 1,017,449 and a metropolitan population of 1,488,307, making it the
fourth-largest city and
fourth-largest metropolitan area in Canada.
Ottawa is the political centre of Canada and the headquarters of the federal government. The city houses numerous
foreign embassies, key buildings, organizations, and institutions of
Canada's government; these include the
Parliament of Canada
The Parliament of Canada () is the Canadian federalism, federal legislature of Canada. The Monarchy of Canada, Crown, along with two chambers: the Senate of Canada, Senate and the House of Commons of Canada, House of Commons, form the Bicameral ...
, the
Supreme Court, the
residence of Canada's viceroy, and
Office of the Prime Minister.
Founded in 1826 as
Bytown, and
incorporated as Ottawa in 1855, its original boundaries were expanded through numerous annexations and were ultimately replaced by a new city incorporation and amalgamation in 2001. The
municipal government of Ottawa is established and governed by the City of Ottawa Act of the
Government of Ontario
The Government of Ontario () is the body responsible for the administration of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. The term ''Government of Ontario'' refers specifically to the executive—political Minister ...
. It has an elected city council across 24 wards and a mayor elected city-wide.
Ottawa has the highest proportion of university-educated residents among Canadian cities
and is home to several colleges and universities, research and cultural institutions, including the
University of Ottawa
The University of Ottawa (), often referred to as uOttawa or U of O, is a Official bilingualism in Canada, bilingual public research university in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is located on directly to the northeast of Downtown Ot ...
,
Carleton University,
Algonquin College,
Collège La Cité, the
National Arts Centre, the
National Gallery of Canada
The National Gallery of Canada (), located in the capital city of Ottawa, Ontario, is Canada's National museums of Canada, national art museum. The museum's building takes up , with of space used for exhibiting art. It is one of the List of large ...
; and
numerous national museums, monuments, and historic sites. It is one of the most visited cities in Canada, with over 11 million visitors annually.
Etymology
The city name ''Ottawa'' was chosen in 1855 in reference to the
Ottawa River
The Ottawa River (, ) is a river in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. It is named after the Algonquin word "to trade", as it was the major trade route of Eastern Canada at the time. For most of its length, it defines the border betw ...
, whose name is itself derived from the
Algonquin , meaning "to trade."
In modern Algonquin, the city is known as .
History
Early history

The
Ottawa Valley became habitable around 10,000 years ago, following the natural draining of the
Champlain Sea.
Archaeological findings of arrowheads, tools and pottery indicate that Indigenous populations first settled in the area about 6,500 years ago.
These findings suggest that these
Algonquin people were engaged in foraging, hunting and fishing, but also trade and travel. Three major rivers meet within Ottawa, making it an important trade and travel area for thousands of years.
The Algonquins are a broad Indigenous people who are closely related to the
Odawa and
Ojibwe
The Ojibwe (; Ojibwe writing systems#Ojibwe syllabics, syll.: ᐅᒋᐺ; plural: ''Ojibweg'' ᐅᒋᐺᒃ) are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland (''Ojibwewaki'' ᐅᒋᐺᐘᑭ) covers much of the Great Lakes region and the Great Plains, n ...
peoples. This period ended with the arrival of settlers and
colonization of North America by Europeans during and after the 15th century.
European exploration and early development
In 1610,
Étienne Brûlé became the first documented European to navigate the
Ottawa River
The Ottawa River (, ) is a river in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. It is named after the Algonquin word "to trade", as it was the major trade route of Eastern Canada at the time. For most of its length, it defines the border betw ...
, passing what would become Ottawa on his way to the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
. Three years later,
Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; 13 August 1574#Fichier]For a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see #Ritch, RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December ...
wrote about the waterfalls in the area and about his encounters with the Algonquin people.
The first non-Indigenous settlement in the area was created by
Philemon Wright, a
New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
er. Wright founded a lumber town in the area on 7 March 1800 on the north side of the river, across from the present-day city of Ottawa in
Hull. He, with five other families and twenty-five
labourers, also created an agricultural community, which was named
Wright's Town. Wright pioneered the
Ottawa Valley timber trade (soon to be the area's most significant economic activity) by transporting timber by river from the Ottawa Valley to
Quebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
.
In 1826, news of the British military's impending construction of the Rideau Canal led to land speculators founding a community on the south side of the Ottawa River. The following year, the town was named after British military engineer Colonel
John By who was responsible for the entire Rideau Waterway construction project. The Rideau canal provided a secure route between
Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
and
Kingston on Lake Ontario. It bypassed a vulnerable stretch of the St. Lawrence River bordering the state of New York that had left re-supply ships bound for southwestern Ontario easily exposed to enemy fire during the
War of 1812.
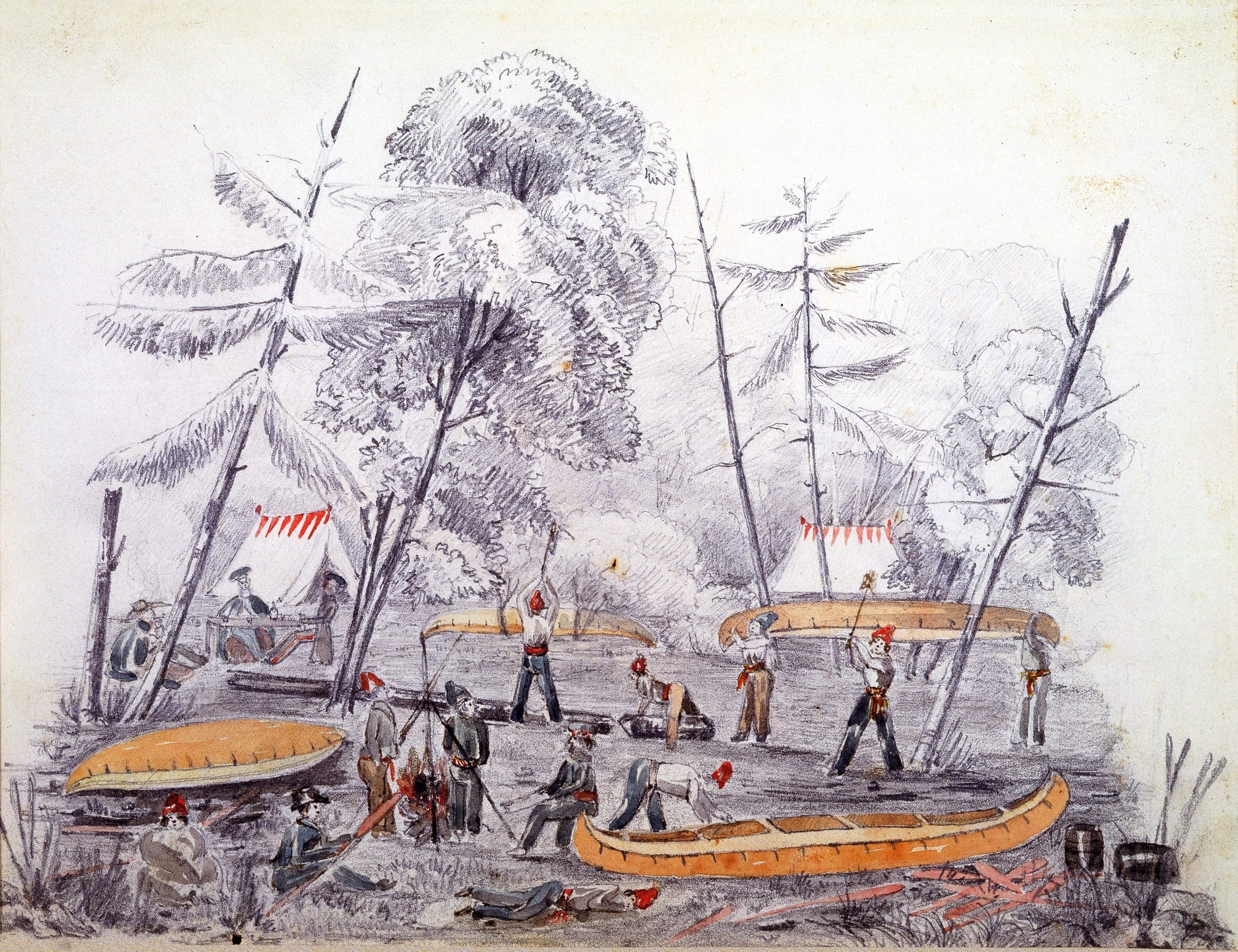

Colonel By set up military barracks on the site of today's
Parliament Hill. He also laid out the streets of the town and created two distinct neighbourhoods named "Upper Town" west of the canal and "
Lower Town" east of the canal. Similar to its
Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada () was a Province, part of The Canadas, British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the Province of Queb ...
and
Lower Canada namesakes, historically, "Upper Town" was predominantly English-speaking and Protestant, whereas "Lower Town" was mostly French, Irish and Catholic.
Bytown's population grew to 1,000 as the Rideau Canal was completed in 1832.
Bytown's early pioneer period saw Irish labour unrest during the
Shiners' War from 1835 to 1845
and political dissension that was evident in the 1849
Stony Monday Riot. In 1855, Bytown was renamed ''Ottawa'' and incorporated as a city.
was installed as the first city clerk, serving from 1844 to 1891, guiding Ottawa through 36 years of development, leading the hiring of key municipal roles, founding civic organizations, and proposing a set of by-laws for the city.
Selection as capital
The selection of Ottawa as the capital of Canada predates the Confederation of Canada. The choice was contentious and not straightforward, with the parliament of the
United Province of Canada holding more than 200 votes over several decades to attempt to settle on a legislative solution to the location of the capital.
The governor-general of the province had designated
Kingston as the capital in 1841. However, the major population centres of
Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a p ...
and
Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
, as well as the former capital of Lower Canada,
Quebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
, all had legislators dissatisfied with Kingston. Anglophone merchants in Quebec were the leading group supportive of the Kingston arrangement. In 1842, a vote rejected Kingston as the capital, and study of potential candidates included the then-named Bytown, but that option proved less popular than Toronto or Montreal. In 1843, a report of the Executive Council recommended Montreal as the capital as a more fortifiable location and commercial centre; however, the governor-general refused to execute a move without a parliamentary vote. In 1844, the
Queen
Queen most commonly refers to:
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a kingdom
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen (band), a British rock band
Queen or QUEEN may also refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Q ...
's acceptance of a parliamentary vote moved the capital to Montreal.
In 1849, after
violence in Montreal, a series of votes was held, with Kingston and Bytown again considered potential capitals. However, the successful proposal was for two cities to share capital status and the legislature to alternate sitting in each: Quebec City and Toronto, in a policy known as perambulation. Logistical difficulties made this an unpopular arrangement, and although an 1856 vote passed for the lower house of parliament to relocate permanently to Quebec City, the upper house refused to approve funding.
The funding impasse led to the ending of the legislature's role in determining the seat of government. The legislature requested the Queen determine the seat of government. The Queen then acted on the advice of her governor general
Edmund Head, who, after reviewing proposals from various cities, selected the recently renamed Ottawa. The Queen sent a letter to colonial authorities selecting Ottawa as the capital, effective 31 December 1857.
George Brown, briefly a co-premier of the Province of Canada, attempted to reverse this decision but was unsuccessful. The Parliament ratified the Queen's choice in 1859, with Quebec serving as interim capital from 1859 to 1865.
The relocation process began in 1865, with the first session of Parliament held in the new buildings in 1866. The buildings were generally well received by legislators.
Ottawa was chosen as the capital for two primary reasons.
First, Ottawa's isolated location, surrounded by dense forest far from the Canada–US border and situated on a cliff face, would make it more defensible from attack.
Second, Ottawa was on the border between
Canada West and
Canada East, making the selection an important political compromise.
Other minor considerations included that despite Ottawa's regional isolation, there was water transportation access from spring to fall, both to Montreal via the Ottawa River, and to Kingston via the
Rideau Waterway. Additionally, by 1854 it also had a modern all-season railway (the
Bytown and Prescott Railway) that carried passengers, lumber and supplies the 82 kilometres (50 miles) to
Prescott on the
Saint Lawrence River and beyond.
Ottawa's small size was also thought to be less prone to politically motivated mob violence, as had happened in the
previous Canadian capitals.
Finally, the government already owned the land that eventually became
Parliament Hill, which it thought would be an ideal location for the Parliament buildings.
The original Parliament buildings, which included the Centre, East and West Blocks, were constructed between 1859 and 1866 in the
Gothic Revival style. At the time, this was the largest North American construction project ever attempted and
Public Works Canada and its architects were not initially well prepared for the relatively shallow-lying bedrock and had to redesign architectural drawings, leading to delays. The
Library of Parliament and Parliament Hill landscaping were completed in 1876.
Post-Confederation

Starting in the 1850s, entrepreneurs known as lumber barons began to build large sawmills, which became some of the largest mills in the world.
Rail lines built in 1854 connected Ottawa to areas south and, from 1886 to the transcontinental rail network via Hull and
Lachute, Quebec. By 1885 Ottawa was the only city in Canada whose downtown street-lights were powered entirely by electricity. In 1889, the Government developed and distributed 60 "water leases" (still in use) to mainly local industrialists which gave them permission to generate electricity and operate hydroelectric generators at
Chaudière Falls. Public transportation began in 1870 with a
horsecar
A horsecar, horse-drawn tram, horse-drawn streetcar (U.S.), or horse-drawn railway (historical), is a tram or streetcar pulled by a horse.
Summary
The horse-drawn tram (horsecar) was an early form of public transport, public rail transport, ...
system, overtaken in the 1890s by a vast
electric streetcar system that operated until 1959.
The
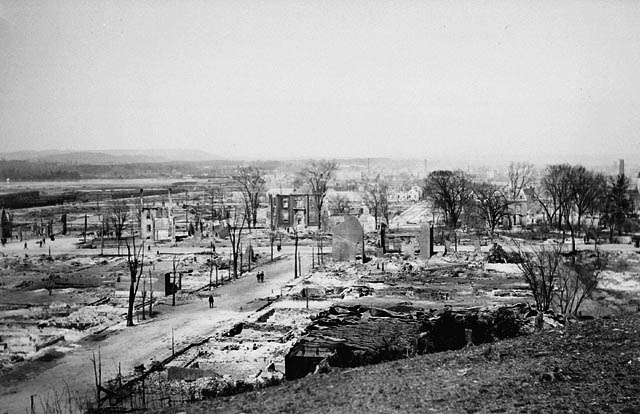
Hull–Ottawa fire of 1900 destroyed two-thirds of Hull, including 40 percent of its residential buildings and most of the buildings of its largest employers along the waterfront. It began as a chimney fire in Hull on the north side of the river, but due to wind, spread rapidly throughout the widespread wooden buildings. In Ottawa, it destroyed about one-fifth of the buildings from the Lebreton Flats south to Booth Street and down to
Dow's Lake. The fire had a disproportionate effect on west-end lower-income neighbourhoods. It had also spread among many lumber yards, a major part of Ottawa's economy. The fire destroyed approximately 3200 buildings and caused an estimated $300 million in damage (in 2020 Canadian dollars). An estimated 14% of Ottawans were left homeless.
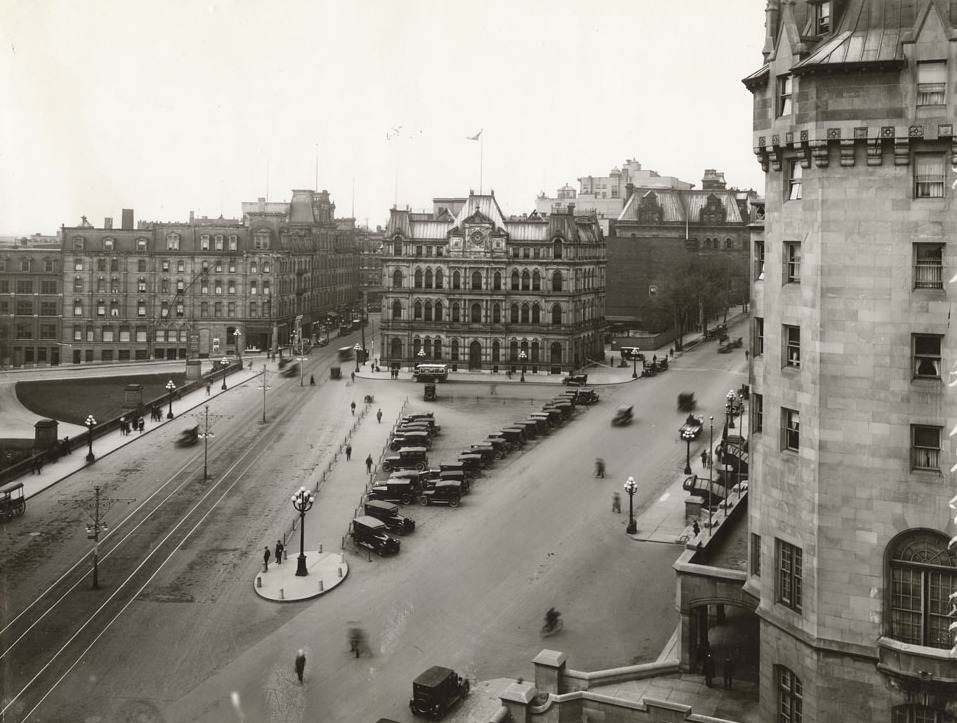

On 1 June 1912, the
Grand Trunk Railway
The Grand Trunk Railway (; ) was a Rail transport, railway system that operated in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario and in the List of states and territories of the United States, American sta ...
opened both the
Château Laurier hotel and its neighbouring downtown
Union Station. On 3 February 1916, the
Centre Block of the Parliament buildings was
destroyed by a fire. The House of Commons and Senate was temporarily relocated to the recently constructed Victoria Memorial Museum, now the
Canadian Museum of Nature until the completion of the new Centre Block in 1922. The centrepiece of the new
Parliament Buildings is a dominant Gothic Revival-styled structure known as the
Peace Tower.
The location of what is now
Confederation Square was a former commercial district centrally located in a triangular area downtown surrounded by historically significant heritage buildings, including the Parliament buildings. It was redeveloped as a ceremonial centre in 1938 as part of the
City Beautiful Movement. It became the site of the
National War Memorial in 1939 and was designated a
National Historic Site in 1984. A new
Central Post Office (now the
Privy Council of Canada) was constructed in 1939 beside the War Memorial because the original post office building on the proposed Confederation Square grounds had to be demolished.
Post–Second World War



Ottawa's former industrial appearance was vastly altered by the 1950
Greber Plan. Prime Minister
Mackenzie King hired French architect-planner
Jacques Greber to design an urban plan for managing development in the National Capital Region, to make it more aesthetically pleasing and a location more befitting for Canada's political centre.
Greber's plan included the creation of the
National Capital Greenbelt, the
Kichi Zibi Mikan and the
Queensway highway system. His plan also called for changes in institutions such as moving downtown Union Station (now the
Senate of Canada Building) to the suburbs, the removal of the street car system, the decentralization of selected government offices, the relocation of industries and removal of substandard housing from the downtown. The plan also recommended the creation of the Rideau Canal and Ottawa River pathways.
In 1958, the
National Capital Commission was established as a
Crown Corporation through the National Capital Act. The commission's original mission was to implement the Greber Plan recommendations conducted during the 1960s and 1970s. This marked the creation of a permanent political infrastructure for managing the
capital region. Prior attempts to do so in the previous 50 years had been temporary. These included plans from the 1899 Ottawa Improvement Commission (OIC), the Todd Plan in 1903, the Holt Report in 1915 and the Federal District Commission (FDC) established in 1927 with a 16-year mandate.
From 1931 to 1958, City Hall had been at the
Transportation Building adjacent to Union Station (now part of the
Rideau Centre). In 1958, a new
City Hall opened on Green Island near Rideau Falls, where urban renewal had recently transformed this industrial location into a green space. In 2001,
Ottawa City Hall returned downtown to a 1990 building on 110 Laurier Avenue West, the home of the now-defunct
Regional Municipality of Ottawa-Carleton. This new location was close to Ottawa's
first (1849–1877) and
second (1877–1931) City Halls. This new city hall complex also contained an adjacent 19th-century restored heritage building formerly known as the
Ottawa Normal School.
From the 1960s to the 1980s, there was a large increase in construction in the National Capital Region, which was followed by large growth in the
high-tech industry during the 1990s and 2000s.
Ottawa became one of Canada's largest high-tech cities and was nicknamed Silicon Valley North. By the 1980s, Bell Northern Research (later
Nortel) employed thousands, and large federally assisted research facilities such as the
National Research Council contributed to an eventual technology boom. The early companies led to newer firms such as
Newbridge Networks,
Mitel and
Corel.
In 1991, provincial and federal governments responded to a
land claim submitted by the Algonquins of Ontario regarding the unceded status of the land on which Ottawa is situated. Negotiations have been ongoing, with an eventual goal to sign a treaty that would release Canada from claims for misuse of land under Algonquin
title
A title is one or more words used before or after a person's name, in certain contexts. It may signify their generation, official position, military rank, professional or academic qualification, or nobility. In some languages, titles may be ins ...
, affirm rights of the Algonquins, and negotiate conditions of the title transfer.
Ottawa's city limits have expanded over time, including a large expansion effective 1 January 2001, when the province of
Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
amalgamated all the constituent municipalities of the
Regional Municipality of Ottawa–Carleton into a single city. Regional Chair
Bob Chiarelli was elected as the new city's first mayor in the
2000 municipal election, defeating
Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean ...
mayor Claudette Cain. The city's growth led to strains on the public transit system and road bridges. On 15 October 2001, a diesel-powered
light rail transit (LRT) line was introduced on an experimental basis. Known today as
O-Train Line 2, it was dubbed the O-Train and connected
downtown Ottawa to the southern suburbs via
Carleton University. The decision to extend the O-Train, and to replace it with an electric light rail system, was a major issue in the
2006 municipal elections, where Chiarelli was defeated by businessman
Larry O'Brien. After O'Brien's election, transit plans were changed to establish a series of light rail stations from the east side of the city into downtown, and for using a tunnel through the downtown core.
Jim Watson, the last mayor of Ottawa before amalgamation, was re-elected in the
2010 election.
In October 2012, the City Council approved the final
Lansdowne Park plan, an agreement with the
Ottawa Sports and Entertainment Group that saw a new stadium, increased green space and housing and retail added to the site. In December 2012, City Council voted unanimously to move forward with the
Confederation Line, a light rail transit line, which was opened on 14 September 2019.
Geography
Districts and neighbourhoods
The present-day city of Ottawa consists of the historic main
urban area
An urban area is a human settlement with a high population density and an infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas originate through urbanization, and researchers categorize them as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbani ...
, as well as other urban, suburban and
rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry are typically desc ...
areas within the city's post-amalgamation limits.
Old Ottawa
Old Ottawa refers to the former pre-amalgamation city, as well as the former city of
Vanier, a densely populated, historically francophone, working class enclave, and the former
village
A village is a human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban v ...
of
Rockcliffe Park, a wealthy residential neighbourhood adjacent to the Prime Minister's official residence at 24 Sussex and the Governor General's residence.
The old city includes the
downtown core and older neighbourhoods to the east, west, and south. These vibrant neighbourhoods include the bustling commercial and cultural areas of Old Ottawa South,
Centretown,
Lower Town, and
Sandy Hill, the affluent tree-lined neighbourhoods of
The Glebe,
Westboro, and
New Edinburgh, and the historically
blue-collar communities of
Hintonburg,
Mechanicsville,
Carlington, and
LeBreton Flats, with a mixture of housing types, artist lofts, and industrial uses. The old city also includes the
ethnic enclaves of
Chinatown and
Little Italy.
Suburbs and outlying communities
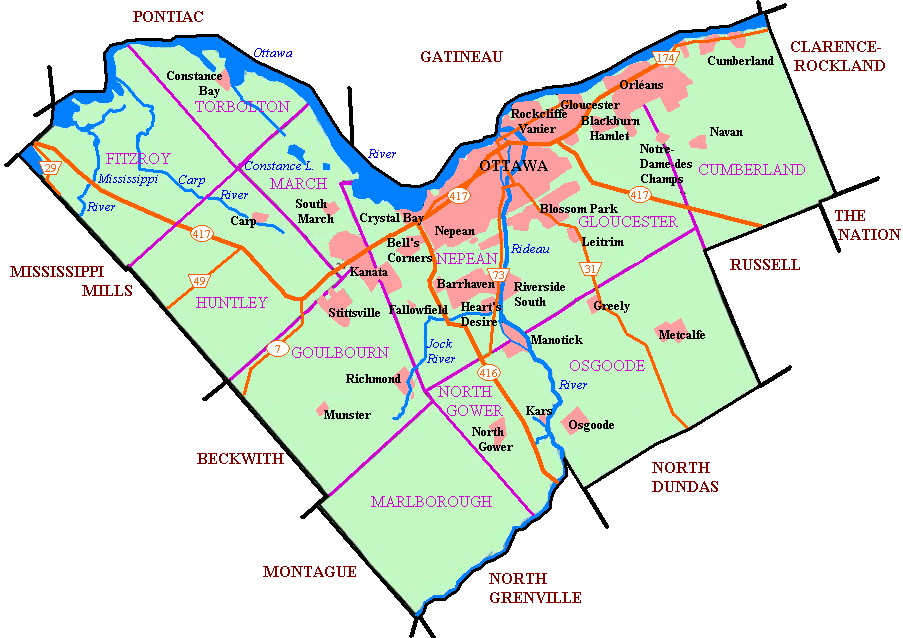
Modern Ottawa is made up of eleven historic townships, ten of which are from the former
Carleton County and one from the former
Russell County. Ottawa city limits are bounded on the east by the
United Counties of Prescott and Russell; by
Renfrew County and
Lanark County in the west; on the south by the
United Counties of Leeds and Grenville and the
United Counties of Stormont, Dundas and Glengarry; and on the north by the
Regional County Municipality of Les Collines-de-l'Outaouais and the City of Gatineau.
The main suburban areas extend a considerable distance to the east, west and south of the inner-city.
These areas also include the former cities of Cumberland, Gloucester (with the large suburban district of
Orleans outside the
greenbelt split between them),
Kanata, and Nepean. The towns of
Stittsville and
Richmond within the former
Goulbourn Township are to the southwest.
Nepean as a suburb also includes
Barrhaven.
The communities of
Manotick and
Riverside South are on the other side of the Rideau River, and
Greely, southeast of Riverside South.
A number of rural communities (villages and
hamlets
A hamlet is a human settlement that is smaller than a town or village. This is often simply an informal description of a smaller settlement or possibly a subdivision or satellite entity to a larger settlement. Sometimes a hamlet is defined f ...
) are also part of the City of Ottawa.
Some of these communities are
Burritts Rapids;
Ashton;
Fallowfield;
Kars;
Fitzroy Harbour;
Munster;
Carp
The term carp (: carp) is a generic common name for numerous species of freshwater fish from the family (biology), family Cyprinidae, a very large clade of ray-finned fish mostly native to Eurasia. While carp are prized game fish, quarries and a ...
;
North Gower;
Metcalfe;
Constance Bay and
Osgoode.
Several
town
A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city.
The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative stat ...
s are within the federally defined National Capital Region but outside of Ottawa's municipal boundaries;
these include communities of
Almonte,
Carleton Place,
Embrun,
Kemptville,
Rockland, and
Russell.
Architecture
Influenced by government structures, much of the city's architecture tends to be formal and
functional; the city is also marked by
Romantic and
Picturesque styles of architecture such as the Parliament Buildings' gothic revival architecture.
Ottawa's domestic architecture contains single-family homes, but also includes smaller numbers of
semi-detached
A semi-detached house (often abbreviated to semi) is a single-family Duplex (building), duplex dwelling that shares one common party wall, wall with its neighbour. The name distinguishes this style of construction from detached houses, with no sh ...
houses,
rowhouses, and
apartment buildings. Many domestic buildings in Centretown are clad in red brick, with trim in wood, stone, or metal; variations are common, depending on the cultural heritage of the neighbourhoods and the time they were built.
The
skyline
A skyline is the wikt:outline, outline or shape viewed near the horizon. It can be created by a city's overall structure, or by human intervention in a rural area, rural setting, or in nature that is formed where the sky meets buildings or the ...
has been controlled by building height restrictions originally implemented to keep Parliament Hill and the Peace Tower at visible from most parts of the city. Today,
several buildings are slightly taller than the Peace Tower, with the tallest being the
Claridge Icon at . Many federal buildings in the National Capital Region are managed by
Public Works Canada, which leads to
heritage conservation in its renovations and management of buildings, such as the renovation of the
Senate Building. Most of the federal land in the region is managed by the National Capital Commission; its control of much undeveloped land and appropriations powers gives the NCC a great deal of influence over the city's development.
Climate
Ottawa has a
warm-summer humid continental climate (
Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author ...
: ''Dfb'',
Trewartha ''Dcbo/Dcbc'') with four distinct seasons and is between Zones 5a and 5b on the Canadian Plant Hardiness Scale. The average July maximum temperature is . The average January minimum temperature is .
The highest temperature ever recorded in Ottawa was on 4 July 1913, 1 August 1917 and 11 August 1944.
Summers are generally warm and humid in Ottawa. On average, there are 13.4 days across the three summer months of June, July and August that have temperatures exceeding .
Periods of hotter weather are normally accompanied by high humidity levels.
Snow and ice are dominant during the winter season. On average, almost every day of January, February and March has more than 5 cm of snowpack (29, 28, and 23 days, respectively), and on average, approximately 13 days a year see 5 cm or more of snowfall, with 5 of those having over 10 cm.
An average of 15 days of the year experience temperatures below .
Spring and fall are variable, prone to extreme changes in temperature and conditions. The month of May, for example, on average gets a day below freezing at night every other year, conversely a day surpassing 30 °C
Annual rainfall averages around 772mm per year, total precipitation 938mm
spread throughout the year, with some variation. May through November are the months more likely to see significant precipitation events, with each month having an average of 3 days of over 10 mm of precipitation, with December through April seeing on average 1–2 days. May through November have, on average, over 80 mm of rainfall per month, with peaks of approximately 90 mm in June and July. December through April have less than 80 mm, with February being the driest month at an average of 5 cm of precipitation.
Ottawa experiences about 2,080 hours of average sunshine annually (45% of possible).
Predominate wind direction in Ottawa is from the
West, Easterly air flow is more common during periods of wet weather as well as localized river/lake-effect
cells on summer afternoons.
Windspeed is on average higher during the winter, with northerly winds predominating during cold waves.
Physical geography

Ottawa is situated on the south bank of the Ottawa River and contains the mouths of the
Rideau River and
Rideau Canal.
The Rideau Canal (Rideau Waterway) first opened in 1832 and is long. It connects the Saint Lawrence River on Lake Ontario at Kingston to the Ottawa River near Parliament Hill. It was able to bypass the unnavigable sections of the
Cataraqui and Rideau rivers and various small lakes along the waterway due to flooding techniques and the construction of 47 water transport
locks.
Ottawa is situated in a lowland on top of
Paleozoic carbonate and shale and is surrounded by more craggy
Precambrian igneous and metamorphic formations. Ottawa has had fluvial
deposition of
till and sands, leading to the widespread formation of
eskers. There are limited distinct features arising from glacial deposits, but Ottawa was affected by the
Late Wisconsian advance. Before the draining of the Champlain Sea, the area had high salinity. After the draining of the sea, the area had pine-dominated forests. Ottawa is located within the
Western Quebec Seismic Zone, and while relatively inactive, the city does occasionally experience earthquakes.
Built environment
During part of the winter season the Ottawa section of the canal forms the world's largest skating rink, thereby providing both a recreational venue and a transportation path to downtown for ice skaters (from Carleton University and Dow's Lake to the Rideau Centre and
National Arts Centre). On 29 June 2007, the Rideau Canal was recognized as a
UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The older part of the city (including what remains of Bytown) is known as
Lower Town, and occupies an area between the canal and the rivers. Across the canal to the west lie both
Centretown and
Downtown Ottawa, which share a border along Gloucester Street. These core neighbourhoods contain streets such as
Elgin and
Bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital m ...
, which fill the role of commercial
main streets in the region.
Centretown is next to downtown, which includes a substantial economic and architectural government presence across multiple branches of government. The
legislature
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial power ...
's work takes place in the parliamentary precinct, which includes buildings on
Parliament Hill and others downtown, such as the
Senate of Canada Building. Important buildings in the executive branch include the
Office of the Prime Minister and Privy Council as well as many civil service buildings. The
Supreme Court of Canada building can also be found in this area.
Across the Ottawa River, which forms the border between Ontario and
Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, lies the city of
Gatineau
Gatineau ( ; ) is a city in southwestern Quebec, Canada. It is located on the northern bank of the Ottawa River, directly across from Ottawa, Ontario. Gatineau is the largest city in the Outaouais administrative region of Quebec and is also p ...
, itself the result of amalgamation of the former Quebec cities of
Hull and
Aylmer.
Although formally and administratively separate cities in two different provinces, Ottawa and Gatineau (along with several nearby municipalities) collectively constitute the
National Capital Region, which is considered a single metropolitan area.
One federal
Crown corporation, the National Capital Commission, or NCC, has significant land holdings in both cities, including sites of historical and touristic importance.
The NCC, through its responsibility for planning and development of these lands, has a crucial role in shaping the development of the city. Around the main urban area is an extensive
greenbelt, administered by the NCC for conservation and leisure, and comprising mostly forest, farmland and marshland.
Demographics

In the
2021 Census of Population conducted by
Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; ), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in ...
, Ottawa had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021.
As of 2021 the Ottawa-Gatineau
census metropolitan area
The census geographic units of Canada are the census subdivisions defined and used by Canada's federal government statistics bureau Statistics Canada to conduct the country's quinquennial census. These areas exist solely for the purposes of stat ...
(CMA) had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021.
Ottawa's median age of 40.1 is below the provincial and national averages as of 2016. Youths under 15 constituted 16.7% of the total population in 2016, while those of retirement age (65 years and older) made up 15.4%.
The
2021 census reported that
immigrants (individuals born outside Canada) comprise 259,215 persons or 25.9% of the total population of Ottawa. Of the total immigrant population, the top countries of origin were
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
(20,320 persons or 7.8%),
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
(16,200 persons or 6.2%),
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
(14,760 persons or 5.7%),
Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
(11,900 persons or 4.6%),
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
(10,505 persons or 4.1%),
United States of America
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguo ...
(8,795 persons or 3.4%),
Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
(6,710 persons or 2.6%),
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
(6,370 persons or 2.5%),
Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
(6,155 persons or 2.4%), and
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
(6,000 persons or 2.3%).
Race and ethnicity
As of 2021, approximately 64.9% of Ottawa's population were white or European, while 2.6% were
Indigenous, and 32.5% were visible minorities (higher than the national percentage of 26.5%).
Religion
According to the
2021 census, religious groups in Ottawa included:
*
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
(528,700 persons or 52.8%)
*
Irreligion
Irreligion is the absence or rejection of religious beliefs or practices. It encompasses a wide range of viewpoints drawn from various philosophical and intellectual perspectives, including atheism, agnosticism, religious skepticism, ...
(316,740 persons or 31.6%)
*
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
(98,920 persons or 9.9%)
*
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
(20,300 persons or 2.0%)
*
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
(10,800 persons or 1.1%)
*
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
(10,600 persons or 1.1%)
*
Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
(6,375 persons or 0.6%)
*
Indigenous Spirituality (445 persons or <0.1%)
* Other (8,055 persons or 0.8%)
, around 65% of Ottawa residents described themselves as Christian, with
Catholics accounting for 38.5% of the population and members of
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
churches 25%. Other religions were also present in Ottawa, the most prominent being
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
(6.7%),
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
(1.4%),
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
(1.3%), and
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
(1.2%). Those with no religious affiliation represented 22.8%.
Language
Bilingualism became official policy for the conduct of municipal business in 2002, and 37.6% of the population can speak both languages as of 2016, making it the largest city in Canada with both English and French as co-official languages.
Those who identify their mother tongue as
English constitute 62.4 percent, while those with
French as their mother tongue make up 14.2 percent of the population. Regarding respondents' knowledge of one or both official languages, 59.9 percent and 1.5 percent of the population know English and French only, respectively, while 37.2 percent know both official languages. The overall Ottawa–Gatineau census metropolitan area (CMA) has a larger proportion of French speakers than Ottawa since Gatineau's population's first language is mostly French. However, Gatineau is also the most bilingual city in Canada, making the region one of the most bilingual. An additional 20.4 percent of the population list languages other than English and French as their mother tongue. These include
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
(3.2%),
Chinese (3.0%),
Spanish (1.2%),
Italian (1.1%), and many others.
Economy

As of 2015, the region of Ottawa-Gatineau has the sixth-highest total household income of all Canadian metropolitan areas ($82,053), and the Ontario portion more directly overlapping the City of Ottawa has a higher household income ($86,451). The median household income after taxes in the City of Ottawa is $73,745 in 2016 was higher than the national median of $61,348.
Ottawa's unemployment rate has remained below the national and provincial unemployment rates since 2006, with a rate of 5.2% in April 2022, low compared to the decade preceding. In 2019
Mercer ranks Ottawa with the third highest quality of living of any Canadian city, and 19th highest in the world. It is also rated the second cleanest city in Canada, and third cleanest city in the world.
Ottawa's primary employers are the
Public Service of Canada and the high-tech industry, although tourism and healthcare also represent increasingly sizeable economic activities. The federal government is the city's largest employer, employing over 116,000 individuals from the National Capital Region.
The national headquarters for many federal departments are in Ottawa, particularly throughout Centretown and in the
Terrasses de la Chaudière and
Place du Portage complexes in Hull. The
National Defence Headquarters in Ottawa is the main command centre for the
Canadian Armed Forces
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; , FAC) are the unified Military, military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air commands referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army and the Royal Canadian Air Force. Under the ''National Defenc ...
. It hosts the
Department of National Defence. During the summer, the city hosts the
Ceremonial Guard, which performs functions such as the
Changing the Guard.
As Canada's national capital, tourism is an important part of Ottawa's economy, particularly after the
150th anniversary of Canada, centred in Ottawa. The lead-up to the festivities saw much investment in civic infrastructure, upgrades to tourist infrastructure and increases in national cultural attractions. The National Capital Region annually attracts an estimated 22 million tourists, who spend about 2.2 billion dollars and support 30,600 jobs directly.

In addition to the economic activities that come with being the national capital, Ottawa is an important technology centre; in 2015, its 1800 companies employed approximately 63,400 people. The concentration of companies in this industry earned the city the nickname of "Silicon Valley North."
Most of these companies specialize in
telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
,
software development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, wri ...
and
environmental technology. Large technology companies such as Nortel, Corel,
Mitel,
Cognos,
Halogen Software,
Shopify and
JDS Uniphase were founded in the city.
Ottawa also has regional locations for
Nokia
Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporation, originally established as a pulp mill in 1 ...
,
3M,
Adobe Systems
Adobe Inc. ( ), formerly Adobe Systems Incorporated, is an American software, computer software company based in San Jose, California. It offers a wide range of programs from web design tools, photo manipulation and vector creation, through to ...
,
Bell Canada,
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
and
Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company. It was founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in 1939 in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California ...
.
Many of the telecommunications and new technology are in the western part of the city (formerly Kanata). The "tech sector" was doing particularly well in 2015/2016.
,
i-Stat and the National Research Council of Canada and
OHRI are part of the growing life science sector.
The health sector is another major employer, which employs over 18,000 people in the city. Business, finance, administration, and sales and service rank high among types of occupations.
Approximately ten percent of Ottawa's GDP is derived from finance, insurance and real estate whereas employment in goods-producing industries is only half the national average.
The City of Ottawa is the second largest employer
with approximately 2,100 people employed by the Ottawa Police service, and 13,300 full-time equivalent non-police employees.
In 2016, Ottawa experienced an increase of 10,000 jobs over the 2012 average growth, which was relatively slower than in the late 1990s.
All major clusters tracked by the city saw increases in employment between 2014 and 2019.
Major areas of growth in the 2010s included local and federal administration, finance and accommodation.
Between 2008 and 2020, there was growth in the number of government employees and a reduction in high-tech jobs, a reversal of previous trends from 2003 to 2008.
Ottawa already has the largest rural economy among Canada's major cities.
In Ottawa, the rural economy contributes over $1 billion to the GDP. Agriculture alone accounts for $400 million, $136.7 million of which is farm-gate sales. Rural economic activity includes agriculture, retail sales, construction, forestry and mining (aggregates), tourism, manufacturing, personal and business services, and transportation, to name a few. Rural employment expanded by a healthy 18% from 1996 to 2001.
Media
Three main daily local newspapers are printed in Ottawa: two English newspapers, the ''
Ottawa Citizen'' established as ''the Bytown Packet'' in 1845 and the ''
Ottawa Sun
The ''Ottawa Sun'' is a daily newspaper in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It is published by Sun Media. It began publication in 1983 as the ''Ottawa Sunday Herald'', until it was acquired by (then) Toronto Sun Publishing Corporation in 1988. In April 2 ...
'', and one French newspaper, ''
Le Droit''. The city is also home to local stations of the television broadcast networks and systems
CBC and
CTV, as well as English and French radio stations.
In addition to the market's local media services, Ottawa is home to several national media operations, including
CPAC (Canada's national legislature broadcaster) and the parliamentary bureau staff of virtually all of Canada's major newsgathering organizations in television, radio and print. The city is also home to the head office of the
Canadian Broadcasting Corporation
The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (), branded as CBC/Radio-Canada, is the Canadian Public broadcasting, public broadcaster for both radio and television. It is a Crown corporation that serves as the national public broadcaster, with its E ...
.
Education


Primary and secondary education
Ottawa has four main public school boards: English, English-Catholic, French, and French-Catholic. The English-language
Ottawa-Carleton District School Board (OCDSB) is the largest board with 147 schools, followed by the English-Catholic
Ottawa Catholic School Board with 85 schools. The two French-language boards are the French-Catholic ''
Conseil des écoles catholiques du Centre-Est'' with 49 schools, and the French ''
Conseil des écoles publiques de l'Est de l'Ontario'' with 37 schools. Ottawa also has numerous
private school
A private school or independent school is a school not administered or funded by the government, unlike a State school, public school. Private schools are schools that are not dependent upon national or local government to finance their fina ...
s which are not part of a board.
The
Ottawa Public Library was created in 1906 as part of the
Carnegie library system. the library system had 2.3 million items at its 34 branches and two mobile libraries. Approximately 9.5 million loans were conducted in 2020, approximately 6.7 million physical loans and the remainder digital items.
Higher education and research
Ottawa is known as the most educated city in Canada, with over half the population having graduated from college and/or university. Ottawa has the highest per capita concentration of
engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, build, maintain and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials. They aim to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while ...
s,
scientist
A scientist is a person who Scientific method, researches to advance knowledge in an Branches of science, area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engag ...
s, and residents with
PhDs in Canada. The city has two main public universities and two main public colleges.
*
Carleton University was founded in 1942 to meet the needs of returning World War II veterans and later became Ontario's first private, non-denominational college. Over time, Carleton transitioned into the highly ranked comprehensive university it is today. The university's main campus sits between
Old Ottawa South and Dow's Lake. Carleton's catholic
affiliated university college, is the Dominican University College.
* The
University of Ottawa
The University of Ottawa (), often referred to as uOttawa or U of O, is a Official bilingualism in Canada, bilingual public research university in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is located on directly to the northeast of Downtown Ot ...
(originally named the "College of Bytown") was the first post-secondary institution established in the city in 1848. The university later grew to become the largest English-French bilingual university in the world.
It is also a member of the
U15, a group of highly respected research-intensive universities in Canada. The university's main campus is in the
Sandy Hill neighbourhood, just adjacent to the city's downtown core. The University of Ottawa's catholic
affiliated university college is
St. Paul University.
*
Algonquin College is a college of applied arts and technology founded in 1967. Its main campus is located in the
City View neighbourhood of
College Ward. The college serves the
National Capital Region and the outlying areas of
Eastern Ontario, Western
Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, and
Upstate New York. The college has satellite campuses in
Pembroke and
Perth
Perth () is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of Western Australia. It is the list of cities in Australia by population, fourth-most-populous city in Australia, with a population of over 2.3 million within Greater Perth . The ...
, as well as four international campuses through their international offshore partnerships.
*
Collège La Cité is the largest French-language college in Ontario. Founded in 1989, its campus is located off the
Aviation Parkway in the
Carson Meadows neighbourhood. La Cité has a satellite campus in
Hawkesbury and a business office in
Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a p ...
.
Other colleges and universities in the metropolitan area are located in the neighbouring suburb of Gatineau, including the
University of Quebec in Outaouais,
Cégep de l'Outaouais, and
Heritage College.
Public health
There are six active general medical hospitals in the city of Ottawa: The
Queensway Carleton Hospital,
The Ottawa Hospital (
Civic Hospital,
General Hospital
''General Hospital'' (often abbreviated as ''GH'') is an American daytime television soap opera created by Frank and Doris Hursley which has been broadcast on American Broadcasting Company, ABC since April 1, 1963. Originally a half-hour seria ...
,
Riverside Hospital),
Montfort Hospital, and
Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario. Several specialized hospital facilities are also present, such as the world-renowned
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the
Royal Ottawa Mental Health Centre, and Élisabeth Bruyère Hospital. There are also several hospitals and major medical centres in neighbouring suburban communities and commuter towns. The
University of Ottawa Faculty of Medicine operates
teaching hospitals in conjunction with partners throughout the city.
Ottawa is the headquarters of numerous major medical organizations and institutions such as
Canadian Red Cross,
Canadian Blood Services,
Health Canada
Health Canada (HC; )Health Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Health (). is the Structure of the Canadian federal government#Departments, with subsidiary units, department of the Gove ...
,
Canadian Medical Association,
Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada,
Canadian Nurses Association, and the
Medical Council of Canada.
Culture and contemporary life

Traditionally, the
ByWard Market (in Lower Town), Parliament Hill and the
Golden Triangle (both in Centretown – Downtown) have been the focal points of the cultural scenes in Ottawa. Modern thoroughfares such as
Wellington Street,
Rideau Street,
Sussex Drive
Sussex Drive (), also known as Ottawa Regional Road93, is an arterial road in Ottawa, Ontario, the capital of Canada. It is one of the city's main ceremonial and institutional routes. Travelling roughly parallel to the Ottawa River, Sussex Drive ...
,
Elgin Street,
Bank Street,
Somerset Street,
Preston Street, Richmond Road in
Westboro, and
Sparks Street are home to many boutiques, museums, theatres, galleries, landmarks and memorials in addition to eating establishments, cafes, bars and nightclubs.
As Canada's capital, Ottawa has played host to many significant cultural events in
Canadian history, including the first visit of the reigning
Canadian sovereign—
King George VI, with
his consort,
Queen Elizabeth—
to his parliament, on 19 May 1939.
was marked with a large celebration on 8 May 1945,
the first raising of
the country's new national flag took place on 15 February 1965,
and the
centennial of Confederation was celebrated on 1 July 1967.
Queen
Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
was in Ottawa on 17 April 1982, to issue a
royal proclamation of the enactment of the
Constitution Act.
In 1983,
Prince Charles and
Diana Princess of Wales came to Ottawa for a state dinner hosted by then Prime Minister
Pierre Trudeau. In 2011, Ottawa was selected as the first city to receive
Prince William, Duke of Cambridge, and
Catherine, Duchess of Cambridge during their
tour of Canada.
Ottawa was featured in the short story collection ''
For Your Eyes Only'', by
Ian Fleming.

Landmarks
There is one
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
in Ottawa, the
Rideau Canal, along with 25
National Historic Sites of Canada in Ottawa, including the Château Laurier, the
Parliament of Canada
The Parliament of Canada () is the Canadian federalism, federal legislature of Canada. The Monarchy of Canada, Crown, along with two chambers: the Senate of Canada, Senate and the House of Commons of Canada, House of Commons, form the Bicameral ...
, Confederation Square, the former Ottawa Teachers' College and
Laurier House. Many other properties of cultural value have been designated as having "heritage elements" by the City of Ottawa under Part IV of the ''
Ontario Heritage Act''.
Arts

Performing and visual arts
The
Ottawa Little Theatre, founded in 1913 as the Ottawa Drama League, is Ottawa's longest-running community theatre company. Since 1969, Ottawa has been the home of the National Arts Centre, a major performing arts venue that houses four stages and is home to the
National Arts Centre Orchestra, the
Ottawa Symphony Orchestra and
Opera Lyra Ottawa.
Established in 1975, the
Great Canadian Theatre Company specializes in the production of Canadian plays at a local level. The cities museum landscape is notable for containing six of Canada's nine national museums, the
Canada Agriculture and Food Museum, the
Canada Aviation and Space Museum
The Canada Aviation and Space Museum () (formerly the Canada Aviation Museum (''Musée de l'aviation du Canada'') and National Aeronautical Collection (''Collection aéronautique nationale'')) is Canada's national aviation history museum. The m ...
, the
Canada Science and Technology Museum, Canadian Museum of Nature,
Canadian War Museum
The Canadian War Museum (CWM) () is a National museums of Canada, national museum on the military history of Canada, country's military history in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The museum serves as both an educational facility on Canadian military hist ...
and National Gallery of Canada. The
National Gallery of Canada
The National Gallery of Canada (), located in the capital city of Ottawa, Ontario, is Canada's National museums of Canada, national art museum. The museum's building takes up , with of space used for exhibiting art. It is one of the List of large ...
; designed by famous architect
Moshe Safdie, it is a permanent home to the
''Maman'' sculpture. The
Canadian War Museum
The Canadian War Museum (CWM) () is a National museums of Canada, national museum on the military history of Canada, country's military history in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The museum serves as both an educational facility on Canadian military hist ...
houses over 3.75 million artifacts and was moved to an expanded facility in 2005. The Canadian Museum of Nature was built in 1905, and underwent a major renovation between 2004 and 2010, leading to a centrepiece Blue Whale skeleton, and the creation of a monthly nightclub experience, ''Nature Nocturne''.
Cuisine
Ottawa is home to several regional dishes. As a city with traditional French-Canadian roots, staples such as
poutine are served throughout the city. However, many consider
shawarma Ottawa's official dish;
the city contains more shawarma restaurants than anywhere else in Canada.
The city is also home to "Ottawa-style"
pizza, consisting usually of a thicker doughy crust and slightly spicy pizza sauce, with the toppings baked under a heavy layer of cheese, keeping the toppings soft.
, a fried dough pastry, were first created in Ottawa in the 1970s.
Le Cordon Bleu has a long-established culinary arts institute in the central Ottawa neighbourhood of Sandy Hill, the only Le Cordon Bleu campus in North America.
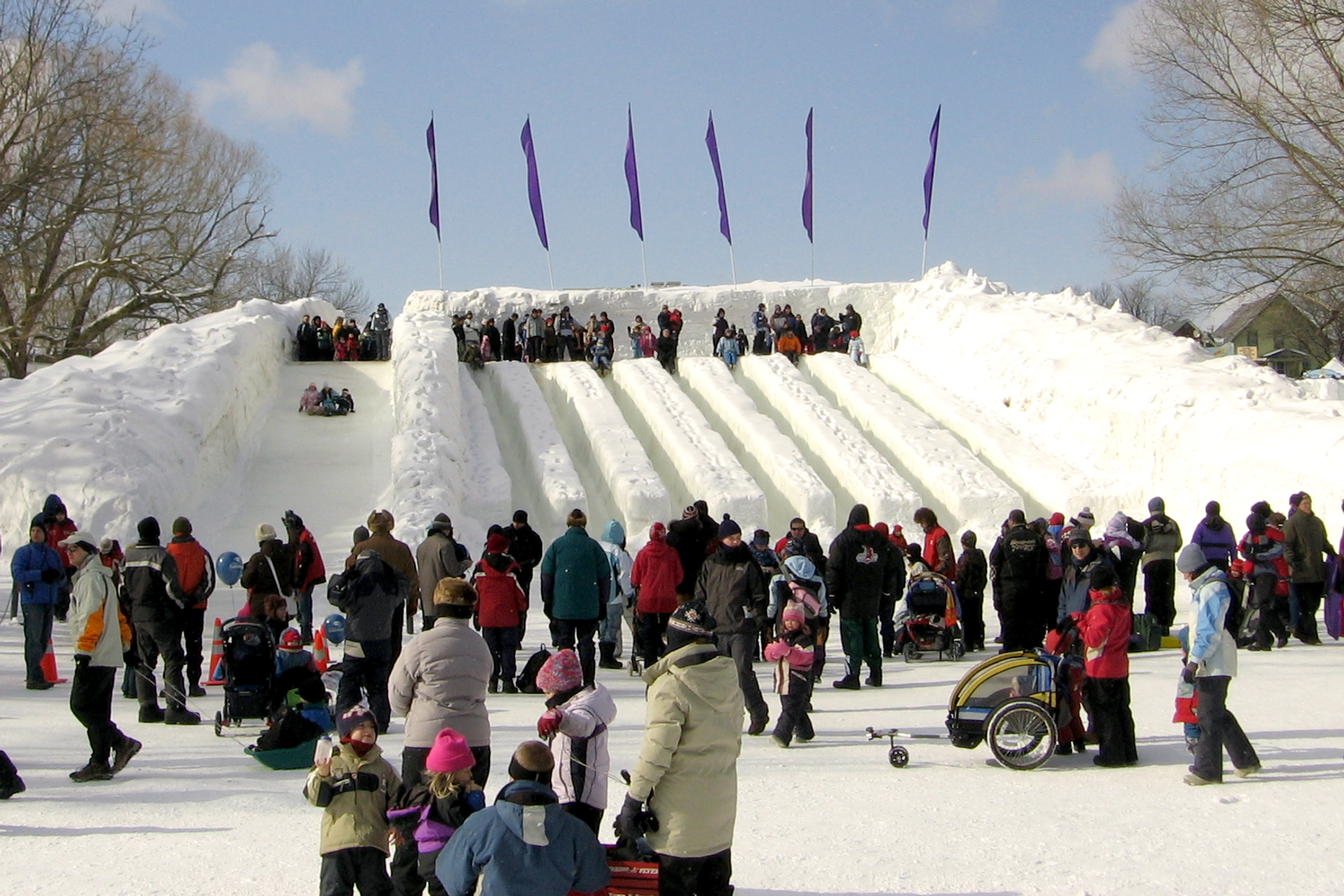

Festivals
Ottawa hosts a variety of annual seasonal activities—such as
Winterlude, the largest festival in Canada, and
Canada Day celebrations on Parliament Hill and surrounding downtown area, as well as
Bluesfest,
Canadian Tulip Festival,
Ottawa Dragon Boat Festival,
Ottawa International Jazz Festival,
Fringe Festival,
Capital Pride, and
CityFolk Festival, that have grown to become some of the largest festivals of their kind in the world. In 2010, Ottawa's Festival industry received the
IFEA "World Festival and Event City Award" for the category of North American cities with a population between 500,000 and 1,000,000.
Sports

Professional sports
Sport in Ottawa has a history dating back to the 19th century. The city is currently home to six professional sports teams. The
Ottawa Senators are a professional ice hockey team playing in the
National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; , ''LNH'') is a professional ice hockey league in North America composed of 32 teams25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. The NHL is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Cana ...
. The Senators history in Ottawa dates back to 1883; the franchise would go on to win the
Stanley Cup
The Stanley Cup () is the championship trophy awarded annually to the National Hockey League (NHL) playoff champion. It is the oldest existing trophy to be awarded to a professional sports franchise in North America, and the International Ic ...
eleven times by 1927. The team is currently a member of the Atlantic Division and play their home games at the
Canadian Tire Centre.
In 2023, the
Ottawa Charge became one of the six charter franchises of the
Professional Women's Hockey League
The Professional Women's Hockey League (PWHL; , LPHF) is a women's professional ice hockey league in North America. The league comprises eight teams, four each from the United States and Canada. The teams play a Season (sports), regular season ...
(PWHL). The Charge play home games at
TD Place Arena.
The
Ottawa Redblacks are a professional Canadian Football team playing in the
Canadian Football League
The Canadian Football League (CFL; , LCF) is a Professional gridiron football, professional Canadian football league in Canada. It comprises nine teams divided into two divisions, with four teams in the East Division (CFL), East Division and f ...
.
Formerly the
Ottawa Rough Riders represented the city until 1996. With a history dating back to 1876, the team was one of the oldest and longest-lived professional sports teams in North America. The professional soccer club,
Atlético Ottawa, plays in the
Canadian Premier League. The team was founded in by Spanish club
Atlético Madrid, and along with the Redblacks, play their home games at
TD Place Stadium.
Ottawa Rapid FC of the
Northern Super League also play at TD Place Stadium. The
Ottawa Black Bears, founded in 2024, compete in the
National Lacrosse League
The National Lacrosse League (NLL) is a professional box lacrosse league in North America. The league comprises 14 teams8 in the United States and 6 in Canada. The NLL is headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
...
and play at the
Canadian Tire Centre in
Kanata. The
Ottawa Blackjacks are a professional basketball team, playing in the
Canadian Elite Basketball League, out of the TD Place Arena. The
Ottawa Titans play professional baseball in the
Frontier League at
Raymond Chabot Grant Thornton Park. Ottawa was previously home to the
Ottawa Lynx, a
Triple-A club, as well as the
Ottawa Champions, an independent baseball team in the
Can-Am League.
Collegiate sports
The University of Ottawa and Carleton University
varsity teams compete in
U Sports in various sports. Algonquin College and Collège La Cité teams compete in the
OCAA.
The
Carleton Ravens are nationally ranked in
basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
and soccer.
Carleton's men's basketball program is regarded as the greatest of all time, having won 17 of the last 20
national championships.
The
Ottawa Gee-Gees are nationally ranked in basketball and soccer.
Non-professional and amateur sports
Several non-professional teams also play in Ottawa, including the
Ottawa 67's junior ice hockey team.
The city is home to an assortment of amateur organized team sports such as
soccer
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 Football player, players who almost exclusively use their feet to propel a Ball (association football), ball around a rectangular f ...
,
basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
,
baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball sport played between two team sport, teams of nine players each, taking turns batting (baseball), batting and Fielding (baseball), fielding. The game occurs over the course of several Pitch ...
,
curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide #Curling stone, stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area that is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take t ...
,
rowing,
ultimate, and
horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance activity, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its bas ...
.
Casual recreational activities, such as
skating,
cycling
Cycling, also known as bicycling or biking, is the activity of riding a bicycle or other types of pedal-driven human-powered vehicles such as balance bikes, unicycles, tricycles, and quadricycles. Cycling is practised around the world fo ...
,
tennis
Tennis is a List of racket sports, racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent (singles (tennis), singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles (tennis), doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket st ...
,
hiking,
sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sa ...
,
golfing,
skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow for basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IOC), and the International S ...
, and
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
/
ice fishing are also popular.
[
Starting in 2025 a new Ironman Triathlon will be starting in Ottawa.
]
Government and politics
The City of Ottawa is a single-tier municipality, meaning it is in itself a census division
Census divisions, in Canada and the United States, are areas delineated for the purposes of statistical analysis and presentation; they have no government in and of themselves. The census divisions of Canada are second-level census geographic uni ...
and has no county or regional municipality government above it, and has no subsidiary municipalities to provide municipal services.Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world.
The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left. For example, while the political systems ...
in federal elections.
Transportation
Public transportation
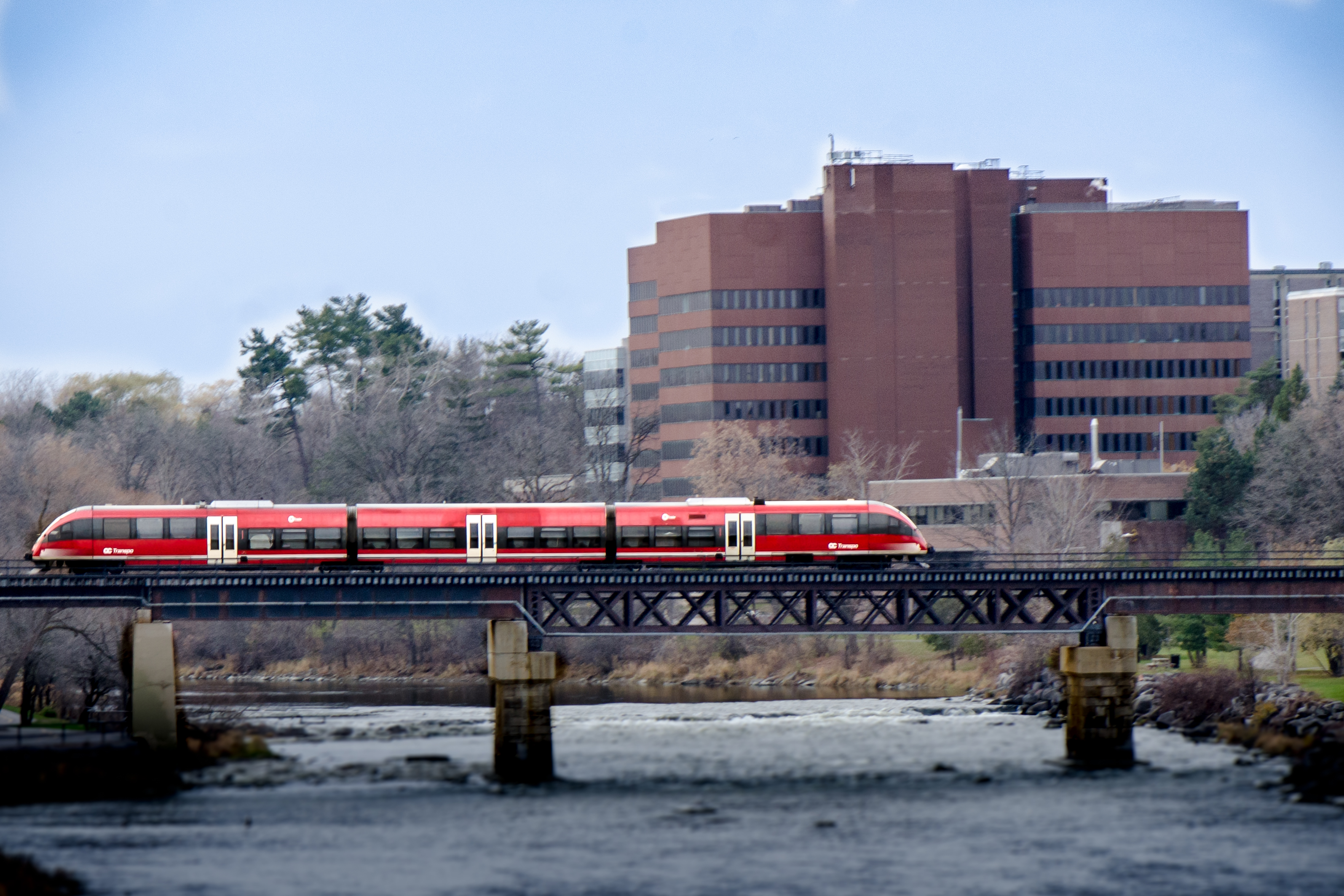

 Ottawa's public transit system is managed by OC Transpo.
Ottawa's public transit system is managed by OC Transpo.
Airports
The Ottawa Macdonald–Cartier International Airport is the city's principal airport. There are also three main regional airports Gatineau-Ottawa Executive Airport, Ottawa/Carp Airport, and Ottawa/Rockcliffe Airport.
Inter-city transportation
Ottawa station is the main inter-city train station operated by Via Rail. It is located to the east of downtown
''Downtown'' is a term primarily used in American and Canadian English to refer to a city's sometimes commercial, cultural and often the historical, political, and geographic heart. It is often synonymous with its central business district ( ...
in Eastway Gardens (adjacent to O-Train Tremblay station) and serves Via Rail's Corridor Route. The city is also served by inter-city passenger rail service at Fallowfield station in the southwestern suburban community of Barrhaven.
Intercity bus services are currently provided by several carriers at various stops throughout the city, following the closure of the former Ottawa Central Station bus terminal on 1 June 2021. Major carriers include: Megabus, Ontario Northland, Autobus Gatineau, and Orléans Express.
Streets and highways
The City of Ottawa has over lane-kilometres of road and a series of freeways. The primary freeways are the east–west provincial Highway 417 (designated as the Queensway and part of the Trans-Canada Highway
The Trans-Canada Highway (Canadian French, French: ; abbreviated as the TCH or T-Can) is a transcontinental federal–provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada, from the Pacific Ocean on the west coast to the A ...
), Ottawa-Carleton Highway 174 (formerly Provincial Highway 17), Highway 7, and the north–south provincial Highway 416 (designated as Veterans' Memorial Highway), which connects to other 400-Series highways via the 401. From downtown there are also freeway connections to Autoroute 5 and Autoroute 50, in neighbouring Gatineau.
The city also has several scenic parkways and promenades, such as the Kichi Zibi Mikan (formerly the Macdonald Parkway), Colonel By Drive, Queen Elizabeth Driveway, the Sir George-Étienne Cartier Parkway (formerly the Rockcliffe Parkway), and the Aviation Parkway. The National Capital Commission manages ceremonial routes linking key attractions on both sides of the Ottawa River, including Confederation Boulevard.
Cycling and pedestrian network
 Numerous paved multi-use trails, mostly operated by the National Capital Commission and the city, wind their way through much of the capital, including along the Ottawa River, Rideau River, and Rideau Canal. These pathways are used for transportation, tourism, and recreation. Because many streets either have wide curb lanes or bicycle lanes, cycling is a mode of transportation used by up to 2.5% of citizens, including in winter. This is the largest percentage of any major Canadian city. As of 31 December 2015, over of cycling facilities are found in Ottawa, including of multi-use pathways, of cycle tracks, of on-road bicycle lanes, and of paved shoulders.
Numerous paved multi-use trails, mostly operated by the National Capital Commission and the city, wind their way through much of the capital, including along the Ottawa River, Rideau River, and Rideau Canal. These pathways are used for transportation, tourism, and recreation. Because many streets either have wide curb lanes or bicycle lanes, cycling is a mode of transportation used by up to 2.5% of citizens, including in winter. This is the largest percentage of any major Canadian city. As of 31 December 2015, over of cycling facilities are found in Ottawa, including of multi-use pathways, of cycle tracks, of on-road bicycle lanes, and of paved shoulders.
Notable people
See also
* Outline of Ottawa
* List of francophone communities in Ontario
* World national capitals
* List of Ottawa buildings
* Geography of Ottawa
* Mark Sutcliffe, Current Mayor of Ottawa
Footnotes
References
Bibliography
*
*
Alt URL
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
*
{{Authority control
1826 establishments in Canada
Capitals in North America
Cities in Ontario
High-technology business districts in Canada
Planned capitals
Populated places established in 1826
Populated places on the Ottawa River
Single-tier municipalities in Ontario
 The Ottawa Valley became habitable around 10,000 years ago, following the natural draining of the Champlain Sea. Archaeological findings of arrowheads, tools and pottery indicate that Indigenous populations first settled in the area about 6,500 years ago. These findings suggest that these Algonquin people were engaged in foraging, hunting and fishing, but also trade and travel. Three major rivers meet within Ottawa, making it an important trade and travel area for thousands of years. The Algonquins are a broad Indigenous people who are closely related to the Odawa and
The Ottawa Valley became habitable around 10,000 years ago, following the natural draining of the Champlain Sea. Archaeological findings of arrowheads, tools and pottery indicate that Indigenous populations first settled in the area about 6,500 years ago. These findings suggest that these Algonquin people were engaged in foraging, hunting and fishing, but also trade and travel. Three major rivers meet within Ottawa, making it an important trade and travel area for thousands of years. The Algonquins are a broad Indigenous people who are closely related to the Odawa and  Colonel By set up military barracks on the site of today's Parliament Hill. He also laid out the streets of the town and created two distinct neighbourhoods named "Upper Town" west of the canal and " Lower Town" east of the canal. Similar to its
Colonel By set up military barracks on the site of today's Parliament Hill. He also laid out the streets of the town and created two distinct neighbourhoods named "Upper Town" west of the canal and " Lower Town" east of the canal. Similar to its  Starting in the 1850s, entrepreneurs known as lumber barons began to build large sawmills, which became some of the largest mills in the world. Rail lines built in 1854 connected Ottawa to areas south and, from 1886 to the transcontinental rail network via Hull and Lachute, Quebec. By 1885 Ottawa was the only city in Canada whose downtown street-lights were powered entirely by electricity. In 1889, the Government developed and distributed 60 "water leases" (still in use) to mainly local industrialists which gave them permission to generate electricity and operate hydroelectric generators at Chaudière Falls. Public transportation began in 1870 with a
Starting in the 1850s, entrepreneurs known as lumber barons began to build large sawmills, which became some of the largest mills in the world. Rail lines built in 1854 connected Ottawa to areas south and, from 1886 to the transcontinental rail network via Hull and Lachute, Quebec. By 1885 Ottawa was the only city in Canada whose downtown street-lights were powered entirely by electricity. In 1889, the Government developed and distributed 60 "water leases" (still in use) to mainly local industrialists which gave them permission to generate electricity and operate hydroelectric generators at Chaudière Falls. Public transportation began in 1870 with a  On 1 June 1912, the
On 1 June 1912, the 
 Ottawa's former industrial appearance was vastly altered by the 1950 Greber Plan. Prime Minister Mackenzie King hired French architect-planner Jacques Greber to design an urban plan for managing development in the National Capital Region, to make it more aesthetically pleasing and a location more befitting for Canada's political centre. Greber's plan included the creation of the National Capital Greenbelt, the Kichi Zibi Mikan and the Queensway highway system. His plan also called for changes in institutions such as moving downtown Union Station (now the Senate of Canada Building) to the suburbs, the removal of the street car system, the decentralization of selected government offices, the relocation of industries and removal of substandard housing from the downtown. The plan also recommended the creation of the Rideau Canal and Ottawa River pathways.
In 1958, the National Capital Commission was established as a Crown Corporation through the National Capital Act. The commission's original mission was to implement the Greber Plan recommendations conducted during the 1960s and 1970s. This marked the creation of a permanent political infrastructure for managing the capital region. Prior attempts to do so in the previous 50 years had been temporary. These included plans from the 1899 Ottawa Improvement Commission (OIC), the Todd Plan in 1903, the Holt Report in 1915 and the Federal District Commission (FDC) established in 1927 with a 16-year mandate.
From 1931 to 1958, City Hall had been at the Transportation Building adjacent to Union Station (now part of the Rideau Centre). In 1958, a new City Hall opened on Green Island near Rideau Falls, where urban renewal had recently transformed this industrial location into a green space. In 2001, Ottawa City Hall returned downtown to a 1990 building on 110 Laurier Avenue West, the home of the now-defunct Regional Municipality of Ottawa-Carleton. This new location was close to Ottawa's first (1849–1877) and second (1877–1931) City Halls. This new city hall complex also contained an adjacent 19th-century restored heritage building formerly known as the Ottawa Normal School.
From the 1960s to the 1980s, there was a large increase in construction in the National Capital Region, which was followed by large growth in the high-tech industry during the 1990s and 2000s. Ottawa became one of Canada's largest high-tech cities and was nicknamed Silicon Valley North. By the 1980s, Bell Northern Research (later Nortel) employed thousands, and large federally assisted research facilities such as the National Research Council contributed to an eventual technology boom. The early companies led to newer firms such as Newbridge Networks, Mitel and Corel.
In 1991, provincial and federal governments responded to a land claim submitted by the Algonquins of Ontario regarding the unceded status of the land on which Ottawa is situated. Negotiations have been ongoing, with an eventual goal to sign a treaty that would release Canada from claims for misuse of land under Algonquin
Ottawa's former industrial appearance was vastly altered by the 1950 Greber Plan. Prime Minister Mackenzie King hired French architect-planner Jacques Greber to design an urban plan for managing development in the National Capital Region, to make it more aesthetically pleasing and a location more befitting for Canada's political centre. Greber's plan included the creation of the National Capital Greenbelt, the Kichi Zibi Mikan and the Queensway highway system. His plan also called for changes in institutions such as moving downtown Union Station (now the Senate of Canada Building) to the suburbs, the removal of the street car system, the decentralization of selected government offices, the relocation of industries and removal of substandard housing from the downtown. The plan also recommended the creation of the Rideau Canal and Ottawa River pathways.
In 1958, the National Capital Commission was established as a Crown Corporation through the National Capital Act. The commission's original mission was to implement the Greber Plan recommendations conducted during the 1960s and 1970s. This marked the creation of a permanent political infrastructure for managing the capital region. Prior attempts to do so in the previous 50 years had been temporary. These included plans from the 1899 Ottawa Improvement Commission (OIC), the Todd Plan in 1903, the Holt Report in 1915 and the Federal District Commission (FDC) established in 1927 with a 16-year mandate.
From 1931 to 1958, City Hall had been at the Transportation Building adjacent to Union Station (now part of the Rideau Centre). In 1958, a new City Hall opened on Green Island near Rideau Falls, where urban renewal had recently transformed this industrial location into a green space. In 2001, Ottawa City Hall returned downtown to a 1990 building on 110 Laurier Avenue West, the home of the now-defunct Regional Municipality of Ottawa-Carleton. This new location was close to Ottawa's first (1849–1877) and second (1877–1931) City Halls. This new city hall complex also contained an adjacent 19th-century restored heritage building formerly known as the Ottawa Normal School.
From the 1960s to the 1980s, there was a large increase in construction in the National Capital Region, which was followed by large growth in the high-tech industry during the 1990s and 2000s. Ottawa became one of Canada's largest high-tech cities and was nicknamed Silicon Valley North. By the 1980s, Bell Northern Research (later Nortel) employed thousands, and large federally assisted research facilities such as the National Research Council contributed to an eventual technology boom. The early companies led to newer firms such as Newbridge Networks, Mitel and Corel.
In 1991, provincial and federal governments responded to a land claim submitted by the Algonquins of Ontario regarding the unceded status of the land on which Ottawa is situated. Negotiations have been ongoing, with an eventual goal to sign a treaty that would release Canada from claims for misuse of land under Algonquin  Modern Ottawa is made up of eleven historic townships, ten of which are from the former Carleton County and one from the former Russell County. Ottawa city limits are bounded on the east by the United Counties of Prescott and Russell; by Renfrew County and Lanark County in the west; on the south by the United Counties of Leeds and Grenville and the United Counties of Stormont, Dundas and Glengarry; and on the north by the Regional County Municipality of Les Collines-de-l'Outaouais and the City of Gatineau.
The main suburban areas extend a considerable distance to the east, west and south of the inner-city. These areas also include the former cities of Cumberland, Gloucester (with the large suburban district of Orleans outside the greenbelt split between them), Kanata, and Nepean. The towns of Stittsville and Richmond within the former Goulbourn Township are to the southwest. Nepean as a suburb also includes Barrhaven. The communities of Manotick and Riverside South are on the other side of the Rideau River, and Greely, southeast of Riverside South.
A number of rural communities (villages and
Modern Ottawa is made up of eleven historic townships, ten of which are from the former Carleton County and one from the former Russell County. Ottawa city limits are bounded on the east by the United Counties of Prescott and Russell; by Renfrew County and Lanark County in the west; on the south by the United Counties of Leeds and Grenville and the United Counties of Stormont, Dundas and Glengarry; and on the north by the Regional County Municipality of Les Collines-de-l'Outaouais and the City of Gatineau.
The main suburban areas extend a considerable distance to the east, west and south of the inner-city. These areas also include the former cities of Cumberland, Gloucester (with the large suburban district of Orleans outside the greenbelt split between them), Kanata, and Nepean. The towns of Stittsville and Richmond within the former Goulbourn Township are to the southwest. Nepean as a suburb also includes Barrhaven. The communities of Manotick and Riverside South are on the other side of the Rideau River, and Greely, southeast of Riverside South.
A number of rural communities (villages and  Ottawa is situated on the south bank of the Ottawa River and contains the mouths of the Rideau River and Rideau Canal. The Rideau Canal (Rideau Waterway) first opened in 1832 and is long. It connects the Saint Lawrence River on Lake Ontario at Kingston to the Ottawa River near Parliament Hill. It was able to bypass the unnavigable sections of the Cataraqui and Rideau rivers and various small lakes along the waterway due to flooding techniques and the construction of 47 water transport locks.
Ottawa is situated in a lowland on top of Paleozoic carbonate and shale and is surrounded by more craggy Precambrian igneous and metamorphic formations. Ottawa has had fluvial deposition of till and sands, leading to the widespread formation of eskers. There are limited distinct features arising from glacial deposits, but Ottawa was affected by the Late Wisconsian advance. Before the draining of the Champlain Sea, the area had high salinity. After the draining of the sea, the area had pine-dominated forests. Ottawa is located within the Western Quebec Seismic Zone, and while relatively inactive, the city does occasionally experience earthquakes.
Ottawa is situated on the south bank of the Ottawa River and contains the mouths of the Rideau River and Rideau Canal. The Rideau Canal (Rideau Waterway) first opened in 1832 and is long. It connects the Saint Lawrence River on Lake Ontario at Kingston to the Ottawa River near Parliament Hill. It was able to bypass the unnavigable sections of the Cataraqui and Rideau rivers and various small lakes along the waterway due to flooding techniques and the construction of 47 water transport locks.
Ottawa is situated in a lowland on top of Paleozoic carbonate and shale and is surrounded by more craggy Precambrian igneous and metamorphic formations. Ottawa has had fluvial deposition of till and sands, leading to the widespread formation of eskers. There are limited distinct features arising from glacial deposits, but Ottawa was affected by the Late Wisconsian advance. Before the draining of the Champlain Sea, the area had high salinity. After the draining of the sea, the area had pine-dominated forests. Ottawa is located within the Western Quebec Seismic Zone, and while relatively inactive, the city does occasionally experience earthquakes.
 As of 2015, the region of Ottawa-Gatineau has the sixth-highest total household income of all Canadian metropolitan areas ($82,053), and the Ontario portion more directly overlapping the City of Ottawa has a higher household income ($86,451). The median household income after taxes in the City of Ottawa is $73,745 in 2016 was higher than the national median of $61,348. Ottawa's unemployment rate has remained below the national and provincial unemployment rates since 2006, with a rate of 5.2% in April 2022, low compared to the decade preceding. In 2019 Mercer ranks Ottawa with the third highest quality of living of any Canadian city, and 19th highest in the world. It is also rated the second cleanest city in Canada, and third cleanest city in the world.
Ottawa's primary employers are the Public Service of Canada and the high-tech industry, although tourism and healthcare also represent increasingly sizeable economic activities. The federal government is the city's largest employer, employing over 116,000 individuals from the National Capital Region. The national headquarters for many federal departments are in Ottawa, particularly throughout Centretown and in the Terrasses de la Chaudière and Place du Portage complexes in Hull. The National Defence Headquarters in Ottawa is the main command centre for the
As of 2015, the region of Ottawa-Gatineau has the sixth-highest total household income of all Canadian metropolitan areas ($82,053), and the Ontario portion more directly overlapping the City of Ottawa has a higher household income ($86,451). The median household income after taxes in the City of Ottawa is $73,745 in 2016 was higher than the national median of $61,348. Ottawa's unemployment rate has remained below the national and provincial unemployment rates since 2006, with a rate of 5.2% in April 2022, low compared to the decade preceding. In 2019 Mercer ranks Ottawa with the third highest quality of living of any Canadian city, and 19th highest in the world. It is also rated the second cleanest city in Canada, and third cleanest city in the world.
Ottawa's primary employers are the Public Service of Canada and the high-tech industry, although tourism and healthcare also represent increasingly sizeable economic activities. The federal government is the city's largest employer, employing over 116,000 individuals from the National Capital Region. The national headquarters for many federal departments are in Ottawa, particularly throughout Centretown and in the Terrasses de la Chaudière and Place du Portage complexes in Hull. The National Defence Headquarters in Ottawa is the main command centre for the  In addition to the economic activities that come with being the national capital, Ottawa is an important technology centre; in 2015, its 1800 companies employed approximately 63,400 people. The concentration of companies in this industry earned the city the nickname of "Silicon Valley North." Most of these companies specialize in
In addition to the economic activities that come with being the national capital, Ottawa is an important technology centre; in 2015, its 1800 companies employed approximately 63,400 people. The concentration of companies in this industry earned the city the nickname of "Silicon Valley North." Most of these companies specialize in 

 Traditionally, the ByWard Market (in Lower Town), Parliament Hill and the Golden Triangle (both in Centretown – Downtown) have been the focal points of the cultural scenes in Ottawa. Modern thoroughfares such as Wellington Street, Rideau Street,
Traditionally, the ByWard Market (in Lower Town), Parliament Hill and the Golden Triangle (both in Centretown – Downtown) have been the focal points of the cultural scenes in Ottawa. Modern thoroughfares such as Wellington Street, Rideau Street, 



 Ottawa's public transit system is managed by OC Transpo. OC Transpo operates an integrated, multi-modal rapid transit system which includes:
* The O-Train light rail system. The four-line public rail system includes three existing lines and one currently under construction.
** Line 1 is an east–west line which operates medium-capacity light rail vehicles and travels under the city's downtown core.
** Line 2 is a north–south rail transit corridor which utilizes a mix of Stadler FLIRTs and Alstom Coradia LINTs connecting the south end of Ottawa to Line 1 at Bayview station.
** Line 3 is an under construction branch of Line 1, splitting at Lincoln Fields station and continuing west.
** Line 4 is a airport link connecting Line 2 to the Ottawa Macdonald–Cartier International Airport
* A vast bus rapid transit (BRT) system that uses a series of dedicated bus-only roadways named the Transitway and reserved lanes on city streets and highways. The Transitway has long distances between stops and full station amenities (including platforms, walkways, fare gates, ticket booths, elevators and convenience stores). It connects Ottawa's suburbs to the inner city. The Rapid bus service network operates all day, seven days a week, reaching the suburban communities of Kanata to the West, Barrhaven to the South-West, Orléans to the East, and South Keys to the South.
* Over 190 local bus routes are served by a fleet of ordinary, articulated and double-decker buses. Both OC Transpo and the Quebec-based Société de transport de l'Outaouais (STO) operate bus transit services between Ottawa and Gatineau. OC Transpo also operates a door-to-door bus service for disabled individuals known as ParaTranspo. There is a proposed LRT system that could link Ottawa with Gatineau.
Ottawa's public transit system is managed by OC Transpo. OC Transpo operates an integrated, multi-modal rapid transit system which includes:
* The O-Train light rail system. The four-line public rail system includes three existing lines and one currently under construction.
** Line 1 is an east–west line which operates medium-capacity light rail vehicles and travels under the city's downtown core.
** Line 2 is a north–south rail transit corridor which utilizes a mix of Stadler FLIRTs and Alstom Coradia LINTs connecting the south end of Ottawa to Line 1 at Bayview station.
** Line 3 is an under construction branch of Line 1, splitting at Lincoln Fields station and continuing west.
** Line 4 is a airport link connecting Line 2 to the Ottawa Macdonald–Cartier International Airport
* A vast bus rapid transit (BRT) system that uses a series of dedicated bus-only roadways named the Transitway and reserved lanes on city streets and highways. The Transitway has long distances between stops and full station amenities (including platforms, walkways, fare gates, ticket booths, elevators and convenience stores). It connects Ottawa's suburbs to the inner city. The Rapid bus service network operates all day, seven days a week, reaching the suburban communities of Kanata to the West, Barrhaven to the South-West, Orléans to the East, and South Keys to the South.
* Over 190 local bus routes are served by a fleet of ordinary, articulated and double-decker buses. Both OC Transpo and the Quebec-based Société de transport de l'Outaouais (STO) operate bus transit services between Ottawa and Gatineau. OC Transpo also operates a door-to-door bus service for disabled individuals known as ParaTranspo. There is a proposed LRT system that could link Ottawa with Gatineau.
 Numerous paved multi-use trails, mostly operated by the National Capital Commission and the city, wind their way through much of the capital, including along the Ottawa River, Rideau River, and Rideau Canal. These pathways are used for transportation, tourism, and recreation. Because many streets either have wide curb lanes or bicycle lanes, cycling is a mode of transportation used by up to 2.5% of citizens, including in winter. This is the largest percentage of any major Canadian city. As of 31 December 2015, over of cycling facilities are found in Ottawa, including of multi-use pathways, of cycle tracks, of on-road bicycle lanes, and of paved shoulders. of new cycling facilities were added between 2011 and 2014.
The entire length of Sparks Street was turned into a pedestrian mall in 1966. Since 1960, additional avenues, streets, and parkways, are reserved for pedestrian and bicycle use only on Saturdays, Sundays and on selected holidays and events. In 2021 city council unanimously approved the Byward Market Public Realm Plan to make the market area more car-free and pedestrian friendly. From 2009 to 2015 the NCC introduced the Capital Bixi bicycle-sharing system. This continued until the company VeloGo took over the program from 2015 to 2018 when the partnership ceased. Scooter-sharing systems have since been introduced in the downtown and inner-city areas.
Numerous paved multi-use trails, mostly operated by the National Capital Commission and the city, wind their way through much of the capital, including along the Ottawa River, Rideau River, and Rideau Canal. These pathways are used for transportation, tourism, and recreation. Because many streets either have wide curb lanes or bicycle lanes, cycling is a mode of transportation used by up to 2.5% of citizens, including in winter. This is the largest percentage of any major Canadian city. As of 31 December 2015, over of cycling facilities are found in Ottawa, including of multi-use pathways, of cycle tracks, of on-road bicycle lanes, and of paved shoulders. of new cycling facilities were added between 2011 and 2014.
The entire length of Sparks Street was turned into a pedestrian mall in 1966. Since 1960, additional avenues, streets, and parkways, are reserved for pedestrian and bicycle use only on Saturdays, Sundays and on selected holidays and events. In 2021 city council unanimously approved the Byward Market Public Realm Plan to make the market area more car-free and pedestrian friendly. From 2009 to 2015 the NCC introduced the Capital Bixi bicycle-sharing system. This continued until the company VeloGo took over the program from 2015 to 2018 when the partnership ceased. Scooter-sharing systems have since been introduced in the downtown and inner-city areas.