Otitis Externa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Otitis externa, also called swimmer's ear, is
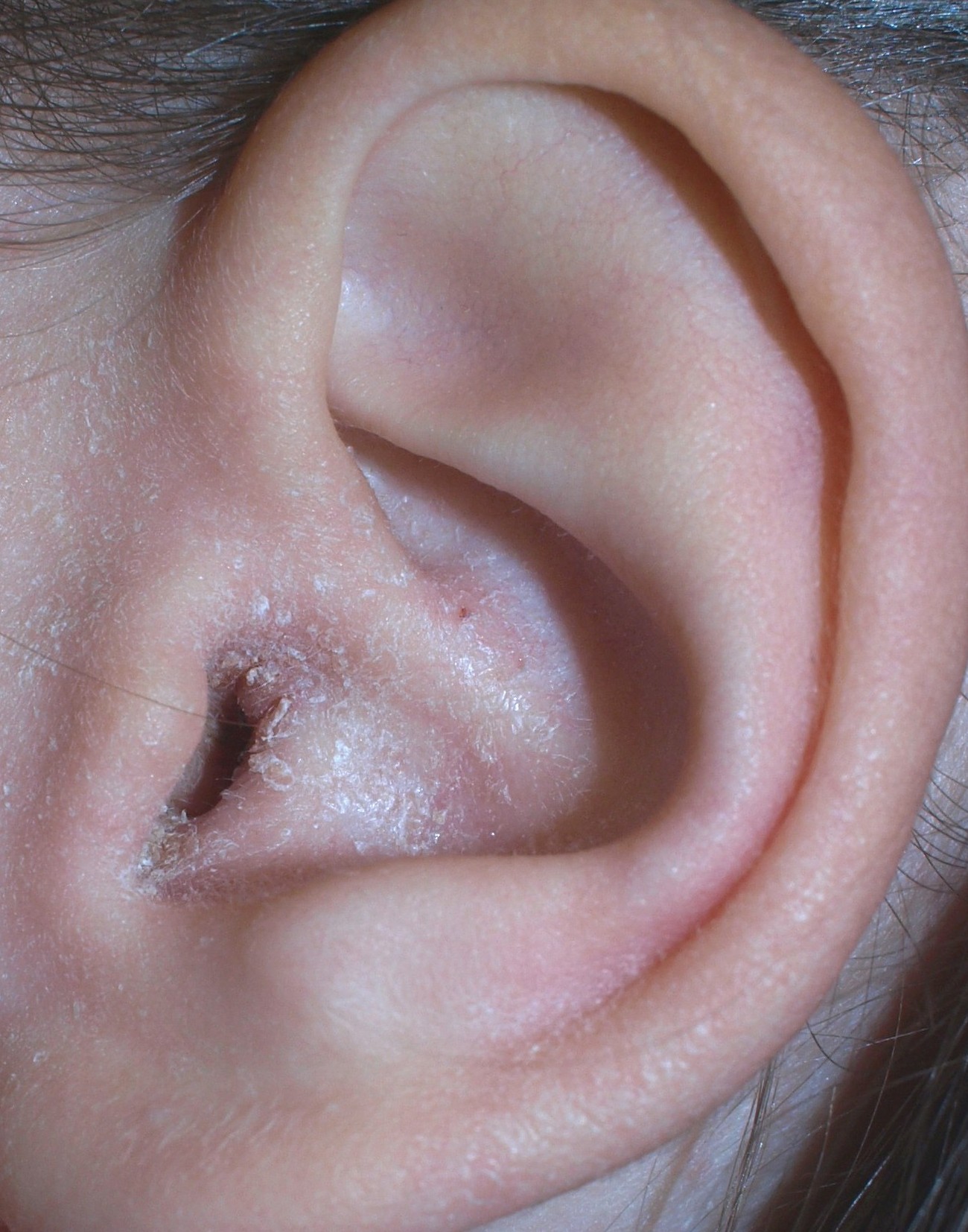
 Tenderness of pinna is the predominant complaint and the only symptom directly related to the severity of acute external otitis. Unlike other forms of ear infections, we observe tenderness in outer ear i.e., the pain of acute external otitis is worsened when the outer ear is touched or pulled gently. Pushing the tragus, the tablike portion of the auricle that projects out just in front of the ear canal opening, also typically causes pain in this condition as to be diagnostic of external otitis on physical examination. People may also experience ear discharge and itchiness. When enough swelling and discharge in the ear canal is present to block the opening, external otitis may cause temporary conductive hearing loss.
Because the symptoms of external otitis lead many people to attempt to clean out the ear canal (or scratch it) with slim implements, self-cleaning attempts generally lead to additional traumas of the injured skin, so rapid worsening of the condition often occurs.
Tenderness of pinna is the predominant complaint and the only symptom directly related to the severity of acute external otitis. Unlike other forms of ear infections, we observe tenderness in outer ear i.e., the pain of acute external otitis is worsened when the outer ear is touched or pulled gently. Pushing the tragus, the tablike portion of the auricle that projects out just in front of the ear canal opening, also typically causes pain in this condition as to be diagnostic of external otitis on physical examination. People may also experience ear discharge and itchiness. When enough swelling and discharge in the ear canal is present to block the opening, external otitis may cause temporary conductive hearing loss.
Because the symptoms of external otitis lead many people to attempt to clean out the ear canal (or scratch it) with slim implements, self-cleaning attempts generally lead to additional traumas of the injured skin, so rapid worsening of the condition often occurs.
inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
of the ear canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna (anatomy), pinna to the eardrum and is about in length and in di ...
. It often presents with ear pain
Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain is ...
, swelling of the ear canal, and occasionally decreased hearing. Typically there is pain with movement of the outer ear. A high fever is typically not present except in severe cases.
Otitis externa may be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting more than three months). Acute cases are typically due to bacterial infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number ...
, and chronic cases are often due to allergies
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermat ...
and autoimmune disorder
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly ...
s. the most common cause of Otitis externa is bacterial. Risk factors for acute cases include swimming, minor trauma from cleaning, using hearing aid
A hearing aid is a device designed to improve hearing by making sound audible to a person with hearing loss. Hearing aids are classified as medical devices in most countries, and regulated by the respective regulations. Small audio amplifiers s ...
s and ear plugs, and other skin problems, such as psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to comple ...
and dermatitis
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved c ...
. People with diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
are at risk of a severe form of ''malignant otitis externa''. Diagnosis is based on the signs and symptoms. Culturing the ear canal may be useful in chronic or severe cases.
Acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main componen ...
ear drops may be used as a preventive measure. Treatment of acute cases is typically with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
drops, such as ofloxacin or acetic acid. Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
drops may be used in addition to antibiotics. Pain medications
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It i ...
such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus ar ...
may be used for the pain. Antibiotics by mouth are not recommended unless the person has poor immune function or there is infection of the skin around the ear. Typically, improvement occurs within a day of the start of treatment. Treatment of chronic cases depends on the cause.
Otitis externa affects 1–3% of people a year; more than 95% of cases are acute. About 10% of people are affected at some point in their lives. It occurs most commonly among children between the ages of seven and twelve and among the elderly. It occurs with near equal frequency in males and females. Those who live in warm and wet climates are more often affected.
Signs and symptoms

Causes
The two factors that are required for external otitis to develop are (1) the presence of germs that can infect the skin and (2) impairments in the integrity of the skin of the ear canal that allow an infection to occur. If the skin is healthy and uninjured, only exposure to a high concentration of pathogens, such as submersion in a pond contaminated bysewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from reside ...
, is likely to set off an episode. However, if there are chronic skin conditions that affect the ear canal skin, such as atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin ( dermatitis). It results in itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. Clear fluid may come from the affected areas, which often thickens over tim ...
, seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to comple ...
or abnormalities of keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail ...
production, or if there has been a break in the skin from trauma, even the normal bacteria found in the ear canal may cause infection and full-blown symptoms of external otitis.
Fungal ear canal infections, also known as otomycosis, range from inconsequential to extremely severe. Fungi can be saprophytic, in which there are no symptoms and the fungus simply co-exists in the ear canal in a harmless parasitic relationship with the host, in which case the only physical finding is the presence of a fungus. If the fungus begins active reproduction, the ear canal can fill with dense fungal debris, causing pressure and ever-increasing pain that is unrelenting until the fungus is removed from the canal and anti-fungal medication is used. Most antibacterial ear drops also contain a steroid to hasten resolution of canal edema and pain. Unfortunately, such drops make the fungal infection worse. Prolonged use of them promotes the growth of fungus in the ear canal. Antibacterial ear drops should be used for a maximum of one week, but 5 days is usually enough. Otomycosis responds more than 95% of the time to a three-day course of the same over-the-counter anti-fungal solutions used
for athlete's foot.
Swimming
Swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, or other liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs and the body to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that r ...
in polluted water is a common way to contract swimmer's ear, but it is also possible to contract swimmer's ear from water trapped in the ear canal after a shower, especially in a humid climate. Prolonged swimming can saturate the skin of the canal, compromising its barrier function and making it more susceptible to further damage if the ear is instrumented with cotton swabs after swimming. Constriction of the ear canal from bone growth ( Surfer's ear) can trap debris leading to infection. Saturation divers have reported otitis externa during occupational exposure.
Objects in ear
Even without exposure to water, the use of objects such as cotton swabs or other small objects to clear the ear canal is enough to cause breaks in the skin, and allow the condition to develop. Once the skin of the ear canal is inflamed, external otitis can be drastically enhanced by either scratching the ear canal with an object or by allowing water to remain in the ear canal for any prolonged length of time.Infections
The majority of cases are due to ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic– facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. a ...
'' and ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posit ...
'', followed by a great number of other gram-positive and gram-negative species. ''Candida albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usu ...
'' and ''Aspergillus
' () is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide.
''Aspergillus'' was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli. Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Mic ...
'' species are the most common fungal pathogens responsible for the condition.
Diagnosis
When the ear is inspected, the canal appears red and swollen in well-developed cases. The ear canal may also appeareczema
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved c ...
-like, with scaly shedding of skin. Touching or moving the outer ear increases the pain, and this maneuver on physical exam is important in establishing the clinical diagnosis. It may be difficult to see the eardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the ...
with an otoscope at the initial examination because of narrowing of the ear canal from inflammation and the presence of drainage and debris. Sometimes the diagnosis of external otitis is presumptive and return visits are required to fully examine the ear. The culture of the drainage may identify the bacteria or fungus causing infection, but is not part of the routine diagnostic evaluation. In severe cases of external otitis, there may be swelling of the lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
(s) directly beneath the ear.
The diagnosis may be missed in most early cases because the examination of the ear, with the exception of pain with manipulation, is nearly normal. In some early cases, the most striking visual finding is the lack of earwax
Earwax, also known by the medical term cerumen, is a brown, orange, red, yellowish or gray waxy substance secreted in the ear canal of humans and other mammals. It protects the skin of the human ear canal, assists in cleaning and lubrication, ...
. As a moderate or severe case of external otitis resolves, weeks may be required before the ear canal again shows a normal amount of it.
Classification
In contrast to the chronic otitis externa, acute otitis externa (AOE) is predominantly a bacterial infection, occurs suddenly, rapidly worsens, and becomes painful. The ear canal has an abundant nerve supply, so the pain is often severe enough to interfere with sleep. Wax in the ear can combine with the swelling of the canal skin and the associated pus to block the canal and dampen hearing, creating a temporary conductive hearing loss. In more severe or untreated cases, the infection can spread to the soft tissues of the face that surround the adjacentparotid gland
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the ma ...
and the jaw joint
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the mandible below; it is from these bones that it ...
, making chewing painful. In its mildest forms, otitis externa is so common that some ear nose and throat physicians have suggested that most people will have at least a brief episode at some point in life.
The skin of the bony ear canal is unique, in that it is not movable but is closely attached to the bone, and it is almost paper-thin. For these reasons, it is easily abraded or torn by even minimal physical force. Inflammation of the ear canal skin typically begins with a physical insult, most often from injury caused by attempts at self-cleaning or scratching with cotton swabs, pen caps, fingernails, hair pins, keys, or other small implements. Another causative factor for acute infection is prolonged water exposure in the forms of swimming or exposure to extreme humidity, which can compromise the protective barrier function of the canal skin, allowing bacteria to flourish, hence the name "swimmer's ear".
Prevention
The strategies for preventing acute external otitis are similar to those for treatment. * Avoid inserting ''anything'' into the ear canal: use of cotton buds or swabs is the most common event leading to acute otitis externa. Most normal ear canals have a self-cleaning and self-drying mechanism, the latter by simple evaporation. * After prolonged swimming, a person prone to external otitis can dry the ears using a small battery-powered ear dryer, available at many retailers, especially shops catering to watersports enthusiasts. Alternatively, drops containing dilute acetic acid (vinegar diluted 3:1) or Burow's solution may be used. It is especially important not to instrument ears when the skin is saturated with water, as it is very susceptible to injury, which can lead to external otitis. * Avoid swimming in polluted water. * Avoid washing hair or swimming if very mild symptoms of acute external otitis begin * Although the use ofearplug
An earplug is a device that is inserted in the ear canal to protect the user's ears from loud noises, intrusion of water, foreign bodies, dust or excessive wind. Since they reduce the sound volume, earplugs are often used to help prevent heari ...
s, when swimming and shampooing hair, may help prevent external otitis, there are important details in the use of plugs. Hard and poorly fitting earplugs can scratch the ear canal skin and set off an episode. When earplugs are used during an acute episode, either disposable plugs are recommended, or used plugs must be cleaned and dried properly to avoid contaminating the healing ear canal with infected discharge.
According to one source, the use of in-ear headphones
Headphones are a pair of small loudspeaker drivers worn on or around the head over a user's ears. They are electroacoustic transducers, which convert an electrical signal to a corresponding sound. Headphones let a single user listen to an a ...
during otherwise "dry" exercise in the summer has been associated with the development of swimmer's ear since the plugs can create a warm and moist environment inside the ears. The source claims that on-ear or over-ear headphones can be a better alternative for preventing swimmer's ear.
Treatment
Medications
Effective solutions for the ear canal include acidifying and drying agents, used either singly or in combination. When the ear canal skin is inflamed from the acute otitis externa, the use of diluteacetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main componen ...
may be painful.
Burow's solution is a very effective remedy against both bacterial and fungal external otitis. This is a buffered mixture of aluminium sulfate
Aluminium sulfate is a salt with the formula Al2 (SO4)3. It is soluble in water and is mainly used as a coagulating agent (promoting particle collision by neutralizing charge) in the purification of drinking water and wastewater treatment plan ...
and acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main componen ...
, and is available without prescription in the United States.
Ear drops are the mainstay of treatment for external otitis. Some contain antibiotics, either antibacterial or antifungal, and others are simply designed to mildly acidify the ear canal environment to discourage bacterial growth. Some prescription drops also contain anti-inflammatory steroids, which help to resolve swelling and itching. Although there is evidence that steroids are effective at reducing the length of treatment time required, fungal otitis externa (also called otomycosis) may be caused or aggravated by overly prolonged use of steroid-containing drops.
Antibiotics by mouth should not be used to treat uncomplicated acute otitis externa., which cites
* Antibiotics by mouth are not a sufficient response to bacteria which cause this condition and have significant side effects including increased risk of opportunistic infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection caused by pathogens (bacteria, fungi, parasites or viruses) that take advantage of an opportunity not normally available. These opportunities can stem from a variety of sources, such as a weakened immun ...
. In contrast, topical products can treat this condition. Oral anti-pseudomonal antibiotics can be used in case of severe soft tissue swelling extending into the face and neck and may hasten recovery.
Although the acute external otitis generally resolves in a few days with topical washes and antibiotics, complete return of hearing and cerumen gland function may take a few more days. Once healed completely, the ear canal is again self-cleaning. Until it recovers fully, it may be more prone to repeat infection from further physical or chemical insult.
Effective medications include ear drop
Ear drops are a form of topical medication for the ears used to treat infection, inflammation, impacted ear wax and local anesthesia. They are commonly used for short-term treatment and can be purchased with or without a prescription. Before u ...
s containing antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s to fight infection, and corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s to reduce itching and inflammation. In painful cases, a topical solution of antibiotics such as aminoglycoside, polymyxin or fluoroquinolone is usually prescribed. Antifungal solutions are used in the case of fungal infections. External otitis is almost always predominantly bacterial or predominantly fungal so that only one type of medication is necessary and indicated.
Cleaning
Removal of debris (wax, shed skin, and pus) from the ear canal promotes direct contact of the prescribed medication with the infected skin and shortens recovery time. When canal swelling has progressed to the point where the ear canal is blocked, ear drops may not penetrate far enough into the ear canal to be effective. The physician may need to carefully insert a wick of cotton or other commercially available, pre-fashioned, absorbent material called an ear wick and then saturate that with the medication. The wick is kept saturated with medication until the canal opens enough that the drops will penetrate the canal without it. Removal of the wick does not require a health professional. Antibiotic ear drops should be dosed in a quantity that allows coating of most of the ear canal and used for no more than 4 to 7 days. The ear should be left open. It is imperative that visualization of an intacttympanic membrane
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the a ...
(eardrum) is noted.
Use of certain medications with a ruptured tympanic membrane can cause tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearin ...
, vertigo
Vertigo is a condition where a person has the sensation of movement or of surrounding objects moving when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. This may be associated with nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties w ...
, dizziness and hearing loss in some cases.
Prognosis
Otitis externa responds well to treatment, but complications may occur if it is not treated. Individuals with underlyingdiabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, disorders of the immune system, or history of radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Rad ...
to the base of the skull are more likely to develop complications, including malignant otitis externa. In these individuals, rapid examination by an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat physician) is very important.
* Chronic otitis externa
* Spread of infection to other areas of the body
* Necrotizing external otitis
* Otitis externa haemorhagica
external otitis
Necrotizing external otitis (malignant otitis externa) is an uncommon form of external otitis that occurs mainly in elderly diabetics, being somewhat more likely and more severe when the diabetes is poorly controlled. Even less commonly, it can develop due to a severely compromised immune system. Beginning as infection of the external ear canal, there is an extension of the infection into the bony ear canal and the soft tissues deep to the bony canal. Unrecognized and untreated, it may result in death. The hallmark of malignant otitis externa (MOE) is unrelenting pain that interferes with sleep and persists even after swelling of the external ear canal may have resolved with topical antibiotic treatment. It can also cause skull base osteomyelitis (SBO), manifested by multiple cranial nerve palsies, described below under the "Treatment" heading.Natural history
MOE follows a much more chronic and indolent course than ordinary acute otitis externa. There may be granulation involving the floor of the external ear canal, most often at the bony-cartilaginous junction. Paradoxically, the physical findings of MOE, at least in its early stages, are often much less dramatic than those of ordinary acute otitis externa. In later stages, there can be soft tissue swelling around the ear, even in the absence of significant canal swelling. While fever and leukocytosis might be expected in response to bacterial infection invading the skull region, MOE does not cause fever or elevation of white blood count.Treatment of MOE
Unlike ordinary otitis externa, MOE requires oral or intravenous antibiotics for cure. Pseudomonas is the most common offending pathogen. Diabetes control is also an essential part of treatment. When MOE goes unrecognized and untreated, the infection continues to smolder and over weeks or months can spread deeper into the head and involve the bones of the skull base, constituting skull base osteomyelitis (SBO). Multiple cranial nerve palsies can result, including the facial nerve (causing facial palsy), the recurrent laryngeal nerve (causing vocal cord paralysis), and the cochlear nerve (causing deafness). The infecting organism is almost always pseudomonas aeruginosa, but it can instead be fungal (aspergillus or mucor). MOE and SBO are not amenable to surgery, but exploratory surgery may facilitate the culture of unusual organism(s) that are not responding to empirically used anti-pseudomonal antibiotics (ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin i ...
being the drug of choice). The usual surgical finding is diffuse cellulitis without localized abscess formation. SBO can extend into the petrous apex of the temporal bone or more inferiorly into the opposite side of the skull base.
The use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure ...
as an adjunct to antibiotic therapy remains controversial.
Complications
As the skull base is progressively involved, the adjacent exiting cranial nerves and their branches, especially thefacial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste ...
and the vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and righ ...
, may be affected, resulting in facial paralysis and hoarseness, respectively. If both of the recurrent laryngeal nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recurrent laryngeal nerves, right and ...
s are paralyzed, shortness of breath may develop and necessitate tracheotomy. Profound deafness can occur, usually later in the disease course due to relative resistance of the inner ear structures. Gallium scans are sometimes used to document the extent of the infection but are not essential to disease management. Skull base osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
is a chronic disease that can require months of IV antibiotic treatment, tends to recur, and has a significant mortality rate.
Epidemiology
The incidence of otitis externa is high. In the Netherlands, it has been estimated at 12–14 per 1000 population per year, and has been shown to affect more than 1% of a sample of the population in the United Kingdom over a 12-month period.History
During the Tektite Project in 1969 there was a great deal of otitis externa. The Diving Medical Officer devised a prophylaxis that came to be known as, "Tektite Solution", equal parts of 15% tannic acid, 15% acetic acid and 50% isopropyl alcohol or ethanol. During Tektite ethanol was used because it was available in the lab for pickling specimens.Other animals
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Otitis Externa Otitis Pediatrics Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions Diseases of external ear Swimming culture Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate