Orthosilicate (ion) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In chemistry, orthosilicate is the
In chemistry, orthosilicate is the
 In chemistry, orthosilicate is the
In chemistry, orthosilicate is the anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
, or any of its salts
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively c ...
and ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
s. It is one of the silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is a ...
anions. It is occasionally called the silicon tetroxide anion or group.C. A. Kumins, and A. E. Gessler (1953), "Short-Cycle Syntheses of Ultramarine Blue". ''Indunstrial & Engineering Chemistry'', volume 45, issue 3, pages 567–572.
Orthosilicate salts, like sodium orthosilicate, are stable, and occur widely in nature as silicate minerals
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.
In mineralogy, silica (silicon dioxide, ) is usually con ...
, being the defining feature of the nesosilicates. Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers qui ...
, a magnesium or iron(II) orthosilicate, is the most abundant mineral in the upper mantle.
The orthosilicate anion is a strong base, the conjugate base
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid donates a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as in the reverse reaction it loses a ...
of the extremely weak orthosilicic acid
Orthosilicic acid () is an inorganic compound with the formula . Although rarely observed, it is the key compound of silica and silicates and the precursor to other silicic acids . Silicic acids play important roles in biomineralization and ...
(p''K''a2 = 13.2 at 25 °C). This equilibrium is difficult to study since the acid tends to decompose into a hydrated silica Hydrated silica is a form of silicon dioxide, which has a variable amount of water in the formula. When dissolved in water it is usually known as silicic acid. It is found in nature, as opal (which has been mined as a gemstone for centuries), and ...
condensate.
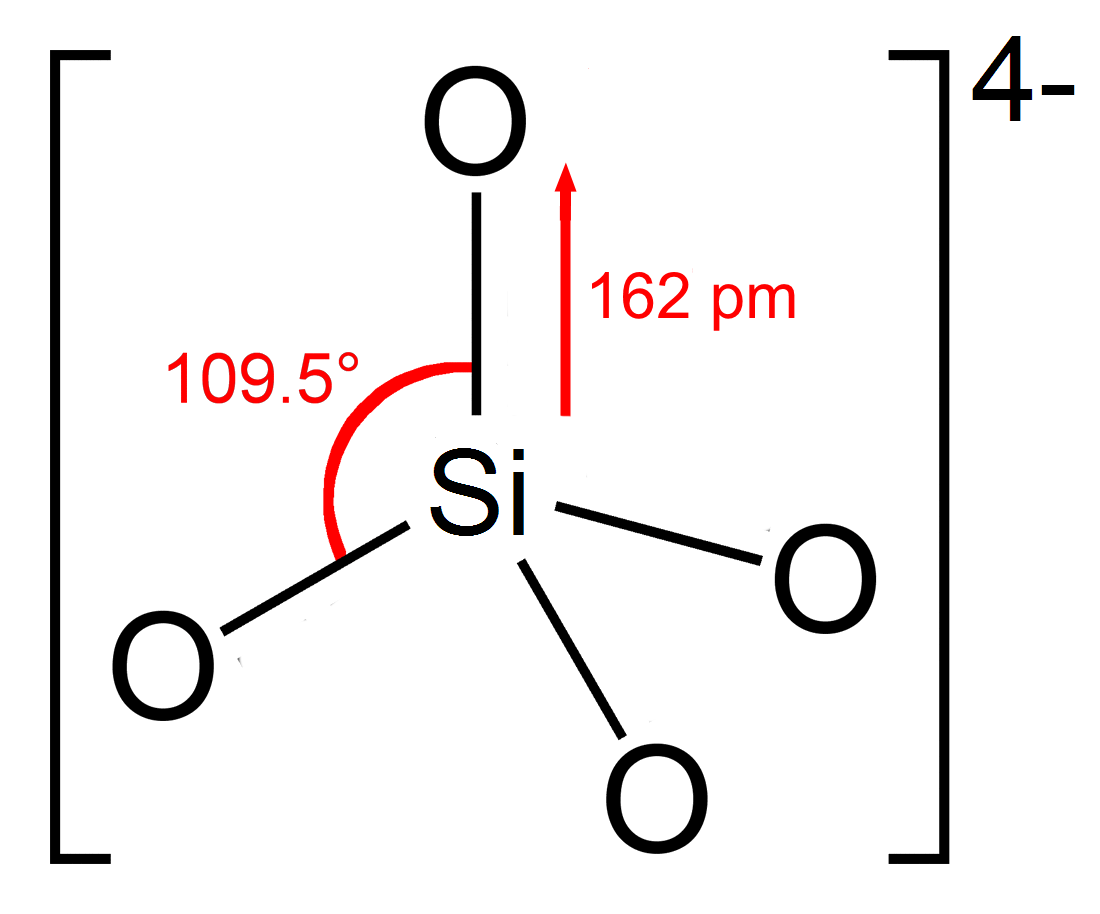
Structure
The orthosilicate ion or group has tetrahedral shape, with one silicon atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms. In the anion, each oxygen carries a unit negative charge. The Si–O bond is 162 pm long. In organic compounds like tetramethyl orthosilicate, each oxygen is formally neutral and is connected to the rest of the molecule by a singlecovalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between ato ...
.
Uses
Europium
Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. Europium is the most reactive lanthanide by far, having to be stored under an inert fluid to protect it from atmospheric oxygen or moisture. Europium is also the softest lan ...
doped barium orthosilicate (Ba2SiO4) is a common phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or v ...
used in green light-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor Electronics, device that Light#Light sources, emits light when Electric current, current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy i ...
s (LEDs). Phosphor for blue LEDs can be made with strontium
Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is e ...
doped barium orthosilicate. Barium orthosilicate is a major cause of cathode poisoning in vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
s.
Organic chemistry
Although very important in inorganic chemistry and geochemistry, the orthosilicate ion is rarely seen in organic chemistry. Two silicate compounds, however, are used inorganic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
: tetraethyl orthosilicate or ''TEOS'' is used to link polymers, and is especially important in the manufacture of aerogels. Tetramethyl orthosilicate or ''TMOS'' is used as an alternative to TEOS, and also has a number of other uses as a reagent. TEOS is preferred over TMOS as TMOS decomposes to produce high concentrations of toxic methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is ...
. Inhaling TMOS can result in toxic build-up of silica in the lungs.
References
{{reflist Silicates