Old Faithful on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Old Faithful is a cone
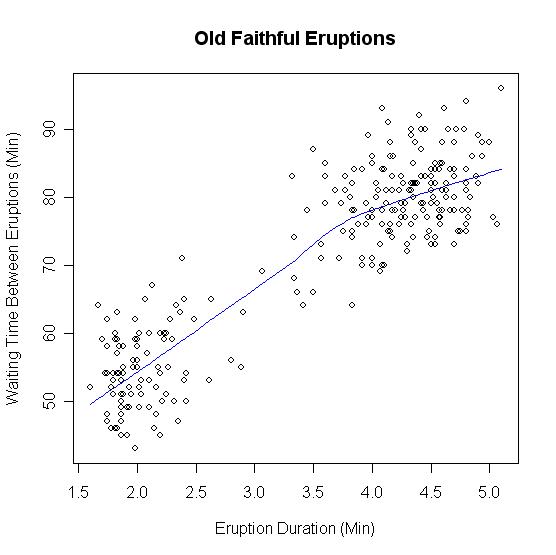 The time between eruptions has a bimodal distribution, with the mean interval being either 65 or 91 minutes, and is dependent on the length of the prior eruption. Within a margin of error of ±10 minutes, Old Faithful will erupt either 65 minutes after an eruption lasting less than 2½ minutes, or 91 minutes after an eruption lasting more than 2½ minutes.
The time between eruptions has a bimodal distribution, with the mean interval being either 65 or 91 minutes, and is dependent on the length of the prior eruption. Within a margin of error of ±10 minutes, Old Faithful will erupt either 65 minutes after an eruption lasting less than 2½ minutes, or 91 minutes after an eruption lasting more than 2½ minutes.
geyser
A geyser (, ) is a spring with an intermittent water discharge ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam. The formation of geysers is fairly rare and is caused by particular hydrogeological conditions that exist only in a few places on Ea ...
in Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States located in the northwest corner of Wyoming, with small portions extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U ...
in Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
, United States. It was named in 1870 during the Washburn–Langford–Doane Expedition and was the first geyser in the park to be named. It is a highly predictable geothermal feature and has erupted every 44 minutes to two hours since 2000. The geyser and the nearby Old Faithful Inn are part of the Old Faithful Historic District.
History
In the afternoon of September 18, 1870, the members of the Washburn-Langford-Doane Expedition traveled down the Firehole River from the Kepler Cascades and entered the Upper Geyser Basin. The first geyser that they saw was Old Faithful. Nathaniel P. Langford wrote in his 1871 Scribner's account of the expedition: In the early days of the park, Old Faithful was often used as a laundry:Eruptions
More than 1,000,000 eruptions have been recorded. Harry Woodward first described a mathematical relationship between the duration and intervals of the eruptions in 1938. Old Faithful is not the tallest or largest geyser in the park; those titles belong to the less predictable Steamboat Geyser. The reliability of Old Faithful can be attributed to the fact that it is not connected to any other thermal features of the Upper Geyser Basin. Eruptions can shoot of boiling water to a height of lasting from 1½ to 5 minutes. The average height of an eruption is . Intervals between eruptions have ranged from 34 to 125 minutes, averaging 66½ minutes in 1939, slowly increasing to an average of 90 minutes apart since 2000, which may be the result ofearthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
s affecting subterranean water levels. The disruptions have made earlier mathematical relationships inaccurate, but have actually made Old Faithful more predictable in terms of its next eruption. After the Borah Peak earthquake in central Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
in October 1983, the eruption intervals of Old Faithful were noticeably lengthened.
 The time between eruptions has a bimodal distribution, with the mean interval being either 65 or 91 minutes, and is dependent on the length of the prior eruption. Within a margin of error of ±10 minutes, Old Faithful will erupt either 65 minutes after an eruption lasting less than 2½ minutes, or 91 minutes after an eruption lasting more than 2½ minutes.
The time between eruptions has a bimodal distribution, with the mean interval being either 65 or 91 minutes, and is dependent on the length of the prior eruption. Within a margin of error of ±10 minutes, Old Faithful will erupt either 65 minutes after an eruption lasting less than 2½ minutes, or 91 minutes after an eruption lasting more than 2½ minutes.
Measurement
Between 1983 and 1994, four probes containing temperature and pressure measurement devices and video equipment were lowered into Old Faithful. The probes were lowered as deep as . Temperature measurements of the water at this depth were , the same as was measured in 1942. The video probes were lowered to a maximum depth of to observe the conduit formation and the processes that took place in the conduit. Some of the processes observed include fog formation from the interaction of cool air from above mixing with heated air from below, the recharge processes of water entering into the conduit and expanding from below, and entry of superheated steam measuring as high as into the conduit.See also
* Strokkur, another naturally-occurring geyser known for erupting frequently and predictably.Images
References
External links
* * * * {{Authority control Geothermal features of Yellowstone National Park Geysers of Wyoming Geothermal features of Teton County, Wyoming Geysers of Teton County, Wyoming Articles containing video clips