open licence on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A free license or open license is a
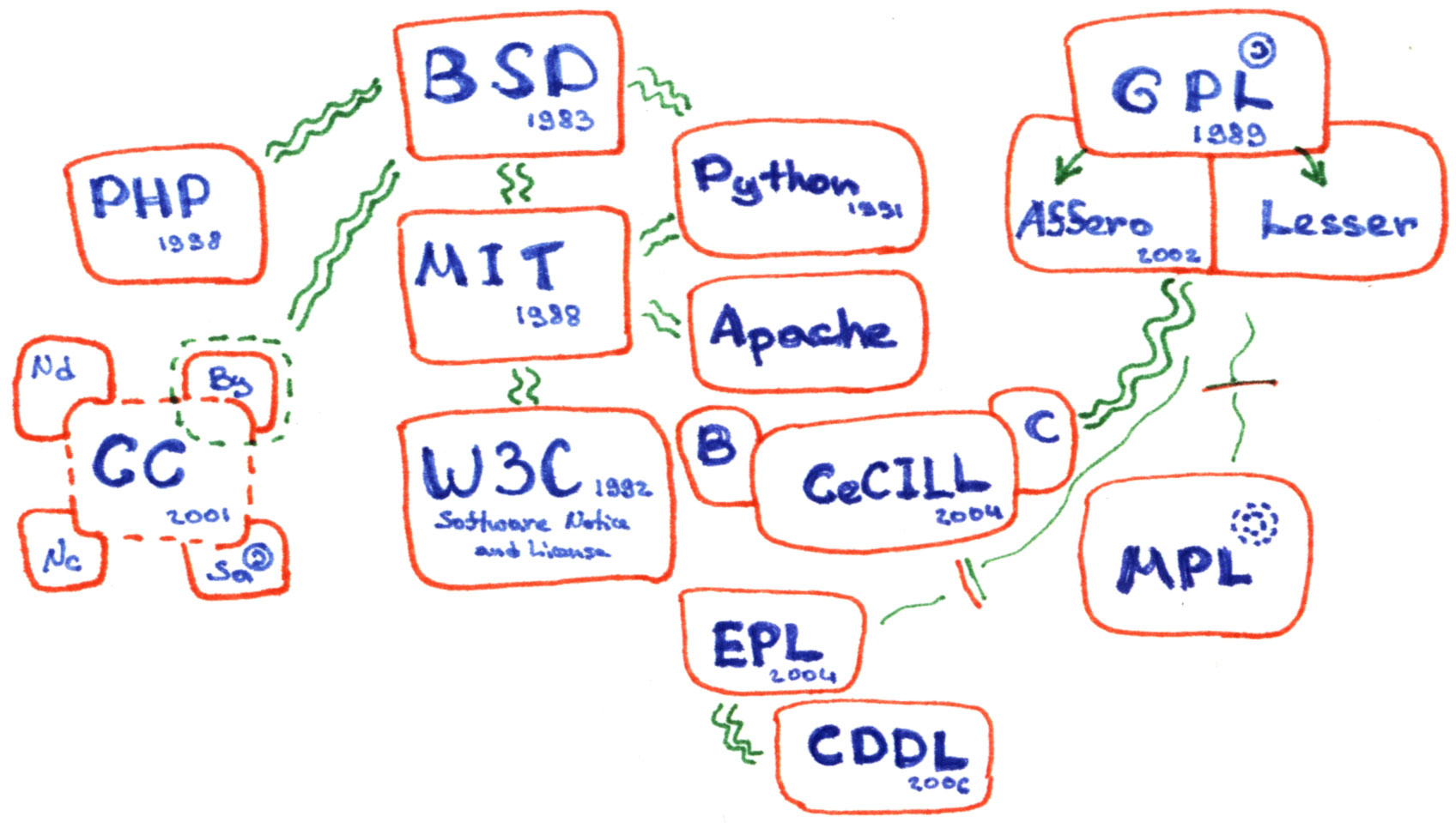 The invention of the term "free license" and the focus on the rights of users were connected to the sharing traditions of the
The invention of the term "free license" and the focus on the rights of users were connected to the sharing traditions of the
on opendefinition.org ''"This essential meaning matches that of “open” with respect to software as in the Open Source Definition and is synonymous with “free” or “libre” as in the Free Software Definition and Definition of Free Cultural Works."'' These definitions were then transformed into licenses, using the

 According to the current definition of open content on the OpenContent website, any general, royalty-free copyright license would qualify as an open license because it 'provides users with the right to make more kinds of uses than those normally permitted under the law. These permissions are granted to users free of charge.' However, the narrower definition used in the Open Definition effectively limits open content to libre content. Any free content license, defined by the Definition of Free Cultural Works, would qualify as an open content license.
According to the current definition of open content on the OpenContent website, any general, royalty-free copyright license would qualify as an open license because it 'provides users with the right to make more kinds of uses than those normally permitted under the law. These permissions are granted to users free of charge.' However, the narrower definition used in the Open Definition effectively limits open content to libre content. Any free content license, defined by the Definition of Free Cultural Works, would qualify as an open content license.
PDDL 1.0
on opendatacommons.org *
Open software licenses
Open licenses
* ttp://freedomdefined.org/Licenses Licenses - Definition of Free Cultural Works
proposed Open Source Hardware (OSHW) Statement of Principles and Definition v1.0
{{Creative Commons topics Free and open-source software licenses Contract law Computer law Copyright licenses Terms of service Open-source hardware Patent law
license
A license (American English) or licence (Commonwealth English) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another part ...
that allows copyrighted work to be reused, modified, and redistributed. These uses are normally prohibited by copyright
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive legal right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, ...
, patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
or other Intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
(IP) laws. The term broadly covers '' free content licenses'' and ''open-source license
Open-source licenses are software licenses that allow content to be used, modified, and shared. They facilitate free and open-source software (FOSS) development. Intellectual property (IP) laws restrict the modification and sharing of creative ...
s'', also known as ''free software licenses
A free-software license is a notice that grants the recipient of a piece of software extensive rights to modify and redistribute that software. These actions are usually prohibited by copyright law, but the rights-holder (usually the author) ...
''.
History
 The invention of the term "free license" and the focus on the rights of users were connected to the sharing traditions of the
The invention of the term "free license" and the focus on the rights of users were connected to the sharing traditions of the hacker culture
The hacker culture is a subculture of individuals who enjoy—often in collective effort—the intellectual challenge of creatively overcoming the limitations of software systems or electronic hardware (mostly digital electronics), ...
of the 1970s public domain software ecosystem, the social and political free software movement
The free software movement is a social movement with the goal of obtaining and guaranteeing certain freedoms for user (computing), software users, namely the freedoms to run, study, modify, and share copies of software. Software which meets thes ...
(since 1980) and the open source movement
The open-source software movement is a social movement that supports the use of open-source licenses for some or all software, as part of the broader notion of open collaboration. The open-source movement was started to spread the concept/idea ...
(since the 1990s). These rights were codified by different groups and organizations for different domains in Free Software Definition, Open Source Definition
''The Open Source Definition'' (OSD) is a policy document published by the Open Source Initiative. Derived from the Debian Free Software Guidelines written by Bruce Perens, the definition is the most common standard for open-source software. ...
, Debian Free Software Guidelines
''The Open Source Definition'' (OSD) is a policy document published by the Open Source Initiative. Derived from the Debian Free Software Guidelines written by Bruce Perens, the definition is the most common standard for open-source software. ...
, Definition of Free Cultural Works
The Definition of Free Cultural Works evaluates and recommends compatible free content licenses.
History
The Open Content Project by David A. Wiley in 1998 was a predecessor project which defined open content. In 2003, Wiley joined the Creati ...
and The Open Definition
The Open Definition (formerly Open Knowledge Definition) is published by the Open Knowledge Foundation (OKF) to define openness for any type of data, content, or other knowledge. The definition's stated purpose is to " akeprecise the meaning ...
.Open Definition 2.1on opendefinition.org ''"This essential meaning matches that of “open” with respect to software as in the Open Source Definition and is synonymous with “free” or “libre” as in the Free Software Definition and Definition of Free Cultural Works."'' These definitions were then transformed into licenses, using the
copyright
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive legal right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, ...
as legal mechanism. Ideas of free/open licenses have since spread into different spheres of society.
Open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use and view the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentrali ...
, free culture
The free-culture movement is a social movement that promotes the freedom to distribute and modify the creative works of others in the form of free content, otherwise known as open content. They encourage creators to create such content by using ...
(unified as free and open-source movement), anticopyright, Wikimedia Foundation
The Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. (WMF) is an American 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization headquartered in San Francisco, California, and registered there as foundation (United States law), a charitable foundation. It is the host of Wikipedia, th ...
projects, public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds ...
advocacy groups and pirate parties are connected with free and open licenses.
Free software license
Free software licenses
A free-software license is a notice that grants the recipient of a piece of software extensive rights to modify and redistribute that software. These actions are usually prohibited by copyright law, but the rights-holder (usually the author) ...
, also known as open-source licenses
Open-source licenses are software licenses that allow content to be used, modified, and shared. They facilitate free and open-source software (FOSS) development. Intellectual property (IP) laws restrict the modification and sharing of creative ...
, are software license
A software license is a legal instrument governing the use or redistribution of software.
Since the 1970s, software copyright has been recognized in the United States. Despite the copyright being recognized, most companies prefer to sell lic ...
s that allow content to be used, modified, and shared. They facilitate free and open-source software
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software available under a license that grants users the right to use, modify, and distribute the software modified or not to everyone free of charge. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term encompassing free ...
(FOSS) development. Intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
(IP) laws restrict the modification and sharing of creative works. Free and open-source licenses use these existing legal structures for an inverse purpose. They grant the recipient the rights to use the software, examine the source code
In computing, source code, or simply code or source, is a plain text computer program written in a programming language. A programmer writes the human readable source code to control the behavior of a computer.
Since a computer, at base, only ...
, modify it, and distribute the modifications. These criteria are outlined in the Open Source Definition
''The Open Source Definition'' (OSD) is a policy document published by the Open Source Initiative. Derived from the Debian Free Software Guidelines written by Bruce Perens, the definition is the most common standard for open-source software. ...
and The Free Software Definition
''The Free Software Definition'' is a policy document written by Richard Stallman and published by the Free Software Foundation (FSF). It defines free software as software that grants users the freedom to use, study, share, and modify the softwar ...
.
After 1980, the United States began to treat software as a literary work covered by copyright law. Richard Stallman
Richard Matthew Stallman ( ; born March 16, 1953), also known by his initials, rms, is an American free software movement activist and programmer. He campaigns for software to be distributed in such a manner that its users have the freedom to ...
founded the free software movement
The free software movement is a social movement with the goal of obtaining and guaranteeing certain freedoms for user (computing), software users, namely the freedoms to run, study, modify, and share copies of software. Software which meets thes ...
in response to the rise of proprietary software
Proprietary software is computer software, software that grants its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner a legal monopoly by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing t ...
. The term "open source" was used by the Open Source Initiative
The Open Source Initiative (OSI) is a California public benefit corporation "actively involved in Open Source community-building, education, and public advocacy to promote awareness and the importance of non-proprietary software".
Governance
The ...
(OSI), founded by free software developers Bruce Perens
Bruce Perens (born around 1958) is an American computer programmer and advocate in the free software movement. He created ''The Open Source Definition'' and published the first formal announcement and manifesto of open source. He co-founded the ...
and Eric S. Raymond
Eric Steven Raymond (born December 4, 1957), often referred to as ESR, is an American software developer, open-source software advocate, and author of the 1997 essay and 1999 book ''The Cathedral and the Bazaar''. He wrote a guidebook for the R ...
. "Open source" is alternative label that emphasizes the strengths of the open development model rather than software freedoms. While the goals behind the terms are different, open-source licenses and free software license
A free-software license is a notice that grants the recipient of a piece of software extensive rights to modify and redistribute that software. These actions are usually prohibited by copyright law, but the rights-holder (usually the author) ...
s describe the same type of licenses.
The two main categories of free and open-source licenses are permissive
Permissiveness may refer to:
* Permissiveness (endocrinology), between hormones and cells.
* Permissiveness (virology), between viruses and cells.
Permissive may refer to:
* Permissive society, a liberalization of social norms in a society.
* ...
and copyleft
Copyleft is the legal technique of granting certain freedoms over copies of copyrighted works with the requirement that the same rights be preserved in derivative works. In this sense, ''freedoms'' refers to the use of the work for any purpose, ...
. Both grant permission to change and distribute software. Typically, they require attribution and disclaim liability. Permissive licenses come from academia. Copyleft licenses come from the free software movement. Copyleft licenses require derivative works
In copyright law, a derivative work is an expressive creation that includes major copyrightable elements of a first, previously created original work (the underlying work). The derivative work becomes a second, separate work independent from t ...
to be distributed with the source code and under a similar license. Since the mid-2000s, courts in multiple countries have upheld the terms of both types of license. Software developers have filed cases as copyright infringement and as breaches of contract.
Free content license
Licenses
By type of license
*Public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds ...
licenses
** Creative Commons CC0
** WTFPL
** Unlicense
The Unlicense is a public domain equivalent license for software which provides a public domain waiver with a fall-back public-domain-like license, similar to the CC Zero for cultural works. It includes language used in earlier software projects ...
** Public Domain Dedication and License (PDDL)on opendatacommons.org *
Permissive license
A permissive software license, sometimes also called BSD-like or BSD-style license, is a free-software license which instead of copyleft protections, carries only minimal restrictions on how the software can be used, modified, and redistributed, ...
s
** Apache License
The Apache License is a permissive free software license written by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF). It allows users to use the software for any purpose, to distribute it, to modify it, and to distribute modified versions of the software ...
** BSD License
BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD lic ...
** MIT License
The MIT License is a permissive software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the late 1980s. As a permissive license, it puts very few restrictions on reuse and therefore has high license compatibility.
Unl ...
** Mozilla Public License
The Mozilla Public License (MPL) is a free and open-source weak copyleft license for most Mozilla Foundation software such as Firefox and Thunderbird. The MPL is developed and maintained by Mozilla, which seeks to balance the concerns of bo ...
(file-based permissive copyleft)
** Creative Commons Attribution
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and bui ...
* Copyleft
Copyleft is the legal technique of granting certain freedoms over copies of copyrighted works with the requirement that the same rights be preserved in derivative works. In this sense, ''freedoms'' refers to the use of the work for any purpose, ...
& patentleft
Patentleft is the practice of licensing patents (especially biological patents) for royalty-free use, on the condition that adopters license related improvements they develop under the same terms. Copyleft-style licensors seek "continuous growt ...
licenses
** GNU GPL
The GNU General Public Licenses (GNU GPL or simply GPL) are a series of widely used free software licenses, or ''copyleft'' licenses, that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, or modify the software. The GPL was the first ...
, LGPL
The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) is a free-software license published by the Free Software Foundation (FSF). The license allows developers and companies to use and integrate a software component released under the LGPL into their own ...
(weaker copyleft), AGPL (stronger copyleft)
** Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike
** Mozilla Public License
The Mozilla Public License (MPL) is a free and open-source weak copyleft license for most Mozilla Foundation software such as Firefox and Thunderbird. The MPL is developed and maintained by Mozilla, which seeks to balance the concerns of bo ...
** Common Development and Distribution License
The Common Development and Distribution License (CDDL) is a free and open-source software license, produced by Sun Microsystems, based on the Mozilla Public License (MPL). Files licensed under the CDDL can be combined with files licensed under oth ...
** GFDL
The GNU Free Documentation License (GNU FDL or GFDL) is a copyleft license for free documentation, designed by the Free Software Foundation (FSF) for the GNU Project. It is similar to the GNU General Public License, giving readers the rights ...
(without invariant sections)
** Free Art License
The Free Art License (FAL) () is a copyleft license that grants the right to freely copy, distribute, and transform creative works except for computer hardware and software, including for commercial use.
History
The license was written in Ju ...
By type of content
*Open-source software
Open-source software (OSS) is Software, computer software that is released under a Open-source license, license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and Software distribution, distribute the software an ...
** The Open Source Definition
''The Open Source Definition'' (OSD) is a policy document published by the Open Source Initiative. Derived from the Debian Free Software Guidelines written by Bruce Perens, the definition is the most common standard for open-source software. T ...
* Open Content
Free content, libre content, libre information, or free information is any kind of creative work, such as a work of art, a book, a software, software program, or any other creative Media (communication), content for which there are very minimal ...
** Open Content License
** Open Publication License
* Open-source hardware
Open-source hardware (OSH, OSHW) consists of physical artifact (software development), artifacts of technology designed and offered by the open-design movement. Both free and open-source software (FOSS) and open-source hardware are created by th ...
* Open database
** Creative Commons
Creative Commons (CC) is an American non-profit organization and international network devoted to educational access and expanding the range of creative works available for others to build upon legally and to share. The organization has release ...
v4
** Open Database License
By authors
*Creative Commons
Creative Commons (CC) is an American non-profit organization and international network devoted to educational access and expanding the range of creative works available for others to build upon legally and to share. The organization has release ...
* Free Software Foundation
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985. The organisation supports the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed ...
* Open Source Initiative
The Open Source Initiative (OSI) is a California public benefit corporation "actively involved in Open Source community-building, education, and public advocacy to promote awareness and the importance of non-proprietary software".
Governance
The ...
* Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
** Microsoft Public License
The Shared Source Initiative (SSI) is a source-available software licensing scheme launched by Microsoft in May 2001. The program includes a spectrum of technologies and licenses, and most of its source code offerings are available for download aft ...
** Microsoft Reciprocal License
The Shared Source Initiative (SSI) is a source-available software licensing scheme launched by Microsoft in May 2001. The program includes a spectrum of technologies and licenses, and most of its source code offerings are available for download aft ...
* Open Content Project
* Open Data Commons
Open data are data that are openly accessible, exploitable, editable and shareable by anyone for any purpose. Open data are generally licensed under an open license.
The goals of the open data movement are similar to those of other "open(-so ...
from Open Knowledge Foundation
Open Knowledge Foundation (OKF) is a global, non-profit network that promotes and shares information at no charge, including both content and data. It was founded by Rufus Pollock on 20 May 2004 in Cambridge, England. It is incorporated in Engla ...
** Public Domain Dedication and License (PDDL)
** Attribution License (ODC-By)
** Open Database License (ODC-ODbL)
*European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
** European Union Public Licence
See also
*License compatibility
License compatibility is a legal framework that allows for pieces of software with different software licenses to be distributed together. The need for such a framework arises because the different licenses can contain contradictory requireme ...
* License proliferation
License proliferation is the phenomenon of an abundance of already existing and the continued creation of new software licenses for software and software packages in the FOSS ecosystem. License proliferation affects the whole FOSS ecosystem neg ...
Notes
References
* ** * * * * * * * * * *External links
Open software licenses
Open licenses
* ttp://freedomdefined.org/Licenses Licenses - Definition of Free Cultural Works
proposed Open Source Hardware (OSHW) Statement of Principles and Definition v1.0
{{Creative Commons topics Free and open-source software licenses Contract law Computer law Copyright licenses Terms of service Open-source hardware Patent law