Open Drain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Open collector, open drain, open emitter, and open source refer to
 An open collector output processes an IC's output through the base of an internal
An open collector output processes an IC's output through the base of an internal
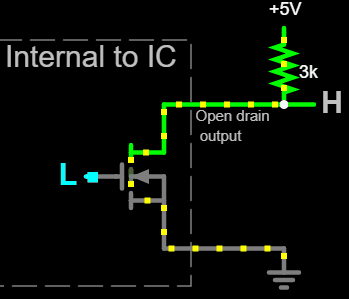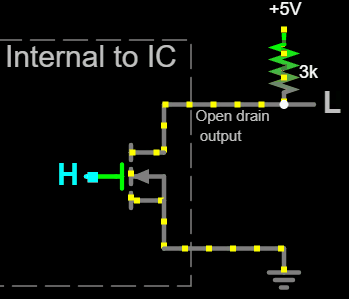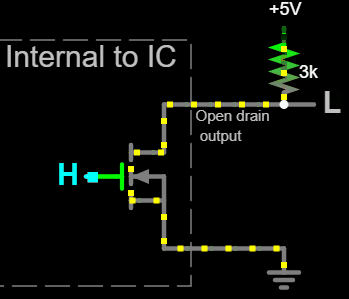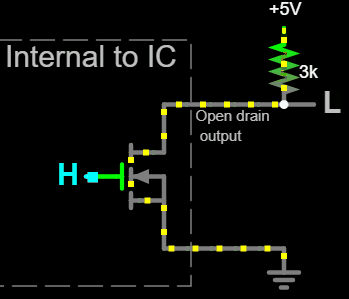 Open drain output uses MOS transistor (MOSFET) instead of BJTs, and expose the MOSFET's drain as output.
An nMOS open drain output connects to ground when a
Open drain output uses MOS transistor (MOSFET) instead of BJTs, and expose the MOSFET's drain as output.
An nMOS open drain output connects to ground when a
 Open output is indicated on
Open output is indicated on
 Another advantage is that more than one open-collector output can be connected to a single line. If all open collector outputs attached to a line are off (i.e. in the high-impedance state), the pull-up resistor will be the only device setting the line's voltage and will pull the line voltage high. But if one or more open-collector outputs attached to the line are on (i.e. conducting to ground), since any one of them are strong enough to overcome the pull-up resistor's limited ability to hold the voltage high, the line voltage will instead be pulled low. This
Another advantage is that more than one open-collector output can be connected to a single line. If all open collector outputs attached to a line are off (i.e. in the high-impedance state), the pull-up resistor will be the only device setting the line's voltage and will pull the line voltage high. But if one or more open-collector outputs attached to the line are on (i.e. conducting to ground), since any one of them are strong enough to overcome the pull-up resistor's limited ability to hold the voltage high, the line voltage will instead be pulled low. This
Pseudo-open drain and Center-tab termination type termination schemes
of both DDR3 and DDR4 termination schemes in terms of skew, eye aperture and power consumption was published in late 2011.
integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
(IC) output pin
A pin is a device, typically pointed, used for fastening objects or fabrics together. Pins can have the following sorts of body:
*a shaft of a rigid inflexible material meant to be inserted in a slot, groove, or hole (as with pivots, hinges, an ...
configurations that process the IC's internal function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-orie ...
through a transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
with an exposed terminal that is internally unconnected (i.e. "open"). One of the IC's internal high or low voltage rails typically connects to another terminal of that transistor. When the transistor is off, the output is internally disconnected from any internal power rail, a state called "high-impedance" ( Hi-Z). Open outputs configurations thus differ from push–pull output
A push–pull amplifier is a type of electronic circuit that uses a pair of active devices that alternately supply current to, or absorb current from, a connected load. This kind of amplifier can enhance both the load capacity and switching s ...
s, which use a pair of transistors to output a specific voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
or current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (hydr ...
.
These open outputs configurations are often used for digital applications when the transistor acts as a switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type o ...
, to allow for logic-level conversion, wired-logic connections, and line sharing. External pull-up/down resistors are typically required to set the output during the Hi-Z state to a specific voltage. Analog applications include analog weighting, summing, limiting, and digital-to-analog converters
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC, D/A, D2A, or D-to-A) is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
DACs are commonly used in music ...
.
The NPN BJT (n-type bipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor (FET), uses only one kind of charge carrier. A ...
) and nMOS (n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor) have greater conductance than their PNP and pMOS relatives, so may be more commonly used for these outputs. Open outputs using PNP and pMOS transistors will use the opposite internal voltage rail used by NPN and nMOS transistors.
Open collector
 An open collector output processes an IC's output through the base of an internal
An open collector output processes an IC's output through the base of an internal bipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor (FET), uses only one kind of charge carrier. A ...
(BJT), whose collector is exposed as the external output pin
A pin is a device, typically pointed, used for fastening objects or fabrics together. Pins can have the following sorts of body:
*a shaft of a rigid inflexible material meant to be inserted in a slot, groove, or hole (as with pivots, hinges, an ...
.
For NPN open collector outputs, the emitter of the NPN transistor is internally connected to ground, so the NPN open collector internally forms either a short-circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit ...
(technically low impedance or "low-Z") connection to the low voltage (which could be ground
Ground may refer to:
Geology
* Land, the solid terrestrial surface of the Earth
* Soil, a mixture of clay, sand and organic matter present on the surface of the Earth
Electricity
* Ground (electricity), the reference point in an electrical circ ...
) when the transistor is switched on
''Switched On'' (also known as ''Switched On Stereolab'' or ''Switched On Volume 1'') is a compilation of Stereolab's first three releases, and was originally released in 1992. The album's name is in tribute to ''Switched-On Bach'' (1968) and ...
, or an open-circuit (technically high impedance
In electronics, high impedance means that a point in a circuit (a node) allows a relatively small amount of current through, per unit of applied voltage at that point. High impedance circuits are low current and potentially high voltage, whereas ...
or "hi-Z") when the transistor is off. The output is usually connected to an external pull-up resistor
In electronic logic circuits, a pull-up resistor (PU) or pull-down resistor (PD) is a resistor used to ensure a known state for a signal. More specifically, a pull-up resistor or pull-down resistor ensures that a wire will have a high logic lev ...
, which pulls the output voltage to the resistor's supply voltage when the transistor is off.
For PNP open collector outputs, the emitter of the PNP transistor is internally connected to the positive voltage rail
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a re ...
, so the collector outputs a high voltage when the transistor is on or is hi-Z when off. This is sometimes called "open collector, drives high".
Open emitter
Open emitter output exposes the emitter as the output. For an NPN open emitter output, the collector is connected to the positivevoltage rail
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a re ...
, so the emitter outputs a high voltage when the transistor is on and is hi-Z when off.
For a PNP open emitter output, the collector is connected to the low voltage supply, so the emitter outputs a low voltage when the transistor is on and is hi-Z when off.
Open drain
 Open drain output uses MOS transistor (MOSFET) instead of BJTs, and expose the MOSFET's drain as output.
An nMOS open drain output connects to ground when a
Open drain output uses MOS transistor (MOSFET) instead of BJTs, and expose the MOSFET's drain as output.
An nMOS open drain output connects to ground when a high voltage
High voltage electricity refers to electrical potential large enough to cause injury or damage. In certain industries, ''high voltage'' refers to voltage above a certain threshold. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant sp ...
is applied to the MOSFET's gate, or presents a high impedance
In electronics, high impedance means that a point in a circuit (a node) allows a relatively small amount of current through, per unit of applied voltage at that point. High impedance circuits are low current and potentially high voltage, whereas ...
when a low voltage is applied to the gate. The voltage in this high impedance state would be ''floating'' (undefined) because the MOSFET is not conducting, which is why nMOS open drain outputs require a pull-up resistor connected to a positive voltage rail for producing a high output voltage.
Microelectronic devices using nMOS open drain output may provide a 'weak' (high-resistance, often on the order of 100 kΩ) internal pull-up resistor to connect the terminal in question to the positive power supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, electric current, current, and frequency to power ...
of the device so their output voltage doesn't float. Such weak pullups reduce power consumption due to their lower ohmic heating
Joule heating (also known as resistive heating, resistance heating, or Ohmic heating) is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor produces heat.
Joule's first law (also just Joule's law), also known in countr ...
and possibly avoid the need for an external pull-up. External pullups may be 'stronger' (lower resistance, perhaps 3 kΩ) to reduce signal rise times (like with I²C
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit; pronounced as "" or ""), alternatively known as I2C and IIC, is a synchronous, multi-master/multi-slave, single-ended, serial communication bus invented in 1980 by Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconduct ...
) or to minimize noise (like on system inputs).
Modern microcontrollers
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
may allow programming particular output pins to use open drain instead of push–pull output
A push–pull amplifier is a type of electronic circuit that uses a pair of active devices that alternately supply current to, or absorb current from, a connected load. This kind of amplifier can enhance both the load capacity and switching s ...
, the strength of the internal pull-up, and allow disabling internal pullups when not desired.
For pMOS open drain, the output instead connects to the positive power rail when the transistor is on, and is hi-Z when off. This is sometimes called "open drain, drives high".
Open source
Open source output exposes the MOSFET's source as the output. For a nMOS open source output, the drain is internally connected to the positive voltage rail, so the source outputs a high voltage when the transistor is on and is hi-Z when off. For a pMOS open source output, the drain is internally connected to the low voltage rail, so the output instead connects to the low voltage rail when the transistor is on, or is hi-Z when off.Summary of configurations
Configurations that internally connect to a high voltage are ''source drivers.'' Configurations that internally connect to a low voltage are ''sink drivers.''Schematic symbol
schematics
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the sc ...
with these IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines.
The IEEE ...
symbols:
: ⎐ – NPN open collector or similar output that can supply a relatively low-impedance low voltage when not turned off. Requires external pullup. Capable of positive-logic wired-AND connection.
:: ⎒ – variant with internal pull-up resistor
In electronic logic circuits, a pull-up resistor (PU) or pull-down resistor (PD) is a resistor used to ensure a known state for a signal. More specifically, a pull-up resistor or pull-down resistor ensures that a wire will have a high logic lev ...
to provide a high voltage when off.
: ⎏ – NPN open emitter or similar output that can supply a relatively low-impedance high voltage when not turned off. Requires external pulldown. Capable of positive-logic wired-OR connection.
:: ⎑ – variant with an internal pull-down resistor to provide a low voltage when off.
Applications
Note: this section primarily deals with npn open collectors, however nMOS open drain generally applies as well.Logic-level conversion
Because the pull-up resistor is external and does not need to be connected to the chip supply voltage, a lower or higher voltage than the chip supply voltage can be used instead (provided it does not exceed the absolute maximum rating of the chip's output). Open outputs are therefore sometimes used to interface different families of devices that have different operating voltage levels. The open collector transistor can be rated to withstand a higher voltage than the chip supply voltage. This technique is commonly used by logic circuits operating at 5 V or lower to drive higher voltage devices such aselectric motors
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate Laplace force i ...
, LEDs in series, 12 V relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switc ...
s, 50 V vacuum fluorescent display
A vacuum fluorescent display (VFD) is a display device once commonly used on consumer electronics equipment such as video cassette recorders, car audio, car radios, and microwave ovens.
A VFD operates on the principle of cathodoluminescence, ...
s, or Nixie tube
A Nixie tube ( ), or cold cathode display, is an electronics, electronic device used for display device, displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge.
The glass tube contains a wire-mesh anode and multiple cathodes, shaped like ...
s requiring more than 100 V.
Wired logic
wired logic connection
A wired logic connection is a logic gate that implements boolean algebra (logic) using only passive components such as diodes and resistors. A wired logic connection can create an AND or an OR gate. Limitations include the inability to create a N ...
has several uses.
By tying the output of several open collectors together and connecting to a pull-up resistor, the common line becomes a ''wired AND'' in active high logic. The output will be high (true) only when all gates are in the high-impedance state, and will be low (false) otherwise, like Boolean AND. When treated as active-low logic, this behaves like Boolean OR, since the output is low (true) when any input is low. See .
Line sharing
Line sharing is used forinterrupts
In digital computers, an interrupt (sometimes referred to as a trap) is a request for the processor to ''interrupt'' currently executing code (when permitted), so that the event can be processed in a timely manner. If the request is accepted, ...
and buses
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a motor vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van, but fewer than the average rail transport. It is most commonly used ...
(such as I²C
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit; pronounced as "" or ""), alternatively known as I2C and IIC, is a synchronous, multi-master/multi-slave, single-ended, serial communication bus invented in 1980 by Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconduct ...
or 1-Wire
1-Wire is a Wired communication, wired half duplex, half-duplex Serial communication, serial Bus (computing), bus designed by Dallas Semiconductor that provides low-speed (16.3 kbit/s) data communication and IC power-supply pin, supply volt ...
). Open-collector output enables one active device to drive the shared line without interference from the other inactive devices. If push–pull output
A push–pull amplifier is a type of electronic circuit that uses a pair of active devices that alternately supply current to, or absorb current from, a connected load. This kind of amplifier can enhance both the load capacity and switching s ...
was mistakenly used instead, the active device attempting to set the line voltage low would be in competition with the other devices attempting to set the line voltage high, which would result in unpredictable output and heat.
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices, best known for its use with storage devices such as hard disk drives. SCSI was introduced ...
-1 devices use open collector for electrical signaling. SCSI-2 and SCSI-3 may use EIA-485
RS-485, also known as TIA-485(-A) or EIA-485, is a standard, originally introduced in 1983, defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in serial communications systems. Electrical signaling is balanced, and multip ...
.
Analog
Open collector outputs can also be useful for analog weighting, summing, limiting,digital-to-analog converters
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC, D/A, D2A, or D-to-A) is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
DACs are commonly used in music ...
, etc., but such applications are not discussed here.
Disadvantages
One problem such open-collector and similar devices with a pull-up resistor is the resistor consumes power constantly while the output is low. Higher operating speeds require lower resistor values for faster pull-up, which consume even more power. Also when driving a load, current through the pull-up resistor reduces the output high voltage by avoltage drop
In electronics, voltage drop is the decrease of electric potential along the path of a current flowing in a circuit. Voltage drops in the internal resistance of the source, across conductors, across contacts, and across connectors are unde ...
equal to the current times resistance, according to Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the electric current through a Electrical conductor, conductor between two Node (circuits), points is directly Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of ...
.
Pseudo open drain (POD)
Pseudo open drain (POD) drivers have a strong pull-down strength but a weaker pull-up strength. The purpose is to reduce the overall power demand compared to using both a strong pull-up and a strong pull-down. A pure open-drain driver, by comparison, has no pull-up strength except for leakage current: all the pull-up action is on the external termination resistor. This is why the term "pseudo" has to be used here: there is some pull-up on the driver side when output is at high state, the remaining pull-up strength is provided by parallel-terminating the receiver at the far end to the high voltage, often using a switchable, on-die terminator instead of a separate resistor.JEDEC
The Joint Electron Device Engineering Council (JEDEC) Solid State Technology Association is a consortium of the semiconductor industry headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia, Arlington, United States. It has over 300 members and is focused ...
standardized the terms POD15, POD125, POD135, and POD12 for 1.5 V, 1.25 V, 1.35 V, and 1.2 V interface supply voltages respectively.
DDR memory
DDR4 memory uses POD12 drivers but with the same driver strength (34 Ω/48 Ω) for pull-down (RonPd) and pull-up (RonPu). The term POD in DDR4 referring only for termination type that is only parallel pull-up without the pull-down termination at the far end. The reference point (VREF) for the input is not half-supply as was in DDR3 and may be higher. A comparisonof both DDR3 and DDR4 termination schemes in terms of skew, eye aperture and power consumption was published in late 2011.
See also
*Common collector
In electronics, a common collector amplifier (also known as an emitter follower) is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer.
In this circuit, the base term ...
and other common terminal transistor amplifiers: Used more for analog voltages than digital.
*Push–pull output
A push–pull amplifier is a type of electronic circuit that uses a pair of active devices that alternately supply current to, or absorb current from, a connected load. This kind of amplifier can enhance both the load capacity and switching s ...
: Consists of transistors to source and sink current in ''both'' logic states, not just one.
*Three-state logic
In digital electronics, a tri-state or three-state buffer is a type of digital buffer that has three stable states: a high voltage output state (logical 1), a low output state (logical 0), and a high-impedance (Hi-Z) state. In the Hi-Z state, th ...
: Consists of transistors to source and sink current in ''both'' logic states, as well as a control to turn off both transistors to isolate the output. This differs from open collector/drain output, which only use a single transistor that can only disconnect the output or connect it to ground.
References
External links
{{Logic Families Digital circuits