Olmecs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Olmecs () or Olmec were an early known major
MIT. The process involved extracting
 The Olmec culture was first defined as an art style, and this continues to be the hallmark of the culture.Coe (2002), p. 62. Wrought in a large number of media – jade, clay, basalt, and greenstone among others – much Olmec art, such as ''The Wrestler'', is naturalistic. Other art expresses fantastic anthropomorphic creatures, often highly stylized, using an iconography reflective of a religious meaning. Common motifs include downturned mouths and a cleft head, both of which are seen in representations of werejaguars. In addition to making human and human-like subjects, Olmec artisans were adept at animal portrayals.
While
The Olmec culture was first defined as an art style, and this continues to be the hallmark of the culture.Coe (2002), p. 62. Wrought in a large number of media – jade, clay, basalt, and greenstone among others – much Olmec art, such as ''The Wrestler'', is naturalistic. Other art expresses fantastic anthropomorphic creatures, often highly stylized, using an iconography reflective of a religious meaning. Common motifs include downturned mouths and a cleft head, both of which are seen in representations of werejaguars. In addition to making human and human-like subjects, Olmec artisans were adept at animal portrayals.
While
 The heads range in size from the Rancho La Cobata head, at high, to the pair at Tres Zapotes, at . Scholars calculate that the largest heads weigh between .
The heads were carved from single blocks or boulders of volcanic
The heads range in size from the Rancho La Cobata head, at high, to the pair at Tres Zapotes, at . Scholars calculate that the largest heads weigh between .
The heads were carved from single blocks or boulders of volcanic
Smarthistory.com
Olmec arts are strongly tied to the Olmec religion, which prominently featured jaguars. The Olmec people believed that in the distant past a race of werejaguars was made between the union of a jaguar and a woman. One werejaguar quality that can be found is the sharp cleft in the forehead of many supernatural beings in Olmec art. This sharp cleft is associated with the natural indented head of jaguars.
Ornamental Mask MET 1978.412.30.jpg, Ornamental mask; 10th century BCE; serpentine; height: 9.2 cm, width: 7.9 cm, depth: 3.2 cm;
British Museum Mesoamerica 052.jpg, 1200–400 BCE; polished green quartz ( aventurine); height: 29 cm, width: 13.5 cm;
 Olmec-style artifacts, designs, figurines, monuments and iconography have been found in the archaeological records of sites hundreds of kilometres outside the Olmec heartland. These sites include:
Olmec-style artifacts, designs, figurines, monuments and iconography have been found in the archaeological records of sites hundreds of kilometres outside the Olmec heartland. These sites include:
 The Long Count calendar used by many subsequent Mesoamerican civilizations, as well as the concept of
The Long Count calendar used by many subsequent Mesoamerican civilizations, as well as the concept of
File:La Venta Stele 19 (Delange).jpg, La Venta stele 19 with an early depiction of a feathered serpent
File:Olmec Head No. 1 at Xalapa, Veracruz, Mexico.jpg, Olmec Head No.1, 1200–900 BCE
File:Olmec kneeling figure, c. 1200-600 BCE.jpg, Kneeling human figure, 1200–600 BCE
File:Piezas del Conjunto Escultórico "Los Gemelos".jpg, The "twins" from El Azuzul, 1200–900 BCE
File:Mesoamerica, reportedly the Tepecoacuilco River Valley, Guerrero, Olmec sty - Carved Bowl - 2013.29 - Cleveland Museum of Art.tif, Carved travertine vessel with an incised pattern, 12th–3rd century BCE
File:Olmec celts from Met.jpg, Three
Scientists Find Earliest "New World" Writings in Mexico
2002. * (1987) ''Paléopaysages et archéologie pré-urbaine du bassin de México. Tomes I & II'' published by Centro Francés de Estudios Mexicanos y Centroamericanos, Mexico, D.F
* (1999
"Olmec Ritual Behavior at El Manatí: A Sacred Space"
in ''Social Patterns in Pre-Classic Mesoamerica'', eds. Grove, D. C.; Joyce, R. A., Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, Washington, D.C., pp. 225–254. * * *
, accessed March 2007. * * * "Art, Ritual, and Rulership in the Olmec World" in ''Ancient Civilizations of Mesoamerica: a Reader'', Blackwell Publishing Ltd., pp. 369–395. * (2005
in ''Archaeology'' (online), the Archaeological Institute of America, accessed February 2007. * * (1999) ''The Seventy Wonders of the Ancient World'', Thames & Hudson, London, . * (1996) "Daily Life in Olmec Times", in ''Olmec Art of Ancient Mexico'', eds. E. P. Benson and B. de la Fuente, National Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C., , pp. 262–263. * * (2007) "Olmec-influenced city found in Mexico", Associated Press, accessed 8 February 2007. * * * * (2006) ''Farming, Hunting, and Fishing in the Olmec World'', University of Texas Press, . * * * * *
Drawings and photographs of the 17 colossal heads
"Stone Etchings Represent Earliest New World Writing"
''
BBC audio file. Discussion of Olmec culture (15 mins)
'' A History of the World in 100 Objects''
Smithsonian Olmec Legacy
{{Authority control 16th-century BC establishments 4th-century BC disestablishments Ancient peoples Archaeological cultures of North America Formative period in the Americas History of Guerrero History of Tabasco History of Veracruz Hyperdiffusionism Mesoamerican cultures Pre-Columbian cultures of Mexico Indigenous peoples in Mexico
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
n civilization, flourishing in the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
and Tabasco
Tabasco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Tabasco, 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It i ...
from roughly 1200 to 400 BCE during Mesoamerica's formative period. They were initially centered at the site of their development in San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán
San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán or San Lorenzo is the collective name for three related archaeological sites—San Lorenzo, Tenochtitlán and Potrero Nuevo—located in the southeast portion of the Mexican state of Veracruz. Along with La Venta and Tre ...
, but moved to La Venta in the 10th century BCE following the decline of San Lorenzo. The Olmecs disappeared mysteriously in the 4th century BCE, leaving the region sparsely populated until the 19th century.
Among other "firsts", the Olmec appeared to practice ritual bloodletting and played the Mesoamerican ballgame, hallmarks of nearly all subsequent Mesoamerican societies. The aspect of the Olmecs most familiar now is their artwork, particularly the colossal heads. The Olmec civilization was first defined through artifacts which collectors purchased on the pre-Columbian art
Pre-Columbian art refers to the Visual arts of indigenous peoples of the Americas, visual arts of indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, North America, North, Central America, Central, and South Americas from at least 13,000 BCE to the European con ...
market in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Olmec artworks are considered among ancient America's most striking.
Etymology
The term Olmecs is derived from theNahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ...
(singular) or (plural). This word is composed of the two words ''ōlli'' , meaning "natural rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds.
Types of polyisoprene ...
", and ''mēcatl'' , meaning "people". Thus literally meaning "rubber people" in Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ...
.
Rubber for the balls used in the ceremonial ballgame was produced by the people in the Gulf Lowlands dating back to as early as 1600 BCE.Rubber ProcessingMIT. The process involved extracting
latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a wikt:milky, milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all floweri ...
from a rubber tree common in the area, '' Castilla elastica'', and mixing the latex with the juice of a local vine, '' Ipomoea alba.'' The Nahuas (including Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
) called their contemporary neighbors in the Gulf Lowlands "rubber people" but this was documented some 2,000 years after the end of the ancient Olmec culture. Archaeologists in the early 20th century mistakenly applied the name "Olmec" to the rediscovered ruins and artifacts in the heartland decades before it was understood that they were not created by the same "rubber people" that were contemporary with the Aztecs. Despite the mistaken identity, the name has stuck.
It is not known what name the ancient Olmec used for themselves; some later Mesoamerican accounts seem to refer to the ancient Olmec as " Tamoanchan". A contemporary term sometimes used for the Olmec culture is ''tenocelome'', meaning "mouth of the jaguar".
Overview
TheOlmec heartland
The Olmec heartland is the southern portion of Mexico's Gulf Coast of Mexico, Gulf Coast region between the Tuxtla mountains and the Olmec archaeological site of La Venta, extending roughly 80 km (50 mi) inland from the Gulf of Mexico coastline ...
is the area in the Gulf
A gulf is a large inlet from an ocean or their seas into a landmass, larger and typically (though not always) with a narrower opening than a bay (geography), bay. The term was used traditionally for large, highly indented navigable bodies of s ...
lowlands where it expanded after early development in Soconusco, Veracruz. This area is characterized by swampy lowlands punctuated by low hills, ridges, and volcanoes. The Sierra de los Tuxtlas rises sharply in the north, along the Gulf of Mexico's Bay of Campeche. Here, the Olmec constructed permanent city-temple complexes at San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán
San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán or San Lorenzo is the collective name for three related archaeological sites—San Lorenzo, Tenochtitlán and Potrero Nuevo—located in the southeast portion of the Mexican state of Veracruz. Along with La Venta and Tre ...
, La Venta, Tres Zapotes, and Laguna de los Cerros. In this region, the first Mesoamerican civilization emerged and reigned from BCE.
Origins
Pre-Olmec cultures had flourished since about 2500 BCE, and it has been speculated that the Olmecs derived in part from the neighboring Mokaya or Mixe–Zoque cultures which developed during this time. The beginnings of Olmec civilization have traditionally been placed between 1400 BCE and 1200 BCE. Past finds of Olmec remains ritually deposited at the shrine El Manatí near the triple archaeological sites known collectively asSan Lorenzo Tenochtitlán
San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán or San Lorenzo is the collective name for three related archaeological sites—San Lorenzo, Tenochtitlán and Potrero Nuevo—located in the southeast portion of the Mexican state of Veracruz. Along with La Venta and Tre ...
moved this back to at least 1600–1500 BCE. It seems that the Olmec had their roots in early farming cultures of Tabasco
Tabasco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Tabasco, 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It i ...
, which began between 5100 BCE and 4600 BCE. These shared the same basic food crops and technologies of the later Olmec civilization.
What is today called Olmec first appeared fully within San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán, where distinctive Olmec features occurred around 1400 BCE. The rise of civilization was assisted by the local ecology of well-watered alluvial soil, as well as by the transportation network provided by the Coatzacoalcos river basin. This environment may be compared to that of other ancient centers of civilization such as the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
, Indus, Yellow River
The Yellow River, also known as Huanghe, is the second-longest river in China and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system on Earth, with an estimated length of and a Drainage basin, watershed of . Beginning in the Bayan H ...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
. This highly productive environment encouraged a densely concentrated population, which in turn triggered the rise of an elite class. The elite class created the demand for the production of the symbolic and sophisticated luxury artifacts that define Olmec culture. Many of these luxury artifacts were made from materials such as jade
Jade is an umbrella term for two different types of decorative rocks used for jewelry or Ornament (art), ornaments. Jade is often referred to by either of two different silicate mineral names: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in t ...
, obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
, and magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula . It is one of the iron oxide, oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetism, ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetization, magnetized to become a ...
, which came from distant locations and suggest that early Olmec elites had access to an extensive trading network in Mesoamerica. The source of the most valued jade was the Motagua River valley in eastern Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
, and Olmec obsidian has been traced to sources in the Guatemala highlands, such as El Chayal and San Martín Jilotepeque, or in Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
, distances ranging from 200 to 400 km (120–250 miles) away, respectively.Pool, p. 103.
The state of Guerrero
Guerrero, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guerrero, is one of the 32 states that compose the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guerrero, 85 municipalities. The stat ...
, and in particular its early Mezcala culture, seem to have played an important role in the early history of Olmec culture. Olmec-style artifacts tend to appear earlier in some parts of Guerrero than in the Veracruz-Tabasco area. In particular, the relevant objects from the Amuco-Abelino site in Guerrero reveal dates as early as 1530 BCE.
La Venta
The first Olmec center, San Lorenzo, was all but abandoned around 900 BCE at about the same time that La Venta rose to prominence. Widespread destruction of many San Lorenzo monuments also occurred around the 950s BCE, which may indicate an internal uprising or, less likely, an invasion. The latest thinking, however, is that environmental changes may have been responsible for this shift in Olmec centers, with certain important rivers changing course. Following the decline of San Lorenzo, La Venta became the most prominent Olmec center, lasting from 900 BCE until its abandonment around 400 BCE. La Venta sustained the Olmec cultural traditions with spectacular displays of power and wealth. The Great Pyramid was the largest Mesoamerican structure of its time. Even today, after 2500 years of erosion, it rises above the naturally flat landscape. Buried deep within La Venta lay opulent, labor-intensive "offerings" – 1000 tons of smooth serpentine blocks, large mosaic pavements, and at least 48 separatevotive offering
A votive offering or votive deposit is one or more objects displayed or deposited, without the intention of recovery or use, in a sacred place for religious purposes. Such items are a feature of modern and ancient societies and are generally ...
s of polished jade celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
, pottery, figurines, and hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
mirrors.
Decline
Scholars have yet to determine the cause of the eventual extinction of the Olmec culture. Between 400 and 350 BCE, the population in the eastern half of the Olmec heartland dropped precipitously, and the area was sparsely inhabited until the 19th century. According to archaeologists, this depopulation was probably the result of "very serious environmental changes that rendered the region unsuited for large groups of farmers", in particular changes to the riverine environment that the Olmec depended upon for agriculture, hunting and gathering, and transportation. These changes may have been triggered bytectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons.
These processes ...
upheavals or subsidence, or the siltation
Siltation is water pollution caused by particulate terrestrial clastic material, with a particle size dominated by silt or clay. It refers both to the increased concentration of suspended sediments and to the increased accumulation (temporary o ...
of rivers due to agricultural practices.
One theory for the considerable population drop during the Terminal Formative period is suggested by Santley and colleagues (Santley et al. 1997), who propose the relocation of settlements due to volcanism, instead of extinction. Volcanic eruptions during the Early, Late and Terminal Formative periods would have blanketed the lands and forced the Olmec to move their settlements.
Whatever the cause, within a few hundred years of the abandonment of the last Olmec cities, successor cultures became firmly established. The Tres Zapotes site, on the western edge of the Olmec heartland, continued to be occupied well past 400 BCE, but without the hallmarks of the Olmec culture. This post-Olmec culture, often labeled the Epi-Olmec, has features similar to those found at Izapa, some to the southeast.
Artifacts
 The Olmec culture was first defined as an art style, and this continues to be the hallmark of the culture.Coe (2002), p. 62. Wrought in a large number of media – jade, clay, basalt, and greenstone among others – much Olmec art, such as ''The Wrestler'', is naturalistic. Other art expresses fantastic anthropomorphic creatures, often highly stylized, using an iconography reflective of a religious meaning. Common motifs include downturned mouths and a cleft head, both of which are seen in representations of werejaguars. In addition to making human and human-like subjects, Olmec artisans were adept at animal portrayals.
While
The Olmec culture was first defined as an art style, and this continues to be the hallmark of the culture.Coe (2002), p. 62. Wrought in a large number of media – jade, clay, basalt, and greenstone among others – much Olmec art, such as ''The Wrestler'', is naturalistic. Other art expresses fantastic anthropomorphic creatures, often highly stylized, using an iconography reflective of a religious meaning. Common motifs include downturned mouths and a cleft head, both of which are seen in representations of werejaguars. In addition to making human and human-like subjects, Olmec artisans were adept at animal portrayals.
While Olmec figurine
Olmec figurines are archetypical figurines produced by the Mesoamerican chronology#Classical Era, Formative Period inhabitants of Mesoamerica. While not all of these figurines were produced in the Olmec heartland, they bear the hallmarks and moti ...
s are found abundantly in sites throughout the Formative Period, the stone monuments such as the colossal heads are the most recognizable feature of Olmec culture. These monuments can be divided into four classes:
*Colossal heads (which can be up to tall);
*Rectangular "altars" (more likely thrones) such as Altar 5 shown below;
*Free-standing in-the-round sculpture, such as the twins from El Azuzul or San Martín Pajapan Monument 1; and
* Stele, such as La Venta Monument 19 above. The stelae form was generally introduced later than the colossal heads, altars, or free-standing sculptures. Over time, the stele changed from simple representation of figures, such as Monument 19 or La Venta Stela 1, toward representations of historical events, particularly acts legitimizing rulers. This trend would culminate in post-Olmec monuments such as La Mojarra Stela 1, which combines images of rulers with script and calendar dates.
Colossal heads
The most recognized aspect of the Olmec civilization are the enormous helmeted heads. As no known pre-Columbian text explains them, these impressive monuments have been the subject of much speculation. Once theorized to be ballplayers, it is now generally accepted that these heads are portraits of rulers, perhaps dressed as ballplayers. Infused with individuality, no two heads are alike and the helmet-like headdresses are adorned with distinctive elements, suggesting personal or group symbols. Some have also speculated that Mesoamerican people believed that the soul, along with all of one's experiences and emotions, was contained inside the head. Seventeen colossal heads have been unearthed to date. The heads range in size from the Rancho La Cobata head, at high, to the pair at Tres Zapotes, at . Scholars calculate that the largest heads weigh between .
The heads were carved from single blocks or boulders of volcanic
The heads range in size from the Rancho La Cobata head, at high, to the pair at Tres Zapotes, at . Scholars calculate that the largest heads weigh between .
The heads were carved from single blocks or boulders of volcanic basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
, found in the Sierra de los Tuxtlas. The Tres Zapotes heads, for example, were sculpted from basalt found at the summit of Cerro el Vigía, at the western end of the Tuxtlas. The San Lorenzo and La Venta heads, on the other hand, were probably carved from the basalt of Cerro Cintepec, on the southeastern side, perhaps at the nearby Llano del Jicaro workshop, and dragged or floated to their final destination dozens of miles away. It has been estimated that moving a colossal head required the efforts of 1,500 people for three to four months.
Some of the heads, and many other monuments, have been variously mutilated, buried and disinterred, reset in new locations and/or reburied. Some monuments, and at least two heads, were recycled or recarved, but it is not known whether this was simply due to the scarcity of stone or whether these actions had ritual or other connotations. Scholars believe that some mutilation had significance beyond mere destruction, but some scholars still do not rule out internal conflicts or, less likely, invasion as a factor.
The flat-faced, thick-lipped heads have caused some debate due to their resemblance to some African facial characteristics. Based on this comparison, some writers have said that the Olmecs were Africans who had emigrated to the New World. But the vast majority of archaeologists and other Mesoamerican scholars reject claims of pre-Columbian contacts with Africa. Explanations for the facial features of the colossal heads include the possibility that the heads were carved in this manner due to the shallow space allowed on the basalt boulders. Others note that in addition to the broad noses and thick lips, the eyes of the heads often show the epicanthic fold, and that all these characteristics can still be found in modern Mesoamerican Indians. For instance, in the 1940s, the artist/art historian Miguel Covarrubias published a series of photos of Olmec artwork and of the faces of modern Mexican Indians with very similar facial characteristics. The African origin hypothesis assumes that Olmec carving was intended to be a representation of the inhabitants, an assumption that is hard to justify given the full corpus of representation in Olmec carving.
Ivan Van Sertima claimed that the seven braids on the Tres Zapotes head was an Ethiopian hair style, but he offered no evidence it was a contemporary style. The Egyptologist Frank J. Yurco has said that the Olmec braids do not resemble contemporary Egyptian or Nubian braids.
Richard Diehl wrote "There can be no doubt that the heads depict the American Indian physical type still seen on the streets of Soteapan, Acayucan, and other towns in the region."
Jade face masks
Another type of artifact is much smaller; hardstone carvings injade
Jade is an umbrella term for two different types of decorative rocks used for jewelry or Ornament (art), ornaments. Jade is often referred to by either of two different silicate mineral names: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in t ...
of a face in a mask form. Jade is a particularly precious material, and it was used as a mark of rank by the ruling classes. By 1500 BCE early Olmec sculptors mastered the human form.Miller, Mary Ellen. "The Art of Mesoamerica From Olmec to Aztec." Thames & Hudson; 4th edition (20 October 2006). This can be determined by wooden Olmec sculptures discovered in the swampy bogs of El Manati. Before radiocarbon dating could tell the exact age of Olmec pieces, archaeologists and art historians noticed the unique "Olmec-style" in a variety of artifacts.
Curators and scholars refer to "Olmec-style" face masks but, to date, no example has been recovered in an archaeologically controlled Olmec context. They have been recovered from sites of other cultures, including one deliberately deposited in the ceremonial altepetl (precinct) of Tenochtitlan
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th annivers ...
in what is now Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
. The mask would presumably have been about 2000 years old when the Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the ...
buried it, suggesting such masks were valued and collected as were Roman antiquities
Antiquities are objects from antiquity, especially the civilizations of the Mediterranean such as the Classical antiquity of Greece and Rome, Ancient Egypt, and the other Ancient Near Eastern cultures such as Ancient Persia (Iran). Artifact ...
in Europe. The 'Olmec-style' refers to the combination of deep-set eyes, nostrils, and strong, slightly asymmetrical mouth. The "Olmec-style" also very distinctly combines facial features of both humans and jaguars.The British Museum. "Olmec Stone Mask.Smarthistory.com
Olmec arts are strongly tied to the Olmec religion, which prominently featured jaguars. The Olmec people believed that in the distant past a race of werejaguars was made between the union of a jaguar and a woman. One werejaguar quality that can be found is the sharp cleft in the forehead of many supernatural beings in Olmec art. This sharp cleft is associated with the natural indented head of jaguars.
Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, colloquially referred to as the Met, is an Encyclopedic museum, encyclopedic art museum in New York City. By floor area, it is the List of largest museums, third-largest museum in the world and the List of larg ...
(New York City)
Mask MET AO1977.187.33.jpg, Mask; 10th–6th century BCE; jadeite; height: 17.1 cm, width: 16.5 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Mask, Gulf Coast Olmec culture, Rio Pesquero, Veracruz state, Middle Formative period, c. 900-500 BC, jadeite - Dallas Museum of Art - DSC04570.jpg, Mask; c. 900–500 BCE; jadeite; Dallas Museum of Art (Dallas
Dallas () is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of Texas metropolitan areas, most populous metropolitan area in Texas and the Metropolitan statistical area, fourth-most ...
, Texas, US)
Olmec mask MIA.jpg, Mask with cinnabar
Cinnabar (; ), or cinnabarite (), also known as ''mercurblende'' is the bright scarlet to brick-red form of Mercury sulfide, mercury(II) sulfide (HgS). It is the most common source ore for refining mercury (element), elemental mercury and is t ...
"tattoos"; c. 900–300 BCE; jadeite with cinnabar; Minneapolis Institute of Art (Minneapolis
Minneapolis is a city in Hennepin County, Minnesota, United States, and its county seat. With a population of 429,954 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the state's List of cities in Minnesota, most populous city. Locat ...
, US)
Kunz axes
The Kunz axes (also known as "votive axes") are figures that represent werejaguars and were apparently used for rituals. In most cases, the head is half the total volume of the figure. All Kunz axes have flat noses and an open mouth. The name "Kunz" comes from George Frederick Kunz, an Americanmineralogist
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical mineralogy, optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifact (archaeology), artifacts. Specific s ...
, who described a figure in 1890.
British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
(London)
Spirit axe, Gulf Coast Olmec culture, Tabasco state, Middle Formative period, c. 900-500 BC, stone - Dallas Museum of Art - DSC04581.jpg, 900–500 BCE; stone; Dallas Museum of Art (Texas, US)
Mexico, Olmec, 1200-300 BC - Celt with Deity - 1954.856 - Cleveland Museum of Art.tif, 12th–3rd century BCE; stone; height: 32.2 cm, width: 14 cm, depth: 11.5 cm; Cleveland Museum of Art
The Cleveland Museum of Art (CMA) is an art museum in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. Located in the Wade Park District of University Circle, the museum is internationally renowned for its substantial holdings of Asian art, Asian and Art of anc ...
(Ohio, US)
Anthropomorphic plaque, possibly the Fire Sepent, possibly a forgery, Olmec, Formative period, 800-400 BC, serpentine, cinnabar - Dallas Museum of Art - DSC04579.jpg, 800–400 BCE; serpentine, cinnabar
Cinnabar (; ), or cinnabarite (), also known as ''mercurblende'' is the bright scarlet to brick-red form of Mercury sulfide, mercury(II) sulfide (HgS). It is the most common source ore for refining mercury (element), elemental mercury and is t ...
; Dallas Museum of Art
Beyond the heartland
Central Mexico
Tlatilco and Tlapacoya, major centers of the Tlatilco culture in the Valley of Mexico, where artifacts include hollow baby-face motif figurines and Olmec designs on ceramics. Chalcatzingo, in Valley of Morelos, central Mexico, which features Olmec-style monumental art and rock art with Olmec-style figures. Also, in 2007, archaeologists unearthed Zazacatla, an Olmec-influenced city in Morelos. Located about south of Mexico City, Zazacatla covered about between 800 and 500 BCE.Western Mexico
Teopantecuanitlan, inGuerrero
Guerrero, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guerrero, is one of the 32 states that compose the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guerrero, 85 municipalities. The stat ...
, which features Olmec-style monumental art as well as city plans with distinctive Olmec features.
Also, the Juxtlahuaca and Oxtotitlán cave paintings feature Olmec designs and motifs.
Southern Mexico and Guatemala
Olmec influence is also seen at several sites in the Southern Maya area. In Guatemala, sites showing probable Olmec influence include San Bartolo, Takalik Abaj and La Democracia.Nature of interaction
Many theories have been advanced to account for the occurrence of Olmec influence far outside the heartland, including long-range trade by Olmec merchants, Olmec colonization of other regions, Olmec artisans travelling to other cities, conscious imitation of Olmec artistic styles by developing towns – some even suggest the prospect of Olmec military domination or that the Olmec iconography was actually developed outside the heartland. The generally accepted, but by no means unanimous, interpretation is that the Olmec-style artifacts, in all sizes, became associated with elite status and were adopted by non-Olmec Formative Period chieftains in an effort to bolster their status.Notable innovations
In addition to their influence with contemporaneous Mesoamerican cultures, as the first civilization in Mesoamerica, the Olmecs are credited, or speculatively credited, with many "firsts", including the bloodletting and perhapshuman sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease deity, gods, a human ruler, public or jurisdictional demands for justice by capital punishment, an authoritative/prie ...
, writing and epigraphy
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the wr ...
, and the invention of popcorn, zero
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. Adding (or subtracting) 0 to any number leaves that number unchanged; in mathematical terminology, 0 is the additive identity of the integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and compl ...
and the Mesoamerican calendar, and the Mesoamerican ballgame, as well as perhaps the compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with No ...
. Some researchers, including artist and art historian Miguel Covarrubias, even postulate that the Olmecs formulated the forerunners of many of the later Mesoamerican deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or god ...
.
Bloodletting and sacrifice speculation
Although the archaeological record does not include explicit representation of Olmec bloodletting, researchers have found other evidence that the Olmec ritually practiced it. For example, numerous natural and ceramic stingray spikes and maguey thorns have been found at Olmec sites, and certain artifacts have been identified as bloodletters. The argument that the Olmec instituted human sacrifice is significantly more speculative. No Olmec or Olmec-influenced sacrificial artifacts have yet been discovered; no Olmec or Olmec-influenced artwork unambiguously shows sacrificial victims (as do the ''danzante'' figures ofMonte Albán
Monte Albán is a large pre-Columbian archaeological site in the Santa Cruz Xoxocotlán Municipality in the southern Mexico, Mexican state of Oaxaca (17.043° N, 96.767°W). The site is located on a low mountainous range rising above the plain i ...
) or scenes of human sacrifice (such as can be seen in the famous ballcourt mural from El Tajín).
At El Manatí, disarticulated skulls and femurs, as well as the complete skeletons of newborns or fetuses, have been discovered amidst the other offerings, leading to speculation concerning infant sacrifice. Scholars have not determined how the infants met their deaths. Some authors have associated infant sacrifice with Olmec ritual art showing limp werejaguar babies, most famously in La Venta's Altar 5 (on the right) or Las Limas figure. Any definitive answer requires further findings.
Writing
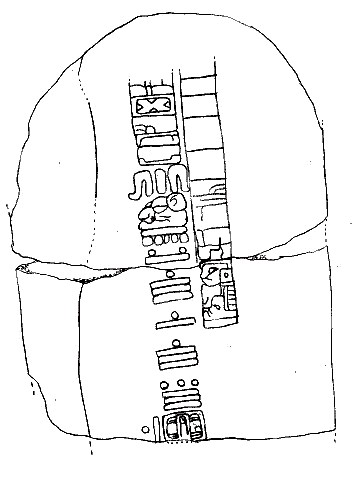
The Olmec may have been the first civilization in the Western Hemisphere to develop a writing system. Symbols found in 2002 and 2006 date from 650 BCE and 900 BCE respectively, preceding the oldest Zapotec writing found so far, which dates from about 500 BCE. The 2002 find at the San Andrés site shows a bird, speech scrolls, and glyphs that are similar to the later Maya script. Known as the Cascajal Block, and dated between 1100 and 900 BCE, the 2006 find from a site near San Lorenzo shows a set of 62 symbols, 28 of which are unique, carved on a serpentine block. A large number of prominent archaeologists have hailed this find as the "earliest pre-Columbian writing". Others are skeptical because of the stone's singularity, the fact that it had been removed from any archaeological context, and because it bears no apparent resemblance to any other Mesoamerican writing system. There are also well-documented later hieroglyphs known as the Isthmian script, and while there are some who believe that the Isthmian may represent a transitional script between an earlier Olmec writing system and the Maya script, the matter remains unsettled.Mesoamerican Long Count calendar and invention of the zero concept
 The Long Count calendar used by many subsequent Mesoamerican civilizations, as well as the concept of
The Long Count calendar used by many subsequent Mesoamerican civilizations, as well as the concept of zero
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. Adding (or subtracting) 0 to any number leaves that number unchanged; in mathematical terminology, 0 is the additive identity of the integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and compl ...
, may have been devised by the Olmecs. Because the six artifacts with the earliest Long Count calendar dates were all discovered outside the immediate Maya homeland, it is likely that this calendar predated the Maya and was possibly the invention of the Olmecs. Indeed, three of these six artifacts were found within the Olmec heartland. But an argument against an Olmec origin is the fact that the Olmec civilization had ended by the 4th century BCE, several centuries before the earliest known Long Count date artifact.
The Long Count calendar required the use of zero as a place-holder within its vigesimal
A vigesimal ( ) or base-20 (base-score) numeral system is based on 20 (number), twenty (in the same way in which the decimal, decimal numeral system is based on 10 (number), ten). ''wikt:vigesimal#English, Vigesimal'' is derived from the Latin a ...
(base-20) positional numeral system. A shell glyph – – was used as a zero symbol for these Long Count dates, the second oldest of which, on Stela C at Tres Zapotes, has a date of 32 BCE. This is one of the earliest uses of the zero concept in history.
Mesoamerican ballgame
The Olmec are strong candidates for originating the Mesoamerican ballgame so prevalent among later cultures of the region and used for recreational and religious purposes. A dozen rubber balls dating to 1600 BCE or earlier have been found in El Manatí, abog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and musk ...
east of San Lorenzo Tenochtitlan. These balls predate the earliest ballcourt yet discovered at Paso de la Amada, c. 1400 BCE, although there is no certainty that they were used in the ballgame.
Ethnicity and language
While the actual ethno-linguistic affiliation of the Olmec remains unknown, various hypotheses have been put forward. For example, in 1968 Michael D. Coe speculated that the Olmec were Maya predecessors. In 1976, linguistsLyle Campbell
Lyle Richard Campbell (born October 22, 1942) is an American scholar and linguist known for his studies of indigenous American languages, especially those of Central America, and on historical linguistics in general. Campbell is professor emeri ...
and Terrence Kaufman
Terrence Kaufman (1937 – March 3, 2022) was an American linguist specializing in documentation of unwritten languages, lexicography, Mesoamerican historical linguistics and language contact phenomena. He was an emeritus professor of linguistic ...
published a paper in which they argued a core number of loanwords had apparently spread from a Mixe–Zoquean language into many other Mesoamerican languages
Mesoamerican languages are the languages Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous to the Mesoamerican cultural area, which covers southern Mexico, all of Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, and parts of Honduras, Nicaragua and Costa Rica. The ar ...
. Campbell and Kaufman proposed that the presence of these core loanwords indicated that the Olmec – generally regarded as the first "highly civilized" Mesoamerican society – spoke a language ancestral to Mixe–Zoquean. The spread of this vocabulary particular to their culture accompanied the diffusion of other Olmec cultural and artistic traits that appears in the archaeological record of other Mesoamerican societies.
Mixe–Zoque specialist Søren Wichmann first critiqued this theory on the basis that most of the Mixe–Zoquean loans seemed to originate only from the Zoquean branch of the family. This implied the loanword transmission occurred in the period ''after'' the two branches of the language family split, placing the time of the borrowings outside of the Olmec period. However, new evidence has pushed back the proposed date for the split of Mixean and Zoquean languages to a period within the Olmec era.Wichmann, Beliaev & Davletshin, (in press Sep 2008). Based on this dating, the architectural and archaeological patterns and the particulars of the vocabulary loaned to other Mesoamerican languages from Mixe–Zoquean, Wichmann now suggests that the Olmecs of San Lorenzo spoke proto-Mixe and the Olmecs of La Venta spoke proto-Zoque.
At least the fact that the Mixe–Zoquean languages are still spoken in an area corresponding roughly to the Olmec heartland
The Olmec heartland is the southern portion of Mexico's Gulf Coast of Mexico, Gulf Coast region between the Tuxtla mountains and the Olmec archaeological site of La Venta, extending roughly 80 km (50 mi) inland from the Gulf of Mexico coastline ...
, and are historically known to have been spoken there, leads most scholars to assume that the Olmec spoke one or more Mixe–Zoquean languages.
Religion
Olmec religious activities were performed by a combination of rulers, full-time priests, andshaman
Shamanism is a spiritual practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into ...
s. The rulers seem to have been the most important religious figures, with their links to the Olmec deities or supernaturals providing legitimacy for their rule. There is also considerable evidence for shamans in the Olmec archaeological record, particularly in the so-called " transformation figures".
As no documentations of Olmec religious narratives and figures comparable to the ''Popol Vuh
''Popol Vuh'' (also ''Popul Vuh'' or ''Pop Vuj'') is a text recounting the mythology and history of the Kʼicheʼ people of Guatemala, one of the Maya peoples who also inhabit the Mexican states of Chiapas, Campeche, Yucatan and Quintana Roo, ...
'' has been left or found, any interpretation of Olmec religious narratives and figures must be based on interpretations of surviving monumental and portable art (such as the ''Señor de Las Limas'' statue at the Xalapa Museum), and comparisons with other seemingly similar elements found throughout nearby Mesoamerican cultures. Olmec art shows that such deities as Feathered Serpent and a supernatural rain were already in the Mesoamerican pantheon in Olmec times.
Social and political organization
Little is directly known about the societal or political structure of Olmec society. Although it is assumed by most researchers that the colossal heads and several other sculptures represent rulers, nothing has been found like the Maya stelae which name specific rulers and provide the dates of their rule. Instead, archaeologists relied on the data that they had, such as large- and small-scale site surveys. These provided evidence of considerable centralization within the Olmec region, first at San Lorenzo and then at La Venta – no other Olmec sites come close to these in terms of area or in the quantity and quality of architecture and sculpture. This evidence of geographic and demographic centralization leads archaeologists to propose that Olmec society itself was hierarchical, concentrated first at San Lorenzo and then at La Venta, with an elite that was able to use their control over materials such as water and monumental stone to exert command and legitimize their regime. Nonetheless, Olmec society is thought to lack many of the institutions of later civilizations, such as a standing army or priestly caste. And there is no evidence that San Lorenzo or La Venta controlled, even during their heyday, all of the Olmec heartland. There is some doubt, for example, that La Venta controlled even Arroyo Sonso, only some away. Studies of the Sierra de los Tuxtlas settlements, some away, indicate that this area was composed of more or less egalitarian communities outside the control of lowland centers.Trade
The wide diffusion of Olmec artifacts and "Olmecoid" iconography throughout much of Mesoamerica indicates the existence of extensive long-distance trade networks. Exotic, prestigious and high-value materials such as greenstone and marine shell were moved in significant quantities across large distances. Some of the reasons for trade revolve around the lack ofobsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
in the heartland. The Olmec used obsidian in many tools because worked edges were very sharp and durable. Most of the obsidian found has been traced back to Guatemala showing the extensive trade. While the Olmec were not the first in Mesoamerica to organize long-distance exchanges of goods, the Olmec period saw a significant expansion in interregional trade routes, more variety in material goods exchanged and a greater diversity in the sources from which the base materials were obtained.
Village life and diet
Despite their size and deliberate urban design, which was copied by other centers, San Lorenzo and La Venta were largely ceremonial centers, and the majority of the Olmec lived in villages similar to present-day villages and hamlets in Tabasco and Veracruz. These villages were located on higher ground and consisted of several scattered houses. A modest temple may have been associated with the larger villages. The individual dwellings would consist of a house, an associated lean-to, and one or more storage pits (similar in function to a root cellar). A nearby garden was used for medicinal and cooking herbs and for smaller crops, such as the domesticatedsunflower
The common sunflower (''Helianthus annuus'') is a species of large annual forb of the daisy family Asteraceae. The common sunflower is harvested for its edible oily seeds, which are often eaten as a snack food. They are also used in the pr ...
. Fruit trees, such as avocado or cacao, were probably available nearby.
Although the river banks were used to plant crops between flooding periods, the Olmecs probably also practiced slash-and-burn
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a form of shifting cultivation that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a Field (agriculture), field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody p ...
agriculture to clear the forests and shrubs, and to provide new fields once the old fields were exhausted. Fields were located outside the village, and were used for maize, beans, squash, cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although ...
, and sweet potato. Based on archaeological studies of two villages in the Tuxtlas Mountains, it is known that maize cultivation became increasingly important to the Olmec over time, although the diet remained fairly diverse.
The fruits and vegetables were supplemented with fish, turtle, snake, and mollusks from the nearby rivers, and crabs and shellfish in the coastal areas. Birds were available as food sources, as were game including peccary, opossum, raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the North American, northern or common raccoon (also spelled racoon) to distinguish it from Procyonina, other species of raccoon, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest ...
, rabbit, and in particular, deer. Despite the wide range of hunting and fishing available, midden surveys in San Lorenzo have found that the domesticated dog was the single most plentiful source of animal protein.
History of archaeological research
Olmec culture was unknown to historians until the mid-19th century. In 1869, the Mexican antiquarian traveller José Melgar y Serrano published a description of the first Olmec monument to have been found '' in situ''. This monument – the colossal head now labelled Tres Zapotes Monument A – had been discovered in the late 1850s by a farm worker clearing forested land on a ''hacienda
A ''hacienda'' ( or ; or ) is an estate (or '' finca''), similar to a Roman '' latifundium'', in Spain and the former Spanish Empire. With origins in Andalusia, ''haciendas'' were variously plantations (perhaps including animals or orchards ...
'' in Veracruz. Hearing about the curious find while travelling through the region, Melgar y Serrano first visited the site in 1862 to see for himself and complete the partially exposed sculpture's excavation. His description of the object, published several years later after further visits to the site, represents the earliest documented report of an artifact of what is now known as the Olmec culture.
In the latter half of the 19th century, Olmec artifacts such as the Kunz Axe (right) came to light and were subsequently recognized as belonging to a unique artistic tradition.
Frans Blom and Oliver La Farge made the first detailed descriptions of La Venta and San Martin Pajapan Monument 1 during their 1925 expedition. However, at this time, most archaeologists assumed the Olmec were contemporaneous with the Maya – even Blom and La Farge were, in their own words, "inclined to ascribe them to the Maya culture".
Matthew Stirling of the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase a ...
conducted the first detailed scientific excavations of Olmec sites in the 1930s and 1940s. Stirling, along with art historian Miguel Covarrubias, became convinced that the Olmec predated most other known Mesoamerican civilizations.
In counterpoint to Stirling, Covarrubias, and Alfonso Caso, however, Mayanists J. Eric Thompson and Sylvanus Morley argued for Classic-era dates for the Olmec artifacts. The question of Olmec chronology came to a head at a 1942 Tuxtla Gutierrez conference, where Alfonso Caso declared that the Olmecs were the "mother culture" ("''cultura madre''") of Mesoamerica.
Shortly after the conference, radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
proved the antiquity of the Olmec civilization, although the "mother culture" question generated considerable debate even 60 years later.
The Olmecs could have had direct influence on the societies around them. Olmec iconography and artwork uses imagery of animals such as the jaguar and the serpent, as well as large heads to depict their leaders. This same artwork and imagery can be seen in later civilizations' art and creations. Many Olmec artifacts have been found beyond their original territory. Despite the evidence, the hypothesis of a "mother culture" is uncertain as the diversity of cultures in Mesoamerica is great enough that the cultural strides made by the Olmec could have been made by other civilizations independently. In some cases, the motifs seen in Olmec archaeology might have been adopted from even earlier civilizations. Examples of these civilizations include the site of Zohapilco, the center for Tlatilco culture, the Zapotecs, and San Jose Mogote. Discoveries of older agriculture, writing, and ceramic creation show that cultures surrounding the Olmecs could have been more advanced, meaning that the Olmecs are not necessarily the "mother culture" that has been hypothesized.
At the site of Zohapilco, some of the oldest ceramics in Mesoamerica have been found dating back to almost 5,000 years ago. The area was known to have had a high population and was a clay-rich source for brickmaking. The ceramic figurines that have been found there represent pregnant women and could have influenced later Olmec civilization. Olmec art shows that they could have adopted very similar styles of art. These connections show the complexity of Mesoamerican culture through the discovery of more and more ceramics throughout the region.
San Jose Mogote is another site that has elements of cultural strides that the Olmecs could have adopted as the site can be dated back to 1500–500 BCE. San Jose Mogote is a site that dates to the early Zapotecs, a civilization that situated well outside the Olmec heartland. The site shows some of the earlier signs of a working irrigation system by diverting water from streams over cropland. This irrigation system created by the Zapotecs existed well before the Olmecs existed as a society. The Olmecs also used various irrigation methods, but because of the difference in dating it is safe to infer that they most likely obtained some of these methods and ideas from the Zapotecs.
Despite evidence existing that at one time pointed in the direction that the Olmecs could have been a "mother culture" in Mesoamerica, these new discoveries largely refute that idea. The older evidence of the Zapotecs and other civilizations show that what was once considered Olmec technological and social evolutions were in fact much more widespread throughout the region before the Olmecs had even arrived at their strongest point. Mesoamerica is filled with many different civilizations that all contributed to the overall development of the region as time went on.
DNA
In the investigations of the San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán Archaeological Project at the sites of San Lorenzo and Loma del Zapote, several human burials from the Olmec period were found. The bone consistency in two of them allowed the study of their mitochondrial DNA to be carried out successfully, as part of an investigation that proposes the comparative analysis of the genetic information of the Olmecs with that obtained from subjects from other Mesoamerican societies under the advice of the specialists Dr. María de Lourdes Muñoz Moreno and Miguel Moreno Galeana, both at CINVESTAV in Mexico. This pioneering study of mitochondrial DNA in 2018 was carried out on two Olmec individuals, one from San Lorenzo and the other from Loma del Zapote, resulted, in both cases, in the unequivocal presence of the distinctive mutations of the haplogroup A maternal lineage. They share the most abundant of the five mitochondrial haplogroups characteristic of the indigenous populations of the Americas: A, B, C, D and X.Alternative origin speculations
Partly because the Olmecs developed the first Mesoamerican civilization, and partly because little is known of them compared to later Mesoamerican civilizations such as the Maya or Aztec, a number of Olmec alternative origin speculations have been put forth. Although several of these speculations, particularly the theory that the Olmecs were of African origin popularized by Ivan Van Sertima's book ''They Came Before Columbus'', have become well known within popular culture, they are not considered credible by the vast majority of Mesoamerican researchers and scientists, who discard them as pop-culture pseudo-science. As of 2018, mitochondrial DNA studies carried out on Olmec remains, one from San Lorenzo and the other from Loma del Zapote, resulted, in both cases, in the "unequivocal presence of the distinctive mutations of the “A" maternal lineage. That is, the maternal ancestry of the Olmecs is not in Africa but in America, since they share the most abundant of the five mitochondrial haplogroups characteristic of the indigenous populations of the continent: A, B, C, D and X.Gallery
celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
, Olmec ritual objects
File:Jaguarbaby.jpg, Olmec were-jaguar
File:Olmec-style bottle 1.jpg, Olmec style bottle, reputedly from Las Bocas, 1100–800 BCE
File:Olmecmask.jpg, Olmec jade mask
File:Juxtlahuaca Ruler (M Lachniet).jpg, Olmec-style painting from the Juxtlahuaca cave
File:Olmec baby-face figurine, Snite.jpg, An Olmec "baby figurine"
File:Chalcatzingo - el rey close.jpg, Olmec-style bas relief "El Rey" from Chalcatzingo
See also
* El Azuzul – a small archaeological site in the Olmec heartland * Cerro de las Mesas – a post-Olmec archaeological site * List of megalithic sites * List of Mesoamerican pyramidsReferences
Bibliography
* * * * (see index) * * * (1975) "Lodestone Compass: Chinese or Olmec Primacy? Multidisciplinary Analysis of an Olmec Hematite Artifact from San Lorenzo, Veracruz, Mexico”, ''Science'', New Series, 189 (4205) (5 September 1975), pp. 753–760 (753). * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * (1996) " atalogue #3. Figure Seated on a Throne with Infant on Lap", in ''Olmec Art of Ancient Mexico'', eds. E. P. Benson and B. de la Fuente, National Gallery of Art, Washington D.C., , p. 218. * * * * * (2002Scientists Find Earliest "New World" Writings in Mexico
2002. * (1987) ''Paléopaysages et archéologie pré-urbaine du bassin de México. Tomes I & II'' published by Centro Francés de Estudios Mexicanos y Centroamericanos, Mexico, D.F
* (1999
"Olmec Ritual Behavior at El Manatí: A Sacred Space"
in ''Social Patterns in Pre-Classic Mesoamerica'', eds. Grove, D. C.; Joyce, R. A., Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, Washington, D.C., pp. 225–254. * * *
, accessed March 2007. * * * "Art, Ritual, and Rulership in the Olmec World" in ''Ancient Civilizations of Mesoamerica: a Reader'', Blackwell Publishing Ltd., pp. 369–395. * (2005
in ''Archaeology'' (online), the Archaeological Institute of America, accessed February 2007. * * (1999) ''The Seventy Wonders of the Ancient World'', Thames & Hudson, London, . * (1996) "Daily Life in Olmec Times", in ''Olmec Art of Ancient Mexico'', eds. E. P. Benson and B. de la Fuente, National Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C., , pp. 262–263. * * (2007) "Olmec-influenced city found in Mexico", Associated Press, accessed 8 February 2007. * * * * (2006) ''Farming, Hunting, and Fishing in the Olmec World'', University of Texas Press, . * * * * *
External links
Drawings and photographs of the 17 colossal heads
"Stone Etchings Represent Earliest New World Writing"
''
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Pri ...
''; Ma. del Carmen Rodríguez Martínez, Ponciano Ortíz Ceballos, Michael D. Coe, Richard A. Diehl, Stephen D. Houston, Karl A. Taube, Alfredo Delgado Calderón, Oldest Writing in the New World, ''Science'', Vol 313, 15 September 2006, pp. 1610–1614.
BBC audio file. Discussion of Olmec culture (15 mins)
'' A History of the World in 100 Objects''
Smithsonian Olmec Legacy
{{Authority control 16th-century BC establishments 4th-century BC disestablishments Ancient peoples Archaeological cultures of North America Formative period in the Americas History of Guerrero History of Tabasco History of Veracruz Hyperdiffusionism Mesoamerican cultures Pre-Columbian cultures of Mexico Indigenous peoples in Mexico