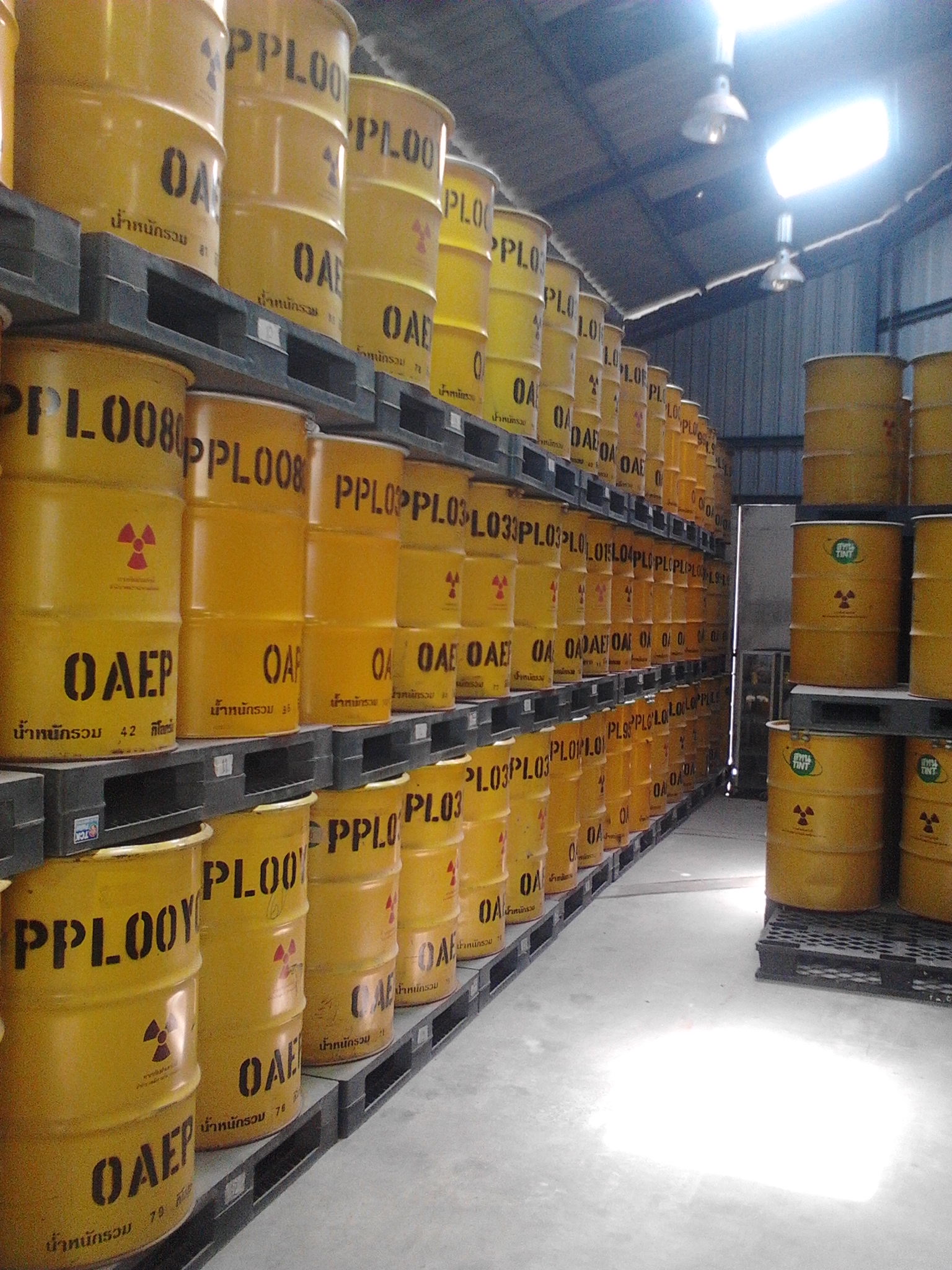

Radioactive waste is a type of
hazardous waste
Hazardous waste is waste that has substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment. Hazardous waste is a type of dangerous goods. They usually have one or more of the following hazardous traits: ignitability, reactivity, cor ...
that contains
radioactive material
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including
nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is " radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emi ...
,
nuclear research,
nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
generation,
rare-earth mining, and
nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
s reprocessing.
The storage and disposal of radioactive waste is regulated by government agencies in order to protect human health and the environment.
Radioactive waste is broadly classified into
low-level waste
Low-level waste (LLW) or Low-level radioactive waste (LLRW) is nuclear waste that does not fit into the categorical definitions for intermediate-level waste (ILW), high-level waste (HLW), spent nuclear fuel (SNF), transuranic waste (TRU), or ce ...
(LLW), such as paper, rags, tools, clothing, which contain small amounts of mostly short-lived radioactivity, intermediate-level waste (ILW), which contains higher amounts of radioactivity and requires some shielding, and high-level waste (HLW), which is highly radioactive and hot due to decay heat, so requires cooling and shielding.
In
nuclear reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing is the chemical separation of fission products and actinides from spent nuclear fuel. Originally, reprocessing was used solely to extract plutonium for producing nuclear weapons. With commercialization of nuclear power, th ...
plants about 96% of
spent nuclear fuel is recycled back into uranium-based and
mixed-oxide (MOX) fuels. The residual 4% is
minor actinides and
fission products
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release ...
the latter of which are a mixture of stable and quickly decaying (most likely already having decayed in the
spent fuel pool) elements, medium lived fission products such as
Strontium-90
Strontium-90 () is a radioactive isotope of strontium produced by nuclear fission, with a half-life of 28.8 years. It undergoes β− decay into yttrium-90, with a decay energy of 0.546 MeV. Strontium-90 has applications in medicine and ...
and
Caesium-137 and finally seven
long-lived fission products with half lives in the hundreds of thousands to millions of years. The minor actinides meanwhile are heavy elements other than uranium and plutonium which are created by
neutron capture
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons ...
. Their half lives range from years to millions of years and as
alpha emitters they are particularly radiotoxic. While there are proposed - and to a much lesser extent current - uses of all those elements, commercial scale reprocessing using the
PUREX
PUREX (plutonium uranium reduction extraction) is a chemical method used to purify fuel for nuclear reactors or nuclear weapons. PUREX is the '' de facto'' standard aqueous nuclear reprocessing method for the recovery of uranium and pluto ...
-process disposes of them as waste together with the fission products. The waste is subsequently
converted into a glass-like ceramic for storage in a
deep geological repository
A deep geological repository is a way of storing hazardous or radioactive waste within a stable geologic environment (typically 200–1000 m deep). It entails a combination of waste form, waste package, engineered seals and geology that is suite ...
.
The time radioactive waste must be stored for depends on the type of waste and radioactive isotopes it contains. Short-term approaches to radioactive waste storage have been segregation and storage on the surface or near-surface. Burial in a
deep geological repository
A deep geological repository is a way of storing hazardous or radioactive waste within a stable geologic environment (typically 200–1000 m deep). It entails a combination of waste form, waste package, engineered seals and geology that is suite ...
is a favored solution for long-term storage of high-level waste, while re-use and
transmutation are favored solutions for reducing the HLW inventory. Boundaries to recycling of spent nuclear fuel are regulatory and economic as well as the issue of
radioactive contamination
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases (including the human body), where their presence is unintended or undesirab ...
if chemical separation processes cannot achieve a very high purity. Furthermore, elements may be present in both useful and troublesome isotopes, which would require costly and energy intensive isotope separation for their use - a currently uneconomic prospect.
A summary of the amounts of radioactive waste and management approaches for most developed countries are presented and reviewed periodically as part of the
International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 195 ...
(IAEA)'s
.
Nature and significance
A quantity of radioactive waste typically consists of a number of
radionuclides, which are unstable isotopes of elements that undergo
decay and thereby emit
ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
, which is harmful to humans and the environment. Different isotopes emit different types and levels of radiation, which last for different periods of time.
Physics
The radioactivity of all radioactive waste weakens with time. All
radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transfer ...
s contained in the waste have a
half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ...
— the time it takes for half of the atoms to decay into another
nuclide
A nuclide (or nucleide, from atomic nucleus, nucleus, also known as nuclear species) is a class of atoms characterized by their number of protons, ''Z'', their number of neutrons, ''N'', and their nuclear energy state.
The word ''nuclide'' was co ...
. Eventually, all radioactive waste decays into non-radioactive elements (i.e.,
stable nuclides). Since radioactive decay follows the half-life rule, the rate of decay is inversely proportional to the duration of decay. In other words, the radiation from a long-lived isotope like
iodine-129 will be much less intense than that of a short-lived isotope like
iodine-131
Iodine-131 (131I, I-131) is an important radioisotope of iodine discovered by Glenn Seaborg and John Livingood in 1938 at the University of California, Berkeley. It has a radioactive decay half-life of about eight days. It is associated with n ...
. The two tables show some of the major radioisotopes, their half-lives, and their
radiation yield as a proportion of the yield of fission of uranium-235.
The energy and the type of the
ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
emitted by a radioactive substance are also important factors in determining its threat to humans. The chemical properties of the radioactive
element will determine how mobile the substance is and how likely it is to spread into the environment and
contaminate humans. This is further complicated by the fact that many radioisotopes do not decay immediately to a stable state but rather to radioactive
decay product
In nuclear physics, a decay product (also known as a daughter product, daughter isotope, radio-daughter, or daughter nuclide) is the remaining nuclide left over from radioactive decay. Radioactive decay often proceeds via a sequence of steps ( ...
s within a
decay chain
In nuclear science, the decay chain refers to a series of radioactive decays of different radioactive decay products as a sequential series of transformations. It is also known as a "radioactive cascade". Most radioisotopes do not decay dire ...
before ultimately reaching a stable state.
Pharmacokinetics
Exposure to radioactive waste may cause health impacts due to ionizing radiation exposure. In humans, a dose of 1
sievert
The sievert (symbol: SvNot be confused with the sverdrup or the svedberg, two non-SI units that sometimes use the same symbol.) is a unit in the International System of Units (SI) intended to represent the stochastic health risk of ionizing rad ...
carries a 5.5% risk of developing cancer,
and regulatory agencies
assume the risk is linearly proportional to dose even for low doses. Ionizing radiation can cause deletions in chromosomes. If a developing organism such as a
fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal dev ...
is irradiated, it is possible a
birth defect
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities ca ...
may be induced, but it is unlikely this defect will be in a
gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce ...
or a gamete-forming
cell. The incidence of radiation-induced mutations in humans is small, as in most mammals, because of natural cellular-repair mechanisms, many just now coming to light. These mechanisms range from DNA,
mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
and protein repair, to internal lysosomic digestion of defective proteins, and even induced cell suicide—apoptosis
Depending on the decay mode and the
pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered ...
of an element (how the body processes it and how quickly), the threat due to exposure to a given activity of a
radioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
will differ. For instance,
iodine-131
Iodine-131 (131I, I-131) is an important radioisotope of iodine discovered by Glenn Seaborg and John Livingood in 1938 at the University of California, Berkeley. It has a radioactive decay half-life of about eight days. It is associated with n ...
is a short-lived
beta
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; grc, βῆτα, bē̂ta or ell, βήτα, víta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiod ...
and
gamma
Gamma (uppercase , lowercase ; ''gámma'') is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter r ...
emitter, but because it concentrates in the
thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The ...
gland, it is more able to cause injury than
caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that a ...
-137 which, being
water soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solub ...
, is rapidly excreted through urine. In a similar way, the
alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ''álpha'', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , whi ...
emitting actinides and
radium
Radium is a chemical element with the symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, but it readily reacts with nitrogen (rat ...
are considered very harmful as they tend to have long
biological half-lives and their radiation has a high
relative biological effectiveness
In radiobiology, the relative biological effectiveness (often abbreviated as RBE) is the ratio of biological effectiveness of one type of ionizing radiation relative to another, given the same amount of absorbed energy. The RBE is an empiric ...
, making it far more damaging to tissues per amount of energy deposited. Because of such differences, the rules determining biological injury differ widely according to the radioisotope, time of exposure, and sometimes also the nature of the chemical compound which contains the radioisotope.
Sources
Radioactive waste comes from a number of sources. In countries with nuclear power plants, nuclear armament, or nuclear fuel treatment plants, the majority of waste originates from the nuclear fuel cycle and nuclear weapons reprocessing. Other sources include medical and industrial wastes, as well as naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM) that can be concentrated as a result of the processing or consumption of coal, oil, and gas, and some minerals, as discussed below.
Nuclear fuel cycle
Front end
Waste from the front end of the
nuclear fuel cycle is usually alpha-emitting waste from the extraction of uranium. It often contains radium and its decay products.
Uranium dioxide
Uranium dioxide or uranium(IV) oxide (), also known as urania or uranous oxide, is an oxide of uranium, and is a black, radioactive, crystalline powder that naturally occurs in the mineral uraninite. It is used in nuclear fuel rods in nuclear re ...
(UO
2) concentrate from mining is a thousand or so times as radioactive as the
granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
used in buildings. It is refined from
yellowcake (U
3O
8), then converted to
uranium hexafluoride gas (UF
6). As a gas, it undergoes
enrichment
Enrichment may refer to:
* Behavioral enrichment, the practice of providing animals under managed care with stimuli such as natural and artificial objects
* Data enrichment, appending or enhancing data with relevant context from other sources, se ...
to increase the
U-235 content from 0.7% to about 4.4% (LEU). It is then turned into a hard
ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, ...
oxide (UO
2) for assembly as reactor fuel elements.
The main by-product of enrichment is
depleted uranium
Depleted uranium (DU; also referred to in the past as Q-metal, depletalloy or D-38) is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope than natural uranium.: "Depleted uranium possesses only 60% of the radioactivity of natural uranium, hav ...
(DU), principally the
U-238 isotope, with a U-235 content of ~0.3%. It is stored, either as UF
6 or as U
3O
8. Some is used in applications where its extremely high density makes it valuable such as
anti-tank
Anti-tank warfare originated from the need to develop technology and tactics to destroy tanks during World War I. Since the Triple Entente deployed the first tanks in 1916, the German Empire developed the first anti-tank weapons. The first dev ...
shells, and on at least
one occasion even a sailboat
keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in Br ...
. It is also used with plutonium for making
mixed oxide fuel (MOX) and to dilute, or
downblend, highly enriched uranium from weapons stockpiles which is now being redirected to become reactor fuel.
Back end
The back-end of the nuclear fuel cycle, mostly spent
fuel rods, contains
fission product
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release ...
s that emit beta and gamma radiation, and
actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The info ...
s that emit
alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be prod ...
s, such as
uranium-234
Uranium-234 (234U or U-234) is an isotope of uranium. In natural uranium and in uranium ore, 234U occurs as an indirect decay product of uranium-238, but it makes up only 0.0055% (55 parts per million) of the raw uranium because its half-life ...
(half-life 245 thousand years),
neptunium-237 (2.144 million years),
plutonium-238
Plutonium-238 (238Pu or Pu-238) is a fissile, radioactive isotope of plutonium that has a half-life of 87.7 years.
Plutonium-238 is a very powerful alpha emitter; as alpha particles are easily blocked, this makes the plutonium-238 isotope suit ...
(87.7 years) and
americium-241 (432 years), and even sometimes some neutron emitters such as
californium
Californium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first synthesized in 1950 at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (then the University of California Radiation Laboratory), by bombarding c ...
(half-life of 898 years for californium-251). These isotopes are formed in
nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat fr ...
s.
It is important to distinguish the processing of uranium to make fuel from the
reprocessing of used fuel. Used fuel contains the highly radioactive products of fission (see high-level waste below). Many of these are neutron absorbers, called
neutron poison
In applications such as nuclear reactors, a neutron poison (also called a neutron absorber or a nuclear poison) is a substance with a large neutron absorption cross-section. In such applications, absorbing neutrons is normally an undesirable eff ...
s in this context. These eventually build up to a level where they absorb so many neutrons that the chain reaction stops, even with the control rods completely removed. At that point, the fuel has to be replaced in the reactor with fresh fuel, even though there is still a substantial quantity of
uranium-235
Uranium-235 (235U or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exi ...
and
plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exh ...
present. In the United States, this used fuel is usually "stored", while in other countries such as Russia, the United Kingdom, France, Japan, and India, the fuel is reprocessed to remove the fission products, and the fuel can then be re-used. The fission products removed from the fuel are a concentrated form of high-level waste as are the chemicals used in the process. While most countries reprocess the fuel carrying out single plutonium cycles, India is planning multiple plutonium recycling schemes
and Russia pursues closed cycle.
Fuel composition and long term radioactivity

The use of different fuels in nuclear reactors results in different
spent nuclear fuel (SNF) composition, with varying activity curves. The most abundant material being U-238 with other uranium isotopes, other actinides, fission products and activation products.
Long-lived radioactive waste from the back end of the fuel cycle is especially relevant when designing a complete waste management plan for SNF. When looking at long-term
radioactive decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
, the actinides in the SNF have a significant influence due to their characteristically long half-lives. Depending on what a
nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat fr ...
is fueled with, the actinide composition in the SNF will be different.
An example of this effect is the use of
nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is material used in nuclear power stations to produce heat to power turbines. Heat is created when nuclear fuel undergoes nuclear fission.
Most nuclear fuels contain heavy fissile actinide elements that are capable of undergo ...
s with
thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
. Th-232 is a fertile material that can undergo a neutron capture reaction and two beta minus decays, resulting in the production of fissile
U-233. The SNF of a cycle with thorium will contain U-233. Its radioactive decay will strongly influence the long-term
activity curve of the SNF around a million years. A comparison of the activity associated to U-233 for three different SNF types can be seen in the figure on the top right. The burnt fuels are thorium with reactor-grade plutonium (RGPu), thorium with weapons-grade plutonium (WGPu), and
Mixed oxide fuel (MOX, no thorium). For RGPu and WGPu, the initial amount of U-233 and its decay around a million years can be seen. This has an effect on the total activity curve of the three fuel types. The initial absence of U-233 and its daughter products in the MOX fuel results in a lower activity in region 3 of the figure on the bottom right, whereas for RGPu and WGPu the curve is maintained higher due to the presence of U-233 that has not fully decayed.
Nuclear reprocessing
Nuclear reprocessing is the chemical separation of fission products and actinides from spent nuclear fuel. Originally, reprocessing was used solely to extract plutonium for producing nuclear weapons. With commercialization of nuclear power, th ...
can remove the actinides from the spent fuel so they can be used or destroyed (see ).
Proliferation concerns
Since uranium and plutonium are
nuclear weapons
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
materials, there have been proliferation concerns. Ordinarily (in
spent nuclear fuel), plutonium is
reactor-grade plutonium. In addition to
plutonium-239
Plutonium-239 (239Pu or Pu-239) is an isotope of plutonium. Plutonium-239 is the primary fissile isotope used for the production of nuclear weapons, although uranium-235 is also used for that purpose. Plutonium-239 is also one of the three mai ...
, which is highly suitable for building nuclear weapons, it contains large amounts of undesirable contaminants:
plutonium-240,
plutonium-241, and
plutonium-238
Plutonium-238 (238Pu or Pu-238) is a fissile, radioactive isotope of plutonium that has a half-life of 87.7 years.
Plutonium-238 is a very powerful alpha emitter; as alpha particles are easily blocked, this makes the plutonium-238 isotope suit ...
. These isotopes are extremely difficult to separate, and more cost-effective ways of obtaining fissile material exist (e.g., uranium enrichment or dedicated plutonium production reactors).
High-level waste is full of highly radioactive
fission products
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release ...
, most of which are relatively short-lived. This is a concern since if the waste is stored, perhaps in
deep geological storage, over many years the fission products decay, decreasing the radioactivity of the waste and making the plutonium easier to access. The undesirable contaminant Pu-240 decays faster than the Pu-239, and thus the quality of the bomb material increases with time (although its quantity decreases during that time as well). Thus, some have argued, as time passes, these deep storage areas have the potential to become "plutonium mines", from which material for nuclear weapons can be acquired with relatively little difficulty. Critics of the latter idea have pointed out the difficulty of recovering useful material from sealed deep storage areas makes other methods preferable. Specifically, high radioactivity and heat (80 °C in surrounding rock) greatly increase the difficulty of mining a storage area, and the enrichment methods required have high capital costs.
Pu-239 decays to
U-235 which is suitable for weapons and which has a very long half-life (roughly 10
9 years). Thus plutonium may decay and leave uranium-235. However, modern reactors are only moderately enriched with U-235 relative to U-238, so the U-238 continues to serve as a
denaturation agent for any U-235 produced by plutonium decay.
One solution to this problem is to recycle the plutonium and use it as a fuel e.g. in
fast reactors. In
pyrometallurgical fast reactors, the separated plutonium and uranium are contaminated by actinides and cannot be used for nuclear weapons.
Nuclear weapons decommissioning
Waste from nuclear weapons decommissioning is unlikely to contain much beta or gamma activity other than
tritium and
americium
Americium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a transuranic member of the actinide series, in the periodic table located under the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was n ...
. It is more likely to contain alpha-emitting actinides such as Pu-239 which is a fissile material used in bombs, plus some material with much higher specific activities, such as Pu-238 or Po.
In the past the neutron trigger for an
atomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
tended to be
beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to for ...
and a high activity alpha emitter such as
polonium; an alternative to polonium is
Pu-238
Plutonium-238 (238Pu or Pu-238) is a fissile, radioactive isotope of plutonium that has a half-life of 87.7 years.
Plutonium-238 is a very powerful alpha emitter; as alpha particles are easily blocked, this makes the plutonium-238 isotope suita ...
. For reasons of national security, details of the design of modern bombs are normally not released to the open literature.
Some designs might contain a
radioisotope thermoelectric generator
A radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG, RITEG), sometimes referred to as a radioisotope power system (RPS), is a type of nuclear battery that uses an array of thermocouples to convert the heat released by the decay of a suitable radioa ...
using Pu-238 to provide a long-lasting source of electrical power for the electronics in the device.
It is likely that the fissile material of an old bomb which is due for refitting will contain decay products of the plutonium isotopes used in it, these are likely to include
U-236 from Pu-240 impurities, plus some U-235 from decay of the Pu-239; due to the relatively long half-life of these Pu isotopes, these wastes from radioactive decay of bomb core material would be very small, and in any case, far less dangerous (even in terms of simple radioactivity) than the Pu-239 itself.
The beta decay of
Pu-241 forms
Am-241
Americium-241 (, Am-241) is an isotope of americium. Like all isotopes of americium, it is radioactive, with a half-life of . is the most common isotope of americium as well as the most prevalent isotope of americium in nuclear waste. It is com ...
; the in-growth of americium is likely to be a greater problem than the decay of Pu-239 and Pu-240 as the americium is a gamma emitter (increasing external-exposure to workers) and is an alpha emitter which can cause the generation of
heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is ...
. The plutonium could be separated from the americium by several different processes; these would include
pyrochemical processes and aqueous/organic
solvent extraction. A truncated
PUREX
PUREX (plutonium uranium reduction extraction) is a chemical method used to purify fuel for nuclear reactors or nuclear weapons. PUREX is the '' de facto'' standard aqueous nuclear reprocessing method for the recovery of uranium and pluto ...
type extraction process would be one possible method of making the separation.
Naturally occurring uranium is not fissile because it contains 99.3% of U-238 and only 0.7% of U-235.
Legacy waste
Due to historic activities typically related to the radium industry, uranium mining, and military programs, numerous sites contain or are contaminated with radioactivity. In the United States alone, the
Department of Energy states there are "millions of gallons of radioactive waste" as well as "thousands of tons of
spent nuclear fuel and material" and also "huge quantities of contaminated soil and water."
[U.S. Department of Energy Environmental Management](_blank)
–
Department of Energy Five Year Plan FY 2007-FY 2011 Volume II
." Retrieved 8 April 2007. Despite copious quantities of waste, the DOE has stated a goal of cleaning all presently contaminated sites successfully by 2025.
The
Fernald,
Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
site for example had "31 million pounds of uranium product", "2.5 billion pounds of waste", "2.75 million cubic yards of contaminated soil and debris", and a "223 acre portion of the underlying Great Miami Aquifer had uranium levels above drinking standards."
The United States has at least 108 sites designated as areas that are contaminated and unusable, sometimes many thousands of acres.
DOE wishes to clean or mitigate many or all by 2025, using the recently developed method of
geomelting, however the task can be difficult and it acknowledges that some may never be completely remediated. In just one of these 108 larger designations,
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is a U.S. multiprogram science and technology national laboratory sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and administered, managed, and operated by UT–Battelle as a federally funded research an ...
, there were for example at least "167 known contaminant release sites" in one of the three subdivisions of the site.
Some of the U.S. sites were smaller in nature, however, cleanup issues were simpler to address, and DOE has successfully completed cleanup, or at least closure, of several sites.
Medicine
Radioactive
medical waste
Biomedical waste or hospital waste is any kind of waste containing infectious (or potentially infectious) materials. It may also include waste associated with the generation of biomedical waste that visually appears to be of medical or laborator ...
tends to contain
beta particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, � ...
and
gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
emitters. It can be divided into two main classes. In diagnostic
nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is " radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emi ...
a number of short-lived gamma emitters such as
technetium-99m
Technetium-99m (99mTc) is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99 (itself an isotope of technetium), symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medica ...
are used. Many of these can be disposed of by leaving it to decay for a short time before disposal as normal waste. Other isotopes used in medicine, with half-lives in parentheses, include:
*
Y-90, used for treating
lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include en ...
(2.7 days)
*
I-131, used for
thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The ...
function tests and for treating
thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck. Ca ...
(8.0 days)
*
Sr-89, used for treating
bone cancer,
intravenous injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
(52 days)
*
Ir-192, used for
brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a form of radiation therapy where a sealed radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. ''Brachy'' is Greek for short. Brachytherapy is commonly used as an effective treatment for cervical, pro ...
(74 days)
*
Co-60
Cobalt-60 (60Co) is a synthetic radioactive isotope of cobalt with a half-life of 5.2713 years. It is produced artificially in nuclear reactors. Deliberate industrial production depends on neutron activation of bulk samples of the monoisoto ...
, used for brachytherapy and external radiotherapy (5.3 years)
*
Cs-137, used for brachytherapy and external radiotherapy (30 years)
*
Tc-99
Technetium-99 (99Tc) is an isotope of technetium which decays with a half-life of 211,000 years to stable ruthenium-99, emitting beta particles, but no gamma rays. It is the most significant long-lived fission product of uranium fission, produci ...
, product of the decay of Technetium-99m (221,000 years)
Industry
Industrial source waste can contain
alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ''álpha'', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , whi ...
,
beta
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; grc, βῆτα, bē̂ta or ell, βήτα, víta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiod ...
,
neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Since protons and ...
or gamma emitters. Gamma emitters are used in
radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeu ...
while neutron emitting sources are used in a range of applications, such as
oil well
An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas ma ...
logging.
Naturally occurring radioactive material

Substances containing natural radioactivity are known as
NORM (naturally occurring radioactive material). After human processing that exposes or concentrates this natural radioactivity (such as mining bringing coal to the surface or burning it to produce concentrated ash), it becomes technologically enhanced naturally occurring radioactive material (TENORM). A lot of this waste is
alpha particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be prod ...
-emitting matter from the decay chains of
uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
and
thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
. The main source of radiation in the human body is
potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmos ...
-40 (
40K), typically 17 milligrams in the body at a time and 0.4 milligrams/day intake. Most rocks, especially
granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
, have a low level of radioactivity due to the potassium-40, thorium and uranium contained.
Usually ranging from 1
millisievert (mSv) to 13 mSv annually depending on location, average radiation exposure from natural radioisotopes is 2.0 mSv per person a year worldwide.
[United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation]
Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, UNSCEAR 2008
This makes up the majority of typical total dosage (with mean annual exposure from other sources amounting to 0.6 mSv from medical tests averaged over the whole populace, 0.4 mSv from
cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
s, 0.005 mSv from the legacy of past atmospheric nuclear testing, 0.005 mSv occupational exposure, 0.002 mSv from the
Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two n ...
, and 0.0002 mSv from the nuclear fuel cycle).
TENORM is not regulated as restrictively as nuclear reactor waste, though there are no significant differences in the radiological risks of these materials.
Coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
contains a small amount of radioactive uranium, barium, thorium, and potassium, but, in the case of pure coal, this is significantly less than the average concentration of those elements in the
Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
. The surrounding strata, if shale or mudstone, often contain slightly more than average and this may also be reflected in the ash content of 'dirty' coals.
The more active ash minerals become concentrated in the
fly ash
Fly ash, flue ash, coal ash, or pulverised fuel ash (in the UK) plurale tantum: coal combustion residuals (CCRs)is a coal combustion product that is composed of the particulates (fine particles of burned fuel) that are driven out of coal-fired ...
precisely because they do not burn well.
The radioactivity of fly ash is about the same as black
shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especiall ...
and is less than
phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
rocks, but is more of a concern because a small amount of the fly ash ends up in the atmosphere where it can be inhaled. According to U.S.
National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) reports, population exposure from 1000-MWe power plants amounts to 490
person-rem/year for coal power plants, 100 times as great as nuclear power plants (4.8 person-rem/year). The exposure from the complete nuclear fuel cycle from mining to waste disposal is 136 person-rem/year; the corresponding value for coal use from mining to waste disposal is "probably unknown".
Oil and gas
Residues from the
oil and gas industry
The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing of petroleum products. The larges ...
often contain radium and its decay products. The sulfate scale from an oil well can be very radium rich, while the water, oil, and gas from a well often contain
radon
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colourless, odourless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains th ...
. The radon decays to form solid radioisotopes which form coatings on the inside of pipework. In an oil processing plant, the area of the plant where
propane
Propane () is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as ...
is processed is often one of the more contaminated areas of the plant as radon has a similar boiling point to propane.
Radioactive elements are an industrial problem in some oil wells where workers operating in direct contact with the crude oil and
brine
Brine is a high-concentration solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for ...
can be actually exposed to doses having negative health effects. Due to the relatively high concentration of these elements in the brine, its disposal is also a technological challenge. In the United States, the brine is however exempt from the dangerous waste regulations and can be disposed of regardless of radioactive or toxic substances content since the 1980s.
Rare-earth mining
Due to natural occurrence of radioactive elements such as
thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
and
radium
Radium is a chemical element with the symbol Ra and atomic number 88. It is the sixth element in group 2 of the periodic table, also known as the alkaline earth metals. Pure radium is silvery-white, but it readily reacts with nitrogen (rat ...
in
rare-earth ore, mining operations also result in production of waste and mineral deposits that are slightly radioactive.
Classification
Classification of radioactive waste varies by country. The IAEA, which publishes the Radioactive Waste Safety Standards (RADWASS), also plays a significant role. The proportion of various types of waste generated in the UK:
* 94% – low-level waste (LLW)
* ~6% – intermediate-level waste (ILW)
* <1% – high-level waste (HLW)
Mill tailings

Uranium tailings are waste by-product materials left over from the rough processing of
uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
-bearing
ore. They are not significantly radioactive. Mill tailings are sometimes referred to as 11(e)2 wastes, from the section of the
Atomic Energy Act of 1946
The Atomic Energy Act of 1946 (McMahon Act) determined how the United States would control and manage the nuclear technology it had jointly developed with its World War II allies, the United Kingdom and Canada. Most significantly, the Act ru ...
that defines them. Uranium mill tailings typically also contain
chemically hazardous heavy metal such as
lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
and
arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, b ...
. Vast mounds of uranium mill tailings are left at many old mining sites, especially in
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the ...
,
New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, and
Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its ...
.
Although mill tailings are not very radioactive, they have long half-lives. Mill tailings often contain radium, thorium and trace amounts of uranium.
Low-level waste
Low-level waste (LLW) is generated from hospitals and industry, as well as the
nuclear fuel cycle. Low-level wastes include paper, rags, tools, clothing, filters, and other materials which contain small amounts of mostly short-lived radioactivity. Materials that originate from any region of an Active Area are commonly designated as LLW as a precautionary measure even if there is only a remote possibility of being contaminated with radioactive materials. Such LLW typically exhibits no higher radioactivity than one would expect from the same material disposed of in a non-active area, such as a normal office block. Example LLW includes wiping rags, mops, medical tubes, laboratory animal carcasses, and more. LLW waste makes 94% of all radioactive waste volume in the UK.
Some high-activity LLW requires shielding during handling and transport but most LLW is suitable for shallow land burial. To reduce its volume, it is often compacted or incinerated before disposal. Low-level waste is divided into four classes: ''class A'', ''class B'', ''class C'', and ''Greater Than Class C'' (''GTCC'').
Intermediate-level waste

Intermediate-level waste (ILW) contains higher amounts of radioactivity compared to low-level waste. It generally requires shielding, but not cooling.
Intermediate-level wastes includes
resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on nat ...
s,
chemical sludge and metal
nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is material used in nuclear power stations to produce heat to power turbines. Heat is created when nuclear fuel undergoes nuclear fission.
Most nuclear fuels contain heavy fissile actinide elements that are capable of undergo ...
cladding, as well as contaminated materials from
reactor decommissioning. It may be solidified in
concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
or
bitumen
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term a ...
or mixed with silica sand and
vitrified
Vitrification (from Latin language, Latin ''vitreum'', "glass" via French language, French ''vitrifier'') is the full or partial transformation of a substance into a glass, that is to say, a non-Crystallinity, crystalline amorphous solid. Glasses ...
for disposal. As a general rule, short-lived waste (mainly non-fuel materials from reactors) is buried in shallow repositories, while long-lived waste (from fuel and
fuel reprocessing) is deposited in
geological repository
A deep geological repository is a way of storing hazardous or radioactive waste within a stable geologic environment (typically 200–1000 m deep). It entails a combination of waste form, waste package, engineered seals and geology that is suited ...
. Regulations in the United States do not define this category of waste; the term is used in Europe and elsewhere. ILW makes 6% of all radioactive waste volume in the UK.
High-level waste
High-level waste (HLW) is produced by nuclear reactors and the reprocessing of nuclear fuel. The exact definition of HLW differs internationally. After a nuclear fuel rod serves one fuel cycle and is removed from the core, it is considered HLW. Spent fuel rods contain mostly uranium with
fission products
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release ...
and
transuranic elements
The transuranium elements (also known as transuranic elements) are the chemical elements with atomic numbers greater than 92, which is the atomic number of uranium. All of these elements are unstable and decay radioactively into other elements. ...
generated in the
reactor core. Spent fuel is highly radioactive and often hot. HLW accounts for over 95% of the total radioactivity produced in the process of nuclear
electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its s ...
but it contributes to less than 1% of volume of all radioactive waste produced in the UK. Overall, the 60-year-long nuclear program in the UK up until 2019 produced 2150 m
3 of HLW.
The radioactive waste from spent fuel rods consists primarily of cesium-137 and strontium-90, but it may also include plutonium, which can be considered transuranic waste.
The half-lives of these radioactive elements can differ quite extremely. Some elements, such as cesium-137 and strontium-90 have half-lives of approximately 30 years. Meanwhile, plutonium has a half-life that can stretch to as long as 24,000 years.
The amount of HLW worldwide is currently increasing by about 12,000
tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s every year. A 1000-
megawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James ...
nuclear power plant produces about 27 t of spent nuclear fuel (unreprocessed) every year. For comparison, the amount of ash produced by coal power plants in the United States alone is estimated at 130,000,000 t per year and fly ash is estimated to release 100 times more radiation than an equivalent nuclear power plant.
In 2010, it was estimated that about 250,000 t of nuclear HLW were stored globally. This does not include amounts that have escaped into the environment from accidents or tests.
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
is estimated to hold 17,000 t of HLW in storage in 2015. As of 2019, the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
has over 90,000 t of HLW. HLW have been shipped to other countries to be stored or reprocessed and, in some cases, shipped back as active fuel.
The ongoing controversy over
high-level radioactive waste disposal is a major constraint on the nuclear power's global expansion.
Most scientists agree that the main proposed long-term solution is deep geological burial, either in a mine or a deep borehole. As of 2019 no dedicated civilian high-level nuclear waste is operational
as small amounts of HLW did not justify the investment before. Finland is in the advanced stage of the construction of the
Onkalo spent nuclear fuel repository, which is planned to open in 2025 at 400–450 m depth. France is in the planning phase for a 500 m deep Cigeo facility in Bure. Sweden is planning a site in
Forsmark. Canada plans a 680 m deep facility near Lake Huron in Ontario. The Republic of Korea plans to open a site around 2028.
The site in Sweden enjoys 80% support from local residents as of 2020.
The
Morris Operation The Morris Operation in Grundy County, Illinois, United States, is the location of the only permanent (the rest are temporary) ''de facto'' high-level radioactive waste storage site in the United States and holds 772 tons of spent nuclear fuel. It ...
in
Grundy County, Illinois
Grundy County is a county in the U.S. state of Illinois. According to the 2010 census, it has a population of 50,063. Its county seat is Morris.
Grundy County is part of the Chicago-Naperville- Elgin, IL- IN- WI Metropolitan Statistical Ar ...
, is currently the only ''de facto'' high-level radioactive waste storage site in the United States.
Transuranic waste
Transuranic waste (TRUW) as defined by U.S. regulations is, without regard to form or origin, waste that is contaminated with
alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ''álpha'', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , whi ...
-emitting transuranic
radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transfer ...
s with
half-lives
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
greater than 20 years and concentrations greater than 100
nCi/g (3.7
MBq/kg), excluding high-level waste. Elements that have an atomic number greater than uranium are called transuranic ("beyond uranium"). Because of their long half-lives, TRUW is disposed of more cautiously than either low- or intermediate-level waste. In the United States, it arises mainly from
nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
s production, and consists of clothing, tools, rags, residues, debris, and other items contaminated with small amounts of radioactive elements (mainly
plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exh ...
).
Under U.S. law, transuranic waste is further categorized into "contact-handled" (CH) and "remote-handled" (RH) on the basis of the radiation dose rate measured at the surface of the waste container. CH TRUW has a surface dose rate not greater than 200
mrem
The roentgen equivalent man (rem) is a CGS unit of equivalent dose, effective dose, and committed dose, which are dose measures used to estimate potential health effects of low levels of ionizing radiation on the human body.
Quantities measu ...
per hour (2 mSv/h), whereas RH TRUW has a surface dose rate of 200 mrem/h (2 mSv/h) or greater. CH TRUW does not have the very high radioactivity of high-level waste, nor its high heat generation, but RH TRUW can be highly radioactive, with surface dose rates up to 1,000,000 mrem/h (10,000 mSv/h). The United States currently disposes of TRUW generated from military facilities at the
Waste Isolation Pilot Plant
The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, or WIPP, is the world's third deep geological repository (after Germany's Repository for radioactive waste Morsleben and the Schacht Asse II salt mine) licensed to store transuranic radioactive waste for 10,00 ...
(WIPP) in a deep salt formation in
New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
.
Prevention
A future way to reduce waste accumulation is to phase out current reactors in favor of
Generation IV reactor
Generation IV reactors (Gen IV) are six nuclear reactor designs recognized by the Generation IV International Forum. The designs target improved safety, sustainability, efficiency, and cost.
The most developed Gen IV reactor design is the sodium ...
s, which output less waste per power generated.
Fast reactors such as
BN-800 in Russia are also able to consume
MOX fuel that is manufactured from recycled spent fuel from traditional reactors.
The UK's
Nuclear Decommissioning Authority
The Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA) is a non-departmental public body of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy, formed by the Energy Act 2004. It evolved from the Coal and Nuclear Liabilities Unit of the Department ...
published a position paper in 2014 on the progress on approaches to the management of separated plutonium, which summarises the conclusions of the work that NDA shared with UK government.
Management

Of particular concern in nuclear waste management are two long-lived fission products, Tc-99 (half-life 220,000 years) and I-129 (half-life 15.7 million years), which dominate spent fuel radioactivity after a few thousand years. The most troublesome transuranic elements in spent fuel are Np-237 (half-life two million years) and Pu-239 (half-life 24,000 years). Nuclear waste requires sophisticated treatment and management to successfully isolate it from interacting with the
biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also ...
. This usually necessitates treatment, followed by a long-term management strategy involving storage, disposal or transformation of the waste into a non-toxic form. Governments around the world are considering a range of waste management and disposal options, though there has been limited progress toward long-term waste management solutions.

In the second half of the 20th century, several methods of disposal of radioactive waste were investigated by nuclear nations, which are :
* "Long-term above-ground storage", not implemented.
* "Disposal in outer space" (for instance, inside the Sun), not implemented—as it would be currently too expensive.
* "
Deep borehole disposal Deep borehole disposal (DBD) is the concept of disposing high-level radioactive waste from nuclear reactors in extremely deep boreholes instead of in more traditional deep geological repositories that are excavated like mines. Deep borehole dispos ...
", not implemented.
* "Rock melting", not implemented.
* "Disposal at subduction zones", not implemented.
*
Ocean disposal, by the USSR, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, the United States, Belgium, France, the Netherlands, Japan, Sweden, Russia, Germany, Italy and South Korea (1954–93). This is no longer permitted by international agreements.
* "
Sub-seabed disposal", not implemented, not permitted by international agreements.
* "Disposal in ice sheets", rejected in
Antarctic Treaty
* "Deep well injection", by USSR and USA.
*
Nuclear transmutation
Nuclear transmutation is the conversion of one chemical element or an isotope into another chemical element. Nuclear transmutation occurs in any process where the number of protons or neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is changed.
A transmutatio ...
, using lasers to cause
beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For ...
to convert the unstable atoms to those with shorter half-lives.
In the United States, waste management policy completely broke down with the ending of work on the incomplete
Yucca Mountain Repository.
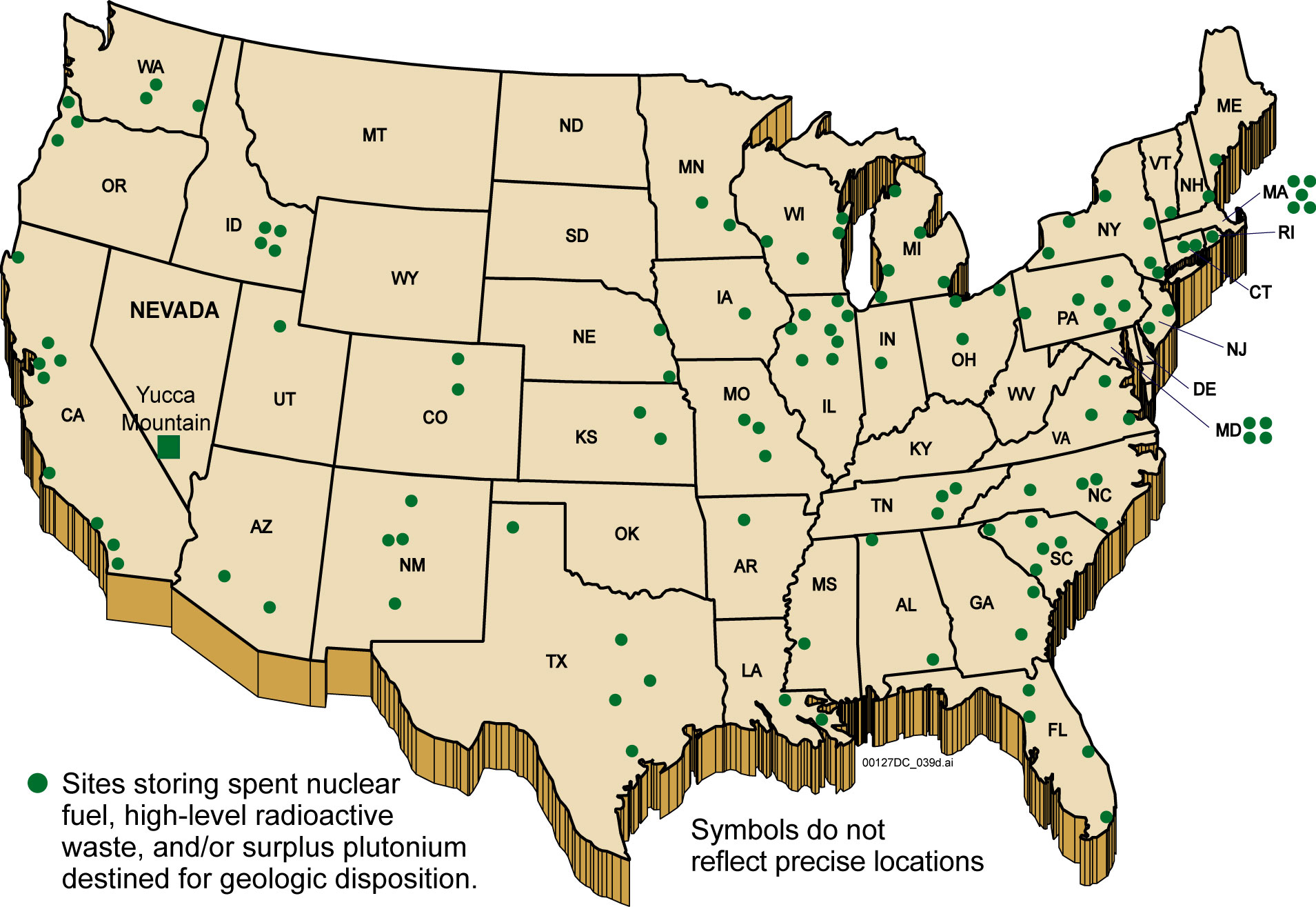
At present there are 70 nuclear power plant sites where
spent fuel is stored. A Blue Ribbon Commission was appointed by President Obama to look into future options for this and future waste. A
deep geological repository
A deep geological repository is a way of storing hazardous or radioactive waste within a stable geologic environment (typically 200–1000 m deep). It entails a combination of waste form, waste package, engineered seals and geology that is suite ...
seems to be favored.
Blue Ribbon Commission on America's Nuclear Future: Executive Summary
'', January 2012. 2018
Nobel Prize for Physics-winner
Gérard Mourou
Gérard Albert Mourou (; born 22 June 1944) is a French scientist and pioneer in the field of electrical engineering and lasers. He was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physics in 2018, along with Donna Strickland, for the invention of chirped pulse a ...
has proposed using
Chirped pulse amplification to generate high-energy and low-duration laser pulses to transmute highly radioactive material (contained in a target) to significantly reduce its half-life, from thousands of years to only a few minutes.
Initial treatment
Vitrification

Long-term storage of radioactive waste requires the stabilization of the waste into a form that will neither react nor degrade for extended periods. It is theorized that one way to do this might be through
vitrification
Vitrification (from Latin ''vitreum'', "glass" via French ''vitrifier'') is the full or partial transformation of a substance into a glass, that is to say, a non- crystalline amorphous solid. Glasses differ from liquids structurally and glasses po ...
. Currently at
Sellafield
Sellafield is a large multi-function nuclear site close to Seascale on the coast of Cumbria, England. As of August 2022, primary activities are nuclear waste processing and storage and nuclear decommissioning. Former activities included nuc ...
the high-level waste (
PUREX
PUREX (plutonium uranium reduction extraction) is a chemical method used to purify fuel for nuclear reactors or nuclear weapons. PUREX is the '' de facto'' standard aqueous nuclear reprocessing method for the recovery of uranium and pluto ...
first cycle
raffinate) is mixed with
sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or do ...
and then calcined.
Calcination
Calcination refers to thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), gen ...
involves passing the waste through a heated, rotating tube. The purposes of calcination are to evaporate the water from the waste and de-nitrate the fission products to assist the stability of the glass produced.
The 'calcine' generated is fed continuously into an induction heated furnace with fragmented
glass
Glass is a non- crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenchin ...
. The resulting glass is a new substance in which the waste products are bonded into the glass matrix when it solidifies. As a melt, this product is poured into
stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's r ...
cylindrical containers ("cylinders") in a batch process. When cooled, the fluid solidifies ("vitrifies") into the glass. After being formed, the glass is highly resistant to water.
After filling a cylinder, a seal is
welded onto the cylinder head. The cylinder is then washed. After being inspected for external contamination, the steel cylinder is stored, usually in an underground repository. In this form, the waste products are expected to be immobilized for thousands of years.
The glass inside a cylinder is usually a black glossy substance. All this work (in the United Kingdom) is done using
hot cell systems. Sugar is added to control the
ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element with the symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most other chemical ...
chemistry and to stop the formation of the volatile
RuO4 containing
radioactive ruthenium isotopes. In the West, the glass is normally a
borosilicate glass (similar to
Pyrex), while in the former
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
it is normal to use a
phosphate glass
Phosphate glass is a class of optical glasses composed of metaphosphates of various metals. Instead of SiO2 in silicate glasses, the glass forming substrate is P2O5.
Discovery
Dr. Alexis G. Pincus of the American Optical Company supplied alum ...
. The amount of fission products in the glass must be limited because some (
palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself ...
, the other Pt group metals, and
tellurium
Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionall ...
) tend to form metallic phases which separate from the glass. Bulk vitrification uses electrodes to melt soil and wastes, which are then buried underground.
In Germany a vitrification plant is in use; this is treating the waste from a small demonstration reprocessing plant which has since been closed down.
Phosphate Ceramics
Vitrification is not the only way to stabilize the waste into a form that will not react or degrade for extended periods. Immobilization via direct incorporation into a phosphate-based crystalline ceramic host is also used. The diverse chemistry of phosphate ceramics under various conditions demonstrates a versatile material that can withstand chemical, thermal, and radioactive degradation over time. The properties of phosphates, particularly ceramic phosphates, of stability over a wide pH range, low porosity, and minimization of secondary waste introduces possibilities for new waste immobilization techniques.
Ion exchange
It is common for medium active wastes in the nuclear industry to be treated with
ion exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, ...
or other means to concentrate the radioactivity into a small volume. The much less radioactive bulk (after treatment) is often then discharged. For instance, it is possible to use a
ferric hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. ...
floc Floc can refer to:
* Farm Labor Organizing Committee, a labor union
* Federated Learning of Cohorts (FLoC), a type of web tracking for interest-based advertising
* Floc (or flock), flake of precipitate that comes out of solution during the process ...
to remove radioactive metals from aqueous mixtures. After the radioisotopes are absorbed onto the ferric hydroxide, the resulting sludge can be placed in a metal drum before being mixed with cement to form a solid waste form. In order to get better long-term performance (mechanical stability) from such forms, they may be made from a mixture of
fly ash
Fly ash, flue ash, coal ash, or pulverised fuel ash (in the UK) plurale tantum: coal combustion residuals (CCRs)is a coal combustion product that is composed of the particulates (fine particles of burned fuel) that are driven out of coal-fired ...
, or
blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheri ...
slag
Slag is a by-product of smelting ( pyrometallurgical) ores and used metals. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous (by-products of processing iron and steel), ferroalloy (by-product of ferroalloy production) or non-ferrous/base metals (by-p ...
, and
Portland cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19t ...
, instead of normal
concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
(made with Portland cement, gravel and sand).
Synroc
The Australian
Synroc Synroc, a portmanteau of "synthetic rock", is a means of safely storing radioactive waste. It was pioneered in 1978 by a team led by Professor Ted Ringwood at the Australian National University, with further research undertaken in collaboration with ...
(synthetic rock) is a more sophisticated way to immobilize such waste, and this process may eventually come into commercial use for civil wastes (it is currently being developed for U.S. military wastes). Synroc was invented by Prof Ted Ringwood (a
geochemist
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the ...
) at the
Australian National University
The Australian National University (ANU) is a public research university located in Canberra, the capital of Australia. Its main campus in Acton encompasses seven teaching and research colleges, in addition to several national academies an ...
. The Synroc contains
pyrochlore and cryptomelane type minerals. The original form of Synroc (Synroc C) was designed for the liquid high-level waste (PUREX raffinate) from a
light-water reactor. The main minerals in this Synroc are
hollandite (BaAl
2Ti
6O
16),
zirconolite
Zirconolite is a mineral, calcium zirconium titanate; formula CaZrTi2O7. Some examples of the mineral may also contain thorium, uranium, cerium, niobium and iron; the presence of thorium or uranium would make the mineral radioactive
Radio ...
(CaZrTi
2O
7) and
perovskite
Perovskite (pronunciation: ) is a calcium titanium oxide mineral composed of calcium titanate (chemical formula ). Its name is also applied to the class of compounds which have the same type of crystal structure as (XIIA2+VIB4+X2−3), known a ...
(CaTiO
3). The zirconolite and perovskite are hosts for the
actinides. The
strontium
Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is e ...
and
barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
will be fixed in the perovskite. The
caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that a ...
will be fixed in the hollandite. A Synroc waste treatment facility began construction in 2018 at
ANSTO.
Long-term management
The time frame in question when dealing with radioactive waste ranges from 10,000 to 1,000,000 years, according to studies based on the effect of estimated radiation doses. Researchers suggest that forecasts of health detriment for such periods should be examined critically. Practical studies only consider up to 100 years as far as effective planning and cost evaluations are concerned. Long term behavior of radioactive wastes remains a subject for ongoing research projects in
geoforecasting.
Remediation
Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
has shown selectivity for
strontium
Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is e ...
in studies, where most plants used in
bioremediation have not shown selectivity between calcium and strontium, often becoming saturated with calcium, which is present in greater quantities in nuclear waste.
Strontium-90
Strontium-90 () is a radioactive isotope of strontium produced by nuclear fission, with a half-life of 28.8 years. It undergoes β− decay into yttrium-90, with a decay energy of 0.546 MeV. Strontium-90 has applications in medicine and ...
with a half life around 30 years, is classified as high-level waste.
Researchers have looked at the bioaccumulation of strontium by ''
Scenedesmus spinosus'' (
algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
) in simulated wastewater. The study claims a highly selective
biosorption capacity for strontium of S. spinosus, suggesting that it may be appropriate for use of nuclear wastewater. A study of the pond alga ''
Closterium moniliferum
''Closterium'' is a genus of unicellular charophyte green algae in the family Closteriaceae.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Closterium Data extracted from the
Taxonomy
''Closterium regulare'' was first described from Lower Normandy by Brebisson. ...
'' using non-radioactive strontium found that varying the ratio of
barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
to strontium in water improved strontium selectivity.
[
]
Above-ground disposal
Dry cask storage typically involves taking waste from a spent fuel pool and sealing it (along with an inert gas
An inert gas is a gas that does not readily undergo chemical reactions with other chemical substances and therefore does not readily form chemical compounds. The noble gases often do not react with many substances and were historically referred to ...
) in a steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistan ...
cylinder, which is placed in a concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
cylinder which acts as a radiation shield. It is a relatively inexpensive method which can be done at a central facility or adjacent to the source reactor. The waste can be easily retrieved for reprocessing.
Geologic disposal
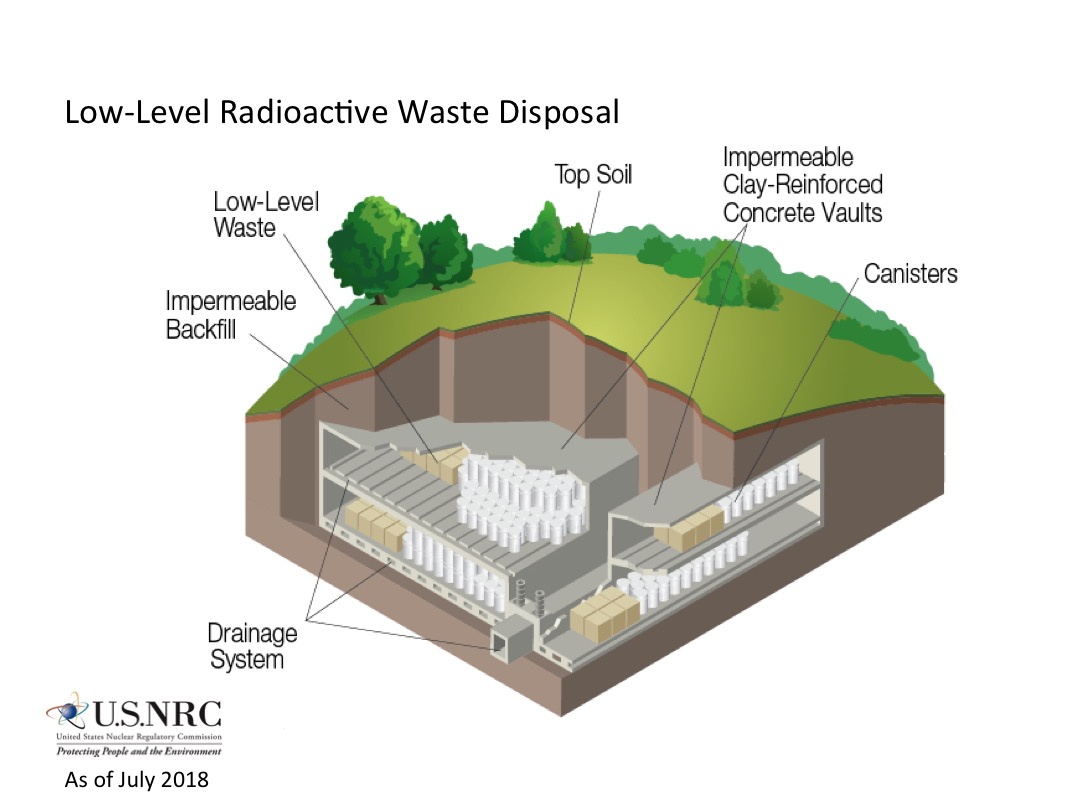
 The process of selecting appropriate deep final repositories for high-level waste and spent fuel is now underway in several countries with the first expected to be commissioned sometime after 2010. The basic concept is to locate a large, stable geologic formation and use mining technology to excavate a tunnel, or large-bore tunnel boring machines (similar to those used to drill the
The process of selecting appropriate deep final repositories for high-level waste and spent fuel is now underway in several countries with the first expected to be commissioned sometime after 2010. The basic concept is to locate a large, stable geologic formation and use mining technology to excavate a tunnel, or large-bore tunnel boring machines (similar to those used to drill the Channel Tunnel
The Channel Tunnel (french: Tunnel sous la Manche), also known as the Chunnel, is a railway tunnel that connects Folkestone (Kent, England, UK) with Coquelles ( Hauts-de-France, France) beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover ...
from England to France) to drill a shaft to below the surface where rooms or vaults can be excavated for disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The goal is to permanently isolate nuclear waste from the human environment. Many people remain uncomfortable with the immediate stewardship cessation of this disposal system, suggesting perpetual management and monitoring would be more prudent.
Because some radioactive species have half-lives longer than one million years, even very low container leakage and radionuclide migration rates must be taken into account. Moreover, it may require more than one half-life until some nuclear materials lose enough radioactivity to cease being lethal to living things. A 1983 review of the Swedish radioactive waste disposal program by the National Academy of Sciences found that country's estimate of several hundred thousand years—perhaps up to one million years—being necessary for waste isolation "fully justified."
Ocean floor disposal
Ocean floor disposal is a method of sequestering radioactive waste in ocean floor sediment where it is unlikely to be disturbed either geologically or by human activity.
Several methods of depositing material in the ocean floor have been proposed ...
of radioactive waste has been suggested by the finding that deep waters in the North Atlantic Ocean do not present an exchange with shallow waters for about 140 years based on oxygen content data recorded over a period of 25 years. They include burial beneath a stable abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between and . Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth's surface ...
, burial in a subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, ...
zone that would slowly carry the waste downward into the Earth's mantle, and burial beneath a remote natural or human-made island. While these approaches all have merit and would facilitate an international solution to the problem of disposal of radioactive waste, they would require an amendment of the Law of the Sea.
Article 1 (Definitions), 7., of the 1996 Protocol to the Convention on the Prevention of Marine Pollution by Dumping of Wastes and Other Matter, (the London Dumping Convention) states:
:""Sea" means all marine waters other than the internal waters of States, as well as the seabed and the subsoil thereof; it does not include sub-seabed repositories accessed only from land."
The proposed land-based subductive waste disposal method disposes of nuclear waste in a subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, ...
zone accessed from land and therefore is not prohibited by international agreement. This method has been described as the most viable means of disposing of radioactive waste, and as the state-of-the-art as of 2001 in nuclear waste disposal technology.
Another approach termed Remix & Return would blend high-level waste with uranium mine
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. Over 50 thousand tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account ...
and mill tailings down to the level of the original radioactivity of the uranium ore, then replace it in inactive uranium mines. This approach has the merits of providing jobs for miners who would double as disposal staff, and of facilitating a cradle-to-grave cycle for radioactive materials, but would be inappropriate for spent reactor fuel in the absence of reprocessing, due to the presence of highly toxic radioactive elements such as plutonium within it.
Deep borehole disposal Deep borehole disposal (DBD) is the concept of disposing high-level radioactive waste from nuclear reactors in extremely deep boreholes instead of in more traditional deep geological repositories that are excavated like mines. Deep borehole dispos ...
is the concept of disposing of high-level radioactive waste from nuclear reactors in extremely deep boreholes. Deep borehole disposal seeks to place the waste as much as beneath the surface of the Earth and relies primarily on the immense natural geological barrier to confine the waste safely and permanently so that it should never pose a threat to the environment. The Earth's crust contains 120 trillion tons of thorium and 40 trillion tons of uranium (primarily at relatively trace concentrations of parts per million each adding up over the crust's 3 × 1019 ton mass), among other natural radioisotopes. Since the fraction of nuclides decaying per unit of time is inversely proportional to an isotope's half-life, the relative radioactivity of the lesser amount of human-produced radioisotopes (thousands of tons instead of trillions of tons) would diminish once the isotopes with far shorter half-lives than the bulk of natural radioisotopes decayed.
In January 2013, Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. ...
county council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
Ireland
The county councils created under British rule in 1899 continue to exist in Irela ...
rejected UK central government proposals to start work on an underground storage dump for nuclear waste near to the Lake District National Park
The Lake District National Park is a national park in North West England that includes all of the central Lake District, though the town of Kendal, some coastal areas, and the Lakeland Peninsulas are outside the park boundary.
The area was desi ...
. "For any host community, there will be a substantial community benefits package and worth hundreds of millions of pounds" said Ed Davey, Energy Secretary, but nonetheless, the local elected body voted 7–3 against research continuing, after hearing evidence from independent geologists that "the fractured strata of the county was impossible to entrust with such dangerous material and a hazard lasting millennia."
Horizontal drillhole disposal describes proposals to drill over one km vertically, and two km horizontally in the earth’s crust, for the purpose of disposing of high-level waste forms such as spent nuclear fuel, Caesium-137, or Strontium-90
Strontium-90 () is a radioactive isotope of strontium produced by nuclear fission, with a half-life of 28.8 years. It undergoes β− decay into yttrium-90, with a decay energy of 0.546 MeV. Strontium-90 has applications in medicine and ...
. After the emplacement and the retrievability period, drillholes would be backfilled and sealed. A series of tests of the technology were carried out in November 2018 and then again publicly in January 2019 by a U.S. based private company. The test demonstrated the emplacement of a test-canister in a horizontal drillhole and retrieval of the same canister. There was no actual high-level waste used in this test.
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
Joint Research Centre report of 2021 (see above) concluded:
Transmutation
There have been proposals for reactors that consume nuclear waste and transmute it to other, less-harmful or shorter-lived, nuclear waste. In particular, the integral fast reactor
The integral fast reactor (IFR, originally advanced liquid-metal reactor) is a design for a nuclear reactor using fast neutrons and no neutron moderator (a "fast" reactor). IFR would breed more fuel and is distinguished by a nuclear fuel cycle ...
was a proposed nuclear reactor with a nuclear fuel cycle that produced no transuranic waste and, in fact, could consume transuranic waste. It proceeded as far as large-scale tests but was eventually canceled by the U.S. Government. Another approach, considered safer but requiring more development, is to dedicate subcritical reactors to the transmutation of the left-over transuranic elements.
An isotope that is found in nuclear waste and that represents a concern in terms of proliferation is Pu-239. The large stock of plutonium is a result of its production inside uranium-fueled reactors and of the reprocessing of weapons-grade plutonium during the weapons program. An option for getting rid of this plutonium is to use it as a fuel in a traditional light-water reactor (LWR). Several fuel types with differing plutonium destruction efficiencies are under study.
Transmutation was banned in the United States in April 1977 by President Carter due to the danger of plutonium proliferation, but President Reagan rescinded the ban in 1981. Due to economic losses and risks, the construction of reprocessing plants during this time did not resume. Due to high energy demand, work on the method has continued in the EU. This has resulted in a practical nuclear research reactor called Myrrha in which transmutation is possible. Additionally, a new research program called ACTINET has been started in the EU to make transmutation possible on a large, industrial scale. According to President Bush's Global Nuclear Energy Partnership (GNEP) of 2007, the United States is actively promoting research on transmutation technologies needed to markedly reduce the problem of nuclear waste treatment.
There have also been theoretical studies involving the use of fusion reactors as so-called "actinide burners" where a fusion reactor plasma such as in a tokamak, could be "doped" with a small amount of the "minor" transuranic atoms which would be transmuted (meaning fissioned in the actinide case) to lighter elements upon their successive bombardment by the very high energy neutrons produced by the fusion of deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being protium, or hydrogen-1). The nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one ...
and tritium in the reactor. A study at MIT found that only 2 or 3 fusion reactors with parameters similar to that of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) could transmute the entire annual minor actinide
The minor actinides are the actinide elements in used nuclear fuel other than uranium and plutonium, which are termed the major actinides. The minor actinides include neptunium (element 93), americium (element 95), curium (element 96), berkeliu ...
production from all of the light-water reactors presently operating in the United States fleet while simultaneously generating approximately 1 gigawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wat ...
of power from each reactor.
Re-use
Spent nuclear fuel contains abundant fertile uranium and traces of fissile materials.strontium-90
Strontium-90 () is a radioactive isotope of strontium produced by nuclear fission, with a half-life of 28.8 years. It undergoes β− decay into yttrium-90, with a decay energy of 0.546 MeV. Strontium-90 has applications in medicine and ...
and a few other isotopes are extracted for certain industrial applications such as food irradiation
Food irradiation is the process of exposing food and food packaging to ionizing radiation, such as from gamma rays, x-rays, or electron beams. Food irradiation improves food safety and extends product shelf life (preservation) by effective ...
and radioisotope thermoelectric generators
A radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG, RITEG), sometimes referred to as a radioisotope power system (RPS), is a type of nuclear battery that uses an array of thermocouples to convert the heat released by the decay of a suitable radioact ...
. While re-use does not eliminate the need to manage radioisotopes, it can reduce the quantity of waste produced.
The Nuclear Assisted Hydrocarbon Production Method, Canadian patent application 2,659,302, is a method for the temporary or permanent storage of nuclear waste materials comprising the placing of waste materials into one or more repositories or boreholes constructed into an unconventional oil
Unconventional oil is petroleum produced or extracted using techniques other than the conventional method (oil well). Industry and governments across the globe are investing in unconventional oil sources due to the increasing scarcity of conventio ...
formation. The thermal flux of the waste materials fractures the formation and alters the chemical and/or physical properties of hydrocarbon material within the subterranean formation to allow removal of the altered material. A mixture of hydrocarbons, hydrogen, and/or other formation fluids is produced from the formation. The radioactivity of high-level radioactive waste affords proliferation resistance to plutonium placed in the periphery of the repository or the deepest portion of a borehole.
Breeder reactors can run on U-238 and transuranic elements, which comprise the majority of spent fuel radioactivity in the 1,000–100,000-year time span.
Space disposal
Space disposal is attractive because it removes nuclear waste from the planet. It has significant disadvantages, such as the potential for catastrophic failure of a launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload ( spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pads, supported by a launch control center and sys ...
, which could spread radioactive material into the atmosphere and around the world. A high number of launches would be required because no individual rocket would be able to carry very much of the material relative to the total amount that needs to be disposed of. This makes the proposal impractical economically and increases the risk of one or more launch failures. To further complicate matters, international agreements on the regulation of such a program would need to be established. Costs and inadequate reliability of modern rocket launch systems for space disposal has been one of the motives for interest in non-rocket spacelaunch systems such as mass drivers, space elevator
A space elevator, also referred to as a space bridge, star ladder, and orbital lift, is a proposed type of planet-to-space transportation system, often depicted in science fiction. The main component would be a cable (also called a space tethe ...
s, and other proposals.
National management plans
 Sweden and Finland are furthest along in committing to a particular disposal technology, while many others reprocess spent fuel or contract with France or Great Britain to do it, taking back the resulting plutonium and high-level waste. "An increasing backlog of plutonium from reprocessing is developing in many countries... It is doubtful that reprocessing makes economic sense in the present environment of cheap uranium."
In many European countries (e.g., Britain, Finland, the Netherlands, Sweden, and Switzerland) the risk or dose limit for a member of the public exposed to radiation from a future high-level nuclear waste facility is considerably more stringent than that suggested by the International Commission on Radiation Protection or proposed in the United States. European limits are often more stringent than the standard suggested in 1990 by the International Commission on Radiation Protection by a factor of 20, and more stringent by a factor of ten than the standard proposed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository for the first 10,000 years after closure.
Sweden and Finland are furthest along in committing to a particular disposal technology, while many others reprocess spent fuel or contract with France or Great Britain to do it, taking back the resulting plutonium and high-level waste. "An increasing backlog of plutonium from reprocessing is developing in many countries... It is doubtful that reprocessing makes economic sense in the present environment of cheap uranium."
In many European countries (e.g., Britain, Finland, the Netherlands, Sweden, and Switzerland) the risk or dose limit for a member of the public exposed to radiation from a future high-level nuclear waste facility is considerably more stringent than that suggested by the International Commission on Radiation Protection or proposed in the United States. European limits are often more stringent than the standard suggested in 1990 by the International Commission on Radiation Protection by a factor of 20, and more stringent by a factor of ten than the standard proposed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository for the first 10,000 years after closure.[ Vandenbosch, p. 248]
The U.S. EPA's proposed standard for greater than 10,000 years is 250 times more permissive than the European limit.United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United States ...
(DOE) predicted that received dose would be much below that limit. Over a timeframe of thousands of years, after the most active short half-life radioisotopes decayed, burying U.S. nuclear waste would increase the radioactivity in the top 2000 feet of rock and soil in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
(10 million km2) by approximately 1 part in 10 million over the cumulative amount of natural radioisotopes in such a volume, but the vicinity of the site would have a far higher concentration of artificial radioisotopes underground than such an average.
Mongolia
After serious opposition about plans and negotiations between Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
with Japan and the United States of America to build nuclear-waste facilities in Mongolia, Mongolia stopped all negotiations in September 2011. These negotiations had started after U.S. Deputy Secretary of Energy Daniel Poneman visited Mongolia in September 2010. Talks took place in Washington, D.C. between officials of Japan, the United States, and Mongolia in February 2011. After this the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia (Middle East, The Middle East). It is ...
(UAE), which wanted to buy nuclear fuel from Mongolia, joined in the negotiations. The talks were kept secret and, although the ''Mainichi Daily News'' reported on them in May, Mongolia officially denied the existence of these negotiations. However, alarmed by this news, Mongolian citizens protested against the plans and demanded the government withdraw the plans and disclose information. The Mongolian President Tsakhiagiin Elbegdorj issued a presidential order on September 13 banning all negotiations with foreign governments or international organizations on nuclear-waste storage plans in Mongolia. The Mongolian government has accused the newspaper of distributing false claims around the world. After the presidential order, the Mongolian president fired the individual who was supposedly involved in these conversations.
Illegal dumping
Authorities in Italy are investigating a 'Ndrangheta
The 'Ndrangheta (, , ) is a prominent Italian Mafia-type organized crime syndicate and secret society, criminal society based in the peninsular and mountainous region of Calabria and dating back to the late 18th century. It is considered one of ...
mafia clan accused of trafficking and illegally dumping nuclear waste. According to a whistleblower
A whistleblower (also written as whistle-blower or whistle blower) is a person, often an employee, who reveals information about activity within a private or public organization that is deemed illegal, immoral, illicit, unsafe or fraudulent. Whi ...
, a manager of the Italy's state energy research agency Enea paid the clan to get rid of 600 drums of toxic and radioactive waste from Italy, Switzerland, France, Germany, and the United States, with Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
as the destination, where the waste was buried after buying off local politicians. Former employees of Enea are suspected of paying the criminals to take waste off their hands in the 1980s and 1990s. Shipments to Somalia continued into the 1990s, while the 'Ndrangheta clan also blew up shiploads of waste, including radioactive hospital waste, sending them to the sea bed off the Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
n coast. According to the environmental group Legambiente, former members of the 'Ndrangheta have said that they were paid to sink ships with radioactive material for the last 20 years.
Accidents
A few incidents have occurred when radioactive material was disposed of improperly, shielding during transport was defective, or when it was simply abandoned or even stolen from a waste store. In the Soviet Union, waste stored in Lake Karachay
Lake Karachay (russian: Карача́й), sometimes spelled Karachai or Karachaj, was a small lake in the southern Ural mountains in central Russia. Starting in 1951, the Soviet Union used Karachay as a dumping site for radioactive waste from May ...
was blown over the area during a dust storm
A dust storm, also called a sandstorm, is a meteorological phenomenon common in arid and semi-arid regions. Dust storms arise when a gust front or other strong wind blows loose sand and dirt from a dry surface. Fine particles are transp ...
after the lake had partly dried out. At Maxey Flat, a low-level radioactive waste facility located in Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
, containment trenches covered with dirt, instead of steel or cement, collapsed under heavy rainfall into the trenches and filled with water. The water that invaded the trenches became radioactive and had to be disposed of at the Maxey Flat facility itself. In other cases of radioactive waste accidents, lakes or ponds with radioactive waste accidentally overflowed into the rivers during exceptional storms. In Italy, several radioactive waste deposits let material flow into river water, thus contaminating water for domestic use. In France in the summer of 2008, numerous incidents happened: in one, at the Areva plant in Tricastin
The Tricastin is a natural and historic region in the southern Rhône valley of southeastern France comprising the southwestern portion of the Drôme department and the northwestern portion of Vaucluse and centered on the modern town of Saint-P ...
, it was reported that, during a draining operation, liquid containing untreated uranium overflowed out of a faulty tank and about 75 kg of the radioactive material seeped into the ground and, from there, into two rivers nearby; in another case, over 100 staff were contaminated with low doses of radiation. There are ongoing concerns around the deterioration of the nuclear waste site on the Enewetak Atoll
Enewetak Atoll (; also spelled Eniwetok Atoll or sometimes Eniewetok; mh, Ānewetak, , or , ; known to the Japanese as Brown Atoll or Brown Island; ja, ブラウン環礁) is a large coral atoll of 40 islands in the Pacific Ocean and with it ...
of the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Inte ...
and a potential radioactive spill.
Scavenging of abandoned radioactive material has been the cause of several other cases of radiation exposure
Radiation is a moving form of energy, classified into ionizing and non-ionizing type. Ionizing radiation is further categorized into electromagnetic radiation (without matter) and particulate radiation (with matter). Electromagnetic radiation con ...
, mostly in developing nations, which may have less regulation of dangerous substances (and sometimes less general education about radioactivity and its hazards) and a market for scavenged goods and scrap metal. The scavengers and those who buy the material are almost always unaware that the material is radioactive and it is selected for its aesthetics
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed t ...
or scrap value.[International Atomic Energy Agency]
''The radiological accident in Goiânia''
, 1988. Retrieved September 2007. Irresponsibility on the part of the radioactive material's owners, usually a hospital, university, or military, and the absence of regulation concerning radioactive waste, or a lack of enforcement of such regulations, have been significant factors in radiation exposures. For an example of an accident involving radioactive scrap originating from a hospital see the Goiânia accident.spent nuclear fuel shipping cask
A nuclear flask is a shipping container that is used to transport active nuclear materials between nuclear power station and spent fuel reprocessing facilities.
Each shipping container is designed to maintain its integrity under normal transport ...
s.International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 195 ...
. Japan did start discussions with the IAEA about the large quantities of enriched uranium and plutonium that were discovered in nuclear waste cleared away by Japanese nuclear operators. At the press conference Fujimura said: "Based on investigations so far, most nuclear substances have been properly managed as waste, and from that perspective, there is no problem in safety management," But according to him, the matter was at that moment still being investigated.
Associated hazard warning signs
File:Radioactive.svg, The trefoil symbol used to indicate ionizing radiation.
File:Logo iso radiation.svg, 2007 ISO radioactivity danger symbol intended for IAEA Category 1, 2 and 3 sources defined as dangerous sources capable of death or serious injury.
See also
* Ducrete DUCRETE (Depleted Uranium Concrete) is a high density concrete alternative investigated for use in construction of casks for storage of radioactive waste. It is a composite material containing depleted uranium dioxide aggregate instead of convent ...
* Environmental remediation
Environmental remediation deals with the removal of pollution or contaminants from environmental media such as soil, groundwater, sediment, or surface water. Remedial action is generally subject to an array of regulatory requirements, and may al ...
* Human Interference Task Force
* Lists of nuclear disasters and radioactive incidents
* Material unaccounted for Material unaccounted for (MUF), in the context of nuclear material, refers to any discrepancy between a nuclear-weapons state's physical inventory of nuclear material, and the book inventory. The difference can be either a positive discrepancy (an ...
* Mixed waste (radioactive/hazardous)
* Microbial corrosion
* Nuclear decommissioning
* Personal protective equipment
* Radiation protection
* Radioactive contamination
* Radioactive scrap metal
* Radioecology
* Toxic waste
* Waste management
References
Cited sources
*
External links
Alsos Digital Library – Radioactive Waste
(annotated bibliography)
Euridice European Interest Group in charge of Hades URL operation
(link)
Ondraf/Niras, the waste management authority in Belgium
(link)
Critical Hour: Three Mile Island, The Nuclear Legacy, And National Security
(PDF)
(documents)
Grist.org – How to tell future generations about nuclear waste
(article)
(links)
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20070227210853/http://www.nuclearfiles.org/menu/key-issues/nuclear-energy/issues/yucca-mountain/index.htm Nuclear Files.org – Yucca Mountain] (documents)
Nuclear Regulatory Commission – Radioactive Waste
(documents)
Nuclear Regulatory Commission – Spent Fuel Heat Generation Calculation
(guide)
Radwaste Solutions
(magazine)
UNEP Earthwatch – Radioactive Waste
(documents and links)
(briefing papers)
Worries can't be buried as nuclear waste piles up, Los Angeles Times, January 21, 2008
{{Authority control
Radioactive waste,
Radioactivity
Environmental impact of nuclear power
 Radioactive waste is a type of
Radioactive waste is a type of  The use of different fuels in nuclear reactors results in different spent nuclear fuel (SNF) composition, with varying activity curves. The most abundant material being U-238 with other uranium isotopes, other actinides, fission products and activation products.
Long-lived radioactive waste from the back end of the fuel cycle is especially relevant when designing a complete waste management plan for SNF. When looking at long-term
The use of different fuels in nuclear reactors results in different spent nuclear fuel (SNF) composition, with varying activity curves. The most abundant material being U-238 with other uranium isotopes, other actinides, fission products and activation products.
Long-lived radioactive waste from the back end of the fuel cycle is especially relevant when designing a complete waste management plan for SNF. When looking at long-term  Substances containing natural radioactivity are known as NORM (naturally occurring radioactive material). After human processing that exposes or concentrates this natural radioactivity (such as mining bringing coal to the surface or burning it to produce concentrated ash), it becomes technologically enhanced naturally occurring radioactive material (TENORM). A lot of this waste is
Substances containing natural radioactivity are known as NORM (naturally occurring radioactive material). After human processing that exposes or concentrates this natural radioactivity (such as mining bringing coal to the surface or burning it to produce concentrated ash), it becomes technologically enhanced naturally occurring radioactive material (TENORM). A lot of this waste is  Uranium tailings are waste by-product materials left over from the rough processing of
Uranium tailings are waste by-product materials left over from the rough processing of  Intermediate-level waste (ILW) contains higher amounts of radioactivity compared to low-level waste. It generally requires shielding, but not cooling. Intermediate-level wastes includes
Intermediate-level waste (ILW) contains higher amounts of radioactivity compared to low-level waste. It generally requires shielding, but not cooling. Intermediate-level wastes includes  In 2010, it was estimated that about 250,000 t of nuclear HLW were stored globally. This does not include amounts that have escaped into the environment from accidents or tests.
In 2010, it was estimated that about 250,000 t of nuclear HLW were stored globally. This does not include amounts that have escaped into the environment from accidents or tests.  Of particular concern in nuclear waste management are two long-lived fission products, Tc-99 (half-life 220,000 years) and I-129 (half-life 15.7 million years), which dominate spent fuel radioactivity after a few thousand years. The most troublesome transuranic elements in spent fuel are Np-237 (half-life two million years) and Pu-239 (half-life 24,000 years). Nuclear waste requires sophisticated treatment and management to successfully isolate it from interacting with the
Of particular concern in nuclear waste management are two long-lived fission products, Tc-99 (half-life 220,000 years) and I-129 (half-life 15.7 million years), which dominate spent fuel radioactivity after a few thousand years. The most troublesome transuranic elements in spent fuel are Np-237 (half-life two million years) and Pu-239 (half-life 24,000 years). Nuclear waste requires sophisticated treatment and management to successfully isolate it from interacting with the  In the second half of the 20th century, several methods of disposal of radioactive waste were investigated by nuclear nations, which are :
* "Long-term above-ground storage", not implemented.
* "Disposal in outer space" (for instance, inside the Sun), not implemented—as it would be currently too expensive.
* "
In the second half of the 20th century, several methods of disposal of radioactive waste were investigated by nuclear nations, which are :
* "Long-term above-ground storage", not implemented.
* "Disposal in outer space" (for instance, inside the Sun), not implemented—as it would be currently too expensive.
* " Long-term storage of radioactive waste requires the stabilization of the waste into a form that will neither react nor degrade for extended periods. It is theorized that one way to do this might be through
Long-term storage of radioactive waste requires the stabilization of the waste into a form that will neither react nor degrade for extended periods. It is theorized that one way to do this might be through 
 The process of selecting appropriate deep final repositories for high-level waste and spent fuel is now underway in several countries with the first expected to be commissioned sometime after 2010. The basic concept is to locate a large, stable geologic formation and use mining technology to excavate a tunnel, or large-bore tunnel boring machines (similar to those used to drill the
The process of selecting appropriate deep final repositories for high-level waste and spent fuel is now underway in several countries with the first expected to be commissioned sometime after 2010. The basic concept is to locate a large, stable geologic formation and use mining technology to excavate a tunnel, or large-bore tunnel boring machines (similar to those used to drill the  Sweden and Finland are furthest along in committing to a particular disposal technology, while many others reprocess spent fuel or contract with France or Great Britain to do it, taking back the resulting plutonium and high-level waste. "An increasing backlog of plutonium from reprocessing is developing in many countries... It is doubtful that reprocessing makes economic sense in the present environment of cheap uranium."
In many European countries (e.g., Britain, Finland, the Netherlands, Sweden, and Switzerland) the risk or dose limit for a member of the public exposed to radiation from a future high-level nuclear waste facility is considerably more stringent than that suggested by the International Commission on Radiation Protection or proposed in the United States. European limits are often more stringent than the standard suggested in 1990 by the International Commission on Radiation Protection by a factor of 20, and more stringent by a factor of ten than the standard proposed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository for the first 10,000 years after closure. Vandenbosch, p. 248
The U.S. EPA's proposed standard for greater than 10,000 years is 250 times more permissive than the European limit. The U.S. EPA proposed a legal limit of a maximum of 3.5 millisieverts (350 millirem) each annually to local individuals after 10,000 years, which would be up to several percent of the exposure currently received by some populations in the highest natural background regions on Earth, though the U.S.
Sweden and Finland are furthest along in committing to a particular disposal technology, while many others reprocess spent fuel or contract with France or Great Britain to do it, taking back the resulting plutonium and high-level waste. "An increasing backlog of plutonium from reprocessing is developing in many countries... It is doubtful that reprocessing makes economic sense in the present environment of cheap uranium."
In many European countries (e.g., Britain, Finland, the Netherlands, Sweden, and Switzerland) the risk or dose limit for a member of the public exposed to radiation from a future high-level nuclear waste facility is considerably more stringent than that suggested by the International Commission on Radiation Protection or proposed in the United States. European limits are often more stringent than the standard suggested in 1990 by the International Commission on Radiation Protection by a factor of 20, and more stringent by a factor of ten than the standard proposed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository for the first 10,000 years after closure. Vandenbosch, p. 248
The U.S. EPA's proposed standard for greater than 10,000 years is 250 times more permissive than the European limit. The U.S. EPA proposed a legal limit of a maximum of 3.5 millisieverts (350 millirem) each annually to local individuals after 10,000 years, which would be up to several percent of the exposure currently received by some populations in the highest natural background regions on Earth, though the U.S.