North River (Hudson River) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
North River () is an alternative name for the southernmost portion of the Hudson River in the vicinity of
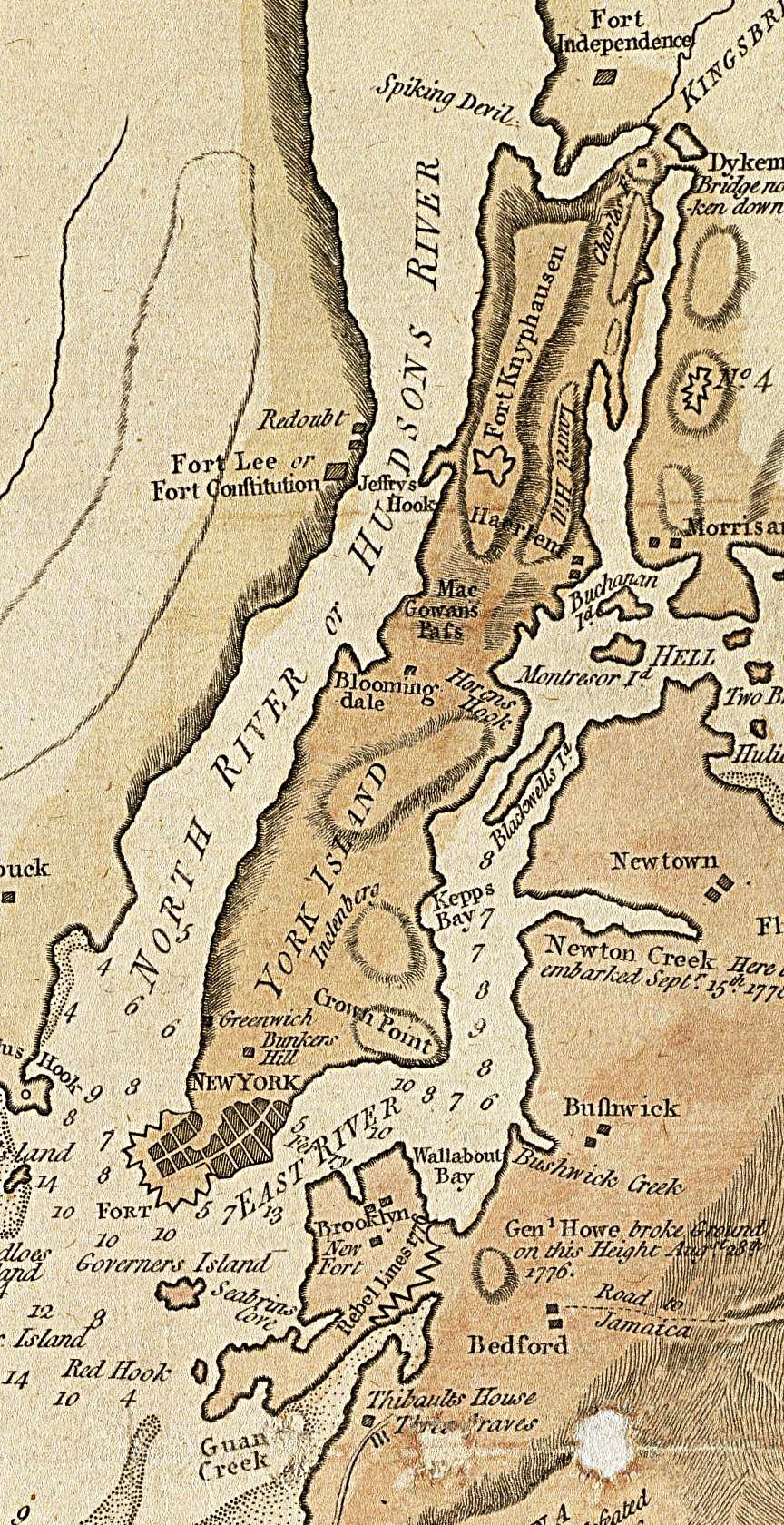 In the early 17th century, the entire watercourse was named the North River (Dutch: Noort Rivier") by the Dutch colonial empire; by the early 18th century, the term fell out of general use for most of the river's 300+ mile course. The name remains in limited use among local mariners and others and on some
In the early 17th century, the entire watercourse was named the North River (Dutch: Noort Rivier") by the Dutch colonial empire; by the early 18th century, the term fell out of general use for most of the river's 300+ mile course. The name remains in limited use among local mariners and others and on some


 * Pier A is a designated national and New York City landmark. The building on the pier dates to 1886, and was used by the city's Department of Docks, Harbor Police, and was later a
* Pier A is a designated national and New York City landmark. The building on the pier dates to 1886, and was used by the city's Department of Docks, Harbor Police, and was later a
, October 18, 2006 After its abandonment, plans created in 2009 called for an improved pier design for commercial use, initially dubbed the SuperPier by its developer. The renovated pier reopened to the public in April 2022, featuring office space for
A Guide to a Hudson River Park Walk from Battery Park to Riverside Park
Wired New York - Hudson River Piers
{{Authority control Borders of New Jersey Borders of New York (state) Hudson River Piers in New York City Port of New York and New Jersey Redeveloped ports and waterfronts in the United States Rivers of Hudson County, New Jersey Rivers of Manhattan Rivers of New Jersey Rivers of New York (state)
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
and northeastern New Jersey in the United States.
History
Name
 In the early 17th century, the entire watercourse was named the North River (Dutch: Noort Rivier") by the Dutch colonial empire; by the early 18th century, the term fell out of general use for most of the river's 300+ mile course. The name remains in limited use among local mariners and others and on some
In the early 17th century, the entire watercourse was named the North River (Dutch: Noort Rivier") by the Dutch colonial empire; by the early 18th century, the term fell out of general use for most of the river's 300+ mile course. The name remains in limited use among local mariners and others and on some nautical chart
A nautical chart or hydrographic chart is a graphic representation of a sea region or water body and adjacent coasts or river bank, banks. Depending on the scale (map), scale of the chart, it may show depths of water (bathymetry) and heights of ...
s and maps. The term is also used to describe infrastructure on and under the river, including the North River piers, North River Tunnels, and Riverbank State Park.
The origin of the name North River is generally attributed to the Dutch. In describing the major rivers in the New Netherland colony, they called the present-day Hudson River the "North River", the present-day Connecticut River the "Fresh River", and the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and is the longest free-flowing (undammed) river in the Eastern United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock, New York, the river flows for a ...
the "South River". Another theory is that the North River and East River
The East River is a saltwater Estuary, tidal estuary or strait in New York City. The waterway, which is not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates Long Island, ...
were so named for the direction of travel they permitted once having entered the Upper New York Bay
New York Harbor is a bay that covers all of the Upper Bay. It is at the mouth of the Hudson River near the East River tidal estuary on the East Coast of the United States.
New York Harbor is generally synonymous with Upper New York Bay ...
.
At various times, North River has referred to:
* The entire Hudson River
* The approximately 160-mile portion of the Hudson below its confluence with the Mohawk River
The Mohawk River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed October 3, 2011 river in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. It is the largest tributary of the Hudson R ...
, which is under tidal influence
* The portion of it running between Manhattan
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the County statistics of the United States#Smallest, larg ...
and New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
* The length flowing between Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan, also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York City, is the southernmost part of the Boroughs of New York City, New York City borough of Manhattan. The neighborhood is History of New York City, the historical birthplace o ...
and Hudson County, New Jersey.
The river's history is strongly connected to the shipping industry
Maritime transport (or ocean transport) or more generally waterborne transport, is the transport of people (passengers or goods (cargo) via waterways. Freight transport by watercraft has been widely used throughout recorded history, as it provi ...
in the Port of New York and New Jersey, which shifted primarily to Port Newark in the mid-20th century due to the construction of the Holland Tunnel and other river crossings and the advent of containerization
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers (also called shipping containers, or International Organization for Standardization, ISO containers). Containerization, also referred as container stuf ...
. Throughout this multi-century history, the name for the lower portion of the river has remained interchangeable with both North River and Hudson River used to describe it.
19th century
In 1808, U.S. Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin issued a report of proposed locations for transportation and communication internal improvements of national importance. The North River figured prominently among his proposals as the best route toward western and northern lands; similar routes were chosen for theErie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east–west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigability, navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, ...
and other early canals built by the New York state
New York, also called New York State, is a state in the northeastern United States. Bordered by New England to the east, Canada to the north, and Pennsylvania and New Jersey to the south, its territory extends into both the Atlantic Ocean and ...
.
Gallatin noted the following in reference to the North and Hudson Rivers, writing:
20th century
In 1909, two tunnels were under construction: one was called the North River Tunnels, the other, the Hudson Tubes. That year the Hudson–Fulton Celebration was held, commemorating Henry Hudson, the first European to record navigating the river, andRobert Fulton
Robert Fulton (November 14, 1765 – February 24, 1815) was an American engineer and inventor who is widely credited with developing the world's first commercially successful steamboat, the (also known as ''Clermont''). In 1807, that steamboat ...
, the first man to use a paddle steamer
A paddle steamer is a steamship or steamboat powered by a steam engine driving paddle wheels to propel the craft through the water. In antiquity, paddle wheelers followed the development of poles, oars and sails, whereby the first uses were wh ...
in America, named the '' North River Steamboat'', to sail up it, leading to controversy over what the waterway should be called.
Much of the shoreline previously used for maritime, rail, and industrial activities has given way to recreational promenade
An esplanade or promenade is a long, open, level area, usually next to a river or large body of water, where people may walk. The historical definition of ''esplanade'' was a large, open, level area outside fortification, fortress or city walls ...
s and piers. On the Hudson Waterfront in New Jersey, the Hudson River Waterfront Walkway
The Hudson River Waterfront Walkway, also known as the Hudson River Walkway, is a promenade along the Hudson Waterfront in New Jersey. The ongoing and incomplete project located on Kill van Kull and the western shore of Upper New York Bay and t ...
runs for about 18 miles. In Manhattan, the Hudson River Park runs from Battery Park
The Battery, formerly known as Battery Park, is a public park located at the southern tip of Manhattan#Manhattan Island, Manhattan Island in New York City facing New York Harbor. The park is bounded by Battery Place on the north, with Bowling ...
to 59th Street.
North River on maps
TheNational Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, ...
's current charts call the lower river the "Hudson", and the United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on Mar ...
lists "North River" as an alternative name of the Hudson River without qualifying it as any particular portion of the river.
Hagstrom Maps, formerly the leading mapmaker in the New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also called the Tri-State area and sometimes referred to as Greater New York, is the List of cities by GDP, largest metropolitan economy in the world, with a List of U.S. metropolitan areas by GDP, gross metropo ...
and known for occasional quirky and anachronistic names, features, and artifacts on their maps, has labeled all or part of the Hudson adjacent to Manhattan as "North River" on several of its products. For instance, on a 1997 Hagstrom ''Map of Manhattan'', the stretch of river between Hudson County, New Jersey, and Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan, also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York City, is the southernmost part of the Boroughs of New York City, New York City borough of Manhattan. The neighborhood is History of New York City, the historical birthplace o ...
, roughly corresponding to the location of the North River piers, was labeled "North River", with the label "Hudson River" used above Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan, serving as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Building, the ...
.
On a 2000 map of "Northern Approaches to New York City" included in Hagstrom's ''New York tateRoad Map'', the entire river adjacent to Manhattan
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the County statistics of the United States#Smallest, larg ...
was labeled "Hudson River (North River)" with the river further north at Tappan Zee labeled the "Hudson River".
North River piers
Piers along the Hudson shore of Manhattan were formerly used for shipping and berthing ocean-going ships. In shipping notices, they were designated as, for example, "Pier 14, North River". As with the river, the name "North River piers" has largely been supplanted by "Hudson River piers", or just by a pier and number, e.g., "Pier 54". Pier 40 is located at Houston Street, and the numbering of the piers to the north correspond to the nearest numbered street plus 40 – thus, for example, North River Pier 86 is at West 46th Street. Most of the piers that once existed in lower Manhattan fell into disuse or were destroyed in the last half of the 20th century. The remaining piers are Pier A at the Battery and piers ranging from Pier 25 at North Moore Street to Pier 99 at 59th Street. Many of these piers and the waterfront between them are part of the Hudson River Park which stretches from 59th Street to the Battery. The park, a joint project betweenNew York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
and New York State
New York, also called New York State, is a state in the northeastern United States. Bordered by New England to the east, Canada to the north, and Pennsylvania and New Jersey to the south, its territory extends into both the Atlantic Ocean and ...
commenced in 1998, consists of several non-contiguous parcels of land and piers totaling , plus another of the river itself. Several piers were rebuilt for adaptive re-use as part of the park project, with approximately 70% of the planned work complete by 2011.
Status


fireboat
A fireboat or Fire-float Pyronaut, fire-float is a specialized watercraft with pumps and nozzles designed for fighting shoreline and shipboard fires. The first fireboats, dating to the late 18th century, were tugboats, retrofitted with ...
station. The pier was closed and renovated from 1992 to November 2014, after which it reopened as a restaurant.
* What little remained of Piers 1 through 21 were buried under landfill
A landfill is a site for the disposal of waste materials. It is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of waste with daily, intermediate and final covers only began in the 1940s. In the past, waste was ...
from the World Trade Center construction project in 1973 and turned into Battery Park City.
*Pier 25 is a sports and docking facility at the foot of North Moore Street with a mini golf course.
*Pier 26 was rebuilt over 2008–2009 and is home to a new park designed by OLIN and Rafael Viñoly and opened in September 2020, featuring a sports court and an engineered wetland.
*Pier 34, at Canal Street, contains a ventilation shaft for the Holland Tunnel.
* Pier 40, at Houston Street, was built as a terminal for the Holland America Line in 1962, and now contains various playing fields, long-term parking spaces and the Trapeze School of New York on the roof (during the summer).
*The term " Christopher Street Pier" usually refers specifically to Pier 45 opposite West 10th Street in Greenwich Village
Greenwich Village, or simply the Village, is a neighborhood on the west side of Lower Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 14th Street (Manhattan), 14th Street to the north, Broadway (Manhattan), Broadway to the east, Houston Street to the s ...
. However, it refers to three other piers as well, between Piers 42–51. Pier 51 houses a water-themed playground, part of Hudson River Park.
* Piers 52 and 53, also known as Gansevoort Peninsula, were formerly a New York City Department of Sanitation facility used for shipping trash out of Manhattan. They are being converted into a public park, expected to be complete in 2023. Also at the end of Pier 53 is the FDNY's Marine 1 fireboat
A fireboat or Fire-float Pyronaut, fire-float is a specialized watercraft with pumps and nozzles designed for fighting shoreline and shipboard fires. The first fireboats, dating to the late 18th century, were tugboats, retrofitted with ...
facility, occupying a new building completed in 2011.
* Pier 54 and Pier 55, part of Hudson River Park since its creation in 1998, was closed in 2011 when it was deemed structurally unsound. Plans were unveiled in November 2014 for a new park designed by Heatherwick Studio and costing $130 million. The project was temporarily canceled in 2017 after costs had grown to $250 million, but was later revived as part of an agreement to complete the remainder of Hudson River Park. The new park, dubbed " Little Island," took the place of the now-dismantled Piers 54 and 55, and opened in May 2021.
* Pier 57, at 15th Street and 11th Avenue, formerly served as a terminal for shipping and storage of cargo for the Grace Line. Between 1969 and 2003, Pier 57 housed the Hudson Pier Bus Depot for the New York City Transit Authority.Testimony by State Senator José M. Serrano given before the City Council Transportation Committee Hearing on MTA Environmental Practices, October 18, 2006 After its abandonment, plans created in 2009 called for an improved pier design for commercial use, initially dubbed the SuperPier by its developer. The renovated pier reopened to the public in April 2022, featuring office space for
Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
, a food hall, and a rooftop park.
*Piers 59–62 are used as Chelsea Piers, which were originally a passenger ship terminal in the early 1900s that was used by the RMS Lusitania and was the destination of the RMS Titanic
RMS ''Titanic'' was a British ocean liner that Sinking of the Titanic, sank in the early hours of 15 April 1912 as a result of striking Iceberg that struck the Titanic, an iceberg on her maiden voyage from Southampton, England, to New York Ci ...
. The Chelsea Piers Sports & Entertainment Complex opened at the site in 1995.
* Pier 63 was the location of a Pavonia Ferry terminal that opened in 1869. The terminal was demolished in 1942, and the pier then housed a Baltimore and Ohio Railroad transfer barge. In the late 1980s, boat enthusiast John Krevey converted an old railroad barge on the Hudson River to a floating jetty.
* Pier 66 is part of Hudson River Park, It is located at 26th Street and is used for sailing and paddle sports.
*Pier 76, formerly the NYPD impound lot, was reopened by the Hudson River Park Trust on June 9, 2021 as a park and cultural space.
*Pier 78 is the only Hudson River pier that is privately owned, and is used for sightseeing cruises.
*Pier 79 is the West Midtown Ferry Terminal used by NY Waterway and NYC Ferry. Pier 79 connects to an Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French (), is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design that first Art Deco in Paris, appeared in Paris in the 1910s just before World War I and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920 ...
style ventilation shaft for the Lincoln Tunnel.
*Pier 81 is site of North River Lobster and World Yacht
*Pier 83 is used by Circle Line Sightseeing Cruises.
*Pier 84 served as a concert venue from the former Schaefer Music Festival. The pier also houses a water-themed playground within Hudson River Park, is a stop for New York Water Taxi, and has a bicycle rental shop and other businesses serving primarily tourists.
*Pier 86 at West 46th Street is home to the ''Intrepid'' Sea, Air & Space Museum, the centerpiece of which is the USS ''Intrepid'', an aircraft carrier that served from World War II to the Vietnam War. This pier once served as the passenger ship terminal for the United States Lines
United States Lines was an organization of the United States Shipping Board's (USSB) Emergency Fleet Corporation (EFC), created to operate German liners seized by the United States in 1917. The ships were owned by the USSB and all finances of t ...
.
*Piers 88–92 are part of the Manhattan Cruise Terminal, used by numerous modern cruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports of call, where passengers may go on Tourism, tours k ...
s and ocean liner
An ocean liner is a type of passenger ship primarily used for transportation across seas or oceans. Ocean liners may also carry cargo or mail, and may sometimes be used for other purposes (such as for pleasure cruises or as hospital ships). The ...
s. In 1942, the USS ''Lafayette'' (formerly SS ''Normandie'') caught fire at Pier 88, remaining capsized there for a year. Pier 92 was subsequently used as an exhibition space, but closed in 2019 after the pier was found to be unsafe.
*Pier 94 was formerly also part of the Passenger Ship Terminal, and until 2020 housed the "UnConvention Center", the second-largest exhibition hall
A convention center (American English; or conference centre in British English) is a large building that is designed to hold a convention, where individuals and groups gather to promote and share common interests. Convention centers typica ...
in New York City. As of 2023, it is slated to be redeveloped into a film studio.
*Pier 96 is part of Hudson River Park. It is the home of Manhattan Community Boathouse, an all-volunteer non-profit organization that offers free kayaking to the public each summer.
*Pier 97 is part of Hudson River Park. It was until 1975 the home of the Swedish American Line passenger ship terminal. The terminal was demolished some time after 1984 and the pier has since been used for various purposes, including many years as a Sanitation Department parking lot and a brief period as a live event venue sponsored by JBL and Live Nation. In November 2019, it was announced that the pier would be converted into a park, with construction expected to start in September 2020. As of September 2020, the pier is now expected to reopen in March 2024.
* Pier 98 is used for Con Edison employee car parking, a training facility and delivery by barge and storage of fuel oil.
* Pier 99 houses the West 59th Street Marine Transfer Station, used by the New York City Sanitation Department.
* Pier I and most of Riverside Park South were originally part of the abandoned Penn Central railyard between 59th and 72nd Streets. These lettered piers were built at a 55-degree angle to the shore to facilitate the transfer of rail cars from their tracks to a waiting barge. Pier I is the only remaining rail pier. The 69th Street Transfer Bridge of the New York Central Railroad
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected New York metropolitan area, gr ...
is still extant and has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government's official United States National Register of Historic Places listings, list of sites, buildings, structures, Hist ...
since 2003.
Railroads and ferries
Prior to the opening of the North River Tunnels and the Hudson and Manhattan Railroad tubes in the early 1900s, passengers and freight were required to cross the river for travel to points east. This led to an extensive network of intermodal terminals, railyards, ferry slips, docks, barges, and carfloats. The west shore of the river from the mid 19th to the mid 20th century was home to expansive facilities operated by competing railroads. Most are now gone, allowing for public access to the waterfront atpier
A pier is a raised structure that rises above a body of water and usually juts out from its shore, typically supported by piling, piles or column, pillars, and provides above-water access to offshore areas. Frequent pier uses include fishing, b ...
s, parks, promenades and marinas along the Hudson River Waterfront Walkway
The Hudson River Waterfront Walkway, also known as the Hudson River Walkway, is a promenade along the Hudson Waterfront in New Jersey. The ongoing and incomplete project located on Kill van Kull and the western shore of Upper New York Bay and t ...
. New ferry slips and terminals exclusively for pedestrian use have been built.
* Communipaw Terminal was in operation from 1864 to 1967. It was owned by the Central Railroad of New Jersey and also hosted trains of the Baltimore and Ohio and the Reading Company. The CRRNJ's main ferry ran to pier 11 at Liberty Street. The historic landmark is now a major feature of Liberty State Park
Liberty State Park (LSP) is a park in the U.S. state of New Jersey, located on Upper New York Bay in Jersey City, New Jersey, Jersey City opposite Liberty Island and Ellis Island. The park opened in 1976 to coincide with United States Bicenten ...
and ferry terminal for service to Ellis Island and Liberty Island. The terminal is adjacent to the Big Basin of the Morris Canal (used to ship anthracite from the mines of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
) which entered the harbor at the river's mouth.
* Exchange Place station was the location of the first waterfront terminal in 1834, and its larger successor was used until 1961. Regular ferry service from Paulus Hook had begun in the early Dutch colonial period. The original station was built by the New Jersey Railroad to meet the world's first steam ferry service which had been initiated in 1812 by Robert Fulton
Robert Fulton (November 14, 1765 – February 24, 1815) was an American engineer and inventor who is widely credited with developing the world's first commercially successful steamboat, the (also known as ''Clermont''). In 1807, that steamboat ...
and Robert Livingston. During the Pennsylvania Railroad era in the 20th century the station was called Exchange Place, local nomenclature for the streetcar
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some include s ...
terminus and Hudson and Manhattan Railroad tube station. The main ferry ran to Cortlandt Street. The district is now sometimes known as " Wall Street West" due to the concentration of financial concerns and skyscrapers located there. Today ferry service travels to Battery Park City Ferry Terminal, Pier 11 at Wall Street, and the West Midtown Ferry Terminal.
* Pavonia Terminal operated from 1861 to 1958. The terminal, completed in 1889 by the Erie Railroad, was at the end of the Long Dock which extended into the partially landfilled Harsimus Cove. The Jersey City Terminal was also used by the New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway. It was named after the seventeenth century New Netherland settlement of Pavonia. Ferry service began in the 1840s. The main Pavonia Ferry later ran to Chambers Street and 23rd Street. The Erie's Pavonia trains were moved to Hoboken Terminal between 1956 and 1958, and the ferries and terminal abandoned. The terminal and yards have now been developed into the residential and commercial district of Newport, Jersey City.
* Hoboken Terminal is the last of the Hudson River terminals still in use and is now operated by NJ Transit. Regular ferry service was started in 1834 by John Stevens. Train service began in 1863 by the Morris and Essex Railroad and was taken over by Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad, which built the terminal in 1908. The DL&W later merged with the Erie to create the Erie Lackawanna Railway which, after becoming part of Conrail, operated until the state takeover in the 1970s. The main routes of the Hoboken Ferry ran to Barclay Street, Christopher Street and 23rd Street; these ferries operated until 1967. Today NY Waterway ferries travel to the Battery Park City Ferry Terminal, Pier 11 at Wall Street and the West Midtown Ferry Terminal.
* Weehawken Terminal operated from 1884 to 1959 as the terminus for New York Central Railroad
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected New York metropolitan area, gr ...
's West Shore Railroad division as well as for the New York, Ontario and Western Railway. The extensive Weehawken Yards also handled freight for the Erie Railroad with the New Jersey Junction Railroad. The New York Central Railroad 69th Street Transfer Bridge is now a historic site. The main Weehawken Ferry travelled directly across the river to 42nd Street and for a time was part of route of the Lincoln Highway. Other ferries included those to 14th Street and Cortland Street. The original tunnel under Bergen Hill is now used by the Hudson–Bergen Light Rail and contains the Bergenline Avenue station. Ferry service is now provided from Weehawken Port Imperial to the West Midtown Ferry Terminal, Battery Park City Ferry Terminal, and Wall Street.
* The New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway terminus in Shadyside, Edgewater, was opened in 1894 for the shipment of coal and other products. This led to extensive landfilling and industrial growth including plants of Hess Oil and Chemical, Lever Brothers
Lever Brothers was a British manufacturing company founded in 1885 by two brothers: William Lever, 1st Viscount Leverhulme, William Hesketh Lever, 1st Viscount Leverhulme (1851–1925), and James Darcy Lever (1854–1916). They invested in and su ...
, Alcoa, and the Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational corporation, multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. T ...
. Many workers from Manhattan used the ferry from 125th Street to reach their jobs. The factories of Edgewater have been demolished, the brownfields redeveloped for residential, retail, and recreational uses. The ferry now travels from Edgewater Landing to West Midtown Ferry Terminal.
Fixed crossings
The last crossing to be built was the south tube of the Lincoln Tunnel in 1957, but in 1962, another deck was added to the George Washington Bridge. Since 2003, various proposals have been made to add a new train line. This includes an extension of the completed 7 Subway Extension, the canceled Access to the Region's Core, and the ongoing Gateway Program.See also
* List of bridges, tunnels, and cuts in Hudson County, New Jersey * List of ferries across the Hudson River to New York City * List of New Jersey rivers * List of New York rivers * New York Harbor * New York–New Jersey Harbor Estuary * Timeline of Jersey City area railroadsReferences
External links
A Guide to a Hudson River Park Walk from Battery Park to Riverside Park
Wired New York - Hudson River Piers
{{Authority control Borders of New Jersey Borders of New York (state) Hudson River Piers in New York City Port of New York and New Jersey Redeveloped ports and waterfronts in the United States Rivers of Hudson County, New Jersey Rivers of Manhattan Rivers of New Jersey Rivers of New York (state)