North Rhine-Westphalia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
North Rhine-Westphalia or North-Rhine/Westphalia, commonly shortened to NRW, is a
 The state of North Rhine-Westphalia was established by the British military administration's "Operation Marriage" on 23 August 1946 by merging the
The state of North Rhine-Westphalia was established by the British military administration's "Operation Marriage" on 23 August 1946 by merging the
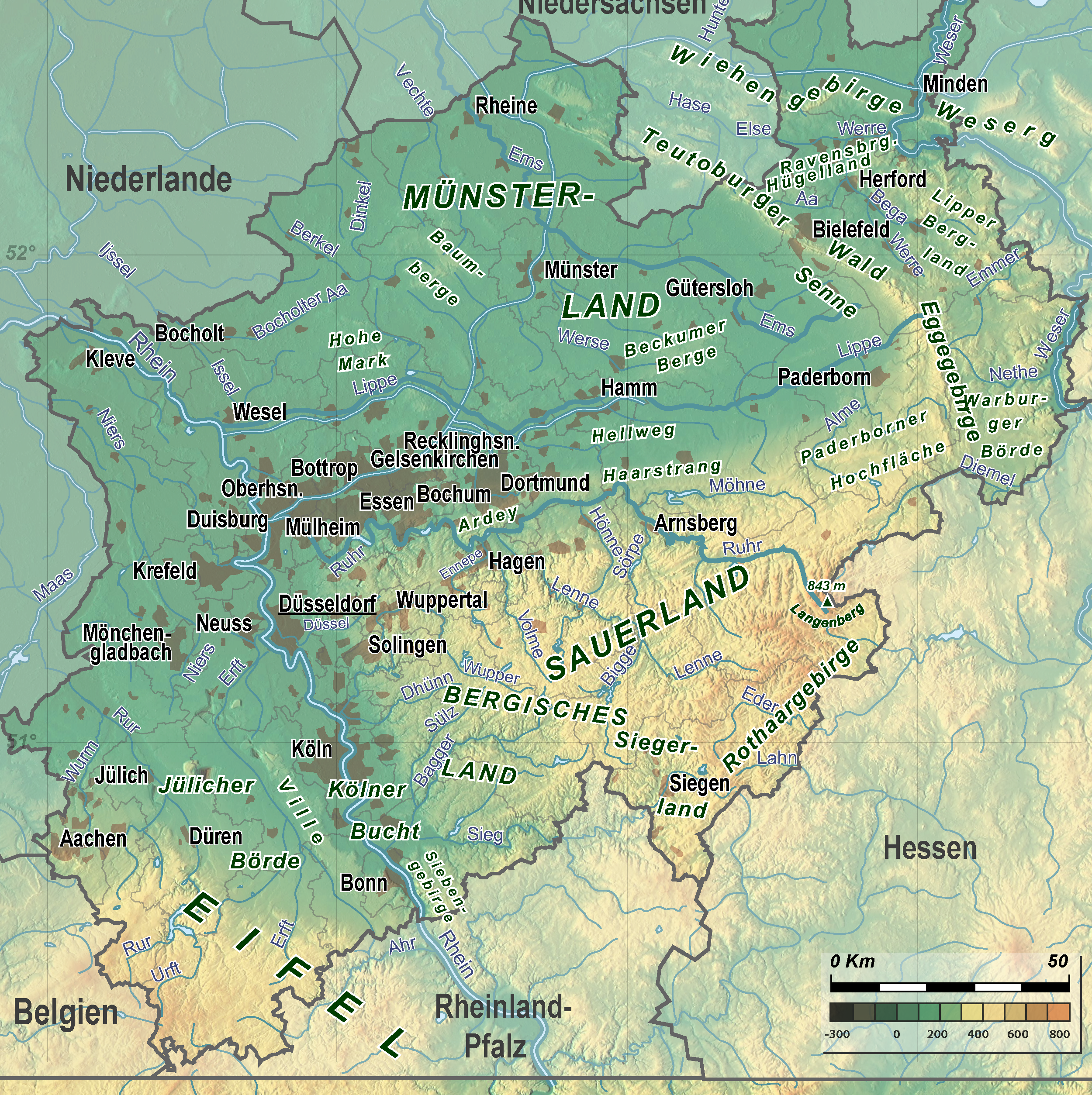 North Rhine-Westphalia encompasses the plains of the
North Rhine-Westphalia encompasses the plains of the
The terrain rises towards the south and in the east of the state into parts of Germany's The planimetrically determined centre of North Rhine-Westphalia is located in the south of Dortmund- Aplerbeck in the Aplerbecker Mark (51° 28' N, 7° 33' Ö). Its westernmost point is situated near
The planimetrically determined centre of North Rhine-Westphalia is located in the south of Dortmund- Aplerbeck in the Aplerbecker Mark (51° 28' N, 7° 33' Ö). Its westernmost point is situated near
 The state consists of five government regions (''Regierungsbezirke''), divided into 31 districts ('' Kreise'') and 23 urban districts (''kreisfreie Städte''). In total, North Rhine-Westphalia has 396 municipalities (1997), including the urban districts, which are municipalities by themselves. The government regions have an assembly elected by the districts and municipalities, while the ''Landschaftsverband'' has a directly elected assembly.
The five government regions of North Rhine-Westphalia each belong to one of the two '' Landschaftsverbände'':
The state consists of five government regions (''Regierungsbezirke''), divided into 31 districts ('' Kreise'') and 23 urban districts (''kreisfreie Städte''). In total, North Rhine-Westphalia has 396 municipalities (1997), including the urban districts, which are municipalities by themselves. The government regions have an assembly elected by the districts and municipalities, while the ''Landschaftsverband'' has a directly elected assembly.
The five government regions of North Rhine-Westphalia each belong to one of the two '' Landschaftsverbände'':
 The politics of North Rhine-Westphalia takes place within a framework of a federal
The politics of North Rhine-Westphalia takes place within a framework of a federal
File:Löwenstein House Aachen (Germany).jpg, Medieval architecture in
File:Zeche Zollern Dortmund.jpg, The Zeche Zollern in
File:Schloss Augustusburg in Brühl 4.jpg, Augustusburg and Falkenlust
File:Aachen Germany Imperial-Cathedral-01.jpg,
 North Rhine-Westphalia has always been Germany's powerhouse with the largest economy among the German states by GDP figures.
In the 1950s and 1960s, Westphalia was known as ''Land von Kohle und Stahl'' (''Land of Coal and Steel''). In the post-World War II recovery, the
North Rhine-Westphalia has always been Germany's powerhouse with the largest economy among the German states by GDP figures.
In the 1950s and 1960s, Westphalia was known as ''Land von Kohle und Stahl'' (''Land of Coal and Steel''). In the post-World War II recovery, the
 The regional rail network is organised around the big cities on the Rhine and Ruhr such as
The regional rail network is organised around the big cities on the Rhine and Ruhr such as
 NRW is home to several football clubs of the
NRW is home to several football clubs of the
Official Government Portal
Visit NRW Tourist Information
The Landtag of North Rhine-Westphalia
Holidays and travel tips in NRW
Information and resources on the history of Westphalia on the Web portal "Westphalian History"
Guidelines for the integration of the Land Lippe within the territory of the federal state North-Rhine-Westphalia of 17 January 1947
* {{Portal bar, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union States and territories established in 1946 1946 establishments in Germany States of Germany
state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
() in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhabitants, it is the most populous state in Germany. Apart from the city-states (Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
, Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
and Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (, ), is the capital of the States of Germany, German state of the Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (), a two-city-state consisting of the c ...
), it is also the most densely populated state in Germany. Covering an area of , it is the fourth-largest German state by size.
North Rhine-Westphalia features 30 of the 81 German municipalities with over 100,000 inhabitants, including Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
(over 1 million), the state capital Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in the state after Cologne and the List of cities in Germany with more than 100,000 inhabitants, seventh-largest city ...
(630,000), Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
and Essen
Essen () is the central and, after Dortmund, second-largest city of the Ruhr, the largest urban area in Germany. Its population of makes it the fourth-largest city of North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne, Düsseldorf and Dortmund, as well as ...
(about 590,000 inhabitants each) and other cities predominantly located in the Rhine-Ruhr
The Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region () is the Metropolitan regions in Germany, largest metropolitan region in Germany, with over ten million inhabitants. A wikt:polycentric, polycentric conurbation with several major urban concentrations, the reg ...
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region consisting of a densely populated urban area, urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories which share Industry (economics), industries, commercial areas, Transport infrastructure, transport network ...
, the largest urban area in Germany and the fourth-largest on the European continent
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the eas ...
. The location of the Rhine-Ruhr at the heart of the European Blue Banana makes it well connected to other major European cities and metropolitan areas like the Randstad
The Randstad (; "Rim City" or "Edge City") is a roughly crescent- or Circular arc, arc-shaped conurbation in the Netherlands, that includes almost half the country's population. With a central-western location, it connects and comprises the Net ...
, the Flemish Diamond and the Frankfurt Rhine-Main Region.
North Rhine-Westphalia was established in 1946 after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
from the Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
n provinces of Westphalia
Westphalia (; ; ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the region is almost identical with the h ...
and the northern part of Rhine Province
The Rhine Province (), also known as Rhenish Prussia () or synonymous with the Rhineland (), was the westernmost Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822 to 1946. ...
( North Rhine), and the Free State of Lippe by the British military administration in Allied-occupied Germany
The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II, from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Nazi Germany was stripped of its sov ...
and became a state of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949. The city of Bonn
Bonn () is a federal city in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located on the banks of the Rhine. With a population exceeding 300,000, it lies about south-southeast of Cologne, in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region. This ...
served as the federal capital until the reunification of Germany
German reunification () was the process of re-establishing Germany as a single sovereign state, which began on 9 November 1989 and culminated on 3 October 1990 with the dissolution of the German Democratic Republic and the integration of i ...
in 1990 and as the seat of government
The seat of government is (as defined by ''Brewer's Politics'') "the building, complex of buildings or the city from which a government exercises its authority".
In most countries, the nation's Capital city, capital is also seat of its governmen ...
until 1999.
Culturally, North Rhine-Westphalia is not a uniform area; there are significant differences, especially in traditional customs, between the Rhineland region on the one hand and the regions of Westphalia and Lippe on the other. Its economy is the largest among German states by GRDP but is below the national average in GRDP per capita.
History
Creation
province of Westphalia
The Province of Westphalia () was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1815 to 1946. In turn, Prussia was the largest component state of the German Empire from 1871 to 1918, of the Weimar ...
and the northern parts of the Rhine Province
The Rhine Province (), also known as Rhenish Prussia () or synonymous with the Rhineland (), was the westernmost Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822 to 1946. ...
, both being political divisions of the former state of Prussia within the German Reich
German ''Reich'' (, from ) was the constitutional name for the German nation state that existed from 1871 to 1945. The ''Reich'' became understood as deriving its authority and sovereignty entirely from a continuing unitary German ''Volk'' ("na ...
. On 21 January 1947, the former state of Lippe
Lippe () is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Herford, Minden-Lübbecke, Höxter, Paderborn, Gütersloh, and district-free Bielefeld, which forms the region Ostwestfalen-Lippe. ...
was merged with North Rhine-Westphalia. The constitution of North Rhine-Westphalia was then ratified through a referendum
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate (rather than their Representative democracy, representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either bin ...
.
Rhineland
The first written account of the area was by its conqueror,Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
, the territories west of the Rhine were occupied by the Eburones and east of the Rhine he reported the Ubii
350px, The Ubii around AD 30
The Ubii were a Germanic tribe first encountered dwelling on the east bank of the Rhine in the time of Julius Caesar, who formed an alliance with them in 55 BC in order to launch attacks across the river. They were ...
(across from Cologne) and the Sugambri to their north. The Ubii and some other Germanic tribes such as the Cugerni were later settled on the west side of the Rhine in the Roman province of Germania Inferior
''Germania Inferior'' ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed ''Germania Secunda'' in the 4th century AD, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Cl ...
. Julius Caesar conquered the tribes on the left bank, and Augustus established numerous fortified posts on the Rhine, but the Romans never succeeded in gaining a firm footing on the right bank, where the Sugambri neighboured several other tribes including the Tencteri
The Tencteri or Tenchteri or Tenctheri (in Plutarch's Greek, Tenteritē and possibly the same as the Tenkeroi mentioned by Claudius Ptolemy if these were not the Tungri) were an ancient tribe, who moved into the area on the right bank (the nort ...
and Usipetes
The Usipetes or Usipii (in Plutarch's Greek, Ousipai, and possibly the same as the Ouispoi of Ptolemy) were an ancient Germanic people who entered the written record when they encountered Julius Caesar in 56/55 BC when they attempted to find a new ...
. North of the Sigambri and the Rhine region were the Bructeri
The Bructeri were a Germanic people, who lived in present-day North Rhine-Westphalia, just outside what was then the Roman Empire. The Romans originally reported them living east of the lower Rhine river, in a large area centred around present day ...
.
As the power of the Roman empire declined, many of these tribes came to be seen collectively as Ripuarian Franks
The Rhineland or Ripuarian Franks, also often referred to using the Latin plurals ''Ribuarii'', or ''Ripuarii'', were the Franks who established themselves in and around the formerly Roman city of Cologne, on the Rhine river in what is now Germa ...
and they pushed forward along both banks of the Rhine, and by the end of the fifth century had conquered all the lands that had formerly been under Roman influence. By the eighth century, the Frankish dominion was firmly established in western Germany and northern Gaul, but at the same time, to the north, Westphalia was being taken over by Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
pushing south.
The Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the ...
and Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Arnulfing and Pippinid c ...
Franks eventually built an empire which controlled first their Ripuarian kin, and then the Saxons. On the division of the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
at the Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (; ), agreed to on 10 August 843, ended the Carolingian civil war and divided the Carolingian Empire between Lothair I, Louis the German, Louis II and Charles the Bald, Charles II, the surviving sons of the emperor Louis the ...
, the part of the province to the east of the river fell to East Francia
East Francia (Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire created in 843 and ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was established through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the for ...
, while that to the west remained with the kingdom of Lotharingia
Lotharingia was a historical region and an early medieval polity that existed during the late Carolingian and early Ottonian era, from the middle of the 9th to the middle of the 10th century. It was established in 855 by the Treaty of Prüm, a ...
.
By the time of Otto I (d. 973), both banks of the Rhine had become part of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, and the Rhenish territory was divided between the duchies of Upper Lorraine on the Moselle
The Moselle ( , ; ; ) is a river that rises in the Vosges mountains and flows through north-eastern France and Luxembourg to western Germany. It is a bank (geography), left bank tributary of the Rhine, which it joins at Koblenz. A sm ...
and Lower Lorraine
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as '' Lothier'' or '' Lottier''
on the Meuse. The Ottonian dynasty
The Ottonian dynasty () was a Saxons, Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman emperors, especially Otto the Great. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German ...
had both Saxon and Frankish ancestry.
As the central power of the Holy Roman Emperor weakened, the Rhineland split into numerous small, independent, separate vicissitudes and special chronicles. The old Lotharingian divisions became obsolete, although the name survives for example in Lorraine
Lorraine, also , ; ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; ; ; is a cultural and historical region in Eastern France, now located in the administrative region of Grand Est. Its name stems from the medieval kingdom of ...
in France, and throughout the Middle Ages and even into modern times, the nobility of these areas often sought to preserve the idea of a preeminent duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of Royal family, royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobi ...
within Lotharingia, something claimed by the Dukes of Limburg, and the Dukes of Brabant
The Duke of Brabant (, ) was the ruler of the Duchy of Brabant since 1183/1184. The title was created by the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in favor of Henry I of the House of Reginar, son of Godfrey III of Leuven (who was duke of L ...
. Such struggles as the War of the Limburg Succession therefore continued to create military and political links between what is now Rhineland-Westphalia and neighbouring Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
and the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
.
In spite of its dismembered condition and the sufferings it underwent at the hands of its French neighbours in various periods of warfare, the Rhenish territory prospered greatly and stood in the foremost rank of German culture and progress. Aachen was the place of coronation of the German emperors, and the ecclesiastical principalities of the Rhine bulked largely in German history.
Prussia first set foot on the Rhine in 1609 by the occupation of the Duchy of Cleves
The Duchy of Cleves (; ) was a state of the Holy Roman Empire which emerged from the medieval . It was situated in the northern Rhineland on both sides of the Lower Rhine, around its capital Cleves and the towns of Wesel, Kalkar, Xanten, Emme ...
and about a century later Upper Guelders {{unreferenced, date=November 2011
Upper Guelders or Spanish Guelders was one of the four quarters in the Imperial Guelders, Duchy of Guelders. In the Dutch Revolt, it was the only quarter that did not secede from the Habsburg monarchy to become pa ...
and Moers
Moers (; older form: ''Mörs''; Dutch language, Dutch: ''Murse'', ''Murs'' or ''Meurs'') is a German List of cities and towns in Germany, city on the western bank of the Rhine, close to Duisburg. Moers belongs to the district of Wesel (distric ...
also became Prussian. At the peace of Basel in 1795, the whole of the left bank of the Rhine was resigned to France, and in 1806, the Rhenish princes all joined the Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austrian Empire, Austria ...
.
After the Congress of Vienna, Prussia was awarded the entire Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
, which included the Grand Duchy of Berg, the ecclesiastic electorates of Trier
Trier ( , ; ), formerly and traditionally known in English as Trèves ( , ) and Triers (see also Names of Trier in different languages, names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle (river), Moselle in Germany. It lies in a v ...
and Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, the free cities of Aachen
Aachen is the List of cities in North Rhine-Westphalia by population, 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, 27th-largest city of Germany, with around 261,000 inhabitants.
Aachen is locat ...
and Cologne, and nearly a hundred small lordships and abbeys. The Prussian Rhine province
The Rhine Province (), also known as Rhenish Prussia () or synonymous with the Rhineland (), was the westernmost Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822 to 1946. ...
was formed in 1822 and Prussia had the tact to leave the lower Rhenish districts in undisturbed possession of the liberal institutions to which they had become accustomed under the republican rule of the French. In 1920, the districts of Eupen
Eupen (, , ; ; ; former ) is the capital of German-speaking Community of Belgium and is a city and municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Belgium, Belgian Liège Province, province of Liège, from the Germany, German border (Aachen ...
and Malmedy
Malmedy (; , historically also ; ) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Liège, Belgium.
On January 1, 2018, Malmedy had a total population of 12,654. The total area is 99.96 km2 which gives a population dens ...
were transferred to Belgium (see German-speaking Community of Belgium
The German-speaking Community (, , DG), also known as East Belgium ( ), is one of the three Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, federal communities of Belgium. The community is composed of nine municipalities in Liège Province, ...
).
Westphalia
Around AD 1, numerous incursions occurred through Westphalia and perhaps even some permanentRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
or Romanized settlements. The Battle of Teutoburg Forest took place near Osnabrück and some of the Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts ...
who fought at this battle came from the area of Westphalia. Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
is thought to have spent considerable time in Paderborn
Paderborn (; Westphalian language, Westphalian: ''Patterbuorn'', also ''Paterboärn'') is a city in eastern North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, capital of the Paderborn (district), Paderborn district. The name of the city derives from the river Pade ...
and nearby parts. His Saxon Wars
The Saxon Wars were the campaigns and insurrections of the thirty-three years from 772, when Charlemagne first entered Saxony with the intent to conquer, to 804, when the last rebellion of tribesmen was defeated. In all, 18 campaigns were fou ...
also partly took place in what is thought of as Westphalia today. Popular legends link his adversary Widukind
Widukind, also known as Wittekind and Wittikund, was a leader of the Saxons and the chief opponent of the Frankish king Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 777 to 785. Charlemagne ultimately prevailed, organized Saxony as a Frankish provinc ...
to places near Detmold, Bielefeld
Bielefeld () is a city in the Ostwestfalen-Lippe Region in the north-east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population of 341,755, it is also the most populous city in the administrative region () of Detmold (region), Detmold and the L ...
, Lemgo
Lemgo (; ) is a university and old Hanseatic League, Hanseatic town in the Lippe district of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.
It is situated between the Teutoburg Forest and the Weser Uplands, 25 km east of Bielefeld and 70 km west of H ...
, Osnabrück, and other places in Westphalia. Widukind was buried in Enger, which is also a subject of a legend.
Along with Angria, Eastphalia
Eastphalia ( �stˈfaːlən Eastphalian: ''Oostfalen'') is a historical region in northern Germany, encompassing the eastern '' Gaue'' (shires) of the historic stem duchy of Saxony, roughly confined by the River Leine in the west and the Elbe a ...
, and Nordalbingia, Westphalia (''Westfalahi'') was originally a district of the Duchy of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony () was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 CE and incorporated into the Carolingian Empire (Francia) by 804. Upon the 84 ...
. In 1180, Westphalia was elevated to the rank of a duchy by Emperor Barbarossa
Barbarossa, a name meaning "red beard" in Italian, primarily refers to:
* Frederick Barbarossa (1122–1190), Holy Roman Emperor
* Hayreddin Barbarossa (c. 1478–1546), Ottoman admiral
* Operation Barbarossa, the Axis invasion of the Soviet Uni ...
. The Duchy of Westphalia
The Duchy of Westphalia () was a historic territory in the Holy Roman Empire, which existed from 1102 to 1803. It was located in the greater region of Westphalia, originally one of the three main regions in the German stem duchy of Saxony and ...
comprised only a small area south of the Lippe River
The Lippe () is a river in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is a right tributary of the Rhine and in length with an elevation difference of 125 metres and a catchment area of 4.890 km².
The source is located at the edge of the Teutoburg ...
.
Parts of Westphalia came under Brandenburg-Prussian control during the 17th and 18th centuries, but most of it remained divided duchies and other feudal areas of power. The Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
of 1648, signed in Münster and Osnabrück, ended the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
. The concept of nation-state sovereignty resulting from the treaty became known as "Westphalian sovereignty
The Westphalian system, also known as Westphalian sovereignty, is a principle in international law that each State (polity), state has exclusive sovereignty over its territory. The principle developed in Europe after the Peace of Westphalia in 1648 ...
".
As a result of the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and ...
, there is no dominant religion in Westphalia. Catholicism and Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
are on relatively equal footing. Lutheranism is strong in the eastern and northern parts with numerous free churches. Münster
Münster (; ) is an independent city#Germany, independent city (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a ...
and especially Paderborn
Paderborn (; Westphalian language, Westphalian: ''Patterbuorn'', also ''Paterboärn'') is a city in eastern North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, capital of the Paderborn (district), Paderborn district. The name of the city derives from the river Pade ...
are thought of as Catholic. Osnabrück is divided almost equally between Catholicism and Protestantism.
After the defeat of the Prussian Army at the Battle of Jena-Auerstedt, the Treaty of Tilsit in 1807 made the Westphalian territories part of the Kingdom of Westphalia
The Kingdom of Westphalia was a client state of First French Empire, France in present-day Germany that existed from 1807 to 1813. While formally independent, it was ruled by Napoleon's brother Jérôme Bonaparte. It was named after Westphalia, ...
from 1807 to 1813. It was founded by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
and was a French vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
. This state only shared the name with the historical region; it contained only a relatively small part of Westphalia, consisting instead mostly of Hessian and Eastphalia
Eastphalia ( �stˈfaːlən Eastphalian: ''Oostfalen'') is a historical region in northern Germany, encompassing the eastern '' Gaue'' (shires) of the historic stem duchy of Saxony, roughly confined by the River Leine in the west and the Elbe a ...
n regions.
After the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
, the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
received a large amount of territory in the Westphalian region and created the province of Westphalia
The Province of Westphalia () was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1815 to 1946. In turn, Prussia was the largest component state of the German Empire from 1871 to 1918, of the Weimar ...
in 1815. The northernmost portions of the former kingdom, including the town of Osnabrück
Osnabrück (; ; archaic English: ''Osnaburg'') is a city in Lower Saxony in western Germany. It is situated on the river Hase in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest. With a population of 168 ...
, had become part of the states of Hanover
Hanover ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the States of Germany, German state of Lower Saxony. Its population of 535,932 (2021) makes it the List of cities in Germany by population, 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-l ...
and Oldenburg.
Flags and coat of arms
Theflag of North Rhine-Westphalia
The flag of the Germany, German State of North Rhine-Westphalia is a horizontal tricolor consisting of green, white and red.
Design
After the establishment of North Rhine-Westphalia in 1946, the tricolor was first introduced in 1948, but was not ...
is green-white-red with the combined coats of arms of the Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
(white line before green background, symbolizing the river Rhine), Westfalen (the white horse) and Lippe
Lippe () is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Herford, Minden-Lübbecke, Höxter, Paderborn, Gütersloh, and district-free Bielefeld, which forms the region Ostwestfalen-Lippe. ...
(the red rose). After the establishment of North Rhine-Westphalia in 1946, the tricolor was first introduced in 1948, but was not formally adopted until 1953. The plain variant of the tricolor is considered the civil flag and state ensign, while government authorities use the state flag (''Landesdienstflagge'') which is defaced with the state's coat of arms. The state ensign can easily be mistaken for a distressed flag of Hungary
The national flag of Hungary () is a horizontal tricolour (flag), tricolour of red, white and green. In this exact form, it has been the official flag of Hungary since 23 May 1957. The flag's form originates from national republican movements of ...
, as well as the former national flag of Iran
The national flag of the Iran, Islamic Republic of Iran, also known as the ''Tricolour Flag of Iran'' (), is a tricolour (flag), tricolour featuring the Pan-Iranian colors comprising equal horizontal bands of green, white and red with the embl ...
(1964–1980). The same flag was used by the Rhenish Republic (1923–1924) as a symbol of independence and freedom.
The horse on the coat of arms is a reference to the Saxon Steed
The Saxon Steed (, , , ; , , ; ) is a heraldic motif associated with the German provinces of Lower Saxony and Westphalia, and the Dutch region of Twente.
Origin and past uses
The horse as a heraldic charge associated with Saxony first appears ...
, a heraldic motif associated with both Westphalia and Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a States of Germany, German state (') in Northern Germany, northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Germany, Federal Re ...
. The horse first featured in the 15th century coat of arms of the Duchy of Westphalia, before being inherited by the Prussian province of Westphalia and finally the modern state of North Rhine-Westphalia.
Geography
 North Rhine-Westphalia encompasses the plains of the
North Rhine-Westphalia encompasses the plains of the Lower Rhine
Lower Rhine (, ; kilometres 660 to 1,033 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between Bonn in Germany and the North Sea at Hook of Holland in the Netherlands, including the '' Nederrijn'' () within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta; alternat ...
region and parts of the Central Uplands
The Central UplandsDickinson (1964), p.18 ff. (N.B. In German die ''Mittelgebirge'' (plural) refers to the Central Uplands; das ''Mittelgebirge'' refers to a low mountain range or upland region (''Mittel'' = "medium" and ''-gebirge'' = "range").) ...
('' die Mittelgebirge'') up to the gorge of Porta Westfalica. The state covers an area of and shares borders with Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
(Wallonia
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—along with Flemish Region, Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the c ...
) in the southwest and the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
( Limburg, Gelderland
Gelderland ( , ), also known as Guelders ( ) in English, is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands, located in the centre-east of the country. With a total area of of which is water, it is the largest province of the Nethe ...
and Overijssel
Overijssel (; ; ; ) is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the eastern part of the country. The province's name comes from the perspective of the Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht, Episcopal principality of Utrecht ...
) in the west and northwest. It has borders with the German states of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a States of Germany, German state (') in Northern Germany, northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Germany, Federal Re ...
to the north and northeast, Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; ; ; ) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the sixteen states. Mainz is the capital and largest city. Other cities are ...
to the south and Hesse
Hesse or Hessen ( ), officially the State of Hesse (), is a States of Germany, state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt, which is also the country's principal financial centre. Two other major hist ...
to the southeast.
Approximately half of the state is located in the relative low-lying terrain of the Westphalian Lowland and the Rhineland
The Rhineland ( ; ; ; ) is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly Middle Rhine, its middle section. It is the main industrial heartland of Germany because of its many factories, and it has historic ties to the Holy ...
, both extending broadly into the North German Plain
The North German Plain or Northern Lowland () is one of the major geographical regions of Germany. It is the German part of the North European Plain. The region is bounded by the coasts of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north, Germany's ...
. A few isolated hill ranges are located within these lowlands, among them the Hohe Mark, the Beckum Hills, the Baumberge and the Stemmer Berge. The terrain rises towards the south and in the east of the state into parts of Germany's
Central Uplands
The Central UplandsDickinson (1964), p.18 ff. (N.B. In German die ''Mittelgebirge'' (plural) refers to the Central Uplands; das ''Mittelgebirge'' refers to a low mountain range or upland region (''Mittel'' = "medium" and ''-gebirge'' = "range").) ...
. These hill ranges are the Weser Uplands – including the Egge Hills, the Wiehen Hills
The Wiehen HillsElkins, T.H. (1972). ''Germany'' (3rd ed.). London: Chatto & Windus, 1972. . (, , also locally, just ''Wiehen'') are a hill range in North Rhine-Westphalia and Lower Saxony in Germany. The hills run from west to east like a long f ...
, the Wesergebirge and the Teutoburg Forest
The Teutoburg Forest ( ; ) is a range of low, forested hills in the German states of Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia. Until the 17th century, the official name of the hill ridge was Osning. It was first renamed the ''Teutoburg Forest'' ...
in the east, the Sauerland
The Sauerland () is a rural, hilly area spreading across most of the south-eastern part of the States of Germany, German federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, in parts heavily forested and, apart from the major valleys, sparsely inhabited.
...
, the Bergisches Land
The Bergisches Land (, ) is a low mountain range in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, east of the Rhine and south of the Ruhr. The landscape is shaped by forests, meadows, rivers and creeks and contains over twenty artificial lakes ...
, the Siegerland and the Siebengebirge
The (), occasionally Sieben Mountains or Seven Mountains, are a hill range of the German Central Uplands on the east bank of the Middle Rhine, southeast of Bonn.
Description
The area, located in the municipalities of Bad Honnef and Königswin ...
in the south, as well as the left-Rhenish Eifel
The Eifel (; , ) is a low mountain range in western Germany, eastern Belgium and northern Luxembourg. It occupies parts of southwestern North Rhine-Westphalia, northwestern Rhineland-Palatinate and the southern area of the German-speaking Com ...
in the southwest of the state. The Rothaargebirge in the border region with Hesse
Hesse or Hessen ( ), officially the State of Hesse (), is a States of Germany, state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt, which is also the country's principal financial centre. Two other major hist ...
rises to height of about 800 m above sea level. The highest of these mountains are the Langenberg, at 843.2 m above sea level, the Kahler Asten
The Kahler Asten () is an 841.9-metre-high mountain in the Rothaar Mountains, Rothaar range in the district of Hochsauerlandkreis, Hochsauerland, in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is a popular destination, receiving more than 500, ...
(840.7 m) and the Clemensberg (839.2 m).
 The planimetrically determined centre of North Rhine-Westphalia is located in the south of Dortmund- Aplerbeck in the Aplerbecker Mark (51° 28' N, 7° 33' Ö). Its westernmost point is situated near
The planimetrically determined centre of North Rhine-Westphalia is located in the south of Dortmund- Aplerbeck in the Aplerbecker Mark (51° 28' N, 7° 33' Ö). Its westernmost point is situated near Selfkant
Selfkant (; or ''Zelfkant'' ; Limburgish: ) is a municipality in the Heinsberg district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the most westerly municipality in Germany.
Geography
Isenbruch in Selfkant is the most westerly point in German ...
close to the Dutch border, the easternmost near Höxter on the Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports o ...
. The southernmost point lies near Hellenthal
Hellenthal is a municipality in the district of Euskirchen in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the Eifel hills, near the border with Belgium, approx. 30 km south-west of Euskirchen and 40 km south-east of Aa ...
in the Eifel
The Eifel (; , ) is a low mountain range in western Germany, eastern Belgium and northern Luxembourg. It occupies parts of southwestern North Rhine-Westphalia, northwestern Rhineland-Palatinate and the southern area of the German-speaking Com ...
region. The northernmost point is the NRW-Nordpunkt near Rahden in the northeast of the state. The Nordpunkt has located the only 100 km to the south of the North Sea coast. The deepest natural dip is arranged in the district Zyfflich in the city of Kranenburg with 9.2 m above sea level in the northwest of the state. Though, the deepest point overground results from mining. The open-pit Hambach reaches at Niederzier
Niederzier is a municipality in the district of Düren in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located approximately 10 km north of Düren
Düren (; Ripuarian language, Ripuarian: Düre) is a town in North Rhine-Westphalia ...
a deep of 293 m below sea level. At the same time, this is the deepest human-made dip in Germany.
The most important rivers flowing at least partially through North Rhine-Westphalia include: the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
, the Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
, the Ems, the Lippe
Lippe () is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Herford, Minden-Lübbecke, Höxter, Paderborn, Gütersloh, and district-free Bielefeld, which forms the region Ostwestfalen-Lippe. ...
, and the Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports o ...
. The Rhine is by far the most important river in North Rhine-Westphalia: it enters the state as Middle Rhine
Middle Rhine (, ; kilometres 529 to 660 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between Bingen and Bonn in Germany. It flows through the Rhine Gorge (), a formation created by erosion, which happened at about the same rate as an uplift i ...
near Bad Honnef, where still being part of the Mittelrhein wine region. It changes into the Lower Rhine
Lower Rhine (, ; kilometres 660 to 1,033 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between Bonn in Germany and the North Sea at Hook of Holland in the Netherlands, including the '' Nederrijn'' () within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta; alternat ...
near Bad Godesberg and leaves North Rhine-Westphalia near Emmerich at a width of 730 metres. Almost immediately after entering the Netherlands, the Rhine splits into many branches.
The Pader, which flows entirely within the city of Paderborn
Paderborn (; Westphalian language, Westphalian: ''Patterbuorn'', also ''Paterboärn'') is a city in eastern North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, capital of the Paderborn (district), Paderborn district. The name of the city derives from the river Pade ...
, is considered Germany's shortest river.
For many, North Rhine-Westphalia is synonymous with industrial areas and urban agglomerations. However, the largest part of the state is used for agriculture (almost 52%) and forests (25%).
Subdivisions
 The state consists of five government regions (''Regierungsbezirke''), divided into 31 districts ('' Kreise'') and 23 urban districts (''kreisfreie Städte''). In total, North Rhine-Westphalia has 396 municipalities (1997), including the urban districts, which are municipalities by themselves. The government regions have an assembly elected by the districts and municipalities, while the ''Landschaftsverband'' has a directly elected assembly.
The five government regions of North Rhine-Westphalia each belong to one of the two '' Landschaftsverbände'':
The state consists of five government regions (''Regierungsbezirke''), divided into 31 districts ('' Kreise'') and 23 urban districts (''kreisfreie Städte''). In total, North Rhine-Westphalia has 396 municipalities (1997), including the urban districts, which are municipalities by themselves. The government regions have an assembly elected by the districts and municipalities, while the ''Landschaftsverband'' has a directly elected assembly.
The five government regions of North Rhine-Westphalia each belong to one of the two '' Landschaftsverbände'':
Borders
The state's area covers a maximum distance of 291 km from north to south, and 266 km from east to west. The total length of the state's borders is 1,645 km. The following countries and states have a border with North Rhine-Westphalia: *Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
(99 km)
* Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
(387 km)
* Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a States of Germany, German state (') in Northern Germany, northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Germany, Federal Re ...
(583 km)
* Hesse
Hesse or Hessen ( ), officially the State of Hesse (), is a States of Germany, state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt, which is also the country's principal financial centre. Two other major hist ...
(269 km)
* Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; ; ; ) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the sixteen states. Mainz is the capital and largest city. Other cities are ...
(307 km)
Demographics
North Rhine-Westphalia has a population of approximately 18.1 million inhabitants (more than the entire former East Germany, and slightly more than theNetherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
) and is centred around the polycentric Rhine-Ruhr
The Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region () is the Metropolitan regions in Germany, largest metropolitan region in Germany, with over ten million inhabitants. A wikt:polycentric, polycentric conurbation with several major urban concentrations, the reg ...
metropolitan region, which includes the industrial Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
region with the largest city of Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
and the Rhenish cities of Bonn
Bonn () is a federal city in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located on the banks of the Rhine. With a population exceeding 300,000, it lies about south-southeast of Cologne, in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region. This ...
, Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
and Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in the state after Cologne and the List of cities in Germany with more than 100,000 inhabitants, seventh-largest city ...
. 30 of the 80 largest cities in Germany are located within North Rhine-Westphalia. The state's capital is Düsseldorf; the state's largest city is Cologne. In 2022, there were 164,496 births and 234,176 deaths.
The following table shows the ten largest cities of North Rhine-Westphalia:
Historical population
The following table shows the population of the state since 1930. The values until 1960 are the average of the yearly population, from 1965 the population at year end is used.Vital statistics
*Births from January–September 2016 = 130,025 *Births from January–September 2017 = 130,088 *Deaths from January–September 2016 = 150,018 *Deaths from January–September 2017 = 153,435 *Natural growth from January–September 2016 = −19,993 *Natural growth from January–September 2017 = −23,347 Source: ''Statistische Ämter des Bundes Und der Länder''Religion
, 32.7% of the population of the state adhered to theRoman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, 20.8% to the Protestant Church in Germany, and 46.5% of the population was irreligious
Irreligion is the absence or rejection of religious beliefs or practices. It encompasses a wide range of viewpoints drawn from various philosophical and intellectual perspectives, including atheism, agnosticism, religious skepticism, rationa ...
or adhered to other denominations or religions. North Rhine-Westphalia ranks first in population among German states for both Roman Catholics and Protestants.
In 2016, the interior ministry of North Rhine-Westphalia reported that the number of mosques with a Salafist influence had increased from three to nine, which indicated both an actual increase and improved reporting. According to German authorities, Salafism
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a Islamic fundamentalism, fundamentalist Islamic revival, revival movement within Sunni Islam, originating in the late 19th century and influential in the Islamic world to this day. The name "''Salafiyya''" ...
is incompatible with the principles codified in the Constitution of the Federal Republic of Germany, in particular: democracy
Democracy (from , ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which political power is vested in the people or the population of a state. Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitiv ...
, the rule of law
The essence of the rule of law is that all people and institutions within a Body politic, political body are subject to the same laws. This concept is sometimes stated simply as "no one is above the law" or "all are equal before the law". Acco ...
, and political order based on human rights
Human rights are universally recognized Morality, moral principles or Social norm, norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both Municipal law, national and international laws. These rights are considered ...
.
Politics
 The politics of North Rhine-Westphalia takes place within a framework of a federal
The politics of North Rhine-Westphalia takes place within a framework of a federal parliamentary
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
representative democratic republic. The two main parties are, as on the federal level, the centre-right Christian Democratic Union and the centre-left Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
Form ...
. From 1966 to 2005, North Rhine-Westphalia was continuously governed by the Social Democrats or SPD-led governments.
The state's legislative body is the Landtag
A ''Landtag'' (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence ...
("state parliament house"). It may pass laws within the competency of the state, e.g. cultural matters, the education system, matters of internal security, i.e. the police, building supervision, health supervision and the media; as opposed to matters that are reserved to Federal law.
North Rhine-Westphalia uses the same electoral system as the Federal level in Germany: "'' Personalized proportional representation''". Every five years the citizens of North Rhine-Westphalia vote in a general election to elect at least 181 members of the Landtag. Only parties who win at least 5% of the votes cast may be represented in parliament.
The Landtag, the parliamentary parties and groups consisting of at least 7 members of parliament have the right to table legal proposals to the Landtag for deliberation. The law that is passed by the Landtag is delivered to the Minister-President, who, together with the ministers involved, is required to sign it and announce it in the Law and Ordinance Gazette.
Landtag after 2022 Election
The vote was held on 15 May, 2022. In the aftermath of the 2022 election, the Christian Democrats (CDU) and the Social Democratic Party (SPD) both had talks with the Greens. An alliance between the Greens and the SPD would have required the help of the Free Democratic Party (FDP) to gain a majority, but the FDP did not take part in these conversations. Rather, its top candidate believed that a Green/CDU alliance was the most likely outcome. All mainstream parties tend to refuse to cooperate with the right-wing Alternative for Germany (AfD). Ultimately, the CDU/Green alliance was the one that prevailed. The new coalition reelectedHendrik Wüst
Hendrik Josef Wüst (born 19 July 1975) is a German politician serving as Minister-President of North Rhine-Westphalia, Minister-President of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia since 2021. He is a member of the Christian Democratic Union of Ger ...
, who had been the Minister President of North Rhine-Westphalia during the last portion of the previous CDU/FDP coalition on 28 June, 2022.
List of minister-presidents
These are the minister-presidents of North Rhine-Westphalia: For further information on the current state government, see Wüst cabinet.Culture
Architecture and building monuments
*The state is known for the most castles and fortresses in Germany. *North Rhine-Westphalia has a high concentration of museums, cultural centres, concert halls and theatres.Historic monuments
Aachen
Aachen is the List of cities in North Rhine-Westphalia by population, 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, 27th-largest city of Germany, with around 261,000 inhabitants.
Aachen is locat ...
File:Früh Brauhaus Köln - Am Hof 12 und 14 (4626-28).jpg, '' Cölner Hofbräu Früh'' in Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
File:Alte Markt Dortmund.JPG, '' Reinoldikirche'' and ''Alter Markt'' in Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
File:Muenster-100725-16053-Rathaus.jpg, The Historical City Hall in Münster
Münster (; ) is an independent city#Germany, independent city (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a ...
File:Warburg Sackturm-mit-Stadttor.jpg, Gate and Tower of the medieval town-fortification in Warburg
File:Alt Monschau - geo.hlipp.de - 6903.jpg, Timber framing in Monschau
File:Aerial image of Schloss Nordkirchen (view from the southeast).jpg, '' Schloss Nordkirchen''
File:Lange Straße 2, 3, Warburg, Landkreis Höxter.jpg, Eckmaenneken-House in Warburg; eldest-dated timber-framed-house of Westphalia
File:Corvey Westwerk 2.jpg, Princely Abbey of Corvey nearby City of Höxter
File:Hermannsdenkmal 2015.jpg, Hermann's Monument nearby Detmold
File:Externsteine 14.jpg, Externsteine
File:PaderbornerDom-2.JPG, Paderborn Cathedral
Paderborn Cathedral () is the cathedral of the Catholic Archdiocese of Paderborn. It is located in the city centre of Paderborn, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The cathedral is dedicated to Mary (mother of Jesus), Saint Mary, Saint Kilian and ...
Modern architecture
Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
File:Düsseldorf, Stresemannstraße 26, 2012 (1).jpg, Hotel Römischer Kaiser in Düsseldorf
File:Düsseldorf, Medienhafen.jpg, '' Neuer Zollhof'' in Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in the state after Cologne and the List of cities in Germany with more than 100,000 inhabitants, seventh-largest city ...
File:Krefeld haus lange gartenseite04 12.jpg, Haus Lange and Haus Esters in Krefeld
Krefeld ( , ; ), also spelled Crefeld until 1925 (though the spelling was still being used in British papers throughout the Second World War), is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, in western Germany. It is located northwest of Düsseldorf, its c ...
File:Langen Foundation.jpg, The Langen Foundation in Neuss
Neuss (; written ''Neuß'' until 1968; ; ) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is on the west bank of the Rhine opposite Düsseldorf. Neuss is the largest city within the Rhein-Kreis Neuss district. It is primarily known for its ...
File:Schwebebahn G15.jpg, The '' Schwebebahn'' in Wuppertal
Wuppertal (; ) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, in western Germany, with a population of 355,000. Wuppertal is the seventh-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and List of cities in Germany by population, 17th-largest in Germany. It ...
File:Herford MARTa 88.jpg, MARTa Herford
MARTa Herford is a contemporary art museum in Herford, Germany.
Building and history
The idea for the museum formed in 2000, drawing from Herford's status as a German center of furniture and home furnishing production. The name ''MARTa'' i ...
World Heritage Sites
The state hasAachen Cathedral
Aachen Cathedral () is a Catholic Church, Catholic church in Aachen, Germany and the cathedral of the Diocese of Aachen.
One of the oldest cathedral buildings in Europe, it was constructed as the royal chapel of the Palace of Aachen of Holy Rom ...
, the Cologne Cathedral
Cologne Cathedral (, , officially , English: Cathedral Church of Saint Peter) is a cathedral in Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia belonging to the Catholic Church. It is the seat of the Archbishop of Cologne and of the administration of the Archd ...
, the Zeche Zollverein in Essen
Essen () is the central and, after Dortmund, second-largest city of the Ruhr, the largest urban area in Germany. Its population of makes it the fourth-largest city of North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne, Düsseldorf and Dortmund, as well as ...
, the Augustusburg Palace in Brühl and the Imperial Abbey of Corvey
The Princely Abbey of Corvey ( or ) is a former Benedictine Order, Benedictine abbey and Hochstift, ecclesiastical principality now in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It was one of the half-dozen self-ruling ''List of Imperial abbeys, princely ...
in Höxter which are all World Heritage Sites
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
.
Aachen Cathedral
Aachen Cathedral () is a Catholic Church, Catholic church in Aachen, Germany and the cathedral of the Diocese of Aachen.
One of the oldest cathedral buildings in Europe, it was constructed as the royal chapel of the Palace of Aachen of Holy Rom ...
File:Kdom.jpg, Cologne Cathedral
Cologne Cathedral (, , officially , English: Cathedral Church of Saint Peter) is a cathedral in Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia belonging to the Catholic Church. It is the seat of the Archbishop of Cologne and of the administration of the Archd ...
File:Zeche Zollverein abends.jpg, The Zollverein Coal Mine
File:Corvey Westwerk 2.jpg, The Imperial Abbey of Corvey
The Princely Abbey of Corvey ( or ) is a former Benedictine Order, Benedictine abbey and Hochstift, ecclesiastical principality now in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It was one of the half-dozen self-ruling ''List of Imperial abbeys, princely ...
Cuisine
Drinks
* Kölsch is a local beer speciality brewed inCologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
.
* Alt is a local beer speciality brewed in Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in the state after Cologne and the List of cities in Germany with more than 100,000 inhabitants, seventh-largest city ...
and the Lower Rhine Region.
* Dortmunder Export is a local pale lager beer speciality brewed in Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
.
Festivals
North Rhine-Westphalia hosts film festivals inCologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, Bonn, Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
, Duisburg
Duisburg (; , ) is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine (Lower Rhine) and the Ruhr (river), Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruh ...
, Münster
Münster (; ) is an independent city#Germany, independent city (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a ...
, Oberhausen
Oberhausen (, ) is a city on the river Emscher in the Ruhr Area, Germany, located between Duisburg and Essen ( ). The city hosts the International Short Film Festival Oberhausen and its Gasometer Oberhausen is an anchor point of the European Rout ...
and Lünen
Lünen () is a town with around 86,000 inhabitants in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located north of Dortmund, on both banks of the Lippe (river), River Lippe. It is the largest town of the Unna (district), Unna district and part of the R ...
.
Other large festivals include Rhenish carnivals, Ruhrtriennale.
Every year Gamescom
Gamescom (stylized as ''gamescom'') is a trade fair for video games held annually at the Koelnmesse in Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Gamescom is the world's largest gaming event, with 370,000 visitors and 1,037 exhibitors from 56 ...
is hosted in Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
. It is the largest video game convention in Europe.
Music
* The composerLudwig van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music repertoire ...
was born in Bonn
Bonn () is a federal city in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located on the banks of the Rhine. With a population exceeding 300,000, it lies about south-southeast of Cologne, in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region. This ...
in 1770.
* A regional anthem is the Lied für NRW (Song for NRW).
* North Rhine-Westphalia is home to many of Germany's best-known heavy metal, speed metal
Speed metal is a subgenre of heavy metal music that originated in the late 1970s from new wave of British heavy metal (NWOBHM) roots.K. Kahn-Harris, ''Extreme Metal: Music and Culture on the Edge'' (Berg Publishers, 2007), , p. 31. It is desc ...
and thrash metal
Thrash metal (or simply thrash) is an Extreme metal, extreme subgenre of heavy metal music characterized by its overall aggression and fast tempo.Kahn-Harris, Keith, ''Extreme Metal: Music and Culture on the Edge'', pp. 2–3, 9. Oxford: Berg, ...
bands: Accept, Angel Dust, Blind Guardian
Blind Guardian is a German power metal band formed in 1984 in Krefeld, West Germany. They are often credited as one of the seminal and most influential bands in the power metal and speed metal subgenres. Nine musicians have been part of the band ...
, Doro (formerly of Warlock
A warlock is a male practitioner of witchcraft.
Etymology and terminology
The most commonly accepted etymology derives '' warlock'' from the Old English '' wǣrloga'', which meant "breaker of oaths" or "deceiver". The term came to apply special ...
), Grave Digger, Holy Moses
Holy Moses were a German thrash metal band active from 1980 to 1994 and from 2000 to 2023. They were well noted for being fronted by Sabina Classen, who was the only constant member of Holy Moses, and for being one of the first German thrash m ...
, Kreator
Kreator is a German thrash metal band from Essen, formed in 1982. Their current line-up consists of lead vocalist and rhythm guitarist Mille Petrozza, Miland "Mille" Petrozza, drummer Jürgen Reil, Jürgen "Ventor" Reil, lead guitarist Sami Yli- ...
, Rage, Scanner and Sodom.
* North Rhine-Westphalia is home to electronic music pioneers Karlheinz Stockhausen
Karlheinz Stockhausen (; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries. He is known for his groun ...
and the band Kraftwerk
Kraftwerk (, ) is a Germany, German Electronic music, electronic band formed in Düsseldorf in 1970 by Ralf Hütter and Florian Schneider. Widely considered innovators and pioneers of electronic music, Kraftwerk was among the first successful a ...
.
Economy
 North Rhine-Westphalia has always been Germany's powerhouse with the largest economy among the German states by GDP figures.
In the 1950s and 1960s, Westphalia was known as ''Land von Kohle und Stahl'' (''Land of Coal and Steel''). In the post-World War II recovery, the
North Rhine-Westphalia has always been Germany's powerhouse with the largest economy among the German states by GDP figures.
In the 1950s and 1960s, Westphalia was known as ''Land von Kohle und Stahl'' (''Land of Coal and Steel''). In the post-World War II recovery, the Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
was one of the most important industrial regions in Europe, and contributed to the German Wirtschaftswunder
The ''Wirtschaftswunder'' (, "economic miracle"), also known as the Miracle on the Rhine, was the rapid reconstruction and development of the Economy, economies of West Germany and Austria after World War II. The expression was first used to re ...
. As of the late 1960s, repeated crises led to contractions of these industrial branches. On the other hand, producing sectors, particularly in mechanical engineering and metal and iron working industry, experienced substantial growth. Despite this structural change and an economic growth which was under national average, the 2018 GDP of 705 billion euro (1/4 of the total German GDP) made NRW the economically strongest state of Germany by GRP figures, as well as one of the most important economical areas in the world. Of Germany's top 100 corporations, 37 are based in North Rhine-Westphalia. On a per capita base, however, North Rhine-Westphalia remains one of the weaker among the Western German states.
North Rhine-Westphalia attracts companies from both Germany and abroad. In 2009, the state had the most foreign direct investments ( FDI) anywhere in Germany. Around 13,100 foreign companies from the most important investment countries control their German or European operations from bases in North Rhine-Westphalia.
There have been many changes in the state's economy in recent times. Among the many changes in the economy, employment in the creative industries is up while the mining sector is employing fewer people. Industrial heritage sites are now workplaces for designers, artists and the advertising industry. The Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
region has – since the 1960s – undergone a significant structural change away from coal mining and steel industry. Many rural parts of Eastern Westphalia
Westphalia (; ; ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the region is almost identical with the h ...
, Bergisches Land
The Bergisches Land (, ) is a low mountain range in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, east of the Rhine and south of the Ruhr. The landscape is shaped by forests, meadows, rivers and creeks and contains over twenty artificial lakes ...
and the Lower Rhine
Lower Rhine (, ; kilometres 660 to 1,033 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between Bonn in Germany and the North Sea at Hook of Holland in the Netherlands, including the '' Nederrijn'' () within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta; alternat ...
ground their economy on " Hidden Champions" in various sectors.
As of June 2014, the unemployment rate is 8.2%, second highest among all western German states. In October 2018 the unemployment rate stood at 6.4% and was higher than the national average.
Transport
With its central location in the most important European economic area, high population density, strong urbanization and numerous business locations, North Rhine-Westphalia has one of the densest transport networks in the world.Regional rail network
 The regional rail network is organised around the big cities on the Rhine and Ruhr such as
The regional rail network is organised around the big cities on the Rhine and Ruhr such as Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in the state after Cologne and the List of cities in Germany with more than 100,000 inhabitants, seventh-largest city ...
and Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
. The public transport companies in the Ruhr area and Düsseldorf are run under the umbrella of the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr
The Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr (), abbreviated VRR, is a public transport association (Verkehrsverbund) in the Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It covers large parts of the Ruhr, Ruhr area, the Lower Rhine region including Düsse ...
, which provides a uniform ticket system valid for the area. The region of Cologne and Bonn is run under the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Sieg. There is also a ticketing system called ''NRW-Tarif'' which offers tickets between all the regions of North Rhine-Westphalia. The state is well-integrated into the national rail system, the , for both passenger and goods services, each city in the region has at least one or more train stations. The bigger central stations have frequent direct connections to most bigger German cities and European cities such as Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
, Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalit ...
, Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
and Basel
Basel ( ; ), also known as Basle ( ), ; ; ; . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine (at the transition from the High Rhine, High to the Upper Rhine). Basel is Switzerland's List of cities in Switzerland, third-most-populo ...
. Some direct trains run to Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
and Zürich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The ...
.
The Rhein-Ruhr area also contains some of the longest tram
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which Rolling stock, vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some ...
system in the world, with tram and Stadtbahn services from Witten to Krefeld
Krefeld ( , ; ), also spelled Crefeld until 1925 (though the spelling was still being used in British papers throughout the Second World War), is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, in western Germany. It is located northwest of Düsseldorf, its c ...
in the VRR zone and Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
to Bad Honnef
Bad Honnef () is a spa town in Germany near Bonn in the Rhein-Sieg district, North Rhine-Westphalia. It is located on the border of the neighbouring state Rhineland-Palatinate. To the north it lies on the slopes of the Drachenfels (Siebengebirge), ...
and Siegburg
Siegburg (; i.e. ''fort on the Sieg (river), Sieg river''; Ripuarian language, Ripuarian: ''Sieburch'') is a city in the district of Rhein-Sieg-Kreis in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located on the banks of the rivers Sieg (river), Sieg ...
via Bonn
Bonn () is a federal city in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located on the banks of the Rhine. With a population exceeding 300,000, it lies about south-southeast of Cologne, in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region. This ...
within the VRS zone. Besides the local public transportation there is an interconnected commuter rail network, with the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn network serving the Ruhr area as well as Düsseldorf and the S-Bahn Köln serving the area around Cologne.
, the VRR network alone consists of 978 lines, of which there are:
* in regional rail transit
** 11 S-Bahn
The S-Bahn ( , ), , is a hybrid urban rail, urban–suburban rail system serving a metropolitan region predominantly in German language, German-speaking countries. Some of the larger S-Bahn systems provide service similar to rapid transit syst ...
lines (''see:'' Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn)
** 15 RegionalExpress lines (''see:'' List of regional railway lines in North Rhine-Westphalia)
** 24 RegionalBahn
The ''Regionalbahn'' (; lit. Regional train; abbreviated ''RB'') is a train categories in Europe, type of Regional rail, local passenger train (stopping train) in Germany. It is similar to the Regionalzug (R) and Regio (Swiss railway train), R ...
lines (''see:'' List of regional railway lines in North Rhine-Westphalia)
* in local rail transit
** 19 Stadtbahn light rail lines (''see:'' Rhine-Ruhr Stadtbahn)
** 45 tram (Straßenbahn) lines
** 1 Schwebebahn line (in Wuppertal
Wuppertal (; ) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, in western Germany, with a population of 355,000. Wuppertal is the seventh-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and List of cities in Germany by population, 17th-largest in Germany. It ...
)
** 2 H-Bahn peoplemover systems made up of three lines (two H-Bahn lines in Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
, and the Düsseldorf SkyTrain at Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in the state after Cologne and the List of cities in Germany with more than 100,000 inhabitants, seventh-largest city ...
airport)
* in bus transit
** 906 bus lines, including
*** 33 express bus lines (Schnellbus, SB)
*** 18 semi-fast bus lines (CityExpress, CE)
** 6 trolleybus
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or troll ...
lines (in Solingen
Solingen (; ) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, 25 km east of Düsseldorf along the northern edge of the Bergisches Land, south of the Ruhr. After Wuppertal, it is the second-largest city in the Bergisches Land, and a member of ...
)
* 15,300 km of route network (bus, light rail, and train)
* 11,500 transit stops
In 2022 the VRS and AVV area contains
* in regional rail transit
** 7 S-Bahn lines (with 4 being part of the Rhein-Ruhr S-Bahn
The Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn () is a Metropolitan area, polycentric S-bahn network covering the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan regions in Germany, Metropolitan Region in the Germany, German States of Germany, federated state of North Rhine-Westphalia. This inc ...
)
** 11 RegionalExpress lines (6 conntected to VRR)
** 18 RegionalBahn
The ''Regionalbahn'' (; lit. Regional train; abbreviated ''RB'') is a train categories in Europe, type of Regional rail, local passenger train (stopping train) in Germany. It is similar to the Regionalzug (R) and Regio (Swiss railway train), R ...
services
* in local rail transit
** 16 Stadtbahn lines (''see:'' Cologne Stadtbahn and Bonn Stadtbahn
The Bonn Stadtbahn () is a ''Stadtbahn'' system in Bonn, Germany, Bonn and the surrounding Rhein-Sieg area, that also includes the Trams in Bonn, Bonn Straßenbahn. Although with six actual Stadtbahn lines (as well as three tram lines) the network ...
)
** 3 streetcar (Straßenbahn) lines within the city of Bonn
Road
North Rhine-Westphalia has the densest network of Autobahns in Germany and similar Schnellstraßen (expressways). The Autobahn network is built in a grid network, with five east–west ( A2, A4, A40, A42, A44) and eight north–south ( A1, A3, A43, A45, A52, A57, A59, A61) routes. The A1, A2, A3, A4 and A61 are mostly used by through traffic, while the other autobahns have a more regional function. Both the A44 and the A52 have several missing links, in various stages of planning. Some missing sections are currently in construction or planned to be constructed in the near future. Additional expressways serve as bypasses and local routes, especially around Dortmund and Bochum. Due to the density of the autobahns and expressways,Bundesstraße
''Bundesstraße'' (, ), abbreviated ''B'', is the denotation for German and Austrian national highways.
Germany
Germany's ''Bundesstraßen'' network has a total length of about 40,000 km.
German ''Bundesstraßen'' are labelled with re ...
n are less important for intercity traffic. The first Autobahns in the Region opened during the mid-1930s. Due to the density of the network, and the number of alternative routes, traffic volumes are generally lower than other major metropolitan areas in Europe. Traffic congestion is an everyday occurrence, but far less so than in the Randstad
The Randstad (; "Rim City" or "Edge City") is a roughly crescent- or Circular arc, arc-shaped conurbation in the Netherlands, that includes almost half the country's population. With a central-western location, it connects and comprises the Net ...
in the Netherlands, another polycentric urban area. Most important Autobahns have six lanes.
Airports
The region benefits from the presence of several airport infrastructure. The main airport is Düsseldorf Airport, world class, which hosted 25.5 million passengers in 2019 and offers flights to various international destinations. Düsseldorf is the fourth-largest airport in Germany afterFrankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
, Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
and Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
and serves as a hub for Eurowings
Eurowings GmbH is a Germany, German low-cost carrier headquartered in Düsseldorf, North Rhine-Westphalia, and a wholly owned subsidiary of the Lufthansa Group. Founded in 1996, it serves a network of domestic and European destinations and main ...
and as focus city for several more airlines. The airport has three passenger terminals and two runways and can handle wide-body aircraft up to the Airbus A380
The Airbus A380 is a very large wide-body airliner, developed and produced by Airbus until 2021. It is the world's largest passenger airliner and the only full-length double-deck jet airliner.
Airbus studies started in 1988, and the pr ...
.
The second airport is the international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports, and feature longer runways and have faciliti ...
of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
's fourth-largest city Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, and also serves Bonn
Bonn () is a federal city in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located on the banks of the Rhine. With a population exceeding 300,000, it lies about south-southeast of Cologne, in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region. This ...
, former capital of West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
. With around 10 million passengers passing through it in 2023, it is the sixth-largest passenger airport in Germany and the third-largest in terms of cargo operations. It is also a hub for Eurowings, but also for some cargo airlines. By traffic units, which combines cargo and passengers, the airport is in fifth position in Germany. As of March 2015, Cologne Bonn Airport had services to 115 passenger destinations in 35 countries. It is named after Konrad Adenauer
Konrad Hermann Joseph Adenauer (5 January 1876 – 19 April 1967) was a German statesman and politician who served as the first Chancellor of Germany, chancellor of West Germany from 1949 to 1963. From 1946 to 1966, he was the first leader of th ...
, a Cologne native and the first post-war Chancellor of West Germany.
Third airport in the region, Dortmund Airport is a minor international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports, and feature longer runways and have faciliti ...
located east of Dortmund
Dortmund (; ; ) is the third-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, after Cologne and Düsseldorf, and the List of cities in Germany by population, ninth-largest city in Germany. With a population of 614,495 inhabitants, it is the largest city ...
. It serves the eastern Rhine-Ruhr area, the largest urban agglomeration
An urban area is a human settlement with a high population density and an infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas originate through urbanization, and researchers categorize them as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbani ...
in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, and is mainly used for low-cost and leisure charter flights. In 2019 the airport served 2,719,563 passengers.
There are three more minor airports within the state: Münster Osnabrück Airport, Airport Weeze and Paderborn Lippstadt Airport
Paderborn Lippstadt Airport (German: ''Flughafen Paderborn Lippstadt'') is a minor international airport in the Ostwestfalen-Lippe area in the Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Despite its name, the airport is actually located nea ...
.
Waterways
TheRhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
flows through North Rhine-Westphalia. Its banks are usually heavily populated and industrialized, in particular the agglomerations Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in the state after Cologne and the List of cities in Germany with more than 100,000 inhabitants, seventh-largest city ...
and Ruhr area
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
. Here the Rhine flows through the largest conurbation in Germany, the Rhine-Ruhr
The Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region () is the Metropolitan regions in Germany, largest metropolitan region in Germany, with over ten million inhabitants. A wikt:polycentric, polycentric conurbation with several major urban concentrations, the reg ...
region. Duisburg Inner Harbour (Duisport) and Dortmund Port are large industrial inland ports and serve as hubs along the Rhine and the German inland water transport system. The country is crossed by many canals like Rhine–Herne Canal
The Rhine–Herne Canal () is a transportation canal in the Ruhrgebiet, Ruhr area of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, with five canal locks. The canal was built over a period of eight years (5 April 1906 – 14 July 1914) and connects the har ...
(RHK), der Wesel-Datteln-Kanal (WDK), der Datteln-Hamm-Kanal (DHK) and Dortmund-Ems-Kanal (DEK) an important role for inland navigation.
Education
RWTH Aachen
RWTH Aachen University (), in German ''Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen'', is a German public research university located in Aachen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With more than 47,000 students enrolled in 144 study prog ...
is one of Germany's leading universities of technology and was chosen by DFG as one of the German Universities of Excellence in 2007, 2012 and again in 2019. North Rhine-Westphalia is home to 14 universities and over 50 partly postgraduate colleges, with a total of over 742,000 students. Largest and oldest university is the University of Cologne
The University of Cologne () is a university in Cologne, Germany. It was established in 1388. It closed in 1798 before being re-established in 1919. It is now one of the largest universities in Germany with around 45,187 students. The Universit ...
''(Universität zu Köln)'', founded in 1388 AD, since 2012 also one of Germany's eleven Universities of Excellence. University of Duisburg-Essen
The University of Duisburg-Essen () is a public research university in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. In the 2019 ''Times Higher Education World University Rankings'', the university was awarded 194th place in the world. It was originally ...
(Universität Duisburg-Essen), is also well known and is one of the largest universities in Germany.
Sports
Football
 NRW is home to several football clubs of the
NRW is home to several football clubs of the Bundesliga
The Bundesliga (; ), sometimes referred to as the Fußball-Bundesliga () or 1. Bundesliga (), is a professional association football league in Germany and the highest level of the German football league system. The Bundesliga comprises 18 teams ...
including Bayer 04 Leverkusen
Bayer 04 Leverkusen, officially known as Bayer 04 Leverkusen Fußball GmbH () and commonly known as Bayer Leverkusen or simply Leverkusen, is a German professional association football, football club based in Leverkusen, North Rhine-Westphalia. ...
, Borussia Dortmund
Ballspielverein Borussia 09 e. V. Dortmund, often known simply as Borussia Dortmund () or by its initialism BVB (), or just Dortmund by International fans, is a German professional sports club based in Dortmund, North Rhine-Westphalia. It is ...
, Borussia Mönchengladbach
Borussia Verein für Leibesübungen 1900 e.V. Mönchengladbach, better known as Borussia Mönchengladbach () and colloquially known as just Gladbach, is a professional Association football, football club based in Mönchengladbach, North Rhine-W ...
, 1. FC Köln and VfL Bochum
Verein für Leibesübungen Bochum 1848 Fußballgemeinschaft, commonly referred to as VfL Bochum (), is a Football in Germany, German professional association football club based in the city of Bochum, North Rhine-Westphalia. They currently play ...
and the 2. Bundesliga including Fortuna Düsseldorf
Düsseldorfer Turn- und Sportverein Fortuna 1895 e.V., commonly known as Fortuna Düsseldorf (), is a Football in Germany, German football club based in Düsseldorf, North Rhine-Westphalia, that competes in the 2. Bundesliga.
Founded in 1895, Fo ...
, FC Schalke 04
Fußballclub Gelsenkirchen-Schalke 04 e. V., commonly known as Schalke 04 (), and abbreviated as S04 (), is a professional sports club from the Schalke district of Gelsenkirchen, North Rhine-Westphalia. It is best known for its football team, ...
and SC Paderborn 07
Sport-Club Paderborn 07 e.V., commonly known as simply SC Paderborn 07 () or SC Paderborn, is a Football in Germany, German association football club based in Paderborn, North Rhine-Westphalia. The club has enjoyed its greatest success since the ...
and the 3. Liga
The 3. Liga is a professional association football league and the third division in Germany. In the German football league system, it is positioned between the 2. Bundesliga and the fourth-tier Regionalliga.
The modern 3. Liga was formed for t ...
including Arminia Bielefeld
DSC Arminia Bielefeld (; full name: ; commonly known as Arminia Bielefeld (), also known as ''Die Arminen'' or ''Die Blauen'' ), or just Arminia (), is a German sports club from Bielefeld, North Rhine-Westphalia. Arminia is most well known as ...
, MSV Duisburg
Meidericher Spielverein 02 e. V. Duisburg, commonly known as simply MSV Duisburg (), is a Football in Germany, German association football club based in Duisburg, North Rhine-Westphalia. Nicknamed ''Die Zebras'' for their traditional striped jer ...
, Rot-Weiß Essen, Preußen Münster
Preußen or Preussen is the German word for Prussia.
It also refers to:
Ships
* Preußen (ship), ''Preußen'' (ship), windjammer built in 1902
* SMS Preußen (1873), SMS ''Preußen'' (1873), armored frigate
* SMS Preußen (1903), SMS ''Preußen ...
, Rot-Weiß Oberhausen, FC Viktoria Köln and SC Verl
SC Verl is a German association football club based in Verl, North Rhine-Westphalia. The club was founded on 6 September 1924, and since 1970 has consistently played in the higher echelons of amateur football. The club was promoted to the profe ...
.
Since the formal establishment of the German Bundesliga in 1963, Borussia Dortmund
Ballspielverein Borussia 09 e. V. Dortmund, often known simply as Borussia Dortmund () or by its initialism BVB (), or just Dortmund by International fans, is a German professional sports club based in Dortmund, North Rhine-Westphalia. It is ...
and Borussia Mönchengladbach
Borussia Verein für Leibesübungen 1900 e.V. Mönchengladbach, better known as Borussia Mönchengladbach () and colloquially known as just Gladbach, is a professional Association football, football club based in Mönchengladbach, North Rhine-W ...
have been the most successful teams in the state, with both winning five titles. 1. FC Köln won two titles, including the first in 1963. Before the league's establishment, North Rhine-Westfalian teams competed for the title of Deutscher Fußballmeister (German Football Champion). Here, FC Schalke 04
Fußballclub Gelsenkirchen-Schalke 04 e. V., commonly known as Schalke 04 (), and abbreviated as S04 (), is a professional sports club from the Schalke district of Gelsenkirchen, North Rhine-Westphalia. It is best known for its football team, ...
brought home seven titles, while Dortmund and Köln won an additional three and one title(s), respectively. Fortuna Düsseldorf
Düsseldorfer Turn- und Sportverein Fortuna 1895 e.V., commonly known as Fortuna Düsseldorf (), is a Football in Germany, German football club based in Düsseldorf, North Rhine-Westphalia, that competes in the 2. Bundesliga.
Founded in 1895, Fo ...
and Rot-Weiß Essen have each been German Champion once. North Rhine-Westphalia has been a very successful footballing state having a combined total of 25 championships, fewer only than Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
.
Basketball
The state is also home to several professional basketball teams that currently either compete in theBasketball Bundesliga
The Basketball Bundesliga (BBL) (English language: ''Federal Basketball League''), for sponsorship reasons named easyCredit BBL, is the German basketball league system, highest level Sports league, league of professional club basketball in German ...
or ProA
The ProA is the German basketball league system, second-tier Sports league, league of professional club basketball in Germany. The league comprises 16 teams. Officially the ProA is part of the ''2. Basketball Bundesliga'', which consists of the t ...
or have competed there in the past.
These teams include Telekom Baskets Bonn
Telekom Baskets Bonn is a German professional basketball club that is based in Bonn, Germany. The club plays in the Basketball Bundesliga, which is German basketball league system, the highest level pro basketball league in Germany. The club's s ...
, Bayer Giants Leverkusen
Bayer Giants Leverkusen is a professional basketball club, part of the Bayer 04 Leverkusen, TSV Bayer 04 Leverkusen sports club based in Leverkusen, Germany. It currently plays in ProB, the third division of German basketball.
Based on the numbe ...
, Paderborn Baskets, Uni Baskets Münster, VfL SparkassenStars Bochum, Phoenix Hagen and Alemannia Aachen.
Ice hockey
North Rhine-Westphalia is home to current and formerDEL
Del, or nabla, is an operator used in mathematics (particularly in vector calculus) as a vector differential operator, usually represented by the nabla symbol ∇. When applied to a function defined on a one-dimensional domain, it denotes ...
teams Düsseldorfer EG, Kölner Haie, Krefeld Pinguine, and Iserlohn Roosters.
See also
* Beckrath * Kunstsammlung Nordrhein-Westfalen * Kunststiftung NRW * NRW Forum *Outline of Germany
The following Outline (list), outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Germany:
Germany – federal parliamentary republic in Western Europe, Western-Central Europe, Central Europe consisting of 16 States of Germany, co ...
* List of rivers of North Rhine-Westphalia
A list of rivers of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany:
A
B
C
* Calenberger Bach
* Casumer Bach
* Compbach
D
* Dalke
* Dammpader
* Darmühlenbach
* Deilbach
* Derenbach
* Dettmers Bach
* Dhünn
* Dichbach
* Dickopsbach
* Dielenpader
* Diemel
* ...
* List of lakes in North Rhine-Westphalia
Notes
References
External links
Official Government Portal
Visit NRW Tourist Information
The Landtag of North Rhine-Westphalia
Holidays and travel tips in NRW
Information and resources on the history of Westphalia on the Web portal "Westphalian History"
Guidelines for the integration of the Land Lippe within the territory of the federal state North-Rhine-Westphalia of 17 January 1947
* {{Portal bar, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union States and territories established in 1946 1946 establishments in Germany States of Germany