North-West Passage on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

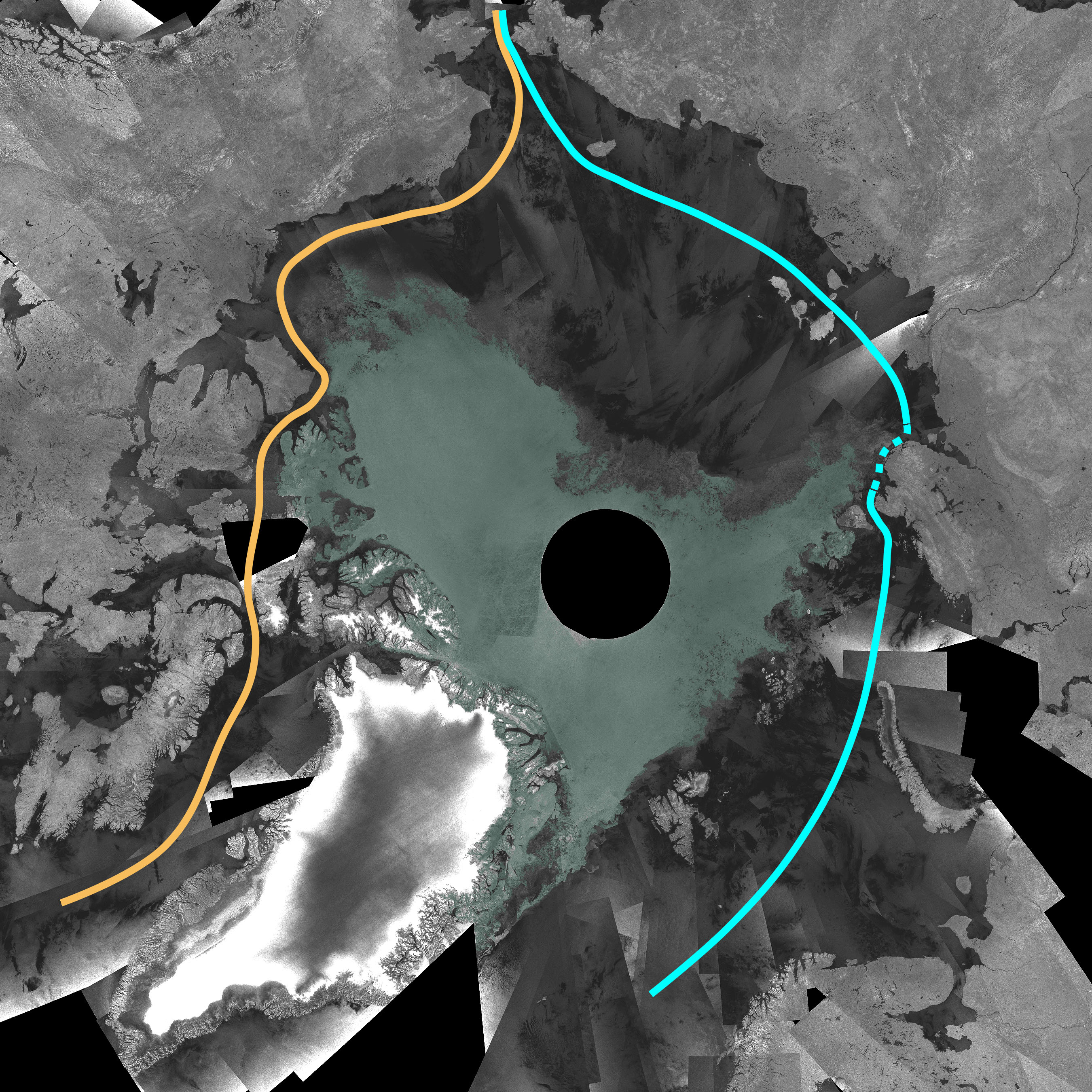 The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the

 The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane
A sea lane, sea road or shipping lane is a regularly used navigable route for large water vessels (ships) on wide waterways such as oceans and large lakes, and is preferably safe, direct and economic. During the Age of Sail, they were determined ...
between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, near the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago
The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland (an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, which is, by itself, much larger ...
of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Siberia is accordingly called the Northeast Passage
The Northeast Passage (abbreviated as NEP; , ) is the Arctic shipping routes, shipping route between the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific Oceans, along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Russia. The western route through the islan ...
(NEP).
The various islands of the archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
are separated from one another and from mainland Canada by a series of Arctic waterways collectively known as the Northwest Passages, Northwestern Passages or the Canadian Internal Waters
In Canadian law, Canadian Internal Waters are the waters "on the landward side of the baselines of the territorial sea of Canada".
Definition
The baselines are defined as "the low-water line along the coast or on a low-tide elevation that is situ ...
.
For centuries, European explorers, beginning with Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
in 1492, sought a navigable passage as a possible trade route to Asia, but were blocked by North, Central, and South America; by ice, or by rough waters (e.g. Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South America, South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan.
The archipelago consists of the main is ...
). An ice-bound northern route was discovered in 1850 by the Irish explorer Robert McClure, whose expedition completed the passage by hauling sledges. Scotsman John Rae explored a more southerly area in 1854 through which Norwegian Roald Amundsen
Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen (, ; ; 16 July 1872 – ) was a Norwegians, Norwegian explorer of polar regions. He was a key figure of the period known as the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration.
Born in Borge, Østfold, Norway, Am ...
made the first complete passage entirely by ship in 1903–1906. Until 2009, the Arctic pack ice prevented regular marine shipping throughout most of the year. Arctic sea ice decline
Sea ice in the Arctic region has declined in recent decades in area and volume due to climate change. It has been melting more in summer than it refreezes in winter. Global warming, caused by Radiative forcing#Forcing due to changes in atmospheri ...
, linked primarily to climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, has rendered the waterways more navigable for ice navigation
Ice navigation is a specialist area of navigation involving the use of maritime skills to determine and monitor the position of ships in cold waters, where ice is a hazard to the safety of navigation. The presence of sea ice requires a ship to e ...
.
The contested sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
claims over the waters may complicate future shipping through the region: the Canadian government
The Government of Canada (), formally His Majesty's Government (), is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. The term ''Government of Canada'' refers specifically to the executive, which includes ministers of the Crown ( ...
maintains that the Northwestern Passages are part of Canadian Internal Waters
In Canadian law, Canadian Internal Waters are the waters "on the landward side of the baselines of the territorial sea of Canada".
Definition
The baselines are defined as "the low-water line along the coast or on a low-tide elevation that is situ ...
, but the United States claims that they are an international strait
An international strait is a narrow natural waterway connecting two parts of the high seas or exclusive economic zones, used for international navigation. Per the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), a transit passage regime pr ...
and transit passage, allowing free and unencumbered passage. If, as the head of a Canadian mining company claims, parts of the eastern end of the Passage are barely deep, the route's viability as a Euro-Asian shipping route is reduced. In 2016, Chinese shipping line COSCO
China Ocean Shipping Company (COSCO) was a former shipping corporation from 1961 to 2016, owned by the State Council of the People's Republic of China, State Council of China. The company merged with China Shipping Group, China Shipping Grou ...
expressed a desire to make regular voyages of cargo ships using the passage to the eastern United States and Europe, after a successful passage by ''Nordic Orion
MS ''Nordic Orion'' is a Danish bulk carrier registered in Panama City. A coal and ore carrier, ''Nordic Orion'' has a capacity of . It was built in 2011 by Oshima Shipbuilding. ''Nordic Orion'' has an ice-strengthened hull, and it is notabl ...
'' of 73,500 tonnes deadweight tonnage
Deadweight tonnage (also known as deadweight; abbreviated to DWT, D.W.T., d.w.t., or dwt) or tons deadweight (DWT) is a measure of how much weight a ship can carry. It is the sum of the weights of cargo, fuel, fresh water
Fresh water or ...
in September 2013. Fully laden, ''Nordic Orion'' sat too deep in the water to sail through the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal () is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean. It cuts across the narrowest point of the Isthmus of Panama, and is a Channel (geography), conduit for maritime trade between th ...
.
Routes
The Northwest Passage has three sections: * East ** East of Baffin Island:Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay (Inuktitut: ''Saknirutiak Imanga''; ; ; ), located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a s ...
between Greenland and Baffin Island
Baffin Island (formerly Baffin Land), in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada, the second-largest island in the Americas (behind Greenland), and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is (slightly smal ...
to Lancaster Sound at the north end of Baffin Island, or
** West of Baffin Island (impractical): Through Hudson Strait
Hudson Strait () in Nunavut links the Atlantic Ocean and the Labrador Sea to Hudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley in Newfoundland and Labrador and Nunavut ...
south of Baffin Island, north through the Foxe Basin, west through the Fury and Hecla Strait
Fury and Hecla Strait is a narrow (from wide) Arctic seawater channel located in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada.
Geography
Situated between Baffin Island to the north and the Melville Peninsula to the south, it connects Foxe Basin o ...
, north to Lancaster Sound through the Gulf of Boothia
The Gulf of Boothia is a body of water in Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 19 ...
and Prince Regent Inlet
Prince Regent Inlet () is a body of water in Nunavut, Canada between the west end of Baffin Island ( Brodeur Peninsula) and Somerset Island on the west. It opens north into Lancaster Sound and to the south merges into the Gulf of Boothia. The A ...
. The Fury and Hecla Strait is usually closed by ice.
* Centre: Canadian Arctic Archipelago
The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland (an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, which is, by itself, much larger ...
** North: From Lancaster Sound west through the Parry Channel to the Prince of Wales Strait on the northwest side of Victoria Island. M'Clure Strait to the northwest is ice-filled; southwest through the Prince of Wales Strait between Victoria Island and Banks Island might be passable, or
** South: From Lancaster Sound west past Prince Regent Inlet
Prince Regent Inlet () is a body of water in Nunavut, Canada between the west end of Baffin Island ( Brodeur Peninsula) and Somerset Island on the west. It opens north into Lancaster Sound and to the south merges into the Gulf of Boothia. The A ...
(basically a cul-de-sac but it may be possible to exit west through the Bellot Strait), past Somerset Island, south through Peel Sound
Peel Sound is an Arctic waterway in the Qikiqtaaluk, Nunavut, Canada. It separates Somerset Island on the east from Prince of Wales Island on the west. To the north it opens onto Parry Channel while its southern end merges with Franklin Str ...
between Somerset Island and Prince of Wales Island, either southwest through Victoria Strait (ice-choked), or directly south along the coast through Rae Strait
Rae Strait is a small strait in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located between King William Island and the Boothia Peninsula on the mainland to the east. It is named after Scottish Arctic explorer John Rae (explorer), John Rae who, ...
and James Ross Strait and west through Simpson Strait south of King William Island (shallow) into Queen Maud Gulf, then west along the mainland coast south of Victoria Island.
* West: There being no major islands, follow the coast to the Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
.
Many attempts were made to find a salt water exit west from Hudson Bay, but the Fury and Hecla Strait in the far north is blocked by ice. The eastern entrance and main axis of the northwest passage, the Parry Channel, was found in 1819. The approach from the west through Bering Strait is impractical because of the need to sail around ice near Point Barrow
Point Barrow or Nuvuk is a headland on the Arctic coast in the U.S. state of Alaska, northeast of Utqiagvik (formerly Barrow). It is the northernmost point of all the territory of the United States, at , south of the North Pole. (The northe ...
. East of Point Barrow the coast is fairly clear in summer. This area was mapped in pieces from overland in 1821–1839. This leaves the large rectangle north of the coast, south of Parry Channel and west of Baffin Island. This area was mostly mapped in 1848–1854 by ships looking for Franklin's lost expedition. The first crossing was made by Roald Amundsen
Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen (, ; ; 16 July 1872 – ) was a Norwegians, Norwegian explorer of polar regions. He was a key figure of the period known as the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration.
Born in Borge, Østfold, Norway, Am ...
in 1903–1906. He used a small ship and hugged the coast.
Overview
Early expeditions
Before theLittle Ice Age
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of regional cooling, particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. It was not a true ice age of global extent. The term was introduced into scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939. Mat ...
(late Middle Ages to the 19th century), Norwegian Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
sailed as far north and west as Ellesmere Island
Ellesmere Island (; ) is Canada's northernmost and List of Canadian islands by area, third largest island, and the List of islands by area, tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of , slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total ...
, Skraeling Island and Ruin Island for hunting expeditions and trading with the Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
and people of the Dorset culture
The Dorset was a Paleo-Eskimo culture, lasting from to between and , that followed the Pre-Dorset and preceded the Thule people (proto-Inuit) in the North American Arctic. The culture and people are named after Cape Dorset (now Kinngait) in ...
who inhabited the region. Between the end of the 15th century and the 20th century, colonial powers from Europe dispatched explorers to discover a commercial sea route north and west around North America. The Northwest Passage represented a new route to the established trading nations of Asia.
England called the hypothetical northern route the "Northwest Passage". The desire to establish such a route motivated much of the European exploration of both coasts of North America, also known as the New World. When it became apparent that there was no route through the heart of the continent, attention turned to the possibility of a passage through northern waters. There was a lack of scientific knowledge about conditions; for instance, some people believed that seawater
Seawater, or sea water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximat ...
was incapable of freezing. (As late as the mid-18th century, Captain James Cook
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 176 ...
had reported that Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole.
The Antar ...
iceberg
An iceberg is a piece of fresh water ice more than long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". Much of an i ...
s had yielded fresh water, seemingly confirming the hypothesis.) Explorers thought that an Open Polar Sea close to the North Pole must exist. The belief that a route lay to the far north persisted for several centuries and led to numerous expeditions into the Arctic. Many ended in disaster, including that by Sir John Franklin
Sir John Franklin (16 April 1786 – 11 June 1847) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer and colonial administrator. After serving in the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812, he led two expeditions into the Northern Canada, Canadia ...
in 1845. While searching for him the McClure Arctic Expedition discovered the Northwest Passage in 1850.
In 1906, the Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen
Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen (, ; ; 16 July 1872 – ) was a Norwegians, Norwegian explorer of polar regions. He was a key figure of the period known as the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration.
Born in Borge, Østfold, Norway, Am ...
was the first to complete the passage solely by ship, from Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
to Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
in the sloop . Since that date, several fortified ships have made the journey.
From east to west, the direction of most early exploration attempts, expeditions entered the passage from the Atlantic Ocean via the Davis Strait
The Davis Strait (Danish language, Danish: ''Davisstrædet'') is a southern arm of the Arctic Ocean that lies north of the Labrador Sea. It lies between mid-western Greenland and Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada. To the north is Baffin Bay. The ...
and through Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay (Inuktitut: ''Saknirutiak Imanga''; ; ; ), located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a s ...
, both of which are in Canada. Five to seven routes have been taken through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, via the McClure Strait, Dease Strait
Dease Strait is an east–west waterway between the mainland's Kent Peninsula and Victoria Island (Canada), Victoria Island in Nunavut, Canada. It is part of the Northwest Passage. At its eastern end, approximately wide, is Cambridge Bay; to th ...
, and the Prince of Wales Strait, but not all of them are suitable for larger ships. From there ships passed through westward through the Beaufort Sea
The Beaufort Sea ( ; ) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, Yukon, and Alaska, and west of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a Hydrography, hydrographer. T ...
and the Chukchi Sea
The Chukchi Sea (, ), sometimes referred to as the Chuuk Sea, Chukotsk Sea or the Sea of Chukotsk, is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, ...
, and then southwards through the Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
(separating Russia and Alaska), into the Pacific Ocean.
Potential as a shipping lane
In the 21st century, major changes to the ice pack due toclimate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
have stirred speculation that the passage may become clear enough of ice to permit safe commercial shipping for at least part of the year. On August 21, 2007, the Northwest Passage became open to ships without the need of an icebreaker
An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters, and provide safe waterways for other boats and ships. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller ...
. According to Nalan Koc of the Norwegian Polar Institute
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; ) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Envir ...
, this was the first time the Passage has been clear since they began keeping records in 1972. The Northwest Passage opened again on August 25, 2008. It is usually reported that ocean thawing will open up the Northwest Passage (and the Northern Sea Route
The Northern Sea Route (NSR) (, shortened to Севморпуть, ''Sevmorput'') is a shipping route about long. The Northern Sea Route (NSR) is the shortest shipping route between the western part of Eurasia and the Asia-Pacific region.
Ad ...
) for various kind of ships, making it possible to sail around the Arctic ice cap and possibly cutting thousands of miles off shipping routes. Warning that the NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
satellite images suggested that the Arctic had entered a "death spiral" caused by climate change, Professor Mark Serreze, a sea ice specialist at the U.S. National Snow and Ice Data Center
The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) is a United States information and referral center in support of polar and cryospheric research. NSIDC archives and distributes digital and analog snow and ice data and also maintains information ab ...
(NSIDC) said: "The passages are open. It's a historic event. We are going to see this more and more as the years go by."
However, some thick sections of ice will remain hard to melt in the shorter term. Drifting and persistence of large chunks of ice, especially in springtime, can be problematic as they can clog entire straits
A strait is a water body connecting two seas or water basins. The surface water is, for the most part, at the same elevation on both sides and flows through the strait in both directions, even though the topography generally constricts the ...
or severely damage a ship's hull. Cargo routes may thus be slow and uncertain, depending on prevailing conditions and the ability to predict them. Because much containerized traffic operates in a just-in-time mode (which does not tolerate delays well) and because of the relative isolation of the passage (which impedes shipping companies from optimizing their operations by grouping multiple stopovers on the same itinerary), the Northwest Passage and other Arctic routes are not always seen as promising shipping lanes
A sea lane, sea road or shipping lane is a regularly used navigable route for large water vessels (ships) on wide waterways such as oceans and large lakes, and is preferably safe, direct and economic. During the Age of Sail, they were determined ...
by industry insiders, at least for the time being. The uncertainty related to physical damage to ships is also thought to translate into higher insurance premiums, especially because of the technical challenges posed by Arctic navigation (as of 2014, only 12 percent of Canada's Arctic waters have been charted to modern standards).
The Beluga group of Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (, ), is the capital of the States of Germany, German state of the Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (), a two-city-state consisting of the c ...
, Germany, sent the first Western commercial vessels through the Northern Sea Route (Northeast Passage) in 2009. Canada's Prime Minister Stephen Harper
Stephen Joseph Harper (born April 30, 1959) is a Canadian politician who served as the 22nd prime minister of Canada from 2006 to 2015. He is to date the only prime minister to have come from the modern-day Conservative Party of Canada, ser ...
announced that "ships entering the North-West passage should first report to his government".
The first commercial cargo ship
A cargo ship or freighter is a merchant ship that carries cargo, goods, and materials from one port to another. Thousands of cargo carriers ply the world's List of seas, seas and Ocean, oceans each year, handling the bulk of international trade. ...
to have sailed through the Northwest Passage was in August 1969. SS ''Manhattan'', of 115,000 deadweight tonnage
Deadweight tonnage (also known as deadweight; abbreviated to DWT, D.W.T., d.w.t., or dwt) or tons deadweight (DWT) is a measure of how much weight a ship can carry. It is the sum of the weights of cargo, fuel, fresh water
Fresh water or ...
, was the largest commercial vessel ever to navigate the Northwest Passage.
The largest passenger ship to navigate the Northwest Passage was the cruise liner of gross tonnage
Gross tonnage (GT, G.T. or gt) is a nonlinear measure of a ship's overall internal volume. Gross tonnage is different from gross register tonnage. Neither gross tonnage nor gross register tonnage should be confused with measures of mass or weig ...
69,000. Starting on August 10, 2016, the ship sailed from Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
to New York City with 1,500 passengers and crew, taking 28 days.
In 2018, two of the freighters leaving Baffinland's port in the Milne Inlet, on Baffin Island
Baffin Island (formerly Baffin Land), in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada, the second-largest island in the Americas (behind Greenland), and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is (slightly smal ...
's north shore, were bound for ports in Asia. Those freighters did not sail west through the remainder of the Northwest Passage; they sailed east, rounded the tip of Greenland, and transited Russia's Northern Sea Route.
Experts predict that the passage may be traversable four months of the year by the end of the 21st century.
Extent
TheInternational Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) (French: ''Organisation Hydrographique Internationale'') is an intergovernmental organization representing hydrography. the IHO comprised 102 member states.
A principal aim of the IHO is to ...
defines the limits of the Northwestern Passages as follows:
Historical expeditions
As a result of their westward explorations and their settlement of Greenland, theViking
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
s sailed as far north and west as Ellesmere Island
Ellesmere Island (; ) is Canada's northernmost and List of Canadian islands by area, third largest island, and the List of islands by area, tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of , slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total ...
, Skraeling Island for hunting expeditions and trading with Inuit groups. The subsequent arrival of the Little Ice Age is thought to have been one of the reasons that European seafaring into the Northwest Passage ceased until the late 15th century.
Strait of Anián
In 1539,Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquis of the Valley of Oaxaca (December 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions o ...
commissioned Francisco de Ulloa to sail along the Baja California Peninsula on the western coast of North America. Ulloa concluded that the Gulf of California
The Gulf of California (), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Vermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California peninsula from ...
was the southernmost section of a strait supposedly linking the Pacific with the Gulf of Saint Lawrence
The Gulf of St. Lawrence is a gulf that fringes the shores of the provinces of Quebec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland and Labrador, in Canada, plus the islands Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, possessions of France, in ...
. His voyage perpetuated the notion of the Island of California
The Island of California () refers to the long-held global misconception, dating from the 16th century, that the California region was not part of mainland North America but rather a large island separated from the continent by a strait no ...
and saw the beginning of a search for the Strait of Anián.
The strait probably took its name from Ania, a Chinese province mentioned in a 1559 edition of Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
's book; it first appears on a map issued by Italian cartographer
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
Giacomo Gastaldi about 1562. Five years later Bolognino Zaltieri issued a map showing a narrow and crooked Strait of Anian separating Asia from the Americas. The strait grew in European imagination as an easy sea lane linking Europe with the residence of Khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Middle Mongol:; or ''Khagan''; ) or zh, c=大汗, p=Dàhán; ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of empire, im ...
(the Great Khan) in Cathay
Cathay ( ) is a historical name for China that was used in Europe. During the early modern period, the term ''Cathay'' initially evolved as a term referring to what is now Northern China, completely separate and distinct from ''China'', which w ...
(northern China).
Cartographers and seamen tried to demonstrate its reality. Sir Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( 1540 – 28 January 1596) was an English Exploration, explorer and privateer best known for making the Francis Drake's circumnavigation, second circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition between 1577 and 1580 (bein ...
sought the western entrance in 1579. The Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
pilot Juan de Fuca, sailing from Acapulco (in Mexico) under the flag of the Spanish crown, claimed he had sailed the strait from the Pacific to the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
and back in 1592. The Spaniard Bartholomew de Fonte claimed to have sailed from Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of Saline water, saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast o ...
to the Pacific via the strait in 1640.
Northern Atlantic
The first recorded attempt to discover the Northwest Passage was the east–west voyage ofJohn Cabot
John Cabot ( ; 1450 – 1499) was an Italians, Italian navigator and exploration, explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England, Henry VII, King of England is the earliest known Europe ...
in 1497, sent by Henry VII in search of a direct route to the Orient
The Orient is a term referring to the East in relation to Europe, traditionally comprising anything belonging to the Eastern world. It is the antonym of the term ''Occident'', which refers to the Western world.
In English, it is largely a meto ...
. In 1524, Charles V Charles V may refer to:
Kings and Emperors
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
Others
* Charles V, Duke ...
sent Estêvão Gomes to find a northern Atlantic passage to the Spice Islands
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for ...
. An English expedition was launched in 1576 by Martin Frobisher, who took three trips west to what is now the Canadian Arctic
Northern Canada (), colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada, variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories a ...
in order to find the passage. Frobisher Bay
Frobisher Bay is an inlet of the Davis Strait in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the southeastern corner of Baffin Island. Its length is about and its width varies from about at its outlet into the Davis Strait ...
, which he first charted, is named after him.
As part of another expedition, in July 1583 Sir Humphrey Gilbert, who had written a treatise on the discovery of the passage and was a backer of Frobisher, claimed the territory of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
for the English crown. On August 8, 1585, the English explorer John Davis entered Cumberland Sound, Baffin Island.
The major rivers on the east coast were also explored in case they could lead to a transcontinental passage. Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from Brittany. Jacques Cartier was the first Europeans, European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, wh ...
's explorations of the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawrenc ...
in 1535 were initiated in hope of finding a way through the continent. Cartier became persuaded that the St. Lawrence was the Passage; when he found the way blocked by rapids at what is now Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
, he was so certain that these rapids were all that was keeping him from China (in French, ''la Chine''), that he named the rapids for China. Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; 13 August 1574#Fichier]For a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see #Ritch, RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December ...
renamed them Sault Saint-Louis in 1611, but the name was changed to Lachine Rapids
The Lachine Rapids () are a series of rapids on the Saint Lawrence River, between the Island of Montreal and the South Shore. They are confusingly located near the borough of Lasalle and not Lachine.
The Lachine Rapids contain large standi ...
in the mid-19th century.
In 1602, George Weymouth became the first European to explore what would later be called Hudson Strait
Hudson Strait () in Nunavut links the Atlantic Ocean and the Labrador Sea to Hudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley in Newfoundland and Labrador and Nunavut ...
when he sailed into the Strait. Weymouth's expedition to find the Northwest Passage was funded jointly by the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
and the Muscovy Company
The Muscovy Company (also called the Russia Company or the Muscovy Trading Company; ) was an English trading company chartered in 1555. It was the first major Chartered company, chartered joint-stock company, the precursor of the type of business ...
. ''Discovery'' was the same ship used by Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the Northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
on his final voyage.
John Knight, employed by the British East India Company and the Muscovy Company, set out in 1606 to follow up on Weymouth's discoveries and find the Northwest Passage. After his ship ran aground and was nearly crushed by ice, Knight disappeared while searching for a better anchorage.
In 1609, Henry Hudson sailed up what is now called the Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
in search of the Passage; encouraged by the saltiness of the water in the estuary,