Newfoundland (island) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Newfoundland ( , ; , ) is a large island within the Canadian province of
 On 5 August 1583, Humphrey Gilbert claimed Newfoundland as England's first overseas colony under Royal Charter of Queen
On 5 August 1583, Humphrey Gilbert claimed Newfoundland as England's first overseas colony under Royal Charter of Queen
 About 500 years later, in 1497, the Italian navigator
About 500 years later, in 1497, the Italian navigator
 In 1583, when Sir Humphrey Gilbert formally claimed Newfoundland as a colony of England, he found numerous English, French and Portuguese vessels at St. John's. There was no permanent European population. Gilbert was lost at sea during his return voyage, and plans of settlement were postponed.
In July 1596 the Scottish vessel the "William" left Aberdeen for "new fund land" (Newfoundland) and returned in 1600.
On 5 July 1610, John Guy set sail from
In 1583, when Sir Humphrey Gilbert formally claimed Newfoundland as a colony of England, he found numerous English, French and Portuguese vessels at St. John's. There was no permanent European population. Gilbert was lost at sea during his return voyage, and plans of settlement were postponed.
In July 1596 the Scottish vessel the "William" left Aberdeen for "new fund land" (Newfoundland) and returned in 1600.
On 5 July 1610, John Guy set sail from  After 1713, with the
After 1713, with the  After the 1783 independence of the thirteen continental colonies that became the
After the 1783 independence of the thirteen continental colonies that became the
 Newfoundland and Labrador is the youngest province in Canada. Newfoundland was organised as a colony in 1825, was self-governing from 1855 to 1934, but after a financial crisis the legislature was suspended and it was ruled through a
Newfoundland and Labrador is the youngest province in Canada. Newfoundland was organised as a colony in 1825, was self-governing from 1855 to 1934, but after a financial crisis the legislature was suspended and it was ruled through a
 As one of the first places in the
As one of the first places in the 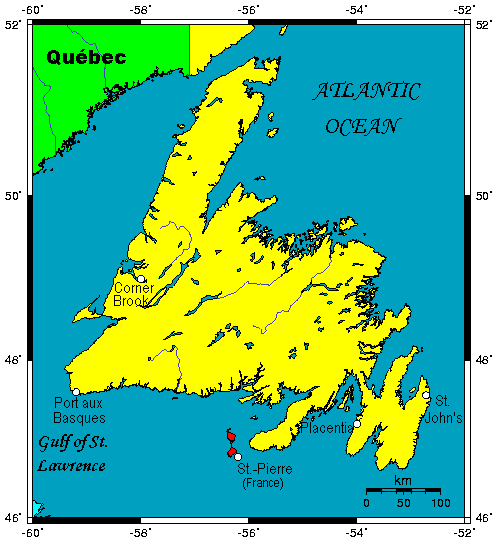 Educational institutions include the provincial university,
Educational institutions include the provincial university,
search and text excerpt
* John Gimlette, ''Theatre of Fish'', (Hutchinson, London, 2005). * Michael Harris. 1992. ''Rare Ambition: The Crosbies of Newfoundland''. Penguin. * Wayne Johnston. 1999. ''The Colony Of Unrequited Dreams'', Vintage Canada, Toronto, Ontario. (0-676-97215-2) * Kevin Major, ''As Near To Heaven by Sea'', (Toronto, 2001) * Peter Neary. 1996. ''Newfoundland in the North Atlantic World, 1929–1949''. McGill-Queen's University Press, Montreal, Quebec. * Neary, Peter, and Patrick O'Flaherty. ''Part of the main : an illustrated history of Newfoundland and Labrador'' (1983
online free to borrow
* Rowe, Frederick William. ''A history of Newfoundland and Labrador'' (1980
online free to borrow
edition
* Hatton, Joseph and Moses Harvey, ''Newfoundland: Its History and Present Condition'', (London, 1883) complete text online* MacKay, R. A. ''Newfoundland: Economic, Diplomatic, and Strategic Studies,'' (1946
online edition
* Millais, John Guille. '' The Newfoundland Guide Book, 1911: Including Labrador and St. Pierre'' (1911)
online edition; also reprinted 2009
* Moyles, Robert Gordon, ed. ''"Complaints is Many and Various, But the Odd Divil Likes It": Nineteenth Century Views of Newfoundland'' (1975). * Pedley, Charles.''History of Newfoundland'', (London, 1863
complete text online
* Prowse, D. W., ''A History of Newfoundland'' (1895), current edition 2002, Portugal Cove, Newfoundland: Boulder Publications
complete text online
* Tocque, Philip. ''Newfoundland as It Was and Is'', (London, 1878
complete text online
{{DEFAULTSORT:Newfoundland (Island) Islands of Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the populatio ...
. It is situated off the eastern coast of the North American mainland and the geographical region of Labrador
Labrador () is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its populatio ...
.
The island contains 29 percent of the province's land area, but is home to over 90% of the province's population, with about 60% of the province's population located on the small southeastern Avalon peninsula
The Avalon Peninsula () is a large peninsula that makes up the southeast portion of the island of Newfoundland in Canada. It is in size.
The peninsula is home to 270,348 people, about 52% of the province's population, according to the 2016 Ca ...
. The island is separated from the Labrador Peninsula
The Labrador Peninsula, also called Quebec-Labrador Peninsula, is a large peninsula in eastern Canada. It is bounded by Hudson Bay to the west, the Hudson Strait to the north, the Labrador Sea to the east, Strait of Belle Isle and the Gulf of ...
by the Strait of Belle Isle
The Strait of Belle Isle ( ; ) is a waterway in eastern Canada, that separates Labrador from the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland, in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Location
The strait is located in the southeast of the ...
and from Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (, formerly '; or '; ) is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although ...
by the Cabot Strait. It blocks the mouth of the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawrenc ...
, creating the Gulf of Saint Lawrence
The Gulf of St. Lawrence is a gulf that fringes the shores of the provinces of Quebec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland and Labrador, in Canada, plus the islands Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, possessions of France, in ...
, the world's largest estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro ...
. Newfoundland's nearest neighbour is the French overseas collectivity
The French overseas collectivities ( abbreviated as COM) are first-order administrative divisions of France, like the French regions, but have a semi-autonomous status. The COMs include some former French overseas colonies and other French ...
of Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon ( ), officially the Territorial Collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon (), is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, located near the Canada, Canadian prov ...
. With an area of , Newfoundland is the world's 16th-largest island, Canada's fourth-largest island, and the largest Canadian island outside the North.
The provincial capital, St. John's, is located on the southeastern coast of the island; Cape Spear, just south of the capital, is the easternmost point of North America, excluding Greenland. It is common to consider all directly neighbouring islands such as New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
, Twillingate, Fogo and Bell Island to be 'part of Newfoundland' (i.e., distinct from Labrador). By that classification, Newfoundland and its associated small islands have a total area of .
According to 2006 official Census Canada
Statistics Canada conducts a national census of population and census of agriculture every five years and releases the data with a two-year lag.
The Census of Population provides demographic and statistical data that is used to plan public servi ...
statistics, 57% of responding Newfoundland and Labradorians claim British or Irish ancestry, with 43.2% claiming at least one English parent, 21.5% at least one Irish parent, and 7% at least one parent of Scottish origin. Additionally, 6.1% claimed at least one parent of French ancestry. The island's total population as of the 2006
2006 was designated as the International Year of Deserts and Desertification.
Events
January
* January 1– 4 – Russia temporarily cuts shipment of natural gas to Ukraine during a price dispute.
* January 12 – A stampede during t ...
census was 479,105.
History
Newfoundland was long inhabited by indigenous peoples of theDorset culture
The Dorset was a Paleo-Eskimo culture, lasting from to between and , that followed the Pre-Dorset and preceded the Thule people (proto-Inuit) in the North American Arctic. The culture and people are named after Cape Dorset (now Kinngait) in ...
and the Beothuk
The Beothuk ( or ; also spelled Beothuck) were a group of Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous people of Canada who lived on the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland.
The Beothuk culture formed around 1500 CE. This may have been ...
, who spoke the now-extinct Beothuk language.
The island was possibly visited by the Icelandic explorer Leif Erikson
Leif Erikson, also known as Leif the Lucky (), was a Norsemen, Norse explorer who is thought to have been the first European to set foot on continental Americas, America, approximately half a millennium before Christopher Columbus. According ...
in the 11th century as a rest settlement when heading farther south to the land believed to be closer to the mouth of the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawren ...
called "Vinland
Vinland, Vineland, or Winland () was an area of coastal North America explored by Vikings. Leif Erikson landed there around 1000 AD, nearly five centuries before the voyages of Christopher Columbus and John Cabot. The name appears in the V ...
". The first confirmed visit was by the Norse who built a temporary base at L'Anse aux Meadows
L'Anse aux Meadows () is an archaeological site, first excavated in the 1960s, of a Norse colonization of North America, Norse settlement dating to approximately 1,000 years ago. The site is located on the northernmost tip of the island of Newf ...
, a Norse settlement near the northernmost tip of Newfoundland (Cape Norman), which has been dated to be approximately 1000 years old. The site is considered the only undisputed evidence of Pre-Columbian contact between the Old and New Worlds if the Norse–Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
contact on Greenland is not counted.
The next European visitors to Newfoundland were Portuguese, Dutch and French fishermen. The island was possibly visited by the Venetian navigator John Cabot
John Cabot ( ; 1450 – 1499) was an Italians, Italian navigator and exploration, explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England, Henry VII, King of England is the earliest known Europe ...
(Giovanni Caboto), working under contract to Henry VII of England
Henry VII (28 January 1457 – 21 April 1509), also known as Henry Tudor, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizure of the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death in 1509. He was the first monarch of the House of Tudor.
Henr ...
on his expedition from Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
in 1497. In 1501 Portuguese brothers Gaspar Corte-Real
Gaspar Corte-Real (1450–1501) was a Portuguese people, Portuguese Exploration, explorer who, alongside his father João Vaz Corte-Real and brother Miguel Corte-Real, Miguel, participated in various exploratory voyages sponsored by the Portuguese ...
and Miguel Corte-Real charted part of the coast of Newfoundland in an attempt to find the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, near the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic ...
.
 On 5 August 1583, Humphrey Gilbert claimed Newfoundland as England's first overseas colony under Royal Charter of Queen
On 5 August 1583, Humphrey Gilbert claimed Newfoundland as England's first overseas colony under Royal Charter of Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
, thus officially establishing a forerunner to the much later British Empire.GILBERT (Saunders Family), SIR HUMPHREY" (history), ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography'' Online, University of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public university, public research university whose main campus is located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park (Toronto), Queen's Park in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was founded by ...
, May 2, 2005 Newfoundland is considered Britain's oldest colony.
Settlers developed a variety of dialects associated with settlement on the island: Newfoundland English, Newfoundland French
Newfoundland French or Newfoundland Peninsular French () is the French spoken on the Port au Port Peninsula (part of the so-called “French Shore”) of Newfoundland. The francophones of the region can trace their origins to Continental French ...
. In the 19th century, it also had a dialect of Irish known as Newfoundland Irish
The Irish language was once spoken by some immigrants to the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland before it disappeared in the early 20th century. The language was introduced through mass immigration by Irish speakers, chiefly from coun ...
. The closely related Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongs ...
was also spoken on the island during the 19th and early 20th centuries, particularly in the Codroy Valley area, chiefly by settlers from Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (, formerly '; or '; ) is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although ...
, Nova Scotia. The Gaelic names reflected the association with fishing: in Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongs ...
, it was called , literally 'Island of the Cod
Cod (: cod) is the common name for the demersal fish genus ''Gadus'', belonging to the family (biology), family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gad ...
'. Similarly, the Irish name means 'Land of the Fish'.
First inhabitants
The first inhabitants of Newfoundland were thePaleo-Eskimo
The Paleo-Eskimo meaning ''"old Eskimos"'', also known as, pre-Thule people, Thule or pre-Inuit, were the peoples who inhabited the Arctic region from Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Chukotka (e.g., Chertov Ovrag) in present-day Russia across North Am ...
, who have no known link to other groups in Newfoundland history. Little is known about them beyond archeological
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology ...
evidence of early settlements. Evidence of successive cultures have been found. The Late Paleo-Eskimo, or Dorset culture
The Dorset was a Paleo-Eskimo culture, lasting from to between and , that followed the Pre-Dorset and preceded the Thule people (proto-Inuit) in the North American Arctic. The culture and people are named after Cape Dorset (now Kinngait) in ...
, settled there about 4,000 years ago. They were descendants of migrations of ancient prehistoric peoples across the High Arctic thousands of years ago, after crossing from Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
via the Bering land bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the ...
. The Dorset died off or abandoned the island prior to the arrival of the Norse.
After this period, the Beothuk
The Beothuk ( or ; also spelled Beothuck) were a group of Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous people of Canada who lived on the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland.
The Beothuk culture formed around 1500 CE. This may have been ...
settled in Newfoundland, migrating from Labrador on the mainland. There is no evidence that the Beothuk inhabited the island before Norse settlement. Scholars believe that the Beothuk are related closely to the Innu
The Innu/Ilnu ('man, person'), formerly called Montagnais (French for ' mountain people'; ), are the Indigenous Canadians who inhabit northeastern Labrador in present-day Newfoundland and Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to ...
of Labrador. The tribe later was declared "extinct" although people of partial Beothuk descent have been documented. The name meant 'people' in the Beothuk language, which is often considered to be a member of the Algonquian language family although the lack of sufficient records means that it is not possible to demonstrate such a connection confidently.
The tribe is now typically considered extinct, but evidence of its culture is preserved in museums and historical and archaeological records. Shanawdithit, a woman who is often regarded as the last full-blood Beothuk, died in St. John's in 1829 of tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
. However, Santu Toney, born around 1835 and died in 1910, was a woman of mixed Mi'kmaq and Beothuk descent, meaning some Beothuk must have lived on beyond 1829. She described her father as Beothuk and mother as Mi'kmaq, both from Newfoundland. The Beothuk may have intermingled and assimilated with Innu
The Innu/Ilnu ('man, person'), formerly called Montagnais (French for ' mountain people'; ), are the Indigenous Canadians who inhabit northeastern Labrador in present-day Newfoundland and Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to ...
in Labrador
Labrador () is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its populatio ...
and Mi'kmaq in Newfoundland. European histories also suggest potential historical competition and hostility between the Beothuk and Mi'kmaq, though this is refuted by indigenous oral history. The Mi'kmaq, Innu and Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
all hunted and fished around Newfoundland but no evidence indicates that they lived on the island for long periods of time and would only travel to Newfoundland temporarily. Inuit have been documented on the Great Northern Peninsula as late as the 18th-Century. Newfoundland was historically the southernmost part of the Inuit's territorial range.
When Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common ancestry, language, faith, historical continuity, etc. There are ...
arrived from 1497 and later, starting with John Cabot
John Cabot ( ; 1450 – 1499) was an Italians, Italian navigator and exploration, explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England, Henry VII, King of England is the earliest known Europe ...
, they established contact with the Beothuk. Estimates of the number of Beothuk on the island at this time vary, typically around 700.
Later both the English and French settled the island. They were followed by the Mi'kmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Mi'kmaw'' or ''Mi'gmaw''; ; , and formerly Micmac) are an Indigenous group of people of the Northeastern Woodlands, native to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces, primarily Nova Scotia, New Bru ...
, an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people from eastern Canada and present-day Nova Scotia. As European and Mi'kmaq settlement became year-round and expanded to new areas of the coast, the area available to the Beothuk to harvest the marine resources they relied upon was diminished. By the beginning of the 19th century, few Beothuk remained. Most died due to infectious diseases
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
carried by Europeans, to which they had no immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity ...
, and starvation. Government attempts to engage with the Beothuk and aid them came too late. The Beothuk did not have friendly relations with foreigners, unlike the Mi'kmaq. The latter readily traded with Europeans and became established in settlements in Newfoundland.
European contact and settlement
Newfoundland is the site of the only authenticated Norse settlement in North America. Anarchaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
site was discovered in 1960 at L'Anse aux Meadows
L'Anse aux Meadows () is an archaeological site, first excavated in the 1960s, of a Norse colonization of North America, Norse settlement dating to approximately 1,000 years ago. The site is located on the northernmost tip of the island of Newf ...
by Norwegian explorer Helge Ingstad and his wife, archaeologist Anne Stine Ingstad. This site was the subject of archaeological studies throughout the 1960s and 1970s. This research estimated that the settlement dates to about the year 1000, and the site contains the earliest-known European structures in North America. In 2021, an interdisciplinary team used the Miyake event
A Miyake event is an observed sharp enhancement of the production of Cosmogenic nuclide, cosmogenic isotopes by cosmic rays. It can be marked by a spike in the concentration of radioactive carbon isotope Carbon-14, in tree rings, as well as Beryl ...
of 993–994 as a benchmark in dendrochronology
Dendrochronology (or tree-ring dating) is the scientific method of chronological dating, dating tree rings (also called growth rings) to the exact year they were formed in a tree. As well as dating them, this can give data for dendroclimatology, ...
(tree-ring studies) to precisely determine that Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
were present in L'Anse aux Meadows in Newfoundland in year 1021.
Designated as a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
by UNESCO, it is believed to be the Vinland
Vinland, Vineland, or Winland () was an area of coastal North America explored by Vikings. Leif Erikson landed there around 1000 AD, nearly five centuries before the voyages of Christopher Columbus and John Cabot. The name appears in the V ...
settlement of explorer Leif Erikson
Leif Erikson, also known as Leif the Lucky (), was a Norsemen, Norse explorer who is thought to have been the first European to set foot on continental Americas, America, approximately half a millennium before Christopher Columbus. According ...
. (The Icelandic Skálholt map of 1570 refers to the area as "Promontorium Winlandiæ" and correctly shows it on a 51°N parallel with Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
, England). Before and after the departure of the Norse, the island was inhabited by indigenous populations.
Exploration by Cabot
 About 500 years later, in 1497, the Italian navigator
About 500 years later, in 1497, the Italian navigator John Cabot
John Cabot ( ; 1450 – 1499) was an Italians, Italian navigator and exploration, explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England, Henry VII, King of England is the earliest known Europe ...
(Zuan/Giovanni Caboto) became the first European since the Norse settlers to set foot on Newfoundland, working under commission of King Henry VII of England
Henry VII (28 January 1457 – 21 April 1509), also known as Henry Tudor, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizure of the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death in 1509. He was the first monarch of the House of Tudor.
Henr ...
. His landing site is unknown but popularly believed to be Cape Bonavista, along the island's East coast. Another site claimed is Cape Bauld, at the tip of the Great Northern Peninsula. A document found in the Spanish National Archives, written by a Bristol merchant, reports that Cabot's crew landed west of Dursey Head, Ireland (latitude 51°35′N), which would put Cabot within sight of Cape Bauld. This document mentions an island that Cabot sailed past to go ashore on the mainland. This description fits with the Cape Bauld theory, as Belle Isle is not far offshore.
Other European explorers
After Cabot, the first European visitors to Newfoundland were Portuguese, Spanish, Basque, French and English migratory fishermen. In 1501, Portuguese explorersGaspar Corte-Real
Gaspar Corte-Real (1450–1501) was a Portuguese people, Portuguese Exploration, explorer who, alongside his father João Vaz Corte-Real and brother Miguel Corte-Real, Miguel, participated in various exploratory voyages sponsored by the Portuguese ...
and his brother Miguel Corte-Real charted part of the coast of Newfoundland in a failed attempt to find the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, near the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic ...
. Late in the 17th century came Irish fishermen, who found so many fisheries that they named the island , meaning 'Land of the Fish', more loosely 'the fishing grounds' in Irish.
Colonization
 In 1583, when Sir Humphrey Gilbert formally claimed Newfoundland as a colony of England, he found numerous English, French and Portuguese vessels at St. John's. There was no permanent European population. Gilbert was lost at sea during his return voyage, and plans of settlement were postponed.
In July 1596 the Scottish vessel the "William" left Aberdeen for "new fund land" (Newfoundland) and returned in 1600.
On 5 July 1610, John Guy set sail from
In 1583, when Sir Humphrey Gilbert formally claimed Newfoundland as a colony of England, he found numerous English, French and Portuguese vessels at St. John's. There was no permanent European population. Gilbert was lost at sea during his return voyage, and plans of settlement were postponed.
In July 1596 the Scottish vessel the "William" left Aberdeen for "new fund land" (Newfoundland) and returned in 1600.
On 5 July 1610, John Guy set sail from Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
, England, with 39 other colonists for Cuper's Cove. This, and other early attempts at permanent settlement failed to make a profit for the English investors, but some settlers remained, forming the very earliest modern European population on the island. By 1620, the fishermen of England's West Country
The West Country is a loosely defined area within southwest England, usually taken to include the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset and Bristol, with some considering it to extend to all or parts of Wiltshire, Gloucestershire and ...
dominated the east coast of Newfoundland. French fishermen dominated the island's south coast and Northern Peninsula. The decline of the fisheries, the wasting of the shoreline forests, and an overstocking of liquor by local merchants influenced the Whitehall government in 1675 to decline to set up a colonial governor on the island.
 After 1713, with the
After 1713, with the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
, the French ceded control of south and north shores of the island to the British. They kept only the nearby islands of St. Pierre and Miquelon, located in the fish-rich Grand Banks
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordfi ...
off the south coast. Despite some early settlements by the English, the Crown discouraged permanent, year-round settlement of Newfoundland by migratory fishery workers. Thomas Nash was an Irish Catholic
Irish Catholics () are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland, defined by their adherence to Catholic Christianity and their shared Irish ethnic, linguistic, and cultural heritage.The term distinguishes Catholics of Irish descent, particul ...
fisherman who permanently settled in Newfoundland. He established the fishing town of Branch
A branch, also called a ramus in botany, is a stem that grows off from another stem, or when structures like veins in leaves are divided into smaller veins.
History and etymology
In Old English, there are numerous words for branch, includ ...
. He and his cousin Father Patrick Power of Callan, County Kilkenny, spread Catholicism in Newfoundland. This settlement attracted a major migration of Irish Catholic immigrants to Newfoundland in the early eighteenth century.
By the late 18th century, permanent settlement increased, peaking in the early years of the 19th century.
The French name for the island is . The name ''Newfoundland'' is one of the oldest European place names in Canada in continuous geographical and cartographical use, dating from a 1502 letter. It was stated in the following 1628 poem:
''A Skeltonicall continued ryme, in praise of my New-found-Land''
:Although in cloaths, company, buildings faire
:With England, New-found-land cannot compare:
:Did some know what contentment I found there,
:Alwayes enough, most times somewhat to spare,
:With little paines, lesse toyle, and lesser care,
:Exempt from taxings, ill newes, Lawing, feare,
:If cleane, and warme, no matter what you weare,
:Healthy, and wealthy, if men careful are,
:With much-much more, then I will now declare,
: (I say) if some wise men knew what this were
: (I doe beleeue) they'd live no other where.
::From ' The First Booke of ''Qvodlibets''
::Composed and done at ''Harbor-Grace'' in
::''Britaniola'', anciently called ''Newfound-Land''
::by Governor Robert Hayman
Robert Hayman (14 August 1575 – November 1629) was a poet, colonist and Proprietary Governor of Bristol's Hope colony in Newfoundland.
Early life and education
Hayman was born in Wolborough near Newton Abbot, Devon, the eldest of nine c ...
– 1628.
 After the 1783 independence of the thirteen continental colonies that became the
After the 1783 independence of the thirteen continental colonies that became the United States of America
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguo ...
, the remaining continental colonies and the North Atlantic Ocean colony of Bermuda
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about to the west-northwest.
Bermuda is an ...
were organised and administered as British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
. All except the Newfoundland Colony
Newfoundland was an English, and later British, colony established in 1610 on the island of Newfoundland. That followed decades of sporadic English settlement on the island, which was at first only seasonal. Newfoundland was made a Crown colony ...
and Bermuda confederated in 1867 to form the Dominion of Canada
While a variety of theories have been postulated for the name of Canada, its origin is now accepted as coming from the St. Lawrence Iroquoian word , meaning 'village' or 'settlement'. In 1535, indigenous inhabitants of the present-day Quebec C ...
. Newfoundland and Bermuda would retain links (possibly explaining similarities between the Newfoundland English and Bermudian English
Bermudian English is a regional dialect of English found in Bermuda, a British overseas territory in the North Atlantic. Standard English is used in professional settings and in writing, while vernacular Bermudian English is spoken on more ca ...
), including settlement in Newfoundland of Bermudians such as Joseph Outerbridge, especially their being grouped under the Bishop of Newfoundland until a separate Bishop of Bermuda was created in 1919, though Newfoundland would become a Dominion
A dominion was any of several largely self-governance, self-governing countries of the British Empire, once known collectively as the ''British Commonwealth of Nations''. Progressing from colonies, their degrees of self-governing colony, colon ...
in its own right from 1907 (the Dominion of Newfoundland
Newfoundland was a British dominion in eastern North America, today the modern Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It included the island of Newfoundland, and Labrador on the continental mainland. Newfoundland was one of the orig ...
), before reverting to colonial status in 1934, and finally joining the Dominion of Canada in 1949 as the Province of Newfoundland.
A new society
The European immigrants, mostly English, Scots, Irish and French, built a society in the New World unlike the ones they had left. It was also different from those that other immigrants would build on the North American mainland. As a fish-exporting society, Newfoundland was in contact with many ports and societies around the Atlantic rim. But its geographic location and political distinctiveness isolated it from its closest neighbours, Canada and the United States. Internally, most of its population was spread widely around a rugged coastline in small outport settlements. Many were distant from larger centres of population and isolated for long periods by winter ice or bad weather. These conditions had an effect on the cultures of the immigrants. They generated new ways of thinking and acting. Newfoundland and Labrador developed a wide variety of distinctive customs, beliefs, stories, songs and dialects. A uniquevocabulary
A vocabulary (also known as a lexicon) is a set of words, typically the set in a language or the set known to an individual. The word ''vocabulary'' originated from the Latin , meaning "a word, name". It forms an essential component of languag ...
arose focused on the sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less density, dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oceans. Much of the world' ...
and weather of this isolated location and the native wildlife
Wildlife refers to domestication, undomesticated animals and uncultivated plant species which can exist in their natural habitat, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wilderness, wild in an area without being species, introdu ...
its residents relied upon for food and income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. F ...
.
Effects of World Wars
TheFirst World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
had a powerful and lasting effect on the society. From a population of about a quarter of a million, 5,482 men went overseas. Nearly 1,500 were killed and 2,300 wounded. On July 1, 1916, at Beaumont-Hamel, France, 753 men of the Royal Newfoundland Regiment
The Royal Newfoundland Regiment (R NFLD R) is a Primary Reserve infantry regiment of the Canadian Army. It is part of the 5th Canadian Division's 37 Canadian Brigade Group.
Predecessor units trace their origins to 1795, and since 1949 Royal ...
went over the top of a trench. The next morning, only 68 men answered the roll-call. Even now, when the rest of Canada celebrates the founding of the country on July 1, many Newfoundlanders take part in solemn ceremonies of remembrance.
The Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
also had a lasting effect on Newfoundland. In particular, the United States assigned forces to the military bases at Argentia, Gander, Stephenville, Goose Bay, and St. John's.
 Newfoundland and Labrador is the youngest province in Canada. Newfoundland was organised as a colony in 1825, was self-governing from 1855 to 1934, but after a financial crisis the legislature was suspended and it was ruled through a
Newfoundland and Labrador is the youngest province in Canada. Newfoundland was organised as a colony in 1825, was self-governing from 1855 to 1934, but after a financial crisis the legislature was suspended and it was ruled through a Commission of Government
The Commission of Government was a non-elected body that governed the Dominion of Newfoundland from 1934 to 1949. Established following the collapse of Newfoundland's economy during the Great Depression, it was dissolved when the dominion became ...
(see Dominion of Newfoundland
Newfoundland was a British dominion in eastern North America, today the modern Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It included the island of Newfoundland, and Labrador on the continental mainland. Newfoundland was one of the orig ...
). On June 22 and July 3, 1948, the population of the colony voted in referendums 52.3% to 47.7% in favour of joining Canada as a province. Opposition to confederation was concentrated among residents of the capital St. John's and its surrounding hinterland on the Avalon Peninsula.
Union with Canada
Newfoundland joined Canada at one minute before midnight on March 31, 1949. Union with Canada has done little to reduce Newfoundlanders' self-image as a distinctive group. In 2003, 72% of residents responding identified first as Newfoundlanders, secondarily as Canadians. Separatist sentiment is low, though, less than 12% in the same 2003 study. The referendum campaign of 1948 was bitterly fought, and interests in both Canada and Britain favoured and supported confederation with Canada. Jack Pickersgill, a western Canadian native and politician, worked with the confederation camp during the campaign. The Catholic Church, whose members were a minority on the island, lobbied for continued independence. Canada offered financial incentives, including a "baby bonus" for each child in a family. The Confederates were led by the charismatic Joseph Smallwood, a former radio broadcaster, who had developedsocialist
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
political inclinations while working for a socialist newspaper in New York City. Following confederation, Smallwood led Newfoundland for decades as the elected premier
Premier is a title for the head of government in central governments, state governments and local governments of some countries. A second in command to a premier is designated as a deputy premier.
A premier will normally be a head of govern ...
. His policies as premier were closer to liberalism
Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality, the right to private property, and equality before the law. ...
than socialism.
Flags of Newfoundland
The first flag to specifically represent Newfoundland is thought to have been an image of a green fir tree on a pink background that was in use in the early 19th century. The first official flag identifying Newfoundland, flown by vessels in service of the colonial government, was the Newfoundland Blue Ensign, adopted in 1870 and used until 1904, when it was modified slightly. In 1904, the crown of the Blue Ensign was replaced with the Great Seal of Newfoundland (having been given royal approval in 1827) and the British Parliament designated Newfoundland Red and Blue ensigns as official flags specifically for Newfoundland. The Red and Blue ensigns with the Great Seal of Newfoundland in the fly were used officially from 1904 until 1965, with the Red Ensign being flown as civil ensign by merchant shipping, and the Blue being flown by governmental ships (after the British tradition of having different flags for merchant/naval and government vessel identification). On September 26, 1907, King Edward VII of the United Kingdom declared the Colony of Newfoundland, as an independentDominion
A dominion was any of several largely self-governance, self-governing countries of the British Empire, once known collectively as the ''British Commonwealth of Nations''. Progressing from colonies, their degrees of self-governing colony, colon ...
within the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
, and from that point until 1965, the Newfoundland Red Ensign was used as the civil ensign of the Dominion of Newfoundland
Newfoundland was a British dominion in eastern North America, today the modern Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It included the island of Newfoundland, and Labrador on the continental mainland. Newfoundland was one of the orig ...
with the Blue Ensign, again, reserved for government shipping identification. In 1931 the Newfoundland National Assembly adopted the Union Jack
The Union Jack or Union Flag is the ''de facto'' national flag of the United Kingdom. The Union Jack was also used as the official flag of several British colonies and dominions before they adopted their own national flags.
It is sometimes a ...
as the official national flag, with the Red and Blue Ensigns retained as ensigns for shipping identification.
On March 31, 1949, Newfoundland became a province of Canada but retained the Union Jack in legislature, still designating it as the "national" flag. This was later reaffirmed by the Revised Statutes Act of 1952, and the Union Jack remained the official flag of Newfoundland until 1980, when it was replaced by the current provincial flag. (See Province of Newfoundland and Labrador for continued discussion of provincial flags.)
Points of interest
 As one of the first places in the
As one of the first places in the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
where Europeans settled, Newfoundland also has a history of European colonization. St. John's is the oldest city in Canada and the oldest continuously settled location in English-speaking North America.
The St. John's census metropolitan area includes 12 suburban communities, the largest of which are the city of Mount Pearl
Mount Pearl is the fourth-largest municipality and second-largest city in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The city is located southwest of St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, on the eastern tip of the Avalon Peninsula on the isla ...
and the towns of Conception Bay South
Conception Bay South is a town in the Province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The town is commonly called CBS.
The town is located on the Avalon Peninsula which forms part of the southern shore of Conception Bay which is in turn part of ...
and Paradise
In religion and folklore, paradise is a place of everlasting happiness, delight, and bliss. Paradisiacal notions are often laden with pastoral imagery, and may be cosmogonical, eschatological, or both, often contrasted with the miseries of human ...
. The province's third-largest city is Corner Brook
Corner Brook ( 2021 population: 19,316 CA 29,762) is a city located on the west coast of the island of Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Corner Brook is the fifth largest settlement in Newfoundland and Labrado ...
, which is situated on the Bay of Islands
The Bay of Islands is an area on the east coast of the Far North District of the North Island of New Zealand. It is one of the most popular fishing, sailing and tourist destinations in the country, and has been renowned internationally for ...
on the west coast of the island. The bay was named by Captain James Cook who surveyed the coast in 1767.
The island of Newfoundland has numerous provincial parks such as Barachois Pond Provincial Park, considered to be a model forest, as well as two national parks.
* Gros Morne National Park is located on the west coast; it was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
in 1987 due to its complex geology and remarkable scenery. It is the largest national park in Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (), is the list of regions of Canada, region of Eastern Canada comprising four provinces: New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. As of 2021, the landma ...
at and is a popular tourist destination.
* Terra Nova National Park, on the island's east side, preserves the rugged geography of the Bonavista Bay region. It allows visitors to explore the historic interplay of land, sea and man.
* L'Anse aux Meadows
L'Anse aux Meadows () is an archaeological site, first excavated in the 1960s, of a Norse colonization of North America, Norse settlement dating to approximately 1,000 years ago. The site is located on the northernmost tip of the island of Newf ...
is an archaeological site located near the northernmost tip of the island (Cape Norman). It is the only known site of a Norse village in North America outside of Greenland, and is designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
. It is the only widely accepted site of pre-Columbian trans-oceanic contact. It has associations with the attempted colony of Vinland established by Leif Ericson
Leif Erikson, also known as Leif the Lucky (), was a Norse explorer who is thought to have been the first European to set foot on continental America, approximately half a millennium before Christopher Columbus. According to the sagas of I ...
around 1003.
* Heart's Content, Newfoundland and Labrador was given its place in the history of international communications by Cyrus West Field who chose it as the terminus of his Transatlantic telegraph cable
Transatlantic telegraph cables were undersea cables running under the Atlantic Ocean for telegraph communications. Telegraphy is a largely obsolete form of communication, and the cables have long since been decommissioned, but telephone and dat ...
, leading to establishment of the Heart's Content Cable Station.
The island has many tourism opportunities, ranging from sea kayaking, camping, fishing and hunting, to hiking. The International Appalachian Trail
The International Appalachian Trail (IAT; , SIA) was originally a hiking trail which ran from Katahdin Woods and Waters National Monument, in Maine, through New Brunswick, to the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec, after which it followed a ferry route ...
(IAT) is being extended along the island's mountainous west coast. On the east coast, the East Coast Trail extends through the Avalon Peninsula
The Avalon Peninsula () is a large peninsula that makes up the southeast portion of the island of Newfoundland in Canada. It is in size.
The peninsula is home to 270,348 people, about 52% of the province's population, according to the 2016 Ca ...
for , beginning near Fort Amherst in St. John's and ending in Cappahayden, with an additional of trail under construction.
The Marble Mountain Ski Resort near Corner Brook
Corner Brook ( 2021 population: 19,316 CA 29,762) is a city located on the west coast of the island of Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Corner Brook is the fifth largest settlement in Newfoundland and Labrado ...
is a major attraction in the winter for skiers in eastern Canada.
Other major communities include the following towns:
* Gander, home to the Gander International Airport.
* Grand Falls-Windsor
Grand Falls-Windsor is a town located in the central region of the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada, with a population of 13,853 at the Canada 2021 Census, 2021 census. The town i ...
, a service centre for the central part of the island.
* Channel-Port aux Basques, the " Gateway to Newfoundland", as it is the closest point on the island to the province of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
, as well as the location of the Marine Atlantic ferry terminal connecting the island to the rest of Canada.
* Stephenville, former location of the Ernest Harmon Air Force Base and currently the Stephenville Airport.
 Educational institutions include the provincial university,
Educational institutions include the provincial university, Memorial University of Newfoundland
Memorial University of Newfoundland, or MUN (), is a Public university, public research university in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, based in St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, with satellite campuses in Corner Brook ...
whose main campus is situated in St. John's, along with the Grenfell Campus in Corner Brook, in addition to the College of the North Atlantic based in Stephenville and other communities.
Bonavista, Placentia and Ferryland are all historic locations for various early European settlement or discovery activities. Tilting Harbour on Fogo Island is a provincial Registered Heritage District, as well as a National Cultural Landscape District of Canada. This is one of only two national historic sites in Canada so recognized for their Irish heritage.
Entertainment opportunities abound in the island's three cities and numerous towns, particularly during summer festivals. For nightlife, George Street, located in downtown St. John's, is closed to traffic 20 hours per day. The Mile One Stadium in St. John's is the venue for large sporting and concert events in the province.
In March, the annual seal hunt (of the harp seal) takes place.
Communities
Largest municipalities (2016 population) # St. John's (108,860) #Conception Bay South
Conception Bay South is a town in the Province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The town is commonly called CBS.
The town is located on the Avalon Peninsula which forms part of the southern shore of Conception Bay which is in turn part of ...
(26,199)
# Mount Pearl
Mount Pearl is the fourth-largest municipality and second-largest city in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The city is located southwest of St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, on the eastern tip of the Avalon Peninsula on the isla ...
(23,120)
# Paradise
In religion and folklore, paradise is a place of everlasting happiness, delight, and bliss. Paradisiacal notions are often laden with pastoral imagery, and may be cosmogonical, eschatological, or both, often contrasted with the miseries of human ...
(21,389)
# Corner Brook
Corner Brook ( 2021 population: 19,316 CA 29,762) is a city located on the west coast of the island of Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Corner Brook is the fifth largest settlement in Newfoundland and Labrado ...
(19,806)
# Grand Falls-Windsor
Grand Falls-Windsor is a town located in the central region of the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada, with a population of 13,853 at the Canada 2021 Census, 2021 census. The town i ...
(14,171)
# Gander (11,688)
# Portugal Cove-St. Philip's (8,147)
# Torbay
Torbay is a unitary authority with a borough status in the ceremonial county of Devon, England. It is governed by Torbay Council, based in the town of Torquay, and also includes the towns of Paignton and Brixham. The borough consists of ...
(7,899)
# Stephenville (6,623)
# Clarenville
Clarenville is a town on the east coast of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Clarenville was incorporated in 1951. It is located in the Shoal Harbour valley, fronting an arm of the Atlant ...
(6,291)
# Bay Roberts (6,012)
# Marystown
Marystown is a town in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada, with a population of around 5,000. Situated 306 km from the province's capital, St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. John's, it is on the Burin Peninsula. Until ...
(5,316)
# Deer Lake (5,249)
Geography
Newfoundland is roughly triangular, with each side being approximately 500 kilometres (310 mi), and having an area of 108,860 square kilometres (42,030 sq mi). Newfoundland and its associated small islands have a total area of 111,390 square kilometres (43,010 sq mi). Newfoundland extends between latitudes 46°36'N and 51°38'N.Climate
Newfoundland is primarily characterized by having asubarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of hemiboreal regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Fennoscandia, Northwestern Russia, Siberia, and the Cair ...
(Köppen Dfc) or a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
(Köppen Dfb). Locations on the extreme southeast of the island receive sufficient maritime influence to qualify as having a subpolar oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring co ...
(Köppen Cfc).
Geology
TheTerreneuvian
The Terreneuvian is the lowermost and oldest Series (stratigraphy), series of the Cambrian geological System (stratigraphy), system. Its base is defined by the first appearance datum of the trace fossil ''Treptichnus pedum'' around million years ...
Epoch that begins the Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
Period of geological time is named for ''Terre Neuve'' (the French term for Newfoundland).Landing, E., Peng, S., Babcock, L. E., Geyer, G., & Moczydlowska-Vidal, M. (2007). Global standard names for the lowermost Cambrian series and stage. Episodes, 30(4), 287
Features
Fauna and flora
Newfoundlanders
Railways
Currently closedNewfoundland Railway
The Newfoundland Railway was a narrow-gauge railway that operated on the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland from 1898 to 1988. With a total track length of , it was the longest narrow-gauge system in North America.
History
Early con ...
See also
* Flag of Newfoundland and Labrador * Heritage Foundation of Newfoundland and Labrador * :Newfoundland and LabradorReferences
Further reading
Modern histories
* Sean T. Cadigan. ''Newfoundland and Labrador: A History'' (2009search and text excerpt
* John Gimlette, ''Theatre of Fish'', (Hutchinson, London, 2005). * Michael Harris. 1992. ''Rare Ambition: The Crosbies of Newfoundland''. Penguin. * Wayne Johnston. 1999. ''The Colony Of Unrequited Dreams'', Vintage Canada, Toronto, Ontario. (0-676-97215-2) * Kevin Major, ''As Near To Heaven by Sea'', (Toronto, 2001) * Peter Neary. 1996. ''Newfoundland in the North Atlantic World, 1929–1949''. McGill-Queen's University Press, Montreal, Quebec. * Neary, Peter, and Patrick O'Flaherty. ''Part of the main : an illustrated history of Newfoundland and Labrador'' (1983
online free to borrow
* Rowe, Frederick William. ''A history of Newfoundland and Labrador'' (1980
online free to borrow
Vintage accounts
* Barnes, Capt. William Morris. ''When Ships Were Ships (And Not Tin Pots)'', 1931. Available in digital format at Memorial University site here. * Birkenhead, Lord. ''The Story of Newfoundland'' (2nd ed., 1920) 192pedition
* Hatton, Joseph and Moses Harvey, ''Newfoundland: Its History and Present Condition'', (London, 1883) complete text online* MacKay, R. A. ''Newfoundland: Economic, Diplomatic, and Strategic Studies,'' (1946
online edition
* Millais, John Guille. '' The Newfoundland Guide Book, 1911: Including Labrador and St. Pierre'' (1911)
online edition; also reprinted 2009
* Moyles, Robert Gordon, ed. ''"Complaints is Many and Various, But the Odd Divil Likes It": Nineteenth Century Views of Newfoundland'' (1975). * Pedley, Charles.''History of Newfoundland'', (London, 1863
complete text online
* Prowse, D. W., ''A History of Newfoundland'' (1895), current edition 2002, Portugal Cove, Newfoundland: Boulder Publications
complete text online
* Tocque, Philip. ''Newfoundland as It Was and Is'', (London, 1878
complete text online
External links
* of the Government of Newfoundland and Labrador{{DEFAULTSORT:Newfoundland (Island) Islands of Newfoundland and Labrador