Natufian culture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Natufian culture ( ) is an
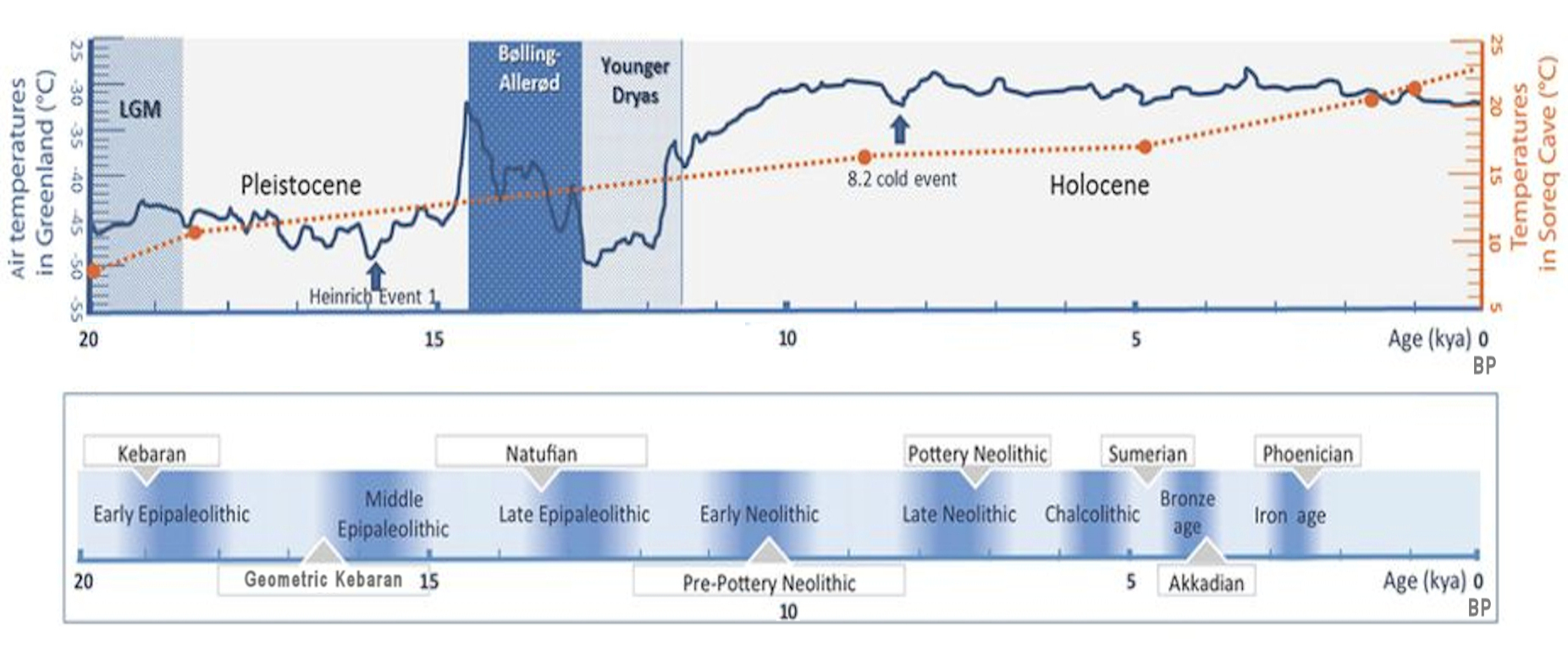
Table S6.1 – Y-chromosome haplogroups
/ref> Natufians have also been described by other anthropologists as a Proto-Mediterranean population, being similar to the Kebarans. According to Bar-Yosef and Belfer-Cohen, "It seems that certain preadaptive traits, developed already by the Kebaran and Geometric Kebaran populations within the Mediterranean park forest, played an important role in the emergence of the new socioeconomic system known as the Natufian culture."


 Natufian
Natufian  In 2008, the 12,400–12,000 cal BC grave of an apparently significant Natufian female was discovered in a ceremonial pit in the Hilazon Tachtit cave in northern Israel. Media reports referred to this person as a "shaman". The burial contained the remains of at least three
In 2008, the 12,400–12,000 cal BC grave of an apparently significant Natufian female was discovered in a ceremonial pit in the Hilazon Tachtit cave in northern Israel. Media reports referred to this person as a "shaman". The burial contained the remains of at least three
File:Israel Museum Stone Age Artifact.jpg, Grinding tool from Gilgal I, Natufian culture, 12,500–9500 BC
File:Basalt Sharpening Stones, Natufian Culture.jpg, Basalt sharpening stones, ʿAin Mallaha and Nahal Oren, Natufian Culture, 12,500–9500 BC
File:Bovine-Rib Dagger, Natufian Culture.jpg, Bovine-rib dagger, HaYonim Cave, Natufian Culture, 12,500–9500 BC
File:Stone Mortars from Eynan, Natufian period.jpg, Stone mortars from ʿAin Mallaha, Natufian period, 12,500–9500 BC
File:Eynan Epipaleolithic mortar.jpg, Stone mortar from ʿAin Mallaha, Natufian period, 12,500–9500 BC
File:Limestone & basalt mortars from Eynan, early Natufian circa 12500 BC.jpg, Limestone and basalt mortars, ʿAin Mallaha, Early Natufian,

Epi-Palaeolithic (European Mesolithic) Natufian Culture of Israel (The History of the Ancient Near East)
*
The genetic structure of the world's first farmers, Lazaridis et al, 2016
{{DEFAULTSORT:Natufian Culture Industries (archaeology) Archaeological cultures of West Asia Archaeological cultures of the Near East Hunter-gatherers of Asia Epipalaeolithic cultures Archaeological cultures in Israel Archaeological cultures in Jordan Archaeological cultures in Lebanon Archaeological cultures in Palestine Archaeological cultures in Syria Epipalaeolithic Younger Dryas
archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
of the late Epipalaeolithic Near East
The Epipalaeolithic Near East designates the Epipalaeolithic ("Final Old Stone Age") in the History of the Middle East#Prehistoric Near East, prehistory of the Near East. It is the period after the Upper Paleolithic, Upper Palaeolithic and befor ...
in West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
from 15–11,500 Before Present
Before Present (BP) or "years before present (YBP)" is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because ...
. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduction of agriculture. Natufian communities may be the ancestors of the builders of the region's first Neolithic settlements, which may have been the earliest in the world. Some evidence suggests deliberate cultivation of cereal
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize ( Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, ...
s, specifically rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is grown principally in an area from Eastern and Northern Europe into Russia. It is much more tolerant of cold weather and poor soil than o ...
, by the Natufian culture at Tell Abu Hureyra
Tell Abu Hureyra () is a prehistoric archaeological site in the Upper Euphrates valley in Syria. The tell was inhabited between 13,300 and 7,800 cal. BP in two main phases: Abu Hureyra 1, dated to the Epipalaeolithic, was a village of sedenta ...
, the site of the earliest evidence of agriculture in the world.
The world's oldest known evidence of the production of bread-like foodstuff has been found at Shubayqa 1, a 14,400-year-old site in Jordan's northeastern desert, 4,000 years before the emergence of agriculture in Southwest Asia. In addition, the oldest known evidence of possible beer-brewing, dating to approximately 13,000 BP, was found in Raqefet Cave on Mount Carmel
Mount Carmel (; ), also known in Arabic as Mount Mar Elias (; ), is a coastal mountain range in northern Israel stretching from the Mediterranean Sea towards the southeast. The range is a UNESCO biosphere reserve. A number of towns are situat ...
, although the beer-related residues may be a result of spontaneous fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduce ...
.
Generally, though, Natufians exploited wild cereals and hunted animals, notably mountain gazelles. Archaeogenetic analysis has revealed derivation of later (Neolithic to Bronze Age) Levantines primarily from Natufians, along with substantial later gene flow from Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
.
Dorothy Garrod coined the term Natufian based on her excavations at the Shuqba Cave at Wadi Natuf.
Discovery
The Natufian culture was discovered by British archaeologist Dorothy Garrod during her excavations of Shuqba Cave in theJudaean Mountains
The Judaean Mountains, or Judaean Hills (, or ,) are a mountain range in the West Bank and Israel where Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Hebron and several other biblical sites are located. The mountains reach a height of . The Judean Mountains can be di ...
of Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine was a British Empire, British geopolitical entity that existed between 1920 and 1948 in the Palestine (region), region of Palestine, and after 1922, under the terms of the League of Nations's Mandate for Palestine.
After ...
in the Cisjordan, now the Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate of Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
. Before the 1930s, the majority of archaeological work taking place in Palestine was biblical archaeology
Biblical archaeology is an academic school and a subset of Biblical studies and Levantine archaeology. Biblical archaeology studies archaeological sites from the Ancient Near East and especially the Holy Land (also known as Land of Israel and ...
focused on historic periods, and little was known about the region's prehistory.
In 1928, Garrod was invited by the British School of Archaeology in Jerusalem (BSAJ, now the Kenyon Institute) to excavate Shuqba Cave, where prehistoric stone tools had been discovered by Père Mallon four years earlier. She found a layer sandwiched between the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories ...
and Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
deposits characterised by the presence of microlith
A microlith is a small Rock (geology), stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 60,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Austral ...
s. She identified this with the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
, a transitional period between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
well-represented in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
but which had not yet been found in West Asia. A year later, when she discovered similar material at el Wad
El Wad is an archaeological site of the Epipalaeolithic Near East in Mount Carmel, Israel. The site has two components: El Wad Cave, also known as Mughārat al-Wād () or HaNahal Cave (); and El Wad Terrace, located immediately outside the cave.
...
(now in the Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve), Garrod suggested the name "the Natufian culture" after the Wadi Natuf, which runs close to Shuqba.
Over the next two decades, Garrod found Natufian material at several of her pioneering excavations in the Mount Carmel
Mount Carmel (; ), also known in Arabic as Mount Mar Elias (; ), is a coastal mountain range in northern Israel stretching from the Mediterranean Sea towards the southeast. The range is a UNESCO biosphere reserve. A number of towns are situat ...
region, including el-Wad, Kebara and Tabun, as did the French archaeologist René Neuville, firmly establishing the Natufian culture in the regional prehistoric chronology. As early as 1931, both Garrod and Neuville drew attention to the presence of stone sickle
A sickle, bagging hook, reaping-hook or grasshook is a single-handed agricultural tool designed with variously curved blades and typically used for harvesting or reaping grain crops, or cutting Succulent plant, succulent forage chiefly for feedi ...
s in Natufian assemblages and the possibility that this represented a very early agriculture.
Dating

Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
places the Natufian culture at an epoch from the terminal Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
to the very beginning of the Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
, a time period between 12,500 and 9,500 BC.
The period is commonly split into two subperiods: Early Natufian (12,000–10,800 BC) and Late Natufian (10,800–9,500 BC). The Late Natufian most likely occurred in tandem with the Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (YD, Greenland Stadial GS-1) was a period in Earth's geologic history that occurred circa 12,900 to 11,700 years Before Present (BP). It is primarily known for the sudden or "abrupt" cooling in the Northern Hemisphere, when the ...
(10,800 to 9,500 BC). The Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
hosts more than a hundred kinds of cereals, fruits, nuts, and other edible parts of plants, and the flora of the Levant during the Natufian period was not the dry, barren, and thorny landscape of today, but rather woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants (trees and shrubs), or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunli ...
.
Precursors and associated cultures
The Natufian developed in the same region as the earlier Kebaran culture. It is generally seen as a successor, which evolved out of elements within that preceding culture. There were also other industries in the region, such as the Mushabian culture of theNegev
The Negev ( ; ) or Naqab (), is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort town, resort city ...
and the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Afri ...
, which are sometimes distinguished from the Kebaran culture or believed to have been involved in the evolution of the Natufian culture.
More generally there has been discussion of the similarities of these cultures with those found in coastal North Africa. Graeme Barker notes there are: "similarities in the respective archaeological records of the Natufian culture of the Levant and of contemporary foragers in coastal North Africa across the late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
and early Holocene boundary". According to Isabelle De Groote and Louise Humphrey, Natufians practiced the Iberomaurusian and Capsian custom of sometimes extracting their maxillary central incisor
The maxillary central incisor is a human tooth in the front upper jaw, or maxilla, and is usually the most visible of all teeth in the mouth. It is located Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, mesial (closer to the mid ...
s (upper front teeth).
Ofer Bar-Yosef
Ofer Bar-Yosef (; 29 August 1937 – 14 March 2020) was an Israeli archaeologist and anthropologist whose main field of study was the Palaeolithic period. Archaeology and academic career
From 1967 Bar-Yosef was Professor of Prehistoric Archaeology ...
has argued that there are signs of influences coming from North Africa to the Levant, citing the microburin technique and "microlithic forms such as arched backed bladelets and La Mouillah points." But recent research has shown that the presence of arched backed bladelets, La Mouillah points, and the use of the microburin technique was already apparent in the Nebekian industry of the Eastern Levant. And Maher et al. state that, "Many technological nuances that have often been always highlighted as significant during the Natufian were already present during the Early and Middle EP pipalaeolithicand do not, in most cases, represent a radical departure in knowledge, tradition, or behavior."
Authors such as Christopher Ehret
Christopher Ehret (27 July 1941 – 25 March 2025), was an American scholar of African history and African historical linguistics who was particularly known for his efforts to correlate linguistic taxonomy and reconstruction with the archeologic ...
have built upon the little evidence available to develop scenarios of intensive usage of plants having built up first in North Africa, as a precursor to the development of true farming in the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
, but such suggestions are considered highly speculative until more North African archaeological evidence can be gathered. In fact, Weiss et al. have shown that the earliest known intensive usage of plants was in the Levant 23,000 years ago at Ohalo II
Ohalo II is an archaeological site in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District, Israel, near Kinneret (archaeological site), Kinneret, on the southwest shore of the Sea of Galilee. It is one of the best preserved hunter-gatherer archaeol ...
on the shores of the Sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee (, Judeo-Aramaic languages, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ), also called Lake Tiberias, Genezareth Lake or Kinneret, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest freshwater lake on Earth ...
by Kinneret.
Anthropologist C. Loring Brace (1993) cross-analysed the craniometric traits of Natufian specimens with those of various ancient and modern groups from the Near East, Africa and Europe. The Late Pleistocene Epipalaeolithic Natufian sample was described as problematic due to its small size (consisting of only three males and one female), as well as the lack of a comparative sample from the Natufians' putative descendants in the Neolithic Near East, such as the PPNB. Nonetheless, Brace observed that the Natufian fossils lay between those of the Niger–Congo-speaking series included and the other samples (Near East, Europe), which he suggested may point to a Sub-Saharan influence in their constitution. Subsequent ancient DNA
Ancient DNA (aDNA) is DNA isolated from ancient sources (typically Biological specimen, specimens, but also environmental DNA). Due to degradation processes (including Crosslinking of DNA, cross-linking, deamination and DNA fragmentation, fragme ...
analysis of Natufian skeletal remains by Lazaridis et al. (2016) instead found that the specimens were a mix of 50% Basal Eurasian ancestral component (see Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
) and 50% West Eurasian Unknown Hunter Gatherer (UHG) related to the western hunter-gatherers of Europe. �Table S6.1 – Y-chromosome haplogroups
/ref> Natufians have also been described by other anthropologists as a Proto-Mediterranean population, being similar to the Kebarans. According to Bar-Yosef and Belfer-Cohen, "It seems that certain preadaptive traits, developed already by the Kebaran and Geometric Kebaran populations within the Mediterranean park forest, played an important role in the emergence of the new socioeconomic system known as the Natufian culture."
Settlements
Settlements occur mostly in Israel and Palestine. This could be deemed the core zone of the Natufian culture, but Israel is a place that has been excavated more frequently than other places hence the greater number of sites. During the years more sites have been found outside the core zone of Israel and Palestine stretching into what now isSyria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
, Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
, the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Afri ...
and the Negev
The Negev ( ; ) or Naqab (), is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort town, resort city ...
desert. The settlements in the Natufian culture were larger and more permanent than in preceding ones. Some Natufian sites had stone built architecture; Ain Mallaha is an example of round stone structures. Cave sites are also seen frequently during the Natufian culture. El Wad
El Wad is an archaeological site of the Epipalaeolithic Near East in Mount Carmel, Israel. The site has two components: El Wad Cave, also known as Mughārat al-Wād () or HaNahal Cave (); and El Wad Terrace, located immediately outside the cave.
...
is a Natufian cave site with occupation in the front part of the cave also called the terrace. Some Natufian sites were located in forest/steppe areas and others near inland mountains. The Natufian settlements appear to be the first to exhibit evidence of food storage; not all Natufian sites have storage facilities, but they have been identified at certain sites. Natufians are also suggested to have visited Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, requiring travel over significant distances of water.

Material culture

Lithics
The Natufian had a microlithic industry centered on shortblade
A blade is the Sharpness (cutting), sharp, cutting portion of a tool, weapon, or machine, specifically designed to puncture, chop, slice, or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they a ...
s and bladelets. The microburin technique was used. Geometric microliths include lunate
Lunate is a crescent or moon-shaped microlith. In the specialized terminology of lithic reduction, a lunate flake is a small, crescent-shaped lithic flake, flake removed from a stone tool during the process of pressure flaking.
In the Natufian cu ...
s, trapezes, and triangles. There are backed blades as well. A special type of retouch ( Helwan retouch) is characteristic for the early Natufian. In the late Natufian, the Harif-point, a typical arrowhead
An arrowhead or point is the usually sharpened and hardened tip of an arrow, which contributes a majority of the projectile mass and is responsible for impacting and penetrating a target, or sometimes for special purposes such as signaling.
...
made from a regular blade, became common in the Negev
The Negev ( ; ) or Naqab (), is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort town, resort city ...
. Some scholars use it to define a separate culture, the Harifian
Harifian is a specialized regional cultural development of the Epipalaeolithic of the Negev Desert, in the southern part of the Levant. It corresponds to the latest stages of the Natufian culture, and represents a culmination of the local Natufi ...
.
Sickle
A sickle, bagging hook, reaping-hook or grasshook is a single-handed agricultural tool designed with variously curved blades and typically used for harvesting or reaping grain crops, or cutting Succulent plant, succulent forage chiefly for feedi ...
blades also appear for the first time in the Natufian lithic industry. The characteristic sickle-gloss shows that they were used to cut the silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
-rich stems of cereals, indirectly suggesting the existence of incipient agriculture. Shaft straighteners made of ground stone
In archaeology, ground stone is a category of stone tool formed by the grinding of a coarse-grained tool stone, either purposely or incidentally. Ground stone tools are usually made of basalt, rhyolite, granite, or other cryptocrystalline and ...
indicate the practice of archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a Bow and arrow, bow to shooting, shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting ...
. There are heavy ground-stone bowl mortars as well.
Art
The '' Ain Sakhri lovers'', a carved stone object held at theBritish Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
, is the oldest known depiction of a couple having sex. It was found in the Ain Sakhri cave in the Judean desert
The Judaean Desert or Judean Desert (, ) is a desert in the West Bank and Israel that stretches east of the ridge of the Judaean Mountains and in their rain shadow, so east of Jerusalem, and descends to the Dead Sea. Under the name El-Bariyah, ...
.
Burials
 Natufian
Natufian grave goods
Grave goods, in archaeology and anthropology, are items buried along with a body.
They are usually personal possessions, supplies to smooth the deceased's journey into an afterlife, or offerings to gods. Grave goods may be classed by researche ...
are typically made of shell, teeth (of red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or Hart (deer), hart, and a female is called a doe or hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Ir ...
), bones, and stone. There are pendants, bracelets, necklaces, earrings, and belt-ornaments as well.
 In 2008, the 12,400–12,000 cal BC grave of an apparently significant Natufian female was discovered in a ceremonial pit in the Hilazon Tachtit cave in northern Israel. Media reports referred to this person as a "shaman". The burial contained the remains of at least three
In 2008, the 12,400–12,000 cal BC grave of an apparently significant Natufian female was discovered in a ceremonial pit in the Hilazon Tachtit cave in northern Israel. Media reports referred to this person as a "shaman". The burial contained the remains of at least three aurochs
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius''; or ; pl.: aurochs or aurochsen) is an extinct species of Bovini, bovine, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of t ...
and 86 tortoises, all of which are thought to have been brought to the site during a funeral feast. The body was surrounded by tortoise shells, the pelvis of a leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a ...
, forearm of a boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
, a wingtip of a golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known bird of pr ...
, and skull of a beech marten.
Long-distance exchange
At Ain Mallaha (in Northern Israel), Anatolianobsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
and shellfish from the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
valley have been found. The source of malachite
Malachite () is a copper Carbonate mineral, carbonate hydroxide mineral, with the chemical formula, formula Basic copper carbonate, Cu2CO3(OH)2. This opaque, green-banded mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, and most often for ...
beads is still unknown. Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
Natufians carried parthenocarpic figs from Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
to the southeastern corner of the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
, .
Other finds
There was a rich bone industry, includingharpoon
A harpoon is a long, spear-like projectile used in fishing, whaling, sealing, and other hunting to shoot, kill, and capture large fish or marine mammals such as seals, sea cows, and whales. It impales the target and secures it with barb or ...
s and fish hook
A fish hook or fishhook, formerly also called an angle (from Old English ''angol'' and Proto-Germanic ''*angulaz''), is a hook used to catch fish either by piercing and embedding onto the inside of the fish mouth (angling) or, more rarely, by i ...
s. Stone and bone were worked into pendants and other ornaments. There are a few human figurines made of limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
(El-Wad, Ain Mallaha, Ain Sakhri), but the favorite subject of representative art seems to have been animals. Ostrich-shell containers have been found in the Negev
The Negev ( ; ) or Naqab (), is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort town, resort city ...
.
In 2018, the world's oldest brewery was found, with the residue of 13,000-year-old beer, in a prehistoric cave near Haifa
Haifa ( ; , ; ) is the List of cities in Israel, third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area i ...
in Israel when researchers were looking for clues into what plant foods the Natufian people were eating. This is 8,000 years earlier than experts previously thought beer was invented.
A study published in 2019 shows an advanced knowledge of lime plaster production at a Natufian cemetery in Nahal Ein Gev II site in the Upper Jordan Valley dated to 12 thousand (calibrated) years before present cal BP Production of plaster of this quality was previously thought to have been achieved some 2,000 years later.
Subsistence
The Natufian people lived by hunting and gathering. The preservation of plant remains is poor because of the soil conditions, but at some sites such asTell Abu Hureyra
Tell Abu Hureyra () is a prehistoric archaeological site in the Upper Euphrates valley in Syria. The tell was inhabited between 13,300 and 7,800 cal. BP in two main phases: Abu Hureyra 1, dated to the Epipalaeolithic, was a village of sedenta ...
substantial amounts of plant remains discovered through flotation have been excavated. However wild cereals like legume
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consum ...
s, almond
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', Synonym (taxonomy)#Botany, syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree from the genus ''Prunus''. Along with the peach, it is classified in the subgenus ''Amygdalus'', distinguished from the other subgenera ...
s, acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
s and pistachio
The pistachio (, ; ''Pistacia vera'') is a small to medium-sized tree of the Anacardiaceae, cashew family, originating in Iran. The tree produces nut (fruit)#Culinary definition and uses, seeds that are widely consumed as food.
In 2022, world ...
s have been collected throughout most of the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
. Animal bones show that mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
and goitered gazelles (''Gazella gazella'' and ''Gazella subgutturosa'') were the main prey.
Additionally, deer
A deer (: deer) or true deer is a hoofed ruminant ungulate of the family Cervidae (informally the deer family). Cervidae is divided into subfamilies Cervinae (which includes, among others, muntjac, elk (wapiti), red deer, and fallow deer) ...
, aurochs
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius''; or ; pl.: aurochs or aurochsen) is an extinct species of Bovini, bovine, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of t ...
and wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
were hunted in the steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
, as well as onager
The onager (, ) (''Equus hemionus''), also known as hemione or Asiatic wild ass, is a species of the family Equidae native to Asia. A member of the subgenus ''Asinus'', the onager was Scientific description, described and given its binomial name ...
s and caprids (ibex
An ibex ( : ibex, ibexes or ibices) is any of several species of wild goat (genus ''Capra''), distinguished by the male's large recurved horns, which are transversely ridged in front. Ibex are found in Eurasia, North Africa and East Africa.
T ...
). Waterfowl and freshwater fish formed part of the diet in the Jordan river valley. Animal bones from Salibiya I (12,300 – 10,800 cal BP) have been interpreted as evidence for communal hunts with nets, however, the radiocarbon dates are far too old compared to the cultural remains of this settlement, indicating contamination of the samples.
Development of agriculture
A pita-like bread has been found from 12,500 BC attributed to Natufians. This bread is made of wild cereal seeds and papyrus cousin tubers, ground into flour. According to one theory, it was a sudden change inclimate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
, the Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (YD, Greenland Stadial GS-1) was a period in Earth's geologic history that occurred circa 12,900 to 11,700 years Before Present (BP). It is primarily known for the sudden or "abrupt" cooling in the Northern Hemisphere, when the ...
event ( to 9500 BC), which inspired the development of agriculture in the region. The Younger Dryas was a 1,000-year-long interruption in the higher temperatures prevailing since the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
, which produced a sudden drought in the Levant. This would have endangered the wild cereals, which could no longer compete with dryland scrub, but upon which the population had become dependent to sustain a relatively large sedentary population. By artificially clearing scrub and planting seeds obtained from elsewhere, they began to practice agriculture. However, this theory of the origin of agriculture is controversial in the scientific community.
Domesticated dog
At the Natufian site of ʿAin Mallaha in Israel, dated to 12,000 BC, the remains of an elderly human and a four-to-five-month-old puppy were found buried together. At another Natufian site at the cave of Hayonim, humans were found buried with two canids.Genetics

Ancient DNA
Ancient DNA (aDNA) is DNA isolated from ancient sources (typically Biological specimen, specimens, but also environmental DNA). Due to degradation processes (including Crosslinking of DNA, cross-linking, deamination and DNA fragmentation, fragme ...
analysis of Natufian skeletal remains found that the Natufian ancestry could be modelled as a mix of about 50% Basal Eurasian ancestry and 50% from a West-Eurasian Unknown Hunter Gatherer (UHG) population, which was related to the western hunter-gatherer group of Mesolithic Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. Vallini et al. (2024) modeled the amount of Basal Eurasian ancestry among Natufians at roughly 15%, with the remainder being associated with West Eurasian sources.
The Natufian population also displays ancestral ties to Paleolithic Taforalt
Taforalt, or Grotte des Pigeons, is a cave in the province of Berkane, Aït Iznasen region, Morocco, possibly the oldest cemetery in North Africa. It contained at least 34 Iberomaurusian adolescent and adult human skeletons, as well as young ...
samples, the makers of the Epipaleolithic Iberomaurusian culture of the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
, the Pre-Pottery Neolithic culture of the Levant, the Early Neolithic Ifri N'Amr Ou Moussa and the Late Neolithic Kelif el Boroud culture of North Africa, with samples associated with these early cultures all sharing a common genomic component dubbed the "Natufian component", which diverged from other West Eurasian lineages ~26,000 years ago, and is most closely linked to the Arabian lineage. Possible bidirectional geneflow events between these groups has also been suggested, with particular evidence for affinity between the Natufians and Iberomaurusians.
Taforalt individuals belonged to the Y-DNA haplogroup E1b1b1a1 (M78), which is closely related to the E1b1b1b (M123) sublineage that has been observed in skeletal remains belonging to the Epipaleolithic Natufian and Pre-Pottery Neolithic
The Pre-Pottery Neolithic (PPN) represents the early Neolithic in the Near East, dating to years ago, (10000 – 6500 BCE).Richard, Suzanne ''Near Eastern archaeology'' Eisenbrauns; illustrated edition (1 Aug 2004) p.24/ref> It succeeds the ...
cultures of the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
, possibly suggesting geneflow.
Contact between Natufians and other Neolithic Levantines, Caucasus hunter-gatherers (CHG), Anatolian and Iranian farmers is believed to have decreased genetic variability among later populations in the Middle East. Migrations from the Near-East also occurred towards Africa, and the West Eurasian-like ancestry among populations in the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
being best represented by the Levant Neolithic, and may be associated with the spread of Afroasiatic languages.
Lazaridis et al. (2016) did not find a greater genetic affinity between Natufians and sub-Saharan Africans than that existing between sub-Saharan Africans and other ancient populations of Western Eurasia, and also stated that the ancestry of a primitive population from North Africa could not be tested because modern North Africans are largely descended from late migrant populations from Eurasia. However, Daniel Shriner (2018), using modern populations as a reference, found 28% autosomal African ancestry in Natufian samples, with 21.2% related to North Africa and 6.8% related to Omotic-speaking populations in southern Ethiopia, which reveals a plausible source for haplogroup E in Natufians; still according to Shriner, the Natufian samples had 61.2% ancestry related to Arabs and 10.8% ancestry related to West Asians.
As summarized by Rosa Fregel, a later preprint from Lazaridis et al. (2018) has contested Loosdrecht's conclusion and argues for a minor sub-Saharan African component in Natufians, stating "that he Iberomaurusians ofTaforalt can be better modeled as a mixture of a Dzudzuana component and a sub-Saharan African component" (or an ancient and now-extinct North African component that diverged prior to the Out-of-Africa migration) and "also argue that (...) the Taforalt people (...) contributed to the genetic composition of Natufians and not the other way around", which, according to Lazaridis et al., would be consistent with morphological and archaeological studies that indicate a dissemination of morphological characteristics and artifacts from North Africa to the Near East, as well as explaining the presence of Y-chromosome haplogroup E in Natufians and Levantine farmers. Fregel summarizes that "More evidence will be needed to determine the specific origin of the North African Upper Paleolithic populations".
In their 2017 paper, Ranajit Das, Paul Wexler, Mehdi Pirooznia and Eran Elhaik analyzed the Lazaridis et al. (2016) study concluding that the Natufians, together with one Neolithic Levantine sample, clustered in the proximity to modern Palestinians
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenou ...
and Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Sy ...
s, and also "marginally overlapped" with Yemenite Jews
Yemenite Jews, also known as Yemeni Jews or Teimanim (from ; ), are a Jewish diaspora group who live, or once lived, in Yemen, and their descendants maintaining their customs. After several waves of antisemitism, persecution, the vast majority ...
. Ferreira et al. (2021) and Almarri et al. (2021) found that ancient Natufians cluster with modern Arabian groups, such as Saudi Arabians
Saudis (; local dialects: , suʿūdiyyīn) or Saudi Arabians are the citizen population of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, who speak the Arabic language, a Central Semitic language, and share a common ancestry, history, and culture. They are mainl ...
and Yemenis
Yemenis or Yemenites () are the Citizenship, citizen population of Yemen.
Genetic studies
Yemen, located in the southwestern corner of the Arabian Peninsula, serves as a crossroads between Africa and Eurasia. The genomes of present-day Yem ...
, which derive most of their ancestry from local Natufian-like hunter-gatherer peoples and have less Neolithic Anatolian ancestry than Levantines. Sirak et al. (2024) found that medieval Socotra
Socotra, locally known as Saqatri, is a Yemeni island in the Indian Ocean. Situated between the Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Sea, it lies near major shipping routes. Socotra is the largest of the six islands in the Socotra archipelago as ...
(the Soqotri people
The Soqotri people, sometimes referred to as Socotran, are a South Arabian Peninsula, Arabian ethnic group native to the Gulf of Aden island of Socotra. They speak the Soqotri language, a Modern South Arabian languages, Modern South Arabian lang ...
), similar to modern Saudis, Yemenis and Bedouins, have a majority component that is "maximized in Late Pleistocene (Epipaleolithic) Natufian hunter–gatherers from the Levant".
Language
Alexander Militarev, Vitaly Shevoroshkin and others have linked the Natufian culture to theproto-Afroasiatic language
Proto-Afroasiatic (PAA), also known as Proto-Hamito-Semitic, Proto-Semito-Hamitic, and Proto-Afrasian, is the reconstructed proto-language from which all modern Afroasiatic languages are descended. Though estimations vary widely, it is believed ...
, which they in turn believe has a Levantine origin. Some scholars, for example Christopher Ehret
Christopher Ehret (27 July 1941 – 25 March 2025), was an American scholar of African history and African historical linguistics who was particularly known for his efforts to correlate linguistic taxonomy and reconstruction with the archeologic ...
, Roger Blench
Roger Marsh Blench (born August 1, 1953) is a British linguist, ethnomusicologist and development anthropologist. He has an M.A. and a Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge and is based in Cambridge, England. He researches, publishes, and work ...
and others, contend that the Proto-Afroasiatic homeland is to be found in North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
or Northeast Africa
Northeast Africa, or Northeastern Africa, or Northern East Africa as it was known in the past, encompasses the countries of Africa situated in and around the Red Sea. The region is intermediate between North Africa and East Africa, and encompasses ...
, probably in the area of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
, Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
or Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
.Blench R (2006) Archaeology, Language, and the African Past, Rowman Altamira, , https://books.google.com/books?doi=esFy3Po57A8CBender ML (1997), Upside Down Afrasian, Afrikanistische Arbeitspapiere 50, pp. 19–34 Within this group, Ehret, who like Militarev believes Afroasiatic may already have been in existence in the Natufian period, would associate Natufians only with the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
ern Proto-Semitic
Proto-Semitic is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Semitic languages. There is no consensus regarding the location of the linguistic homeland for Proto-Semitic: scholars hypothesize that it may have originated in the Levant, the Sahara, ...
branch of Afroasiatic.Militarev A (2005) Once more about glottochronology and comparative method: the Omotic-Afrasian case, Аспекты компаративистики – 1 (Aspects of comparative linguistics – 1). FS S. Starostin. Orientalia et Classica II (Moscow), p. 339-408. http://starling.rinet.ru/Texts/fleming.pdf
John Bengtson
John D. Bengtson (1948-2024) was an American historical and anthropological linguist. He had been president and vice-president of the Association for the Study of Language in Prehistory, and had served as editor (or co-editor) of the journal '' ...
documented that archeological and physical anthropological evidence showed Natufians are closely related to modern Semitic-speaking people from the Levant. Under his hypothesis, Afro-Asiatic branches originated in North Africa proper (Egypt), and the age of these languages can be dated to the periods of the Natufian culture around ~12,000 years ago. He postulated this based on the biological discontinuity between Pleistocene and Holocene North Africa, where there was population replacement and admixture in this region involving external migrants from northern areas, who were the ancestral Afro-Asiatic speakers.
Sites
The Natufian culture has been documented at dozens of sites. Around 90 have been excavated, including: * Aammiq 2 *Tell Abu Hureyra
Tell Abu Hureyra () is a prehistoric archaeological site in the Upper Euphrates valley in Syria. The tell was inhabited between 13,300 and 7,800 cal. BP in two main phases: Abu Hureyra 1, dated to the Epipalaeolithic, was a village of sedenta ...
* Abu Salem
* Abu Usba
* Ain Choaab
* Ain Mallaha (Eynan)
* Ain Rahub
* Ain Sakhri
* Ala Safat
* Antelias Cave
* Azraq 18 (Ain Saratan)
* Baaz
* Bawwab al Ghazal
* Beidha
* Dederiyeh
* Dibsi Faraj
* El Khiam
* El Kowm I
* El Wad
El Wad is an archaeological site of the Epipalaeolithic Near East in Mount Carmel, Israel. The site has two components: El Wad Cave, also known as Mughārat al-Wād () or HaNahal Cave (); and El Wad Terrace, located immediately outside the cave.
...
* Erq el Ahmar
* Fazael IV & VI
* Gilgal II
* Givat Hayil I
* Har Harif K7
* Hatoula
* Hayonim Cave and Hayonim Terrace
* Hilazon Tachtit
* Hof Shahaf
* Huzuq Musa
* Iraq ed Dubb
* Iraq el Barud
* Iraq ez Zigan
* J202
* J203
* J406a
* J614
* Jayroud 1–3 & 9
* Jebel Saaidé II
* Jeftelik
* Jericho
Jericho ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and the capital of the Jericho Governorate. Jericho is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It had a population of 20,907 in 2017.
F ...
* Kaus Kozah
* Kebara
* Kefar Vitkin 3
* Khallat Anaza (BDS 1407)
* Khirbat Janba
* Kosak Shamali
* Maaleh Ramon East
* Maaleh Ramon West
* Moghr el Ahwal
* Mureybet
* Mushabi IV & XIX
* Nachcharini Cave
* Nahal Ein Gev II
* Nahal Hadera I and Nahal Hadera IV (Hefsibah)
* Nahal Oren
* Nahal Sekher 23
* Nahal Sekher VI
* Nahr el Homr 2
* Qarassa 3
* Ramat Harif
The glossary of Hebrew toponyms gives translations of Hebrew language, Hebrew terms commonly found as components in Hebrew toponyms. B
E
G
H
I
K
M
N
R
T
See also
*L ...
(G8)
* Raqefet Cave
* Rosh Horesha
* Rosh Zin
* Sabra 1
* Saflulim
* Salibiya 1
* Salibiya 9
* Sands of Beirut
* Shluhat Harif
* Shubayqa 1
* Shubayqa 6
* Shukhbah Cave
* Shunera VI
* Shunera VII
* Tabaqa (WHS 895)
* Taibé
* TBAS 102
* TBAS 212
* Tor at Tariq (WHS 1065)
* Tugra I
* Upper Besor 6
* Wadi Hammeh 27
* Wadi Jilat 22
* Wadi Judayid (J2)
* Wadi Mataha
* Yabrud 3
* Yutil al Hasa (WHS 784)
See also
* Afroasiatic Urheimat * Prehistory of the Levant *Proto-Afroasiatic language
Proto-Afroasiatic (PAA), also known as Proto-Hamito-Semitic, Proto-Semito-Hamitic, and Proto-Afrasian, is the reconstructed proto-language from which all modern Afroasiatic languages are descended. Though estimations vary widely, it is believed ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * *External links
Epi-Palaeolithic (European Mesolithic) Natufian Culture of Israel (The History of the Ancient Near East)
*
The genetic structure of the world's first farmers, Lazaridis et al, 2016
{{DEFAULTSORT:Natufian Culture Industries (archaeology) Archaeological cultures of West Asia Archaeological cultures of the Near East Hunter-gatherers of Asia Epipalaeolithic cultures Archaeological cultures in Israel Archaeological cultures in Jordan Archaeological cultures in Lebanon Archaeological cultures in Palestine Archaeological cultures in Syria Epipalaeolithic Younger Dryas