National Commission on Fiscal Responsibility and Reform on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The National Commission on Fiscal Responsibility and Reform (often called Simpson–Bowles or Bowles–Simpson from the names of co-chairs Alan Simpson and Erskine Bowles; or NCFRR) was a bipartisan Presidential Commission on deficit reduction, created in 2010 by President
Panel Seeks Social Security Cuts and Higher Taxes
''New York Times'' (November 10, 2010). first met on April 27, 2010. A report was released on December 1, recommending a combination of spending cuts (including an increase in the
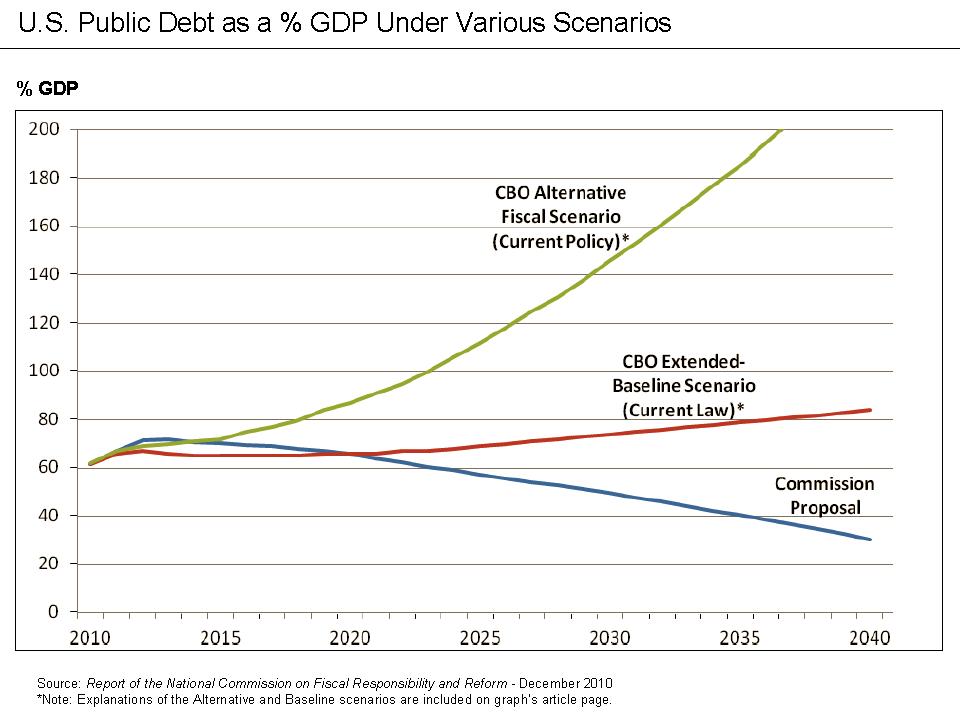 On November 10, co-chairs Simpson and Bowles released a draft proposal for consideration by other commission members providing the basis for the final report to be released later. The co-chairs proposal reduced the deficit by $4 trillion, reformed Social Security and the tax code and included health-care savings and an illustrative savings of $200 billion of discretionary cuts.
After the chairmen's briefing to the commission members, two Democratic Party members, Senator Durbin and Representative Schakowsky, publicly criticized the plan. Senator Kent Conrad (D-ND), however, declined to criticize the proposal, saying " stead of shooting this down propose an alternative. But one that does as good a job as this one does in getting us back on a sound fiscal course." Senator
On November 10, co-chairs Simpson and Bowles released a draft proposal for consideration by other commission members providing the basis for the final report to be released later. The co-chairs proposal reduced the deficit by $4 trillion, reformed Social Security and the tax code and included health-care savings and an illustrative savings of $200 billion of discretionary cuts.
After the chairmen's briefing to the commission members, two Democratic Party members, Senator Durbin and Representative Schakowsky, publicly criticized the plan. Senator Kent Conrad (D-ND), however, declined to criticize the proposal, saying " stead of shooting this down propose an alternative. But one that does as good a job as this one does in getting us back on a sound fiscal course." Senator
"Fiscal experts sternly warn supercommittee"
''
Official website
of the commission (archives through the University of North Texas Libraries Cyber Cemetery project) *
The Moment of Truth: Report of the National Commission on Fiscal Responsibility and Reform
December 2010 *
Co-chairs' draft proposal
November 2010
White House Announcement
February 18, 2010 President's Executive Order
Erskine Bowles and Alan Simpson, Co-chairs, US Deficit Commission
on ''
Erskine Bowles and Alan Simpson, Co-chairs, US Deficit Commission
on ''
Rep. Jan Schakowsky on the Deficit Commission Report
on The Real News (TRNN), December 3, 2010 (video 5:14)
The Bowles-Simpson "Chairmen’s Mark" Deficit Reduction Plan
summary and detailed analysis from the
Fix the Debt
campaign founded by Simpson and Bowles
Center on Budget & Policy Priorities – What Was Actually in Bowles-Simpson – And How Can We Compare it With Other Plans?
October 2012 {{DEFAULTSORT:National Commission On Fiscal Responsibility And Reform Fiscal Responsibility and Reform, National Commission on 2010 in American politics Fiscal policy Publications of the United States government United States economic policy Presidency of Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
to identify "policies to improve the fiscal situation in the medium term and to achieve fiscal sustainability over the long run". The 18-member Commission, consisting of 12 members of Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
and six private citizens,Jackie CalmesPanel Seeks Social Security Cuts and Higher Taxes
''New York Times'' (November 10, 2010). first met on April 27, 2010. A report was released on December 1, recommending a combination of spending cuts (including an increase in the
Social Security
Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance ...
retirement age and cuts to military, benefit, and domestic spending) and tax
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax co ...
increases (including restricting or eliminating certain tax credit
A tax credit is a tax incentive which allows certain taxpayers to subtract the amount of the credit they have accrued from the total they owe the state. It may also be a credit granted in recognition of taxes already paid or a form of state "dis ...
s and deductions and increasing the federal gasoline tax
A fuel tax (also known as a petrol, gasoline or gas tax, or as a fuel duty) is an excise tax imposed on the sale of fuel. In most countries, the fuel tax is imposed on fuels which are intended for transportation. Fuel tax receipts are often dedica ...
).
The commission's recommendations were politically controversial. Under the executive order
In the United States, an executive order is a directive by the president of the United States that manages operations of the federal government. The legal or constitutional basis for executive orders has multiple sources. Article Two of the ...
that created the commission, a supermajority of 14 of the 18 commissioners had to agree to a recommendation before it was sent to Congress for a vote. In a vote in December 2010, the commission fell short of that requirement, with only 11 out of the 18 commissioners (five Republicans, five Democrats, and one independent) voting to endorse the commission's blueprint.
Proponents of the plan praised it for hitting all parts of the federal budget and for putting the national debt on a stable and then downward path. Prominent supporters include JPMorgan Chase
JPMorgan Chase & Co. (stylized as JPMorganChase) is an American multinational financial services, finance corporation headquartered in New York City and incorporated in Delaware. It is List of largest banks in the United States, the largest ba ...
CEO Jamie Dimon
James Dimon ( ; born March 13, 1956) is an American businessman who has been the chairman and chief executive officer (CEO) of JPMorgan Chase since 2006.
Dimon began his career as a management consultant at Boston Consulting Group. After earnin ...
, House Speaker Nancy Pelosi
Nancy Patricia Pelosi ( ; ; born March 26, 1940) is an American politician who was the List of Speakers of the United States House of Representatives, 52nd speaker of the United States House of Representatives, serving from 2007 to 2011 an ...
(although at first she opposed the proposal), then- Secretary of State Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, lawyer and diplomat. She was the 67th United States secretary of state in the administration of Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, a U.S. senator represent ...
, and Republican Senator Tom Coburn
Thomas Allen Coburn (March 14, 1948 – March 28, 2020) was an American politician and medical doctor, physician who served as a United States senator from Oklahoma from 2005 to 2015. A Republican Party (United States), Republican, Coburn ...
; Democratic Representative Chris Van Hollen
Christopher Van Hollen Jr. ( ; born January 10, 1959) is an American attorney and politician serving as the senior United States senator from Maryland, a seat he has held since 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as the U.S. re ...
has called for a deal based on the Simpson–Bowles framework.
Critics on the left, such as Democratic Representative Jan Schakowsky
Janice Schakowsky ( ; née Danoff; born May 26, 1944) is an American politician who has served as the United States House of Representatives, U.S. representative from since 1999, and she previously served as a member of the Illinois House of Re ...
(a Commission member) and economist Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman ( ; born February 28, 1953) is an American New Keynesian economics, New Keynesian economist who is the Distinguished Professor of Economics at the CUNY Graduate Center, Graduate Center of the City University of New York. He ...
, opposed the Simpson–Bowles proposal because it would cut entitlement and social safety net
A social safety net (SSN) consists of non-contributory assistance existing to improve lives of vulnerable families and individuals experiencing poverty and destitution. Examples of SSNs are previously-contributory social pensions, in-kind and foo ...
programs, including Social Security and Medicare. Critics on the right, such as Republican commission members Paul Ryan
Paul Davis Ryan (born January 29, 1970) is an American politician who served as the List of Speakers of the United States House of Representatives, 54th speaker of the United States House of Representatives from 2015 to 2019. A member of the ...
, Jeb Hensarling
Thomas Jeb Hensarling (born May 29, 1957) is an American politician who served as the U.S. representative for Texas's 5th congressional district from 2003 to 2019. A member of the Republican Party, he chaired the House Republican Conference f ...
, and Dave Camp
David Lee Camp (born July 9, 1953) is a former American politician who served as a member of the United States House of Representatives from 1991 to 2015. Camp represented since 1993, and previously served one term representing . A member of the ...
, and anti-tax activist Grover Norquist of Americans for Tax Reform
Americans for Tax Reform (ATR) is a politically conservative U.S. advocacy group whose stated goal is "a system in which taxes are simpler, flatter, more visible, and lower than they are today." According to ATR, "The government's power to contr ...
, objected to the Simpson-Bowles proposal because it would raise taxes.
History
The original proposal for a commission came from bipartisan legislation that would have required Congress to vote on its recommendations as presented, without any amendment. In January 2010, that bill failed in theSenate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
by a vote of 53–46, when six Republicans who had co-sponsored it nevertheless voted against it. Thereafter, President Obama established the commission by Executive Order 13531. Former Republican Senator Alan Simpson (Wyo.), after his appointment to co-chair the commission, criticized the former supporters who had voted against the bill, saying that their purpose "was to stick it to the president." In the absence of special legislation, the commission's proposals are not guaranteed to be considered by Congress in a single up-or-down vote, although then-Speaker of the House of Representatives Nancy Pelosi and Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid
Harry Mason Reid Jr. (; December 2, 1939 – December 28, 2021) was an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States Senate, United States senator from Nevada from 1987 to 2017. He led the Senate Democratic Caucus from 2005 to 2 ...
pledged to bring its recommendations for an up or down vote.
Commission members
The Commission included 18 members and one executive director appointed by the president. This included six members of theU.S. House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is a chamber of the bicameral United States Congress; it is the lower house, with the U.S. Senate being the upper house. Together, the House and Senate have the authority under Article One of th ...
, and six members of the U.S. Senate.
The first vote on the final recommendations, originally set for December 1, 2010, was delayed until December 3 when the commission fell short of the supermajority of 14 of 18 votes needed to approve the report. The eleven voting for it were five Democrats (Bowles, Conrad, Durbin, Rivlin, Spratt) and five Republicans (Coburn, Cote, Crapo, Gregg, Simpson) and one Independent (Fudge); the seven voting against it were four Democrats (Baucus, Becerra, Schakowsky, Stern) and three Republicans (Camp, Hensarling, Ryan).
Public outreach
During the time of the commission, the co-chairs spent time holding public hearings and appearing on various media outlets. There were six public meetings of testimony and deliberation of the commission, with numerous private ones. # April 27, 2010 –Ben Bernanke
Ben Shalom Bernanke ( ; born December 13, 1953) is an American economist who served as the 14th chairman of the Federal Reserve from 2006 to 2014. After leaving the Federal Reserve, he was appointed a distinguished fellow at the Brookings Insti ...
, Federal Reserve; Director Peter Orszag, Office of Management and Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). The office's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, while it also examines agency pro ...
; Rudolph Penner, The Urban Institute; Robert Reischauer, frm. Congressional Budget Office.
# May 26, 2010 – Carmen Reinhart
Carmen M. Reinhart (née Castellanos, born October 7, 1955) is a Cuban-American economist and the Minos A. Zombanakis Professor of the International Financial System at Harvard Kennedy School. Previously, she was the Dennis Weatherstone Senior Fe ...
, Professor, University of Maryland
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD is the flagship institution of the Univ ...
; Carlo Cottarelli, International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
# June 30, 2010 – Doug Elmendorf, Director, Congressional Budget Office
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency within the United States Congress, legislative branch of the United States government that provides budget and economic information to Congress.
I ...
; public forum featuring nearly 90 groups and individuals.
# July 28, 2010 – Maya MacGuineas, Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget (CRFB) is a non-profit public policy organization based in Washington, D.C. that addresses United States federal budget, federal budget and fiscal issues. It was founded in 1981 by former United Sta ...
; Barry Anderson, fmr. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
# September 29, 2010 – Paul Posner, George Mason University
George Mason University (GMU) is a Public university, public research university in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. Located in Northern Virginia near Washington, D.C., the university is named in honor of George Mason, a Founding Father ...
; Janet S. Laurent, Government Accountability Office
The United States Government Accountability Office (GAO) is an independent, nonpartisan government agency within the legislative branch that provides auditing, evaluative, and investigative services for the United States Congress. It is the s ...
; Patricia Dalton, Government Accountability Office
# December 1, 2010 – The Commission released its final report.
In April 2010, Al Simpson was interviewed by Neil Cavuto
Neil Patrick Cavuto (born September 22, 1958) is an American television news anchor, executive, commentator, and business journalist. He was the host of '' Your World with Neil Cavuto'' and '' Cavuto Live,'' both on Fox News, and ''Cavuto: Coast ...
on Fox News
The Fox News Channel (FNC), commonly known as Fox News, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conservatism in the United States, conservative List of news television channels, news and political commentary Television stati ...
, covering tax-vs-spending balance in the commission's work.
Simpson and Bowles were also interviewed by Chris Wallace
Christopher Wallace (born October 12, 1947) is an American broadcast journalist. He is known for his tough and wide-ranging interviews, for which he is often compared to his father, ''60 Minutes'' journalist Mike Wallace. Over his 60-year care ...
on the eve of the first Commission meeting. Simpson's latter appearance, particularly as it bore on entitlements
An entitlement is a government program guaranteeing access to some benefit by members of a specific group and based on established rights or by legislation. A "right" is itself an entitlement associated with a moral or social principle, while an ...
, attracted comment from the Columbia Journalism Review
The ''Columbia Journalism Review'' (''CJR'') is a biannual magazine for professional journalists that has been published by the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism since 1961. Its original purpose was "to assess the performance ...
and James Ridgeway, among others.
Chairmen's draft proposal
 On November 10, co-chairs Simpson and Bowles released a draft proposal for consideration by other commission members providing the basis for the final report to be released later. The co-chairs proposal reduced the deficit by $4 trillion, reformed Social Security and the tax code and included health-care savings and an illustrative savings of $200 billion of discretionary cuts.
After the chairmen's briefing to the commission members, two Democratic Party members, Senator Durbin and Representative Schakowsky, publicly criticized the plan. Senator Kent Conrad (D-ND), however, declined to criticize the proposal, saying " stead of shooting this down propose an alternative. But one that does as good a job as this one does in getting us back on a sound fiscal course." Senator
On November 10, co-chairs Simpson and Bowles released a draft proposal for consideration by other commission members providing the basis for the final report to be released later. The co-chairs proposal reduced the deficit by $4 trillion, reformed Social Security and the tax code and included health-care savings and an illustrative savings of $200 billion of discretionary cuts.
After the chairmen's briefing to the commission members, two Democratic Party members, Senator Durbin and Representative Schakowsky, publicly criticized the plan. Senator Kent Conrad (D-ND), however, declined to criticize the proposal, saying " stead of shooting this down propose an alternative. But one that does as good a job as this one does in getting us back on a sound fiscal course." Senator Judd Gregg
Judd Alan Gregg (born February 14, 1947) is an American politician and attorney who served as the 76th governor of New Hampshire from 1989 to 1993 and a United States senator from New Hampshire from 1993 to 2011 where he was Chairman of the Heal ...
, the senior Republican on the Senate Budget Committee, noted that the report was a "starting point."
The proposal was dismissed as "unserious" by New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
columnist Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman ( ; born February 28, 1953) is an American New Keynesian economics, New Keynesian economist who is the Distinguished Professor of Economics at the CUNY Graduate Center, Graduate Center of the City University of New York. He ...
for its large cuts in income tax rates. Krugman dismissed the idea that current marginal rates are a drag on economic growth. Further, he doubted that proposed combination of rate cuts and removal of deductions and loopholes will be revenue neutral, let alone increase revenue.
Union leaders such as Richard Trumka and several Democrats Representative Raul Grijalva rejected the plan saying it cut spending, especially on Social Security, too much. The Economic Policy Institute
The Economic Policy Institute (EPI) is a 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) non-profit think tank based in Washington, D.C., that carries out economic research and analyzes the economic impact of policies and proposals. Affiliated with the Labor un ...
calculated that the proposed spending cuts would reduce payroll employment by roughly 1.9 million jobs by 2014, and that the resulting loss in the government's tax revenues would cut the proposal's deficit-reducing effect in half. The institute called instead for "budgeting for more desperately needed fiscal stimulus in the near-term." The chairmen's proposal was also criticized by conservative interest groups such as defense contractors, for cutting spending on defense, and Americans for Tax Reform
Americans for Tax Reform (ATR) is a politically conservative U.S. advocacy group whose stated goal is "a system in which taxes are simpler, flatter, more visible, and lower than they are today." According to ATR, "The government's power to contr ...
, a group opposed to both increases in marginal rates and overall Federal revenue.
The proposal was better received by the Democrat-affiliated think tank Third Way
The Third Way is a predominantly centrist political position that attempts to reconcile centre-right and centre-left politics by advocating a varying synthesis of Right-wing economics, right-wing economic and Left-wing politics, left-wing so ...
, the Progressive Policy Institute, Representative Jim Cooper (D-Tenn.), Senator Ron Wyden
Ronald Lee Wyden ( ; born May 3, 1949) is an American politician serving as the Seniority in the United States Senate, senior United States Senate, United States senator from Oregon, a seat he has held since 1996 United States Senate special el ...
(D-Oregon) and Harvard economist Greg Mankiw
Nicholas Gregory Mankiw ( ; born February 3, 1958) is an American macroeconomist who is currently the Robert M. Beren Professor of Economics at Harvard University. Mankiw is best known in academia for his work on New Keynesian economics.
Man ...
. Senator-elect Rand Paul
Randal Howard Paul (born January 7, 1963) is an American politician serving as the Seniority in the United States Senate, junior United States senator from Kentucky since 2011.
A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
(R-KY), a Tea Party supporter, stated that the proposed changes to entitlement spending should take effect sooner instead of in future decades but praised the proposal for also having "some good ideas". The Concord Coalition, a non-profit and non-partisan anti-deficit activist group, applauded the report and labeled it a "promising start."
Final plan
The final plan, released on December 1, 2010, aimed to reduce the federal deficit by nearly $4 trillion, stabilizing the growth of debt held by the public by 2014, reduce debt 60 percent by 2023 and 40 percent by 2035. Outlays would equal 21.6 percent of GDP in 2015, compared to 23.8 percent in 2010 and would fall to 21.0 percent by 2035. Revenues would rise from 14.9 percent in 2010 to 19.3 percent in 2015 and would equal 21.0 percent in 2035. Built off a baseline called the "Plausible Baseline", which closely resembled the Congressional Budget Office's Alternative Fiscal Scenario, the plan proposed roughly $2 in spending cuts to $1 in revenue increases. The Plausible Baseline built off of a current law baseline by assuming that the 2001/2003 tax cuts were extended except for those above $250,000, the estate tax and Alternative Minimum Tax would continue at 2009 levels, the Medicare physicians pay freeze would continue and war spending would decrease based on current administration policy. The final plan was broken down into six major components (savings are 2012–2020): # $1,661 billion of discretionary spending cuts by putting in place discretionary spending caps into law lower than what is projected to be spent. # $995 billion in additional revenue with $785 billion in new revenues from tax reform by lowering income and corporate tax rates and broadening the base by eliminating tax expenditures. An additional $210 billion in revenue is also raised in other revenue by switching to the Chained-CPI and an increase in the federal gasoline tax # $341 billion in federal health care savings by reforming the Sustainable Growth Rate for Medicare, repeals the CLASS Act (which has already happened), increase Medicare cost sharing, reform health-care tort, change provider payments, increase drug rebates and establishes a long-term budget for total federal health-care spending after 2020 to GDP + 1 percent. # $215 billion in other mandatory savings by moving to the Chained CPI for all inflation-indexed programs, reform the military and civil service retirement system, reduce farm subsidies, reduce student loans and various other reforms. # $238 billion in Social Security reform, to be used to ensure the program is sustainably solvent in the infinite horizon by slowing benefit growth for high and medium-income workers, increase the early and normal retirement age to 68 by 2050 and 69 by 2075 by indexing it to longevity, index cost of living adjustments to the Chained-CPI, include newly hired state and local workers after 2020, increase the payroll tax cap to cover 90 percent of wages by 2050 and creates a new minimum and old-age benefit. # Budget Process Reforms by creating discretionary spending caps and caps total federal revenue at 20 percent of GDP. The plan also proposed an additional $673 billion in savings, due to lower projected spending interest payments as a result from lower deficits.Final vote
The plan, released on December 1, 2010, fell short of a supermajority during voting on December 3, with 11 of 18 votes in favor. Voting for the report were Bowles, Coburn, Conrad, Crapo, Cote, Durbin,Fudge
''Fudge'' is a generic role-playing game system for use in freeform role-playing games. The name "''FUDGE''" was once an acronym for ''Freeform Universal Donated'' (later, ''Do-it-yourself'') ''Gaming Engine'' and, though the acronym has since b ...
, Gregg, Rivlin, Simpson
Simpson may refer to:
* Simpson (name), a British surname
Organizations Schools
*Simpson College, in Indianola, Iowa
*Simpson University, in Redding, California
Businesses
*Simpson (appliance manufacturer), former manufacturer and brand of w ...
, and Spratt. Voting against were Baucus, Becerra, Camp, Hensarling, Ryan, Schakowsky, and Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. O ...
.
On March 28, 2012, Representatives Jim Cooper (D-TN) and Steve LaTourette (R-OH) put a bill modeled on the plan, with, according to analyst Ezra Klein
Ezra Klein (born May 9, 1984) is an American American liberalism, liberal political commentator and journalist. He is currently a ''The New York Times, New York Times'' columnist and the host of ''The Ezra Klein Show'' podcast. He is a co-founde ...
, "somewhat less in tax increases," to a vote in the House where it was rejected 382 to 38. 22 Democrats and 16 Republicans supported the bill.
Reaction
There was mixed reaction to the plan. Some praised the recommendations of the proposal while others attacked it.Praise
One proponent, Maya MacGuineas at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget, said of the plan, "the Commission released not only a credible plan, but an excellent plan. Of course it is filled with things people don't like—that is the nature of deficit reduction. And yet the plan received bipartisan support from a majority of the Commission at a time where, up until now, fiscal leadership has been in short supply" Other prominent supporters of the plan include New York mayorMichael Bloomberg
Michael Rubens Bloomberg (born February 14, 1942) is an American businessman and politician. He is the majority owner and co-founder of Bloomberg L.P., and was its CEO from 1981 to 2001 and again from 2014 to 2023. He served as the 108th mayo ...
, former Chairmen of the Federal Reserve Alan Greenspan
Alan Greenspan (born March 6, 1926) is an American economist who served as the 13th chairman of the Federal Reserve from 1987 to 2006. He worked as a private adviser and provided consulting for firms through his company, Greenspan Associates L ...
, Senator John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 – August 25, 2018) was an American statesman and United States Navy, naval officer who represented the Arizona, state of Arizona in United States Congress, Congress for over 35 years, first as ...
and Democratic Minority Whip Steny Hoyer
Steny Hamilton Hoyer ( ; born June 14, 1939) is an American politician and retired attorney who has served as the United States House of Representatives, U.S. representative for since 1981. He also served as House Majority Leader from 2007 to 20 ...
.
As time has gone on, there has been increased support for the plan, including some who initially opposed it such as former union leader Andy Stern and Democratic leader Nancy Pelosi
Nancy Patricia Pelosi ( ; ; born March 26, 1940) is an American politician who was the List of Speakers of the United States House of Representatives, 52nd speaker of the United States House of Representatives, serving from 2007 to 2011 an ...
.
Criticism
The plan was not universally praised. Commission member Jan Schakowsky, who voted against the Bowles-Simpson plan, released an alternative plan of her own, proposing a liberal budget plan that would cut the deficit by $441 billion. Schakowsky's plan would raise revenue (by eliminating the FICA cap; eliminating the foreign earned income exclusion, raising the taxes on capital gains, dividends, and bonds, and establishing acap-and-trade
Carbon emission trading (also called carbon market, emission trading scheme (ETS) or cap and trade) is a type of emissions trading scheme designed for carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs). A form of carbon pricing, its purpose ...
system taxing corporate carbon emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
); cut defense spending by $110 billion and non-defense spending by $33 billion; and spend $200 billion on infrastructure and other measures aimed at boosting economic growth.
Dean Baker
Dean Baker (born July 13, 1958) is an American macroeconomist who co-founded the Center for Economic and Policy Research (CEPR) with Mark Weisbrot. Baker has been credited as one of the first economists to have identified the 2007–08 United S ...
of the Center for Economic and Policy Research
The Center for Economic and Policy Research (CEPR) is an American think tank that specializes in economic policy. Based in Washington, D.C. CEPR was co-founded by economists Dean Baker and Mark Weisbrot in 1999.
Considered a left-leaning orga ...
in Washington criticized the deficit report for omitting a tax on the financial industry, as was recommended by the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
.
Economist and ''New York Times'' columnist Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman ( ; born February 28, 1953) is an American New Keynesian economics, New Keynesian economist who is the Distinguished Professor of Economics at the CUNY Graduate Center, Graduate Center of the City University of New York. He ...
wrote, "Simpson–Bowles is terrible. It mucks around with taxes, but is obsessed with lowering marginal rates despite a complete absence of evidence that this is important. It offers nothing on Medicare that isn't already in the Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) and informally as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by Presid ...
. And it raises the Social Security retirement age because life expectancy has risen completely ignoring the fact that life expectancy has only gone up for the well-off and well-educated, while stagnating or even declining among the people who need the program most."
Continuing outreach and current status
Bowles-Simpson, while never officially coming to a vote, has received significant attention since its inception. '' The National Journal'' noted that, "Hardly a day goes by in Congress or on the hustings without some lawmaker extolling Simpson–Bowles as the kind of potent fiscal medicine Americans must swallow if the country is to fix its debt and deficit problems, reform government and revive the economy." The Simpson–Bowles framework and its goal of $4 trillion of deficit reduction has been used by other, such as President Obama and Speaker Boehner in their negotiations during the summer of 2011. A Senate "Gang of Six", with Senators Mark Warner, Kent Conrad, Richard Durbin, Tom Coburn, Mike Crapo andSaxby Chambliss
Clarence Saxby Chambliss (; born November 10, 1943) is an American lawyer and retired politician who was a United States Senate, United States Senator from Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia from 2003 to 2015. A member of the Republican Party (Unite ...
, was formed attempting to forge a consensus on deficit reduction. Later, Senators Mike Bennett and Mike Johans. The Gang of 6 released their plan during the summer of 2011, during the Debt Ceiling negotiations, but since then has continued to work on ways to forge a way to avoid the fiscal cliff.
Additionally, during the spring of 2012, a Budget Resolution based in part on the Simpson–Bowles plan was voted on in the House of Representatives. The plan was voted down 382–38.
Simpson and Bowles have done further outreach themselves. In November, 2011, Simpson and Bowles submitted written testimony to the "supercommittee" charged with making budget adjustments by Congress, urging the 12 supercommittee members to "go big" toward the $4 trillion in savings the NCFRR had recommended ''v.'' the $1.2 trillion deficit reduction most discussed by the committee of congresspeople and senators. Simpson and Bowles also warned that failure to reach some agreement "might result in another downgrade", though separately Moody's
Moody's Ratings, previously and still legally known as Moody's Investors Service and often referred to as Moody's, is the bond credit rating business of Moody's Corporation, representing the company's traditional line of business and its histo ...
said such failure alone would not result in a change in U.S. ratings, as the trigger would still result in $1.2 trillion in cuts. In that regard, Simpson and Bowles stated, "the only thing worse than failure by the committee to agree on savings would be removing the 'sequester' 'trigger'">United States Congress Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction#Congressional vote">'trigger'mechanism for automatic cuts".Schroeder, Robert"Fiscal experts sternly warn supercommittee"
''
MarketWatch
''MarketWatch'' is a website that provides financial information, business news, analysis, and stock market data. It is a subsidiary of Dow Jones & Company, a property of News Corp, along with ''The Wall Street Journal'' and '' Barron's.''
...
'', Nov. 1, 2011, 3:12 pm EDT. Retrieved November 1, 2011. Bowles said in verbal testimony that " llectively, I'm worried you're going to fail".
Both Simpson and Bowles have appeared on numerous media outlets discussing their plan and the current fiscal situation such as the fiscal cliff at the end of 2012 and are widely quoted in the press on fiscal issues. In addition, Simpson and Bowles have helped form two organizations that are working in part for their plan—the Moment of Truth Project and the Campaign to Fix the Debt.
Finally, some aspects of the Simpson–Bowles plan have become law. The Budget Control Act of 2011
The Budget Control Act of 2011 () is a Law of the United States#Federal law, federal statute enacted by the 112th United States Congress and signed into law by President of the United States, US President Barack Obama on August 2, 2011. The Act ...
included discretionary spending caps, albeit at a lower level. Additionally, the CLASS Act was enacted as Title VIII of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health ...
but was repealed January 1, 2013.
See also
*United States Congress Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction
The Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction,Budget Control Act of 2011, , Title IV colloquially referred to as the Supercommittee, was a Joint committee (legislative), joint Select or special committee (United States Congress), select committ ...
("Supercommittee")
* Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1993
The Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1993 (or OBRA-93) was a federal law that was enacted by the 103rd United States Congress and signed into law by President Bill Clinton on August 10, 1993. It has also been unofficially referred to as the ...
* Deficit Reduction Act of various years
* National Economic Commission of 1987
* United States Federal Budget
The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. Th ...
* Budget Control Act of 2011
The Budget Control Act of 2011 () is a Law of the United States#Federal law, federal statute enacted by the 112th United States Congress and signed into law by President of the United States, US President Barack Obama on August 2, 2011. The Act ...
References
External links
Official website
of the commission (archives through the University of North Texas Libraries Cyber Cemetery project) *
The Moment of Truth: Report of the National Commission on Fiscal Responsibility and Reform
December 2010 *
Co-chairs' draft proposal
November 2010
White House Announcement
February 18, 2010 President's Executive Order
Erskine Bowles and Alan Simpson, Co-chairs, US Deficit Commission
on ''
Charlie Rose
Charles Peete Rose Jr. (born January 5, 1942) is an American journalist and talk show host. From 1991 to 2017, he was the host and executive producer of the talk show ''Charlie Rose (talk show), Charlie Rose'' on PBS and Bloomberg L.P., Bloombe ...
'', November 16, 2010 (50:37 video)
Erskine Bowles and Alan Simpson, Co-chairs, US Deficit Commission
on ''
Charlie Rose
Charles Peete Rose Jr. (born January 5, 1942) is an American journalist and talk show host. From 1991 to 2017, he was the host and executive producer of the talk show ''Charlie Rose (talk show), Charlie Rose'' on PBS and Bloomberg L.P., Bloombe ...
'', March 29, 2012 (51:43 video)
Rep. Jan Schakowsky on the Deficit Commission Report
on The Real News (TRNN), December 3, 2010 (video 5:14)
The Bowles-Simpson "Chairmen’s Mark" Deficit Reduction Plan
summary and detailed analysis from the
Tax Policy Center
The Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center, typically shortened to the Tax Policy Center (TPC), is a nonpartisan think tank based in Washington D.C., United States. A joint venture of the Urban Institute and the Brookings Institution, it aims to pr ...
Fix the Debt
campaign founded by Simpson and Bowles
Center on Budget & Policy Priorities – What Was Actually in Bowles-Simpson – And How Can We Compare it With Other Plans?
October 2012 {{DEFAULTSORT:National Commission On Fiscal Responsibility And Reform Fiscal Responsibility and Reform, National Commission on 2010 in American politics Fiscal policy Publications of the United States government United States economic policy Presidency of Barack Obama